Gram-negative

On this page
🦠 Gram-Negative Bacterial Arsenal: The Clinical Command Center
Gram-negative bacteria are among medicine's most formidable adversaries, armed with a double-membrane fortress that deflects many antibiotics and houses potent endotoxins capable of triggering septic shock. You'll master the clinical signatures, virulence mechanisms, and diagnostic approaches that distinguish these pathogens, then build a strategic framework for selecting targeted antimicrobials while combating the rising threat of resistance. This lesson transforms pattern recognition into clinical power, equipping you to identify, treat, and outmaneuver infections from Pseudomonas to E. coli with precision and confidence.
The Gram-Negative Structural Blueprint
The gram-negative cell envelope creates a dual-membrane fortress that fundamentally alters antibiotic penetration and immune recognition. This architecture includes:
-
Outer Membrane Barrier
- Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) endotoxin layer
- Porins controlling molecular entry (1.2-1.5 nm diameter)
- β-lactamase enzyme concentration zone
- Extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) in 15-25% of clinical isolates
- Carbapenemases in 5-10% of resistant strains
- AmpC β-lactamases in 30-40% of Enterobacter species
-
Periplasmic Space Weaponry
- β-lactamase enzyme storage compartment
- Binding proteins for nutrient acquisition
- Resistance enzyme concentration (10-100x higher than cytoplasm)
-
Inner Membrane Transport Systems
- Efflux pump mechanisms removing antibiotics
- Multi-drug resistance (MDR) pumps in 60-80% of Pseudomonas isolates
- Energy-dependent antibiotic extrusion
📌 Remember: PORE - Porins control entry, Outer membrane blocks penetration, Resistance enzymes concentrate in periplasm, Efflux pumps remove antibiotics. This quadruple defense system explains why gram-negatives require 2-4x higher antibiotic concentrations than gram-positives.
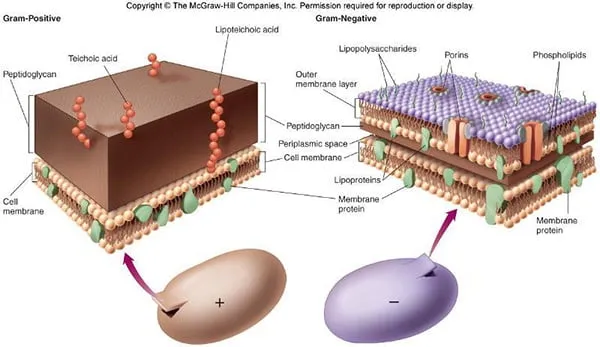
| Feature | Gram-Positive | Gram-Negative | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall Thickness | 20-80 nm peptidoglycan | 2-7 nm peptidoglycan | Affects antibiotic penetration |
| Outer Membrane | Absent | Present with LPS | Endotoxin shock potential |
| Antibiotic Resistance | 10-20% MRSA prevalence | 25-40% ESBL prevalence | Treatment complexity |
| β-lactamase Production | 5-15% of isolates | 40-60% of isolates | Empiric therapy selection |
| Sepsis Mortality | 15-25% mortality rate | 25-35% mortality rate | Prognostic implications |
Connect this structural foundation through virulence mechanisms to understand how gram-negative pathogens exploit anatomical vulnerabilities and overwhelm host defenses.
🦠 Gram-Negative Bacterial Arsenal: The Clinical Command Center
⚔️ Virulence Arsenal: The Pathogenic Powerhouse
The Multi-Factor Attack Strategy
Gram-negative pathogens coordinate virulence through sophisticated molecular systems:
-
Adhesion Systems
- Type 1 fimbriae binding mannose receptors (90% of E. coli strains)
- P fimbriae targeting kidney epithelium (80% of pyelonephritis isolates)
- Curli fibers promoting biofilm formation
- Biofilm resistance 100-1000x higher than planktonic bacteria
- Chronic infection establishment in 60-70% of device-related cases
-
Invasion Mechanisms
- Type III secretion systems (T3SS) in 40-50% of pathogenic strains
- Direct cytoplasm injection bypassing membrane barriers
- Actin cytoskeleton manipulation for intracellular survival
- Salmonella survival in macrophages >72 hours
- Shigella cell-to-cell spread avoiding extracellular antibodies
📌 Remember: SITE - Secretion systems inject toxins, Invasins penetrate cells, Toxins damage tissues, Evasion mechanisms avoid immunity. This coordinated attack explains why gram-negative infections progress 2-3x faster than gram-positive infections.
Endotoxin: The Universal Weapon
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) endotoxin represents the most clinically significant virulence factor shared by all gram-negative bacteria:
-
Structural Components
- Lipid A: toxic component triggering TLR4 receptors
- Core polysaccharide: structural stability
- O-antigen: antigenic variation (>180 serotypes in E. coli)
-
Inflammatory Cascade Activation
- TNF-α release within 30-60 minutes of exposure
- IL-1β and IL-6 elevation 5-10x normal levels
- Complement activation consuming 50-80% of C3 levels
- Coagulation cascade triggering DIC in 15-25% of severe cases
| Endotoxin Level | Clinical Manifestation | Mortality Risk | Treatment Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| <5 EU/mL | Asymptomatic | <1% | Monitoring |
| 5-50 EU/mL | Fever, malaise | 5-10% | Antibiotics |
| 50-500 EU/mL | Sepsis syndrome | 20-30% | ICU management |
| >500 EU/mL | Septic shock | 40-60% | Aggressive resuscitation |
💡 Master This: Every gram-negative infection carries endotoxin risk regardless of bacterial species. This universal threat explains why empiric broad-spectrum coverage targets gram-negatives aggressively, and why source control becomes critical within 6-12 hours of recognition.
Connect these virulence mechanisms through clinical pattern recognition to identify gram-negative infections before culture confirmation and implement appropriate empiric therapy.
⚔️ Virulence Arsenal: The Pathogenic Powerhouse
🎯 Clinical Pattern Recognition: The Diagnostic Detective Framework
Anatomical Territory Mapping
Gram-negative pathogens demonstrate predictable anatomical preferences that guide diagnostic suspicion:
-
Urinary Tract Dominance
- E. coli: 80-85% of uncomplicated UTIs
- Klebsiella: 10-15% of UTIs, 60% of complicated cases
- Proteus: 5-10% overall, 40% of stone-related infections
- Urease production creating alkaline urine (pH >8.0)
- Struvite stone formation in 70-80% of chronic cases
-
Respiratory Tract Patterns
- Pseudomonas: 15-20% of hospital-acquired pneumonia
- Haemophilus: 10-15% of community-acquired pneumonia
- Legionella: 2-5% of CAP, 15-20% of severe cases
- Hyponatremia in 60-70% of Legionella pneumonia
- Elevated LDH >500 U/L in 80% of cases
-
Gastrointestinal Invasion
- Salmonella: 1-2 million cases annually in US
- Shigella: 500,000 cases with 5-10% hospitalization rate
- Campylobacter: 1.5 million cases, leading bacterial gastroenteritis
📌 Remember: URGE - Urinary tract (E. coli dominance), Respiratory (Pseudomonas/Haemophilus), Gastrointestinal (Salmonella/Shigella), Everywhere else (consider resistance patterns). This anatomical mapping predicts 70-80% of gram-negative infections.

Rapid Recognition Algorithms
Clinical decision frameworks for gram-negative infection suspicion:
-
High-Risk Presentations
- Rapid onset shock (<6 hours symptom to hypotension)
- Temperature >39°C or <36°C with rigors
- WBC >15,000 or <4,000 with left shift >10%
- Lactate >2.0 mmol/L without obvious cause
- Procalcitonin >0.5 ng/mL (gram-negative likelihood 80%)
-
Anatomical Clues
- UTI symptoms + systemic toxicity = urosepsis risk
- Productive cough + rapid deterioration = gram-negative pneumonia
- Diarrhea + dehydration + fever = enteric gram-negatives
- Device-related infection + biofilm = Pseudomonas consideration
| Clinical Syndrome | Gram-Negative Likelihood | Key Discriminators | Empiric Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Complicated UTI | 85-90% | Fever, flank pain, immunocompromise | Fluoroquinolone or ceftriaxone |
| Hospital Pneumonia | 60-70% | Ventilator, ICU stay >48h | Anti-pseudomonal β-lactam |
| Intra-abdominal Sepsis | 70-80% | Perforation, abscess, surgery | Carbapenem or pip-tazo |
| Device-Related BSI | 40-50% | Central line, urinary catheter | Remove device + broad spectrum |
💡 Master This: Time-sensitive recognition saves lives in gram-negative sepsis. The "Golden Hour" concept applies: appropriate antibiotics within 1 hour of shock recognition reduces mortality by 7.6% per hour of delay, with gram-negatives showing steeper mortality curves than gram-positives.
Connect these recognition patterns through systematic diagnostic approaches to confirm gram-negative infections and guide targeted antimicrobial selection.
🎯 Clinical Pattern Recognition: The Diagnostic Detective Framework
🔬 Diagnostic Precision: The Laboratory Intelligence Network
Rapid Diagnostic Revolution
Contemporary gram-negative diagnostics integrate multiple technological platforms:
-
Molecular Diagnostics
- PCR-based identification within 2-4 hours
- Multiplex panels detecting 15-20 pathogens simultaneously
- Resistance gene detection (ESBL, carbapenemase) in 1-2 hours
- mecA gene detection >95% sensitivity for resistance
- blaCTX-M identification predicting ESBL >90% accuracy
- blaKPC detection confirming carbapenem resistance
-
Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF)
- Species identification within 30 minutes of colony growth
- >95% accuracy for gram-negative identification
- Cost reduction 60-70% compared to biochemical methods
- Direct blood culture identification protocols
-
Automated Susceptibility Testing
- MIC determination within 6-8 hours
- Real-time resistance detection algorithms
- Expert system interpretation reducing errors 40-50%
📌 Remember: RAPID - Resistance genes detected early, Automated systems reduce errors, PCR identifies pathogens quickly, Identification via mass spectrometry, Direct testing from blood cultures. This integrated approach provides actionable data 12-24 hours faster than traditional methods.
Resistance Pattern Recognition
Systematic interpretation of gram-negative susceptibility patterns guides therapeutic decisions:
-
ESBL Detection Patterns
- Ceftriaxone MIC ≥2 μg/mL with ceftazidime resistance
- Clavulanate potentiation ≥3-fold MIC reduction
- Carbapenem susceptibility maintained (meropenem MIC ≤1 μg/mL)
- Prevalence: E. coli 15-25%, Klebsiella 25-35% globally
-
Carbapenemase Recognition
- Meropenem MIC ≥2 μg/mL or ertapenem ≥1 μg/mL
- Modified Hodge test positivity >90% sensitivity
- Carbapenem inactivation method (CIM) confirmation
- Rising prevalence: 5-15% in healthcare-associated infections
| Resistance Mechanism | Prevalence | Key Antibiotics Affected | Preferred Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| ESBL Production | 20-30% Enterobacterales | Cephalosporins, aztreonam | Carbapenems |
| AmpC β-lactamase | 15-25% Enterobacter spp | Cephalosporins, cephamycins | Carbapenems, fluoroquinolones |
| Carbapenemase | 5-10% CRE isolates | All β-lactams including carbapenems | Colistin, tigecycline, ceftazidime-avibactam |
| MDR Efflux Pumps | 40-60% Pseudomonas | Multiple classes | Combination therapy |
💡 Master This: Resistance pattern recognition guides empiric therapy before final susceptibility results. The combination of patient risk factors + gram stain morphology + institutional antibiogram predicts resistance patterns with 70-80% accuracy, enabling appropriate initial therapy selection.
Connect diagnostic precision through evidence-based treatment algorithms to optimize gram-negative infection outcomes while minimizing resistance development.
🔬 Diagnostic Precision: The Laboratory Intelligence Network
💊 Treatment Mastery: The Antimicrobial Command Strategy
Strategic Antimicrobial Selection
Evidence-based treatment algorithms for gram-negative infections:
-
First-Line Empiric Agents
- Ceftriaxone: 1-2g daily, excellent CNS penetration
- Ceftazidime: 2g q8h, anti-Pseudomonas activity
- Piperacillin-tazobactam: 4.5g q6h, broad anaerobic coverage
- Meropenem: 1g q8h, carbapenem for resistant organisms
-
Resistance-Targeted Therapy
- ESBL infections: Carbapenems preferred (90-95% clinical success)
- Carbapenemase producers: Colistin + tigecycline (60-70% success)
- MDR Pseudomonas: Combination therapy (75-85% success)
- Ceftazidime-avibactam: New β-lactamase inhibitor (85% CRE success)
📌 Remember: COMBAT - Carbapenems for ESBL, Optimize dosing for PK/PD, Monitor resistance patterns, Broad spectrum for sepsis, Adjust based on cultures, Targeted therapy when possible. This systematic approach improves outcomes 20-30% compared to empiric continuation.
Pharmacokinetic Optimization
Advanced dosing strategies maximize antimicrobial efficacy against gram-negative pathogens:
-
β-lactam Optimization
- Extended infusions: 3-4 hour infusions vs 30 minutes
- Target 40-50% time above MIC for bactericidal effect
- Continuous infusion for critically ill patients
- Meropenem continuous: 3-6g/24h after loading dose
- Piperacillin-tazobactam: 16-18g/24h continuous infusion
-
Aminoglycoside Dosing
- Once-daily dosing: 5-7 mg/kg gentamicin/tobramycin
- Target peak 5-10 μg/mL, trough <2 μg/mL
- Synergy with β-lactams against gram-negatives
- Duration ≤7 days to minimize nephrotoxicity
| Antibiotic Class | PK/PD Target | Optimization Strategy | Clinical Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| β-lactams | 40-50% T>MIC | Extended/continuous infusion | 15-20% mortality reduction |
| Fluoroquinolones | AUC/MIC >125 | High-dose therapy | 25-30% resistance prevention |
| Aminoglycosides | Cmax/MIC >8-10 | Once-daily dosing | 30-40% toxicity reduction |
| Carbapenems | 40% T>MIC | Extended infusion | 20-25% clinical success improvement |
💡 Master This: Combination therapy for MDR gram-negatives requires mechanistic synergy, not just additive effects. β-lactam + aminoglycoside combinations achieve 2-4 log greater bacterial killing than either agent alone, explaining superior outcomes in Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter infections.
Connect treatment optimization through resistance prevention strategies to preserve antimicrobial effectiveness for future patients while achieving current therapeutic goals.
💊 Treatment Mastery: The Antimicrobial Command Strategy
🛡️ Resistance Prevention: The Stewardship Shield Network
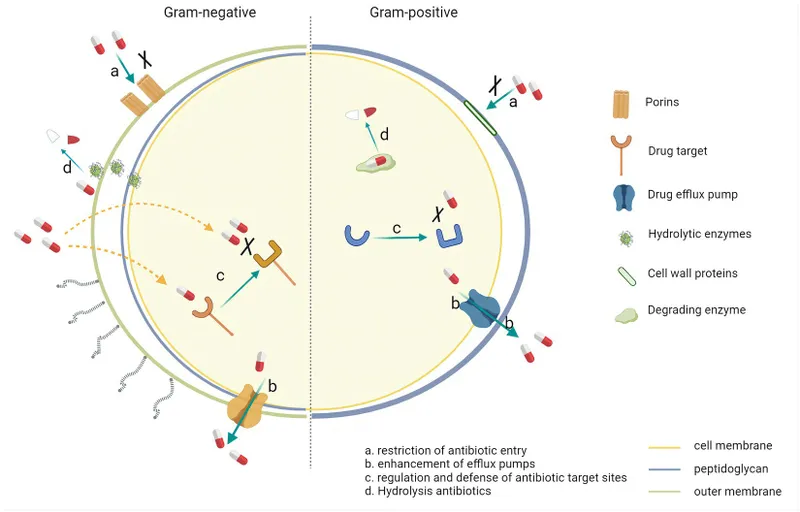
Resistance Mechanism Mastery
Gram-negative bacteria employ sophisticated resistance strategies that require targeted countermeasures:
-
Enzymatic Resistance
- β-lactamases: >1,000 different enzymes identified
- ESBLs: CTX-M family >90% of global ESBL production
- Carbapenemases: KPC, NDM, OXA-48 families spreading globally
- KPC prevalence: 40-60% of CRE in US
- NDM prevalence: 20-30% of CRE globally
- OXA-48: 30-50% of CRE in Europe/Middle East
-
Efflux Pump Systems
- Multi-drug resistance pumps in 60-80% of Pseudomonas
- AcrAB-TolC system in Enterobacterales
- MexAB-OprM system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Pump inhibitors under development showing 4-8 fold MIC reduction
📌 Remember: SPREAD - Selection pressure drives resistance, Plasmids enable horizontal transfer, Resistant clones expand rapidly, Enzymatic mechanisms predominate, Antibiotic exposure accelerates process, De-escalation prevents resistance. Understanding these dynamics guides stewardship interventions.
Stewardship Implementation Framework
Evidence-based interventions that reduce gram-negative resistance while maintaining clinical outcomes:
-
Diagnostic Stewardship
- Rapid diagnostics reducing time to targeted therapy 24-48 hours
- Procalcitonin-guided therapy reducing duration 20-30%
- Blood culture optimization improving yield 15-25%
- Molecular diagnostics enabling same-day pathogen identification
-
Prescribing Optimization
- Automatic stop orders at 48-72 hours requiring justification
- Dose optimization protocols improving PK/PD target attainment
- De-escalation protocols reducing broad-spectrum use 30-40%
- Combination therapy guidelines for MDR organisms
| Stewardship Intervention | Resistance Impact | Clinical Outcomes | Implementation Success |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rapid Diagnostics | 20-30% ↓ broad-spectrum use | No change in mortality | 80-90% adoption rates |
| Automatic Stop Orders | 25-35% ↓ duration | 10-15% ↓ C. diff infections | 70-80% compliance |
| De-escalation Protocols | 30-40% ↓ carbapenem use | Maintained clinical success | 60-70% implementation |
| Combination Therapy Guidelines | 15-25% ↓ resistance emergence | 20-30% ↑ MDR success rates | 85-95% adherence |
💡 Master This: The "Antibiotic Timeout" at 48-72 hours represents the critical decision point for gram-negative therapy. This interval allows culture results to guide targeted therapy while minimizing resistance selection pressure from prolonged broad-spectrum coverage.
Connect stewardship principles through clinical mastery frameworks to develop expertise in gram-negative infection management that balances individual patient care with antimicrobial preservation responsibilities.
🛡️ Resistance Prevention: The Stewardship Shield Network
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Gram-Negative Command Center

Essential Clinical Arsenal
Rapid Recognition Triggers
- Rigors + fever + healthcare exposure = 85% gram-negative likelihood
- Shock onset <6 hours + WBC >15,000 = empiric broad-spectrum indication
- UTI symptoms + systemic toxicity = urosepsis protocol activation
- Device-related infection + biofilm = anti-Pseudomonas coverage
Critical Numbers Mastery
- ESBL prevalence: E. coli 15-25%, Klebsiella 25-35%
- Carbapenemase prevalence: 5-10% healthcare-associated infections
- Mortality impact: 7.6% increase per hour of delayed appropriate therapy
- PK/PD targets: β-lactams 40-50% T>MIC, fluoroquinolones AUC/MIC >125
📌 Remember: MASTER - Mortality increases with delays, Antibiotic optimization saves lives, Stewardship preserves effectiveness, Targeted therapy when possible, Empiric coverage for sepsis, Resistance patterns guide selection. This framework enables 90% appropriate initial therapy selection.
| Clinical Scenario | Empiric Choice | Key Considerations | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Community UTI | Ceftriaxone 1g daily | Local ESBL rates <20% | 90-95% |
| Healthcare Pneumonia | Pip-tazo 4.5g q6h | Anti-Pseudomonas coverage | 80-85% |
| Septic Shock | Meropenem 1g q8h | Broad spectrum + source control | 75-80% |
| MDR Gram-Negative | Combination therapy | Synergy mechanisms critical | 60-70% |
💡 Master This: Gram-negative mastery requires integration of microbiology, pharmacology, and clinical medicine into rapid decision-making algorithms. The clinician who understands resistance mechanisms, optimizes pharmacokinetics, and implements stewardship principles achieves superior patient outcomes while preserving antimicrobial effectiveness for future generations.
Master these gram-negative principles, and you possess the clinical framework for managing medicine's most challenging infectious diseases with confidence, precision, and optimal patient outcomes.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Gram-Negative Command Center
Practice Questions: Gram-negative
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 42-year-old man with a history of gout and hypertension presents to his family physician with a complaint of increased left knee pain over the past 2 days. He also reports swelling and redness of the left knee and is unable to bear weight on that side. He denies any prior surgery or inciting trauma to the knee. His temperature is 97.0°F (36.1°C), blood pressure is 137/98 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, respirations are 13/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical examination reveals a left knee that is erythematous, swollen, warm-to-touch, and extremely tender to palpation and with attempted flexion/extension movement. His left knee range of motion is markedly reduced compared to the contralateral side. Joint aspiration of the left knee is performed with synovial fluid analysis showing turbid fluid with a leukocyte count of 95,000/mm^3, 88% neutrophils, and a low glucose. Gram stain of the synovial fluid is negative. Results from synovial fluid culture are pending. Which of the following is the best treatment regimen for this patient?








