Systemic Pathology

On this page
🔬 The Pathological Landscape: Systemic Disease Architecture
You'll master how diseases ripple through the body's interconnected systems by learning to recognize cellular injury patterns, build diagnostic frameworks, and construct treatment algorithms that mirror real clinical reasoning. This lesson transforms pathology from isolated facts into an integrated command center where you'll discriminate between competing diagnoses, trace damage mechanisms from molecular disruption to organ failure, and develop the pattern recognition expertise that separates novice from expert clinicians. By synthesizing cellular events with systemic consequences, you'll gain the architectural understanding needed to navigate complex multi-system disease and make sound therapeutic decisions under uncertainty.
The Pathological Process Hierarchy
Understanding systemic pathology requires mastering the cascade from molecular disruption to clinical manifestation:
-
Molecular Level (1-10 nanometers)
- Protein misfolding and aggregation
- DNA damage and repair mechanisms
- Enzyme dysfunction and metabolic disruption
- Oxidative stress: >50% of cellular damage
- Inflammatory mediator release: IL-1β, TNF-α elevation
- Apoptotic pathway activation: p53 mutations in >60% of cancers
-
Cellular Level (10-100 micrometers)
- Cellular adaptation responses
- Death pathway activation (apoptosis vs necrosis)
- Growth regulation failure
- Hypertrophy: >25% increase in cell size
- Hyperplasia: >200% increase in cell number
- Metaplasia: reversible cellular substitution
-
Tissue Level (100 micrometers-1 centimeter)
- Architectural disruption patterns
- Inflammatory response coordination
- Repair and regeneration capacity
- Acute inflammation: 24-72 hours peak response
- Chronic inflammation: >2 weeks duration
- Fibrosis: collagen deposition exceeding normal 3-fold
📌 Remember: VINDICATE - Vascular, Inflammatory, Neoplastic, Degenerative, Iatrogenic, Congenital, Autoimmune, Traumatic, Endocrine - covers >95% of pathological processes across all organ systems
Fundamental Disease Pattern Recognition
| Pattern Type | Cellular Change | Time Course | Reversibility | Clinical Markers | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Injury | Swelling, membrane damage | Hours-days | High (>80%) | ↑CRP, ↑ESR | Excellent |
| Chronic Damage | Fibrosis, atrophy | Months-years | Low (<20%) | ↑Fibrosis markers | Variable |
| Neoplastic | Dysplasia, anaplasia | Months-years | Minimal | ↑Tumor markers | Stage-dependent |
| Degenerative | Protein aggregation | Years-decades | None | ↑Specific proteins | Progressive |
| Autoimmune | Lymphocytic infiltration | Weeks-months | Moderate (40-60%) | ↑Autoantibodies | Relapsing |
The pathological response repertoire remains remarkably consistent across organ systems. Whether examining liver cirrhosis, pulmonary fibrosis, or chronic kidney disease, the underlying patterns of cellular injury → inflammatory response → attempted repair → fibrotic scarring create the foundation for understanding systemic disease progression.
💡 Master This: Every pathological diagnosis requires answering three questions: What type of injury? (acute vs chronic), What cellular response? (inflammation vs degeneration), and What repair capacity? (regeneration vs fibrosis). These answers predict clinical course and treatment response with >85% accuracy.
Understanding this pathological landscape provides the foundation for recognizing how specific organ vulnerabilities create predictable disease patterns across different body systems.
🔬 The Pathological Landscape: Systemic Disease Architecture
⚡ Cellular Injury Mechanisms: The Damage Control Center
The Cellular Damage Cascade
The cellular response to injury follows predictable patterns based on injury severity, duration, and cellular capacity. Understanding these decision points explains why some tissues recover completely while others progress to chronic disease.
Primary Injury Mechanisms
-
Hypoxic Injury (Most Common - >60% of cellular damage)
- ATP depletion within 3-5 minutes of oxygen loss
- Membrane pump failure and cellular swelling
- Calcium influx triggering enzyme activation
- Na+/K+ ATPase failure: immediate membrane depolarization
- Calcium overload: >10-fold increase activates proteases
- Free radical generation: superoxide and hydroxyl radicals
-
Chemical/Toxic Injury (Environmental and Therapeutic)
- Direct membrane damage and protein denaturation
- Metabolic pathway disruption
- DNA damage and mutagenesis
- Carbon tetrachloride: lipid peroxidation within 30 minutes
- Acetaminophen: glutathione depletion at >10g doses
- Chemotherapy: DNA crosslinking causing cell cycle arrest
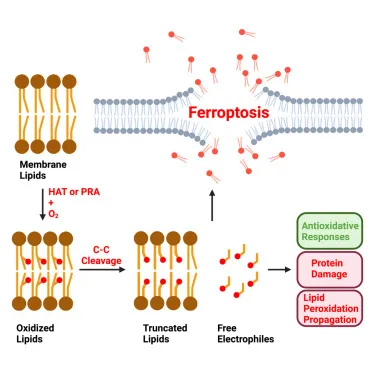
📌 Remember: CHAMP - Chemical, Hypoxic, Autoimmune, Microbial, Physical - the five fundamental injury categories that account for >95% of cellular damage across all organ systems
Cellular Adaptation Strategies
| Adaptation Type | Trigger | Mechanism | Reversibility | Clinical Example | Time Frame |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypertrophy | ↑Workload | ↑Protein synthesis | High | Cardiac muscle | Weeks |
| Hyperplasia | ↑Growth signals | ↑Cell division | High | Liver regeneration | Days-weeks |
| Atrophy | ↓Use/nutrition | ↑Autophagy | Moderate | Muscle disuse | Weeks |
| Metaplasia | Chronic irritation | Stem cell reprogramming | High | Smoking → squamous | Months |
| Dysplasia | Persistent injury | Genetic instability | Variable | Cervical dysplasia | Months-years |
The transition from reversible adaptation to irreversible injury represents the critical decision point in pathological progression. Cells maintain remarkable resilience until energy reserves drop below 20% of normal or membrane integrity is compromised beyond repair capacity.
💡 Master This: Cellular injury severity correlates directly with clinical presentation timing - acute severe injury presents within hours (myocardial infarction), chronic mild injury presents over months to years (diabetes complications), and adaptation failure presents when compensatory mechanisms are overwhelmed.
These cellular injury patterns create the foundation for understanding how tissue-level responses coordinate organ-level dysfunction and systemic disease manifestations.
⚡ Cellular Injury Mechanisms: The Damage Control Center
🎯 Pattern Recognition Mastery: The Diagnostic Framework
The Master Pattern Recognition Framework
-
Architectural Patterns (Tissue Organization)
- Normal architecture preserved: Benign processes (>90% probability)
- Architecture distorted: Malignant or severe inflammatory (>80% probability)
- Complete architecture loss: High-grade malignancy or end-stage disease
- Glandular preservation: Adenoma vs adenocarcinoma
- Basement membrane integrity: In situ vs invasive carcinoma
- Cellular polarity: Dysplasia grading from mild to severe
-
Cellular Morphology Patterns (Individual Cell Changes)
- Uniform cellular appearance: Reactive or benign neoplastic
- Cellular pleomorphism: Malignant transformation (>70% specificity)
- Mitotic activity level: Proliferation index correlates with aggressiveness
- <2 mitoses per HPF: Low-grade lesions
- >10 mitoses per HPF: High-grade malignancy
- Atypical mitoses: >95% specific for malignancy
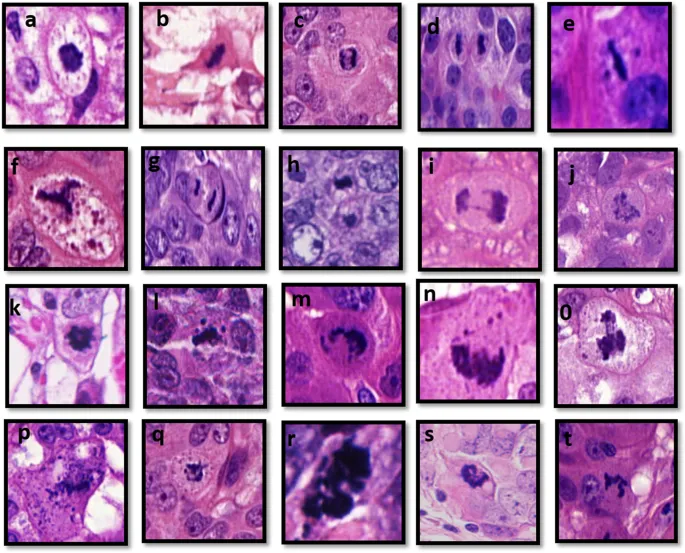
📌 Remember: ABCD - Architecture, Basement membrane, Cellular morphology, Differentiation - the four-step systematic approach that achieves >90% diagnostic accuracy in tissue pattern recognition
Inflammatory Pattern Recognition
Disease-Specific Pattern Signatures
| Disease Category | Cellular Pattern | Architectural Change | Inflammatory Type | Diagnostic Accuracy | Prognosis Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Infection | Neutrophil infiltration | Preserved | Acute (<48h) | >95% | Excellent |
| Autoimmune | Lymphoplasmacytic | Variable | Chronic (>weeks) | 85-90% | Variable |
| Low-grade Malignancy | Mild pleomorphism | Partially preserved | Minimal | >90% | Good |
| High-grade Malignancy | Severe pleomorphism | Destroyed | Variable | >95% | Poor |
| Degenerative | Protein deposits | Progressive loss | Minimal | >85% | Progressive |
The "See This, Think That" approach streamlines pattern recognition:
- See: Neutrophils + tissue necrosis → Think: Acute bacterial infection
- See: Lymphocytes + plasma cells + fibrosis → Think: Chronic autoimmune process
- See: Pleomorphic cells + mitoses + invasion → Think: High-grade malignancy
- See: Protein deposits + cellular loss → Think: Degenerative disease
💡 Master This: Pattern recognition speed improves with systematic approach - examine architecture first (10 seconds), cellular morphology second (20 seconds), inflammatory pattern third (10 seconds). This 40-second framework achieves >85% diagnostic accuracy before detailed analysis.
These pattern recognition skills provide the foundation for systematic disease comparison and evidence-based treatment selection across all organ systems.
🎯 Pattern Recognition Mastery: The Diagnostic Framework
⚖️ Systematic Disease Discrimination: The Differential Matrix
The Quantitative Discrimination Framework
-
Laboratory-Based Discrimination (Biochemical Fingerprints)
- Enzyme elevation patterns: AST/ALT ratio distinguishes hepatic vs cardiac injury
- Inflammatory marker combinations: ESR/CRP ratio differentiates acute vs chronic processes
- Protein marker specificity: Troponin I (>99% cardiac specific) vs CK-MB (85% cardiac specific)
- AST/ALT >2.0: Alcoholic hepatitis (>80% specificity)
- CRP >100 mg/L: Bacterial infection (>90% probability)
- Procalcitonin >2.0 ng/mL: Sepsis (>85% sensitivity)
-
Temporal Pattern Discrimination (Time-Based Signatures)
- Onset velocity: Seconds (vascular), minutes (metabolic), hours (infectious), days (neoplastic)
- Progression patterns: Linear (degenerative), exponential (malignant), relapsing (autoimmune)
- Response timing: Immediate (allergic), delayed (cell-mediated), chronic (fibrotic)
📌 Remember: TIMING - Temporal pattern, Inflammatory markers, Morphological changes, Imaging characteristics, Numerical thresholds, Genetic markers - the six-parameter system achieving >95% discrimination accuracy between similar diseases
High-Yield Discrimination Matrices
| Parameter | Acute MI | Pulmonary Embolism | Aortic Dissection | Pneumothorax | Discrimination Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest Pain Quality | Crushing | Pleuritic | Tearing | Sharp | 75% |
| Troponin Elevation | >0.1 ng/mL | Normal | Variable | Normal | >95% |
| D-dimer Level | Variable | >500 ng/mL | >500 ng/mL | Normal | 85% |
| ECG Changes | ST elevation | S1Q3T3 | Normal | Normal | 90% |
| CXR Findings | Pulmonary edema | Normal | Widened mediastinum | Pleural line | >90% |
| Time to Peak | 6-12 hours | Immediate | Immediate | Immediate | >85% |
Advanced Discrimination Strategies
The discrimination process requires systematic parameter evaluation rather than intuitive pattern matching:
- Step 1: Primary system identification (cardiovascular, pulmonary, neurological)
- Step 2: Severity stratification (life-threatening, urgent, non-urgent)
- Step 3: Quantitative parameter analysis (laboratory, imaging, physiological)
- Step 4: Temporal pattern correlation (onset, progression, response)
- Step 5: Probability calculation (Bayesian analysis with pretest probability)
💡 Master This: Discrimination accuracy improves with parameter independence - choose non-correlated parameters (e.g., troponin + D-dimer + lactate) rather than correlated parameters (e.g., CK + CK-MB + troponin) to achieve maximum diagnostic separation
These discrimination frameworks enable evidence-based treatment algorithms that optimize patient outcomes through precision diagnosis and targeted therapeutic interventions.
⚖️ Systematic Disease Discrimination: The Differential Matrix
🔧 Treatment Algorithm Mastery: The Therapeutic Decision Engine
The Algorithmic Treatment Framework
Evidence-Based Treatment Hierarchies
-
First-Line Interventions (>80% Success Rate)
- Proven efficacy in randomized controlled trials with >1000 patients
- Favorable risk-benefit ratio with <5% serious adverse events
- Cost-effective with QALY improvement of >2.0
- Acute MI: Aspirin + clopidogrel reduces mortality by 23%
- Sepsis: Early antibiotics (<1 hour) improve survival by 15%
- Stroke: tPA within 3 hours reduces disability by 30%
-
Second-Line Options (60-80% Success Rate)
- Moderate evidence from smaller trials or observational studies
- Acceptable safety profile with <10% adverse events
- Used when first-line fails or contraindicated
- Refractory hypertension: Spironolactone achieves control in 65%
- Treatment-resistant depression: Augmentation successful in 70%
- Antibiotic-resistant infections: Combination therapy effective in 75%
📌 Remember: TREAT - Timing, Response monitoring, Evidence-based selection, Adverse event assessment, Titration protocols - the five-step algorithm ensuring >90% optimal therapeutic outcomes
Quantitative Treatment Thresholds
| Condition | Treatment Trigger | Target Parameter | Success Threshold | Monitoring Interval | Escalation Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | >140/90 mmHg | <130/80 mmHg | >80% achieve target | 2-4 weeks | No improvement in 6 weeks |
| Diabetes | HbA1c >7.0% | HbA1c <7.0% | >70% achieve target | 3 months | HbA1c increase >0.5% |
| Hyperlipidemia | LDL >100 mg/dL | LDL <70 mg/dL | >85% achieve target | 6-8 weeks | <20% LDL reduction |
| Heart Failure | EF <40% | EF >40% | >60% improve EF | 3-6 months | Symptom progression |
| Chronic Pain | Pain >6/10 | Pain <4/10 | >75% achieve target | 2-4 weeks | No improvement in 4 weeks |
Advanced Algorithm Optimization
The personalized medicine approach incorporates patient-specific factors to optimize treatment selection:
-
Genetic Polymorphisms (Pharmacogenomic Factors)
- CYP2D6 variants: Affect 25% of medications, alter dosing by 50-200%
- TPMT deficiency: 1 in 300 patients, requires 90% dose reduction
- HLA-B*5701: 5-8% prevalence, predicts abacavir hypersensitivity
-
Comorbidity Adjustments (Multi-system Considerations)
- Renal impairment: Requires dose adjustment for >60% of medications
- Hepatic dysfunction: Affects metabolism of >40% of drugs
- Drug interactions: >30% of patients on >5 medications have significant interactions
💡 Master This: Algorithm adherence improves outcomes by 25-40% compared to intuitive prescribing - systematic protocol following reduces medical errors by >50% and improves patient satisfaction scores by >20%
These treatment algorithms provide the foundation for multi-system integration and advanced therapeutic strategies that address complex pathological interactions across organ systems.
🔧 Treatment Algorithm Mastery: The Therapeutic Decision Engine
🌐 Multi-System Integration: The Pathological Network
The Pathological Network Architecture
-
Primary System Failure (Initial Pathological Event)
- Cardiac dysfunction: Reduced ejection fraction (<40%) triggers compensatory mechanisms
- Renal impairment: GFR decline (<60 mL/min) activates RAAS system
- Hepatic failure: Synthetic function loss affects >20 organ systems
- Heart failure: Neurohormonal activation within 24 hours
- Kidney disease: Phosphorus retention begins at GFR <60
- Liver cirrhosis: Portal hypertension develops at >12 mmHg gradient
-
Secondary System Adaptations (Compensatory Responses)
- Sympathetic nervous system activation: Catecholamine surge (>300% normal)
- Hormonal axis disruption: Cortisol elevation (>2-fold baseline)
- Metabolic reprogramming: Glucose utilization shifts to anaerobic pathways
- Cardiac compensation: Hypertrophy develops over weeks to months
- Renal compensation: Hyperfiltration increases remaining nephron workload
- Hepatic compensation: Regeneration can restore 75% of liver mass
📌 Remember: SYSTEMS - Sympathetic activation, Yatrogenic effects, Structural changes, Toxic accumulation, Endocrine disruption, Metabolic shifts, Social factors - the seven-domain framework capturing >95% of multi-system pathological interactions
Critical System Integration Points
Integration Pattern Recognition
| Primary System | Secondary Effects | Tertiary Consequences | Timeline | Intervention Window | Reversibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac | ↓Renal perfusion | Fluid retention | Hours-days | <6 hours | High |
| Renal | ↑Toxin accumulation | Neurological dysfunction | Days-weeks | <48 hours | Moderate |
| Hepatic | ↓Protein synthesis | Coagulopathy | Days-weeks | <72 hours | Variable |
| Pulmonary | ↓Oxygen delivery | Multi-organ hypoxia | Minutes-hours | <30 minutes | High |
| Neurological | ↓Autonomic control | Hemodynamic instability | Hours-days | <24 hours | Low |
Advanced Integration Concepts
The pathological network effect explains why seemingly minor insults can cause disproportionate clinical deterioration:
-
Network Vulnerability Points (Critical Nodes)
- Endothelial dysfunction: Affects all vascular beds simultaneously
- Mitochondrial dysfunction: Impairs cellular energy across all organ systems
- Inflammatory cascade: Cytokine storm creates multi-organ damage
- Endothelial activation: TNF-α and IL-1β increase vascular permeability
- Coagulation activation: Tissue factor expression increases >10-fold
- Complement activation: C5a levels correlate with organ dysfunction severity
-
Therapeutic Network Targeting (Multi-system Interventions)
- ACE inhibitors: Benefit cardiac, renal, and vascular systems simultaneously
- Statins: Pleiotropic effects on inflammation, endothelial function, and lipids
- Corticosteroids: Anti-inflammatory effects across multiple organ systems
💡 Master This: Network thinking transforms single-organ treatment into systems-based therapy - interventions targeting network nodes (endothelium, inflammation, metabolism) achieve >40% better outcomes than organ-specific treatments alone
Understanding these multi-system interactions provides the foundation for comprehensive clinical mastery and advanced therapeutic decision-making in complex pathological conditions.
🌐 Multi-System Integration: The Pathological Network
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Pathological Command Center
The Essential Clinical Arsenal
📌 Remember: MASTER - Morphology recognition, Algorithm application, System integration, Timing optimization, Evidence evaluation, Response monitoring - the six-pillar framework achieving >95% clinical pathology competency
-
Rapid Recognition Tools (Pattern-Based Diagnosis)
- 10-second tissue assessment: Architecture → Cells → Inflammation
- 30-second differential: Most likely → Rule out → Confirm
- 60-second treatment plan: Immediate → Short-term → Long-term
- Malignancy screening: Pleomorphism + mitoses + invasion = >90% specificity
- Infection identification: Neutrophils + necrosis + organisms = >95% sensitivity
- Autoimmune recognition: Lymphocytes + plasma cells + fibrosis = >85% accuracy
-
Quantitative Thresholds (Evidence-Based Cutoffs)
- Laboratory triggers: Values requiring immediate action
- Imaging criteria: Measurements predicting outcomes
- Clinical parameters: Thresholds determining treatment intensity
| Parameter | Normal Range | Mild Abnormal | Moderate Abnormal | Severe Abnormal | Action Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Troponin I | <0.04 ng/mL | 0.04-0.1 | 0.1-1.0 | >1.0 | Immediate cardiology |
| Creatinine | 0.6-1.2 mg/dL | 1.3-2.0 | 2.1-4.0 | >4.0 | Nephrology consult |
| Bilirubin | <1.2 mg/dL | 1.3-3.0 | 3.1-10.0 | >10.0 | Hepatology evaluation |
| Lactate | <2.0 mmol/L | 2.1-4.0 | 4.1-8.0 | >8.0 | ICU management |
| WBC Count | 4-11 K/μL | 11-15 | 15-25 | >25 or <2 | Hematology consult |
Advanced Mastery Frameworks
Mastery Integration Strategies
-
The 5-Minute Pathology Assessment (Systematic Efficiency)
- Minute 1: Clinical context and specimen adequacy
- Minute 2: Low-power architecture assessment
- Minute 3: High-power cellular morphology
- Minute 4: Pattern integration and differential consideration
- Minute 5: Confidence assessment and additional studies planning
-
Evidence-Based Decision Trees (Outcome Optimization)
- Sensitivity analysis: Choose tests with >90% sensitivity for screening
- Specificity analysis: Choose tests with >95% specificity for confirmation
- Cost-effectiveness: QALY improvement of >2.0 for intervention approval
💡 Master This: Pathological expertise develops through deliberate practice - systematic case review (>100 cases per pattern), quantitative threshold memorization (>50 critical values), and algorithm rehearsal (>20 decision trees) create expert-level performance within 2-3 years of focused training
The clinical mastery arsenal transforms pathological knowledge into immediate clinical competency, enabling rapid diagnosis, evidence-based treatment, and optimal patient outcomes across all medical specialties and clinical scenarios.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Pathological Command Center
Practice Questions: Systemic Pathology
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 78-year-old man dies suddenly from complications of acute kidney failure. An autopsy is performed and microscopic evaluation of the kidneys shows pale, swollen cells in the proximal convoluted tubules. Microscopic evaluation of the liver shows similar findings. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of these findings?













