Dialysis access procedures and complications US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Dialysis access procedures and complications. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
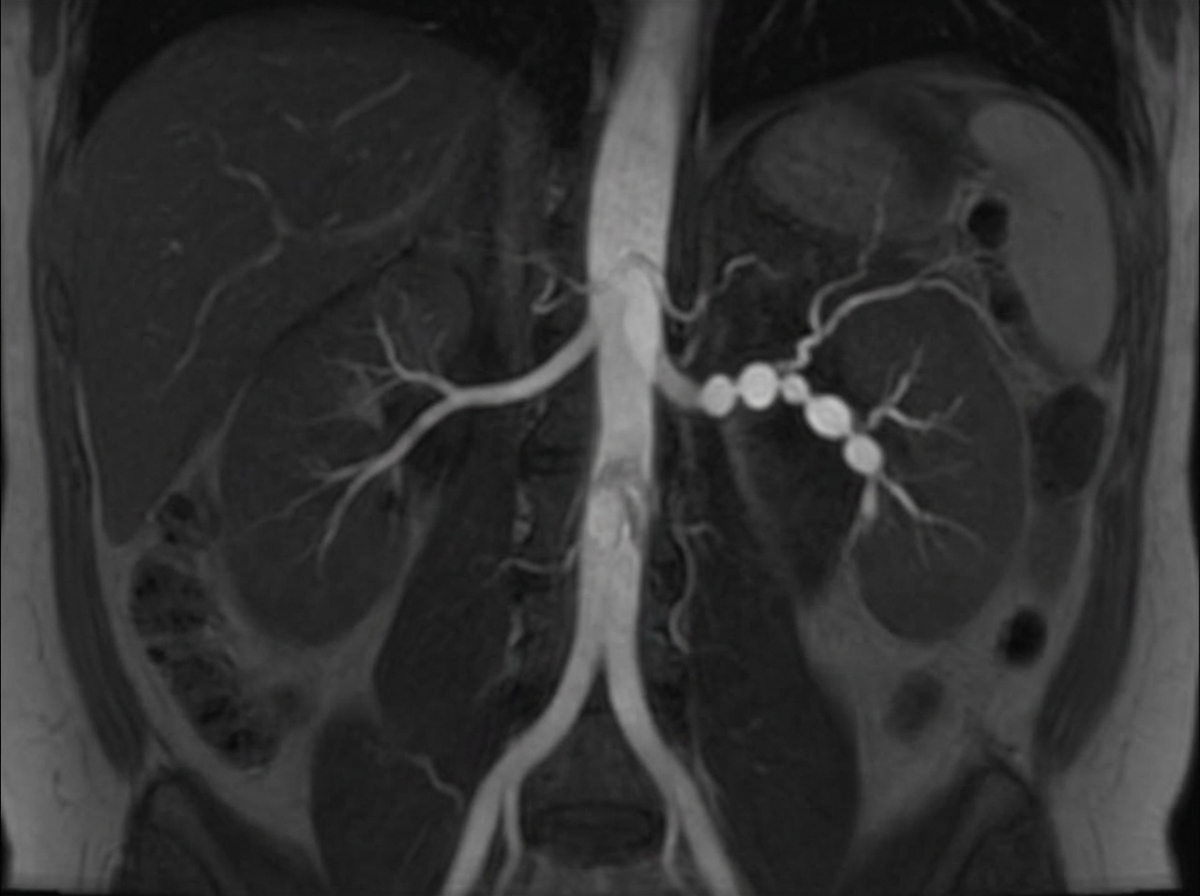
Dialysis access procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 1: A 31-year-old woman returns to her primary care provider for a follow-up visit. At a routine health maintenance visit 2 months ago, her blood pressure (BP) was 181/97 mm Hg. She has adhered to a low-salt diet and exercises regularly. On repeat examination 1 month later, her BP was 178/93, and she was prescribed hydrochlorothiazide and lisinopril. The patient denies any complaint, except for occasional headaches. Now, her BP is 179/95 in the right arm and 181/93 in the left arm. Physical examination reveals an abdominal bruit that lateralizes to the left. A magnetic resonance angiogram of the renal arteries is shown in the image. Which of the following is the best next step for the management of this patient condition?
- A. Balloon angioplasty (Correct Answer)
- B. Intravenous phentolamine
- C. Stenting
- D. Add statin and aspirin
- E. Surgical reconstruction
Dialysis access procedures and complications Explanation: ***Balloon angioplasty***
- This patient presents with **severe hypertension, particularly diastolic hypertension**, that is **refractory to standard medical therapy** (hydrochlorothiazide and lisinopril).
- The combination of uncontrolled hypertension in a young woman, a **lateralizing abdominal bruit**, and the **magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) findings consistent with fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD)** strongly suggests renovascular hypertension, for which **renal artery angioplasty is the preferred treatment**, especially in FMD due to its high success rate and low complication rate compared to stenting.
*Intravenous phentolamine*
- **Phentolamine is an alpha-adrenergic blocker** used for the short-term control of hypertensive crises, particularly those due to **pheochromocytoma** or sympathomimetic overdose.
- It is **not a definitive, long-term treatment for renovascular hypertension** and would not address the underlying anatomical lesion.
*Stenting*
- **Stenting is typically reserved for renal artery stenosis caused by atherosclerosis**, especially in older patients, or for cases of FMD with **recurrent stenosis after angioplasty or with aneurysmal disease**.
- For **initial treatment of FMD**, balloon angioplasty alone is generally preferred due to the lower rate of complications and avoidance of leaving an intimal foreign body in a young patient.
*Add statin and aspirin*
- **Statins and aspirin are crucial for managing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk factors**, especially in patients with established atherosclerosis.
- While general cardiovascular health is important, these medications **do not address the underlying renovascular cause of this patient's hypertension**, which is likely fibromuscular dysplasia, and therefore will not control her severe blood pressure.
*Surgical reconstruction*
- **Surgical revascularization is typically reserved for complex cases of renovascular hypertension** where endovascular approaches have failed or are technically not feasible.
- Given the patient's likely diagnosis of FMD, **endovascular balloon angioplasty is the first-line treatment**, and surgery carries higher risks and is more invasive.
Dialysis access procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 2: A 71-year old man is brought to the emergency department because of progressively worsening shortness of breath and fatigue for 3 days. During the last month, he has also noticed dark colored urine. He had an upper respiratory infection 6 weeks ago. He underwent a cholecystectomy at the age of 30 years. He has hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. He immigrated to the US from Italy 50 years ago. Current medications include simvastatin, lisinopril, and metformin. He appears pale. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), pulse is 96/min, respirations are 21/min, and blood pressure is 150/80 mm Hg. Auscultation of the heart shows a grade 4/6 systolic murmur over the right second intercostal space that radiates to the carotids. Laboratory studies show:
Leukocyte count 9,000/mm3
Hemoglobin 8.3 g/dL
Hematocrit 24%
Platelet count 180,000/mm3
LDH 212 U/L
Haptoglobin 15 mg/dL (N=41–165)
Serum
Na+ 138 mEq/L
K+ 4.5 mEq/L
CL- 102 mEq/L
HCO3- 24 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 20 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.2 mg/dL
Total bilirubin 1.8 mg/dL
Stool testing for occult blood is negative. Direct Coombs test is negative. Echocardiography shows an aortic jet velocity of 4.2 m/s and a mean pressure gradient of 46 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management to treat this patient's anemia?
- A. Aortic valve replacement (Correct Answer)
- B. Administration of corticosteroids
- C. Discontinuation of medication
- D. Administration of hydroxyurea
- E. Supplementation with iron
Dialysis access procedures and complications Explanation: ***Aortic valve replacement***
- The patient's **severe aortic stenosis** (aortic jet velocity >4.0 m/s and mean pressure gradient >40 mmHg) is causing **shear stress** on red blood cells, leading to **microangiopathic hemolytic anemia**. This is characterized by low hemoglobin, high LDH, low haptoglobin, and negative Coombs test.
- **Aortic valve replacement** is the definitive treatment to reduce the shear stress, resolve the hemolysis, and improve the patient's symptoms of anemia and heart failure.
*Administration of corticosteroids*
- Corticosteroids are primarily used in **autoimmune hemolytic anemia** (positive Coombs test), which is not the case here as the direct Coombs test is negative.
- They would not address the underlying **mechanical destruction of red blood cells** due to aortic stenosis.
*Discontinuation of medication*
- The patient's current medications (simvastatin, lisinopril, metformin) are for managing his chronic conditions and are **not associated with hemolytic anemia**. Discontinuing them would be inappropriate and potentially harmful.
- There is no evidence to suggest a **drug-induced hemolytic anemia** in this case.
*Administration of hydroxyurea*
- Hydroxyurea is used in conditions like **sickle cell anemia** or **polycythemia vera** to modify red blood cell production or reduce cell counts, respectively.
- It has no role in treating **mechanical hemolytic anemia** caused by valvular heart disease.
*Supplementation with iron*
- While the patient has anemia, it is a **hemolytic anemia**, not an iron deficiency anemia, as indicated by the low haptoglobin and elevated LDH.
- Iron supplementation would **not stop the destruction of red blood cells** caused by the turbulent flow across the aortic valve.
Dialysis access procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 3: You are called to a hemodialysis suite. The patient is a 61-year-old man with a history of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and type-2 diabetes mellitus-induced end-stage renal disease who has required hemodialysis for the past year. His current hemodialysis session is nearing the end when the nurse notices that his blood pressure has dropped to 88/60 mm Hg from his normal of 142/90 mm Hg. The patient denies any shortness of breath or chest pain. He took his daily bisoprolol, metformin, and insulin this morning before coming to the hospital. On examination, the patient’s blood pressure is 92/60 mm Hg, and his heart rate is 119/min. Chest auscultation is unremarkable. What is the most appropriate next management step?
- A. Infuse 1 liter of 0.9% saline
- B. Administer intravenous calcium gluconate
- C. Transfuse the patient with 1 unit of packed red blood cells
- D. Stop ultrafiltration and decrease blood flow into the machine (Correct Answer)
- E. Start the patient on an epinephrine drip
Dialysis access procedures and complications Explanation: ***Stop ultrafiltration and decrease blood flow into the machine***
- The patient's **hypotension** and **tachycardia** during hemodialysis strongly suggest **intradialytic hypotension**, which is often caused by excessive fluid removal (ultrafiltration) or rapid fluid shifts.
- **Stopping ultrafiltration** and **reducing blood flow** allows for gradual re-equilibration of fluid and helps stabilize blood pressure without adding more fluid to a patient with end-stage renal disease.
*Infuse 1 liter of 0.9% saline*
- Administering a large volume of saline is generally **contraindicated in ESRD patients** given their inability to excrete fluid, which could lead to **fluid overload** and pulmonary edema.
- While fluid resuscitation might be considered for severe hypotension, the initial step in intradialytic hypotension is to adjust the dialysis settings.
*Administer intravenous calcium gluconate*
- **Calcium gluconate** is primarily used to stabilize the cardiac membrane in cases of **severe hyperkalemia**, which is not indicated by the current clinical picture.
- There is no mention of ECG changes or lab results to suggest hyperkalemia.
*Transfuse the patient with 1 unit of packed red blood cells*
- There is no clinical evidence of **acute blood loss** or **severe anemia** presenting with hypovolemic shock.
- Transfusion is an intervention for significant blood loss or severe anemia, not for intradialytic hypotension caused by fluid shifts.
*Start the patient on an epinephrine drip*
- **Vasopressors** like epinephrine are typically reserved for **refractory hypotension** after more conservative measures have failed, or in cases of **septic shock** or **anaphylaxis**.
- Initiating a powerful vasopressor as a first step without addressing the potential underlying cause related to dialysis is inappropriate.
Dialysis access procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 4: A 68-year-old man presents for a screening ultrasound scan. He has been feeling well and is in his usual state of good health. His medical history is notable for mild hypertension and a 100-pack-year tobacco history. He has a blood pressure of 128/86 and heart rate of 62/min. Physical examination is clear lung sounds and regular heart sounds. On ultrasound, an infrarenal aortic aneurysm of 4 cm in diameter is identified. Which of the following is the best initial step for this patient?
- A. Reassurance
- B. Beta-blockers
- C. Urgent repair
- D. Surveillance (Correct Answer)
- E. Elective repair
Dialysis access procedures and complications Explanation: **Surveillance**
- An **infrarenal aortic aneurysm** of 4 cm in diameter in an asymptomatic patient is typically managed with **regular surveillance** to monitor for growth.
- Surgical intervention is generally reserved for aneurysms larger than 5.5 cm or those that are rapidly expanding or symptomatic.
*Reassurance*
- While it's important to provide reassurance, simply doing so without a concrete plan for follow-up would be inappropriate given the potential for **aneurysm expansion** and rupture.
- The patient's **tobacco history** is a significant risk factor for aneurysm progression and warrants monitoring.
*Beta-blockers*
- Beta-blockers may be part of the medical management for **hypertension** and could theoretically slow aneurysm growth by reducing pulsatile stress.
- However, they are not the primary **initial step** for an asymptomatic aneurysm of this size and do not replace the need for surveillance.
*Urgent repair*
- **Urgent repair** is indicated for symptomatic aneurysms, those that are rapidly expanding, or those showing signs of rupture or impending rupture, none of which are present here.
- A 4 cm aneurysm in an asymptomatic patient does not meet the criteria for **urgent intervention**.
*Elective repair*
- **Elective repair** is typically considered for aneurysms exceeding 5.5 cm in diameter or those that are symptomatic or rapidly growing.
- A 4 cm aneurysm is below the threshold for **elective repair** in an asymptomatic patient without other high-risk features.
Dialysis access procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 5: Two hours after admission to the intensive care unit, a 56-year-old man with necrotizing pancreatitis develops profound hypotension. His blood pressure is 80/50 mm Hg and he is started on vasopressors. A central venous access line is placed. Which of the following is most likely to decrease the risk of complications from this procedure?
- A. Placement of the central venous line in the femoral vein
- B. Replacement of the central venous line every 7-10 days
- C. Initiation of anticoagulation after placement
- D. Preparation of the skin with chlorhexidine and alcohol (Correct Answer)
- E. Initiation of periprocedural systemic antibiotic prophylaxis
Dialysis access procedures and complications Explanation: ***Preparation of the skin with chlorhexidine and alcohol***
- **Chlorhexidine** with alcohol is the most effective skin antiseptic for preventing **catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSIs)** by significantly reducing skin microbial counts.
- Proper skin preparation is a cornerstone of preventing **infectious complications** associated with central venous catheter insertion.
*Placement of the central venous line in the femoral vein*
- The femoral site is generally associated with a **higher risk of infection** and **deep venous thrombosis** compared to subclavian or internal jugular sites in adult patients.
- Femoral access is often reserved for situations where other sites are inaccessible or contraindicated, due to its **less favorable complication profile**.
*Replacement of the central venous line every 7-10 days*
- Routine replacement of central venous lines at fixed intervals, without clinical indication, has **not been shown to reduce infection rates**.
- This practice can actually **increase the risk** of mechanical complications and introduce new opportunities for infection with each procedure.
*Initiation of anticoagulation after placement*
- Routine systemic **anticoagulation** after central venous line placement is generally **not recommended** due to an increased risk of **bleeding complications**.
- Anticoagulation is typically reserved for specific indications such as documented **catheter-related thrombosis**.
*Initiation of periprocedural systemic antibiotic prophylaxis*
- Routine **systemic antibiotic prophylaxis** is **not recommended** for central venous catheter insertion as it promotes **antibiotic resistance** without significantly reducing CRBSIs.
- Strict adherence to **aseptic technique** and proper skin antisepsis are more effective for preventing infections.
Dialysis access procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 6: A 27-year-old soldier stationed in Libya sustains a shrapnel injury during an attack, causing a traumatic above-elbow amputation. The resulting arterial bleed is managed with a tourniquet prior to transport to the military treatment facility. On arrival, he is alert and oriented to person, place, and time. His armor and clothing are removed. His pulse is 145/min, respirations are 28/min, and blood pressure is 95/52 mm Hg. Pulmonary examination shows symmetric chest rise. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Abdominal examination shows no abnormalities. There are multiple shrapnel wounds over the upper and lower extremities. A tourniquet is in place around the right upper extremity; the right proximal forearm has been amputated. One large-bore intravenous catheter is placed in the left antecubital fossa. Despite multiple attempts, medical staff is unable to establish additional intravenous access. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Irrigate the shrapnel wounds
- B. Perform endotracheal intubation
- C. Establish intraosseous access (Correct Answer)
- D. Establish central venous access
- E. Replace the tourniquet with a pressure dressing
Dialysis access procedures and complications Explanation: ***Establish intraosseous access***
- The patient is in **hemorrhagic shock** (tachycardia, hypotension) and requires rapid fluid resuscitation, but peripheral intravenous access is difficult to obtain. **Intraosseous (IO) access** provides a rapid and reliable route for fluids and medications, especially in emergencies when IV access is challenging.
- IO access is a **bridge to definitive venous access** and is crucial for immediate life-saving interventions in trauma.
*Irrigate the shrapnel wounds*
- While wound irrigation is important for preventing infection, it is **not the immediate priority** when the patient is in hemorrhagic shock.
- Addressing the circulatory compromise takes precedence over local wound care.
*Perform endotracheal intubation*
- The patient is **alert and oriented** with symmetric chest rise and clear lungs, indicating he does not currently have an airway crisis requiring intubation.
- Intubation is an invasive procedure that carries risks and should only be performed when indicated for airway protection or respiratory failure.
*Establish central venous access*
- While central venous access is useful for long-term fluid management and monitoring, it is generally **more time-consuming and technically challenging** to establish than IO access, especially in an emergent, unstable patient.
- Given the urgency of rapid fluid administration, IO access is preferred as the immediate next step.
*Replace the tourniquet with a pressure dressing*
- The patient has an above-elbow amputation, suggesting significant injury, and the tourniquet is currently controlling the bleed. Removing the tourniquet prematurely without proximal surgical control can lead to **recurrent catastrophic hemorrhage**.
- A definitive surgical approach is needed to manage the amputation, not simply replacing the tourniquet with a pressure dressing, which may be insufficient to control arterial bleeding.
Dialysis access procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 7: A 43-year-old man comes to the physician because of increasing shortness of breath for 1 month. He has been using two pillows at night but frequently wakes up feeling as if he is choking. Five months ago, he underwent surgery for creation of an arteriovenous fistula in his left upper arm. He has hypertension and chronic kidney disease due to reflux nephropathy. He receives hemodialysis three times a week. His current medications are enalapril, vitamin D3, erythropoietin, sevelamer, and atorvastatin. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), respirations are 22/min, pulse is 103/min and bounding, and blood pressure is 106/58 mm Hg. Examination of the lower extremities shows bilateral pitting pedal edema. There is jugular venous distention. A prominent thrill is heard over the brachiocephalic arteriovenous fistula. There are crackles heard at both lung bases. Cardiac examination shows an S3 gallop. The abdomen is soft and nontender. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. AV fistula aneurysm
- B. Pulmonary embolism
- C. Constrictive pericarditis
- D. Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome
- E. High-output heart failure (Correct Answer)
Dialysis access procedures and complications Explanation: ***High-output heart failure***
- The patient's symptoms of **dyspnea, orthopnea, pitting edema, jugular venous distention, crackles**, and **S3 gallop** strongly indicate **heart failure**. The **bounding pulse** and **wide pulse pressure** (systolic 106, diastolic 58) in the presence of an **arteriovenous fistula** suggest a **high-output state**.
- An **arteriovenous fistula** used for hemodialysis can significantly increase **cardiac preload** and reduce **afterload**, leading to a persistent increase in **cardiac output**. Over time, this chronic increase in demand can overwhelm the heart, resulting in **high-output heart failure**.
*AV fistula aneurysm*
- An **AV fistula aneurysm** is a localized dilatation of the fistula and would typically present as a painful or compressible mass.
- While it's a complication of AV fistulas, it does not directly explain the systemic signs of **heart failure** observed in this patient.
*Pulmonary embolism*
- **Pulmonary embolism** typically presents with sudden onset **dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain**, and sometimes **tachycardia** and **hypoxia**.
- This patient's symptoms are of gradual onset, accompanied by clear signs of **fluid overload** and **cardiac dysfunction** like an S3 gallop, which are not typical for a PE.
*Constrictive pericarditis*
- **Constrictive pericarditis** causes symptoms of **right-sided heart failure** due to impaired diastolic filling, often with a **pericardial knock** and **Kussmaul's sign**.
- While it can manifest with pedal edema and JVD, the **S3 gallop** and especially the **bounding pulse** and **wide pulse pressure** are inconsistent with constrictive pericarditis, which would typically cause a low-output state.
*Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome*
- **Dialysis disequilibrium syndrome** occurs shortly after hemodialysis, usually during or immediately after the first few sessions. It is characterized by neurological symptoms such as **headache, nausea, vomiting, confusion**, and **seizures**.
- The patient's symptoms have been evolving over a month and describe a state of **fluid overload** and **cardiac dysfunction**, not acute neurological symptoms related to dialysis.
Dialysis access procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 8: A 60-year-old man with a long-standing history of type 2 diabetes and hypertension managed with lisinopril and metformin presents with itchy skin. He also describes moderate nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, and fatigue. The vital signs include: temperature 36.8°C (98.2°F), heart rate 98/min, respiratory rate 15/min, blood pressure 135/85 mm Hg, oxygen saturation 100% on room air. Physical exam is notable for pale conjunctivae, pitting edema, and ascites. Laboratory findings are shown below:
BUN 78 mg/dL
pCO2 25 mm Hg
Creatinine 7.2 mg/dL
Glucose 125 mg/dL
Serum chloride 102 mmol/L
Serum potassium 6.3 mEq/L
Serum sodium 130 mEq/L
Total calcium 1.3 mmol/L
Magnesium 1.2 mEq/L
Phosphate 1.9 mmol/L
Hemoglobin 9.5 g/dL
MCV 86 μm3
Bicarbonate (HCO3) 10 mmol/L
Shrunken kidneys are identified on renal ultrasound. The doctor explains to the patient that he will likely need dialysis due to his significant renal failure until a renal transplant can be performed. The patient is concerned because he is very busy and traveling a lot for work. Given his lifestyle requirements, what is a potential complication of the most appropriate dialysis modality for this patient?
- A. Excessive bleeding
- B. Muscle cramping
- C. Hypotension
- D. Hypertriglyceridemia (Correct Answer)
- E. Hypoglycemia
Dialysis access procedures and complications Explanation: ***Hypertriglyceridemia***
- The patient's **lifestyle requirements** (busy, traveling a lot) suggest **peritoneal dialysis (PD)** as the most appropriate modality due to its flexibility and home-based nature.
- **Hypertriglyceridemia** is a common complication of PD due to the absorption of glucose from the dialysate, which stimulates hepatic triglyceride synthesis.
*Excessive bleeding*
- This is a rare complication in both hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
- While **anti-coagulation** is used in hemodialysis, it's carefully monitored, and significant bleeding is not a typical long-term complication of the chosen modality (PD).
*Muscle cramping*
- **Muscle cramps** can occur with hemodialysis, typically due to rapid fluid and electrolyte shifts.
- This is less common in peritoneal dialysis, which involves a slower and more continuous exchange process.
*Hypotension*
- **Hypotension** can be a complication of hemodialysis due to rapid fluid removal.
- Peritoneal dialysis, with its gradual fluid exchange, is generally less associated with significant hypotensive episodes.
*Hypoglycemia*
- The **glucose-rich dialysate** used in peritoneal dialysis can actually lead to **hyperglycemia**, not hypoglycemia, especially in diabetic patients.
- Regular insulin adjustments are often required for diabetic patients on PD.
Dialysis access procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 9: A 45-year-old man presents to the emergency department because of fever and scrotal pain for 2 days. Medical history includes diabetes mellitus and morbid obesity. His temperature is 40.0°C (104.0°F), the pulse is 130/min, the respirations are 35/min, and the blood pressure is 90/68 mm Hg. Physical examination shows a large area of ecchymosis, edema, and crepitus in his perineal area. Fournier gangrene is suspected. A right internal jugular central venous catheter is placed without complication under ultrasound guidance for vascular access in preparation for the administration of vasopressors. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- A. Confirm line placement by ultrasound
- B. Begin to use the line after documenting the return of dark, non-pulsatile blood from all ports
- C. Begin infusion of normal saline through a central line
- D. Obtain an immediate portable chest radiograph to evaluate line placement (Correct Answer)
- E. Begin infusion of norepinephrine to maintain systolic blood pressure over 90 mm Hg
Dialysis access procedures and complications Explanation: **Obtain an immediate portable chest radiograph to evaluate line placement**
- The most appropriate next step after central venous catheter placement is to **confirm its correct position** and rule out complications like **pneumothorax** via imaging.
- A **chest radiograph** is the standard and immediate method to confirm proper placement of the tip in the lower superior vena cava and rule out pneumothorax, especially given the patient's critical condition.
*Confirm line placement by ultrasound*
- While ultrasound is used during placement to visualize the vessel and guide needle insertion, it is **not sufficient for confirming the final tip position** of the catheter or for ruling out pneumothorax.
- Ultrasound confirmation usually involves visualizing a **saline flush** in the right atrium, but a chest X-ray is still required for comprehensive evaluation.
*Begin to use the line after documenting the return of dark, non-pulsatile blood from all ports*
- Documenting blood return confirms that the catheter is in a vein but does not confirm **optimal tip placement** or exclude potential complications like **pneumothorax**.
- Using the line without radiological confirmation can lead to administering medications into incorrect locations (e.g., subclavian artery) or exacerbating unnoticed complications.
*Begin infusion of normal saline through a central line*
- Administering fluids before confirming proper line placement carries the risk of **extravasation** or infusing into an artery or other unintended space, which could worsen the patient's condition.
- Although IV fluids are needed in this septic patient, **confirmation of line placement** is a higher priority before commencing infusions.
*Begin infusion of norepinephrine to maintain systolic blood pressure over 90 mm Hg*
- While norepinephrine is crucial for managing septic shock and **hypotension** in this patient, starting it before confirming central line placement is dangerous.
- **Vasopressors require a secure central line** to prevent severe local tissue damage if extravasation occurs.
Dialysis access procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 10: A 34-year-old woman is brought into the emergency department by emergency medical services after an electrical fire in her apartment. She is coughing with an O2 saturation of 98%, on 2L of nasal cannula. The patient's physical exam is significant for a burn on her right forearm that appears to be dry, white, and leathery in texture. Her pulses and sensations are intact in all extremities. The patient's vitals are HR 110, BP 110/80, T 99.2, RR 20. She has no evidence of soot in her mouth and admits to leaving the room as soon as the fire started. Which of the following is the best treatment for this patient?
- A. Excision and grafting (Correct Answer)
- B. Bacitracin
- C. Amputation
- D. Mafenide acetate
- E. Pain relievers
Dialysis access procedures and complications Explanation: ***Excision and grafting***
* The burn is described as **dry, white, and leathery**, which are classic features of a **full-thickness (third-degree) burn**.
* Full-thickness burns destroy all skin layers including the dermis, and typically have **loss of sensation** at the burn site due to nerve ending destruction.
* **Excision and grafting** is the definitive treatment for full-thickness burns, involving removal of necrotic tissue and skin grafting to promote healing and prevent infection.
* The patient has intact pulses and sensations in all extremities (indicating no compartment syndrome or vascular compromise), making her a good candidate for this procedure.
*Bacitracin*
* **Bacitracin** is an antibiotic ointment used for **superficial (first-degree) or minor partial-thickness burns**.
* It is insufficient for a **full-thickness burn**, which requires surgical debridement and grafting for proper healing.
*Amputation*
* **Amputation** is reserved for cases of **irreversible tissue damage** with compromised vascularity, extensive non-viable tissue, or severe crush injuries.
* This patient has **intact pulses and sensations in all extremities**, indicating the limb is viable and perfused, making amputation inappropriate.
*Mafenide acetate*
* **Mafenide acetate** is a topical antimicrobial agent that penetrates eschar and can be used for deep burns to prevent infection.
* While useful as adjunctive therapy, it does **not replace the need for surgical excision and grafting**, which is the definitive treatment for full-thickness burns.
*Pain relievers*
* **Pain relievers** are important supportive care for burn patients but are **not definitive treatment**.
* They manage symptoms but do not address the underlying need for debridement and wound closure through grafting.
More Dialysis access procedures and complications US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.