Urology Basics

On this page
🏗️ The Urological Foundation: Your Surgical Command Center
You'll master the complete urological framework from anatomical foundations through diagnostic reasoning to evidence-based intervention, building the systematic approach that transforms scattered facts into clinical confidence. This lesson integrates structural knowledge with pattern recognition skills, teaching you to discriminate between similar presentations and deploy the right treatment at the right time. By connecting urological pathology to multi-system effects, you'll develop the contextual thinking that separates competent clinicians from exceptional ones.
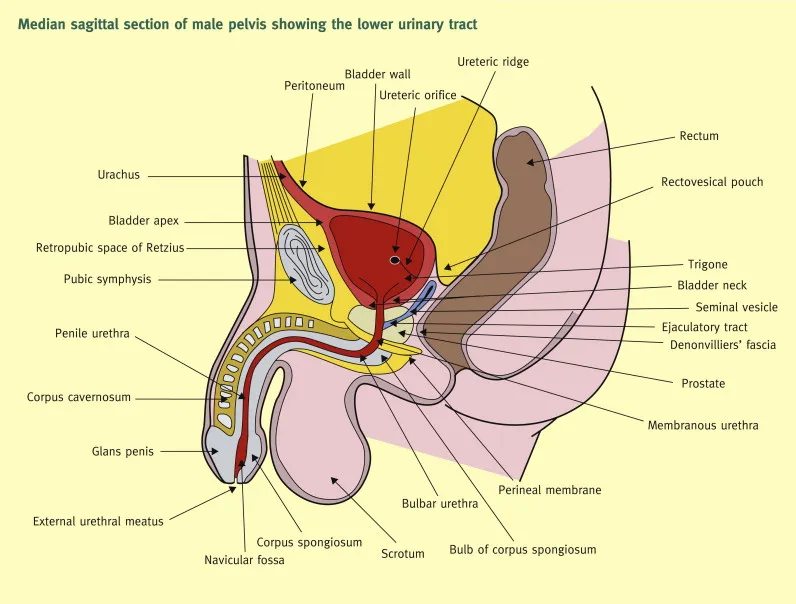
The urological system operates as an integrated network where 4 critical zones determine surgical approach: the retroperitoneal space, pelvis, perineum, and external genitalia. Each zone has distinct vascular territories, innervation patterns, and surgical access points that dictate treatment strategies.
📌 Remember: RIPE - Retroperitoneal (kidneys, ureters), Intrapelvic (bladder, prostate), Perineal (bulbar urethra), External (penile, scrotal). Each zone requires different surgical approaches and has unique complication profiles.
- Retroperitoneal Zone (Zone 1)
- Contains kidneys, ureters, major vessels
- Surgical access: flank, subcostal, or laparoscopic approaches
- Critical structures: renal vessels (15-20% of cardiac output), ureter (3 anatomical narrowings)
- Ureteropelvic junction: 2-4mm diameter
- Pelvic brim crossing: 4-6mm diameter
- Ureterovesical junction: 1-5mm diameter
- Intrapelvic Zone (Zone 2)
- Bladder capacity: 400-600mL normal, >800mL retention
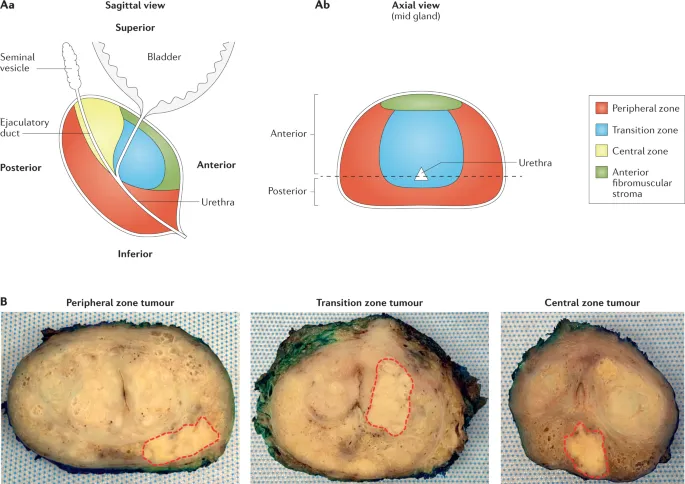
- Prostate zones: transition zone (5% volume, 90% BPH), peripheral zone (70% volume, 85% cancers)
- Surgical landmarks: bladder neck at 15-20 degrees from horizontal
- Perineal Zone (Zone 3)
- Bulbar urethra: 3-4cm length, 8-9mm diameter
- Corpus spongiosum blood supply: 95% retrograde from glans
- Critical for stricture repair and trauma management
| Zone | Key Structures | Surgical Access | Complication Risk | Blood Loss Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retroperitoneal | Kidneys, ureters, vessels | Flank, laparoscopic | Vascular injury (2-5%) | 200-500mL |
| Intrapelvic | Bladder, prostate | Suprapubic, perineal | Incontinence (5-15%) | 100-300mL |
| Perineal | Bulbar urethra, corpus | Perineal approach | Stricture (10-20%) | <100mL |
| External | Glans, scrotum | Direct access | Cosmetic (5-10%) | <50mL |
The urological emergency spectrum follows time-critical patterns where intervention windows determine outcomes. Testicular torsion requires detorsion within 6 hours for >90% salvage rates, dropping to <10% after 24 hours. Urethral trauma with complete disruption needs immediate suprapubic drainage, while renal trauma with active bleeding requires intervention within 2-4 hours.
💡 Master This: Every urological emergency has a "golden window" - torsion (6 hours), priapism (4-6 hours), urinary retention (>1L bladder volume), and trauma with hemodynamic instability (<2 hours). Missing these windows transforms salvageable situations into permanent disabilities.
Understanding these foundational zones and time-critical patterns creates the framework for systematic urological assessment. Connect this anatomical blueprint through mechanism mastery to understand how normal function becomes pathological crisis.
🏗️ The Urological Foundation: Your Surgical Command Center
⚙️ The Urological Engine: Mechanism Mastery
Flow Dynamics Mastery reveals why urological emergencies follow predictable patterns. Normal urine flow requires pressure gradients of 15-25 cmH2O from renal pelvis to bladder, with coordinated sphincter relaxation reducing outlet resistance to <10 cmH2O. When these gradients fail, specific clinical presentations emerge.
📌 Remember: FLOW - Force (pressure gradient 15-25 cmH2O), Lumen (patent pathways), Outlet (sphincter coordination), Wall (smooth muscle function). Disruption of any component creates characteristic flow patterns and symptoms.
- Pressure System Mechanics
- Normal bladder pressure: 5-15 cmH2O filling, 40-60 cmH2O voiding
- Detrusor overactivity: pressures >40 cmH2O during filling
- Outlet obstruction: voiding pressures >80 cmH2O with poor flow
- BPH progression: Grade 1 (<50g), Grade 2 (50-80g), Grade 3 (>80g)
- Flow rates: Normal >15 mL/sec, concerning <10 mL/sec, obstructed <5 mL/sec
- Vascular Perfusion Patterns
- Renal blood flow: 20-25% cardiac output (1200 mL/min)
- Autoregulation range: 80-180 mmHg mean arterial pressure
- Testicular perfusion: 2-4 mL/min baseline, <0.5 mL/min with torsion
- Salvage rates: >90% if detorsed <6 hours, <20% if >12 hours
Pathological Cascade Recognition transforms complex presentations into systematic interventions. Understanding how normal mechanisms fail predicts both immediate complications and long-term sequelae.
| Mechanism Failure | Primary Effect | Secondary Changes | Intervention Window | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Torsion (vascular) | Ischemia onset | Necrosis >6h | <6 hours | >90% |
| Obstruction (flow) | Pressure rise | Hydronephrosis | <48 hours | >85% |
| Trauma (structural) | Bleeding/leak | Infection risk | <4 hours | >80% |
| Retention (outlet) | Bladder distension | Renal impairment | <24 hours | >95% |
| Stone (mechanical) | Ureteral spasm | Kidney damage | <72 hours | >75% |
Failure Pattern Integration reveals why certain complications cluster together. Outlet obstruction leads to elevated bladder pressures (>40 cmH2O), causing detrusor hypertrophy, trabeculation, and eventually decompensation with overflow incontinence. This progression takes months to years, allowing staged interventions.
💡 Master This: Acute vs chronic failure patterns have different intervention strategies - acute torsion requires immediate surgical detorsion, while chronic obstruction allows medical optimization before elective surgery. Understanding timeline determines urgency level.
These mechanism patterns create the foundation for pattern recognition frameworks. Connect this functional understanding through clinical application to master diagnostic approaches and treatment selection.
⚙️ The Urological Engine: Mechanism Mastery
🎯 The Recognition Matrix: Pattern Mastery Framework
Pain Pattern Recognition provides the most critical diagnostic framework, as urological pain follows anatomical distributions that predict underlying pathology with remarkable consistency.
📌 Remember: SHARP - Sudden onset (torsion, stone), Hematuria (trauma, tumor), Anatomical distribution (renal, ureteral, bladder), Radiation patterns (flank to groin), Positional changes (stone movement). Each pattern suggests specific pathology.
- Acute Onset Pain Patterns (<6 hours)
- Testicular torsion: sudden, severe, no relief with position
- Age distribution: neonatal peak, adolescent peak (12-16 years)
- Physical findings: high-riding testis, absent cremasteric reflex
- Doppler sensitivity: 85-95% for detecting absent flow
- Renal colic: sudden, severe, colicky, flank to groin
- Stone size correlation: <5mm (90% pass), >10mm (<10% pass)
- Pain severity: 10/10 intensity, restless behavior
- Testicular torsion: sudden, severe, no relief with position
- Chronic Pain Patterns (>weeks)
- Chronic prostatitis: perineal pressure, post-ejaculatory pain
- Bladder pain syndrome: suprapubic pressure, frequency (>8/day)
- Testicular pain: dull ache, positional relief, gradual onset
Flow Disturbance Recognition reveals obstructive vs irritative patterns that guide treatment selection and urgency assessment.
| Pattern Type | Flow Rate | Frequency | Urgency | Post-void Residual | Intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obstructive | <10 mL/sec | Normal | Minimal | >100 mL | Surgical |
| Irritative | Normal | >8/day | Severe | <50 mL | Medical |
| Mixed | <15 mL/sec | >6/day | Moderate | 50-100 mL | Combined |
| Neurogenic | Variable | Variable | Variable | >200 mL | Specialized |
| Retention | 0 mL/sec | Overflow | Absent | >500 mL | Emergency |
Emergency Pattern Recognition creates systematic triage frameworks where specific combinations of findings predict time-critical interventions.
- Immediate Intervention Required (<2 hours)
- Testicular torsion: sudden pain + high-riding testis + absent Doppler flow
- Priapism: >4 hours erection + rigid corpora + ischemic pain
- Urinary retention: >1L bladder volume + inability to void + suprapubic pain
- Bladder capacity: >800 mL abnormal, >1200 mL emergency
- Catheter drainage: immediate relief, monitor post-obstructive diuresis
- Urgent Assessment (<6 hours)
- Renal trauma: flank pain + hematuria + hemodynamic instability
- Ureteral obstruction: severe colic + hydronephrosis + fever (Charcot's triad)
- Paraphimosis: painful swelling + constricting band + glans congestion
💡 Master This: Pattern clustering predicts pathology - sudden + severe + specific anatomical distribution suggests vascular compromise (torsion) or mechanical obstruction (stone). Gradual + progressive + systemic symptoms suggests infectious or neoplastic processes.
These recognition patterns create systematic approaches to complex presentations. Connect this diagnostic framework through analytical comparison to master differential diagnosis and treatment selection strategies.
🎯 The Recognition Matrix: Pattern Mastery Framework
🔬 The Differential Engine: Systematic Discrimination
Acute Scrotal Pain Discrimination represents the highest-stakes differential in urology, where missing torsion results in testicular loss while unnecessary surgery for epididymitis creates avoidable morbidity.
📌 Remember: TWIST - Timing (sudden vs gradual), Wave (continuous vs intermittent), Intensity (10/10 vs 6-8/10), Signs (high-riding vs normal position), Tests (absent vs present Doppler flow). These discriminators achieve >95% diagnostic accuracy.
- Testicular Torsion Discriminators
- Age distribution: bimodal peaks (neonatal, 12-16 years)
- Pain onset: sudden (<1 hour), maximal intensity immediately
- Physical findings: high-riding testis (85%), absent cremasteric reflex (90%)
- Testicular lie: horizontal vs normal vertical orientation
- Pain relief: none with elevation vs improved with elevation (Prehn's sign)
- Duration tolerance: <6 hours before >90% necrosis risk
- Epididymitis Discriminators
- Age distribution: sexually active (<35 years) or elderly (>60 years)
- Pain onset: gradual (hours to days), progressive intensity
- Laboratory findings: pyuria (>10 WBC/hpf), positive cultures (60-80%)
- Urinalysis: abnormal in 80-90% epididymitis vs normal in 90% torsion
- Inflammatory markers: elevated CRP (>50 mg/L), leukocytosis (>12,000)
Hematuria Discrimination Framework separates benign from malignant causes using systematic risk stratification and quantitative thresholds.
| Hematuria Type | RBC Count | Age Risk | Cancer Risk | Imaging Required | Cystoscopy Needed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gross visible | Any amount | >35 years | 15-25% | CT urogram | Always |
| Microscopic | >3 RBC/hpf | >35 years | 5-10% | Ultrasound | If risk factors |
| Exercise-induced | Variable | Any age | <1% | None initially | If persistent |
| Post-catheter | <100 RBC/hpf | Any age | <1% | None | No |
| Menstrual | Variable | Reproductive | <1% | None | No |
Urinary Retention Discrimination distinguishes between mechanical obstruction, neurogenic dysfunction, and medication-induced causes, each requiring different treatment approaches.
- Mechanical Obstruction Patterns
- BPH progression: gradual onset, weak stream, nocturia (>2/night)
- Prostate size correlation: >40g symptomatic, >80g high retention risk
- Flow rates: <10 mL/sec significant, <5 mL/sec severe obstruction
- Post-void residual: >100 mL abnormal, >200 mL concerning
- Bladder wall thickness: >5mm suggests chronic obstruction
- Neurogenic Dysfunction Patterns
- Spinal injury: acute onset, complete retention, absent sensation
- Diabetic neuropathy: gradual onset, overflow incontinence, large residuals
- Multiple sclerosis: intermittent, urgency alternating with retention
- Neurological examination: abnormal in >90% neurogenic cases
- Urodynamics: detrusor areflexia or detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia
💡 Master This: Retention pattern + neurological examination + medication history provides >95% diagnostic accuracy. Acute retention in young males suggests neurogenic cause, while gradual retention in older males suggests BPH progression.
These discrimination frameworks create systematic approaches to complex differential diagnoses. Connect this analytical foundation through evidence-based treatment algorithms to master therapeutic decision-making.
🔬 The Differential Engine: Systematic Discrimination
🎯 The Treatment Arsenal: Evidence-Based Intervention
Surgical Intervention Algorithms provide systematic approaches where specific thresholds trigger escalation from conservative to invasive management.
📌 Remember: SCALE - Severity assessment (mild/moderate/severe), Conservative trial (4-6 weeks), Alternative medical therapy (2-4 weeks), Last resort surgery (when medical fails), Emergency intervention (life-threatening). Each step has defined success criteria.
- BPH Treatment Escalation
- Watchful waiting: IPSS <8, QoL score <3, no complications
- Success rate: 70-80% remain stable at 5 years
- Progression risk: 15-20% require intervention annually
- Medical therapy: IPSS 8-19, bothersome symptoms, PVR <200 mL
- Alpha-blockers: 60-70% symptom improvement, 2-4 week onset
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors: 30-40% improvement, 6-12 month onset
- Combination therapy: 70-80% improvement, reduced progression (66%)
- Surgical intervention: IPSS >20, refractory retention, complications
- TURP success: 85-95% symptom relief, 1-3% incontinence risk
- Laser procedures: 80-90% efficacy, <1% transfusion rate
- Watchful waiting: IPSS <8, QoL score <3, no complications
Emergency Treatment Protocols define time-critical interventions where delay significantly impacts outcomes.
| Emergency | Intervention Window | Success Rate | Complication Rate | Alternative Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testicular torsion | <6 hours | >90% salvage | <5% complications | Manual detorsion |
| Priapism (ischemic) | <4 hours | >80% function | 10-20% ED | Aspiration + injection |
| Urinary retention | <24 hours | >95% relief | <2% complications | Suprapubic catheter |
| Renal trauma (Grade 4-5) | <2 hours | 70-85% salvage | 15-25% complications | Angioembolization |
| Ureteral obstruction + sepsis | <6 hours | >90% recovery | 5-10% complications | Nephrostomy |
Stone Management Algorithms demonstrate systematic escalation based on stone characteristics and patient factors.
- Conservative Management (Stone <5mm)
- Spontaneous passage: 90% for <5mm, 50% for 5-10mm
- Medical expulsive therapy: alpha-blockers increase passage 15-20%
- Timeline: 4-6 weeks observation period, pain control, hydration
- Passage rates by location: distal ureter (95%), mid-ureter (75%), proximal (60%)
- Active Intervention (Stone >5mm or complications)
- Shock wave lithotripsy: 70-90% success for <20mm stones
- Ureteroscopy: 85-95% success, <5% complication rate
- Percutaneous nephrolithotomy: >95% success for >20mm stones
- Complication rates: SWL (<5%), URS (5-10%), PCNL (10-20%)
💡 Master This: Stone size and location determine treatment success rates - distal ureteral stones <5mm have >90% spontaneous passage, while renal stones >20mm require PCNL for >95% stone-free rates. Patient factors (age, comorbidities) modify these probabilities.
These evidence-based treatment algorithms create systematic approaches to intervention selection. Connect this therapeutic framework through multi-system integration to understand complex urological relationships and cutting-edge management strategies.
🎯 The Treatment Arsenal: Evidence-Based Intervention
🌐 The Integration Network: Multi-System Mastery
Renal-Cardiovascular Integration demonstrates how kidney function directly impacts cardiac performance and vascular health, creating bidirectional pathophysiology that affects surgical planning and outcomes.
📌 Remember: HEART - Hypertension (renal artery stenosis), Electrolytes (K+, Na+ balance), Anemia (EPO deficiency), Retention (volume overload), Toxins (uremic cardiomyopathy). Each component affects surgical risk and recovery.
- Chronic Kidney Disease Cardiovascular Impact
- CKD Stage 3: GFR 30-59, 15-20% increased cardiac risk
- CKD Stage 4: GFR 15-29, 40-50% increased cardiac risk
- CKD Stage 5: GFR <15, >100% increased cardiac risk
- Anemia threshold: Hgb <11 g/dL increases surgical complications 2-3 fold
- Electrolyte management: K+ >5.5 mEq/L requires pre-operative correction
- Volume status: >2L positive balance increases pulmonary complications 3-4 fold
- Surgical Risk Stratification
- Low risk: GFR >60, normal cardiac function, Hgb >12 g/dL
- Moderate risk: GFR 30-60, controlled hypertension, Hgb 10-12 g/dL
- High risk: GFR <30, heart failure, Hgb <10 g/dL
- Perioperative mortality: <1% low risk, 3-5% moderate risk, >10% high risk
Endocrine-Reproductive Integration reveals how hormonal systems control prostate growth, testicular function, and sexual health, creating treatment opportunities through hormonal manipulation.
| Hormone System | Target Organ | Normal Range | Pathological Effect | Treatment Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testosterone | Prostate | 300-1000 ng/dL | BPH growth | 5-ARI reduces 50% |
| DHT | Prostate cells | 30-85 ng/dL | Cancer promotion | Finasteride blocks |
| LH/FSH | Testes | LH 1.7-8.6 mIU/mL | Hypogonadism | HCG stimulation |
| Prolactin | Sexual function | <25 ng/mL | ED, decreased libido | Dopamine agonists |
| Insulin | Vascular health | <100 mg/dL fasting | ED, bladder dysfunction | Glycemic control |
Neurological-Bladder Integration demonstrates how central and peripheral nervous system disorders create complex voiding dysfunction requiring specialized management approaches.
- Neurogenic Bladder Classification
- Suprapontine lesions: detrusor overactivity, coordinated sphincters
- Stroke, Parkinson's: urgency, frequency, normal emptying
- Management: anticholinergics (70-80% improvement), botulinum toxin (60-70% success)
- Spinal cord lesions: detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia, high pressures
- Complete injury: areflexic bladder, retention, overflow incontinence
- Incomplete injury: mixed symptoms, variable patterns
- Management: intermittent catheterization (gold standard), sphincterotomy for dyssynergia
- Suprapontine lesions: detrusor overactivity, coordinated sphincters
- Diabetic Neuropathy Progression
- Early stage: decreased sensation, increased capacity (>600 mL)
- Advanced stage: detrusor areflexia, large residuals (>300 mL)
- End stage: overflow incontinence, recurrent UTIs, renal impairment
- Progression timeline: 10-15 years from diabetes onset
- Prevention: tight glycemic control (HbA1c <7%) reduces neuropathy 60-70%
💡 Master This: Multi-system integration requires coordinated care teams - nephrologists for CKD management, endocrinologists for hormonal optimization, neurologists for neurogenic bladder. Urologists coordinate care but cannot manage complex patients in isolation.
These integration patterns reveal cutting-edge approaches where personalized medicine, biomarker-guided therapy, and minimally invasive techniques are transforming urological care. Connect this systems understanding through rapid mastery frameworks to develop clinical expertise tools.
🌐 The Integration Network: Multi-System Mastery
⚡ The Clinical Arsenal: Rapid Mastery Toolkit
Essential Numbers Arsenal provides the quantitative foundation for all urological decision-making, where specific thresholds trigger immediate actions.
📌 Remember: VITAL - Vascular (torsion <6h, priapism <4h), Infection (sepsis <1h antibiotics), Trauma (bleeding <2h intervention), Acute retention (>1L immediate drainage), Laboratory (Cr >2.0 nephrology consult). These numbers save organs and lives.
- Time-Critical Thresholds
- Testicular salvage: >90% if <6 hours, <20% if >12 hours
- Priapism function: >80% if <4 hours, <30% if >24 hours
- Stone passage: 90% for <5mm, 10% for >10mm
- Bladder capacity: 400-600 mL normal, >800 mL abnormal, >1200 mL emergency
- Laboratory Decision Points
- Creatinine: >1.5 mg/dL concerning, >2.0 mg/dL nephrology consult
- PSA: >4.0 ng/mL abnormal, >10 ng/mL high risk, >20 ng/mL advanced disease
- Hematuria: >3 RBC/hpf microscopic, any gross requires evaluation if >35 years
- Post-void residual: >100 mL abnormal, >200 mL concerning, >300 mL intervention
Clinical Pattern Recognition Drills create systematic approaches to common presentations where rapid pattern matching leads to correct diagnoses.
| Clinical Scenario | Key Features | Immediate Action | Success Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute scrotal pain | Sudden + severe + high-riding | Surgical exploration | <6h to OR |
| Gross hematuria | Age >35 + no trauma | CT urogram + cystoscopy | Complete workup |
| Urinary retention | >1L bladder + inability void | Immediate catheterization | Relief + monitoring |
| Flank pain + fever | CVA tenderness + pyuria | Antibiotics + drainage | <1h treatment |
| Priapism >4h | Rigid corpora + ischemic pain | Aspiration + injection | Detumescence |
Rapid Assessment Frameworks provide systematic evaluation tools that ensure critical findings are not missed during high-pressure situations.
- Urological Emergency Assessment (ABCDE + Urology)
- Airway: stable (rarely affected in urology)
- Breathing: assess for pulmonary edema (renal failure)
- Circulation: BP, HR, signs of shock (bleeding, sepsis)
- Disability: neurological status (spinal injury, altered mental status)
- Exposure: complete examination including genitalia, flanks, abdomen
- Urology specific: pain pattern, voiding history, previous surgeries
- Pain assessment: location, radiation, timing, severity (1-10)
- Voiding symptoms: frequency, urgency, stream, nocturia
- Associated symptoms: fever, nausea, hematuria, discharge
💡 Master This: Systematic assessment prevents missed diagnoses - always examine both testes (bilateral pathology 5-10%), check post-void residual (retention often asymptomatic), and assess renal function (baseline for interventions). Shortcuts in emergency situations lead to missed critical findings.
This rapid mastery toolkit transforms theoretical knowledge into practical clinical expertise, providing the essential tools for confident urological practice and optimal patient outcomes.
⚡ The Clinical Arsenal: Rapid Mastery Toolkit
Practice Questions: Urology Basics
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 97-year-old man visits the urology clinic 5 days after experiencing urinary retention at an emergency department visit. The patient has a history of hypertension, type II diabetes mellitus, stroke, dyslipidemia, a past myocardial infarction, and severe osteoarthritis in his right hip. He is not compliant with his medications and his multiple comorbidities are poorly managed. In the hospital, the patient’s urinary retention was treated with Foley catheterization. At clinic, the patient’s serum-specific prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is 6.0 ng/mL (normal is < 4 ng/mL). Digital rectal examination (DRE) demonstrates a nontender prostate with several rock hard nodules. The patient's Foley is removed and he is able to urinate on his own. Which is the most appropriate next step in management?












