Heart transplantation US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Heart transplantation. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Heart transplantation US Medical PG Question 1: A 31-year-old female receives a kidney transplant for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Three weeks later, the patient experiences acute, T-cell mediated rejection of the allograft and is given sirolimus. Which of the following are side effects of this medication?
- A. Nephrotoxicity, hypertension
- B. Hyperlipidemia, thrombocytopenia (Correct Answer)
- C. Nephrotoxicity, gingival hyperplasia
- D. Pancreatitis
- E. Cytokine release syndrome, hypersensitivity reaction
Heart transplantation Explanation: ***Hyperlipidemia, thrombocytopenia***
- **Sirolimus** (rapamycin) is an **mTOR inhibitor** commonly used in transplant immunology, which frequently causes **hyperlipidemia** (elevated cholesterol and triglycerides) and **thrombocytopenia** (low platelet count).
- Other common side effects include **myelosuppression** (leukopenia, anemia), **mouth ulcers**, and **impaired wound healing**.
*Nephrotoxicity, hypertension*
- **Nephrotoxicity** and **hypertension** are more characteristic side effects of **calcineurin inhibitors** like **tacrolimus** and **cyclosporine**, which are also used in transplant immunosuppression but have a different mechanism of action than sirolimus.
- While sirolimus can indirectly affect kidney function, it is generally considered less nephrotoxic than calcineurin inhibitors.
*Nephrotoxicity, gingival hyperplasia*
- **Gingival hyperplasia** is a hallmark side effect of **cyclosporine**, a calcineurin inhibitor, along with **hirsutism** and **nephrotoxicity**.
- Sirolimus does not typically cause gingival hyperplasia.
*Pancreatitis*
- While some immunosuppressants can rarely cause pancreatitis, it is not a common or characteristic side effect of **sirolimus**.
- **Azathioprine** is more frequently associated with pancreatitis among immunosuppressive agents.
*Cytokine release syndrome, hypersensitivity reaction*
- **Cytokine release syndrome** and acute **hypersensitivity reactions** are more often associated with **monoclonal antibodies** (e.g., **basiliximab**, **daclizumab**) used for induction therapy or treatment of acute rejection, particularly within hours or days of administration.
- Sirolimus is less likely to cause these immediate severe reactions.
Heart transplantation US Medical PG Question 2: A 42-year-old woman presents to the physician with symptoms of vague abdominal pain and bloating for several months. Test results indicate that she has ovarian cancer. Her physician attempts to reach her by phone multiple times but cannot reach her. Next of kin numbers are in her chart. According to HIPAA regulations, who should be the primary person the doctor discusses this information with?
- A. The patient's brother
- B. The patient's husband
- C. The patient's daughter
- D. All of the options
- E. The patient (Correct Answer)
Heart transplantation Explanation: ***The patient***
- Under **HIPAA**, the patient has the **right to privacy** regarding their protected health information (PHI). Therefore, the physician must make all reasonable attempts to contact the patient directly to convey their diagnosis.
- Sharing sensitive medical information like a cancer diagnosis with anyone other than the patient, without their explicit consent, would be a **violation of HIPAA regulations**.
*The patient's brother*
- The patient's brother is not automatically authorized to receive her medical information, even if listed as **next of kin**, without the patient's explicit consent or a documented **healthcare power of attorney**.
- Discussing the diagnosis with the brother without the patient's direct consent would be a **breach of patient confidentiality**.
*The patient's husband*
- Even a spouse does not automatically have the right to access a patient's **PHI** without the patient's express permission, according to **HIPAA**.
- While often a trusted contact, without explicit consent, revealing the diagnosis to the husband would still violate the patient's **privacy rights**.
*The patient's daughter*
- Similar to other family members, the patient's daughter is not legally entitled to receive her mother's confidential medical information without explicit authorization or a medical **power of attorney**.
- The physician's primary responsibility is to the patient herself, ensuring her **privacy** is maintained.
*All of the options*
- According to **HIPAA**, sharing the patient's diagnosis with any family member without her explicit consent would be a **breach of confidentiality**.
- This option incorrectly assumes that **next of kin** automatically have the right to receive sensitive medical information.
Heart transplantation US Medical PG Question 3: A 66-year-old man is transferred from another hospital after 3 days of progressively severe headache, vomiting, low-grade fever, and confusion. According to his partner, the patient has been dealing with some memory loss and complaining about headaches for the past 2 weeks. He has a history of interstitial pulmonary disease that required lung transplantation 2 years ago. Upon admission, he is found with a blood pressure of 160/100 mm Hg, a pulse of 58/min, a respiratory rate of 15/min, and a body temperature of 36°C (97°F). During the examination, he is found with oral thrush and symmetric and reactive pupils; there are no focal neurological signs or papilledema. A lumbar puncture is performed. Which of the following features would be expected to be found in this case?
- A. Aspect: clear, opening pressure: normal, cell count: < 5 cells/µL, protein: normal, glucose: normal
- B. Aspect: clear, opening pressure: normal, cell count: ↑ lymphocytes, protein: normal, glucose: normal
- C. Aspect: cloudy, opening pressure: ↑, cell count: ↑ neutrophils, protein: ↑, glucose: ↓
- D. Aspect: xanthochromic, opening pressure: normal, cell count: ↑ red blood cells, protein: normal, glucose: normal
- E. Aspect: clear, opening pressure: ↑, cell count: ↑ lymphocytes, protein: ↑, glucose: ↓ (Correct Answer)
Heart transplantation Explanation: ***Aspect: clear, opening pressure: ↑, cell count: ↑ lymphocytes, protein: ↑, glucose: ↓***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **cryptococcal meningitis**, a common opportunistic infection in immunocompromised individuals like transplant recipients.
- **Cryptococcal meningitis** characteristically presents with **clear CSF** (not cloudy, which differentiates it from bacterial meningitis), **markedly elevated opening pressure** (often >25 cm H₂O), **lymphocytic pleocytosis**, **elevated protein**, and **decreased glucose** due to fungal metabolism.
- The presence of **oral thrush** strongly suggests fungal infection in this immunocompromised patient.
*Aspect: clear, opening pressure: normal, cell count: < 5 cells/µL, protein: normal, glucose: normal*
- This describes **normal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)** parameters, which would not be expected in a patient presenting with signs and symptoms of meningitis, such as headache, vomiting, fever, and confusion.
- The patient's history of lung transplantation and oral thrush suggests an immunocompromised state and an opportunistic infection, ruling out normal CSF.
*Aspect: clear, opening pressure: normal, cell count: ↑ lymphocytes, protein: normal, glucose: normal*
- While **increased lymphocytes** can be seen in aseptic or viral meningitis, the overall picture of normal opening pressure, protein, and glucose does not fit this immunocompromised patient with subacute meningitis.
- The presence of **oral thrush** and **2 weeks of symptoms** indicate a more severe opportunistic infection like cryptococcal meningitis, which would show elevated opening pressure and abnormal protein and glucose levels.
*Aspect: cloudy, opening pressure: ↑, cell count: ↑ neutrophils, protein: ↑, glucose: ↓*
- This CSF profile is characteristic of **bacterial meningitis**, which is primarily marked by **cloudy CSF** due to significant **neutrophilic pleocytosis**.
- While the patient is immunocompromised, the history of **subacute symptoms** (2 weeks of headache/memory loss) and gradual deterioration is more typical of a fungal infection like **cryptococcal meningitis** rather than acute bacterial meningitis, which presents more acutely.
*Aspect: xanthochromic, opening pressure: normal, cell count: ↑ red blood cells, protein: normal, glucose: normal*
- **Xanthochromic CSF** with **elevated red blood cells** indicates subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- While headache is present, the patient's symptoms of fever, progressive confusion, oral thrush, and immunocompromised status point away from a primary hemorrhagic event and towards an infectious etiology.
Heart transplantation US Medical PG Question 4: A 52-year-old man is diagnosed with chronic renal failure. He is on hemodialysis. The physicians have advised him that he needs a renal transplant. The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genotype is A7/A5, B2/B9, and C8/C3. For each locus, the maternal allele is listed 1st and the paternal allele is listed 2nd. There are several potential donors available for the renal graft. Which of the following donors would be the closest match?
- A. Donor E: A7/A8, B9/B27, C3/C4
- B. Donor D: A4/A7, B1/B8, C8/C3
- C. Donor B: A5/A12, B22/9, C4/C3
- D. Donor C: A7/A4, B2/B4, C8/C3
- E. Donor A: A7/A5, B8/B2, C3/C8 (Correct Answer)
Heart transplantation Explanation: ***Donor A: A7/A5, B8/B2, C3/C8***
- **A locus:** Perfect match (A7 and A5 both shared) - 2/2 alleles
- **B locus:** Partial match (B2 shared, B8 not) - 1/2 alleles
- **C locus:** Perfect match (C8 and C3 both shared) - 2/2 alleles
- **Total: 5 out of 6 alleles match** - This is the **best possible match** among all donors, minimizing risk of graft rejection through maximum HLA compatibility.
*Donor C: A7/A4, B2/B4, C8/C3*
- A locus: Partial match (A7 shared) - 1/2 alleles
- B locus: Partial match (B2 shared) - 1/2 alleles
- C locus: Perfect match (C8 and C3 both shared) - 2/2 alleles
- Total: 4 out of 6 alleles match - Second best option
*Donor B: A5/A12, B22/9, C4/C3*
- A locus: Partial match (A5 shared) - 1/2 alleles
- B locus: Partial match (B9 shared) - 1/2 alleles
- C locus: Partial match (C3 shared) - 1/2 alleles
- Total: 3 out of 6 alleles match
*Donor D: A4/A7, B1/B8, C8/C3*
- A locus: Partial match (A7 shared) - 1/2 alleles
- B locus: No match (neither B1 nor B8 shared) - 0/2 alleles
- C locus: Perfect match (C8 and C3 both shared) - 2/2 alleles
- Total: 3 out of 6 alleles match
*Donor E: A7/A8, B9/B27, C3/C4*
- A locus: Partial match (A7 shared) - 1/2 alleles
- B locus: Partial match (B9 shared) - 1/2 alleles
- C locus: Partial match (C3 shared) - 1/2 alleles
- Total: 3 out of 6 alleles match
Heart transplantation US Medical PG Question 5: A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of palpitations, dry cough, and shortness of breath for 1 week. She immigrated to the United States from Korea at the age of 20. She says that her heart is racing and she has never felt these symptoms before. Her cough is dry and is associated with shortness of breath that occurs with minimal exertion. Her past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. She has no allergies and is not currently taking any medications. She is a nonsmoker and an occasional drinker. She denies illicit drug use. Her blood pressure is 100/65 mm Hg, pulse is 76/min, respiratory rate is 23/min, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F). Her physical examination is significant for bibasilar lung crackles and a non-radiating, low-pitched, mid-diastolic rumbling murmur best heard at the apical region. In addition, she has jugular vein distention and bilateral pitting edema in her lower extremities. Which of the following best describes the infectious agent that led to this patient’s condition?
- A. A bacterium that induces partial lysis of red cells with hydrogen peroxide
- B. A bacterium that requires an anaerobic environment to grow properly
- C. A bacterium that does not lyse red cells
- D. A bacterium that induces heme degradation of the red cells of a blood agar plate
- E. A bacterium that induces complete lysis of the red cells of a blood agar plate with an oxygen-sensitive cytotoxin (Correct Answer)
Heart transplantation Explanation: ***A bacterium that induces complete lysis of the red cells of a blood agar plate with an oxygen-sensitive cytotoxin***
- This describes **Group A Streptococcus (GAS)**, specifically *Streptococcus pyogenes*, which causes **rheumatic fever** leading to **mitral stenosis**. Mitral stenosis is characterized by a **mid-diastolic rumbling murmur** at the apex, left atrial enlargement causing **palpitations**, and **pulmonary congestion** leading to dyspnea, cough, and bibasilar crackles.
- The delayed onset of symptoms (immigrated at 20, symptoms at 43) is typical for **rheumatic heart disease**, where repeated GAS infections in childhood/adolescence lead to valve damage that manifests years later. GAS produces **streptolysin O**, an **oxygen-labile cytotoxin** responsible for **beta-hemolysis** (complete lysis) on blood agar.
*A bacterium that induces partial lysis of red cells with hydrogen peroxide*
- This describes **alpha-hemolytic** bacteria like *Streptococcus pneumoniae* or *Viridans streptococci*, which cause **partial hemolysis** (greenish discoloration) on blood agar due to **hydrogen peroxide** production.
- While *Viridans streptococci* can cause **infective endocarditis**, the clinical picture of **rheumatic mitral stenosis** is more consistent with a history of recurrent streptococcal pharyngitis (GAS).
*A bacterium that requires an anaerobic environment to grow properly*
- This description typically refers to **anaerobic bacteria**, such as *Clostridium* or *Bacteroides* species.
- These bacteria are generally not associated with the primary cause of acute rheumatic fever or the subsequent development of chronic valvular heart disease like mitral stenosis.
*A bacterium that does not lyse red cells*
- This describes **gamma-hemolytic** (non-hemolytic) bacteria, such as *Enterococcus faecalis* or some *Staphylococcus* species.
- These organisms do not cause the characteristic hemolysis seen with the streptococci responsible for rheumatic fever.
*A bacterium that induces heme degradation of the red cells of a blood agar plate*
- This description is **too vague** and does not specifically identify the organism. While heme degradation occurs with various types of hemolysis, the key distinguishing feature of **Group A Streptococcus** is **complete lysis (beta-hemolysis)** combined with production of the **oxygen-sensitive toxin streptolysin O**.
- This option lacks the specificity needed to identify GAS as the causative agent of rheumatic fever. Both alpha- and beta-hemolytic organisms can degrade heme, but only beta-hemolytic GAS causes rheumatic heart disease.
Heart transplantation US Medical PG Question 6: A 58-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of confusion, weight loss, and anuria. He has chronic kidney disease, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. He was diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia at the age of 8 years and was treated with an allogeneic stem cell transplantation. He is HIV-positive and has active hepatitis C virus infection. He drinks around 8 cans of beer every week. His current medications include tenofovir, emtricitabine, atazanavir, daclatasvir, sofosbuvir, insulin, amlodipine, and enalapril. He appears lethargic. His temperature is 36°C (96.8°F), pulse is 130/min, respirations are 26/min, and blood pressure is 145/90 mm Hg. Examination shows severe edema in his legs and generalized muscular weakness. Auscultation of the lung shows crepitant rales. Laboratory studies show positive HCV antibody and positive HCV RNA. His HIV viral load is undetectable and his CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 589/μL. Six months ago, his CD4+ T-lymphocyte count was 618/μL. An ECG of the heart shows arrhythmia with frequent premature ventricular contractions. Arterial blood gas analysis on room air shows:
pH 7.23
PCO2 31 mm Hg
HCO3- 13 mEq/L
Base excess -12 mEq/L
The patient states he would like to donate organs or tissues in the case of his death. Which of the following is an absolute contraindication for organ donation in this patient?
- A. HIV infection
- B. Childhood leukemia (Correct Answer)
- C. Alcoholism
- D. No absolute contraindications
- E. Acute kidney injury
Heart transplantation Explanation: ***Correct: Childhood leukemia***
- **History of hematologic malignancy** (including acute lymphoblastic leukemia) is an **absolute contraindication** for solid organ donation according to UNOS and OPTN guidelines.
- Even though this patient was treated 50 years ago with allogeneic stem cell transplantation, the concern for **residual malignant cells** or **transmission to immunosuppressed recipients** makes this an absolute exclusion.
- Unlike solid tumors (which may be acceptable after long disease-free intervals), **leukemias and lymphomas carry lifelong exclusion** from organ donation due to their systemic nature and potential for dormant cells.
*Incorrect: Acute kidney injury*
- **Acute kidney injury (AKI)** is NOT an absolute contraindication for organ donation.
- While the kidneys themselves may not be suitable for transplantation, other organs (heart, liver, lungs, corneas) could still be viable.
- Each organ is assessed individually for suitability.
*Incorrect: HIV infection*
- **Well-controlled HIV infection** (undetectable viral load, stable CD4 count >200) is no longer an absolute contraindication.
- Under the **HOPE Act (HIV Organ Policy Equity Act)**, organs from HIV-positive donors can be transplanted into HIV-positive recipients.
- This patient has excellent viral control (undetectable VL, CD4 589), making HIV not an absolute barrier.
*Incorrect: Alcoholism*
- **Alcohol use disorder** alone is not an absolute contraindication for organ donation.
- The suitability depends on individual organ assessment (e.g., liver function, cardiac health).
- This patient drinks 8 beers/week, which is moderate consumption and doesn't preclude donation of undamaged organs.
*Incorrect: No absolute contraindications*
- This patient **does have an absolute contraindication**: his history of hematologic malignancy (acute lymphoblastic leukemia).
- Despite the long time since treatment, hematologic cancers remain absolute exclusions for organ donation.
Heart transplantation US Medical PG Question 7: A 68-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. Three months ago, she underwent heart transplantation for restrictive cardiomyopathy and was started on transplant rejection prophylaxis. Her pulse is 76/min and blood pressure is 148/82 mm Hg. Physical examination shows enlargement of the gum tissue. There is a well-healed scar on her chest. Serum studies show hyperlipidemia. The physician recommends removing a drug that decreases T cell activation by inhibiting the transcription of interleukin-2 from the patient's treatment regimen and replacing it with a different medication. Which of the following drugs is the most likely cause of the adverse effects seen in this patient?
- A. Mycophenolate mofetil
- B. Azathioprine
- C. Tacrolimus
- D. Cyclosporine (Correct Answer)
- E. Prednisolone
Heart transplantation Explanation: ***Cyclosporine***
- The patient's symptoms of **gingival hyperplasia**, **hypertension**, and **hyperlipidemia** are classic side effects associated with cyclosporine.
- Cyclosporine is a calcineurin inhibitor that **decreases T-cell activation** by inhibiting IL-2 transcription, matching the drug description.
*Mycophenolate mofetil*
- Mycophenolate mofetil is an **antiproliferative agent** that inhibits purine synthesis, primarily affecting lymphocytes.
- Its common side effects are mainly **hematologic** (leukopenia, anemia) and **gastrointestinal** (diarrhea, nausea), not gingival hyperplasia or hypertension.
*Azathioprine*
- Azathioprine is a **purine analog** that impairs DNA synthesis and inhibits lymphocyte proliferation.
- Key side effects include **myelosuppression** (leukopenia, thrombocytopenia) and **hepatotoxicity**, which are not present here.
*Tacrolimus*
- Tacrolimus is also a **calcineurin inhibitor** that inhibits IL-2 transcription, similar to cyclosporine.
- While it can cause **hypertension** and **hyperlipidemia**, it is less commonly associated with **gingival hyperplasia** than cyclosporine.
*Prednisolone*
- Prednisolone is a **corticosteroid** used for immunosuppression, acting broadly on the immune system.
- Common side effects include **hyperglycemia**, **osteoporosis**, and **cataracts**, not specific gingival overgrowth.
Heart transplantation US Medical PG Question 8: A 65-year-old man is admitted to the hospital because of a 1-month history of fatigue, intermittent fever, and weakness. Results from a peripheral blood smear taken during his evaluation are indicative of possible acute myeloid leukemia. Bone marrow aspiration and subsequent cytogenetic studies confirm the diagnosis. The physician sets aside an appointed time-slot and arranges a meeting in a quiet office to inform him about the diagnosis and discuss his options. He has been encouraged to bring someone along to the appointment if he wanted. He comes to your office at the appointed time with his daughter. He appears relaxed, with a full range of affect. Which of the following is the most appropriate opening statement in this situation?
- A. Your lab reports show that you have an acute myeloid leukemia
- B. What is your understanding of the reasons we did bone marrow aspiration and cytogenetic studies? (Correct Answer)
- C. You must be curious and maybe even anxious about the results of your tests.
- D. I may need to refer you to a blood cancer specialist because of your diagnosis. You may need chemotherapy or radiotherapy, which we are not equipped for.
- E. Would you like to know all the details of your diagnosis, or would you prefer I just explain to you what our options are?
Heart transplantation Explanation: ***"What is your understanding of the reasons we did bone marrow aspiration and cytogenetic studies?"***
- This **open-ended question** allows the patient to express their current knowledge and perceptions, which helps the physician tailor the discussion.
- It establishes a **patient-centered approach**, respecting the patient's existing understanding and preparing them for further information.
*"You must be curious and maybe even anxious about the results of your tests."*
- While empathic, this statement makes an **assumption about the patient's feelings** rather than inviting them to share their own.
- It is often better to ask directly or use more open-ended questions that allow the patient to express their true emotions, especially given their **relaxed demeanor**.
*"I may need to refer you to a blood cancer specialist because of your diagnosis. You may need chemotherapy or radiotherapy, which we are not equipped for.”"*
- This statement immediately introduces **overwhelming and potentially alarming information** (referral, chemotherapy, radiotherapy) without first establishing the diagnosis or assessing the patient's readiness to receive it.
- It prematurely jumps to treatment and logistics, potentially causing **unnecessary distress** before the patient has processed the core diagnosis.
*"Would you like to know all the details of your diagnosis, or would you prefer I just explain to you what our options are?""*
- While it attempts to assess the patient's preference for information, this question is a **closed-ended "either/or" choice** that might limit the patient's ability to express nuanced needs.
- It also prematurely introduces the idea of "options" without first explaining the diagnosis in an understandable context.
*"Your lab reports show that you have an acute myeloid leukemia"*
- This is a **direct and blunt delivery of a serious diagnosis** without any preparatory context or assessment of the patient's existing knowledge or emotional state.
- Delivering such news abruptly can be shocking and overwhelming, potentially **hindering effective communication** and rapport building.
Heart transplantation US Medical PG Question 9: An 18-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents because he suddenly collapsed while playing football. His parents mention that he had complained of dizziness while playing before, but never fainted in the middle of a game. On physical examination, the blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg, the respirations are 15/min, and the pulse is 110/min. The chest is clear, but a systolic ejection murmur is present. The remainder of the examination revealed no significant findings. An electrocardiogram is ordered, along with an echocardiogram. He is diagnosed with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and the physician lists all the precautions he must follow. Which of the following drugs will be on the list of contraindicated substances?
- A. Βeta-blockers
- B. Dobutamine
- C. Nitrates (Correct Answer)
- D. Calcium channel blockers
- E. Potassium channel blockers
Heart transplantation Explanation: ***Nitrates***
- **Nitrates** cause **vasodilation**, which decreases **preload** and worsens **left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO)** in **hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)**, potentially leading to syncope or sudden death.
- Reduced preload exacerbates the dynamic obstruction, causing a critical drop in cardiac output.
- **Commonly encountered substances** patients must avoid include nitroglycerin, isosorbide, and **phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors** (sildenafil, tadalafil) which potentiate nitrate effects.
- This is a critical counseling point for HCM patients in everyday life.
*Beta-blockers*
- **Beta-blockers** are **first-line treatment** for **hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)** as they reduce heart rate, improve diastolic filling, and decrease contractility, thereby reducing **LVOTO**.
- They alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death in HCM.
*Dobutamine*
- **Dobutamine** is a **beta-1 adrenergic agonist** that increases contractility and heart rate, which would worsen **LVOTO** in HCM.
- While also contraindicated in HCM, dobutamine is only used in **controlled hospital settings** for stress testing or hemodynamic support, not a substance patients encounter in daily life.
- The question focuses on outpatient counseling about substances to avoid in everyday situations.
*Calcium channel blockers*
- **Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers** (verapamil, diltiazem) are used in **HCM management**, particularly in patients who cannot tolerate beta-blockers.
- They improve **diastolic function** and reduce **LVOTO** by decreasing contractility and heart rate.
- **Caution:** Dihydropyridines (nifedipine, amlodipine) can worsen obstruction and should be avoided.
*Potassium channel blockers*
- **Antiarrhythmics** like **amiodarone** (potassium channel blocker) are used in **HCM** patients for atrial or ventricular arrhythmias.
- Not contraindicated; therapeutically indicated for rhythm management.
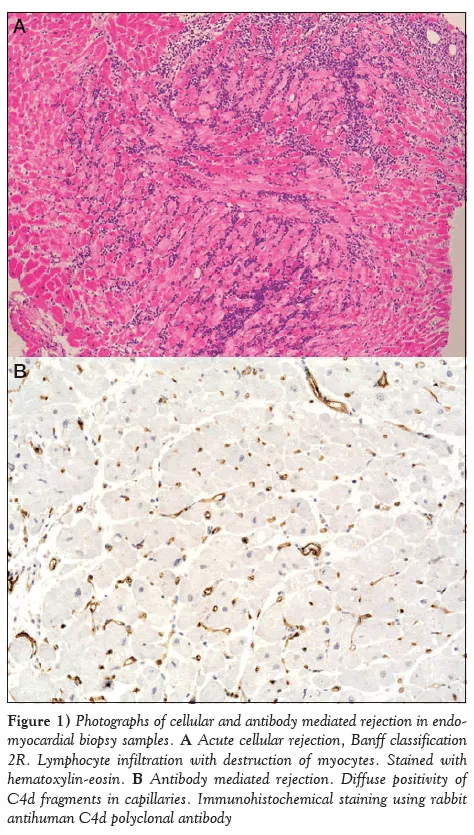
Heart transplantation US Medical PG Question 10: A 48-year-old Caucasian male suffering from ischemic heart disease is placed on a heart transplant list. Months later, he receives a heart from a matched donor. During an endomyocardial biopsy performed 3 weeks later, there is damage consistent with acute graft rejection. What is most likely evident on the endomyocardial biopsy?
- A. Granuloma
- B. Atherosclerosis
- C. Lymphocytic infiltrate (Correct Answer)
- D. Tissue necrosis
- E. Fibrosis
Heart transplantation Explanation: ***Lymphocytic infiltrate***
- Acute graft rejection, especially within weeks of transplantation, is characterized by a **cellular immune response** dominated by **T lymphocytes** invading the allograft.
- These lymphocytes target donor major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, leading to myocyte damage and dysfunction, which would be visible as a lymphocytic infiltrate on biopsy.
*Granuloma*
- Granulomas are aggregates of **macrophages**, often seen in chronic inflammatory conditions like tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, or fungal infections.
- They are not typical findings in the context of acute allograft rejection.
*Atherosclerosis*
- Atherosclerosis is a disease of large and medium-sized arteries characterized by **plaque formation**, primarily involving lipid deposition and inflammation, which narrows the arterial lumen.
- While it can affect transplanted organs (e.g., transplant vasculopathy, a form of chronic rejection), it is not the primary mechanism or histological finding in **acute cellular rejection** occurring three weeks post-transplant.
*Tissue necrosis*
- While acute rejection can *lead* to tissue necrosis due to severe inflammation and ischemia, necrosis alone is a broad term and not the most specific or defining histological feature of acute cellular rejection.
- The preceding and primary histopathological hallmark of acute cellular rejection is the **inflammatory cell infiltrate**, particularly lymphocytes attacking the graft.
*Fibrosis*
- Fibrosis, or the deposition of excess connective tissue, is a characteristic feature of **chronic rejection** or chronic injury processes.
- It indicates long-standing damage and repair, which is unlikely to be the predominant finding in a biopsy three weeks after transplantation indicative of acute rejection.
More Heart transplantation US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.