Brain death criteria US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Brain death criteria. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Brain death criteria US Medical PG Question 1: A 22-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance 1 hour after a motor vehicle accident. He did not require any circulatory resuscitation at the scene, but he was intubated because he was unresponsive. He has no history of serious illnesses. He is on mechanical ventilation with no sedation. His blood pressure is 121/62 mm Hg, the pulse is 68/min, and the temperature is 36.5°C (97.7°F). His Glasgow coma scale (GCS) is 3. Early laboratory studies show no abnormalities. A search of the state donor registry shows that he has registered as an organ donor. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in evaluation?
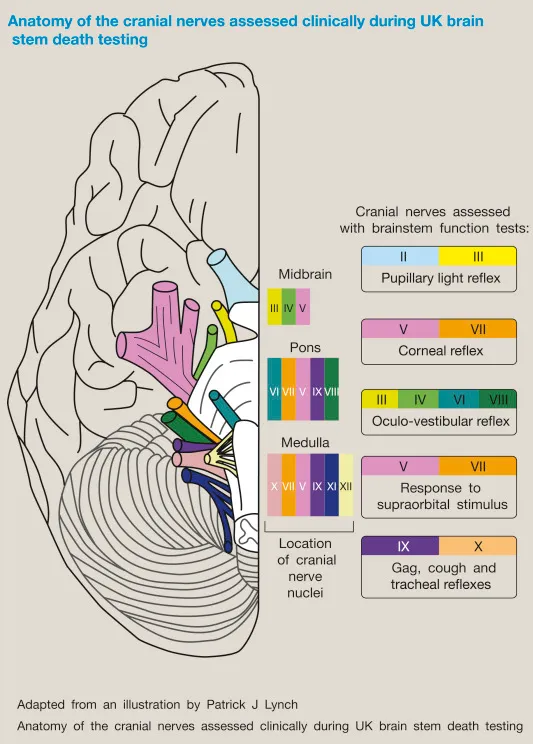
- A. Evaluation of brainstem reflexes (Correct Answer)
- B. Brain MRI
- C. Electroencephalography
- D. Cerebral angiography
- E. Apnea test
Brain death criteria Explanation: ***Evaluation of brainstem reflexes***
- In a patient with a **Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) of 3** and no response to noxious stimuli/sedation, assessment of **brainstem reflexes** is a critical step in determining brain death.
- This evaluation includes checking for pupillary light reflex, corneal reflex, vestibulo-ocular reflex (doll's eyes), oculocephalic reflex, and gag/cough reflexes to ascertain the complete absence of brainstem function.
*Brain MRI*
- While a brain MRI can provide detailed anatomical information regarding brain injury, it is **not the primary diagnostic test** for determining brain death.
- Brain death is a **clinical diagnosis** based on the irreversible loss of brain and brainstem function, which can be confirmed rapidly by clinical examination.
*Electroencephalography*
- **EEG** measures electrical activity in the brain and can show electrocerebral silence, which is consistent with brain death.
- However, EEG is **not always required** for the diagnosis of brain death and is often used as a confirmatory test in specific situations, such as when clinical examination is inconclusive or legal requirements necessitate it.
*Cerebral angiography*
- **Cerebral angiography** can demonstrate the absence of cerebral blood flow, which is a criterion for brain death.
- This is an **invasive procedure** and is generally reserved for situations where clinical examination tests are difficult to perform or interpret (e.g., severe facial trauma, drug intoxication), and is not the initial step.
*Apnea test*
- The **apnea test** is a critical component of the brain death evaluation, confirming the absence of spontaneous breathing response to hypercapnia.
- It is performed **after the absence of brainstem reflexes** has been established and all confounding factors (e.g., hypothermia, hypotension, sedatives) have been ruled out.
Brain death criteria US Medical PG Question 2: A 3-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after losing consciousness. His parents report that he collapsed and then had repetitive, twitching movements of the right side of his body that lasted approximately one minute. He recently started to walk with support. He speaks in bisyllables and has a vocabulary of almost 50 words. Examination shows a large purple-colored patch over the left cheek. One week later, he dies. Which of the following is the most likely finding on autopsy of the brain?
- A. Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
- B. Periventricular calcification
- C. Brainstem glioma
- D. Leptomeningeal vascular malformation (Correct Answer)
- E. Intraparenchymal cyst
Brain death criteria Explanation: ***Leptomeningeal vascular malformation***
- The constellation of **seizures** and a **large purple patch** on the face (**port-wine stain** or nevus flammeus) strongly suggests **Sturge-Weber syndrome**.
- **Leptomeningeal angioma** (vascular malformation) is the characteristic brain finding in Sturge-Weber syndrome, often leading to neurological deficits, seizures, and increased intracranial pressure.
*Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma*
- This tumor is pathognomonic for **tuberous sclerosis complex**, which is typically associated with **facial angiofibromas** (adenoma sebaceum) and other skin lesions like ash-leaf spots.
- While tuberous sclerosis can present with seizures, the facial lesion described in the patient (large purple patch, or port-wine stain) is not consistent with the typical skin findings of tuberous sclerosis.
*Periventricular calcification*
- **Periventricular calcifications** are a hallmark sign of **congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV)** infection.
- While CMV can cause neurological sequelae and developmental delay, the clinical presentation with a distinct facial lesion and recent onset seizures is more indicative of Sturge-Weber syndrome.
*Brainstem glioma*
- **Brainstem gliomas** typically present with **cranial nerve deficits**, **ataxia**, and long tract signs, rather than focal seizures and a port-wine stain.
- The sudden onset of seizures and collapse, along with the characteristic facial lesion, points away from a primary brainstem tumor.
*Intraparenchymal cyst*
- An **intraparenchymal cyst** is a non-specific finding that could result from various causes, such as infection, trauma, or developmental anomalies.
- It does not specifically account for the combination of seizures and the facial **port-wine stain** seen in this patient.
Brain death criteria US Medical PG Question 3: Four days after being hospitalized, intubated, and mechanically ventilated, a 30-year-old man has no cough response during tracheal suctioning. He was involved in a motor vehicle collision and was obtunded on arrival in the emergency department. The ventilator is at a FiO2 of 100%, tidal volume is 920 mL, and positive end-expiratory pressure is 5 cm H2O. He is currently receiving vasopressors. His vital signs are within normal limits. The pupils are dilated and nonreactive to light. Corneal, gag, and oculovestibular reflexes are absent. There is no facial or upper extremity response to painful stimuli; the lower extremities show a triple flexion response to painful stimuli. Serum concentrations of electrolytes, urea, creatinine, and glucose are within the reference range. Arterial blood gas shows:
pH 7.45
pCO2 41 mm Hg
pO2 99 mm Hg
O2 saturation 99%
Two days ago, a CT scan of the head showed a left intracerebral hemorrhage with mass effect. The apnea test is positive. There are no known family members, advanced directives, or individuals with power of attorney. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Ethics committee consultation (Correct Answer)
- B. Remove the ventilator
- C. Court order for further management
- D. Repeat CT scan of the head
- E. Cerebral angiography
Brain death criteria Explanation: ***Ethics committee consultation***
- The patient meets criteria for **brain death**, but there are no family members or advance directives to guide end-of-life decisions. An **ethics committee consultation** is essential to navigate the complex legal and ethical implications of withdrawing life support in such a situation.
- The committee can provide guidance on hospital policies, relevant laws, and ethical principles to ensure a decision that respects the patient's presumed wishes and societal values, especially given the absence of surrogates.
*Remove the ventilator*
- While the patient appears to meet the criteria for **brain death**, premature withdrawal of the ventilator without proper legal and ethical guidance is inappropriate, especially given the lack of identified next of kin or advance directives.
- A formal process, including definitive declaration of brain death by two separate physicians and addressing legal and ethical considerations, must precede such an action.
*Court order for further management*
- A court order might be necessary if there are intractable disagreements among stakeholders or if brain death cannot be definitively declared. However, an **ethics committee consult** is typically the initial step to resolve complex cases lacking surrogate decision-makers before escalating to legal action.
- Seeking a court order is a more extreme measure usually reserved when internal hospital mechanisms and ethical consultations fail to provide a clear path forward.
*Repeat CT scan of the head*
- A repeat CT scan would typically be performed to assess changes in the intracerebral hemorrhage or mass effect if there were signs of ongoing neurological deterioration that might be reversible, or to guide surgical intervention.
- However, in this patient, the clinical picture, including absent brainstem reflexes and a positive apnea test indicating **brain death**, suggests that further imaging for diagnostic purposes related to hemorrhage progression is unlikely to alter the prognosis or management related to end-of-life decisions.
*Cerebral angiography*
- **Cerebral angiography** is used to assess cerebral blood flow and can be a confirmatory test for brain death if clinical examination and apnea testing are inconclusive, especially in cases where sedative medications might confound the clinical picture.
- In this case, the comprehensive clinical examination and positive apnea test strongly suggest brain death, making angiography unnecessary at this stage, particularly without surrogate decision-makers.
Brain death criteria US Medical PG Question 4: A 24-year-old man presents to the emergency department after a motor vehicle collision. He was in the front seat and unrestrained driver in a head on collision. His temperature is 99.2°F (37.3°C), blood pressure is 90/65 mmHg, pulse is 152/min, respirations are 16/min, and oxygen saturation is 100% on room air. Physical exam is notable for a young man who opens his eyes spontaneously and is looking around. He answers questions with inappropriate responses but discernible words. He withdraws from pain but does not have purposeful movement. Which of the following is this patient's Glasgow coma scale?
- A. 9
- B. 15
- C. 7
- D. 11 (Correct Answer)
- E. 13
Brain death criteria Explanation: ***11***
- **Eye-opening (E)**: The patient opens his eyes spontaneously, scoring **E4**.
- **Verbal response (V)**: He gives inappropriate responses but discernible words, scoring **V3**.
- **Motor response (M)**: He withdraws from pain but does not have purposeful movement, scoring **M4**.
- Therefore, the total Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score is **E4 + V3 + M4 = 11**.
*9*
- This score would imply a lower verbal or motor response, such as **incomprehensible sounds (V2)** or **abnormal flexion (M3)**, which is not consistent with the patient's presentation.
- For example, E4 + V2 + M3 would equal 9.
*15*
- A GCS of 15 indicates **normal neurological function**, meaning the patient would be fully oriented, obey commands, and open eyes spontaneously, which is not the case here.
- This score is for a patient who is fully conscious and responsive.
*7*
- A GCS of 7 suggests a **severe brain injury**, which would typically present with a much poorer response, such as **no verbal response (V1)** or **abnormal extension (M2)**.
- For example, E4 + V1 + M2 would equal 7.
*13*
- This score would mean a higher level of consciousness, such as **confused conversation (V4)** or **localizing pain (M5)**, which is better than the patient's described responses.
- For example, E4 + V4 + M5 would equal 13.
Brain death criteria US Medical PG Question 5: A 68-year-old man presents with shortness of breath, particularly when walking up stairs and when lying down to go to sleep at night. He also complains of a chronic cough and states that he now uses 2 extra pillows at night. The patient has a history of type 2 diabetes that is well-managed with metformin. He also takes Prozac for a long-standing history of depression. The patient has a 60-pack-year smoking history. He also has a history significant for alcohol abuse, but he quit cold turkey 15 years ago when his brother was killed in a drunk driving accident. Both he and his brother were adopted, and he does not know other members of his biological family. Despite repeated efforts of patient counseling, the patient is not interested in quitting smoking. The physical exam is significant for an obese male using accessory muscles of respiration. The vital signs include: temperature 36.8°C (98.2°F), heart rate 95/min, respiratory rate 16/min, and blood pressure 130/85 mm Hg. The oxygen saturation is 90% on room air. Additional physical exam findings include cyanotic lips, peripheral edema, hepatomegaly, and ascites. The cardiovascular exam is significant for an S3 heart sound and elevated JVP. The pulmonary exam is significant for expiratory wheezing, diffuse rhonchi, and hyperresonance on percussion. The laboratory test results are as follows:
BUN 15 mg/dL
pCO2 60 mm Hg
Bicarbonate (HCO3) 32 mmol/L
Creatinine 0.8 mg/dL
Glucose 95 mg/dL
Serum chloride 103 mmol/L
Serum potassium 3.9 mEq/L
Serum sodium 140 mEq/L
Total calcium 2.3 mmol/L
Hemoglobin 26 g/dL
Bilirubin total 0.9 mg/dL
Bilirubin indirect 0.4 mg/dL
Iron 100
Ferritin 70
TIBC 300
The posterior-anterior chest X-ray is shown in the image. Which of the following interventions is indicated for decreasing the mortality of this patient?
- A. Flu vaccine
- B. Inhaled anticholinergics
- C. ACE inhibitors
- D. Smoking cessation alone
- E. Both smoking cessation and oxygen administration (Correct Answer)
Brain death criteria Explanation: **Both smoking cessation and oxygen administration**
- Given the patient's **60-pack-year smoking history**, current respiratory symptoms, and **hypoxemia** (SpO2 90% on room air), **smoking cessation is the single most important intervention to slow the progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)**.
- **Long-term oxygen therapy (LTOT)** has been shown to **reduce mortality in COPD patients with chronic hypoxemia**. The patient's oxygen saturation of 90% on room air meets the criteria for LTOT.
*Flu vaccine*
- While **influenza vaccination is crucial for preventing exacerbations and reducing morbidity in COPD patients**, it does not directly decrease overall mortality from the underlying disease in the same way as smoking cessation and oxygen therapy.
- It is a recommended prophylactic measure for patients with chronic respiratory conditions, but its impact on all-cause mortality is less direct than the key interventions mentioned.
*Inhaled anticholinergics*
- **Inhaled anticholinergics (e.g., tiotropium)** are bronchodilators that help **improve lung function and reduce symptoms** in COPD, but they do not alter the disease's natural progression or directly reduce mortality.
- They are a cornerstone of **symptomatic management** for COPD but are not considered a mortality-reducing intervention.
*ACE inhibitors*
- **Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors** are primarily used in conditions like **hypertension, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease**.
- Although the patient has signs of right-sided heart failure (peripheral edema, hepatomegaly, ascites), which could be secondary to severe COPD (cor pulmonale), ACE inhibitors are **not indicated as a primary treatment for COPD itself** or **to reduce mortality in this context**.
*Smoking cessation alone*
- While **smoking cessation is the most important intervention to slow COPD progression and reduce mortality**, the patient's current **hypoxemia (SpO2 90%) also warrants oxygen administration** for mortality benefit.
- Therefore, **smoking cessation combined with oxygen administration** offers a more comprehensive approach to reducing mortality in this patient.
Brain death criteria US Medical PG Question 6: A 60-year-old male is admitted to the ICU for severe hypertension complicated by a headache. The patient has a past medical history of insulin-controlled diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. He smokes 2 packs of cigarettes per day. He states that he forgot to take his medications yesterday and started getting a headache about one hour ago. His vitals on admission are the following: blood pressure of 160/110 mmHg, pulse 95/min, temperature 98.6 deg F (37.2 deg C), and respirations 20/min. On exam, the patient has an audible abdominal bruit. After administration of antihypertensive medications, the patient has a blood pressure of 178/120 mmHg. The patient reports his headache has increased to a 10/10 pain level, that he has trouble seeing, and he can't move his extremities. After stabilizing the patient, what is the best next step to diagnose the patient's condition?
- A. Doppler ultrasound of the carotids
- B. CT head with intravenous contrast
- C. MRI head without intravenous contrast
- D. CT head without intravenous contrast (Correct Answer)
- E. MRI head with intravenous contrast
Brain death criteria Explanation: ***CT head without intravenous contrast***
- The sudden onset of severe headache, visual disturbances, and neurological deficits (inability to move extremities), coupled with uncontrolled severe hypertension despite initial treatment, is highly suggestive of an **intracranial pathology**, most likely a **hemorrhagic stroke**.
- A **non-contrast CT scan of the head** is the **gold standard** for rapidly identifying acute intracranial hemorrhage, as it can be performed quickly and is readily available in emergency settings.
*Doppler ultrasound of the carotids*
- This test is primarily used to evaluate **carotid artery stenosis** due to atherosclerosis, which can lead to ischemic stroke.
- While the patient has risk factors for atherosclerosis, his acute presentation with severe central neurological symptoms points more towards an acute intracranial event rather than carotid disease.
*CT head with intravenous contrast*
- While a contrast CT can be useful for identifying tumors, abscesses, or vascular malformations, it is **contraindicated in the initial assessment of acute stroke** if an intracranial hemorrhage is suspected.
- Contrast can sometimes obscure subtle bleeds or complicate the interpretation of acute hemorrhage, and it also carries a risk of **contrast-induced nephropathy**, especially in a patient with diabetes.
*MRI head without intravenous contrast*
- An MRI provides superior soft tissue resolution compared to CT and is excellent for detecting ischemic strokes in later stages, as well as subtle hemorrhages, tumors, and other conditions.
- However, it is **less available, takes longer to perform**, and is often not the first choice in an acute neurological emergency where time is critical, particularly when differentiating between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
*MRI head with intravenous contrast*
- Similar to a contrast CT, an MRI with contrast is generally **not the initial imaging choice for acute stroke** due to time constraints and the need to quickly rule out hemorrhage before considering contrast administration.
- Contrast agents for MRI, such as gadolinium, have their own risks, including **nephrogenic systemic fibrosis** in patients with renal impairment, which is a concern in a diabetic patient.
Brain death criteria US Medical PG Question 7: A 22-year-old female is brought to the emergency department by her friends. She was supposed to attend her first job interview in a few hours when she started having palpitations. Her past medical history is insignificant, and she currently takes no medications. Her vitals show the following: pulse rate is 90/min, respiratory rate is 28/min, and blood pressure is 136/86 mm Hg. Her ECG is normal. What will be the patient’s approximate alveolar carbon dioxide pressure (PACO2) given her normal respiratory rate is 14/min and PACO2 is 36 mm Hg? Ignore dead space and assume carbon dioxide production is constant.
- A. 18 mm Hg (Correct Answer)
- B. 72 mm Hg
- C. 36 mm Hg
- D. 27 mm Hg
- E. 44 mm Hg
Brain death criteria Explanation: ***18 mm Hg***
- **PACO2** is inversely proportional to **alveolar ventilation (VA)**. If ventilation doubles, PACO2 halves assuming constant **CO2 production**.
- The patient's respiratory rate has doubled from 14/min to 28/min. Therefore, the new PACO2 will be 36 mmHg / 2 = **18 mm Hg**.
*72 mm Hg*
- This value would suggest a reduction in **alveolar ventilation**, which is contrary to the increased respiratory rate observed.
- If ventilation were halved, PACO2 would double, but the patient is **hyperventilating**.
*36 mm Hg*
- This is the initial **PACO2** at a respiratory rate of 14/min.
- An increase in respiratory rate from 14/min to 28/min will change the **PACO2**.
*27 mm Hg*
- This value suggests a less than doubling of **alveolar ventilation**, which doesn't align with the doubling of the respiratory rate.
- This would imply a more complex change in ventilation beyond simple rate adjustment.
*44 mm Hg*
- This value would represent a slight increase in **PACO2**, indicating **hypoventilation**.
- The patient's increased respiratory rate of 28/min indicates **hyperventilation**, which leads to a decrease in PACO2.
Brain death criteria US Medical PG Question 8: A 75-year-old female presents to your office with her daughter. The patient states that she feels perfectly well and that she does not know why she is present. The daughter states that over the last several years, the patient has become forgetful and recently forgot her grandchild's name, along with the groceries she was supposed to buy. She was also found lost 10 miles away from her house last week. The daughter also states that the patient has had urinary incontinence over the last few months and has been seeing little children in the morning that are not present. The patient denies any recent falls. Her vitals are normal and her physical exam does not reveal any focal neurological deficits. Her mini-mental status exam is scored 22/30. What is the most accurate test for this patient?
- A. CT angiography of head
- B. CT scan of head
- C. Lumbar puncture
- D. MRI scan of head (Correct Answer)
- E. PET scan of head
Brain death criteria Explanation: ***MRI scan of head***
- An MRI scan of the head is the **most accurate initial test** to evaluate cognitive decline and rule out structural/reversible causes of dementia.
- This patient's presentation includes **progressive memory loss, disorientation, urinary incontinence, and visual hallucinations** - suggestive of **Lewy Body Dementia (LBD)** or potentially **Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH)**, though gait disturbance (a key NPH feature) is notably absent.
- MRI provides detailed visualization of **brain atrophy patterns**, **ventricular enlargement** (for NPH), **white matter lesions** (vascular dementia), **hippocampal atrophy** (Alzheimer's), and excludes other reversible causes like **subdural hematoma, tumor, or stroke**.
- **Must be performed first** before any invasive procedures like lumbar puncture.
*CT scan of head*
- A CT scan is useful for acute conditions like **hemorrhage, stroke, or mass lesions**, but it is **significantly less sensitive** than MRI for detecting subtle changes critical for dementia diagnosis.
- Cannot adequately visualize **cortical atrophy, hippocampal volume loss, or subtle white matter changes** that help differentiate dementia subtypes.
- While faster and more accessible, it is not the "most accurate" test for cognitive decline evaluation.
*CT angiography of head*
- CT angiography specifically visualizes **blood vessels** to detect **aneurysms, stenoses, or vascular malformations**.
- While vascular disease can contribute to dementia, this test does not evaluate the **brain parenchyma** or structural changes necessary for diagnosing neurodegenerative conditions.
- Not indicated as the initial test for cognitive impairment without focal vascular symptoms.
*Lumbar puncture*
- Lumbar puncture analyzes **cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)** for biomarkers (**amyloid-beta, tau, alpha-synuclein**), infection, or inflammation.
- It is an **invasive procedure** that should only be performed **after neuroimaging** to rule out increased intracranial pressure, hydrocephalus, or mass lesions.
- While useful for confirming specific dementia diagnoses (e.g., Alzheimer's or LBD biomarkers), it is a **second-line test**, not the initial most accurate diagnostic study.
*PET scan of head*
- PET imaging (FDG-PET or amyloid-PET) measures **metabolic activity** or **specific protein deposits** and is highly specific for certain dementias like **Alzheimer's disease** or **Frontotemporal dementia**.
- It is typically a **specialized second-line test** used after structural imaging when the diagnosis remains unclear.
- **More expensive and less available** than MRI, and not necessary as the initial most accurate test for broad cognitive impairment evaluation.
Brain death criteria US Medical PG Question 9: A 37-year-old man is presented to the emergency department by paramedics after being involved in a serious 3-car collision on an interstate highway while he was driving his motorcycle. On physical examination, he is responsive only to painful stimuli and his pupils are not reactive to light. His upper extremities are involuntarily flexed with hands clenched into fists. The vital signs include temperature 36.1°C (97.0°F), blood pressure 80/60 mm Hg, and pulse 102/min. A non-contrast computed tomography (CT) scan of the head shows a massive intracerebral hemorrhage with a midline shift. Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis shows partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood (PaCO2) of 68 mm Hg, and the patient is put on mechanical ventilation. His condition continues to decline while in the emergency department and it is suspected that this patient is brain dead. Which of the following results can be used to confirm brain death and legally remove this patient from the ventilator?
- A. Electrocardiogram
- B. Apnea test (Correct Answer)
- C. Lumbar puncture and CSF culture
- D. Electromyography with nerve conduction studies
- E. CT scan
Brain death criteria Explanation: ***Correct: Apnea test***
- The **apnea test** is a **mandatory component** of brain death determination according to American Academy of Neurology (AAN) guidelines
- It directly confirms the **irreversible absence of brainstem function** by demonstrating no respiratory drive despite adequate stimulus (PaCO2 ≥60 mm Hg or 20 mm Hg rise from baseline)
- This patient already has a PaCO2 of 68 mm Hg, making the apnea test particularly relevant for confirmation
- Brain death requires both **clinical examination** (absent brainstem reflexes, coma) and a **positive apnea test** to legally declare death and discontinue mechanical ventilation
- The apnea test is performed by disconnecting the ventilator, providing supplemental oxygen, and observing for any respiratory effort while PaCO2 rises to adequate levels
*Incorrect: CT scan*
- While a **CT scan showing massive intracerebral hemorrhage with midline shift** provides anatomical evidence of severe, irreversible structural brain damage, it is **NOT sufficient to confirm brain death**
- CT imaging is used to establish the **etiology** and rule out reversible causes, but does not directly test brainstem function
- Brain death is a **clinical and functional diagnosis**, not purely an anatomical one—imaging alone cannot confirm cessation of all brain function
- A patient can have devastating structural damage on CT but still retain some brainstem reflexes
*Incorrect: Electrocardiogram*
- An **electrocardiogram (ECG)** measures cardiac electrical activity and provides no information about brain or brainstem function
- Cardiac activity commonly persists after brain death due to the heart's intrinsic automaticity
- ECG findings are irrelevant to brain death determination
*Incorrect: Lumbar puncture and CSF culture*
- **Lumbar puncture and CSF culture** are used to diagnose CNS infections (meningitis, encephalitis) or inflammatory conditions
- These tests are **completely irrelevant** for brain death diagnosis, which is based on irreversible cessation of all brain function, not infection
- In this trauma case with known intracerebral hemorrhage, LP would be contraindicated due to increased intracranial pressure and risk of herniation
*Incorrect: Electromyography with nerve conduction studies*
- **EMG and nerve conduction studies** assess peripheral nerve and muscle function, used for diagnosing neuromuscular disorders
- These tests provide no information about brain or brainstem function
- They are not part of brain death determination protocols
Brain death criteria US Medical PG Question 10: A 22-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 30 minutes after being involved in a high-speed motor vehicle collision in which he was the unrestrained driver. After extrication, he had severe neck pain and was unable to move his arms and legs. On arrival, he is lethargic and cannot provide a history. Hospital records show that eight months ago, he underwent an open reduction and internal fixation of the right humerus. His neck is immobilized in a cervical collar. Intravenous fluids are being administered. His pulse is 64/min, respirations are 8/min and irregular, and blood pressure is 104/64 mm Hg. Examination shows multiple bruises over the chest, abdomen, and extremities. There is flaccid paralysis and absent reflexes in all extremities. Sensory examination shows decreased sensation below the shoulders. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. The abdomen is soft. There is swelling of the right ankle and right knee. Squeezing of the glans penis does not produce anal sphincter contraction. A focused assessment with sonography for trauma shows no abnormalities. He is intubated and mechanically ventilated. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Cervical x-ray
- B. CT of the head
- C. Intravenous dexamethasone therapy
- D. MRI of the spine (Correct Answer)
- E. Placement of Foley catheter
Brain death criteria Explanation: **MRI of the spine**
- The patient presents with clear signs of a **spinal cord injury** (flaccid paralysis, absent reflexes, decreased sensation below the shoulders, severe neck pain after trauma). **MRI** is the most sensitive and specific imaging modality to visualize soft tissue injuries, including the spinal cord, ligaments, and disc herniations, which are crucial for diagnosing and guiding treatment for a spinal cord injury.
- Given the patient's **hemodynamic stability** after initial resuscitation and intubation, and the suspicion of spinal cord injury, a thorough evaluation with MRI is the next appropriate step to delineate the extent and location of the injury.
*Cervical x-ray*
- While cervical X-rays are often performed in trauma cases, they have **limited sensitivity** for detecting all spinal injuries, especially soft tissue damage, ligamentous injuries, or non-displaced fractures.
- In a patient with clear neurological deficits suggesting spinal cord involvement, X-rays alone are **insufficient** for a definitive diagnosis and treatment planning.
*CT of the head*
- A CT scan of the head would be appropriate if there were signs of a **head injury**, such as focal neurological deficits suggestive of intracranial pathology, or a change in mental status not fully explained by other injuries.
- In this case, the predominant neurological signs point to a **spinal cord injury** rather than a primary head injury, making head CT a lower priority at this stage.
*Intravenous dexamethasone therapy*
- The use of high-dose corticosteroids like dexamethasone for acute spinal cord injury is **controversial** and its routine use is **not recommended** by current guidelines due to a lack of clear benefit and potential for harm.
- Imaging to characterize the injury is a more urgent and appropriate step before considering any pharmacological interventions for spinal cord protection.
*Placement of Foley catheter*
- While a **Foley catheter** will likely be needed for this patient to manage neurogenic bladder dysfunction that often accompanies spinal cord injury, it is a supportive measure.
- It does not address the immediate diagnostic need to characterize the spinal cord injury, which is paramount for guiding surgical or medical management and preventing further damage.
More Brain death criteria US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.