Transplant medicine

On this page
🏥 The Transplant Medicine Command Center
Transplant medicine transforms dying organs into second chances, but success hinges on mastering the delicate immunological balance between acceptance and rejection. You'll learn to recognize rejection patterns, interpret diagnostic signals from biopsies to biomarkers, and deploy precise immunosuppressive strategies while managing infections, malignancies, and multi-organ complications. This lesson builds your command of the transplant ecosystem-from understanding why the immune system attacks grafted tissue to orchestrating long-term care that keeps both graft and patient thriving.
📌 Remember: HEART - HLA matching, Evaluation protocols, Allograft function, Rejection monitoring, Toxicity management. These five pillars determine transplant success, with HLA compatibility reducing acute rejection risk by 40-60% and proper immunosuppression maintaining 90%+ five-year survival in optimal candidates.
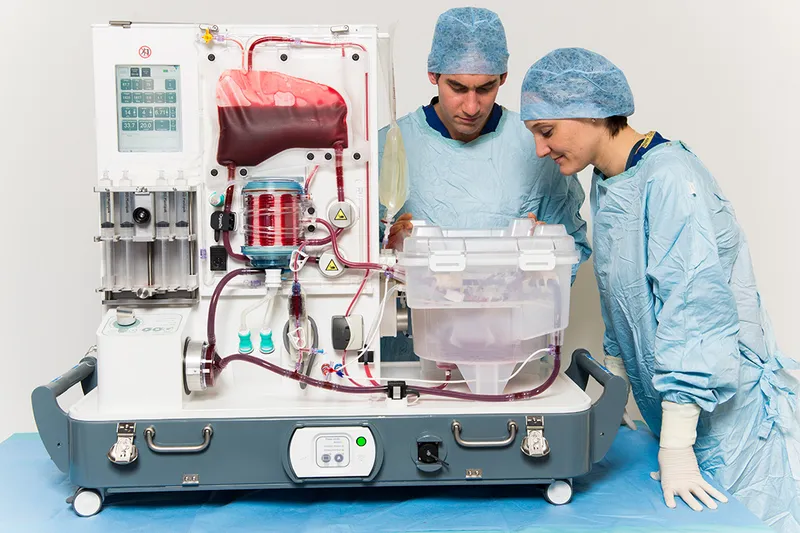
The transplant process follows a systematic progression from donor identification through long-term management. Brain death criteria must be met in <1% of hospital deaths, creating a critical organ shortage with >100,000 Americans currently on transplant waiting lists. Understanding this scarcity drives the precision required in donor-recipient matching and post-transplant care.
| Organ System | 1-Year Survival | 5-Year Survival | Rejection Episodes | Immunosuppression Protocol | Critical Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kidney | 98% | 85% | 15-20% | Triple therapy | Creatinine, BUN |
| Liver | 91% | 75% | 25-30% | Tacrolimus-based | Bilirubin, ALT |
| Heart | 91% | 72% | 20-25% | MMF + CNI | Biopsy, echo |
| Lung | 89% | 54% | 35-40% | Triple therapy | Spirometry, biopsy |
| Pancreas | 95% | 83% | 10-15% | Induction + maintenance | Glucose, C-peptide |
- Donor Selection Mastery
- Age limits: Heart/lung <55 years, kidney <70 years, liver <80 years
- Ischemia tolerance: Heart <4 hours, liver <12 hours, kidney <24 hours
- Cold ischemia time directly correlates with delayed graft function
- Every hour beyond optimal time increases complications by 8-12%
- Immunological Compatibility
- ABO matching: Mandatory for all organs except liver (some flexibility)
- HLA typing: Class I (A,B) and Class II (DR) most critical
- 6/6 HLA match: Reduces rejection risk by 60%, extends graft survival 5-7 years
- Zero mismatch kidneys: Allocated nationally due to superior outcomes
💡 Master This: Transplant success depends on the "Golden Triangle" - optimal donor selection, precise surgical technique, and aggressive immunosuppression balanced against infection risk. Calcineurin inhibitor levels must be monitored 2-3 times weekly initially, with target tacrolimus levels 8-12 ng/mL in the first month, then 5-8 ng/mL long-term to prevent both rejection and nephrotoxicity.
Understanding transplant medicine fundamentals establishes the foundation for mastering organ-specific protocols and recognizing the complex interplay between surgical technique and immunological management that determines long-term graft survival.
🏥 The Transplant Medicine Command Center
🧬 Immunological Warfare: The Host-Graft Battle
📌 Remember: MATCH - MHC compatibility, Antigen presentation, T-cell activation, Cytokine release, Hypersensitivity responses. Each step amplifies immune activation 10-100 fold, with complete HLA mismatches generating >1000x stronger rejection responses than matched organs.
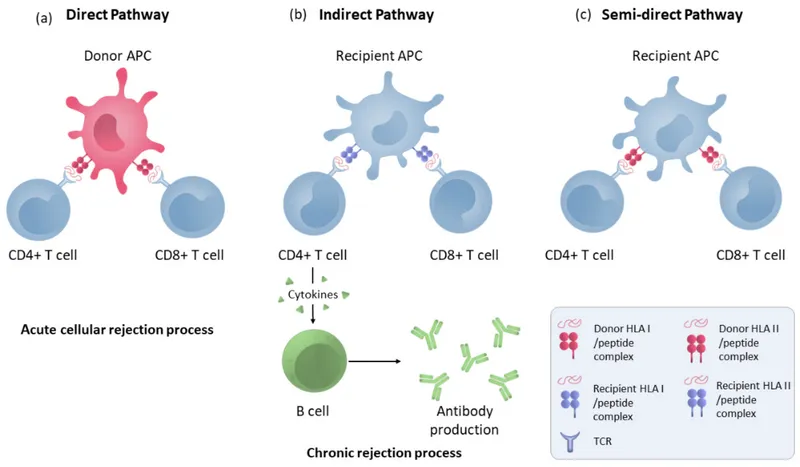
Rejection Timeline and Mechanisms:
- Hyperacute Rejection (<24 hours)
- Pre-formed antibodies against donor HLA or ABO antigens
- Complement activation within minutes to hours
- Massive thrombosis and graft necrosis
- 100% graft loss if occurs, prevented by crossmatch testing
- Acute Cellular Rejection (Days to months)
- T-cell mediated destruction of graft tissue
- Peak incidence 1-6 months post-transplant
- Reversible with pulse steroids in 80-90% of episodes
- Banff criteria grade severity from IA to III
- Chronic Rejection (Months to years)
- Antibody-mediated vascular changes and fibrosis
- Leading cause of late graft loss across all organs
- Irreversible process affecting 40-60% of grafts by 10 years
| Rejection Type | Timeline | Mechanism | Reversibility | Treatment Response | Graft Survival Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyperacute | <24 hours | Preformed antibodies | 0% | None effective | 100% loss |
| Acute Cellular | Days-months | T-cell mediated | 80-90% | Pulse steroids | 5-10% loss |
| Acute Humoral | Days-weeks | De novo antibodies | 60-70% | Plasmapheresis + IVIG | 15-20% loss |
| Chronic | Months-years | Fibrosis + vasculopathy | <10% | Limited options | 40-60% loss |
Immunosuppression Mechanisms and Targets:
- Calcineurin Inhibitors (Tacrolimus, Cyclosporine)
- Block IL-2 transcription in activated T-cells
- Nephrotoxicity in 60-80% of patients long-term
- Target tacrolimus levels: 8-12 ng/mL (month 1), 5-8 ng/mL (maintenance)
- Therapeutic drug monitoring essential due to narrow therapeutic window
- Antiproliferative Agents (Mycophenolate, Azathioprine)
- Inhibit purine synthesis in rapidly dividing lymphocytes
- GI toxicity and bone marrow suppression dose-limiting
- Mycophenolic acid levels 1-3.5 mg/L optimize efficacy while minimizing toxicity
- mTOR Inhibitors (Sirolimus, Everolimus)
- Block T-cell proliferation and B-cell antibody production
- Wound healing impairment and proteinuria major concerns
- Sirolimus levels 4-12 ng/mL depending on combination therapy
💡 Master This: Triple immunosuppression (CNI + antiproliferative + steroid) reduces acute rejection to <15% in most organs while maintaining >90% one-year survival. The key is therapeutic drug monitoring with 2-3 weekly levels initially, adjusting doses to maintain target ranges while monitoring for drug-specific toxicities through comprehensive metabolic panels and complete blood counts every 2-4 weeks.
Mastering immunological principles provides the foundation for understanding organ-specific rejection patterns and developing personalized immunosuppression strategies that balance efficacy against long-term complications.
🧬 Immunological Warfare: The Host-Graft Battle
🎯 Pattern Recognition: The Clinical Detective Framework
The "TRANSPLANT" Recognition Framework provides systematic approach to post-transplant complications:
- Temperature elevation (>38°C) - Infection vs rejection differential
- Renal function changes (>25% creatinine rise) - Drug toxicity vs rejection
- Allograft dysfunction (organ-specific parameters)
- New symptoms (fatigue, decreased appetite, organ-specific signs)
- Serologic changes (rising inflammatory markers)
- Pharmacologic levels (subtherapeutic immunosuppression)
- Laboratory trends (trending vs isolated abnormalities)
- Antibody development (donor-specific antibodies)
- Non-adherence assessment (medication compliance)
- Timing considerations (early vs late post-transplant period)
📌 Remember: FEVER - First rule out infection, Evaluate drug levels, Verify compliance, Examine graft function, Review recent biopsies. >80% of early fevers (<3 months) represent infection, while >60% of late fevers (>1 year) suggest malignancy or chronic complications.
Infection vs Rejection Discrimination Matrix:
- Timing Patterns
- 0-1 month: Bacterial infections (60%), CMV reactivation (20%)
- 1-6 months: Opportunistic infections (40%), acute rejection (25%)
- CMV disease peaks at 2-4 months in D+/R- patients
- PCP pneumonia risk highest 3-6 months without prophylaxis
- >6 months: Community-acquired infections, malignancy, chronic rejection
- Laboratory Discriminators
- Procalcitonin >0.5 ng/mL: 85% sensitivity for bacterial infection
- CMV PCR >1000 copies/mL: 90% predictive for CMV disease
- Quantitative CMV monitoring essential in high-risk patients
- Preemptive therapy initiated at >2000 copies/mL
| Clinical Scenario | Infection Probability | Rejection Probability | Key Discriminators | Immediate Action | Diagnostic Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fever + ↑Creatinine | 70% | 25% | Procalcitonin, urinalysis | Blood cultures | Infection workup |
| Fever + Normal function | 85% | 10% | Chest X-ray, CBC | Broad cultures | Infection focus |
| Afebrile + ↑Creatinine | 20% | 60% | Drug levels, DSA | Biopsy consideration | Rejection workup |
| Fever + Diarrhea | 90% | 5% | C. diff, CMV PCR | Stool studies | GI infection |
| Dyspnea + Fever | 80% | 15% | Chest CT, BAL | Respiratory cultures | Pulmonary infection |
Organ-Specific Rejection Patterns:
- Kidney Transplant Red Flags
- Creatinine rise >25% from baseline over 48-72 hours
- Decreased urine output (<0.5 mL/kg/hr) with oliguria
- Doppler ultrasound shows increased resistive index >0.8
- Biopsy indicated for unexplained creatinine rise >0.3 mg/dL
- Liver Transplant Warning Signs
- AST/ALT elevation >2x baseline or bilirubin >3 mg/dL
- Synthetic dysfunction: INR >1.5, albumin <3.0 g/dL
- Hepatic artery thrombosis must be excluded with Doppler ultrasound
- Liver biopsy gold standard for rejection vs infection differentiation
- Heart Transplant Surveillance
- Endomyocardial biopsy every 3 months first year
- Echocardiographic changes: wall motion abnormalities, decreased EF
- Grade 2R rejection requires treatment intensification
- Cardiac catheterization annually to assess transplant vasculopathy
💡 Master This: "When in doubt, biopsy" - Tissue diagnosis remains the gold standard for rejection diagnosis across all organs. Protocol biopsies at 3, 6, 12 months detect subclinical rejection in 15-25% of patients, allowing early intervention before irreversible damage occurs. Banff criteria provide standardized grading with inter-observer agreement >85% among experienced pathologists.
Developing systematic pattern recognition enables rapid differentiation of post-transplant complications and guides appropriate therapeutic interventions before irreversible graft damage occurs.
🎯 Pattern Recognition: The Clinical Detective Framework
🔬 Systematic Discrimination: The Diagnostic Precision Matrix
Rejection Grading and Treatment Thresholds:
The Banff Classification System provides standardized criteria for rejection diagnosis across organ systems, with specific histological features determining treatment intensity and prognosis. Understanding these quantitative thresholds enables evidence-based therapeutic decisions and outcome prediction.
- Kidney Transplant Banff Criteria
- Borderline Changes: t1, i1 (minimal tubulitis, interstitial inflammation <25%)
- Type IA Rejection: t2, i2 (moderate tubulitis, inflammation 25-50%)
- Treatment: Pulse methylprednisolone 500mg x 3 days
- Response rate: 85-90% with complete reversal
- Type IB Rejection: t3, i3 (severe tubulitis, inflammation >50%)
- Treatment: Anti-thymocyte globulin 1.5mg/kg x 7-14 days
- Response rate: 70-80% with partial reversal common
Antibody-Mediated Rejection (AMR) Diagnostic Criteria:
- Histological Evidence: g+ptc ≥2 (glomerulitis + peritubular capillaritis)
- Immunological Evidence: C4d staining >50% peritubular capillaries
- Serological Evidence: Donor-specific antibodies with MFI >1000
| Rejection Grade | Histological Features | Treatment Protocol | Response Rate | Graft Survival Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borderline | t1, i1 | Optimize immunosuppression | 95% | Minimal |
| Type IA | t2, i2 | Pulse steroids | 85-90% | <5% loss |
| Type IB | t3, i3 | ATG + steroids | 70-80% | 10-15% loss |
| Type II | Arterial involvement | ATG + plasmapheresis | 50-60% | 25-30% loss |
| AMR | g+ptc ≥2, C4d+, DSA+ | Plasmapheresis + IVIG | 60-70% | 20-25% loss |
Drug-Induced Nephrotoxicity vs Rejection:
Calcineurin inhibitor toxicity affects 60-80% of transplant recipients, requiring careful differentiation from acute rejection through combined clinical, laboratory, and histological assessment.
- CNI Toxicity Features
- Arteriolar hyalinosis and tubular atrophy on biopsy
- Dose-dependent relationship with drug levels >15 ng/mL (tacrolimus)
- Reversible if caught early (<6 months)
- Irreversible fibrosis develops with chronic exposure
- Improvement with dose reduction or drug conversion
- Acute Rejection Features
- Lymphocytic infiltration with tubulitis and arteritis
- No correlation with drug levels (may occur with therapeutic levels)
- Progressive without immunosuppression intensification
- Responds to anti-rejection therapy within 7-14 days
⭐ Clinical Pearl: "Trough levels >12 ng/mL tacrolimus" increase nephrotoxicity risk 3-fold without improving rejection prevention. Target levels 5-8 ng/mL after 6 months maintain efficacy while reducing long-term complications. eGFR decline >5 mL/min/year suggests chronic toxicity requiring drug modification.
Infection Discrimination in Immunocompromised Hosts:
Opportunistic infections follow predictable timelines based on immunosuppression intensity and prophylaxis protocols. Risk stratification enables targeted prevention and early recognition.
- High-Risk Periods and Pathogens
- 0-1 month: Bacterial infections (Gram-negative 60%, Gram-positive 30%)
- 1-6 months: CMV (40% D+/R-), PCP (15% without prophylaxis)
- CMV prophylaxis with valganciclovir 900mg daily for 3-6 months
- PCP prophylaxis with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole indefinitely
- >6 months: Community-acquired plus late opportunistic infections
| Pathogen | Risk Period | Clinical Presentation | Diagnostic Test | Treatment | Mortality Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMV | 1-4 months | Fever, leukopenia, GI symptoms | Quantitative PCR | Ganciclovir | 5-10% |
| PCP | 2-6 months | Dyspnea, dry cough, hypoxia | BAL + staining | High-dose TMP-SMX | 15-20% |
| Aspergillus | 1-6 months | Pulmonary nodules, cavitation | Galactomannan + CT | Voriconazole | 30-40% |
| BK Virus | 6-24 months | Rising creatinine, hematuria | Urine PCR | Reduce immunosuppression | Graft loss 10-15% |
| PTLD | >6 months | Lymphadenopathy, B symptoms | Tissue biopsy + EBV | Reduce IS + rituximab | 20-30% |
Systematic discrimination between rejection, toxicity, and infection requires integrated assessment of clinical presentation, laboratory trends, histological findings, and therapeutic responses to optimize long-term graft survival.
🔬 Systematic Discrimination: The Diagnostic Precision Matrix
⚖️ Treatment Algorithms: The Evidence-Based Response Matrix
Acute Cellular Rejection Treatment Algorithm:
📌 Remember: PULSE - Prednisolone first-line, Upgrade to ATG if severe, Levels must be therapeutic, Steroid-resistant needs rescue, Early treatment improves outcomes. Pulse methylprednisolone 500mg IV daily x 3 days reverses 85-90% of Type IA rejection with minimal side effects when used early.
Evidence-Based Treatment Protocols:
- First-Line Acute Rejection Treatment
- Methylprednisolone 500-1000mg IV daily x 3-5 days
- Response assessment at day 7 with repeat creatinine
- >50% improvement: Continue maintenance immunosuppression
- <25% improvement: Consider steroid-resistant rejection
- Success rate: 85-90% for Type IA, 70-75% for Type IB
- Second-Line Rescue Therapy
- Anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG) 1.5mg/kg daily x 7-14 days
- Premedication: Methylprednisolone 250mg, diphenhydramine 50mg
- Monitor: CD3+ count target <50 cells/μL
- Complications: Cytokine release syndrome (30%), serum sickness (15%)
- Alternative: Alemtuzumab 30mg x 2 doses for refractory cases
Antibody-Mediated Rejection (AMR) Treatment Protocol:
AMR represents 20-30% of acute rejection episodes and requires aggressive combination therapy targeting both antibody removal and B-cell suppression.
- Plasmapheresis Protocol
- 5-7 sessions over 2 weeks removing 1-1.5 plasma volumes
- Replacement fluid: 5% albumin or fresh frozen plasma
- Goal: Reduce DSA MFI by >50% from baseline
- Monitor: Daily DSA levels during treatment course
- IVIG Administration
- 2g/kg divided over 2-4 days following final plasmapheresis
- Premedication: Acetaminophen, diphenhydramine, slow infusion rate
- Complications: Hemolysis (5%), renal dysfunction (10%)
- Contraindications: IgA deficiency, severe heart failure
| Treatment Modality | Mechanism | Dosing Protocol | Response Rate | Major Complications | Monitoring Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulse Steroids | Anti-inflammatory | 500mg x 3 days | 85-90% | Hyperglycemia (60%) | Daily glucose |
| ATG | T-cell depletion | 1.5mg/kg x 7-14d | 70-80% | Cytokine release (30%) | CD3+ counts |
| Plasmapheresis | Antibody removal | 5-7 sessions | 60-70% | Bleeding (15%) | Coagulation studies |
| IVIG | Antibody neutralization | 2g/kg over 2-4d | 50-60% | Hemolysis (5%) | Hemoglobin, LDH |
| Rituximab | B-cell depletion | 375mg/m² x 4 | 40-50% | Hypogammaglobulinemia | IgG levels |
Steroid-Resistant Rejection Management:
10-15% of acute cellular rejection episodes prove steroid-resistant, requiring escalation to lymphocyte-depleting agents with higher complication rates but salvage potential in 60-70% of cases.
- ATG Dosing and Monitoring
- Test dose: 0.1mg/kg to assess hypersensitivity reactions
- Therapeutic dose: 1.5mg/kg daily adjusted for CD3+ counts
- Target: CD3+ <50 cells/μL or <10% of baseline
- Duration: 7-14 days based on clinical response
- Complications Management
- Cytokine release syndrome: Premedication with steroids and antihistamines
- Serum sickness: Joint pain, rash, fever in 15-20% of patients
- Increased infection risk: CMV reactivation in 40-50% of patients
💡 Master This: Combination immunosuppression following rejection treatment requires careful balance between preventing recurrent rejection and avoiding over-immunosuppression. Target drug levels: Tacrolimus 8-12 ng/mL, mycophenolic acid 1.5-3.0 mg/L, with gradual reduction over 3-6 months to maintenance levels while monitoring for rejection recurrence through protocol biopsies.
Long-term Immunosuppression Optimization:
Post-rejection immunosuppression requires individualized protocols based on rejection severity, treatment response, and patient risk factors for complications.
- High-Risk Maintenance Protocol
- Triple therapy: CNI + antiproliferative + steroid
- Enhanced monitoring: Monthly labs for 6 months, then quarterly
- Drug level monitoring: Weekly x 4, then monthly x 6
- DSA surveillance: Every 3 months for high immunological risk
- Complication Prevention
- Infection prophylaxis: Extended CMV and PCP prophylaxis
- Malignancy screening: Annual skin exams, colonoscopy, mammography
- PTLD surveillance: EBV PCR if high viral load pre-transplant
- Cardiovascular protection: Statin therapy, blood pressure control
Evidence-based treatment algorithms enable systematic rejection management with predictable outcomes while minimizing complications through careful monitoring and protocol adherence.
⚖️ Treatment Algorithms: The Evidence-Based Response Matrix
🔗 Multi-System Integration: The Transplant Ecosystem
The Transplant-Cardiovascular Interface:
Cardiovascular disease represents the leading cause of late mortality in transplant recipients, with 3-5x higher risk compared to age-matched controls. Immunosuppressive medications create unique cardiovascular risk profiles requiring specialized management strategies.
- Calcineurin Inhibitor Cardiovascular Effects
- Hypertension in 70-90% of recipients within 6 months
- Mechanism: Afferent arteriolar vasoconstriction and sodium retention
- Target BP: <130/80 mmHg to preserve graft function
- First-line agents: ACE inhibitors or ARBs (avoid hyperkalemia)
- Hyperlipidemia with total cholesterol >200 mg/dL in 60% of patients
- Statin therapy reduces cardiovascular events by 30-40%
- Target LDL: <100 mg/dL (<70 mg/dL if diabetes or CAD)
📌 Remember: CARDIAC - Calcineurin causes hypertension, Atherosclerosis accelerated, Renal function affects BP, Diabetes increases risk, Infection causes inflammation, Arrhythmias from electrolytes, Coronary disease screening essential. Annual cardiac risk assessment prevents >50% of late cardiovascular events.
Metabolic Syndrome in Transplant Recipients:
Post-transplant diabetes mellitus (PTDM) develops in 20-50% of recipients, with tacrolimus conferring 2-3x higher risk than cyclosporine. Early recognition and aggressive management prevent long-term complications.
- PTDM Risk Factors and Timeline
- Peak incidence: 3-6 months post-transplant during high-dose immunosuppression
- Risk factors: Age >45, BMI >30, family history, hepatitis C
- African American and Hispanic patients have 2x higher risk
- Steroid dose >10 mg/day increases diabetes risk by 40%
- Screening protocol: Fasting glucose and HbA1c at 3, 6, 12 months
- OGTT if fasting glucose 100-125 mg/dL (impaired fasting glucose)
| Metabolic Complication | Incidence | Timeline | Risk Factors | Management Strategy | Target Goals |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTDM | 20-50% | 3-6 months | Age, obesity, steroids | Metformin + insulin | HbA1c <7% |
| Hypertension | 70-90% | 1-3 months | CNI, steroids | ACE-I/ARB | <130/80 mmHg |
| Hyperlipidemia | 60-80% | 6-12 months | Steroids, CNI | Statin therapy | LDL <100 mg/dL |
| Bone Disease | 30-50% | 6-24 months | Steroids, CKD | Bisphosphonates | T-score >-2.5 |
| Obesity | 25-35% | 12-24 months | Steroids, lifestyle | Diet + exercise | BMI <30 |
Renal Function Preservation Strategies:
Chronic kidney disease affects >60% of non-kidney transplant recipients by 5 years, primarily due to calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity. Proactive management preserves long-term function.
- CNI Minimization Protocols
- Target tacrolimus levels: 8-12 ng/mL (0-3 months), 5-8 ng/mL (>6 months)
- Conversion strategies: mTOR inhibitor substitution in stable patients
- Sirolimus conversion improves eGFR by 10-15 mL/min over 2 years
- Contraindications: Proteinuria >800 mg/day, wound healing issues
- Monitoring protocol: Monthly creatinine and eGFR calculation
- >30% eGFR decline: Consider drug modification or nephrology consultation
Infection Risk Stratification and Prevention:
Opportunistic infections remain leading causes of morbidity and mortality, with risk directly proportional to net immunosuppression and environmental exposures.
- Risk-Adapted Prophylaxis Strategies
- CMV high-risk (D+/R-): Valganciclovir 900mg daily x 6 months
- PCP prophylaxis: TMP-SMX 1 DS 3x/week indefinitely
- Alternative: Dapsone 100mg daily if sulfa allergy
- Pentamidine 300mg inhaled monthly for severe allergies
- Fungal prophylaxis: Fluconazole 200mg daily in high-risk centers
- Aspergillus endemic areas: Consider voriconazole or posaconazole
💡 Master This: "Net state of immunosuppression" concept guides individualized management - recent rejection treatment, lymphocyte counts, viral loads, and environmental exposures determine infection risk. CD4+ counts <200 cells/μL warrant enhanced prophylaxis similar to HIV patients, while normal counts allow standard protocols.
Malignancy Surveillance and Prevention:
Cancer incidence increases 2-4x in transplant recipients, with skin cancers (20-50x higher) and PTLD (10-20x higher) showing dramatic increases. Systematic screening enables early detection and improved outcomes.
- Enhanced Screening Protocols
- Dermatology: Every 6 months with total body examination
- Colonoscopy: Every 3-5 years starting age 45 (or 5 years earlier than family history)
- Annual if inflammatory bowel disease or previous polyps
- Mammography/Pap smears: Annual regardless of age at transplant
- PTLD surveillance: Annual EBV PCR if high-risk (EBV-negative recipient)
| Cancer Type | Relative Risk | Screening Protocol | Early Detection Signs | Treatment Modifications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin (NMSC) | 20-50x | 6-month dermatology | New/changing lesions | Reduce immunosuppression |
| PTLD | 10-20x | Annual EBV PCR | Lymphadenopathy, B symptoms | Reduce IS + rituximab |
| Renal Cell | 3-5x | Annual abdominal imaging | Hematuria, flank pain | Standard oncology care |
| Colorectal | 2-3x | Colonoscopy q3-5y | Bleeding, weight loss | Standard protocols |
| Breast | 1.5-2x | Annual mammography | Palpable mass | Hormone receptor status |
🔗 Multi-System Integration: The Transplant Ecosystem
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Transplant Command Center
The Essential Numbers Arsenal:
📌 Remember: SURVIVAL - Screening protocols, Urgent complications, Rejection thresholds, Viral monitoring, Immunosuppression levels, Vaccination schedules, Annual assessments, Long-term surveillance. Master these quantitative thresholds for immediate clinical application.
- Critical Drug Levels and Timing
- Tacrolimus: 8-12 ng/mL (0-3 months), 5-8 ng/mL (maintenance)
- Mycophenolic acid: 1.5-3.0 mg/L (therapeutic range)
- Sirolimus: 4-12 ng/mL (combination therapy), 12-20 ng/mL (monotherapy)
- Monitoring frequency: 2-3x weekly initially, monthly after 3 months
- Dose adjustments: 25% changes maximum to avoid toxicity
Rapid Assessment Framework:
| Parameter | Normal Range | Action Threshold | Urgent Intervention | Monitoring Frequency | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Creatinine | <1.5 mg/dL | >25% increase | >50% increase | 2-3x weekly | Rejection vs toxicity |
| Tacrolimus | 5-12 ng/mL | <3 or >15 | <2 or >20 | Weekly initially | Efficacy vs toxicity |
| WBC | 4-10 K/μL | <3 or >15 | <1 or >20 | Weekly initially | Infection vs over-IS |
| CMV PCR | Undetectable | >1000 copies | >10,000 copies | Weekly x 12 | Preemptive therapy |
| DSA MFI | <1000 | >3000 | >10,000 | 3, 6, 12 months | Rejection risk |
Emergency Recognition Patterns:
- Immediate Threats (Call Within 1 Hour)
- Creatinine >50% increase from baseline
- Fever >38.5°C with WBC <2000 or >20,000
- Tacrolimus level <2 ng/mL or >20 ng/mL
- Acute rejection risk increases 5-10x with subtherapeutic levels
- Nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity with supratherapeutic levels
- CMV PCR >10,000 copies/mL (high risk for CMV disease)
💡 Master This: "The 48-72 Hour Rule" - Most transplant emergencies declare themselves within 48-72 hours of onset. Daily monitoring during high-risk periods (first 3 months, post-rejection treatment) enables early intervention before irreversible complications develop.
Long-term Surveillance Checklist:
- Annual Comprehensive Assessment
- Cardiovascular: Echo, stress test if >50 years or diabetes
- Malignancy: Skin exam, colonoscopy (q3-5y), mammography
- Bone health: DEXA scan, vitamin D, calcium levels
- Bisphosphonate therapy if T-score <-2.5 or fragility fracture
- Vaccination updates: Annual influenza, COVID boosters, avoid live vaccines
Clinical Decision Trees for Common Scenarios:
This clinical mastery arsenal provides immediate reference tools for rapid decision-making, systematic monitoring, and evidence-based interventions that optimize transplant outcomes through proactive management and early complication recognition.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Transplant Command Center
Practice Questions: Transplant medicine
Test your understanding with these related questions
A research team develops a new monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitor for advanced melanoma that has shown promise in animal studies as well as high efficacy and low toxicity in early phase human clinical trials. The research team would now like to compare this drug to existing standard of care immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. The research team decides to conduct a non-randomized study where the novel drug will be offered to patients who are deemed to be at risk for toxicity with the current standard of care immunotherapy, while patients without such risk factors will receive the standard treatment. Which of the following best describes the level of evidence that this study can offer?













