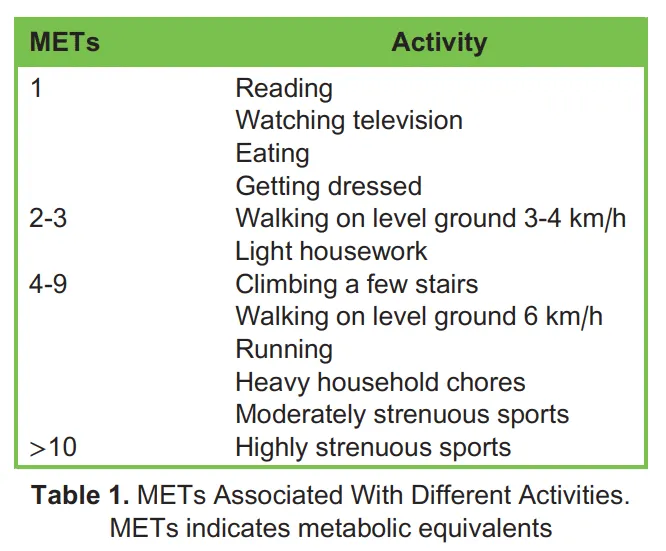
Functional capacity evaluation US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Functional capacity evaluation. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Functional capacity evaluation US Medical PG Question 1: A 40-year-old female volunteers for an invasive study to measure her cardiac function. She has no previous cardiovascular history and takes no medications. With the test subject at rest, the following data is collected using blood tests, intravascular probes, and a closed rebreathing circuit:
Blood hemoglobin concentration 14 g/dL
Arterial oxygen content 0.22 mL O2/mL
Arterial oxygen saturation 98%
Venous oxygen content 0.17 mL O2/mL
Venous oxygen saturation 78%
Oxygen consumption 250 mL/min
The patient's pulse is 75/min, respiratory rate is 14/ min, and blood pressure is 125/70 mm Hg. What is the cardiac output of this volunteer?
- A. Body surface area is required to calculate cardiac output.
- B. Stroke volume is required to calculate cardiac output.
- C. 250 mL/min
- D. 5.0 L/min (Correct Answer)
- E. 50 L/min
Functional capacity evaluation Explanation: ***5.0 L/min***
- Cardiac output can be calculated using the **Fick principle**: Cardiac Output $(\text{CO}) = \frac{{\text{Oxygen Consumption}}}{{\text{Arterial } \text{O}_2 \text{ Content} - \text{Venous O}_2 \text{ Content}}}$.
- Given Oxygen Consumption = 250 mL/min, Arterial O$_2$ Content = 0.22 mL/mL, and Venous O$_2$ Content = 0.17 mL/mL. Thus, CO = $\frac{{250 \text{ mL/min}}}{{(0.22 - 0.17) \text{ mL } \text{O}_2/\text{mL blood}}} = \frac{{250 \text{ mL/min}}}{{0.05 \text{ mL } \text{O}_2/\text{mL blood}}} = 5000 \text{ mL/min } = 5.0 \text{ L/min}$.
*Body surface area is required to calculate cardiac output.*
- **Body surface area (BSA)** is used to calculate **cardiac index**, which is cardiac output normalized to body size, but not cardiac output directly.
- While a normal cardiac output might be compared to a patient's BSA for context, it is not a necessary component for calculating the absolute cardiac output.
*Stroke volume is required to calculate cardiac output.*
- Cardiac output can be calculated as **Stroke Volume (SV) x Heart Rate (HR)**. However, stroke volume is not provided directly in this question.
- The Fick principle allows for the calculation of cardiac output **without explicit knowledge of stroke volume** or heart rate, using oxygen consumption and arteriovenous oxygen difference.
*250 mL/min*
- 250 mL/min represents the **oxygen consumption**, not the cardiac output.
- Cardiac output is the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute, which is influenced by both oxygen consumption and the difference in oxygen content between arterial and venous blood.
*50 L/min*
- A cardiac output of 50 L/min is an **extremely high and physiologically impossible** value for a resting individual.
- This value is 10 times higher than the calculated cardiac output and typically represents a calculation error.
Functional capacity evaluation US Medical PG Question 2: A 50-year-old woman comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. She has no personal or family history of serious illness. She smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 5 years during her 20s. Her pulse is 70/min, and blood pressure is 120/78 mm Hg. Serum lipid studies and glucose concentration are within the reference ranges. Which of the following health maintenance recommendations is most appropriate at this time?
- A. Perform BRCA gene test
- B. Perform abdominal ultrasound
- C. Perform 24-hour ECG
- D. Perform DEXA scan
- E. Perform colonoscopy (Correct Answer)
Functional capacity evaluation Explanation: ***Perform colonoscopy***
- **Colorectal cancer screening** with colonoscopy is generally recommended for individuals at average risk starting at age **45-50 years**.
- This patient is **50 years old** and has no increased risk factors, making routine colonoscopy the most appropriate screening.
*Perform BRCA gene test*
- **BRCA gene testing** is indicated for individuals with a strong **family history** of breast or ovarian cancer, or those with personal history suggesting a genetic predisposition.
- This patient has **no personal or family history** of serious illness, so BRCA testing is not warranted.
*Perform abdominal ultrasound*
- **Abdominal ultrasound** is typically used to investigate specific symptoms or screen for conditions like **abdominal aortic aneurysm** in high-risk individuals (e.g., male smokers over 65).
- This patient has **no relevant symptoms** or risk factors for which routine abdominal ultrasound screening is recommended.
*Perform 24-hour ECG*
- A **24-hour ECG (Holter monitor)** is used to detect paroxysmal **arrhythmias** or evaluate symptoms like palpitations, syncope, or dizziness.
- This patient is asymptomatic with a normal pulse and blood pressure; therefore, **routine 24-hour ECG** is not indicated.
*Perform DEXA scan*
- A **DEXA scan** is recommended for **osteoporosis screening** in women typically starting at age **65**, or earlier if they have significant risk factors like a history of fragility fractures or certain medical conditions.
- At **50 years old** and with no apparent risk factors for osteoporosis, a DEXA scan is not yet routinely indicated according to general guidelines.
Functional capacity evaluation US Medical PG Question 3: An epidemiologist is evaluating the efficacy of Noxbinle in preventing HCC deaths at the population level. A clinical trial shows that over 5 years, the mortality rate from HCC was 25% in the control group and 15% in patients treated with Noxbinle 100 mg daily. Based on this data, how many patients need to be treated with Noxbinle 100 mg to prevent, on average, one death from HCC?
- A. 20
- B. 73
- C. 10 (Correct Answer)
- D. 50
- E. 100
Functional capacity evaluation Explanation: ***10***
- The **number needed to treat (NNT)** is calculated by first finding the **absolute risk reduction (ARR)**.
- **ARR** = Risk in control group - Risk in treatment group = 25% - 15% = **10%** (or 0.10).
- **NNT = 1 / ARR** = 1 / 0.10 = **10 patients**.
- This means that **10 patients must be treated with Noxbinle to prevent one death from HCC** over 5 years.
*20*
- This would result from an ARR of 5% (1/0.05 = 20), which is not supported by the data.
- May arise from miscalculating the risk difference or incorrectly halving the actual ARR.
*73*
- This value does not correspond to any standard calculation of NNT from the given mortality rates.
- May result from confusion with other epidemiological measures or calculation error.
*50*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 2% (1/0.02 = 50), which significantly underestimates the actual risk reduction.
- Could result from incorrectly calculating the difference as a proportion rather than absolute percentage points.
*100*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 1% (1/0.01 = 100), grossly underestimating the treatment benefit.
- May result from confusing ARR with relative risk reduction or other calculation errors.
Functional capacity evaluation US Medical PG Question 4: A 71-year-old man is admitted to the hospital one hour after he was found unconscious. His pulse is 80/min and systolic blood pressure is 98 mm Hg; diastolic blood pressure cannot be measured. He is intubated and mechanically ventilated with supplemental oxygen at a tidal volume of 450 mL and a respiratory rate of 10/min. Arterial blood gas analysis shows:
PCO2 43 mm Hg
O2 saturation 94%
O2 content 169 mL/L
Pulmonary artery catheterization shows a pulmonary artery pressure of 15 mm Hg and a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure of 7 mm Hg. Bedside indirect calorimetry shows a rate of O2 tissue consumption of 325 mL/min. Given this information, which of the following additional values is sufficient to calculate the cardiac output in this patient?
- A. Left ventricular end-diastolic volume
- B. Partial pressure of inspired oxygen
- C. End-tidal carbon dioxide pressure
- D. Pulmonary artery oxygen content (Correct Answer)
- E. Total peripheral resistance
Functional capacity evaluation Explanation: ***Pulmonary artery oxygen content***
- Cardiac output can be calculated using the **Fick principle**, which states that **Cardiac Output = (Oxygen Consumption) / (Arteriovenous Oxygen Difference)**.
- We are provided with **O2 tissue consumption (325 mL/min)** and **arterial O2 content (169 mL/L)**. To complete the Fick equation, we need the **mixed venous oxygen content**, which is represented by the **pulmonary artery oxygen content**.
*Left ventricular end-diastolic volume*
- While **left ventricular end-diastolic volume** is a determinant of stroke volume (and thus cardiac output), it alone is not sufficient to calculate cardiac output without knowing heart rate and ejection fraction.
- This value is more relevant for assessing **preload** and ventricular function.
*Partial pressure of inspired oxygen*
- The **partial pressure of inspired oxygen** is used to calculate the **alveolar oxygen partial pressure** and is important for assessing oxygenation and respiratory function.
- It is not directly used in the Fick principle for calculating cardiac output.
*End-tidal carbon dioxide pressure*
- **End-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2)** is a measure of the partial pressure of CO2 at the end of exhalation and reflects ventilation and pulmonary perfusion.
- While it can be correlated with cardiac output in certain clinical contexts, it is not a direct input for the **Fick principle** calculation of cardiac output.
*Total peripheral resistance*
- **Total peripheral resistance (TPR)** can be calculated from cardiac output and mean arterial pressure using the formula: **(MAP - CVP) / CO**, but it cannot be used to calculate cardiac output directly without knowing the other variables.
- TPR is a measure of the **resistance to blood flow** in the systemic circulation.
Functional capacity evaluation US Medical PG Question 5: An orthopaedic surgeon at a local community hospital has noticed that turnover times in the operating room have been unnecessarily long. She believes that the long wait times may be due to inefficient communication between the surgical nursing staff, the staff in the pre-operative area, and the staff in the post-operative receiving area. She believes a secure communication mobile phone app would help to streamline communication between providers and improve efficiency in turnover times. Which of the following methods is most appropriate to evaluate the impact of this intervention in the clinical setting?
- A. Plan-Do-Study-Act cycle (Correct Answer)
- B. Failure modes and effects analysis
- C. Standardization
- D. Forcing function
- E. Root cause analysis
Functional capacity evaluation Explanation: ***Plan-Do-Study-Act cycle***
- The **Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle** is a structured, iterative model used for continuous improvement in quality and efficiency, making it ideal for evaluating the impact of a new intervention like a communication app.
- This cycle allows for small-scale testing of changes, observation of results, learning from the observations, and refinement of the intervention before full implementation.
*Failure modes and effects analysis*
- **Failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA)** is a prospective method to identify potential failures in a process, predict their effects, and prioritize actions to prevent them.
- While useful for process improvement, FMEA is typically performed *before* implementing a change to identify risks, rather than to evaluate the impact of an already implemented intervention.
*Standardization*
- **Standardization** involves creating and implementing consistent processes or protocols to reduce variability and improve reliability.
- While the communication app might contribute to standardization, standardization itself is a *method of improvement* rather than a method for *evaluating the impact* of an intervention.
*Forcing function*
- A **forcing function** is a design feature that physically prevents an error from occurring, making it impossible to complete a task incorrectly.
- An app that streamlines communication does not act as a forcing function, as it facilitates a process rather than physically preventing an incorrect action.
*Root cause analysis*
- **Root cause analysis (RCA)** is a retrospective method used to investigate an event that has already occurred (e.g., an adverse event) to identify its underlying causes.
- This method is used *after* a problem has manifested to understand *why* it happened, not to evaluate the *impact* of a new intervention designed to prevent future problems.
Functional capacity evaluation US Medical PG Question 6: A 45-year-old woman presents to your office with a serum glucose of 250 mg/dL and you diagnose diabetes mellitus type II. You intend to prescribe the patient metformin, but you decide to order laboratory tests before proceeding. Which of the following basic metabolic panel values would serve as a contraindication to the use of metformin?
- A. HCO3- > 30
- B. Na+ > 140
- C. K+ > 4.0
- D. Glucose > 300
- E. Creatinine > 2.0 (Correct Answer)
Functional capacity evaluation Explanation: ***Creatinine > 2.0***
- An elevated **serum creatinine** level indicating significant renal impairment is a contraindication to metformin use, as it markedly increases the risk of **lactic acidosis**.
- **Metformin** is primarily excreted by the kidneys unchanged, and impaired renal function leads to drug accumulation and potential toxicity.
- Traditional contraindication thresholds include serum creatinine >1.5 mg/dL in men or >1.4 mg/dL in women; a value **>2.0 mg/dL** clearly indicates significant renal dysfunction requiring avoidance of metformin.
- Current guidelines emphasize using **eGFR** (contraindicated if <30 mL/min/1.73m²), but creatinine remains a key marker of renal function on basic metabolic panels.
*HCO3- > 30*
- An elevated **bicarbonate level** (HCO3-) above 30 mEq/L typically indicates **metabolic alkalosis**, which is not a direct contraindication for metformin.
- While metabolic alkalosis should be investigated, it does not pose the specific risk of lactic acidosis associated with renal dysfunction and metformin use.
*Na+ > 140*
- A slightly elevated **sodium level** (Na+) above 140 mEq/L (normal: 135-145 mEq/L) is often associated with **dehydration** or other electrolyte imbalances and is not a contraindication for metformin.
- While significant electrolyte imbalances should be addressed, mild hypernatremia does not directly increase the risk of metformin-induced lactic acidosis.
*K+ > 4.0*
- A potassium level of >4.0 mEq/L is within the **normal range** (typically 3.5-5.0 mEq/L) and is not a contraindication for metformin.
- Significant hyperkalemia or hypokalemia would require evaluation and management, but a normal or slightly elevated potassium level does not preclude metformin use.
*Glucose > 300*
- While a blood **glucose level** >300 mg/dL indicates poorly controlled diabetes, this is actually an **indication** for initiating glucose-lowering therapy like metformin, not a contraindication.
- Metformin's primary therapeutic purpose is to lower elevated glucose levels, and severe hyperglycemia itself does not increase the risk of metformin's specific adverse effects.
Functional capacity evaluation US Medical PG Question 7: A 69-year-old man is scheduled to undergo radical retropubic prostatectomy for prostate cancer in 2 weeks. He had a myocardial infarction at the age of 54 years. He has a history of GERD, unstable angina, hyperlipidemia, and severe osteoarthritis in the left hip. He is unable to climb up stairs or walk fast because of pain in his left hip. He had smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 30 years but quit 25 years ago. He drinks one glass of wine daily. Current medications include aspirin, metoprolol, lisinopril, rosuvastatin, omeprazole, and ibuprofen as needed. His temperature is 36.4°C (97.5°F), pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 136/88 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. A 12-lead ECG shows Q waves and inverted T waves in leads II, III, and aVF. His B-type natriuretic protein is 84 pg/mL (N < 125). Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management to assess this patient's perioperative cardiac risk?
- A. No further testing
- B. 24-hour ambulatory ECG monitoring
- C. Radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging (Correct Answer)
- D. Treadmill stress test
- E. Resting echocardiography
Functional capacity evaluation Explanation: ***Radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging***
- This patient requires **perioperative cardiac risk assessment** before intermediate-risk surgery (radical prostatectomy).
- Key factors include: history of **myocardial infarction**, current cardiac risk factors, and **inability to exercise** due to severe osteoarthritis.
- Since he cannot perform exercise stress testing, **pharmacologic stress testing** with radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging (using agents like adenosine, dipyridamole, or regadenoson) is the most appropriate test to assess for **inducible myocardial ischemia**.
- This provides functional assessment of coronary perfusion under pharmacologic stress, helping guide perioperative risk stratification and management.
- *Note: The presence of unstable angina would typically require cardiac stabilization first; this question focuses on selecting the appropriate stress test modality for a patient unable to exercise.*
*No further testing*
- This patient has significant cardiac risk factors including **prior MI**, ongoing cardiac medications, and ECG changes suggesting old infarction.
- Proceeding directly to surgery without functional cardiac assessment would be **inappropriate** given his risk profile and the intermediate-risk nature of the planned surgery.
*24-hour ambulatory ECG monitoring*
- Holter monitoring detects arrhythmias and silent ischemic episodes but does not provide **functional capacity assessment** or evaluation of inducible ischemia under stress conditions.
- It is not the primary tool for **perioperative cardiac risk stratification** before major surgery.
*Treadmill stress test*
- The patient's **severe osteoarthritis** prevents him from climbing stairs or walking fast, making him unable to achieve adequate exercise workload for a treadmill stress test.
- This functional limitation makes **exercise stress testing contraindicated**; pharmacologic stress testing is required instead.
*Resting echocardiography*
- Resting echocardiography assesses **baseline left ventricular function**, wall motion abnormalities from prior infarction, and valvular disease.
- While useful for structural assessment, it does **not evaluate for exercise-induced or stress-induced ischemia**, which is critical for perioperative risk assessment in patients with coronary artery disease.
- His normal BNP (84 pg/mL) suggests adequate baseline ventricular function, making functional ischemia assessment more relevant than structural evaluation alone.
Functional capacity evaluation US Medical PG Question 8: A person is exercising strenuously on a treadmill for 1 hour. An arterial blood gas measurement is then taken. Which of the following are the most likely values?
- A. pH 7.56, PaO2 100, PCO2 44, HCO3 38
- B. pH 7.32, PaO2 42, PCO2 50, HCO3 27
- C. pH 7.57 PaO2 100, PCO2 23, HCO3 21 (Correct Answer)
- D. pH 7.38, PaO2 100, PCO2 69 HCO3 42
- E. pH 7.36, PaO2 100, PCO2 40, HCO3 23
Functional capacity evaluation Explanation: ***pH 7.57, PaO2 100, PCO2 23, HCO3 21***
- After 1 hour of strenuous exercise, this represents **respiratory alkalosis with mild metabolic compensation**, which is the expected finding in a healthy individual during sustained vigorous exercise.
- The **low PCO2 (23 mmHg)** reflects appropriate **hyperventilation** in response to increased metabolic demands and lactic acid production. During intense exercise, minute ventilation increases dramatically, often exceeding the rate of CO2 production.
- The **slightly elevated pH (7.57)** and **mildly decreased HCO3 (21 mEq/L)** indicate that respiratory compensation has slightly overshot, creating mild alkalosis, while the bicarbonate is consumed both in buffering lactate and through renal compensation.
- **Normal PaO2 (100 mmHg)** confirms adequate oxygenation maintained by increased ventilation.
*pH 7.36, PaO2 100, PCO2 40, HCO3 23*
- These are **completely normal arterial blood gas values** with no evidence of any physiological stress or compensation.
- After 1 hour of strenuous exercise, we would expect **hyperventilation with decreased PCO2**, not a normal PCO2 of 40 mmHg. This profile would be consistent with rest, not vigorous exercise.
- The absence of any respiratory or metabolic changes makes this inconsistent with the clinical scenario.
*pH 7.56, PaO2 100, PCO2 44, HCO3 38*
- This profile suggests **metabolic alkalosis** (high pH, high HCO3) with inadequate respiratory compensation (normal to slightly elevated PCO2).
- This is **not consistent with strenuous exercise**, which produces metabolic acid (lactate), not metabolic base. The elevated HCO3 suggests vomiting, diuretic use, or other causes of metabolic alkalosis.
*pH 7.32, PaO2 42, PCO2 50, HCO3 27*
- This indicates **respiratory acidosis** (low pH, high PCO2) with **severe hypoxemia** (PaO2 42 mmHg).
- During strenuous exercise, healthy individuals **increase ventilation** to enhance O2 delivery and remove CO2, so both hypoxemia and hypercapnia are unexpected and would suggest severe cardiopulmonary disease or hypoventilation.
*pH 7.38, PaO2 100, PCO2 69, HCO3 42*
- This demonstrates **compensated respiratory acidosis** (normal pH, markedly elevated PCO2 and HCO3).
- The **very high PCO2 (69 mmHg)** indicates severe **hypoventilation**, which is the opposite of what occurs during exercise. This profile suggests chronic respiratory failure with metabolic compensation, such as in severe COPD.
Functional capacity evaluation US Medical PG Question 9: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Functional capacity evaluation Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Functional capacity evaluation US Medical PG Question 10: A 66-year-old man with severe aortic stenosis (valve area 0.7 cm², mean gradient 55 mmHg) and Class III heart failure requires emergent hemicolectomy for perforated diverticulitis with peritonitis. He is hemodynamically stable on pressors. Cardiology states he is high-risk for valve replacement but could undergo TAVR in 2-3 weeks. The surgeon believes he needs surgery within 6-8 hours. Evaluate the management approach.
- A. Delay surgery, perform urgent TAVR, then colectomy in 2-3 weeks
- B. Proceed with colectomy under invasive monitoring with cardiology backup (Correct Answer)
- C. Perform colostomy only under local anesthesia, defer resection
- D. Medical management of perforation with antibiotics pending TAVR
- E. Simultaneous TAVR and emergency colectomy in hybrid OR
Functional capacity evaluation Explanation: ***Proceed with colectomy under invasive monitoring with cardiology backup***
- Perforated diverticulitis with **peritonitis** is an immediate surgical emergency requiring intervention within hours to prevent **sepsis** and death.
- Management of **severe aortic stenosis** in non-cardiac emergencies involves **invasive hemodynamic monitoring** to maintain a fixed cardiac output, adequate **preload**, and stable **systemic vascular resistance**.
*Delay surgery, perform urgent TAVR, then colectomy in 2-3 weeks*
- Waiting 2-3 weeks for a **TAVR** is not feasible for a patient with **peritonitis**, as the risk of mortality from untreated perforation is nearly 100%.
- **TAVR** requires a recovery period and often **antiplatelet therapy**, which would further complicate and delay the necessary abdominal surgery.
*Perform colostomy only under local anesthesia, defer resection*
- **Local anesthesia** is insufficient for managing generalized **peritonitis** and would not allow for the necessary thorough abdominal washout and source control.
- A simple colostomy without **resection** of the perforated segment fails to eliminate the source of **fecal contamination**, leading to persistent sepsis.
*Medical management of perforation with antibiotics pending TAVR*
- Antibiotics alone are inadequate for **Hinchey III/IV peritonitis**; the lack of **source control** results in high mortality regardless of cardiac status.
- The patient is already on **pressors**, indicating that the septic process is advanced and requires mechanical/surgical correction rather than conservative medical therapy.
*Simultaneous TAVR and emergency colectomy in hybrid OR*
- Combining a **clean-contaminated** or dirty surgery (colectomy) with a sterile cardiac procedure (TAVR) carries an unacceptable risk of **prosthetic valve infection**.
- The physiological stress of both procedures simultaneously would likely exceed the patient's **hemodynamic compensatory** mechanisms in the setting of acute sepsis.
More Functional capacity evaluation US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.