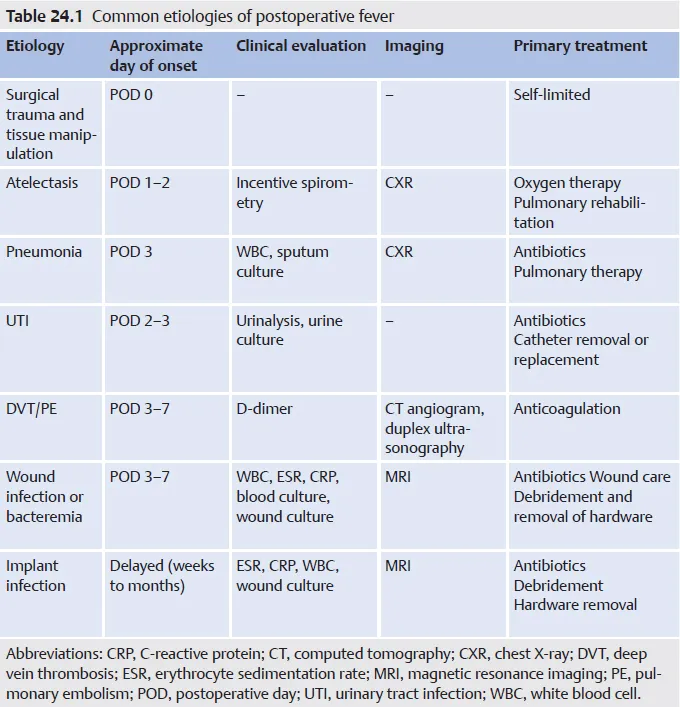
Postoperative fever evaluation US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Postoperative fever evaluation. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Postoperative fever evaluation US Medical PG Question 1: A 56-year-old previously healthy woman with no other past medical history is post-operative day one from an open reduction and internal fixation of a fractured right radius and ulna after a motor vehicle accident. What is one of the primary ways of preventing postoperative pneumonia in this patient?
- A. Shallow breathing exercises
- B. Incentive spirometry (Correct Answer)
- C. Outpatient oral antibiotics
- D. Hyperbaric oxygenation
- E. In-hospital intravenous antibiotics
Postoperative fever evaluation Explanation: ***Incentive spirometry***
- **Incentive spirometry** is a cornerstone of postoperative care, actively encouraging patients to take slow, deep breaths. This expands the lungs and prevents the collapse of alveoli, reducing the risk of **atelectasis** and subsequent **pneumonia**.
- Its effectiveness lies in promoting lung aeration and clearing secretions, which are crucial after anesthesia and surgery, especially in patients with reduced mobility or pain.
*Shallow breathing exercises*
- **Shallow breathing** is insufficient for adequate lung expansion and can actually contribute to **atelectasis** and the pooling of secretions in the lungs.
- Effective pulmonary hygiene requires **deep breaths** to maximize alveolar recruitment and prevent respiratory complications.
*Outpatient oral antibiotics*
- **Prophylactic antibiotics** are typically given around the time of surgery to prevent surgical site infections, not primarily to prevent postoperative pneumonia in an outpatient setting.
- Administering antibiotics without a diagnosed infection can lead to **antibiotic resistance** and is not a standard practice for preventing pneumonia unless a specific risk factor or existing infection is identified.
*Hyperbaric oxygenation*
- **Hyperbaric oxygenation** involves breathing 100% oxygen in a pressurized chamber and is used for conditions like **decompression sickness**, non-healing wounds, or severe infections.
- It is not a standard or primary method for preventing postoperative pneumonia, as its mechanism of action is unrelated to common pulmonary hygiene techniques.
*In-hospital intravenous antibiotics*
- While antibiotics can treat pneumonia, their routine, **prophylactic use** intravenously in-hospital solely for preventing postoperative pneumonia is generally unwarranted and can contribute to **antibiotic resistance**.
- Antibiotics are indicated if there is evidence of an active infection, but the primary prevention of pneumonia focuses on mechanical lung expansion and airway clearance.
Postoperative fever evaluation US Medical PG Question 2: A 76-year-old woman presents to the primary care physician for a regular check-up. History reveals that she has had episodes of mild urinary incontinence over the past 2 years precipitated by sneezing or laughing. However, over the past week, her urinary incontinence has occurred during regular activities. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, heart rate is 86/min, respiratory rate is 22/min, and temperature is 37.7°C (99.9°F). Physical examination is remarkable for suprapubic tenderness. Urinalysis reveals 15 WBCs/HPF, positive nitrites, and positive leukocyte esterase. Which of the following is the best next step for this patient?
- A. Pelvic floor muscle training
- B. Ultrasound scan of the kidneys, urinary tract, and bladder
- C. Cystoscopy
- D. Urine culture (Correct Answer)
- E. Start empirical antibiotic therapy
Postoperative fever evaluation Explanation: ***Urine culture***
- The patient presents with classic **signs of a urinary tract infection (UTI)**: new onset urinary incontinence worsening, suprapubic tenderness, and urinalysis positive for **WBCs, nitrites, and leukocyte esterase**.
- A urine culture is essential to **confirm the diagnosis of UTI**, identify the causative organism, and determine antibiotic sensitivity before initiating targeted treatment.
*Pelvic floor muscle training*
- This intervention is appropriate for **stress urinary incontinence (SUI)**, which the patient initially experienced, but it will not address the acute infection.
- While it may be considered after UTI treatment for managing chronic incontinence, it's NOT the immediate priority given the acute infectious symptoms.
*Ultrasound scan of the kidneys, urinary tract, and bladder*
- An ultrasound might be considered if there were concerns for **obstruction**, **pyelonephritis**, or recurrent UTIs after treatment, but it is not the immediate diagnostic step for an acute, uncomplicated UTI.
- The primary goal is to identify and treat the infection first.
*Cystoscopy*
- **Cystoscopy** is an invasive procedure generally reserved for investigating causes of recurrent UTIs, hematuria, or bladder abnormalities after initial treatment failures or in specific clinical scenarios, not for initial diagnosis of an apparent UTI.
- It would be premature and unnecessary at this stage without ruling out a simple infection.
*Start empirical antibiotic therapy*
- While antibiotics are indeed needed, starting empirical therapy without a culture could lead to **antibiotic resistance** or ineffective treatment if the causative organism is not susceptible to the chosen antibiotic.
- Given the suprapubic tenderness and urinalysis findings, a UTI is highly likely, but **culture and sensitivity guided therapy** is the best practice for optimal patient outcomes and to prevent resistance, especially in an elderly patient.
Postoperative fever evaluation US Medical PG Question 3: A general surgery intern is paged to the bedside of a 59-year-old male who underwent a successful sigmoidectomy for treatment of recurrent diverticulitis. The patient's nurse just recorded a temperature of 38.7 C, and relates that the patient is complaining of chills. The surgery was completed 8 hours ago and was complicated by extensive bleeding, with an estimated blood loss of 1,700 mL. Post-operative anemia was diagnosed after a hemoglobin of 5.9 g/dL was found; 2 units of packed red blood cells were ordered, and the transfusion was initiated 90 minutes ago. The patient's vital signs are as follows: T 38.7 C, HR 88, BP 138/77, RR 18, SpO2 98%. Physical examination does not show any abnormalities. After immediately stopping the transfusion, which of the following is the best management of this patient's condition?
- A. Hydrate with 1 L bolus of normal saline followed by maintenance fluids at 125 cc/hr
- B. Prescribe diphenhydramine
- C. Monitor patient and administer acetaminophen (Correct Answer)
- D. Start supplemental oxygen by nasal cannula
- E. Initiate broad spectrum antibiotics
Postoperative fever evaluation Explanation: ***Monitor patient and administer acetaminophen***
- This patient is experiencing a **febrile non-hemolytic transfusion reaction (FNHTR)**, characterized by a temperature increase of ≥1°C during or within hours of transfusion, and chills, in the absence of other causes. **Acetaminophen** is the primary treatment for fever and discomfort, and careful monitoring is crucial to rule out more severe reactions.
- The patient's vital signs are otherwise stable, and there are no signs of anaphylaxis, hemolysis, or bacterial contamination, making supportive care with antipyretics the most appropriate initial management after stopping the transfusion.
*Hydrate with 1 L bolus of normal saline followed by maintenance fluids at 125 cc/hr*
- While hydration is generally important post-surgery, there is **no indication of hypovolemia or dehydration** (BP 138/77, HR 88, SpO2 98%) that would necessitate an immediate fluid bolus for this specific reaction.
- Excessive fluid administration could potentially worsen underlying cardiac conditions or lead to fluid overload, especially in an elderly patient.
*Prescribe diphenhydramine*
- **Diphenhydramine** (an antihistamine) is primarily used for **allergic transfusion reactions**, which typically present with urticaria, pruritus, or respiratory symptoms like wheezing, none of which are observed in this patient.
- This patient's symptoms are fever and chills, not allergic manifestations.
*Start supplemental oxygen by nasal cannula*
- The patient's **oxygen saturation is 98%**, indicating he is not hypoxic.
- There is no clinical sign of respiratory distress or hypoxemia that would warrant supplemental oxygen.
*Initiate broad spectrum antibiotics*
- While fever is present, there is **no evidence of bacterial infection** (e.g., hypotension, rapid deterioration, signs of sepsis) that would require immediate broad-spectrum antibiotics for a transfusion reaction at this early stage.
- Unnecessary antibiotic use contributes to antibiotic resistance and can have side effects.
Postoperative fever evaluation US Medical PG Question 4: A 37-year-old man presents to the emergency department for a persistent fever. The patient states he has felt unwell for the past week and has felt subjectively febrile. The patient has a past medical history of a suicide attempt and alcohol abuse. He is not currently taking any medications. The patient admits to using heroin and cocaine and drinking 5-8 alcoholic drinks per day. His temperature is 103°F (39.4°C), blood pressure is 92/59 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, respirations are 20/min, and oxygen saturation is 96% on room air. Cardiopulmonary exam is notable for a systolic murmur heard best along the left sternal border. Dermatologic exam reveals scarring in the antecubital fossa. Which of the following is the next best step in management?
- A. CT scan
- B. Ultrasound
- C. Chest radiograph
- D. Blood cultures (Correct Answer)
- E. Vancomycin and gentamicin
Postoperative fever evaluation Explanation: ***Blood cultures***
- The patient's history of **intravenous drug use (IVDU)**, persistent fever, and a **new systolic murmur** strongly suggest **infective endocarditis**.
- **Blood cultures** are crucial for identifying the causative organism and guiding appropriate antibiotic therapy, serving as the cornerstone of diagnosis in suspected endocarditis.
*CT scan*
- While CT scans can be useful for identifying complications of endocarditis (e.g., septic emboli in the brain or lungs), they are **not the initial diagnostic step** for identifying the source of infection.
- CT scans expose the patient to **radiation** and are more expensive, making them less suitable as a first step compared to blood cultures.
*Ultrasound*
- An **echocardiogram** (a type of ultrasound) is essential for visualizing vegetations on heart valves, but it is typically performed *after* blood cultures reveal bacteremia to confirm the diagnosis and assess severity.
- A general ultrasound of other body areas would be non-specific and **unlikely to pinpoint the cause** of persistent fever in this clinical context.
*Chest radiograph*
- A chest radiograph can identify **pulmonary infiltrates** or **septic emboli in the lungs**, which are potential complications of right-sided endocarditis (common in IVDU).
- However, a chest radiograph **does not identify the causative organism** or confirm the primary diagnosis of endocarditis, making it a secondary investigation.
*Vancomycin and gentamicin*
- This combination represents a broad-spectrum antibiotic regimen often used for **empiric treatment of infective endocarditis**, particularly in IVDU patients due to concerns for MRSA or resistant streptococcal species.
- While ultimately necessary, administering antibiotics *before* obtaining **blood cultures** can significantly reduce the yield of cultures and hinder definitive diagnosis and tailored treatment.
Postoperative fever evaluation US Medical PG Question 5: A 68-year-old woman presents to the hospital for an elective right hemicolectomy. She is independently mobile and does her own shopping. She has had type 2 diabetes mellitus for 20 years, essential hypertension for 15 years, and angina on exertion for 6 years. She has a 30-pack-year history of smoking. The operation was uncomplicated. On post-op day 5, she becomes confused. She has a temperature of 38.5°C (101.3°F), respiratory rate of 28/min, and oxygen saturation of 92% on 2 L of oxygen. She is tachycardic at 118/min and her blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg. On chest auscultation, she has coarse crackles in the right lung base. Her surgical wound appears to be healing well, and her abdomen is soft and nontender. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Malignant hyperthermia
- B. Drug-induced fever
- C. Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
- D. Sepsis (Correct Answer)
- E. Non-infectious systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)
Postoperative fever evaluation Explanation: ***Sepsis***
- The patient exhibits several signs of **systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)** (fever, tachycardia, tachypnea) coupled with evidence of infection (coarse crackles in the lung base suggests **pneumonia**).
- The combination of **SIRS criteria** and a likely infection source in a postoperative patient strongly points to sepsis, a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection.
*Malignant hyperthermia*
- This is a rare, life-threatening condition typically triggered by **volatile anesthetic agents** or **succinylcholine** during surgery.
- It usually presents **intraoperatively or immediately postoperatively** with rapid onset of hyperthermia, muscle rigidity, and metabolic acidosis, which is not consistent with a presentation on post-op day 5.
*Drug-induced fever*
- While drug-induced fever is possible, particularly in polymedicated patients, it would be a **diagnosis of exclusion** when other more likely causes of fever, such as infection, are present.
- There are no specific clinical features in this case that strongly suggest a drug as the singular cause of fever and the systemic inflammatory response.
*Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome*
- **MODS** is the progressive failure of two or more organ systems and is often a **complication of severe sepsis or septic shock**, rather than an initial diagnosis.
- While the patient is unwell, her current presentation describes a potential precursor (sepsis) rather than established multi-organ dysfunction.
*Non-infectious systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)*
- SIRS caused by non-infectious etiologies (e.g., pancreatitis, trauma, burns) can occur, but the presence of **localized lung crackles** and a **postoperative fever** makes an infectious etiology much more likely.
- Postoperative SIRS can occur due to surgical stress, but the signs of infection (especially respiratory) shift the diagnosis towards sepsis.
Postoperative fever evaluation US Medical PG Question 6: Three days after undergoing laparoscopic colectomy, a 67-year-old man reports swelling and pain in his right leg. He was diagnosed with colon cancer 1 month ago. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F). Physical examination shows swelling of the right leg from the ankle to the thigh. There is no erythema or rash. Which of the following is likely to be most helpful in establishing the diagnosis?
- A. D-dimer level
- B. Compression ultrasonography (Correct Answer)
- C. CT pulmonary angiography
- D. Transthoracic echocardiography
- E. Blood cultures
Postoperative fever evaluation Explanation: ***Compression ultrasonography***
- This patient's presentation with **unilateral leg swelling and pain** after surgery, especially given his recent **colon cancer diagnosis** (a hypercoagulable state), is highly suspicious for a **deep vein thrombosis (DVT)**.
- **Compression ultrasonography** is the gold standard, non-invasive imaging modality for diagnosing DVT, allowing direct visualization of thrombi and assessing venous compressibility.
*D-dimer level*
- While a **positive D-dimer** indicates recent or ongoing clot formation, it is **non-specific** and can be elevated in many conditions, including surgery, cancer, and infection.
- A normal D-dimer can rule out DVT in low-probability patients, but a high D-dimer in a high-probability patient (like this case) requires further imaging for confirmation, making it less definitive than ultrasound.
*CT pulmonary angiography*
- This imaging is used to diagnose a **pulmonary embolism (PE)**, which is a complication of DVT, but the primary symptoms here are localized to the leg.
- While PE is a concern, diagnosing the source (DVT) in the leg is the immediate priority for treatment and prevention of future complications.
*Transthoracic echocardiography*
- **Echocardiography** evaluates cardiac structure and function and can sometimes detect large clots in the right heart leading to PE, but it is not the primary diagnostic tool for DVT in the leg.
- It would be done if signs of cardiac strain or shunting associated with acute PE were prominent, which is not the case here.
*Blood cultures*
- **Blood cultures** are used to diagnose **bacteremia or sepsis**, which might explain a fever, but the prominent, unilateral leg swelling and pain are not typical for a primary infectious cause in the leg without local signs of cellulitis or abscess.
- While a low-grade fever is present, the absence of erythema or rash makes a primary infectious etiology less likely than DVT given the risk factors.
Postoperative fever evaluation US Medical PG Question 7: A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with fatigue, dry cough, and shortness of breath for 3 days. He reports a slight fever and has also had 3 episodes of watery diarrhea earlier that morning. Last week, he attended a business meeting at a hotel and notes some of his coworkers have also become sick. He has a history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He takes atorvastatin, hydrochlorothiazide, and lisinopril. He appears in mild distress. His temperature is 102.1°F (38.9°C), pulse is 56/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 150/85 mm Hg. Diffuse crackles are heard in the thorax. Examination shows a soft and nontender abdomen. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 13.5 g/dL
Leukocyte count 15,000/mm3
Platelet count 130,000/mm3
Serum
Na+ 129 mEq/L
Cl- 100 mEq/L
K+ 4.6 mEq/L
HCO3- 22 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 14 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.3 mg/dL
An x-ray of the chest shows infiltrates in both lungs. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
- A. Urine antigen assay (Correct Answer)
- B. CT Chest
- C. Direct immunofluorescent antibody test
- D. Stool culture
- E. Polymerase chain reaction
Postoperative fever evaluation Explanation: ***Urine antigen assay***
- This patient presents with **pneumonia symptoms** (low-grade fever, dry cough, dyspnea, bilateral infiltrates) along with **gastrointestinal symptoms** (watery diarrhea) and **hyponatremia**, after attending a hotel meeting with other sick attendees. These are classic features of **Legionnaires' disease**.
- A **urine antigen assay** is a rapid and highly specific test for **Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1**, which causes the majority of Legionnaires' disease cases.
*CT Chest*
- A CT scan of the chest would provide more detailed imaging of the lung infiltrates but is typically used to characterize findings once pneumonia is diagnosed or to rule out other lung pathologies, not as an initial diagnostic test for the specific pathogen.
- While it can reveal characteristic patterns, it doesn't identify the causative organism and is not the most appropriate *next step in diagnosis* for a presumed Legionella infection.
*Direct immunofluorescent antibody test*
- A **direct immunofluorescent antibody (DFA) test** is used to identify legionella in respiratory secretions. However, collecting a sufficiently good sputum sample can be difficult, especially with a **dry cough**.
- Its sensitivity is lower than urine antigen testing for serogroup 1 and requires a respiratory sample, making it less convenient for initial diagnosis.
*Stool culture*
- While the patient has diarrhea, a **stool culture** would primarily detect typical bacterial enteric pathogens (e.g., Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter) and would not identify **Legionella**.
- The diarrhea, in this context, is likely an extrapulmonary manifestation of Legionnaires' disease caused by Legionella, not a separate primary enteric infection.
*Polymerase chain reaction*
- **PCR testing** can detect Legionella DNA in respiratory samples, offering high sensitivity and specificity.
- However, it is generally less rapid and widely available than the urine antigen test for initial diagnosis of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1, which is the most common cause of Legionnaires' disease.
Postoperative fever evaluation US Medical PG Question 8: Three days after undergoing an open cholecystectomy, a 73-year-old man has fever and abdominal pain. He has hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and benign prostatic hyperplasia. He had smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years but quit 1 year ago. He does not drink alcohol. Prior to admission to the hospital, his medications included lisinopril, metformin, ipratropium, and tamsulosin. He appears acutely ill and lethargic. His temperature is 39.5°C (103.1°F), pulse is 108/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 110/84 mm Hg. He is oriented only to person. Examination shows a 10-cm subcostal incision that appears dry and non-erythematous. Scattered expiratory wheezing is heard throughout both lung fields. His abdomen is distended with tenderness to palpation over the lower quadrants. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.1 g/dl
Leukocyte count 19,000/mm3
Serum
Glucose 180 mg/dl
Urea Nitrogen 25 mg/dl
Creatinine 1.2 mg/dl
Lactic acid 2.5 mEq/L (N = 0.5 - 2.2 mEq/L)
Urine
Protein 1+
RBC 1–2/hpf
WBC 32–38/hpf
Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of this patient's current condition?
- A. Wound contamination
- B. Peritoneal inflammation
- C. Impaired alveolar ventilation
- D. Intraabdominal abscess formation (Correct Answer)
- E. Bladder outlet obstruction
Postoperative fever evaluation Explanation: ***Intraabdominal abscess formation***
- The patient presents with **fever**, **leukocytosis**, **abdominal pain** and **distension** three days post-cholecystectomy. These symptoms, coupled with signs of systemic illness (lethargy, altered mental status, tachycardia, elevated lactic acid), are highly suggestive of an **intraabdominal infection** such as an abscess.
- The surgical site incision appears dry and non-erythematous, making a superficial wound infection less likely to explain the systemic symptoms and deep abdominal pain.
*Wound contamination*
- While wound contamination can cause infection, the incision site is described as **dry and non-erythematous**, suggesting that a superficial surgical site infection is not the primary cause of the patient's systemic illness and deep abdominal pain.
- A simple wound infection generally would not lead to such significant systemic symptoms, including **lethargy** and **altered mental status**, within three days post-surgery, especially without local signs of inflammation.
*Peritoneal inflammation*
- Peritoneal inflammation (peritonitis) is a consequence of an intraabdominal process like an abscess or anastomotic leak, rather than the primary underlying mechanism itself.
- The symptoms of **localized tenderness** and **distension** are more indicative of a contained process like an abscess rather than diffuse peritoneal inflammation as the initial cause.
*Impaired alveolar ventilation*
- While the patient has COPD and scattered expiratory wheezing, suggesting some degree of respiratory compromise, **impaired alveolar ventilation** alone does not explain the fever, elevated leukocyte count, abdominal pain, and an elevated lactic acid (though respiratory distress can contribute to lactic acidemia, an infection is a more direct cause here).
- Post-operative pulmonary complications are common, but the abdominal findings and systemic signs of infection point away from a purely respiratory origin for this acute deterioration.
*Bladder outlet obstruction*
- The patient has BPH and is on tamsulosin, but his current symptoms of fever, leukocytosis, abdominal pain, and elevated lactic acid are not typical for **bladder outlet obstruction**.
- Although the urine analysis shows pyuria (WBC 32-38/hpf), which could suggest a urinary tract infection (UTI), a UTI alone is less likely to cause this degree of systemic illness with **significant abdominal distension** and **tenderness** in the lower quadrants shortly after abdominal surgery; it's more probable that the pyuria is a secondary finding or contributing factor in a patient with a more severe intraabdominal process.
Postoperative fever evaluation US Medical PG Question 9: A 37-year-old-woman presents to the emergency room with complaints of fever and abdominal pain. Her blood pressure is 130/74 mmHg, pulse is 98/min, temperature is 101.5°F (38.6°C), and respirations are 23/min. The patient reports that she had a laparoscopic cholecystectomy 4 days ago but has otherwise been healthy. She is visiting her family from Nebraska and just arrived this morning from a 12-hour drive. Physical examination revealed erythema and white discharge from abdominal incisions and tenderness upon palpations at the right upper quadrant. What is the most probable cause of the patient’s fever?
- A. Pulmonary atelectasis
- B. Residual gallstones
- C. Urinary tract infection
- D. Wound infection (Correct Answer)
- E. Pulmonary embolism
Postoperative fever evaluation Explanation: ***Wound infection***
- The presence of **erythema**, **white discharge from abdominal incisions**, and **fever** 4 days post-laparoscopic cholecystectomy strongly indicates a surgical site infection.
- This is a common complication after surgery, especially with visible signs of local inflammation and purulent discharge.
*Pulmonary atelectasis*
- **Atelectasis** typically presents within **24-48 hours post-op** and usually resolves spontaneously.
- While it can cause fever, the prominent local wound signs and the timing (4 days post-op) make it less likely to be the primary cause of fever.
*Residual gallstones*
- **Residual gallstones** would typically present with symptoms resembling acute cholecystitis or cholangitis, such as **right upper quadrant pain**, **jaundice**, or **elevated liver enzymes**, without direct signs of wound infection.
- These do not account for the **erythema and discharge from the incision sites**.
*Urinary tract infection*
- A **urinary tract infection (UTI)** would present with **dysuria**, **frequency**, **urgency**, or **suprapubic pain**, and would not explain the local wound findings.
- While surgery can increase the risk of nosocomial UTIs, the clinical presentation is primarily focused on the surgical site.
*Pulmonary embolism*
- A **pulmonary embolism (PE)** would likely cause **dyspnea**, **tachycardia**, **hypoxia**, and **pleuritic chest pain**, which are not reported in this case.
- Though prolonged immobility (e.g., long drive) is a risk factor, the specific local signs of infection are not consistent with PE.
Postoperative fever evaluation US Medical PG Question 10: A 72-year-old man comes to the physician because of a lesion on his eyelid for 6 months. The lesion is not painful or pruritic. He initially dismissed it as a 'skin tag' but the lesion has increased in size over the past 3 months. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, and left hemiplegia from a stroke 3 years ago. Current medications include sitagliptin, metformin, aspirin, and simvastatin. He used to work as a construction contractor and retired 3 years ago. Examination shows a 1-cm (0.4-in) flesh-colored, nodular, nontender lesion with rolled borders. There is no lymphadenopathy. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Muscle strength is reduced in the left upper and lower extremities. Visual acuity is 20/20. The pupils are equal and reactive to light. A shave biopsy confirms the diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Laser ablation
- B. Cryotherapy
- C. Topical chemotherapy
- D. Wide local excision
- E. Mohs micrographic surgery (Correct Answer)
Postoperative fever evaluation Explanation: ***Mohs micrographic surgery***
- The lesion's location on the **eyelid** (a cosmetically and functionally sensitive area), its **nodular appearance** with **rolled borders**, and the likely diagnosis of **basal cell carcinoma (BCC)** make Mohs surgery the most appropriate treatment.
- Mohs surgery offers the highest cure rates for BCCs and preserves the maximum amount of healthy tissue, which is crucial for lesions on the face and eyelids.
*Wide local excision*
- While effective for many skin cancers, **wide local excision** might lead to significant cosmetic or functional defects on the eyelid due to the need for a wider margin of healthy tissue removal.
- Its cure rates are generally lower than Mohs surgery for high-risk BCCs, especially in sensitive areas.
*Laser ablation*
- **Laser ablation** is typically used for superficial or precancerous lesions, not for nodular, invasive basal cell carcinoma.
- It does not allow for histological margin control, which is essential to ensure complete tumor removal and reduce recurrence.
*Cryotherapy*
- **Cryotherapy** is suitable for small, superficial, or pre-malignant lesions, but not for a nodular lesion on the eyelid where tissue preservation and precise margin control are critical.
- It does not offer histological confirmation of clear margins, increasing the risk of recurrence.
*Topical chemotherapy*
- **Topical chemotherapy** (e.g., imiquimod, 5-fluorouracil) is generally reserved for superficial basal cell carcinomas distant from critical structures.
- It is not effective for nodular BCCs and lacks the ability to confirm complete tumor removal via microscopic margin assessment.
More Postoperative fever evaluation US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.