Congenital diaphragmatic hernia US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
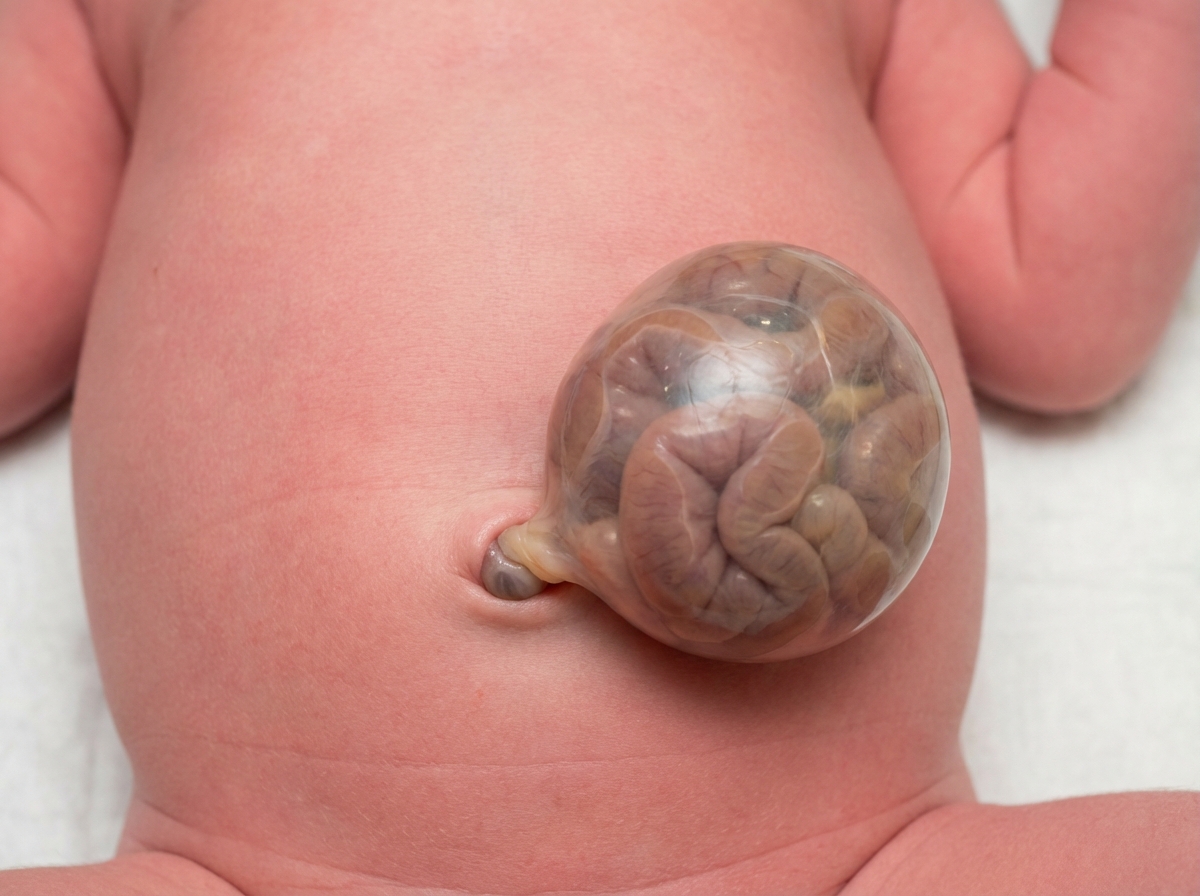
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia US Medical PG Question 1: A 42-year-old woman presents to the emergency department in active labor. She has had no prenatal care and is unsure of the gestational age. Labor progresses rapidly and spontaneous vaginal delivery of a baby boy occurs 3 hours after presentation. On initial exam, the child is 1.9 kg (4.2 lb) with a small head and jaw. A sac-like structure containing intestine, as can be seen in the picture, protrudes from the abdominal wall. What complication is closely associated with this presentation?
- A. Lack of abdominal wall muscles
- B. Dehydration and necrosis of bowel
- C. Duodenal atresia
- D. Twisting of the bowel around itself
- E. Cardiac defect (Correct Answer)
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Explanation: ***Cardiac defect***
- The presentation of a **sac-like structure containing intestine protruding from the abdominal wall** (suggesting an **omphalocele**) along with **microcephaly** (small head), **micrognathia** (small jaw), and **low birth weight** are classic features of **Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13)** or **Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18)**.
- These chromosomal abnormalities are strongly associated with various significant anomalies, including severe **cardiac defects** (e.g., ventricular septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus, atrial septal defects), which occur in **>80% of cases**.
- **Omphalocele** itself is associated with cardiac anomalies in approximately **30-50% of cases**, making cardiac defects the most closely associated complication.
*Lack of abdominal wall muscles*
- This description is more indicative of **prune belly syndrome (Eagle-Barrett syndrome)**, characterized by absence or deficiency of abdominal wall musculature.
- With **gastroschisis**, there is also an abdominal wall defect, but the defect is typically lateral to the umbilicus and there is no protective sac covering the bowel.
*Dehydration and necrosis of bowel*
- This complication is more characteristic of **gastroschisis** due to the direct exposure of the unprotected bowel to amniotic fluid, leading to inflammation, thickening, and potential vascular compromise.
- In an **omphalocele**, the bowel is protected by a sac (containing peritoneum and amnion), significantly reducing the immediate risk of dehydration and necrosis unless the sac ruptures.
*Duodenal atresia*
- **Duodenal atresia** is strongly associated with **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)**, characterized by a "double bubble" sign on imaging.
- While omphalocele can occasionally occur with Trisomy 21, the constellation of findings in this case (microcephaly, micrognathia, low birth weight) is more consistent with Trisomy 13 or 18 rather than Trisomy 21.
*Twisting of the bowel around itself*
- **Volvulus** refers to the twisting of a loop of intestine around its mesentery, which can lead to bowel obstruction and ischemia.
- While volvulus can occur with intestinal malrotation (which may be present with omphalocele), it is not the most closely associated **congenital** complication of the chromosomal syndrome suggested by this clinical presentation.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia US Medical PG Question 2: A 3900-g (8.6-lb) newborn is delivered at 38 weeks' gestation to a 27-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, via spontaneous vaginal delivery. Immediately after delivery, he spontaneously cries, grimaces, and moves all four extremities. Over the next five minutes, he becomes cyanotic, dyspneic, and tachypneic. Mask ventilation with 100% oxygen is begun, but ten minutes after delivery the baby continues to appear cyanotic. His temperature is 37.2°C (99.0°F), pulse is 155/min, respirations are 65/min, and blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on 100% oxygen mask ventilation shows an oxygen saturation of 83%. Breath sounds are normal on the right and absent on the left. Heart sounds are best heard in the right midclavicular line. The abdomen appears concave. An x-ray of the chest is shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in the management of this patient?
- A. Intubation and mechanical ventilation (Correct Answer)
- B. Surfactant administration
- C. Chest tube placement
- D. Extracorporeal life support
- E. Surgical repair
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Explanation: ***Intubation and mechanical ventilation***
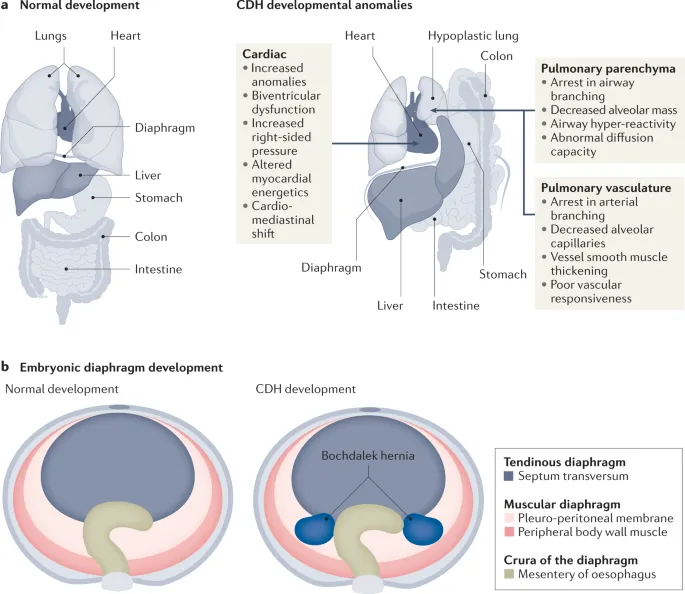
- The patient's presentation with **cyanosis**, **dyspnea**, **tachypnea**, **absent breath sounds on the left**, **shifted heart sounds (dextrocardia)**, **concave abdomen**, and **bowel loops in the left hemithorax on X-ray** is highly suggestive of **congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH)**.
- **Intubation** and **mechanical ventilation** are crucial initial steps for **respiratory support** and to prevent further expansion of bowel gas with positive pressure ventilation, which can worsen lung compression.
*Surfactant administration*
- **Surfactant** is primarily used for **respiratory distress syndrome** in preterm infants with underdeveloped lungs, characterized by diffuse bilateral lung disease.
- While CDH can lead to **pulmonary hypoplasia**, surfactant alone would not address the underlying anatomical defect or the severe respiratory compromise from bowel in the chest.
*Chest tube placement*
- **Chest tube placement** is indicated for **pneumothorax** or **pleural effusion**.
- While a pneumothorax can cause respiratory distress, the X-ray and other clinical signs clearly point to CDH, not a pneumothorax requiring chest tube drainage.
*Extracorporeal life support*
- **Extracorporeal life support (ECLS)**, such as **ECMO**, is a highly advanced intervention reserved for severe respiratory or cardiac failure refractory to conventional management.
- It is a consideration for CDH if mechanical ventilation fails, but it is not the *initial* appropriate step in management.
*Surgical repair*
- **Surgical repair** is the definitive treatment for CDH, as it involves repositioning the abdominal organs and closing the diaphragmatic defect.
- However, it is an **elective procedure** performed once the infant is **stabilized**, as immediate surgery carries high risks due to the critically ill state of the neonate.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia US Medical PG Question 3: An 8-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her parents with severe difficulty in breathing for an hour. She is struggling to breathe. She was playing outside with her friends, when she suddenly fell to the ground, out of breath. She was diagnosed with asthma one year before and has since been on treatment for it. At present, she is sitting leaning forward with severe retractions of the intercostal muscles. She is unable to lie down. Her parents mentioned that she has already taken several puffs of her inhaler since this episode began but without response. On physical examination, her lungs are hyperresonant to percussion and there is decreased air entry in both of her lungs. Her vital signs show: blood pressure 110/60 mm Hg, pulse 110/min, respirations 22/min, and a peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) of 50%. She is having difficulty in communicating with the physician. Her blood is sent for evaluation and a chest X-ray is ordered. Her arterial blood gas reports are as follows:
PaO2 50 mm Hg
pH 7.38
PaCO2 47 mm Hg
HCO3 27 mEq/L
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Intravenous corticosteroid (Correct Answer)
- B. Inhaled corticosteroid
- C. Mechanical ventilation
- D. Methacholine challenge test
- E. Inhaled β-agonist
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Explanation: ***Intravenous corticosteroid***
- The patient exhibits severe asthma exacerbation with **poor response to inhaled β-agonists**, marked respiratory distress, and an alarming **PEFR of 50%**.
- **Intravenous corticosteroids** are crucial in this scenario to reduce airway inflammation and prevent progression to respiratory failure.
*Inhaled corticosteroid*
- While essential for **long-term asthma control**, inhaled corticosteroids are **not effective enough for acute, severe exacerbations** due to their slower onset of action.
- The patient's inability to effectively inhale deeply due to distress also limits the utility of inhaled delivery in this emergency.
*Mechanical ventilation*
- Mechanical ventilation is a **last-resort intervention** for impending respiratory failure, indicated by signs like declining consciousness, hypercapnia, or respiratory arrest.
- While concerning, the patient's current ABG with a **near-normal pH (7.38)** despite hypercapnia suggests she is not yet in full respiratory failure, and less invasive measures should be initiated first.
*Methacholine challenge test*
- The methacholine challenge test is used to **diagnose asthma in stable patients** with normal spirometry, by assessing airway hyperresponsiveness.
- It is **absolutely contraindicated** in an acute, severe asthma exacerbation as it could worsen bronchoconstriction and respiratory distress.
*Inhaled β-agonist*
- The patient has **already taken several puffs of her inhaler** (likely a β-agonist) without response, indicating **refractory bronchospasm**.
- While initially appropriate, repeated administration when ineffective suggests the need for other therapeutic interventions to address the underlying inflammation.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia US Medical PG Question 4: A 4-week-old infant is brought to the emergency department by his parents with violent vomiting. It started about 3 days ago and has slowly gotten worse. He vomits after most feedings but seems to keep some formula down. His mother notes that he is eager to feed between episodes and seems to be putting on weight. Other than an uncomplicated course of chlamydia conjunctivitis, the infant has been healthy. He was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery. He is up to date on all vaccines and is meeting all developmental milestones. The physical exam is significant for a palpable mass in the right upper quadrant. What is the first-line confirmatory diagnostic test and associated finding?
- A. Abdominal ultrasound; elongated pyloric channel and muscle hypertrophy (Correct Answer)
- B. Barium upper GI series; GE junction and portion of the stomach in thorax
- C. Air enema; filling defect and coil spring sign
- D. Barium upper GI series; bird beak sign and corkscrewing
- E. Abdominal X-ray; ‘double bubble’ sign
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Explanation: ***Abdominal ultrasound; elongated pyloric channel and muscle hypertrophy***
- The clinical picture of **projectile vomiting** in a 4-week-old infant, **eagerness to feed** ("hungry vomiter"), and **palpable olive-shaped mass** in the right upper quadrant is classic for **pyloric stenosis**.
- **Abdominal ultrasonography** is the gold standard for diagnosis, revealing an **elongated pyloric channel** (>16mm) and thickened pyloric muscle (>3-4mm).
- Pyloric stenosis typically presents between 3-6 weeks of age with progressive non-bilious vomiting.
*Barium upper GI series; GE junction and portion of the stomach in thorax*
- A **barium upper GI series** showing the **GE junction and stomach in the thorax** would indicate a **hiatal hernia**, which is not consistent with the palpable mass or "hungry vomiter" presentation.
- While hiatal hernias can cause vomiting and reflux, they typically don't present with this specific type of projectile vomiting or a palpable abdominal mass.
*Air enema; filling defect and coil spring sign*
- An **air enema** showing a **filling defect** and **coil spring sign** is characteristic of **intussusception**, which usually presents with sudden onset of **crampy abdominal pain**, **currant jelly stools**, and a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant.
- The clinical presentation does not fit intussusception, which typically occurs in older infants (6-36 months) and has a more acute presentation.
*Barium upper GI series; bird beak sign and corkscrewing*
- A **barium upper GI series** showing a **bird beak sign** and **corkscrewing** is pathognomonic for **midgut volvulus**, a surgical emergency.
- While volvulus can cause bilious vomiting and abdominal distension, the presentation of non-bilious vomiting with a palpable pyloric mass is more typical of pyloric stenosis.
*Abdominal X-ray; 'double bubble' sign*
- An **abdominal X-ray** revealing a **'double bubble' sign** is indicative of **duodenal atresia** or **annular pancreas**, leading to complete duodenal obstruction.
- This condition typically presents with **bilious vomiting** shortly after birth (within first day of life) and does not involve a palpable hypertrophied pylorus.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia US Medical PG Question 5: A two-month-old female presents to the emergency department for difficulty feeding. The patient was born at 38 weeks gestation to a 29-year-old primigravid via vaginal delivery. The newborn period has thus far been uncomplicated. The patient has been exclusively breastfed since birth. Her parents report that feeding had previously seemed to be going well, and the patient has been gaining weight appropriately. Over the past several days, the patient’s mother has noticed that the patient seems to tire out before the end of the feeding. She has also noticed that the patient begins to appear short of breath and has a bluish discoloration of her lips. The patient’s height and weight were in the 20th and 10th percentile at birth, respectively. Her current height and weight are in the 20th and 15th percentiles, respectively. Her temperature is 98.0°F (36.7°C), blood pressure is 60/48 mmHg, pulse is 143/min, and respirations are 40/min. On physical exam, the patient is in no acute distress and appears well developed. A systolic crescendo-decrescendo murmur can be heard at the left upper sternal border. Her abdomen is soft, non-tender, and non-distended. During the abdominal exam, the patient begins crying and develops cyanosis of the perioral region.
Which of the following is the best initial test to diagnose this patient’s condition?
- A. Chest radiograph
- B. Electrocardiogram
- C. Genetic testing
- D. Echocardiogram (Correct Answer)
- E. CT angiography
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Explanation: ***Echocardiogram***
- The patient's symptoms (difficulty feeding, cyanosis, fatigue during feeding, crescendo-decrescendo murmur at the left upper sternal border) are highly suggestive of a **congenital heart defect**, specifically **Tetralogy of Fallot** given the cyanosis with crying.
- An **echocardiogram** is the gold standard for diagnosing and characterizing congenital heart defects, providing detailed visualization of cardiac structures, blood flow abnormalities, and ventricular function.
*Chest radiograph*
- While a chest radiograph can show overall heart size and pulmonary vasculature, it does not provide the detailed anatomical and functional information needed to definitively diagnose a specific **complex congenital heart defect**.
- For example, in **Tetralogy of Fallot**, it might show a **boot-shaped heart** but cannot visualize the ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, or overriding aorta as clearly as an echocardiogram.
*Electrocardiogram*
- An **ECG** can assess electrical activity of the heart and detect arrhythmias or ventricular hypertrophy (e.g., right ventricular hypertrophy in TOF).
- However, it does not provide anatomical information, which is crucial for the initial diagnosis and characterization of **structural heart defects**.
*Genetic testing*
- Some congenital heart defects can be associated with **genetic syndromes** (e.g., DiGeorge syndrome with Tetralogy of Fallot).
- Genetic testing may be considered *after* a cardiac diagnosis is established to investigate underlying syndromes, but it is not the initial diagnostic test for the cardiac condition itself.
*CT angiography*
- **CT angiography** provides excellent anatomical detail, especially for vascular structures and complex anatomy, and can be useful pre-operatively for surgical planning in some cases.
- However, it involves **radiation exposure** and usually requires sedation in infants, making an **echocardiogram** (non-invasive, no radiation, readily available) the preferred initial diagnostic imaging modality for congenital heart disease.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia US Medical PG Question 6: A 3580-g (7-lb 14-oz) male newborn is delivered at 36 weeks' gestation to a 26-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1 after an uncomplicated pregnancy. His temperature is 36.7°C (98.1°F), heart rate is 96/min, and respirations are 55/min and irregular. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 65% measured in the right hand. He sneezes and grimaces during suction of secretions from his mouth. There is some flexion movement. The trunk is pink and the extremities are blue. The cord is clamped and the newborn is dried and wrapped in a prewarmed towel. Which of the following is the most appropriate next best step in management?
- A. Administer positive pressure ventilation (Correct Answer)
- B. Perform endotracheal intubation
- C. Administer intravenous epinephrine
- D. Perform chest compressions
- E. Administer erythromycin ophthalmic ointment
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Explanation: ***Administer positive pressure ventilation***
- The newborn exhibits **cyanosis** (oxygen saturation 65%), **respiratory distress** (irregular respirations, 55/min), and a **heart rate below 100/min** (96/min), which are indications for positive pressure ventilation.
- Initial steps like drying, warming, and stimulation have been performed, and the infant's condition has not improved, necessitating ventilatory support.
*Perform endotracheal intubation*
- Endotracheal intubation is generally reserved for situations where positive pressure ventilation is ineffective or prolonged, or for specific conditions requiring **direct airway management**, such as meconium aspiration with poor respiratory effort.
- Given the current vital signs and initial response, **bag-mask ventilation** (a form of positive pressure ventilation) should be attempted first.
*Administer intravenous epinephrine*
- Epinephrine is typically administered when the heart rate remains **below 60 bpm** despite adequate positive pressure ventilation and chest compressions.
- The newborn's heart rate of 96/min does not meet the criteria for epinephrine administration at this stage.
*Perform chest compressions*
- Chest compressions are indicated when the heart rate is persistently **below 60 bpm** despite 30 seconds of effective positive pressure ventilation.
- The newborn's heart rate of 96/min is above this threshold, making chest compressions premature.
*Administer erythromycin ophthalmic ointment*
- Erythromycin ophthalmic ointment is a prophylactic measure against **gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum** and is typically administered after the stabilization of the newborn's vital signs.
- It is not an immediate life-saving intervention and should be delayed until the infant's respiratory and circulatory status is stable.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia US Medical PG Question 7: A baby is born after the 32nd gestational week by cesarean delivery. The mother suffered from gestational diabetes; however, she had no other pregnancy-related diseases and was otherwise healthy. The baby has a blood pressure of 100/58 mm Hg, heart rate of 104/min, and oxygen saturation of 88%. The child has tachypnea, subcostal and intercostal retractions, nasal flaring, and cyanosis. The cyanosis is responding well to initial administration of oxygen. The nasogastric tube was positioned without problems. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Tracheoesophageal fistula
- B. Pneumonia
- C. Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (NRDS) (Correct Answer)
- D. Sepsis
- E. Congenital heart anomaly with right-to-left shunt
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Explanation: ***Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (NRDS)***
- The premature birth (32nd week), presence of **tachypnea**, **retractions**, **nasal flaring**, **cyanosis** responding to oxygen, and maternal **gestational diabetes** are all highly suggestive of NRDS.
- Maternal gestational diabetes can delay fetal lung maturity, increasing the risk of **surfactant deficiency**, which is the primary cause of NRDS.
*Tracheoesophageal fistula*
- This condition typically presents with **choking**, **coughing**, and **regurgitation** during feeding, often with inability to pass a nasogastric tube into the stomach.
- The successful positioning of the **nasogastric tube** makes this diagnosis less likely.
*Pneumonia*
- While pneumonia can cause respiratory distress, the **early onset** in a premature infant with maternal gestational diabetes points more strongly towards **NRDS**.
- Pneumonia would typically have signs of **infection** such as fever, though early neonatal pneumonia can be atypical.
*Sepsis*
- Sepsis can cause respiratory distress, but it's usually accompanied by other signs of systemic infection, such as **fever or hypothermia**, **lethargy**, and poor feeding and often signs of **circulatory compromise**.
- The clinical picture provided primarily points towards a respiratory rather than a systemic infectious cause primarily.
*Congenital heart anomaly with right-to-left shunt*
- While this can cause **cyanosis** and respiratory distress, the prompt response to oxygen management makes a significant right-to-left shunt less likely.
- A significant right-to-left shunt would typically cause **cyanosis** that is refractory to oxygen administration.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia US Medical PG Question 8: A P2G1 diabetic woman is at risk of delivering at 29 weeks gestation. Her obstetrician counsels her that there is a risk the baby could have significant pulmonary distress after it is born. However, she states she will give the mother corticosteroids, which will help prevent this from occurring. Additionally, the obstetrician states she will perform a test on the amniotic fluid which will indicate the likelihood of the infant being affected by this syndrome. Which of the following ratios would be most predictive of the infant having pulmonary distress?
- A. lecithin:phosphatidylserine < 1.5
- B. lecithin:sphingomyelin < 1.5 (Correct Answer)
- C. lecithin:sphingomyelin > 1.5
- D. lecithin:phosphatidylserine > 3.0
- E. lecithin:sphingomyelin > 3.0
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Explanation: ***lecithin:sphingomyelin < 1.5***
- A lecithin:sphingomyelin (L:S) ratio less than 2:1 (or 1.5 in some clinical contexts) indicates **fetal lung immaturity** and a **high risk for respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)**.
- The **lecithin level increases** significantly in the amniotic fluid during the third trimester as fetal lungs mature, while **sphingomyelin levels remain relatively constant**.
*lecithin:phosphatidylserine < 1.5*
- While **phosphatidylserine** is a component of surfactant, the **Lecithin:Sphingomyelin (L:S) ratio** is the established and most commonly used marker for fetal lung maturity.
- There is **no widely recognized or clinically validated threshold** for a lecithin:phosphatidylserine ratio in predicting respiratory distress syndrome.
*lecithin:sphingomyelin > 1.5*
- An L:S ratio **greater than 2:1 (or 1.5, in some labs)** generally indicates **fetal lung maturity** and a low risk for respiratory distress syndrome.
- Therefore, this ratio would suggest a **lower likelihood of pulmonary distress**, which contradicts the aim of identifying risk.
*lecithin:phosphatidylserine > 3.0*
- As with an L:S ratio, a higher ratio would generally indicate **lung maturity**, not increased risk for pulmonary distress.
- There is **no clinical standard for lecithin:phosphatidylserine ratio** to assess lung maturity for preventing RDS.
*lecithin:sphingomyelin > 3.0*
- An L:S ratio of **greater than 2:1 (or 3.0 in certain clinical scenarios)** is a strong indicator of **fetal lung maturity**, meaning the risk of respiratory distress syndrome is low.
- The question asks for a ratio that would be **predictive of pulmonary distress**, whereas this ratio indicates the opposite.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia US Medical PG Question 9: A 79-year-old man is admitted to the intensive care unit for hospital acquired pneumonia, a COPD flare, and acute heart failure requiring intubation and mechanical ventilation. On his first night in the intensive care unit, his temperature is 99.7°F (37.6°C), blood pressure is 107/58 mm Hg, and pulse is 150/min which is a sudden change from his previous vitals. Physical exam is notable for jugular venous distension and a rapid heart rate. The ventilator is checked and is functioning normally. Which of the following is the best next step in management for the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Tube thoracostomy
- B. FAST exam
- C. Needle thoracostomy (Correct Answer)
- D. Chest radiograph
- E. Thoracotomy
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Explanation: ***Needle thoracostomy***
- The patient's sudden deterioration with **tachycardia**, **hypotension**, and **jugular venous distension** (JVD) in the setting of positive pressure ventilation strongly suggests a **tension pneumothorax**.
- **Needle decompression** is the immediate life-saving intervention for suspected tension pneumothorax, as delaying treatment for diagnostic imaging could be fatal.
*Tube thoracostomy*
- While a **tube thoracostomy** (chest tube insertion) is the definitive treatment for pneumothorax, it requires more time and resources than needle decompression.
- In a true emergency with signs of tension, needle decompression should be performed first to stabilize the patient, followed by a chest tube.
*FAST exam*
- A **Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (FAST) exam** is primarily used to detect free fluid (usually blood) in the abdomen or pericardium in trauma patients.
- While it can sometimes identify pneumothorax, it is not the fastest or most direct intervention for a suspected tension pneumothorax causing hemodynamic instability.
*Chest radiograph*
- A **chest radiograph (CXR)** is the standard diagnostic tool for pneumothorax, but obtaining and interpreting it would delay urgent intervention in a hemodynamically unstable patient with suspected tension pneumothorax.
- The diagnosis of tension pneumothorax is primarily clinical; treatment should not wait for imaging.
*Thoracotomy*
- A **thoracotomy** is a major surgical procedure involving opening the chest, typically reserved for severe trauma, massive hemorrhage, or complex thoracic issues.
- It is an overly aggressive and inappropriate initial intervention for a suspected tension pneumothorax.
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia US Medical PG Question 10: A 27-year-old man presents to the emergency department with severe dyspnea and sharp chest pain that suddenly started an hour ago after he finished exercising. He has a history of asthma as a child, and he achieves good control of his acute attacks with Ventolin. On examination, his right lung field is hyperresonant along with diminished lung sounds. Chest wall motion during respiration is asymmetrical. His blood pressure is 105/67 mm Hg, respirations are 22/min, pulse is 78/min, and temperature is 36.7°C (98.0°F). The patient is supported with oxygen, given corticosteroids, and has had analgesic medications via a nebulizer. Considering the likely condition affecting this patient, what is the best step in management?
- A. CT scan
- B. ABG
- C. Chest X-rays (Correct Answer)
- D. Tube insertion
- E. Sonogram
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia Explanation: ***Chest X-rays***
- The patient's presentation with **sudden onset dyspnea** and **sharp chest pain** post-exercise, along with **hyperresonance** and **diminished lung sounds** in the right lung field, is highly suggestive of a **spontaneous pneumothorax**.
- However, the patient is **hemodynamically stable** (BP 105/67, HR 78/min) with no signs of tension physiology (no severe hypotension, marked tachycardia, or cardiovascular collapse).
- In a stable patient with suspected pneumothorax, **chest X-ray is the appropriate first step** to confirm the diagnosis, determine the size of the pneumothorax, and guide subsequent management (observation for small pneumothorax <20%, aspiration, or tube thoracostomy for larger pneumothoraces).
- Immediate intervention without imaging is reserved for unstable patients with tension pneumothorax.
*Tube insertion*
- Chest tube insertion is the definitive treatment for large pneumothoraces (>20%) or hemodynamically unstable patients with tension pneumothorax.
- In this **stable patient**, proceeding directly to tube insertion without imaging confirmation would be premature and not following standard of care.
- The diagnosis should be confirmed and the size estimated via chest X-ray before determining if tube thoracostomy is necessary.
*CT scan*
- CT scan is not indicated as the initial diagnostic test for suspected pneumothorax.
- It provides more detail than needed for this clinical scenario and causes unnecessary delay and radiation exposure when chest X-ray is sufficient.
- CT may be useful for detecting small pneumothoraces not visible on X-ray or evaluating underlying lung disease, but is not the first-line test.
*ABG*
- An Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) might show hypoxia and respiratory alkalosis, providing information about gas exchange.
- However, ABG does not confirm the diagnosis of pneumothorax or guide immediate management decisions.
- It is an adjunctive test that does not take priority over diagnostic imaging in this scenario.
*Sonogram*
- Lung ultrasound can rapidly detect pneumothorax by showing absent lung sliding and is increasingly used in emergency settings, particularly for bedside evaluation.
- While potentially useful, **chest X-ray remains the standard initial imaging modality** for suspected pneumothorax in most emergency departments, as it provides clear documentation of pneumothorax size and is more universally available and interpreted.
- Ultrasound may be preferred in specific situations (unstable patients, point-of-care evaluation), but chest X-ray is the conventional first-line imaging test.
More Congenital diaphragmatic hernia US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.