Sports medicine injuries US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Sports medicine injuries. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
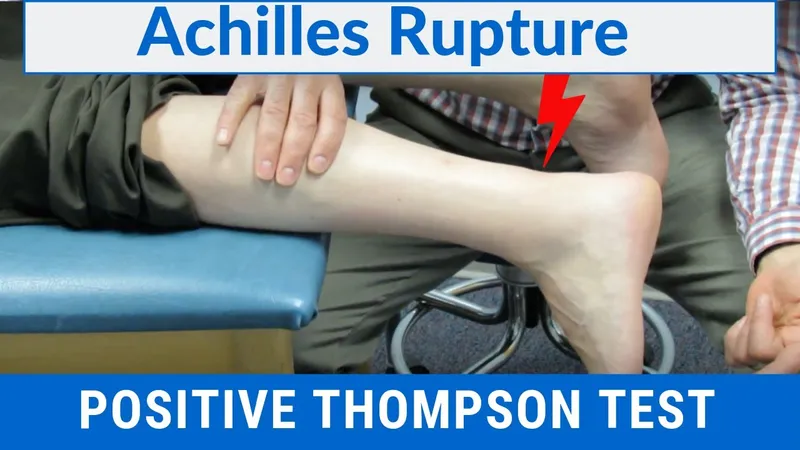
Sports medicine injuries US Medical PG Question 1: A 30-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for pain in his left ankle. The patient states that he was at karate practice when he suddenly felt severe pain in his ankle forcing him to stop. The patient has a past medical history notable for type I diabetes and is currently being treated for an episode of acute bacterial sinusitis with moxifloxacin. The patient recently had to have his insulin dose increased secondary to poorly controlled blood glucose levels. Otherwise, the patient takes ibuprofen for headaches and loratadine for seasonal allergies. Physical exam reveals a young healthy man in no acute distress. Pain is elicited over the Achilles tendon with dorsiflexion of the left foot. Pain is also elicited with plantar flexion of the left foot against resistance. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Refrain from athletic activities for 1 to 2 weeks
- B. Rehabilitation exercises and activity as tolerated
- C. Ibuprofen and rest
- D. Change antibiotics and refrain from athletic activities (Correct Answer)
Sports medicine injuries Explanation: The patient is experiencing **Achilles tendonitis**, likely a side effect of **moxifloxacin**, which is known to cause **tendinopathy** and **tendon rupture**, especially in patients with **diabetes** or those initiating **corticosteroids** [1]. **Discontinuation of moxifloxacin** and avoidance of strenuous activities are crucial to prevent further tendon damage, with alternative antibiotics for sinusitis [1].
*Refrain from athletic activities for 1 to 2 weeks*
- While **refraining from activity** is important, it is insufficient on its own because the underlying cause (moxifloxacin) would persist, potentially worsening the tendon injury.
- This option does not address the need to **change the causative medication**, which is the primary intervention for fluoroquinolone-induced tendinopathy [1].
*Rehabilitation exercises and activity as tolerated*
- **Rehabilitation exercises** are typically introduced in later stages of recovery, after the acute inflammation has subsided and the causative agent is removed.
- **Activity as tolerated** is inappropriate when there is a high risk of **tendon rupture** due to drug-induced tendinopathy; initial management requires strict rest.
*Ibuprofen and rest*
- **Ibuprofen** can help with pain and inflammation, but it does not address the underlying **fluoroquinolone-induced tendinopathy**.
- While **rest** is important, the continued use of moxifloxacin would still predispose the patient to further tendon injury or rupture, making simply resting an incomplete solution.
Sports medicine injuries US Medical PG Question 2: A 22-year-old man presents to the emergency department after being tackled in a game of football. The patient was hit from behind and fell to the ground. After the event, he complained of severe pain in his knee. The patient has a past medical history of anabolic steroid use. His current medications include whey protein supplements, multivitamins, and fish oil. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 137/68 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. On physical exam, you see a muscular young man clutching his knee in pain. The knee is inflamed and erythematous. When valgus stress is applied to the leg, there is some laxity when compared to the contralateral leg. The patient is requesting surgery for his injury. Arthrocentesis is performed and demonstrates no abnormalities of the synovial fluid. Which of the following physical exam findings is most likely to be seen in this patient?
- A. Anterior displacement of the femur relative to the tibia
- B. Severe pain with compression of the patella
- C. Anterior displacement of the tibia relative to the femur
- D. A palpable click with passive motion of the knee (Correct Answer)
- E. Laxity to varus stress
Sports medicine injuries Explanation: ***A palpable click with passive motion of the knee***
- The patient's presentation with a **football injury**, **severe knee pain**, **inflammation**, and **laxity with valgus stress** (suggesting MCL injury) points towards significant knee trauma. A palpable click can indicate a torn meniscus, which is a common accompanying injury in such forceful knee trauma, particularly with a simultaneous MCL tear.
- While the primary injury might involve ligaments, the absence of synovial fluid abnormalities upon arthrocentesis makes a pure ligamentous tear without associated meniscal damage less likely to produce a palpable click, and given the forceful impact, meniscal injury is highly probable.
*Anterior displacement of the femur relative to the tibia*
- This finding would indicate a **posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injury**, which typically results from a direct blow to the tibiofemoral joint while the knee is in flexion, or a hyperextension injury.
- The mechanism described (hit from behind with valgus stress) and the laxity to valgus stress are not consistent with a PCL injury.
*Severe pain with compression of the patella*
- Severe pain with patellar compression is characteristic of **patellofemoral pain syndrome** or **chondromalacia patellae**, which are typically overuse injuries or degenerative conditions.
- This finding is less likely to be the primary presentation following acute, forceful traumatic injury to the knee resulting in ligamentous laxity.
*Anterior displacement of the tibia relative to the femur*
- This is the classic sign of an **anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear**, which is tested using the **Lachman test** or **anterior drawer test**.
- While an ACL tear can occur in football, the described injury mechanism ("hit from behind" and "valgus stress") is more indicative of MCL damage, and an isolated ACL tear does not directly correlate with the valgus laxity observed.
*Laxity to varus stress*
- Laxity to varus stress indicates an injury to the **lateral collateral ligament (LCL)**.
- The clinical presentation specifically mentions laxity with **valgus stress**, which points to a medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury, not an LCL injury.
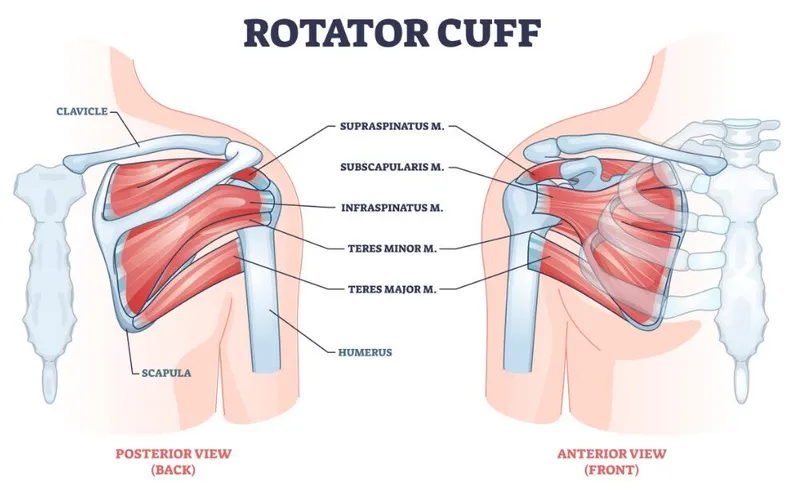
Sports medicine injuries US Medical PG Question 3: A 28-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of pain in his left shoulder. He is physically active and plays baseball twice a week. The pain is reproduced when the shoulder is externally rotated against resistance. Injury of which of the following tendons is most likely in this patient?
- A. Infraspinatus (Correct Answer)
- B. Subscapularis
- C. Pectoralis major
- D. Supraspinatus
- E. Teres major
Sports medicine injuries Explanation: ***Infraspinatus***
- Pain during **external rotation against resistance** is a classic sign of infraspinatus tendon injury, as it is a primary muscle for this action.
- The patient's history of playing baseball and experiencing pain, especially with resistive external rotation, points to an injury of this **rotator cuff muscle**.
*Subscapularis*
- The subscapularis primarily causes **internal rotation** of the shoulder; injury would typically present with pain during resisted internal rotation, not external.
- While it is a rotator cuff muscle, its function does not align with the specific maneuver causing pain described in the patient.
*Pectoralis major*
- The pectoralis major is a large chest muscle involved primarily in **adduction**, **internal rotation**, and **flexion of the humerus**, not external rotation.
- Injury to this muscle would present with pain during these specific movements, not resisted external rotation.
*Supraspinatus*
- The supraspinatus is primarily involved in **initiation of abduction** and helps stabilize the shoulder joint, and pain would usually be elicited during these movements.
- While a common site of rotator cuff injury, its function does not directly cause pain with resisted external rotation as described.
*Teres major*
- The teres major acts as an **adductor** and **internal rotator** of the humerus, similar to the latissimus dorsi.
- Pain from a teres major injury would be associated with these actions, not with resisted external rotation.
Sports medicine injuries US Medical PG Question 4: A 16-year-old boy presents to the emergency room with severe right shoulder pain following a painful overhead swing during a competitive volleyball match. On physical examination, the patient has limited active range of motion of the right shoulder and significant pain with passive motion. Suspecting a rotator cuff injury, the physician obtains an MRI, which indicates a minor tear in the tendon of the rotator cuff muscle that is innervated by the axillary nerve. Which of the following muscles was affected?
- A. Teres major
- B. Supraspinatus
- C. Teres minor (Correct Answer)
- D. Infraspinatus
- E. Subscapularis
Sports medicine injuries Explanation: ***Correct: Teres minor***
- **Teres minor** is the only rotator cuff muscle innervated by the **axillary nerve** (C5-C6)
- Functions as an **external rotator** of the shoulder and stabilizes the humeral head
- The axillary nerve courses through the **quadrangular space** (bordered by teres minor superiorly, teres major inferiorly, long head of triceps medially, and surgical neck of humerus laterally)
- Injury to this muscle can occur with overhead activities, though less commonly injured than supraspinatus
*Incorrect: Supraspinatus*
- Innervated by the **suprascapular nerve** (C5-C6), not the axillary nerve
- Most commonly injured rotator cuff muscle, particularly with overhead activities
- Functions primarily in **abduction** (initiates first 15° of abduction)
*Incorrect: Infraspinatus*
- Innervated by the **suprascapular nerve** (C5-C6), not the axillary nerve
- Functions as the primary **external rotator** of the shoulder
- Second most commonly injured rotator cuff muscle
*Incorrect: Subscapularis*
- Innervated by the **upper and lower subscapular nerves** (C5-C7), not the axillary nerve
- Only rotator cuff muscle on the **anterior** surface of the scapula
- Functions as an **internal rotator** of the shoulder
*Incorrect: Teres major*
- **NOT part of the rotator cuff** (forms part of the posterior axillary fold)
- Innervated by the **lower subscapular nerve** (C5-C7), not the axillary nerve
- Functions as an **internal rotator, adductor, and extensor** of the shoulder
Sports medicine injuries US Medical PG Question 5: A 45-year-old man with a body mass index of 45 kg/m^2 presents to his primary care doctor with right hip pain. He asserts that the pain is instigated by walking up and down stairs around a construction site which he oversees. On physical exam, his hips are symmetric and equal with no tenderness to palpation bilaterally. His left lower extremity appears grossly normal with full range of motion. His right knee appears symmetric, but the patient whimpers when the anteromedial part of the tibial plateau is pressed. No other parts of his knee are tender. No tenderness is elicited with extension, flexion, varus, and valgus movements of the knee. McMurray's test is negative with both internal and external rotation of the right leg. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Patellar tendinitis
- B. Prepatellar bursitis
- C. Medial meniscus tear
- D. Pes anserine bursitis (Correct Answer)
- E. Lateral meniscus tear
Sports medicine injuries Explanation: **Pes anserine bursitis**
- The patient's presentation with **right hip pain (referred from the knee)**, exacerbated by climbing stairs and tenderness specifically over the **anteromedial tibial plateau**, is highly characteristic of pes anserine bursitis. The patient's **obesity (BMI 45 kg/m^2)** is a significant risk factor.
- The **lack of tenderness** with other knee movements and a **negative McMurray's test** helps rule out meniscal tears. The pain is often described as hip pain due to radiation from the knee.
*Patellar tendinitis*
- This condition typically presents with localized pain and tenderness directly over the **patellar tendon**, just below the patella.
- Pain is usually worsened by activities involving jumping or squatting, and not primarily by pressure on the anteromedial tibial plateau.
*Prepatellar bursitis*
- This involves inflammation of the bursa located directly **over the patella**, often due to direct trauma or prolonged kneeling.
- The hallmark is **swelling and tenderness directly over the patella**, which is not described in this patient.
*Medial meniscus tear*
- While a medial meniscus tear can cause pain on the medial side of the knee, it is often associated with a **positive McMurray's test**, catching, locking, or giving way.
- Tenderness would typically be along the **medial joint line**, and not specifically the more distal anteromedial tibial plateau where the pes anserinus bursa is located.
*Lateral meniscus tear*
- A lateral meniscus tear would cause pain and tenderness predominantly on the **lateral aspect of the knee**.
- Similar to a medial meniscus tear, it is often associated with a **positive McMurray's test**, catching, or locking symptoms, none of which are present here.
Sports medicine injuries US Medical PG Question 6: A 25-year-old man presents with pain and a limited range of motion in his right shoulder. He is a collegiate baseball player and says he has not been playing for approx. 1 week because his shoulder hurts when he throws. He also noticed trouble raising his arm over his head. He describes the pain as moderate, dull, and aching in character and worse when he moves his arm above his shoulder or when he lays in bed on his side. He denies any recent acute trauma to the shoulder or other joint pain. The medical history is significant for asthma, which is managed medically. The current medications include albuterol inhaled and fluticasone. He reports a 5-year history of chewing tobacco but denies smoking, alcohol, or drug use. The temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F); blood pressure is 110/85 mm Hg; pulse is 97/min; respiratory rate is 15/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. The physical examination is significant for tenderness to palpation on the anterolateral aspect of the right shoulder. The active range of motion on abduction of the right shoulder is decreased. The passive range of motion is intact. No swelling, warmth, or erythema is noted. The sensation is intact. The deep tendon reflexes are 2+ bilaterally. The peripheral pulses are 2+. The laboratory results are all within normal limits. A plain radiograph of the right shoulder shows no evidence of fracture or bone deformities. An MRI of the right shoulder shows increased T1 and T2 signals in the rotator cuff tendon. Which of the following is the best initial course of treatment for this patient?
- A. No further treatment is needed
- B. Acromioplasty
- C. Intra-articular corticosteroid injection
- D. NSAIDs and conservative measures (Correct Answer)
- E. Conservative measures (rest and ice)
Sports medicine injuries Explanation: ***NSAIDs and conservative measures***
- The patient presents with symptoms and MRI findings consistent with **rotator cuff tendinitis**, common in overhead athletes. Initial treatment should focus on **reducing inflammation** and pain, and promoting healing.
- **NSAIDs** combined with conservative measures like **rest from inciting activities** and **ice application** are the mainstay of initial treatment for tendinitis, aiming to alleviate pain and improve function.
*No further treatment is needed*
- This option is incorrect because the patient is experiencing significant pain, limitation in his sport, and MRI findings of **tendinitis**, which warrants intervention.
- Doing nothing would likely lead to worsening symptoms and potentially chronic issues, especially given his athletic demands.
*Acromioplasty*
- **Acromioplasty** is a surgical procedure typically reserved for cases of **subacromial impingement syndrome** that have failed extensive conservative management, or for larger, more symptomatic tears.
- The patient's presentation suggests **tendinitis** without clear evidence of chronic impingement or a full-thickness tear requiring immediate surgical intervention.
*Intra-articular corticosteroid injection*
- **Corticosteroid injections** can provide temporary pain relief but are generally reserved for cases that have failed conservative therapy with oral NSAIDs and physical therapy.
- They also carry risks like **tendon weakening** and potential for rupture, which is particularly concerning in an athlete with tendinitis.
*Conservative measures (rest and ice)*
- While **rest and ice** are crucial components of conservative management, this option is incomplete as it omits the important role of **NSAIDs** in managing the inflammatory component of tendinitis.
- Simply resting and icing might not be sufficient for adequate pain control and inflammation reduction in an active individual with this degree of symptoms.
Sports medicine injuries US Medical PG Question 7: A 23-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for knee pain. The pain started yesterday and has not improved since then. The patient is generally in good health. She attends college and plays soccer for her school's team. Three days ago, she was slide tackled during a game and her leg was struck from the inside. She fell to the ground and sat out for the rest of the game. It was not until yesterday that she noticed swelling in her knee. She also feels as if her knee is unstable and does not feel confident bearing weight on her leg during athletic activities. Her past medical history is notable for asthma, which is currently treated with an albuterol inhaler. On physical exam, you note bruising over her leg, knee, and medial thigh, and edema of her knee. Passive range of motion of the knee is notable only for minor clicking and catching of the joint. The patient's gait appears normal, though the patient states that her injured knee does not feel stable. Further physical exam is performed and imaging is ordered. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Iliotibial band syndrome
- B. Lateral meniscal tear (Correct Answer)
- C. Medial collateral ligament tear
- D. Anterior cruciate ligament tear
- E. Posterior cruciate ligament tear
Sports medicine injuries Explanation: ***Lateral meniscal tear***
- The sensation of **clicking and catching** in the knee joint during passive range of motion is highly suggestive of a **meniscal tear**.
- The mechanism of injury (force from the **inside** of the knee creating **varus stress**) and subsequent **instability** during athletic activities are consistent with **lateral** meniscal damage.
- Delayed onset of swelling (1-2 days post-injury) is typical for meniscal tears, as opposed to immediate hemarthrosis seen with ligamentous injuries.
*Iliotibital band syndrome*
- Characterized by **lateral knee pain** caused by friction between the **iliotibial band** and the lateral femoral epicondyle, often seen in runners.
- It typically presents as a **gradual onset** of pain with repetitive activities, not an acute injury with immediate swelling and instability following trauma.
*Medial collateral ligament tear*
- This injury commonly results from a **valgus stress** (force to the **outside** of the knee) and would primarily cause **medial knee pain** and valgus instability on examination.
- The mechanism described (medial blow/varus stress) does not match MCL injury patterns, and the prominent "clicking and catching" is more characteristic of meniscal pathology.
*Anterior cruciate ligament tear*
- ACL tears present with immediate onset of **severe pain**, rapid **swelling (hemarthrosis)** within hours, and typically a "popping" sensation at the time of injury.
- While instability is also a key feature, the **delayed swelling** (occurred 2 days post-injury) and presence of "clicking and catching" makes a meniscal tear the more likely primary diagnosis.
*Posterior cruciate ligament tear*
- PCL tears usually result from a direct blow to the **anterior knee** when the knee is flexed (e.g., dashboard injury) or a **hyperextension injury**.
- Symptoms include posterior knee pain and a positive posterior drawer test, but "clicking and catching" is not a hallmark symptom of isolated PCL injury.
Sports medicine injuries US Medical PG Question 8: A 20-year-old woman college volleyball player presents with left shoulder pain and difficulty elevating her left arm. The patient began to experience dull pain in her left shoulder 5 days ago after a volleyball game. The pain is worse when she sleeps with her arm under the pillow or elevates or abducts her left arm. Her temperature is 37.0℃ (98.6℉), the blood pressure is 110/75 mm Hg, the pulse is 66/min, the respiratory rate is 13/min, and the oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. On physical examination, she is alert and cooperative. The left shoulder is normal on the inspection with no swelling or bony deformities. There is point tenderness to palpation of the anterolateral aspect of the left shoulder. Active range of motion of abduction of the left arm is restricted to 70°. Passive range of motion of abduction of the left arm is normal but elicits pain. Strength in the left shoulder is 4/5 and strength in the right shoulder is 5/5. Deep tendon reflexes are 2+ bilaterally. The sensation is intact. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s condition?
- A. Tear of the supraspinatus muscle (Correct Answer)
- B. Shoulder joint dislocation
- C. Intra-articular humeral fracture
- D. Entrapment of the axillary nerve
- E. Intervertebral disk protrusion at the C4-5 level
Sports medicine injuries Explanation: ***Tear of the supraspinatus muscle***
- Pain on **palpation of the anterolateral aspect of the shoulder**, pain with **elevation** and **abduction**, and **restricted active range of motion** with normal but painful passive range of motion are classic signs of rotator cuff injury, often involving the supraspinatus in athletes.
- The volleyball player's history of **dull shoulder pain** after a game, worsened by sleeping on the arm or abducting/elevating it, further points towards a **rotator cuff tear** or tendinopathy, with the supraspinatus being the most commonly affected.
*Intervertebral disk protrusion at the C4-5 level*
- **Cervical radiculopathy** would typically present with **neuropathic pain**, sensory deficits, or motor weakness in a dermatomal or myotomal distribution, which is not evident here.
- The localized shoulder pain and tenderness, along with pain on **active movement** but normal passive movement, are more indicative of a local shoulder issue rather than a cervical spine problem.
*Shoulder joint dislocation*
- A shoulder dislocation would present with **severe pain**, **obvious deformity** of the shoulder joint, and a complete inability to move the arm, which is not described.
- The patient has restricted active range of motion but normal passive range of motion, and no bony deformities or swelling, ruling out a dislocation.
*Intra-articular humeral fracture*
- A fracture would cause **severe, acute pain**, **swelling**, **bruising**, and a likely **deformity** of the shoulder, along with an inability to move the arm actively or passively.
- The absence of swelling, deformity, and severe acute pain that would typically follow a fracture makes this diagnosis less likely.
*Entrapment of the axillary nerve*
- **Axillary nerve entrapment** would primarily cause **deltoid muscle weakness**, leading to difficulty with abduction, and **sensory loss over the lateral shoulder**.
- While there is some weakness with abduction, the specific point tenderness and pain with active movement point more towards a musculoskeletal injury rather than isolated nerve entrapment.
Sports medicine injuries US Medical PG Question 9: A 65-year-old man comes to the physician for evaluation of severe pain in his left shoulder for several days. He did not fall or injure his shoulder. He has a history of osteoarthritis of both knees that is well-controlled with indomethacin. He spends most of his time at a retirement facility and does not do any sports. There is no family history of serious illness. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 35 years. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows tenderness of the greater tuberosity of the left humerus. There is no swelling or erythema. The patient is unable to slowly adduct his arm after it is passively abducted to 90 degrees. External rotation is limited by pain. Subacromial injection of lidocaine does not relieve his symptoms. An x-ray of the left shoulder shows sclerosis of the acromion and humeral head. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. CT scan of the shoulder
- B. Reassurance
- C. Surgical fixation
- D. Biopsy of the humerus
- E. Musculoskeletal ultrasound (Correct Answer)
Sports medicine injuries Explanation: ***Musculoskeletal ultrasound***
- The patient's symptoms (pain, inability to adduct arm after passive abduction to 90° - **positive drop arm sign**, limited external rotation, tenderness of the **greater tuberosity**) are highly suggestive of a **rotator cuff tear**.
- **Ultrasound** is a validated imaging modality for assessing soft tissue structures like tendons and can readily identify rotator cuff tears with high sensitivity and specificity.
- While **MRI is considered the gold standard** for rotator cuff evaluation, ultrasound is a reasonable initial imaging choice when available, especially given the failed diagnostic lidocaine injection pointing to structural pathology.
- Ultrasound can demonstrate the presence, size, and location of rotator cuff tears and guide further management decisions.
*CT scan of the shoulder*
- A **CT scan** is primarily used for evaluating **bony structures** and complex fractures, which are not the primary concern here given the symptoms pointing to soft tissue injury.
- While it can indirectly show rotator cuff pathology through secondary signs, it is **less sensitive** than ultrasound or MRI for direct visualization of tendon tears.
- The x-ray findings (sclerosis) already provide adequate bony detail for this clinical scenario.
*Reassurance*
- Given the severe, persistent pain, functional deficit (inability to adduct - **positive drop arm sign**), and specific physical exam findings, **reassurance alone** is inappropriate and would delay necessary diagnosis and intervention.
- The patient clearly has a significant underlying shoulder pathology requiring further investigation and likely treatment.
*Surgical fixation*
- **Surgical fixation** is a treatment, not a diagnostic step. It would only be considered after a definitive diagnosis, such as a severe rotator cuff tear, has been made with imaging confirmation.
- The immediate next step should be diagnostic imaging to confirm the nature, extent, and characteristics of the suspected injury.
*Biopsy of the humerus*
- A **biopsy of the humerus** would be indicated if there was suspicion of a bony tumor or infection, which is not suggested by the patient's presentation.
- The x-ray findings (sclerosis of acromion and humeral head) are consistent with chronic degenerative changes or impingement syndrome, not neoplastic or infectious processes.
- The clinical picture clearly points to a **soft tissue injury** rather than primary bone pathology requiring biopsy.
Sports medicine injuries US Medical PG Question 10: A 25-year-old male wrestler presents to his primary care physician for knee pain. He was in a wrestling match yesterday when he was abruptly taken down. Since then, he has had pain in his left knee. The patient states that at times it feels as if his knee locks as he moves it. The patient has a past medical history of anabolic steroid abuse; however, he claims to no longer be using them. His current medications include NSAIDs as needed for minor injuries from participating in sports. On physical exam, you note medial joint tenderness of the patient’s left knee, as well as some erythema and bruising. The patient has an antalgic gait as you observe him walking. Passive range of motion reveals a subtle clicking of the joint. There is absent anterior displacement of the tibia relative to the femur on an anterior drawer test. The rest of the physical exam, including examination of the contralateral knee is within normal limits. Which of the following structures is most likely damaged in this patient?
- A. Lateral meniscus
- B. Lateral collateral ligament
- C. Anterior cruciate ligament
- D. Medial collateral ligament
- E. Medial meniscus (Correct Answer)
Sports medicine injuries Explanation: ***Medial meniscus***
- The patient's history of knee trauma during a wrestling match, followed by **locking** and **clicking** sensations, is highly indicative of a meniscal tear.
- **Medial joint line tenderness** specifically points towards involvement of the medial meniscus, which is more commonly injured than the lateral meniscus.
*Lateral meniscus*
- While a meniscal tear is likely, the presence of **medial joint tenderness** makes a lateral meniscus tear less probable.
- A lateral meniscus tear would typically present with pain localized to the **lateral aspect** of the knee.
*Lateral collateral ligament*
- Injury to the LCL typically results from a **varus stress** to the knee, often causing pain on the lateral side and instability, which are not primary complaints here.
- The physical exam did not describe any instability on **varus stress testing**, making an isolated LCL injury less likely.
*Anterior cruciate ligament*
- ACL injuries usually involve a distinct "pop" sensation and **knee instability**, particularly during activities requiring pivoting or cutting.
- The **absent anterior displacement** on the anterior drawer test effectively rules out an acute ACL tear.
*Medial collateral ligament*
- MCL injuries result from a **valgus stress** to the knee, causing pain and tenderness along the medial aspect of the knee and often **instability** during valgus stress testing.
- While there is medial tenderness, the presence of **locking and clicking** strongly points towards a meniscal injury rather than an isolated ligamentous injury, and significant instability is not described.
More Sports medicine injuries US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.