Orthopedic trauma priorities US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Orthopedic trauma priorities. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Orthopedic trauma priorities US Medical PG Question 1: A 22-year-old man presents to the emergency department after being tackled in a game of football. The patient was hit from behind and fell to the ground. After the event, he complained of severe pain in his knee. The patient has a past medical history of anabolic steroid use. His current medications include whey protein supplements, multivitamins, and fish oil. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 137/68 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. On physical exam, you see a muscular young man clutching his knee in pain. The knee is inflamed and erythematous. When valgus stress is applied to the leg, there is some laxity when compared to the contralateral leg. The patient is requesting surgery for his injury. Arthrocentesis is performed and demonstrates no abnormalities of the synovial fluid. Which of the following physical exam findings is most likely to be seen in this patient?
- A. Anterior displacement of the femur relative to the tibia
- B. Severe pain with compression of the patella
- C. Anterior displacement of the tibia relative to the femur
- D. A palpable click with passive motion of the knee (Correct Answer)
- E. Laxity to varus stress
Orthopedic trauma priorities Explanation: ***A palpable click with passive motion of the knee***
- The patient's presentation with a **football injury**, **severe knee pain**, **inflammation**, and **laxity with valgus stress** (suggesting MCL injury) points towards significant knee trauma. A palpable click can indicate a torn meniscus, which is a common accompanying injury in such forceful knee trauma, particularly with a simultaneous MCL tear.
- While the primary injury might involve ligaments, the absence of synovial fluid abnormalities upon arthrocentesis makes a pure ligamentous tear without associated meniscal damage less likely to produce a palpable click, and given the forceful impact, meniscal injury is highly probable.
*Anterior displacement of the femur relative to the tibia*
- This finding would indicate a **posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injury**, which typically results from a direct blow to the tibiofemoral joint while the knee is in flexion, or a hyperextension injury.
- The mechanism described (hit from behind with valgus stress) and the laxity to valgus stress are not consistent with a PCL injury.
*Severe pain with compression of the patella*
- Severe pain with patellar compression is characteristic of **patellofemoral pain syndrome** or **chondromalacia patellae**, which are typically overuse injuries or degenerative conditions.
- This finding is less likely to be the primary presentation following acute, forceful traumatic injury to the knee resulting in ligamentous laxity.
*Anterior displacement of the tibia relative to the femur*
- This is the classic sign of an **anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear**, which is tested using the **Lachman test** or **anterior drawer test**.
- While an ACL tear can occur in football, the described injury mechanism ("hit from behind" and "valgus stress") is more indicative of MCL damage, and an isolated ACL tear does not directly correlate with the valgus laxity observed.
*Laxity to varus stress*
- Laxity to varus stress indicates an injury to the **lateral collateral ligament (LCL)**.
- The clinical presentation specifically mentions laxity with **valgus stress**, which points to a medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury, not an LCL injury.
Orthopedic trauma priorities US Medical PG Question 2: A 27-year-old soldier stationed in Libya sustains a shrapnel injury during an attack, causing a traumatic above-elbow amputation. The resulting arterial bleed is managed with a tourniquet prior to transport to the military treatment facility. On arrival, he is alert and oriented to person, place, and time. His armor and clothing are removed. His pulse is 145/min, respirations are 28/min, and blood pressure is 95/52 mm Hg. Pulmonary examination shows symmetric chest rise. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Abdominal examination shows no abnormalities. There are multiple shrapnel wounds over the upper and lower extremities. A tourniquet is in place around the right upper extremity; the right proximal forearm has been amputated. One large-bore intravenous catheter is placed in the left antecubital fossa. Despite multiple attempts, medical staff is unable to establish additional intravenous access. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Irrigate the shrapnel wounds
- B. Perform endotracheal intubation
- C. Establish intraosseous access (Correct Answer)
- D. Establish central venous access
- E. Replace the tourniquet with a pressure dressing
Orthopedic trauma priorities Explanation: ***Establish intraosseous access***
- The patient is in **hemorrhagic shock** (tachycardia, hypotension) and requires rapid fluid resuscitation, but peripheral intravenous access is difficult to obtain. **Intraosseous (IO) access** provides a rapid and reliable route for fluids and medications, especially in emergencies when IV access is challenging.
- IO access is a **bridge to definitive venous access** and is crucial for immediate life-saving interventions in trauma.
*Irrigate the shrapnel wounds*
- While wound irrigation is important for preventing infection, it is **not the immediate priority** when the patient is in hemorrhagic shock.
- Addressing the circulatory compromise takes precedence over local wound care.
*Perform endotracheal intubation*
- The patient is **alert and oriented** with symmetric chest rise and clear lungs, indicating he does not currently have an airway crisis requiring intubation.
- Intubation is an invasive procedure that carries risks and should only be performed when indicated for airway protection or respiratory failure.
*Establish central venous access*
- While central venous access is useful for long-term fluid management and monitoring, it is generally **more time-consuming and technically challenging** to establish than IO access, especially in an emergent, unstable patient.
- Given the urgency of rapid fluid administration, IO access is preferred as the immediate next step.
*Replace the tourniquet with a pressure dressing*
- The patient has an above-elbow amputation, suggesting significant injury, and the tourniquet is currently controlling the bleed. Removing the tourniquet prematurely without proximal surgical control can lead to **recurrent catastrophic hemorrhage**.
- A definitive surgical approach is needed to manage the amputation, not simply replacing the tourniquet with a pressure dressing, which may be insufficient to control arterial bleeding.
Orthopedic trauma priorities US Medical PG Question 3: A 25-year-old man comes to the physician for severe back pain. He describes the pain as shooting and stabbing. On a 10-point scale, he rates the pain as a 9 to 10. The pain started after he lifted a heavy box at work; he works at a supermarket and recently switched from being a cashier to a storekeeper. The patient appears to be in severe distress. Vital signs are within normal limits. On physical examination, the spine is nontender without paravertebral muscle spasms. Range of motion is normal. A straight-leg raise test is negative. After the physical examination has been completed, the patient asks for a letter to his employer attesting to his inability to work as a storekeeper. Which of the following is the most appropriate response?
- A. “Yes. Since work may worsen your condition, I would prefer that you stay home a few days. I will write a letter to your employer to explain the situation.”
- B. You say you are in severe pain. However, the physical examination findings do not suggest a physical problem that can be addressed with medications or surgery. I'd like to meet on a regular basis to see how you're doing.
- C. I understand that you are uncomfortable, but the findings do not match the severity of your symptoms. Let's talk about the recent changes at your job. (Correct Answer)
- D. The physical exam findings do not match your symptoms, which suggests a psychological problem. I would be happy to refer you to a mental health professional.
- E. The physical exam findings suggest a psychological rather than a physical problem. But there is a good chance that we can address it with cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Orthopedic trauma priorities Explanation: ***"I understand that you are uncomfortable, but the findings do not match the severity of your symptoms. Let's talk about the recent changes at your job."***
- This response acknowledges the patient's reported discomfort while gently highlighting the **discrepancy between symptoms and objective findings**, which is crucial in cases of suspected **somatoform or functional pain**.
- It also opens communication about potential **psychosocial stressors** related to his job change, which could be contributing to his symptoms, without dismissing his pain or making a premature diagnosis.
*"You say you are in severe pain. However, the physical examination findings do not suggest a physical problem that can be addressed with medications or surgery. I'd like to meet on a regular basis to see how you're doing."*
- While this option correctly identifies the lack of physical findings, it can be perceived as dismissive of the patient's pain, potentially damaging the **physician-patient relationship**.
- Suggesting regular meetings without a clear plan for addressing his immediate concerns or exploring underlying issues might not be the most effective initial approach.
*“Yes. Since work may worsen your condition, I would prefer that you stay home a few days. I will write a letter to your employer to explain the situation.”*
- This response would **validate the patient's claim of severe pain** without objective evidence, potentially reinforcing illness behavior and avoiding addressing the underlying issue.
- Providing a doctor's note for inability to work without a clear diagnostic basis or understanding of the pain's origin is **medically inappropriate** and could set a precedent for future such requests.
*"The physical exam findings do not match your symptoms, which suggests a psychological problem. I would be happy to refer you to a mental health professional."*
- Directly labeling the problem as "psychological" can be **stigmatizing and alienating** to the patient, leading to distrust and resistance to care.
- While a psychological component might be present, immediately referring to mental health without further exploration of the patient's situation or current stressors is premature and lacks empathy.
*"The physical exam findings suggest a psychological rather than a physical problem. But there is a good chance that we can address it with cognitive-behavioral therapy."*
- Similar to the previous option, explicitly stating a "psychological problem" can be **stigmatizing**.
- Jumping directly to recommending **cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)** without a comprehensive discussion and patient buy-in is premature and may lead to non-compliance.
Orthopedic trauma priorities US Medical PG Question 4: A 23-year-old patient presents to the emergency department after a motor vehicle accident. The patient was an unrestrained driver involved in a head-on collision. The patient is heavily intoxicated on what he claims is only alcohol. An initial trauma assessment is performed, and is notable for significant bruising of the right forearm. The patient is in the trauma bay, and complains of severe pain in his right forearm. A physical exam is performed and is notable for pallor, decreased sensation, and cool temperature of the skin of the right forearm. Pain is elicited upon passive movement of the right forearm and digits. A thready radial pulse is palpable. A FAST exam is performed, and is negative for signs of internal bleeding. The patient's temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), pulse is 100/min, blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, respirations are 12/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Radiography of the right forearm is ordered. The patient is still heavily intoxicated. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Fasciotomy (Correct Answer)
- B. IV fluids
- C. Analgesics
- D. Pressure measurement
- E. Detoxification
Orthopedic trauma priorities Explanation: ***Fasciotomy***
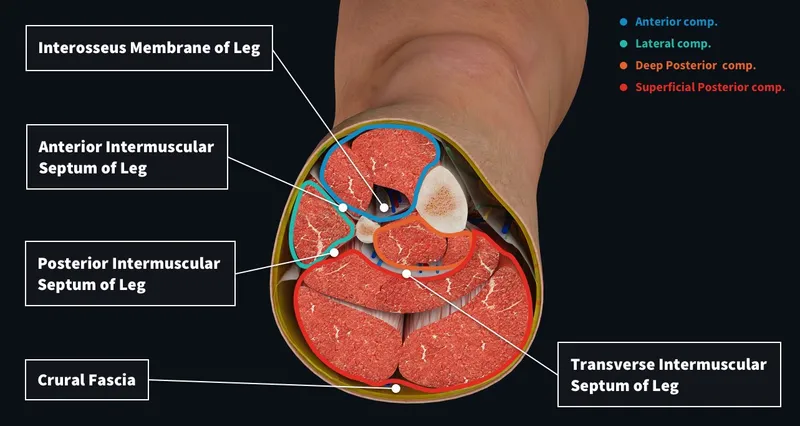
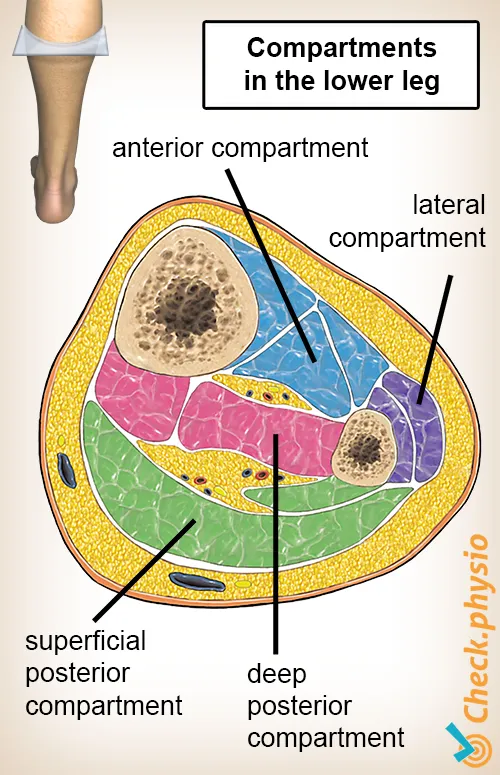
- The patient exhibits classic signs of **acute compartment syndrome**, including severe pain out of proportion to injury, pain on passive stretch, pallor, decreased sensation, and cool extremity, despite a palpable pulse. These symptoms necessitate immediate surgical intervention to relieve pressure.
- A **fasciotomy** is the definitive treatment for acute compartment syndrome to prevent irreversible muscle and nerve damage, and potentially limb loss.
*IV fluids*
- While fluid resuscitation is important in trauma, the patient's current vital signs (BP 110/70 mmHg, pulse 100/min) do not indicate immediate shock requiring aggressive IV fluid administration over addressing the limb-threatening compartment syndrome.
- Prioritizing IV fluids without addressing **compartment syndrome** could lead to permanent loss of limb function.
*Analgesics*
- Administering analgesics might mask the escalating pain a key symptom of compartment syndrome, which could delay diagnosis and definitive treatment.
- While pain control is important, it should not supersede measures to prevent irreversible tissue damage.
*Pressure measurement*
- While compartment pressure measurement can confirm the diagnosis of compartment syndrome, the clinical presentation in this case is so compelling that delaying definitive treatment for pressure measurement is not the best next step.
- Clinical signs and symptoms are often sufficient for diagnosis, and surgical intervention should not be deferred pending pressure readings in clear-cut cases.
*Detoxification*
- Detoxification for alcohol intoxication is not an emergent and immediate priority in comparison to the limb-threatening condition of acute compartment syndrome.
- Addressing the **compartment syndrome** is critical for preserving limb viability, whereas detoxification can be managed once acute medical emergencies are controlled.
Orthopedic trauma priorities US Medical PG Question 5: A 16-year-old boy presents to the emergency department after a skateboarding accident. He fell on a broken bottle and received a 4 cm wound on the dorsal aspect of his left hand. His vitals are stable and he was evaluated by the surgeon on call who determined that suturing was not required. After several weeks the wound has almost completely healed (see image). Which of the following is the correct description of this patient's wound before healing?
- A. Incised wound (Correct Answer)
- B. Abrasion
- C. Laceration
- D. Avulsion
- E. Puncture
Orthopedic trauma priorities Explanation: ***Incised wound***
- An **incised wound** is caused by a sharp object, such as a broken bottle, resulting in a clean, straight cut with well-defined edges and minimal tissue damage.
- The characteristics of the injury (sharp object mechanism, 4 cm linear wound) and the clinical decision that suturing was not required suggest a relatively clean incised wound with edges that could approximate well.
- Incised wounds typically heal with **fine linear scars** as shown in the image, especially when the edges are well-approximated.
*Abrasion*
- An abrasion is a **superficial wound** caused by friction or scraping, leading to removal of the epidermis and sometimes the superficial dermis.
- This mechanism does not match the described injury from a broken bottle, and abrasions produce broad, shallow wounds rather than deep linear cuts.
- Abrasions heal with minimal scarring and would not produce the linear scar pattern shown.
*Laceration*
- A laceration is a wound with **irregular, torn edges** typically caused by blunt force trauma or crushing injury.
- While broken glass can sometimes cause lacerations, the description of a clean "4 cm wound" from falling on a broken bottle more strongly suggests a sharp cutting mechanism rather than tearing.
- Lacerations have jagged edges with more tissue damage and typically require debridement or careful closure.
*Avulsion*
- An **avulsion** involves forcible tearing away of tissue, often resulting in significant tissue loss with irregular, gaping wounds.
- This injury pattern is much more severe than described and would typically require complex surgical management, including possible skin grafting.
- The mechanism (falling on broken glass) and the relatively straightforward healing do not support an avulsion injury.
*Puncture*
- A puncture wound is caused by a **pointed object** penetrating the skin, creating a small entry hole with depth greater than width.
- The description of a "4 cm wound" indicates a linear length, not a deep narrow penetration typical of puncture wounds.
- Puncture wounds carry high infection risk and would not produce the linear scar pattern shown in the image.
Orthopedic trauma priorities US Medical PG Question 6: A 24-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after being assaulted. The paramedics report that the patient was found conscious and reported being kicked many times in the torso. She is alert and able to respond to questions. She denies any head trauma. She has a past medical history of endometriosis and a tubo-ovarian abscess that was removed surgically two years ago. Her only home medication is oral contraceptive pills. Her temperature is 98.5°F (36.9°C), blood pressure is 82/51 mmHg, pulse is 136/min, respirations are 24/min, and SpO2 is 94%. She has superficial lacerations to the face and severe bruising over her chest and abdomen. Her lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally and her abdomen is soft, distended, and diffusely tender to palpation. Her skin is cool and clammy. Her FAST exam reveals fluid in the perisplenic space.
Which of the following is the next best step in management?
- A. Emergency laparotomy (Correct Answer)
- B. Abdominal radiograph
- C. Abdominal CT
- D. Fluid resuscitation
- E. Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
Orthopedic trauma priorities Explanation: ***Emergency laparotomy***
- The patient presents with **hemodynamic instability** (BP 82/51 mmHg, HR 136/min) and a **positive FAST exam** showing fluid in the perisplenic space, indicating intra-abdominal hemorrhage.
- According to **ATLS guidelines**, a hemodynamically unstable patient with a positive FAST exam requires **immediate operative intervention** to control bleeding. This is the definitive management for ongoing hemorrhage.
- While fluid resuscitation is initiated simultaneously (en route to OR), **surgical control of the bleeding source** is the priority and should not be delayed.
*Fluid resuscitation*
- Fluid resuscitation with IV crystalloids is essential and should be started immediately in this patient with hypovolemic shock.
- However, in a patient with **uncontrolled intra-abdominal hemorrhage** (positive FAST, hemodynamic instability), fluids alone will not stop the bleeding. Continued fluid resuscitation without surgical intervention can lead to dilutional coagulopathy and worsening outcomes.
- Fluid resuscitation occurs **concurrently with preparation for surgery**, not as a separate step that delays definitive management.
*Diagnostic peritoneal lavage*
- DPL is an invasive diagnostic procedure that has largely been replaced by FAST exam in modern trauma care.
- Given that the **FAST is already positive**, DPL would provide no additional useful information and would only **delay definitive surgical management**.
- In hemodynamically unstable patients with positive FAST, proceeding directly to laparotomy is indicated.
*Abdominal radiograph*
- Plain radiographs have **limited sensitivity** for detecting intra-abdominal bleeding or solid organ injury.
- They may show free air (indicating hollow viscus perforation) but cannot assess for fluid or characterize solid organ injuries.
- This would **delay necessary operative intervention** without providing actionable information.
*Abdominal CT*
- CT abdomen is the imaging modality of choice for **hemodynamically stable** trauma patients to characterize injuries and guide management.
- For **unstable patients**, CT is **contraindicated** as it delays definitive treatment and removes the patient from a resuscitation environment where deterioration can be immediately addressed.
Orthopedic trauma priorities US Medical PG Question 7: A 31-year-old man presents to the Emergency Department with severe left leg pain and paresthesias 4 hours after his leg got trapped by the closing door of a bus. Initially, he had a mild pain which gradually increased to unbearable levels. Past medical history is noncontributory. In the Emergency Department, his blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, heart rate is 87/min, respiratory rate is 14/min, and temperature is 36.8℃ (98.2℉). On physical exam, his left calf is firm and severely tender on palpation. The patient cannot actively dorsiflex his left foot, and passive dorsiflexion is limited. Posterior tibial and dorsalis pedis pulses are 2+ in the right leg and 1+ in the left leg. Axial load does not increase the pain. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Lower limb CT scan
- B. Lower limb ultrasound
- C. Splinting and limb rest
- D. Fasciotomy (Correct Answer)
- E. Lower limb X-ray in two projections
Orthopedic trauma priorities Explanation: ***Fasciotomy***
- The patient presents with classic signs and symptoms of **acute compartment syndrome**, including unrelieved pain by analgesics, paresthesias, pain with passive stretching, and a tense compartment due to the bus door trauma.
- **Fasciotomy** is the definitive and urgent treatment to relieve pressure within the muscle compartments, prevent muscle ischemia, and avoid permanent nerve damage or limb loss.
*Lower limb CT scan*
- A **CT scan** is primarily used to evaluate bony structures and soft tissue injuries but is not the most immediate or definitive diagnostic tool for acute compartment syndrome.
- Delaying **fasciotomy** for imaging in a clear case of compartment syndrome can lead to irreversible damage.
*Lower limb ultrasound*
- **Ultrasound** can assess vascular flow and some soft tissue aspects but is not accurate or rapid enough for diagnosing compartment syndrome.
- It would not provide the necessary information to guide urgent surgical intervention.
*Splinting and limb rest*
- This approach is appropriate for fractures or soft tissue injuries without compartment syndrome; however, in acute compartment syndrome, **splinting or limb rest** will worsen the condition.
- **Immobilization** and elevation are contraindicated as they can further decrease blood flow and increase compartment pressure.
*Lower limb X-ray in two projections*
- An **X-ray** is useful for ruling out fractures but will not provide information about compartment pressure or muscle viability.
- While a fracture can sometimes cause compartment syndrome, the immediate concern here is the compartment syndrome itself, for which **X-rays** are not diagnostic.
Orthopedic trauma priorities US Medical PG Question 8: A 67-year-old man is brought to the emergency room after being involved in a traffic accident. He currently complains of bilateral hip pain. His vital signs are within the normal range, and he is hemodynamically stable. The pelvic compression test is positive. External genitalia appears normal, except there is blood at the urethral meatus and a contusion at the base of the scrotum. Digital rectal examination (DRE) shows a high-riding ballotable prostate. An X-ray reveals the presence of a pelvic fracture. Which of the following initial actions is the most appropriate for this patient?
- A. Insert a Foley catheter
- B. Take the patient emergently to the operating room and check for a urethral injury with IV indigo carmine
- C. Obtain a retrograde urethrogram (RUG), including a pre-injection kidney, ureter, and bladder (KUB) film (Correct Answer)
- D. Obtain a urinalysis to detect microscopic hematuria
- E. Perform a suprapubic cystostomy
Orthopedic trauma priorities Explanation: ***Obtain a retrograde urethrogram (RUG), including a pre-injection kidney, ureter, and bladder (KUB) film***
- The combination of **blood at the urethral meatus**, a **high-riding ballotable prostate** on DRE, and a **pelvic fracture** are classic signs of a **urethral injury**, specifically a posterior urethral tear.
- A **retrograde urethrogram (RUG)** is the gold standard diagnostic test to confirm urethral injury and determine its location and extent, which is crucial before any attempt at catheterization.
*Insert a Foley catheter*
- **Insertion of a Foley catheter is contraindicated** in suspected urethral injuries, as it can worsen a partial tear into a complete transection or create a false passage.
- Doing so blindly could lead to further damage, stricture formation, and increased morbidity.
*Take the patient emergently to the operating room and check for a urethral injury with IV indigo carmine*
- This approach is premature before confirming the diagnosis and extent of urethral injury; **indigo carmine is used to assess ureteral integrity**, not urethral injury.
- Surgical exploration for urethral injury as an initial step is typically reserved for cases where RUG cannot be performed or for severe complex injuries with other indications for immediate surgery.
*Obtain a urinalysis to detect microscopic hematuria*
- While microscopic hematuria would likely be present, it is a **nonspecific finding** and does not provide information about the integrity of the urethra itself.
- It would not change the need for a RUG to assess for urethral injury in the presence of more specific signs.
*Perform a suprapubic cystostomy*
- A **suprapubic cystostomy** is the appropriate method for urinary diversion in a patient with a confirmed urethral injury if a Foley catheter cannot be safely placed.
- However, it is an intervention chosen *after* diagnosing the injury with a RUG, not the initial diagnostic step itself.
Orthopedic trauma priorities US Medical PG Question 9: A 56-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 25 minutes after he was involved in a high-speed motor vehicle collision where he was the unrestrained passenger. He has severe lower abdominal and pelvic pain. On arrival, he is alert and oriented. His pulse is 95/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 106/62 mm Hg. Examination shows severe tenderness to palpation over the lower abdomen and over the left anterior superior iliac spine. There is no limb length discrepancy. Application of downward pressure over the pelvis shows no springy resistance or instability. Rectal examination is unremarkable. A focused assessment with sonography shows no free fluid in the abdomen. There is no blood at the urethral meatus. Placement of a Foley catheter shows gross hematuria. An x-ray of the pelvis shows a fracture of the left pelvic edge. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Intravenous pyelography
- B. External fixation of the pelvis
- C. Cystoscopy
- D. Retrograde urethrography
- E. Retrograde cystography (Correct Answer)
Orthopedic trauma priorities Explanation: ***Retrograde cystography***
- The presence of **gross hematuria** in a patient with a **pelvic fracture** necessitates ruling out **bladder injury**. A retrograde cystography directly visualizes the bladder and can detect extravasation of contrast if a bladder rupture is present.
- This imaging study specifically investigates the bladder using retrograde contrast filling, which is crucial for diagnosing **intraperitoneal** or **extraperitoneal bladder rupture**.
*Intravenous pyelography*
- This study evaluates the **kidneys** and **ureters** for injury, but the primary concern with gross hematuria and pelvic fracture is the bladder.
- An IV pyelogram provides less detailed imaging of the bladder compared to a retrograde cystogram and is less effective for detecting bladder rupture.
*External fixation of the pelvis*
- While the patient has a pelvic fracture, the immediate priority in a hemodynamically stable patient with gross hematuria is to identify and manage potential **life-threatening urologic injuries** before definitive orthopedic repair.
- **Pelvic external fixation** is primarily indicated for **unstable pelvic fractures** or those causing significant hemorrhage, neither of which is explicitly described as an immediate concern requiring intervention before urologic evaluation.
*Cystoscopy*
- **Cystoscopy** is an endoscopic procedure that allows direct visualization of the bladder's interior. While it can identify bladder injuries, it is generally considered after imaging studies like **retrograde cystography** to confirm findings or address specific issues like clot evacuation or stent placement.
- The initial diagnostic step should focus on assessing for rupture via contrast study, which is often less invasive than a direct endoscopic procedure in the acute trauma setting.
*Retrograde urethrography*
- **Retrograde urethrography (RUG)** is used to evaluate for **urethral injury**, especially when there is blood at the urethral meatus, a high-riding prostate, or an inability to pass a Foley catheter.
- The patient's Foley catheter was successfully placed, and there was **no blood at the urethral meatus**, making urethral injury less likely and thus RUG a lower priority as the initial step compared to assessing for bladder injury.
Orthopedic trauma priorities US Medical PG Question 10: Two hours after undergoing a left femoral artery embolectomy, an obese 63-year-old woman has severe pain, numbness, and tingling of the left leg. The surgery was without complication and peripheral pulses were weakly palpable postprocedure. She has type 2 diabetes mellitus, peripheral artery disease, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia. Prior to admission, her medications included insulin, enalapril, carvedilol, aspirin, and rosuvastatin. She appears uncomfortable. Her temperature is 37.1°C (99.3°F), pulse is 98/min, and blood pressure is 132/90 mm Hg. Examination shows a left groin surgical incision. The left lower extremity is swollen, stiff, and tender on palpation. Dorsiflexion of her left foot causes severe pain in her calf. Femoral pulses are palpated bilaterally. Pedal pulses are weaker on the left side as compared to the right side. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 12.1
Leukocyte count 11,300/mm3
Platelet count 189,000/mm3
Serum
Glucose 222 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.1 mg/dL
Urinalysis is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Reperfusion injury (Correct Answer)
- B. Cellulitis
- C. Cholesterol embolism
- D. Deep vein thrombosis
- E. Rhabdomyolysis
Orthopedic trauma priorities Explanation: ***Reperfusion injury***
- The patient's symptoms of **severe pain, numbness, and tingling** in the left leg following an embolectomy, along with **swelling, stiffness, and tenderness** of the extremity, and pain on passive dorsiflexion (**pain with passive stretch**), are classic signs of **acute compartment syndrome**.
- In this context, compartment syndrome is caused by **reperfusion injury** following prolonged limb ischemia. When blood flow is restored after prolonged ischemia, the reperfusion causes **oxidative stress, inflammatory mediator release, and increased capillary permeability**, leading to **tissue edema and elevated intracompartmental pressure** that compresses nerves and vessels.
- The **2-hour timeline** post-embolectomy and the clinical triad of pain out of proportion, pain with passive stretch, and paresthesias make reperfusion injury leading to compartment syndrome the most likely diagnosis.
*Cellulitis*
- While cellulitis causes **pain, swelling, and redness**, it typically has a more **gradual onset** and is associated with warmth, erythema, and signs of infection.
- The **acute onset** (2 hours post-surgery), **severe neurologic symptoms** (numbness, tingling), and **pain with passive stretch** are not characteristic of cellulitis.
- The absence of fever, significant leukocytosis, or spreading erythema makes cellulitis unlikely.
*Cholesterol embolism*
- **Cholesterol emboli** can occur after vascular procedures and typically present with **livedo reticularis**, **"blue toe" syndrome**, **renal impairment**, or **eosinophilia**.
- While possible after arterial manipulation, the acute presentation with signs of **elevated compartment pressure** (pain with passive stretch, swelling, paresthesias) points to a pressure-related compartment issue rather than distal microembolization.
*Deep vein thrombosis*
- **DVT** causes **unilateral leg swelling, pain, and tenderness** but typically presents with a more **gradual onset** over hours to days.
- DVT would not explain the **acute severe pain with passive stretch**, **rapid neurologic symptoms** (paresthesias), or the **compartment syndrome findings** seen immediately (2 hours) post-procedure.
- The clinical picture of acute compartment syndrome better fits ischemia-reperfusion injury.
*Rhabdomyolysis*
- **Rhabdomyolysis** involves muscle breakdown due to prolonged ischemia or trauma and is characterized by **elevated creatinine kinase (CK)**, **myoglobinuria**, and potentially **acute kidney injury**.
- While rhabdomyolysis can occur **secondary to** both the initial ischemia and subsequent compartment syndrome, it is a **consequence or complication** rather than the **primary cause** of the acute compartment syndrome findings.
- The immediate clinical presentation (severe pain with passive stretch, paresthesias, swelling) reflects **elevated intracompartmental pressure from reperfusion injury**, not rhabdomyolysis itself.
More Orthopedic trauma priorities US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.