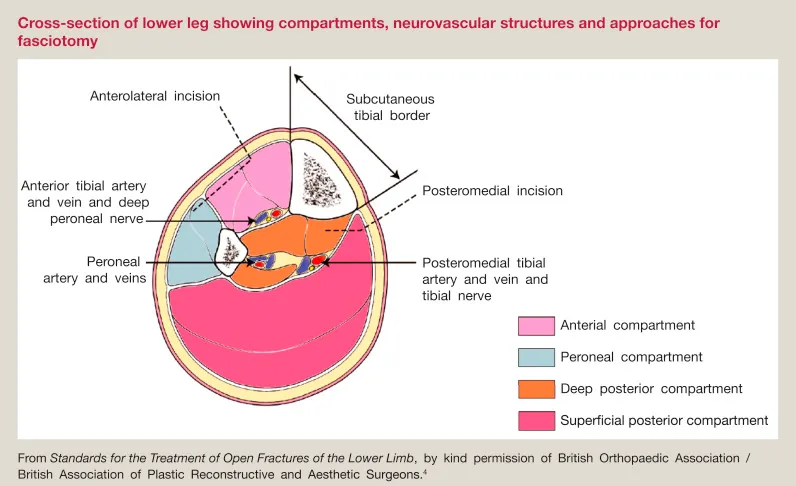
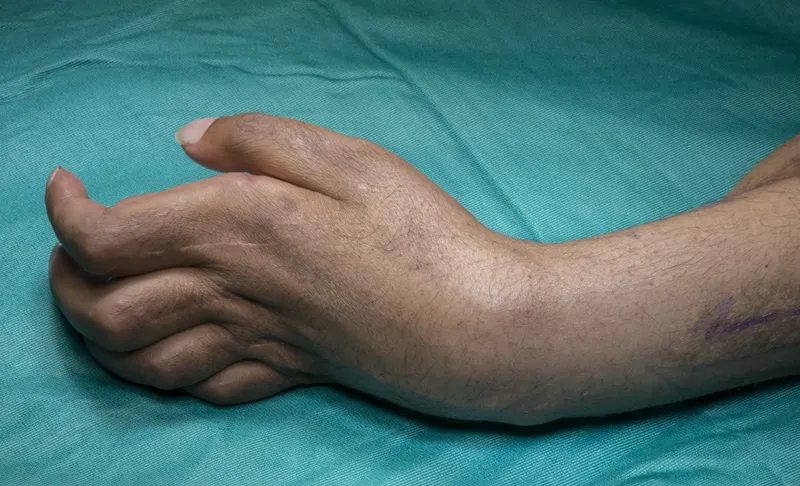
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy US Medical PG Question 1: A 62-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of severe left leg pain accompanied by numbness and weakness. His medical history is remarkable for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. His vital signs include a blood pressure of 155/92 mm Hg, a temperature of 37.1°C (98.7°F), and an irregular pulse of 92/min. Physical examination reveals absent left popliteal and posterior tibial pulses. His left leg is noticeably cold and pale. There is no significant tissue compromise, nerve damage, or sensory loss. Which of the following will most likely be required for this patient's condition?
- A. Antibiotics
- B. Warfarin
- C. Fasciotomy
- D. Amputation
- E. Thromboembolectomy (Correct Answer)
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy Explanation: ***Thromboembolectomy***
- The sudden onset of severe leg pain, numbness, and weakness with absent pulses, a cold, pale limb, and an irregular pulse suggests **acute limb ischemia** likely due to an **arterial embolus**, which requires emergent surgical removal.
- Given the symptoms and history of an irregular pulse (suggesting possible atrial fibrillation), a thromboembolectomy is the most appropriate first-line treatment to restore blood flow and prevent permanent damage.
*Antibiotics*
- Antibiotics are used to treat **bacterial infections** and are not indicated for acute limb ischemia caused by a vascular occlusion.
- There are no signs of infection present, such as fever, redness, or purulent discharge, that would warrant antibiotic therapy.
*Warfarin*
- Warfarin is an **anticoagulant** used for long-term prevention of clot formation, particularly in conditions like atrial fibrillation or deep vein thrombosis.
- While anticoagulation may eventually be part of management to prevent future events, it is insufficient as immediate therapy for an acute, established arterial embolus causing critical limb ischemia.
*Fasciotomy*
- Fasciotomy is performed to relieve **compartment syndrome**, which occurs when increased pressure within a muscle compartment compromises circulation and nerve function.
- While compartment syndrome can be a complication of reperfusion after prolonged ischemia, it is not the primary treatment for the initial arterial occlusion; the first step is to restore blood flow to prevent the need for it.
*Amputation*
- Amputation is a last resort considered when the limb is **irreversibly ischemic** and non-viable, or when revascularization attempts have failed and there is extensive tissue necrosis or infection.
- In this case, there is no significant tissue compromise or nerve damage mentioned, indicating that the limb is still salvageable with timely intervention.
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy US Medical PG Question 2: A 27-year-old soldier stationed in Libya sustains a shrapnel injury during an attack, causing a traumatic above-elbow amputation. The resulting arterial bleed is managed with a tourniquet prior to transport to the military treatment facility. On arrival, he is alert and oriented to person, place, and time. His armor and clothing are removed. His pulse is 145/min, respirations are 28/min, and blood pressure is 95/52 mm Hg. Pulmonary examination shows symmetric chest rise. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Abdominal examination shows no abnormalities. There are multiple shrapnel wounds over the upper and lower extremities. A tourniquet is in place around the right upper extremity; the right proximal forearm has been amputated. One large-bore intravenous catheter is placed in the left antecubital fossa. Despite multiple attempts, medical staff is unable to establish additional intravenous access. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Irrigate the shrapnel wounds
- B. Perform endotracheal intubation
- C. Establish intraosseous access (Correct Answer)
- D. Establish central venous access
- E. Replace the tourniquet with a pressure dressing
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy Explanation: ***Establish intraosseous access***
- The patient is in **hemorrhagic shock** (tachycardia, hypotension) and requires rapid fluid resuscitation, but peripheral intravenous access is difficult to obtain. **Intraosseous (IO) access** provides a rapid and reliable route for fluids and medications, especially in emergencies when IV access is challenging.
- IO access is a **bridge to definitive venous access** and is crucial for immediate life-saving interventions in trauma.
*Irrigate the shrapnel wounds*
- While wound irrigation is important for preventing infection, it is **not the immediate priority** when the patient is in hemorrhagic shock.
- Addressing the circulatory compromise takes precedence over local wound care.
*Perform endotracheal intubation*
- The patient is **alert and oriented** with symmetric chest rise and clear lungs, indicating he does not currently have an airway crisis requiring intubation.
- Intubation is an invasive procedure that carries risks and should only be performed when indicated for airway protection or respiratory failure.
*Establish central venous access*
- While central venous access is useful for long-term fluid management and monitoring, it is generally **more time-consuming and technically challenging** to establish than IO access, especially in an emergent, unstable patient.
- Given the urgency of rapid fluid administration, IO access is preferred as the immediate next step.
*Replace the tourniquet with a pressure dressing*
- The patient has an above-elbow amputation, suggesting significant injury, and the tourniquet is currently controlling the bleed. Removing the tourniquet prematurely without proximal surgical control can lead to **recurrent catastrophic hemorrhage**.
- A definitive surgical approach is needed to manage the amputation, not simply replacing the tourniquet with a pressure dressing, which may be insufficient to control arterial bleeding.
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy US Medical PG Question 3: A 38-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 35 minutes after he sustained a gunshot wound to the right thigh. He has type 1 diabetes mellitus. On arrival, his pulse is 112/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 115/69 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 98%. There is an entrance wound on the anteromedial surface of the right thigh 2 cm below the inguinal ligament. There is no bruit or thrill. There is no exit wound. The pedal pulse is diminished on the right side compared to the left. The abdomen is soft and nontender. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hematocrit 46%
Serum
Urea nitrogen 24 mg/dL
Glucose 160 mg/dL
Creatinine 3.1 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Digital subtraction angiography
- B. Wound cleaning and tetanus toxoid
- C. CT angiography
- D. Duplex ultrasonography (Correct Answer)
- E. Fasciotomy
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy Explanation: ***Duplex ultrasonography***
- The patient has suffered a **gunshot wound** to the thigh with a **diminished pedal pulse**, indicating potential **vascular injury** (a "soft sign" requiring imaging).
- Given his **significantly elevated creatinine (3.1 mg/dL)** and **type 1 diabetes mellitus**, imaging studies requiring **IV iodinated contrast** carry substantial risk for **contrast-induced nephropathy** and further renal deterioration.
- **Duplex ultrasonography** is a **non-invasive, contrast-free method** to assess vascular flow and identify injuries like **arterial dissection**, **thrombosis**, or **pseudoaneurysm**. While operator-dependent, it is the most appropriate initial diagnostic step in this hemodynamically stable patient with significant renal impairment.
- This allows vascular assessment while **minimizing nephrotoxic risk** in a patient with pre-existing renal dysfunction.
*CT angiography*
- **CT angiography** is the **gold standard** for evaluating penetrating extremity trauma with soft signs of vascular injury in most cases, offering rapid and highly accurate vascular imaging.
- However, it requires administration of **intravenous iodinated contrast**, which poses significant risk for **contrast-induced nephropathy** in this patient with **baseline creatinine of 3.1 mg/dL** and **diabetes mellitus**.
- While CTA would typically be preferred in trauma settings, the severe renal impairment makes duplex ultrasonography the safer initial choice in this stable patient.
*Digital subtraction angiography*
- This is an **invasive angiographic technique** that uses **iodinated contrast** and carries even higher contrast load than CTA, posing substantial risk for **contrast-induced nephropathy** given the patient's **elevated creatinine**.
- While it offers high resolution and therapeutic capability, the risks associated with contrast and invasive arterial access outweigh its benefits for initial assessment in this scenario.
- Reserved for cases where intervention is anticipated or non-invasive imaging is inconclusive.
*Wound cleaning and tetanus toxoid*
- These are essential components of wound care for any penetrating injury but do not address the immediate concern of **potential vascular injury** causing the diminished pedal pulse.
- Prioritizing definitive diagnosis of vascular compromise is critical before focusing solely on local wound management, as a missed arterial injury could lead to limb loss.
*Fasciotomy*
- **Fasciotomy** is a surgical procedure to relieve **compartment syndrome**, which can develop secondary to vascular injury, reperfusion, or significant soft tissue trauma.
- While compartment syndrome is a risk with this injury, there is no immediate clinical evidence of it (no severe pain out of proportion to exam, no tense compartments documented).
- Diagnosis of the vascular injury should be established first, as fasciotomy may be needed later if ischemia is prolonged or after revascularization.
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy US Medical PG Question 4: A 35-year-old man is brought to the emergency department from a kitchen fire. The patient was cooking when boiling oil splashed on his exposed skin. His temperature is 99.7°F (37.6°C), blood pressure is 127/82 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 12/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. He has dry, nontender, and circumferential burns over his arms bilaterally, burns over the anterior portion of his chest and abdomen, and tender spot burns with blisters on his shins. A 1L bolus of normal saline is administered and the patient is given morphine and his pulse is subsequently 80/min. A Foley catheter is placed which drains 10 mL of urine. What is the best next step in management?
- A. Additional fluids and escharotomy (Correct Answer)
- B. Escharotomy
- C. Continuous observation
- D. Moist dressings and discharge
- E. Additional fluids and admission to the ICU
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy Explanation: ***Additional fluids and escharotomy***
- The patient has **circumferential full-thickness burns** on both arms (dry, nontender), which require **escharotomy** to prevent compartment syndrome and vascular compromise to the limbs.
- The **oliguria** (10 mL urine output) despite a 1L fluid bolus indicates **inadequate fluid resuscitation** from burn shock. With approximately 40% TBSA burns, the patient requires aggressive fluid resuscitation per the Parkland formula (4 mL/kg/% TBSA), which would be approximately 11 liters in the first 24 hours. Adequate resuscitation targets urine output of 0.5-1 mL/kg/hr (35-70 mL/hr for this patient).
- Both interventions are immediately necessary: fluids for burn shock and escharotomy for circumferential burns.
*Escharotomy*
- While **escharotomy** is essential for the circumferential full-thickness burns to prevent compartment syndrome, it alone will not address the **severe fluid deficit** causing oliguria and hypoperfusion.
- The low urine output reflects systemic hypovolemia from burn shock, not just local compartment issues, requiring aggressive fluid resuscitation.
*Continuous observation*
- **Continuous observation** is inappropriate given the patient's critical findings: circumferential full-thickness burns requiring urgent escharotomy and oliguria indicating inadequate resuscitation.
- Delaying escharotomy can lead to irreversible ischemic damage to the limbs, and inadequate fluid resuscitation can progress to multiorgan failure.
*Moist dressings and discharge*
- This option is completely inappropriate for a patient with **extensive deep burns** (approximately 40% TBSA) including full-thickness injuries requiring hospitalization and specialized burn care.
- Discharge would lead to severe complications including infection, inadequate fluid resuscitation, compartment syndrome, and potential limb loss.
*Additional fluids and admission to the ICU*
- While ICU admission and additional fluids are necessary components of care, this option is **incomplete** because it omits **escharotomy**, which is urgently needed for the circumferential full-thickness burns.
- Escharotomy is a time-sensitive procedure that must be performed promptly to prevent ischemic injury to the limbs from vascular compromise.
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy US Medical PG Question 5: A patient presents to the emergency department with arm pain. The patient recently experienced an open fracture of his radius when he fell from a ladder while cleaning his house. Surgical reduction took place and the patient's forearm was put in a cast. Since then, the patient has experienced worsening pain in his arm. The patient has a past medical history of hypertension and asthma. His current medications include albuterol, fluticasone, loratadine, and lisinopril. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 150/95 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 19/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. The patient's cast is removed. On physical exam, the patient's left arm is tender to palpation. Passive motion of the patient's wrist and fingers elicits severe pain. The patient's left radial and ulnar pulse are both palpable and regular. The forearm is soft and does not demonstrate any bruising but is tender to palpation. Which of the following is the next best step in management?
- A. Replace the cast with a sling
- B. Measurement of compartment pressure (Correct Answer)
- C. Ibuprofen and reassurance
- D. Emergency fasciotomy
- E. Radiography
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy Explanation: ***Measurement of compartment pressure***
- The patient exhibits classic signs of **compartment syndrome**, including severe pain out of proportion to injury, pain with passive stretching, and a history of trauma followed by casting. Measuring compartment pressure is crucial for diagnosis despite palpable pulses.
- Early measurement of compartment pressures can confirm the diagnosis and guide the decision for an **emergency fasciotomy** to prevent irreversible tissue damage.
*Replace the cast with a sling*
- This action would likely worsen the patient's condition by delaying the diagnosis and treatment of potential **compartment syndrome**.
- A sling does not address the underlying issue of increased pressure within the muscle compartments.
*Ibuprofen and reassurance*
- Administering **Ibuprofen (NSAID)** might mask the pain but will not resolve the increased pressure within the compartment, which is a surgical emergency.
- Reassurance without proper assessment of compartment syndrome could lead to irreversible muscle and nerve damage.
*Emergency fasciotomy*
- While a fasciotomy is the definitive treatment for confirmed compartment syndrome, it should only be performed **after compartment pressures have been measured** and the diagnosis confirmed, unless the clinical suspicion is extremely high and pressures cannot be obtained.
- Performing a fasciotomy without objective confirmation is generally not the immediate next step, as it is an invasive procedure with its own risks.
*Radiography*
- **Radiography** would be useful to assess the healing of the fracture or rule out new fractures, but it will not provide information about the soft tissue pressure changes characteristic of compartment syndrome.
- The patient's symptoms are more indicative of a circulatory or soft tissue issue rather than a new bony problem.
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy US Medical PG Question 6: A 35-year-old man is referred to a physical therapist due to limitation of movement in the wrist and fingers of his left hand. He cannot hold objects or perform daily activities with his left hand. He broke his left arm at the humerus one month ago. The break was simple and treatment involved a cast for one month. Then he lost his health insurance and could not return for follow up. Only after removing the cast did he notice the movement issues in his left hand and wrist. His past medical history is otherwise insignificant, and vital signs are within normal limits. On examination, the patient’s left hand is pale and flexed in a claw-like position. It is firm and tender to palpation. Right radial pulse is 2+ and left radial pulse is 1+. The patient is unable to actively extend his fingers and wrist, and passive extension is difficult and painful. Which of the following is a proper treatment for the presented patient?
- A. Surgical release (Correct Answer)
- B. Botulinum toxin injections
- C. Collagenase injections
- D. Needle fasciotomy
- E. Corticosteroid injections
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy Explanation: ***Surgical release***
- The patient presents with classic signs of **established Volkmann's ischemic contracture** (claw-like hand, firm fibrotic tissue, limited movement, decreased radial pulse), which is the end-stage result of untreated compartment syndrome that occurred during fracture healing.
- Since this is **chronic contracture (one month post-injury)**, the appropriate surgical treatment involves **reconstructive procedures** such as muscle slide operations, tendon lengthening, tendon transfers, neurolysis, or in severe cases, free functional muscle transfer to restore hand function.
- Emergency fasciotomy would have been appropriate for **acute compartment syndrome** (within 6-8 hours of onset), but at this stage, the treatment focuses on releasing fibrotic tissue and restoring function through reconstructive surgery.
*Botulinum toxin injections*
- **Botulinum toxin** is used to relax spastic muscles in neurological conditions (e.g., cerebral palsy, stroke), but it does not address the underlying **ischemic fibrosis and muscle necrosis** of Volkmann's contracture.
- It would not improve the structural contracture or restore blood flow in this patient.
*Collagenase injections*
- **Collagenase injections** are used for localized fascial contractures like Dupuytren's contracture, where enzymatic breakdown of collagen cords can restore finger extension.
- They are ineffective for **Volkmann's contracture**, which involves widespread ischemic muscle necrosis, fibrosis, and nerve damage requiring surgical reconstruction.
*Needle fasciotomy*
- **Needle fasciotomy** is a minimally invasive technique for Dupuytren's contracture, involving percutaneous disruption of fascial cords.
- It is not suitable for **Volkmann's contracture**, which requires extensive surgical release of fibrotic muscle compartments, possible tendon transfers, and neurolysis—procedures that cannot be accomplished with needle techniques.
*Corticosteroid injections*
- **Corticosteroids** reduce inflammation in conditions like tenosynovitis or trigger finger.
- They would not address the **ischemic muscle necrosis and fibrotic contracture** in Volkmann's contracture and could potentially delay appropriate surgical treatment.
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy US Medical PG Question 7: A boy with diabetic ketoacidosis is admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit for closer monitoring. Peripheral venous access is established. He is treated with IV isotonic saline and started on an insulin infusion. This patient is at the highest risk for which of the following conditions in the next 24 hours?
- A. Cerebral edema (Correct Answer)
- B. Intrinsic kidney injury
- C. Cognitive impairment
- D. Hyperkalemia
- E. Deep venous thrombosis
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy Explanation: ***Cerebral edema***
- **Cerebral edema** is a severe and potentially fatal complication of **diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)** treatment, particularly in children.
- It results from a rapid decrease in serum osmolality during treatment, causing water to shift into brain cells.
*Intrinsic kidney injury*
- While dehydration in DKA can lead to **prerenal acute kidney injury**, **intrinsic kidney injury** is less common as an acute risk directly from DKA treatment in the first 24 hours.
- Initial fluid resuscitation often improves renal perfusion, reducing the risk of intrinsic damage unless other predisposing factors are present.
*Cognitive impairment*
- Cognitive impairment after DKA is more commonly observed in the long term, potentially due to recurrent episodes or severe DKA with cerebral edema.
- It is not the most immediate and highest risk acute complication in the short-term (next 24 hours).
*Hyperkalemia*
- Patients with DKA typically present with **hyperkalemia** due to acidosis and insulin deficiency, which resolves with insulin therapy as potassium shifts back into cells.
- The more immediate risk during treatment, especially after initial fluid resuscitation and insulin, is **hypokalemia**, not hyperkalemia, due to the intracellular shift of potassium.
*Deep venous thrombosis*
- **Dehydration** and **hyperviscosity** associated with DKA can increase the risk of **thrombosis**, but **deep venous thrombosis** is not the highest or most immediate acute risk in the next 24 hours.
- **Cerebral edema** is a more specific and life-threatening complication directly related to the treatment of DKA in children.
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy US Medical PG Question 8: Two hours after undergoing a left femoral artery embolectomy, an obese 63-year-old woman has severe pain, numbness, and tingling of the left leg. The surgery was without complication and peripheral pulses were weakly palpable postprocedure. She has type 2 diabetes mellitus, peripheral artery disease, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia. Prior to admission, her medications included insulin, enalapril, carvedilol, aspirin, and rosuvastatin. She appears uncomfortable. Her temperature is 37.1°C (99.3°F), pulse is 98/min, and blood pressure is 132/90 mm Hg. Examination shows a left groin surgical incision. The left lower extremity is swollen, stiff, and tender on palpation. Dorsiflexion of her left foot causes severe pain in her calf. Femoral pulses are palpated bilaterally. Pedal pulses are weaker on the left side as compared to the right side. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 12.1
Leukocyte count 11,300/mm3
Platelet count 189,000/mm3
Serum
Glucose 222 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.1 mg/dL
Urinalysis is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Reperfusion injury (Correct Answer)
- B. Cellulitis
- C. Cholesterol embolism
- D. Deep vein thrombosis
- E. Rhabdomyolysis
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy Explanation: ***Reperfusion injury***
- The patient's symptoms of **severe pain, numbness, and tingling** in the left leg following an embolectomy, along with **swelling, stiffness, and tenderness** of the extremity, and pain on passive dorsiflexion (**pain with passive stretch**), are classic signs of **acute compartment syndrome**.
- In this context, compartment syndrome is caused by **reperfusion injury** following prolonged limb ischemia. When blood flow is restored after prolonged ischemia, the reperfusion causes **oxidative stress, inflammatory mediator release, and increased capillary permeability**, leading to **tissue edema and elevated intracompartmental pressure** that compresses nerves and vessels.
- The **2-hour timeline** post-embolectomy and the clinical triad of pain out of proportion, pain with passive stretch, and paresthesias make reperfusion injury leading to compartment syndrome the most likely diagnosis.
*Cellulitis*
- While cellulitis causes **pain, swelling, and redness**, it typically has a more **gradual onset** and is associated with warmth, erythema, and signs of infection.
- The **acute onset** (2 hours post-surgery), **severe neurologic symptoms** (numbness, tingling), and **pain with passive stretch** are not characteristic of cellulitis.
- The absence of fever, significant leukocytosis, or spreading erythema makes cellulitis unlikely.
*Cholesterol embolism*
- **Cholesterol emboli** can occur after vascular procedures and typically present with **livedo reticularis**, **"blue toe" syndrome**, **renal impairment**, or **eosinophilia**.
- While possible after arterial manipulation, the acute presentation with signs of **elevated compartment pressure** (pain with passive stretch, swelling, paresthesias) points to a pressure-related compartment issue rather than distal microembolization.
*Deep vein thrombosis*
- **DVT** causes **unilateral leg swelling, pain, and tenderness** but typically presents with a more **gradual onset** over hours to days.
- DVT would not explain the **acute severe pain with passive stretch**, **rapid neurologic symptoms** (paresthesias), or the **compartment syndrome findings** seen immediately (2 hours) post-procedure.
- The clinical picture of acute compartment syndrome better fits ischemia-reperfusion injury.
*Rhabdomyolysis*
- **Rhabdomyolysis** involves muscle breakdown due to prolonged ischemia or trauma and is characterized by **elevated creatinine kinase (CK)**, **myoglobinuria**, and potentially **acute kidney injury**.
- While rhabdomyolysis can occur **secondary to** both the initial ischemia and subsequent compartment syndrome, it is a **consequence or complication** rather than the **primary cause** of the acute compartment syndrome findings.
- The immediate clinical presentation (severe pain with passive stretch, paresthesias, swelling) reflects **elevated intracompartmental pressure from reperfusion injury**, not rhabdomyolysis itself.
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy US Medical PG Question 9: Three hours later, the patient is reassessed. Her right arm is put in an elevated position and physical examination of the extremity is performed. The examination reveals reduced capillary return and peripheral pallor. Pulse oximetry of her right index finger on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 84%. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Perform fasciotomy
- B. Obtain split-thickness skin graft
- C. Decrease rate of IV fluids
- D. Perform right upper extremity amputation
- E. Perform escharotomy (Correct Answer)
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy Explanation: ***Perform escharotomy***
- The patient's symptoms of **reduced capillary return**, **peripheral pallor**, and **low oxygen saturation** in the setting of an elevated arm indicate **compartment syndrome** due to circumferential burn-related edema.
- **Escharotomy** is the appropriate immediate intervention to relieve pressure and restore circulation in deep circumferential burns.
*Perform fasciotomy*
- **Fasciotomy** is indicated for compartment syndrome due to **non-burn-related trauma** or other causes, where the tight fascia is the primary constricting factor.
- In burns, the **tough, inelastic eschar** itself is usually the constricting element, requiring escharotomy.
*Obtain split-thickness skin graft*
- A **split-thickness skin graft** is a reconstructive procedure performed after the burn wound has been adequately debrided and the patient is stable.
- It is not an emergent intervention to address acute limb ischemia from compartment syndrome.
*Decrease rate of IV fluids*
- While excessive fluid resuscitation can contribute to edema, the immediate and critical issue is the **compromised circulation** due to the constricting eschar, not solely fluid overload.
- Reducing IV fluids would not rapidly reverse the existing limb ischemia and could potentially lead to **hypoperfusion** if the patient is already under-resuscitated.
*Perform right upper extremity amputation*
- **Amputation** is a last resort, considered only after all attempts to salvage the limb, including escharotomy, have failed and there is irreversible tissue necrosis.
- It is not the appropriate first-line response to acute compartment syndrome from burns.
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy US Medical PG Question 10: A 36-year-old man comes to the emergency department 4 hours after a bike accident for severe pain and swelling in his right leg. He has not had a headache, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or blood in his urine. He has a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease and allergic rhinitis. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 17 years and drinks an average of one alcoholic beverage daily. His medications include levocetirizine and pantoprazole. He is in moderate distress. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 112/min, and blood pressure is 140/80 mm Hg. Examination shows multiple bruises over both lower extremities and the face. There is swelling surrounding a 2 cm laceration 13 cm below the right knee. The lower two-thirds of the tibia is tender to palpation and the skin is pale and cool to the touch. The anterior tibial, posterior tibial, and dorsalis pedis pulses are weak. Capillary refill time of the right big toe is 4 seconds. Dorsiflexion of his right foot causes severe pain in his calf. Cardiopulmonary examination is normal. An x-ray is ordered, which is shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Above knee cast
- B. IVC filter placement
- C. Fasciotomy (Correct Answer)
- D. Low molecular weight heparin
- E. Open reduction and internal fixation
Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy Explanation: ***Fasciotomy***
- The patient's symptoms (severe pain, swelling, pain with passive dorsiflexion, weak pulses, pale/cool skin, and prolonged capillary refill) after a traumatic injury are highly suggestive of **acute compartment syndrome**.
- **Fasciotomy** is the definitive treatment for acute compartment syndrome to relieve pressure and prevent irreversible tissue damage.
*Above knee cast*
- While a cast is used for immobilization of fractures, it would worsen **compartment syndrome** by externally compressing an already swollen limb.
- This patient has signs of compartment syndrome which requires urgent surgical decompression, not just immobilization.
*IVC filter placement*
- **IVC filter placement** is indicated for preventing pulmonary embolism in patients with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) who have contraindications to anticoagulation.
- There is no clinical evidence to suggest DVT in this patient, and the primary concern is acute compartment syndrome.
*Low molecular weight heparin*
- **Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH)** is an anticoagulant used for DVT prophylaxis or treatment.
- It is not indicated for the immediate management of acute compartment syndrome and could increase the risk of bleeding in a patient who likely needs urgent surgery.
*Open reduction and internal fixation*
- **Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF)** is a surgical procedure to stabilize complex fractures, which may be needed later for a tibial fracture if present.
- However, the immediate priority is to address the limb-threatening acute compartment syndrome before performing definitive fracture repair.
More Compartment syndrome diagnosis and fasciotomy US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.