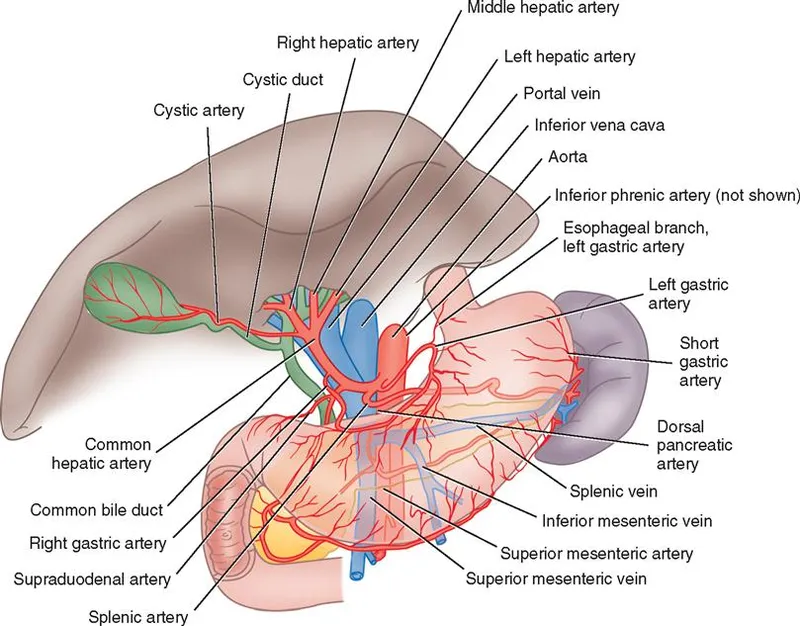
Pancreatic surgery procedures US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Pancreatic surgery procedures. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Pancreatic surgery procedures US Medical PG Question 1: During a surgical procedure to repair an abdominal aortic aneurysm, the surgeon must be careful to avoid injury to which of the following arterial structures that originates near the level of the renal vessels?
- A. Left renal artery (Correct Answer)
- B. Celiac trunk
- C. Right renal artery
- D. Superior mesenteric artery
Pancreatic surgery procedures Explanation: ***Left renal artery***
- The **left renal artery** arises from the aorta usually just below the superior mesenteric artery, making it susceptible to injury during an **abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair** if the aneurysm extends proximally.
- Its proximity to the typical location of AAA, often near or involving the **infrarenal aorta**, necessitates careful identification and protection during clamping or graft placement.
*Celiac trunk*
- The **celiac trunk** originates higher up from the aorta, typically at the level of **T12-L1 vertebrae**, well above the common infrarenal AAA repair site.
- While important, it is generally less directly threatened during a typical infrarenal AAA repair compared to arteries immediately adjacent to or within the aneurysm sac.
*Right renal artery*
- The **right renal artery** also originates from the aorta near the level of the renal veins, but it is typically located more posteriorly and usually passes behind the inferior vena cava.
- Although it can be at risk, the left renal artery's course is often more anterior and directly in the field of dissection for the **aortic neck** during AAA repair.
*Superior mesenteric artery*
- The **superior mesenteric artery (SMA)** originates from the aorta proximal to the renal arteries, typically around the L1 vertebral level.
- While crucial, its origin is usually cephalad to the infrarenal aneurysm neck, making it generally less prone to direct injury during infrarenal AAA repair, though flow must be monitored.
Pancreatic surgery procedures US Medical PG Question 2: A 47-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain. The patient states that she felt this pain come on during dinner last night. Since then, she has felt bloated, constipated, and has been vomiting. Her current medications include metformin, insulin, levothyroxine, and ibuprofen. Her temperature is 99.0°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 139/79 mmHg, pulse is 95/min, respirations are 12/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. On physical exam, the patient appears uncomfortable. Abdominal exam is notable for hypoactive bowel sounds, abdominal distension, and diffuse tenderness in all four quadrants. Cardiac and pulmonary exams are within normal limits. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Metoclopramide
- B. Nasogastric tube, NPO, and IV fluids (Correct Answer)
- C. Stool guaiac
- D. Emergency surgery
- E. IV antibiotics and steroids
Pancreatic surgery procedures Explanation: ***Nasogastric tube, NPO, and IV fluids***
- The patient's symptoms (abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, vomiting, distension, and hypoactive bowel sounds) are highly suggestive of a **bowel obstruction**.
- **Nasogastric tube decompression** relieves pressure, **NPO status** prevents further bowel distension, and **intravenous fluids** address dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, stabilizing the patient for further evaluation.
*Metoclopramide*
- This is a **prokinetic agent** that increases gastrointestinal motility.
- Using it in the context of a suspected bowel obstruction could worsen the condition by increasing pressure against the obstruction and potentially leading to **perforation**.
*Stool guaiac*
- A stool guaiac test detects the presence of **occult blood in the stool**, which is useful for evaluating gastrointestinal bleeding.
- While it can be part of a complete workup, it is not the immediate priority for a patient presenting with symptoms of **acute bowel obstruction** requiring stabilization.
*Emergency surgery*
- While surgery may ultimately be required for a bowel obstruction, it is not the immediate first step unless there are clear signs of **perforation**, **ischemia**, or **strangulation**, which are not specified here.
- Initial management involves **stabilization** with NG decompression, NPO, and IV fluids.
*IV antibiotics and steroids*
- **IV antibiotics** are indicated for suspected infection (e.g., appendicitis, diverticulitis with perforation), but the primary presentation here is mechanical obstruction, not infection.
- **Steroids** are typically used for inflammatory conditions or adrenal insufficiency, neither of which is indicated given the patient's symptoms.
Pancreatic surgery procedures US Medical PG Question 3: Five days after undergoing a pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic cancer, a 46-year-old woman has 2 episodes of non-bilious vomiting and mild epigastric pain. She has a patient-controlled analgesia pump. She has a history of hypertension. She has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 25 years. She drinks 3–4 beers daily. Prior to admission to the hospital, her only medications were amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide. Her temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), pulse is 98/min, and blood pressure is 116/82 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 96%. Examination shows a midline surgical incision over the abdomen with minimal serous discharge and no erythema. The abdomen is soft with mild tenderness to palpation in the epigastrium. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 11.6 g/dL
Leukocyte count 16,000/mm3
Serum
Na+ 133 mEq/L
K+ 3.4 mEq/L
Cl- 115 mEq/L
Glucose 77 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.2 mg/dL
Arterial blood gas on room air shows:
pH 7.20
pCO2 23 mm Hg
pO2 91 mm Hg
HCO3- 10 mEq/L
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's acid-base status?
- A. Excessive alcohol intake
- B. Adrenal insufficiency
- C. Rhabdomyolysis
- D. Adverse effect of medication
- E. Fistula (Correct Answer)
Pancreatic surgery procedures Explanation: ***Fistula***
- The patient's **metabolic acidosis** (pH 7.20, HCO3- 10 mEq/L) with normal anion gap (Na+ - (Cl- + HCO3-) = 133 - (115 + 10) = 8 mEq/L) suggests **bicarbonate loss**.
- A pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure) involves multiple anastomoses, making **fistula formation** (e.g., pancreatic, biliary, or enteric) a significant complication that can lead to large volume losses of electrolyte-rich fluids, including bicarbonate.
*Excessive alcohol intake*
- While chronic alcohol intake can cause various metabolic derangements, an acute episode of acidosis due to alcohol typically presents as **alcoholic ketoacidosis** (high anion gap) or lactic acidosis.
- The patient's presentation of a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis does not align with the typical acid-base disturbances directly caused by acute alcohol intoxication or withdrawal.
*Adrenal insufficiency*
- Adrenal insufficiency can cause **hyponatremia**, hyperkalemia, and sometimes **non-anion gap metabolic acidosis** due to impaired aldosterone function leading to decreased H+ secretion and bicarbonate reabsorption.
- However, the patient's **potassium (3.4 mEq/L)** is within the normal range to slightly low, and the clinical picture following recent major surgery points more directly to surgical complications.
*Rhabdomyolysis*
- Rhabdomyolysis typically causes a **high anion gap metabolic acidosis** due to the release of phosphorous and other organic acids from damaged muscle cells, as well as potential acute kidney injury.
- This patient has a **normal anion gap acidosis**, and there are no clinical signs (e.g., muscle pain, elevated creatine kinase) pointing towards rhabdomyolysis.
*Adverse effect of medication*
- The patient's medications, amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide, are not typically associated with a severe normal anion gap metabolic acidosis in this context.
- While **thiazide diuretics** can rarely cause mild metabolic alkalosis due to volume contraction, they would not cause this degree of acidosis, especially with a normal anion gap, and are not known to directly cause bicarbonate loss associated with a fistula.
Pancreatic surgery procedures US Medical PG Question 4: A 50-year-old Caucasian man is admitted to the ER with an 8-hour history of intense abdominal pain that radiates to the back, nausea, and multiple episodes of vomiting. Past medical history is insignificant. His blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 20/min, and body temperature is 37.8°C (100°F). Upon examination, he has significant epigastric tenderness, and hypoactive bowel sounds. Serum lipase and amylase are elevated and the patient rapidly deteriorates, requiring transfer to the intensive care unit for a month. After being stabilized, he is transferred to the general medicine floor with an abdominal computed tomography (CT) reporting a well-circumscribed collection of fluid of homogeneous density. Which of the following best describes the condition this patient has developed?
- A. Acute necrotic collection
- B. Fistula formation
- C. Walled-off necrosis
- D. Pancreatic pseudocyst (Correct Answer)
- E. Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic surgery procedures Explanation: ***Pancreatic pseudocyst***
- The patient experienced an episode of **severe acute pancreatitis**, followed by the development of a well-circumscribed collection of fluid with homogeneous density, which is characteristic of a **pancreatic pseudocyst**.
- **Pseudocysts** are collections of pancreatic fluid and inflammatory exudates that become encapsulated by a fibrous wall, typically appearing around 4 weeks after an episode of acute pancreatitis.
*Acute necrotic collection*
- An **acute necrotic collection** is an early phase (within 4 weeks) of peripancreatic fluid collection that contains both fluid and non-viable pancreatic or peripancreatic tissue, which is not described as homogeneous in density.
- This term usually refers to the initial, unorganized collection of necrotic material, prior to the development of a well-defined wall.
*Fistula formation*
- **Fistula formation** involves an abnormal connection between two epithelialized organs or between an organ and the skin, which is not described by a well-circumscribed fluid collection.
- While it can be a complication of pancreatitis, the CT finding of a homogeneous fluid collection does not directly indicate a fistula.
*Walled-off necrosis*
- **Walled-off necrosis (WON)** is a mature collection (typically >4 weeks) of pancreatic and/or peripancreatic necrotic tissue that has developed a well-defined inflammatory wall but contains a significant solid/necrotic component.
- The CT description of a "homogeneous density" fluid collection does not align with WON, which would typically show heterogeneous density due to solid necrotic debris.
*Pancreatic cancer*
- **Pancreatic cancer** is an abnormal growth of cells within the pancreas and would typically present as a mass lesion, often with tissue invasion.
- While a pseudocyst can sometimes mimic a cystic tumor, the history of acute pancreatitis and the specific CT description of a homogeneous fluid collection make pancreatic cancer less likely in this context.
Pancreatic surgery procedures US Medical PG Question 5: A 66-year-old man comes to the physician because of yellowish discoloration of his eyes and skin, abdominal discomfort, and generalized fatigue for the past 2 weeks. He has had dark urine and pale stools during this period. He has had a 10-kg (22-lb) weight loss since his last visit 6 months ago. He has hypertension. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 34 years. He drinks three to four beers over the weekends. His only medication is amlodipine. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 89/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 114/74 mm Hg. Examination shows jaundice of the sclera and skin and excoriation marks on his trunk and extremities. The lungs are clear to auscultation. The abdomen is soft and nontender. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 12 g/dL
Leukocyte count 5,000/mm3
Platelet count 400,000/mm3
Serum
Urea nitrogen 28 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.2 mg/dL
Bilirubin
Total 7.0 mg/dL
Direct 5.5 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 615 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, GOT) 170 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, GPT) 310 U/L
γ-Glutamyltransferase (GGT) 592 U/L (N = 5–50 U/L)
An ultrasound shows extrahepatic biliary dilation. A CT scan of the abdomen shows a 2.5-cm (1-in) mass in the head of the pancreas with no abdominal lymphadenopathy. The patient undergoes biliary stenting. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Gemcitabine and 5-fluorouracil therapy
- B. Stereotactic radiation therapy
- C. Central pancreatectomy
- D. Gastroenterostomy
- E. Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Correct Answer)
Pancreatic surgery procedures Explanation: ***Pancreaticoduodenectomy***
- The patient presents with **obstructive jaundice**, a **pancreatic head mass** on CT, and **significant weight loss**, highly suggestive of **pancreatic adenocarcinoma**.
- Given the mass is localized to the head of the pancreas without evidence of metastases or lymphadenopathy on CT, **surgical resection (Whipple procedure)** is the only potentially curative treatment.
*Gemcitabine and 5-fluorouracil therapy*
- This is a form of **chemotherapy** commonly used for **advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer**, or as adjuvant therapy after surgical resection.
- It is not the most appropriate *initial* step for a potentially resectable tumor, as surgery offers the best chance for cure.
*Stereotactic radiation therapy*
- **Radiation therapy** is typically used for **locally advanced, unresectable pancreatic cancer** to control tumor growth and symptoms, or as an adjunct to chemotherapy.
- It is not a primary curative treatment for resectable pancreatic head masses.
*Central pancreatectomy*
- **Central pancreatectomy** is a less common procedure typically reserved for tumors in the **neck or body of the pancreas**, aiming to preserve the pancreatic head and tail.
- It is not appropriate for a mass located in the **head of the pancreas** that is causing biliary obstruction.
*Gastroenterostomy*
- **Gastroenterostomy** is a **palliative surgical procedure** used to bypass an obstructed duodenum, often due to an **unresectable pancreatic head mass** causing gastric outlet obstruction.
- While the patient has obstructive jaundice, the primary goal here is to resect the tumor, not merely bypass the obstruction, especially since it appears resectable.
Pancreatic surgery procedures US Medical PG Question 6: A 64-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office to find out the results of her recent abdominal CT. She had been complaining of fatigue, weight loss, and jaundice for 6 months prior to seeing the physician. The patient has a significant medical history of hypothyroidism, generalized anxiety disorder, and hyperlipidemia. She takes levothyroxine, sertraline, and atorvastatin. The vital signs are stable today. On physical examination, her skin shows slight jaundice, but no scleral icterus is present. The palpation of the abdomen reveals no tenderness, guarding, or masses. The CT results shows a 3 x 3 cm mass located at the head of the pancreas. Which of the following choices is most appropriate for delivering bad news to the patient?
- A. Refer the patient to an oncologist without informing the patient of their cancer
- B. Ask that a spouse or close relative come to the appointment, explain to them the bad news, and see if they will tell the patient since they have a closer relationship
- C. Set aside an appropriate amount of time in your schedule, and ensure you will not have any interruptions as you explain the bad news to the patient (Correct Answer)
- D. Call the patient over the phone to break the bad news, and tell them they can make an office visit if they prefer
- E. Train one of the nursing staff employees on this matter, and delegate this duty as one of their job responsibilities
Pancreatic surgery procedures Explanation: ***Set aside an appropriate amount of time in your schedule, and ensure you will not have any interruptions as you explain the bad news to the patient***
- Delivering bad news requires a **dedicated, uninterrupted environment** to allow for clear communication, emotional support, and time for the patient to process the information and ask questions.
- Adequate time ensures that the physician can address immediate concerns, explore the patient's understanding, and collaboratively plan the next steps, fostering **trust and patient-centered care**.
*Refer the patient to an oncologist without informing the patient of their cancer*
- This approach violates the principle of **patient autonomy** and the ethical obligation to provide complete and accurate information about their diagnosis.
- Patients have a right to know their medical status and actively participate in decisions regarding their care, which includes being informed of a **cancer diagnosis**.
*Ask that a spouse or close relative come to the appointment, explain to them the bad news, and see if they will tell the patient since they have a closer relationship*
- While involving family is important for support, the **primary responsibility** to deliver difficult medical news rests with the physician directly to the patient.
- This avoids potential miscommunication, ensures the patient receives accurate information from the medical professional, and respects the patient's individual right to hear their diagnosis without an intermediary.
*Call the patient over the phone to break the bad news, and tell them they can make an office visit if they prefer*
- Delivering significant bad news, especially a potential cancer diagnosis, over the phone is generally **inappropriate and insensitive**, as it lacks the personal presence and immediate support needed.
- A phone call does not allow for non-verbal cues, immediate emotional support, or a comprehensive discussion of complex medical information, making an **in-person consultation preferential**.
*Train one of the nursing staff employees on this matter, and delegate this duty as one of their job responsibilities*
- Delivering a new and serious medical diagnosis, such as cancer, is primarily the **responsibility of the treating physician** due to the complexity of the information and the need for medical expertise.
- While nurses play a crucial role in patient education and support, conveying initial diagnoses of this gravity falls outside their typical scope of practice and could erode **patient trust**.
Pancreatic surgery procedures US Medical PG Question 7: A 27-year-old-man is brought to the emergency department 30 minutes after being involved in a motorcycle accident. He lost control at high speed and was thrown forward onto the handlebars. On arrival, he is alert and responsive. He has abdominal pain and superficial lacerations on his left arm. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows a tender, erythematous area over his epigastrium. The abdomen is soft and non-distended. A CT scan of the abdomen shows no abnormalities. Treatment with analgesics is begun, the lacerations are cleaned and dressed, and the patient is discharged home after 2 hours of observation. Four days later, the patient returns to the emergency department with gradually worsening upper abdominal pain, fever, poor appetite, and vomiting. His pulse is 91/min and blood pressure is 135/82 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Abdominal compartment syndrome
- B. Aortic dissection
- C. Splenic rupture
- D. Pancreatic ductal injury (Correct Answer)
- E. Diaphragmatic rupture
Pancreatic surgery procedures Explanation: ***Pancreatic ductal injury***
- A forceful impact to the **epigastrium** (e.g., falling onto handlebars) can cause **pancreatic injury**, particularly a **ductal transection**, due to the pancreas being compressed against the vertebral column.
- Initial CT scans can be normal because the injury to the **ductal system** takes time to manifest, leading to delayed symptoms like **worsening abdominal pain, fever, vomiting**, and **poor appetite** several days later due to **pancreatitis** or a **pseudocyst** formation.
*Abdominal compartment syndrome*
- This typically presents with **acute abdominal distension**, increased intra-abdominal pressure, and organ dysfunction (e.g., oliguria, respiratory compromise), which are not described here.
- It's an immediate complication of severe trauma or fluid resuscitation, not a delayed presentation like described.
*Aortic dissection*
- Characterized by **sudden-onset, severe, tearing chest or back pain** and often involves hypertension or Marfan syndrome.
- It would manifest immediately with hemodynamic instability and distinct pain, not a delayed presentation of progressive abdominal symptoms.
*Splenic rupture*
- Often causes **left upper quadrant pain**, **Kehr's sign** (referred shoulder pain), and **hemodynamic instability** due to significant blood loss.
- While possible in trauma, a normal initial CT scan makes this less likely, and its symptoms usually appear earlier or are more severe.
*Diaphragmatic rupture*
- Can present with **dyspnea, shoulder pain**, or signs of **herniated abdominal organs** into the chest.
- It causes more immediate respiratory distress or gastrointestinal obstruction symptoms, and the abdominal symptoms described are not typical for this injury.
Pancreatic surgery procedures US Medical PG Question 8: A 37-year-old man presents to the emergency department after he cut his hand while working on his car. The patient has a past medical history of antisocial personality disorder and has been incarcerated multiple times. His vitals are within normal limits. Physical exam is notable for a man covered in tattoos with many bruises over his face and torso. Inspection of the patient's right hand reveals 2 deep lacerations on the dorsal aspects of the second and third metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints. The patient is given a tetanus vaccination, and the wound is irrigated. Which of the following is appropriate management for this patient?
- A. Closure of the wound with sutures
- B. Clindamycin and topical erythromycin
- C. Ciprofloxacin and topical erythromycin
- D. Surgical irrigation, debridement, and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (Correct Answer)
- E. No further management necessary
Pancreatic surgery procedures Explanation: ***Surgical irrigation, debridement, and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid***
- The presence of deep lacerations over the metacarpophalangeal joints, combined with an injury mechanism suggestive of a **fight bite** (laceration from striking another person's teeth), mandates **aggressive surgical management**.
- **Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid** is the appropriate antibiotic choice for **human bite wounds** due to its broad spectrum covering common oral flora like *Eikenella corrodens*, *Streptococci*, and anaerobes.
*Closure of the wound with sutures*
- **Primary closure** of human bite wounds, especially those on the hand, is strongly **contraindicated** due to the high risk of severe infection.
- These wounds should be left open to drain and heal by **secondary intention** following thorough debridement.
*Clindamycin and topical erythromycin*
- **Clindamycin** has good anaerobic coverage but lacks sufficient coverage for common aerobes found in human bites like *Eikenella corrodens*.
- **Topical erythromycin** is ineffective for deep soft tissue infections and does not provide systemic protection against the likely pathogens.
*Ciprofloxacin and topical erythromycin*
- **Ciprofloxacin** has limited activity against many oral anaerobes and *Eikenella corrodens*, making it a poor choice for human bite prophylaxis.
- As mentioned, **topical antibiotics** are insufficient for preventing serious infections in deep bite wounds.
*No further management necessary*
- This patient has sustained a **deep, contaminated wound** with a high risk of serious infection, potentially involving joints or tendons.
- Failing to provide further management, including surgical exploration and appropriate antibiotics, would likely lead to severe complications such as **osteomyelitis** or **septic arthritis**.
More Pancreatic surgery procedures US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.