Liver resection principles US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Liver resection principles. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Liver resection principles US Medical PG Question 1: A 34-year-old patient presents with severe pain in the right upper quadrant that radiates to the right shoulder. During laparoscopic cholecystectomy, which of the following anatomical spaces must be carefully identified to prevent bile duct injury?
- A. Foramen of Winslow
- B. Lesser sac
- C. Calot's triangle (Correct Answer)
- D. Morrison's pouch
Liver resection principles Explanation: ***Calot's triangle***
- **Calot's triangle** is the critical anatomical landmark containing the **cystic artery** and **cystic duct**, whose proper identification is essential to prevent injury to the hepatic artery or bile ducts during cholecystectomy.
- Its boundaries are the **cystic duct** (lateral), the **common hepatic duct** (medial), and the **inferior border of the liver** (superior, sometimes described as the cystic artery).
*Foramen of Winslow*
- The **Foramen of Winslow** (epiploic foramen) is an opening connecting the **greater and lesser sacs** of the peritoneal cavity.
- It is not directly relevant to identifying structures during cholecystectomy, but rather to accessing the lesser sac or for surgical procedures involving structures like the portal triad.
*Lesser sac*
- The **lesser sac** (omental bursa) is a peritoneal cavity posterior to the stomach and lesser omentum.
- It is explored in procedures involving the pancreas, posterior gastric wall, or for assessing fluid collections, but not for direct identification of cystic structures during standard cholecystectomy.
*Morrison's pouch*
- **Morrison's pouch** is the **hepatorenal recess**, a potential space between the posterior aspect of the liver and the right kidney and adrenal gland.
- It is a common site for **fluid accumulation** (e.g., ascites, blood) but is not directly incised or dissected for preventing bile duct injury during cholecystectomy.
Liver resection principles US Medical PG Question 2: The surgical equipment used during a craniectomy is sterilized using pressurized steam at 121°C for 15 minutes. Reuse of these instruments can cause transmission of which of the following pathogens?
- A. Non-enveloped viruses
- B. Sporulating bacteria
- C. Prions (Correct Answer)
- D. Enveloped viruses
- E. Yeasts
Liver resection principles Explanation: ***Prions***
- Prions are **abnormally folded proteins** that are highly resistant to standard sterilization methods like steam autoclaving at 121°C, making them a risk for transmission through reused surgical instruments.
- They cause transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) like **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease**, where even trace amounts can be highly infectious.
*Non-enveloped viruses*
- Non-enveloped viruses are generally **more resistant to heat and disinfectants** than enveloped viruses but are typically inactivated by recommended steam sterilization protocols.
- Standard autoclaving conditions are effective in destroying most non-enveloped viruses.
*Sporulating bacteria*
- **Bacterial spores**, such as those from *Clostridium* or *Bacillus*, are known for their high resistance to heat and chemicals, but are usually **inactivated by steam sterilization at 121°C** for 15 minutes.
- This method is specifically designed to kill bacterial spores effectively.
*Enveloped viruses*
- Enveloped viruses are the **least resistant to heat and chemical disinfectants** due to their lipid envelope.
- They are readily **inactivated by standard steam sterilization** at 121°C.
*Yeasts*
- **Yeasts** are eukaryotic microorganisms that are typically **susceptible to heat sterilization**.
- They are effectively killed by typical steam autoclaving conditions used for surgical instruments.
Liver resection principles US Medical PG Question 3: A 35-year-old woman seeks evaluation at a clinic with a complaint of right upper abdominal pain for greater than 1 month. She says that the sensation is more of discomfort than pain. She denies any history of weight loss, changes in bowel habit, or nausea. Her medical history is unremarkable. She takes oral contraceptive pills and multivitamins every day. Her physical examination reveals a palpable liver mass that is 2 cm in diameter just below the right costal margin in the midclavicular line. An abdominal CT scan reveals 2 hypervascular lesions in the right hepatic lobe. The serum α-fetoprotein level is within normal limits. What is the next best step in the management of this patient’s condition?
- A. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
- B. CT-guided biopsy
- C. Observation
- D. Referral for surgical excision
- E. Discontinue oral contraceptives (Correct Answer)
Liver resection principles Explanation: **Discontinue oral contraceptives**
- The patient's presentation with a **palpable liver mass**, **hypervascular lesions** on CT, and history of **oral contraceptive pill (OCP) use** is highly suggestive of a **hepatic adenoma**.
- The first and most crucial step in managing hepatic adenomas is to **discontinue OCPs**, as this often leads to regression of the tumor.
*Referral for surgical excision*
- Surgical excision is considered for **large adenomas** (typically >5 cm), those that are **symptomatic** and do not regress after OCP cessation, or those with features suspicious for **malignant transformation**.
- While this patient has a palpable mass, its size (2 cm) does not immediately warrant surgical excision as a first line and observation after OCP cessation is preferred.
*CT-guided biopsy*
- **Biopsy** is generally **avoided** in suspected hepatic adenomas due to the risk of **hemorrhage** from these highly vascular lesions and the potential for false negatives due to tumor heterogeneity.
- The diagnosis is usually made clinically with imaging and reversal upon stopping OCPs.
*Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)*
- **RFA** is a local ablative therapy typically reserved for cases where surgery is contraindicated or for specific types of **unresectable tumors**, often in the context of hepatocellular carcinoma or metastatic disease.
- It is not the initial treatment for an unconfirmed hepatic adenoma, especially before attempting OCP cessation.
*Observation*
- While observation is part of the management, it only follows **discontinuation of OCPs** and involves serial imaging to monitor for regression or growth.
- Simply observing the patient without addressing the potential precipitating factor (OCPs) is not the best initial step.
Liver resection principles US Medical PG Question 4: A mother brings her 3-day-old son to the pediatrician with a concern over drops of a clear yellow discharge from the clamped umbilical cord. These drops have formed every few hours every day. The vital signs are within normal limits and a cursory physical shows no abnormalities. On closer examination, the discharge is shown to be urine. The skin around the umbilical cord appears healthy and healing. The umbilical cord is appropriately discolored. An ultrasound shows a fistula tract that connects the urinary bladder and umbilicus. Which of the following structures failed to form in this patient?
- A. Round ligament of the liver
- B. Lateral umbilical ligament
- C. Median umbilical ligament (Correct Answer)
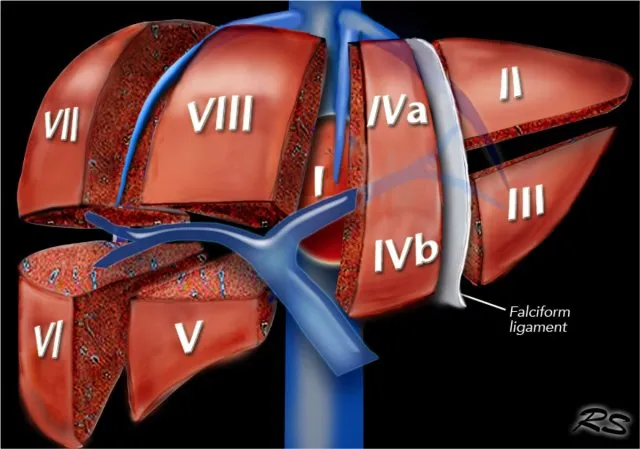
- D. Falciform ligament
- E. Medial umbilical ligament
Liver resection principles Explanation: ***Median umbilical ligament***
- The discharge of urine from the **umbilical cord stump** is indicative of a **patent urachus**, which occurs when the embryological connection between the bladder and umbilicus (the urachus) fails to close.
- The urachus should normally obliterate and form the **median umbilical ligament** in adults, so its failure to form or close is the underlying cause for the fistula.
*Round ligament of the liver*
- This ligament is the remnant of the **umbilical vein** and is responsible for connecting the umbilicus to the liver.
- A defect in the round ligament of the liver would typically present with symptoms related to hepatic circulation or umbilical hernias, not urinary discharge.
*Lateral umbilical ligament*
- This option likely refers to the **medial umbilical ligaments** (lateral umbilical folds), which are remnants of the **obliterated umbilical arteries**.
- These paired structures carry blood from the internal iliac arteries to the placenta during fetal life and obliterate after birth.
- Failure of these structures to obliterate would typically involve vascular issues, not a urinary fistula from the bladder.
*Falciform ligament*
- The falciform ligament is a **peritoneal fold** that attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and contains the round ligament of the liver in its free edge.
- While it is related to the umbilicus, its primary role is in supporting the liver, and its failure to form would not cause persistent urinary discharge from the umbilicus.
*Medial umbilical ligament*
- The medial umbilical ligaments are remnants of the **umbilical arteries**, which carry deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta.
- Failure of these structures to obliterate would typically involve vascular issues or persistent patent arteries, not a urinary fistula.
Liver resection principles US Medical PG Question 5: A 32-year-old woman comes to the emergency department for a 2-week history of right upper quadrant abdominal pain. She has also been feeling tired and nauseous for the past 5 weeks. She has a history of depression and suicidal ideation. She is a social worker for an international charity foundation. She used intravenous illicit drugs in the past but quit 4 months ago. Her only medication is sertraline. Her temperature is 37.8°C (100.0°F), pulse is 100/min, and blood pressure is 128/76 mm Hg. She is alert and oriented. Scleral icterus is present. Abdominal examination shows tenderness to palpation in the right upper quadrant. The liver edge is palpated 3 cm below the right costal margin. There is no rebound tenderness or guarding. The abdomen is non-distended and the fluid wave test is negative. She is able to extend her arms with wrists in full extension and hold them steady without flapping. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 13.8 g/dL
Leukocytes 13,700/mm3
Platelets 165,000/mm3
Prothrombin time 14 seconds
Partial thromboplastin time 35 seconds
Serum:
Total bilirubin 4.8 mg/dL
Direct bilirubin 1.3 mg/dL
Aspartate aminotransferase 1852 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase 2497 U/L
Urea nitrogen 21 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.2 mg/dL
Hepatitis A IgM antibody Negative
Hepatitis B surface antigen Negative
Hepatitis B surface antibody Negative
Hepatitis B core IgM antibody Positive
Hepatitis C antibody Positive
Hepatitis C RNA Negative
Urine beta-hCG Negative
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Supportive therapy (Correct Answer)
- B. Vaccination against Hepatitis B
- C. Ribavirin and interferon
- D. Tenofovir
- E. Pegylated interferon-alpha
Liver resection principles Explanation: ***Supportive therapy***
- The patient has **acute hepatitis B** based on positive **hepatitis B core IgM antibody** and highly elevated **ALT** and **AST** (>2000 U/L).
- The serological pattern (**HBsAg negative, HBcore IgM positive, HBsAb negative**) represents the **"window period"** of acute hepatitis B, occurring when HBsAg has cleared but HBsAb has not yet developed.
- Acute hepatitis B in **immunocompetent adults** is typically **self-limiting** (>95% clearance rate), making **supportive care** the appropriate management.
- No signs of **hepatic encephalopathy** (no asterixis), **coagulopathy** (PT normal), or **fulminant hepatic failure** are present, so antiviral therapy is not indicated.
- While she has **Hepatitis C antibody positive**, the **Hepatitis C RNA is negative**, indicating **resolved past infection** (likely from prior IV drug use) and not the cause of her current acute hepatitis.
*Vaccination against Hepatitis B*
- **Vaccination is contraindicated** during active/acute hepatitis B infection, as evidenced by positive **Hepatitis B core IgM antibody**.
- Vaccination is for **prevention**, not treatment, of existing infection.
*Ribavirin and interferon*
- This combination therapy was historically used for **chronic hepatitis C infection**, which this patient does not have (negative HCV RNA indicates resolved infection).
- It is **not indicated for acute hepatitis B** treatment.
*Tenofovir*
- **Tenofovir** is an antiviral agent used to treat **chronic hepatitis B** or **severe/fulminant acute hepatitis B** with signs of liver failure.
- Given the patient's **immunocompetent status**, absence of hepatic decompensation, and the typically **self-limiting nature of acute HBV** in adults, antiviral therapy is **not indicated**.
- Treatment would only be considered if signs of **fulminant hepatic failure** develop (encephalopathy, severe coagulopathy, rapidly rising bilirubin).
*Pegylated interferon-alpha*
- **Pegylated interferon-alpha** is used in some cases of **chronic hepatitis B and C**, but it is **not indicated for acute hepatitis B** in immunocompetent adults.
- The infection is expected to resolve spontaneously with supportive care in >95% of immunocompetent adults.
- Side effects are significant, and its use is reserved for chronic cases, not acute self-limiting presentations.
Liver resection principles US Medical PG Question 6: A patient with HCC and a long history of alcohol dependence and chronic hepatitis C has been using the mTOR inhibitor sirolimus 100 mg for cancer treatment. Her cancer has shown a partial response. She also has a history of hypertension and poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by diabetic retinopathy. Current medications include enalapril and insulin. She asks her oncologist and hepatologist if she could try everolimus for its purported survival benefit in treating HCC. Based on clinical considerations, which of the following statements is most accurate?
- A. The patient should start everolimus 50 mg because of the survival benefit relative to sirolimus 100 mg
- B. The patient is not a good candidate for everolimus due to her history of hypertension
- C. The patient should start everolimus 100 mg because of the survival benefit relative to sirolimus 100 mg
- D. The patient should start everolimus 50 mg because of her history of alcohol use disorder and hepatitis C
- E. The patient is not a good candidate for everolimus due to her history of diabetes (Correct Answer)
Liver resection principles Explanation: ***The patient is not a good candidate for Noxbinle due to her history of diabetes***
- The current medication is sirolimus, an **mTOR inhibitor** and its successor everolimus, also an mTOR inhibitor, is not beneficial for this patient due to her **poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus**.
- mTOR inhibitors, including everolimus, are known to **worsen hyperglycemia** and **accelerate the progression of diabetes**, making it contraindicated in patients with already complicated diabetes.
*The patient should start everolimus 50 mg because of the survival benefit relative to sirolimus 100 mg*
- There is **no established evidence** that everolimus at any dose offers a superior survival benefit compared to sirolimus in HCC, particularly after a partial response to sirolimus.
- **Switching mTOR inhibitors** without a compelling clinical reason, especially with existing comorbidities, is not standard practice.
*The patient is not a good candidate for everolimus due to her history of hypertension*
- While mTOR inhibitors can contribute to **hypertension**, this patient is already on **enalapril** for her existing hypertension.
- Her **poorly controlled diabetes** presents a more direct and severe contraindication due to the metabolic side effects of everolimus.
*The patient should start everolimus 100 mg because of the survival benefit relative to sirolimus 100 mg*
- No clinical data supports a **superior survival benefit** of everolimus 100 mg over sirolimus 100 mg in HCC.
- Given the patient's existing **poorly controlled diabetes**, increasing the dose of an mTOR inhibitor or switching to an equivalent dose of another would heighten the risk of severe metabolic complications.
*The patient should start everolimus 50 mg because of her history of alcohol use disorder and hepatitis C*
- The patient's history of alcohol dependence and chronic hepatitis C are **risk factors for HCC** but do not directly contraindicate a specific dose of everolimus more than her diabetes.
- While liver impairment due to these conditions might influence dosing of various medications, the **primary concern for everolimus** in this case remains the uncontrolled diabetes.
Liver resection principles US Medical PG Question 7: A 55-year-old patient who immigrated from the Middle East to the United States 10 years ago presents to the emergency department because of excessive weakness, abdominal discomfort, and weight loss for the past 10 months. He has had type 2 diabetes mellitus for 10 years for which he takes metformin. He had an appendectomy 12 years ago in his home country, and his postoperative course was not complicated. He denies smoking and drinks alcohol socially. His blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 75/min, and temperature is 37.1°C (98.7°F). On physical examination, the patient appears exhausted, and his sclerae are yellowish. A firm mass is palpated in the right upper abdominal quadrant. Abdominal ultrasonography shows liver surface nodularity, splenomegaly, and increased diameter of the portal vein. Which of the following is the most common complication of this patient condition?
- A. Hepatopulmonary syndrome
- B. Ascites (Correct Answer)
- C. Hepatic encephalopathy
- D. Hepatorenal syndrome
- E. Hepatic osteodystrophy
Liver resection principles Explanation: ***Ascites***
- The patient presents with classic signs of **portal hypertension** (splenomegaly, increased portal vein diameter, liver surface nodularity suggesting cirrhosis), and **ascites** is the most common and often the earliest major complication.
- The presence of **abdominal discomfort** and an **RUQ mass** could be related to severe liver disease and its complications, including fluid accumulation or an underlying liver malignancy often associated with cirrhosis.
*Hepatopulmonary syndrome*
- This involves **intrapulmonary vascular dilatations** in the setting of liver disease leading to oxygenation defects, typically marked by platypnea and orthodeoxia, which are not described here.
- While a complication of **cirrhosis**, it is less common than ascites and typically presents with respiratory symptoms not highlighted in this case.
*Hepatic encephalopathy*
- Characterized by **neuropsychiatric symptoms** due to the accumulation of toxins (e.g., ammonia) that the liver cannot detoxify.
- The patient's presentation mainly focuses on physical weakness, abdominal issues, and jaundice, without mention of confusion, asterixis, or altered mental status.
*Hepatorenal syndrome*
- This is a form of **functional renal failure** that occurs in patients with advanced liver disease, presenting with rapidly progressive azotemia due to severe splanchnic vasodilation.
- It is a **later and more severe complication** of liver failure, and while possible, ascites is typically seen much earlier and more frequently.
*Hepatic osteodystrophy*
- This refers to a group of **metabolic bone disorders** (osteoporosis, osteomalacia) that can occur in chronic liver disease.
- While it can manifest as bone pain, it is not a direct or immediate complication of portal hypertension and would not explain the acute abdominal findings.
Liver resection principles US Medical PG Question 8: A 52-year-old man comes to the physician because of progressive abdominal distention and weight gain over the last 2 months. He was diagnosed with alcoholic liver cirrhosis with large ascites 1 year ago. He has congestive heart failure with a depressed ejection fraction related to his alcohol use. For the last 6 months, he has abstained from alcohol and has followed a low-sodium diet. His current medications include propranolol, spironolactone, and furosemide. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 109/56 mm Hg. Physical examination shows reddening of the palms, telangiectasias on the face and trunk, and prominent blood vessels around the umbilicus. The abdomen is tense and distended; there is no abdominal tenderness. On percussion of the abdomen, there is dullness that shifts when the patient moves from the supine to the right lateral decubitus position. When the patient stretches out his arms with the wrists extended, a jerky, flapping motion of the hands is seen. Mental status examination shows a decreased attention span. Serum studies show:
Sodium 136 mEq/L
Creatinine 0.9 mg/dL
Albumin 3.6 mg/dL
Total bilirubin 1.9 mg/dL
INR 1.0
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in treatment?
- A. Refer for liver transplantation
- B. Perform large-volume paracentesis (Correct Answer)
- C. Refer for peritoneovenous shunt
- D. Change propranolol to carvedilol
- E. Refer for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
Liver resection principles Explanation: ***Perform large-volume paracentesis***
- The patient presents with **tense, distended ascites** refractory to diuretics and a low-sodium diet, evidenced by progressive abdominal distention and weight gain despite current management. **Large-volume paracentesis** is the most effective approach for immediate symptomatic relief
- The patient's clinical picture includes signs of **hepatic encephalopathy** (decreased attention span, asterixis) and **decompensated cirrhosis** (ascites, portal hypertension signs), but the immediate priority is to relieve the discomfort and respiratory compromise associated with large ascites.
*Refer for liver transplantation*
- While ultimately this patient may be a candidate for a **liver transplant** due to decompensated cirrhosis, it is not the immediate next step for managing **symptomatic tense ascites**.
- Liver transplantation involves extensive evaluation and a waiting period, and the acute issue needs to be addressed first.
*Refer for peritoneovenous shunt*
- **Peritoneovenous shunts** are rarely used due to high complication rates, including shunt thrombosis, infection, and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
- They are considered only in cases of **refractory ascites** where paracentesis is not feasible or effective long-term, which is not the case here as paracentesis has not been attempted for the current increase in ascites.
*Change propranolol to carvedilol*
- Both **propranolol** and **carvedilol** are non-selective beta-blockers used to reduce portal pressure, but **carvedilol** has additional alpha-1 blocking properties that may offer slightly more hemodynamic effects.
- However, switching beta-blockers will not directly address the immediate issue of **tense ascites** and could potentially worsen **hypotension** given the current blood pressure of 109/56 mm Hg.
*Refer for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt*
- A **TIPS** procedure is considered for **refractory ascites** that does not respond to repeated large-volume paracentesis and aggressive diuretic therapy.
- Given that a large-volume paracentesis has not been performed for the current exacerbation, **TIPS** would be a premature intervention and is associated with risks such as worsening hepatic encephalopathy.
Liver resection principles US Medical PG Question 9: A 55-year-old man presents to the emergency department with hematemesis that started 1 hour ago but has subsided. His past medical history is significant for cirrhosis with known esophageal varices which have been previously banded. His temperature is 97.5°F (36.4°C), blood pressure is 114/64 mmHg, pulse is 130/min, respirations are 12/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. During the patient's physical exam, he begins vomiting again and his heart rate increases with a worsening blood pressure. He develops mental status changes and on exam he opens his eyes and flexes his arms only to sternal rub and is muttering incoherent words. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Transfuse blood products
- B. Intubation (Correct Answer)
- C. Emergency surgery
- D. IV fluids and fresh frozen plasma
- E. Emergency variceal banding
Liver resection principles Explanation: ***Intubation***
- The patient exhibits signs of **airway compromise** and hypoxemic respiratory failure due to continuous vomiting and worsening mental status, indicated by a GCS score consistent with severe neurological impairment (GCS < 8).
- **Securing the airway via intubation** is the priority to prevent aspiration and ensure adequate ventilation and oxygenation in a patient with active hematemesis and altered mental status.
*Transfuse blood products*
- While transfusion is often necessary for significant bleeding in variceal hemorrhage, the immediate priority in this deteriorating patient is **airway protection and stabilization**.
- Transfusion alone will not address the immediate risk of **aspiration** or progressive respiratory compromise.
*Emergency surgery*
- Emergency surgery (e.g., portosystemic shunt) for variceal bleeding is typically considered only after **endoscopic and pharmacological therapies have failed** to control hemorrhage.
- It is a **more invasive** and higher-risk procedure that is not the immediate first-line intervention for acute variceal bleeding.
*IV fluids and fresh frozen plasma*
- **IV fluids** are crucial for initial resuscitation in hypovolemic shock, and **fresh frozen plasma (FFP)** can help correct coagulopathy in cirrhotic patients.
- However, these interventions do not address the immediate and critical need for **airway protection** in a patient with active vomiting and declining mental status.
*Emergency variceal banding*
- **Endoscopic variceal banding** is a primary treatment for acute variceal bleeding but requires a **secured airway** and patient cooperation.
- Given the patient's deteriorating mental status and ongoing hematemesis, performing endoscopy immediately without prior intubation carries a high risk of **aspiration**.
Liver resection principles US Medical PG Question 10: A 52-year-old man presents to his physician after his routine screening revealed that he has elevated liver enzymes. He complains of occasional headaches during the past year, but otherwise feels well. The patient reports that he was involved in a serious car accident in the 1980s. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. He has no history of illicit intravenous drug use. He does not currently take any medications and has no known allergies. His father had a history of alcoholism and died of liver cancer. The patient appears thin. His temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), pulse is 100/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. The physical examination reveals no abnormalities. The laboratory test results show the following:
Complete blood count
Hemoglobin 14 g/dL
Leukocyte count 10,000/mm3
Platelet count 146,000/mm3
Comprehensive metabolic profile
Glucose 150 mg/dL
Albumin 3.2 g/dL
Total bilirubin 1.5 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 75 IU/L
AST 95 IU/L
ALT 73 IU/L
Other lab tests
HIV negative
Hepatitis B surface antigen negative
Hepatitis C antibody positive
HCV RNA positive
HCV genotype 1
A liver biopsy is performed and shows mononuclear infiltrates localized to portal tracts that reveal periportal hepatocyte necrosis. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Peginterferon alpha therapy
- B. Interferon and ribavirin therapy
- C. Sofosbuvir and ledipasvir therapy (Correct Answer)
- D. Tenofovir and entecavir therapy
- E. Tenofovir and velpatasvir therapy
Liver resection principles Explanation: ***Sofosbuvir and ledipasvir therapy***
- This patient has chronic **Hepatitis C (HCV) infection** (HCV antibody positive, HCV RNA positive). **Sofosbuvir/ledipasvir** is an effective **direct-acting antiviral (DAA)** regimen for **genotype 1 HCV**, which is indicated for treatment-naïve patients without cirrhosis.
- The liver biopsy findings of **mononuclear infiltrates** and **periportal necrosis** confirm active hepatitis and the need for antiviral treatment to prevent progression to cirrhosis.
*Peginterferon alpha therapy*
- **Peginterferon alpha** was historically used for HCV, but its use has largely been replaced by **DAAs** due to significant side effects and lower efficacy.
- This therapy is associated with numerous adverse effects, including **flu-like symptoms**, **depression**, and **bone marrow suppression**.
*Interferon and ribavirin therapy*
- This combination was a standard treatment for HCV before the advent of DAAs, but it is associated with a high burden of **side effects** like **hemolytic anemia** (from ribavirin) and **flu-like symptoms** (from interferon).
- Given the availability of highly effective and well-tolerated DAAs, this regimen is no longer considered first-line for chronic HCV.
*Tenofovir and entecavir therapy*
- **Tenofovir** and **entecavir** are antiviral medications primarily used for the treatment of **chronic Hepatitis B (HBV) infection**.
- This patient's **Hepatitis B surface antigen is negative**, ruling out chronic HBV infection as the primary issue requiring these specific drugs.
*Tenofovir and velpatasvir therapy*
- While **velpatasvir** is a DAA used for HCV, its combination with **tenofovir** is not a standard HCV treatment for genotype 1.
- **Tenofovir** is primarily an anti-HBV drug; for HCV, velpatasvir is typically combined with **sofosbuvir** (as in Epclusa) for pan-genotypic coverage.
More Liver resection principles US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.