Hepatobiliary surgery basics US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Hepatobiliary surgery basics. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Hepatobiliary surgery basics US Medical PG Question 1: A 34-year-old patient presents with severe pain in the right upper quadrant that radiates to the right shoulder. During laparoscopic cholecystectomy, which of the following anatomical spaces must be carefully identified to prevent bile duct injury?
- A. Foramen of Winslow
- B. Lesser sac
- C. Calot's triangle (Correct Answer)
- D. Morrison's pouch
Hepatobiliary surgery basics Explanation: ***Calot's triangle***
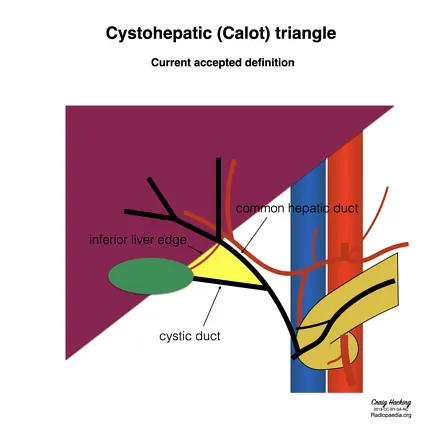
- **Calot's triangle** is the critical anatomical landmark containing the **cystic artery** and **cystic duct**, whose proper identification is essential to prevent injury to the hepatic artery or bile ducts during cholecystectomy.
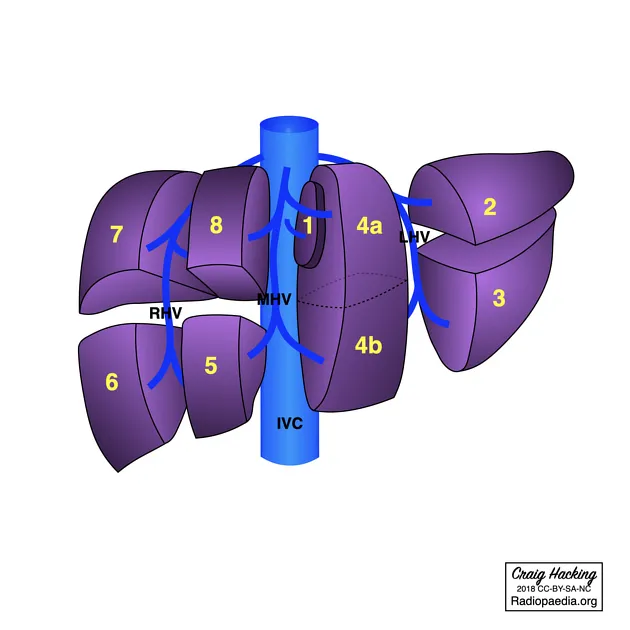
- Its boundaries are the **cystic duct** (lateral), the **common hepatic duct** (medial), and the **inferior border of the liver** (superior, sometimes described as the cystic artery).
*Foramen of Winslow*
- The **Foramen of Winslow** (epiploic foramen) is an opening connecting the **greater and lesser sacs** of the peritoneal cavity.
- It is not directly relevant to identifying structures during cholecystectomy, but rather to accessing the lesser sac or for surgical procedures involving structures like the portal triad.
*Lesser sac*
- The **lesser sac** (omental bursa) is a peritoneal cavity posterior to the stomach and lesser omentum.
- It is explored in procedures involving the pancreas, posterior gastric wall, or for assessing fluid collections, but not for direct identification of cystic structures during standard cholecystectomy.
*Morrison's pouch*
- **Morrison's pouch** is the **hepatorenal recess**, a potential space between the posterior aspect of the liver and the right kidney and adrenal gland.
- It is a common site for **fluid accumulation** (e.g., ascites, blood) but is not directly incised or dissected for preventing bile duct injury during cholecystectomy.
Hepatobiliary surgery basics US Medical PG Question 2: A 65-year-old obese female presents to the emergency room complaining of severe abdominal pain. She reports pain localized to the epigastrium that radiates to the right scapula. The pain occurred suddenly after a fast food meal with her grandchildren. Her temperature is 100.9°F (38.2°C), blood pressure is 140/85 mmHg, pulse is 108/min, and respirations are 20/min. On examination, she demonstrates tenderness to palpation in the epigastrium. She experiences inspiratory arrest during deep palpation of the right upper quadrant but this exam finding is not present on the left upper quadrant. A blockage at which of the following locations is most likely causing this patient’s symptoms?
- A. Common hepatic duct
- B. Ampulla of Vater
- C. Cystic duct (Correct Answer)
- D. Pancreatic duct of Wirsung
- E. Common bile duct
Hepatobiliary surgery basics Explanation: ***Cystic duct***
- This patient presents with **fever**, **right upper quadrant pain with inspiratory arrest (Murphy's sign)**, and a history of fatty meal ingestion, all classic signs of **acute cholecystitis** due to a gallstone obstructing the cystic duct.
- Obstruction of the cystic duct leads to bile stasis, inflammation, and potential infection within the gallbladder, causing the characteristic symptoms.
*Common hepatic duct*
- Obstruction of the **common hepatic duct** would typically cause **jaundice**, as it would block bile flow from both the left and right hepatic ducts, leading to systemic bilirubin accumulation.
- While it can cause right upper quadrant pain, the presence of Murphy's sign points more specifically to gallbladder inflammation.
*Ampulla of Vater*
- Obstruction at the **Ampulla of Vater** would lead to both **obstructive jaundice** and **pancreatitis** (due to blockage of both bile and pancreatic ducts), which are not fully reflected in this patient's presentation.
- The patient's symptoms are more localized to the gallbladder rather than a diffuse obstruction of bile flow.
*Pancreatic duct of Wirsung*
- Obstruction of the **pancreatic duct of Wirsung** typically causes **acute pancreatitis**, characterized by severe epigastric pain often radiating to the back, elevated lipase and amylase, and potentially nausea/vomiting.
- While the patient has epigastric pain, the radiation to the right scapula and positive Murphy's sign are more indicative of biliary pathology.
*Common bile duct*
- Obstruction of the **common bile duct** (choledocholithiasis) would cause **jaundice** due to the blockage of bile flow from the liver to the small intestine.
- Although it can cause right upper quadrant pain and fever (if cholangitis develops), the prominent **Murphy's sign** makes acute cholecystitis from cystic duct obstruction a more direct diagnosis.
Hepatobiliary surgery basics US Medical PG Question 3: Ten days after undergoing emergent colectomy for a ruptured bowel that she sustained in a motor vehicle accident, a 59-year-old woman has abdominal pain. During the procedure, she was transfused 3 units of packed red blood cells. She is currently receiving total parenteral nutrition. Her temperature is 38.9°C (102.0°F), pulse is 115/min, and blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg. Examination shows tenderness to palpation in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. Bowel sounds are hypoactive. Serum studies show:
Aspartate aminotransferase 142 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase 86 U/L
Alkaline phosphatase 153 U/L
Total bilirubin 1.5 mg/dL
Direct bilirubin 1.0 mg/dL
Amylase 20 U/L
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Hemolytic transfusion reaction
- B. Acalculous cholecystitis (Correct Answer)
- C. Acute cholecystitis (calculous)
- D. Small bowel obstruction
- E. Acute pancreatitis
Hepatobiliary surgery basics Explanation: ***Acalculous cholecystitis***
- This patient's clinical picture of **fever**, **RUQ tenderness**, **leukocytosis**, and mildly elevated liver enzymes in the setting of recent **major surgery**, **trauma**, and **total parenteral nutrition (TPN)** is highly suggestive of **acalculous cholecystitis**.
- **Acalculous cholecystitis** often occurs in critically ill patients due to gallbladder stasis, ischemia, and inflammation, usually without the presence of stones.
*Hemolytic transfusion reaction*
- While the patient received blood transfusions, a **hemolytic transfusion reaction** typically presents with fever, chills, flank pain, and **hemoglobinuria**, none of which are explicitly mentioned.
- Liver enzyme elevations can occur, but the significant RUQ tenderness and absence of signs of hemolysis make it less likely.
*Acute cholecystitis (calculous)*
- **Acute cholecystitis with gallstones** typically presents with similar symptoms to acalculous cholecystitis (pain, fever), but requires the presence of gallstones causing obstruction.
- The clinical context of critical illness, recent surgery, and TPN use points more towards acalculous inflammation rather than stone-related disease.
*Small bowel obstruction*
- **Small bowel obstruction** would present with more pronounced **abdominal distention**, **vomiting**, and often **high-pitched bowel sounds** followed by absent sounds, which is not the primary picture here.
- Although bowel sounds are hypoactive, the focal RUQ tenderness and liver enzyme changes are not typical of a primary small bowel obstruction.
*Acute pancreatitis*
- **Acute pancreatitis** is usually characterized by **severe epigastric pain** radiating to the back, and significantly elevated **amylase** and **lipase** levels.
- The patient's amylase is normal, and lipase is not mentioned but usually tracks with amylase in pancreatitis.
Hepatobiliary surgery basics US Medical PG Question 4: Many large clinics have noticed that the prevalence of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) has increased significantly over the past 20 years. An epidemiologist is working to identify possible reasons for this. After analyzing a series of nationwide health surveillance databases, the epidemiologist finds that the incidence of PBC has remained stable over the past 20 years. Which of the following is the most plausible explanation for the increased prevalence of PBC?
- A. Improved quality of care for PBC (Correct Answer)
- B. Increased availability of diagnostic testing for PBC
- C. Increased exposure to environmental risk factors for PBC
- D. Increased awareness of PBC among clinicians
- E. Increased average age of the population at risk for PBC
Hepatobiliary surgery basics Explanation: ***Improved quality of care for PBC***
- This leads to a **longer survival time** for patients with PBC. When incidence remains stable but patients live longer, the cumulative number of living cases (prevalence) naturally increases.
- An increase in prevalence with stable incidence is a classic indicator of **improved patient survival** due to better management or treatment.
*Increased availability of diagnostic testing for PBC*
- This would primarily impact the **incidence** of PBC by detecting more cases that were previously undiagnosed. The question states that the incidence has remained stable.
- While improved diagnostics might initially increase *reported* incidence, if the true incidence is stable, it wouldn't explain a sustained rise in prevalence without a corresponding change in incidence or survival.
*Increased exposure to environmental risk factors for PBC*
- This would directly lead to an **increase in the incidence** of PBC, as more people would be developing the disease.
- Since the incidence is stable, an increase in environmental risk factors is not the most plausible explanation for increased prevalence.
*Increased awareness of PBC among clinicians*
- Similar to increased diagnostic testing, increased awareness would likely lead to the diagnosis of more new cases, thus **increasing the incidence** of PBC.
- A stable incidence despite increased awareness means that the actual rate of new cases developing the disease has not changed, ruling this out as the primary cause of increased prevalence.
*Increased average age of the population at risk for PBC*
- An aging population could potentially increase the incidence of age-related diseases. However, if the **incidence has remained stable**, it implies that even with an older population, the rate of new diagnoses has not increased.
- While age is a risk factor for PBC, an increase in prevalence without a change in incidence suggests a factor influencing the duration of the disease rather than its onset.
Hepatobiliary surgery basics US Medical PG Question 5: A 37-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain. She reports that the pain is not new and usually starts within half an hour of eating a meal. The pain has been previously diagnosed as biliary colic, and she underwent a cholecystectomy three months ago for symptomatic biliary colic. Her liver reportedly looked normal at that time. The patient dates the onset of these episodes to shortly after she underwent a sleeve gastrectomy several years ago, and the episodes were more severe immediately following that surgery. Her postsurgical course was otherwise uncomplicated, and she has lost fifty pounds since then. She has a past medical history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, osteoarthritis, and obesity. She denies alcohol or tobacco use. Her home medications are hydrochlorothiazide, enalapril, atorvastatin, and vitamin supplements. RUQ ultrasound reveals a surgically absent gallbladder and a dilated common bile duct without evidence of stones. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) shows no evidence of biliary compression or obstruction, and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) shows no evidence of biliary stones or sludge. Laboratory tests are performed which reveal the following:
ALT: 47 U/L
AST: 56 U/L
Alkaline phosphatase: 165 U/L
Total bilirubin: 1.6 mg/dL
Amylase: 135 U/L
Lipase: 160 U/L
Which of the following is definitive treatment of this patient's condition?
- A. Pancreatic enzyme replacement
- B. Pancreaticoduodenectomy
- C. Biliary stent
- D. Sphincterotomy (Correct Answer)
- E. Surgical revascularization
Hepatobiliary surgery basics Explanation: ***Sphincterotomy***
- The patient's symptoms (postprandial RUQ pain, elevated LFTs, dilated common bile duct without stones after cholecystectomy) are highly suggestive of **sphincter of Oddi dysfunction (SOD)**. Sphincterotomy is the definitive treatment for SOD, relieving the obstruction caused by sphincter spasm or stenosis.
- This procedure can be performed endoscopically (ERCP with sphincterotomy) and aims to cut the muscle of the sphincter of Oddi, allowing bile and pancreatic juices to drain freely, thereby resolving pain.
*Pancreatic enzyme replacement*
- This treatment is primarily used for **exocrine pancreatic insufficiency** (e.g., in chronic pancreatitis or cystic fibrosis) where the pancreas does not produce enough digestive enzymes.
- The patient's amylase and lipase levels are only mildly elevated, not indicative of severe pancreatic insufficiency, and enzyme replacement would not address the mechanical obstruction of the sphincter of Oddi if SOD is present.
*Pancreaticoduodenectomy*
- **Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure)** is a major surgical operation typically performed for periampullary tumors, chronic pancreatitis with ductal obstruction, or severe trauma involving the head of the pancreas.
- It is an overly aggressive and inappropriate intervention for suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, which is a functional or mechanical obstruction of the distal common bile duct or pancreatic duct.
*Biliary stent*
- A biliary stent is used to **bypass an obstruction** in the bile duct, often in cases of strictures (benign or malignant) or stones that cannot be otherwise removed.
- While it might provide temporary relief by facilitating bile flow, it does not address the underlying pathology of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction and is not considered a definitive treatment.
*Surgical revascularization*
- **Surgical revascularization** procedures are performed to restore blood flow to an organ, typically in cases of arterial insufficiency (e.g., mesenteric ischemia affecting the bowel, or renal artery stenosis).
- The patient's symptoms and diagnostic findings point to a biliary issue, not a vascular problem, and there is no indication of ischemia that would warrant revascularization.
Hepatobiliary surgery basics US Medical PG Question 6: A 36-year-old woman presents for a pre-employment health assessment. She has no complaints. Her last annual physical examination 8 months ago was normal. She has no significant past medical history. She is a nonsmoker and says she quit all alcohol consumption last year. A complete hepatic biochemistry panel is performed, which is significant for a serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) level 5 times the upper limit of the normal range. Immunologic tests are positive for antimitochondrial antibodies. A liver biopsy is performed and reveals an inflammatory infiltrate surrounding the biliary ducts. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Pancreatic cancer
- B. Primary biliary cholangitis (Correct Answer)
- C. Hepatic amyloidosis
- D. Choledocolithiasis
- E. Fascioliasis
Hepatobiliary surgery basics Explanation: ***Primary biliary cholangitis***
- The combination of significantly elevated **alkaline phosphatase** (indicating cholestasis), positive **antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA)**, and an inflammatory infiltrate around the bile ducts on biopsy is highly diagnostic of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC).
- PBC is a **chronic autoimmune liver disease** predominantly affecting middle-aged women, characterized by progressive destruction of small intrahepatic bile ducts.
*Pancreatic cancer*
- Pancreatic cancer typically presents with symptoms like **jaundice**, weight loss, and abdominal pain, none of which are present in this asymptomatic patient.
- While it can cause cholestasis and elevated ALP, it would usually be associated with a **dilated common bile duct** on imaging and often obstructive symptoms.
*Hepatic amyloidosis*
- Hepatic amyloidosis can elevate ALP, but it would not typically be associated with **positive antimitochondrial antibodies**.
- Liver biopsy would show **amyloid deposits** rather than an inflammatory infiltrate surrounding biliary ducts.
*Choledocolithiasis*
- Choledocolithiasis (bile duct stones) would cause an **obstructive pattern** of elevated ALP, but it is often acutely symptomatic with **biliary colic** or cholangitis.
- It would not typically involve positive **antimitochondrial antibodies** or an inflammatory infiltrate characteristic of an autoimmune bile duct disease on biopsy.
*Fascioliasis*
- Fascioliasis is a **parasitic infection** that can cause eosinophilia and liver enzyme elevation, but it is associated with exposure to contaminated watercress or aquatic plants.
- It would not typically present with positive **antimitochondrial antibodies** and the specific inflammatory infiltrate seen in PBC.
Hepatobiliary surgery basics US Medical PG Question 7: Fourteen days after a laparoscopic cholecystectomy for cholelithiasis, a 45-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of persistent episodic epigastric pain for 3 days. The pain radiates to her back, occurs randomly throughout the day, and is associated with nausea and vomiting. Each episode lasts 30 minutes to one hour. Antacids do not improve her symptoms. She has hypertension and fibromyalgia. She has smoked 1–2 packs of cigarettes daily for the past 10 years and drinks 4 cans of beer every week. She takes lisinopril and pregabalin. She appears uncomfortable. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6° F), pulse is 84/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 127/85 mm Hg. Abdominal examination shows tenderness to palpation in the upper quadrants without rebound or guarding. Bowel sounds are normal. The incisions are clean, dry, and intact. Serum studies show:
AST 80 U/L
ALT 95 U/L
Alkaline phosphatase 213 U/L
Bilirubin, total 1.3 mg/dL
Direct 0.7 mg/dL
Amylase 52 U/L
Abdominal ultrasonography shows dilation of the common bile duct and no gallstones. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Counseling on alcohol cessation
- B. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (Correct Answer)
- C. Proton pump inhibitor therapy
- D. CT scan of the abdomen
- E. Reassurance and follow-up in 4 weeks
Hepatobiliary surgery basics Explanation: ***Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography***
- The patient's symptoms (epigastric pain radiating to the back, nausea, vomiting, elevated liver enzymes, and **common bile duct (CBD) dilation** on ultrasound after cholecystectomy) are highly suggestive of **postcholecystectomy syndrome**, specifically due to a retained or de novo **CBD stone** or **sphincter of Oddi dysfunction**.
- **ERCP** is both diagnostic and therapeutic in this setting, allowing for visualization of the bile ducts, stone extraction (if present), or sphincterotomy.
*Counseling on alcohol cessation*
- While **alcohol cessation** is beneficial for overall health, especially with a history of alcohol use, it is not the most immediate or appropriate next step for the acute and severe symptoms presented.
- The patient's symptoms are more indicative of a **biliary obstruction** rather than alcohol-related chronic pancreatitis or liver disease, given the acute onset post-surgery.
*Proton pump inhibitor therapy*
- **PPI therapy** is used for acid-related disorders such as GERD or peptic ulcers, which typically present with burning epigastric pain that improves with antacids.
- This patient's pain radiates to the back, is associated with nausea and vomiting, does not improve with antacids, and has abnormal imaging/labs (CBD dilation, elevated liver enzymes), ruling out a simple acid-related issue.
*CT scan of the abdomen*
- An abdominal **CT scan** could provide more detailed imaging but is generally less effective than ERCP for evaluating **biliary duct pathology** and is not therapeutic.
- Given the ultrasound findings of **CBD dilation** and the patient's symptoms, a more invasive but definitive diagnostic and therapeutic procedure is warranted.
*Reassurance and follow-up in 4 weeks*
- The patient is experiencing severe, persistent symptoms with abnormal liver enzymes and imaging findings indicating **biliary obstruction** post-cholecystectomy.
- **Reassurance and delayed follow-up** would be inappropriate and could lead to worsening of her condition, including cholangitis or pancreatitis if left untreated.
Hepatobiliary surgery basics US Medical PG Question 8: A 30-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 30 weeks' gestation is brought to the emergency department because of progressive upper abdominal pain for the past hour. The patient vomited once on her way to the hospital. She said she initially had dull, generalized stomach pain about 6 hours prior, but now the pain is located in the upper abdomen and is more severe. There is no personal or family history of any serious illnesses. She is sexually active with her husband. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Medications include folic acid and a multivitamin. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 100/min, and blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg. Physical examination shows right upper quadrant tenderness. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show a leukocyte count of 12,000/mm3. Urinalysis shows mild pyuria. Which of the following is the most appropriate definitive treatment in the management of this patient?
- A. Laparoscopic removal of ovarian cysts
- B. Cefoxitin and azithromycin
- C. Appendectomy
- D. Cholecystectomy (Correct Answer)
- E. Intramuscular ceftriaxone followed by cephalexin
Hepatobiliary surgery basics Explanation: ***Cholecystectomy***
- The patient's presentation (fever, RUQ pain, leukocytosis, vomiting) is classic for **acute cholecystitis** in pregnancy, which requires **cholecystectomy** as the definitive treatment.
- **Laparoscopic cholecystectomy** is safe during pregnancy and is the **preferred definitive treatment** for acute cholecystitis, ideally performed in the second trimester but can be done in the third trimester when indicated.
- While conservative management with antibiotics and supportive care can be attempted initially, cholecystectomy remains the definitive treatment and is increasingly performed during pregnancy to avoid recurrent symptoms and complications.
- The mild pyuria is likely secondary to adjacent inflammation rather than a primary UTI.
*Laparoscopic removal of ovarian cysts*
- Ovarian cysts typically present with **pelvic or lower abdominal pain**, not RUQ tenderness.
- The clinical picture with fever, leukocytosis, and RUQ pain strongly suggests biliary pathology, not ovarian pathology.
*Cefoxitin and azithromycin*
- This regimen is used for **pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)**, which presents with lower abdominal/pelvic pain, cervical motion tenderness, and vaginal discharge.
- The patient's RUQ localization and fever pattern do not support PID as the primary diagnosis.
*Intramuscular ceftriaxone followed by cephalexin*
- This regimen treats **gonorrhea/chlamydia** or uncomplicated UTIs.
- While mild pyuria is present, the dominant clinical features (fever, RUQ pain, leukocytosis) point to cholecystitis, not a primary genitourinary infection.
- Antibiotics alone would not provide definitive treatment for acute cholecystitis.
*Appendectomy*
- **Appendicitis** in pregnancy typically causes **RLQ pain** (though it can migrate superiorly in the third trimester due to uterine displacement).
- The distinct **RUQ localization** with the classic triad of fever, RUQ pain, and leukocytosis makes cholecystitis far more likely than appendicitis.
Hepatobiliary surgery basics US Medical PG Question 9: A 39-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with right upper quadrant abdominal discomfort for the past couple of hours. She says that the pain is dull in nature and denies any radiation. She admits to having similar episodes of pain in the past which subsided on its own. Her temperature is 37°C (99.6°F), respirations are 16/min, pulse is 78/min, and blood pressure is 122/98 mm Hg. Physical examination is normal except for diffuse tenderness of her abdomen. She undergoes a limited abdominal ultrasound which reveals a 1.4 cm gallbladder polyp. What is the next best step in the management of this patient?
- A. Barium swallow study
- B. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
- C. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- D. No further treatment required
- E. Cholecystectomy (Correct Answer)
Hepatobiliary surgery basics Explanation: ***Cholecystectomy***
- This patient has a **gallbladder polyp** measuring **1.4 cm**, which is above the threshold for concern (typically >1 cm), indicating a higher risk of **malignancy**.
- Given her recurrent **right upper quadrant pain**, even if dull and self-resolving, surgical removal (cholecystectomy) is the recommended management to prevent complications and rule out cancer.
*Barium swallow study*
- A **barium swallow study** is used to evaluate the **esophagus** and **upper gastrointestinal tract** for conditions like dysphagia, reflux, or strictures.
- It is not indicated for the evaluation or management of gallbladder polyps or right upper quadrant pain of biliary origin.
*Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)*
- **MRCP** is a non-invasive imaging technique primarily used to visualize the **biliary and pancreatic ducts** for conditions like gallstones, strictures, or tumors.
- While it can provide more detail on biliary anatomy, it is not the primary intervention for a large gallbladder polyp with symptomatic presentation; surgery is more definitive given the size.
*Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)*
- **ERCP** is an invasive endoscopic procedure used to diagnose and treat conditions of the **biliary and pancreatic ducts**, often involving stone removal or stent placement.
- It carries risks and is typically reserved for therapeutic interventions or when MRCP is inconclusive, and not for the initial management of a symptomatic gallbladder polyp.
*No further treatment required*
- A **gallbladder polyp over 1 cm** carries a significant risk of **malignant transformation** and requires intervention.
- This patient also has recurrent symptoms, which further supports the need for treatment rather than watchful waiting, to alleviate symptoms and address the polyp.
Hepatobiliary surgery basics US Medical PG Question 10: A 45-year-old woman comes to the emergency department complaining of abdominal pain for the past day. The pain is situated in the right upper quadrant, colicky, 8/10, and radiates to the tip of the right shoulder with no aggravating or relieving factors. The pain is associated with nausea but no vomiting. She tried to take over-the-counter antacids which relieved her pain to a certain extent, but not entirely. She does not smoke cigarettes or drink alcohol. She has no past medical illness. Her father died of pancreatic cancer at the age of 75, and her mother has diabetes controlled with medications. Temperature is 38°C (100.4°F), blood pressure is 125/89 mm Hg, pulse is 104/min, respiratory rate is 20/min, and BMI is 29 kg/m2. On abdominal examination, her abdomen is tender to shallow and deep palpation of the right upper quadrant.
Laboratory test
Complete blood count
Hemoglobin 13 g/dL
WBC 15,500/mm3
Platelets 145,000/mm3
Basic metabolic panel
Serum Na+ 137 mEq/L
Serum K+ 3.6 mEq/L
Serum Cl- 95 mEq/L
Serum HCO3- 25 mEq/L
BUN 10 mg/dL
Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dL
Liver function test
Total bilirubin 1.3 mg/dL
AST 52 U/L
ALT 60 U/L
Ultrasonography of the abdomen shows normal findings. What is the best next step in management of this patient?
- A. Emergency cholecystectomy
- B. CT scan
- C. Reassurance and close follow up
- D. Cholescintigraphy (Correct Answer)
- E. Percutaneous cholecystostomy
Hepatobiliary surgery basics Explanation: ***Cholescintigraphy***
- The patient presents with **right upper quadrant pain**, fever, **leukocytosis**, and elevated liver enzymes, pointing towards **acute cholecystitis**. Despite a normal ultrasound, cholescintigraphy (HIDA scan) is the gold standard for diagnosing acute cholecystitis when imaging is equivocal.
- Cholescintigraphy can assess the **patency of the cystic duct**, which is often obstructed in acute cholecystitis, by observing whether the gallbladder fills with tracer.
*Emergency cholecystectomy*
- **Acute cholecystitis** usually requires cholecystectomy, but it's typically performed **after confirmation** of the diagnosis, often after a period of stabilization with antibiotics and fluids, not immediately as an emergency for this stable patient.
- There is no evidence of severe complications such as **gallbladder perforation** or gangrene that would necessitate immediate emergency surgery without further diagnostic confirmation.
*CT scan*
- A **CT scan** is not the primary imaging modality for acute cholecystitis as it is **less sensitive** than ultrasound or cholescintigraphy for detecting gallbladder inflammation and cystic duct obstruction.
- While CT can identify complications such as abscess formation or perforation, the initial diagnostic work-up should focus on confirming the inflammation of the gallbladder itself.
*Reassurance and close follow up*
- The patient's symptoms (severe **colicky pain**, fever, **leukocytosis**, elevated liver enzymes) indicate an **acute inflammatory process** requiring active medical management and diagnosis, not mere reassurance.
- Delaying appropriate diagnosis and treatment for acute cholecystitis can lead to severe complications like gallbladder perforation, sepsis, or cholangitis.
*Percutaneous cholecystostomy*
- **Percutaneous cholecystostomy** is generally reserved for patients with acute cholecystitis who are **too unstable for surgery**, or in cases where surgical risk is very high.
- The patient is hemodynamically stable and does not have contraindications for surgery, making a definitive surgical approach (after diagnosis) preferable over a temporizing measure.
More Hepatobiliary surgery basics US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.