Bariatric surgery procedures and complications US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Bariatric surgery procedures and complications. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
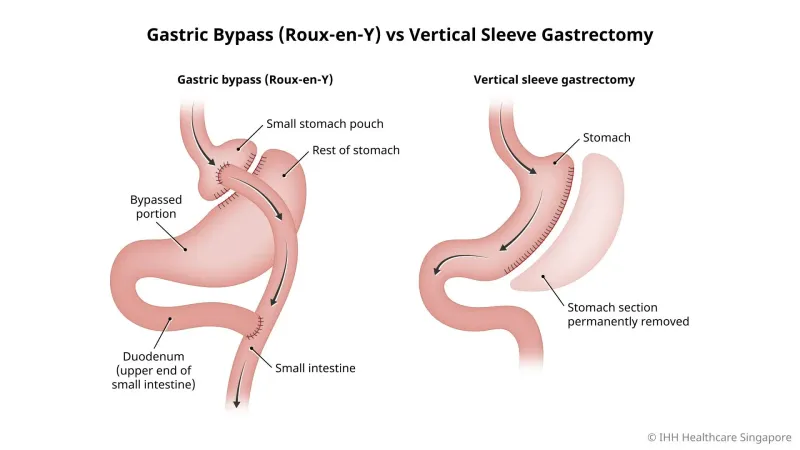
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 1: A morbidly obese 43-year-old man presents for elective bariatric surgery after previously failing several non-surgical weight loss plans. After discussing the risks and benefits of several different procedures, a sleeve gastrectomy is performed. During the surgery, the surgeon begins by incising into the right half of the greater curvature of the stomach. Which of the following arteries most likely directly provides the blood supply to this region of the stomach?
- A. Short gastric arteries
- B. Right gastric artery
- C. Right gastroduodenal artery
- D. Right gastroepiploic artery (Correct Answer)
- E. Splenic artery
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications Explanation: ***Right gastroepiploic artery***
- The **right gastroepiploic artery** (also known as the **right gastroomental artery**) is a branch of the **gastroduodenal artery** that runs along the **greater curvature of the stomach** from right to left.
- This artery is the primary blood supply to the **right portion of the greater curvature**, which corresponds to the region where an incision into the right half of the greater curvature would be made during a sleeve gastrectomy.
- It anastomoses with the left gastroepiploic artery along the greater curvature.
*Short gastric arteries*
- The **short gastric arteries** supply the **fundus** and a small portion of the superior body of the stomach, specifically to the left of the midline.
- They originate from the **splenic artery** and supply the left superior portion of the greater curvature, not the right half described in the question.
*Right gastric artery*
- The **right gastric artery** primarily supplies the **pyloric part of the stomach** and a portion of the **lesser curvature**.
- It arises from the **hepatic artery proper** and is not the main supply to the greater curvature.
*Right gastroduodenal artery*
- The **gastroduodenal artery** supplies the **duodenum** and the **head of the pancreas**.
- This artery is located inferior to the stomach and gives rise to the right gastroepiploic artery but does not directly supply the greater curvature itself.
*Splenic artery*
- The **splenic artery** is a large artery that primarily supplies the **spleen** and gives off branches like the **short gastric arteries** and the **left gastroepiploic artery**.
- While it contributes indirectly via its branches to the left portion of the greater curvature, it does not directly supply the right half of the greater curvature.
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 2: A 19-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room by her mother. She found her daughter pale, cold to the touch, and collapsed next to her bed earlier this morning. The patient has no previous medical or psychiatric history, but the mother does report that her daughter has not had her periods for the last 3 months. In the emergency department, the patient is alert and oriented. Her vitals include: blood pressure 80/60 mm Hg supine, heart rate 55/min. On physical examination, the patient appears pale and emaciated. A urine pregnancy test is negative. She is suspected of having an eating disorder. Which of the following treatment options would be contraindicated in this patient?
- A. Olanzapine
- B. Bupropion (Correct Answer)
- C. Cognitive-behavioral therapy
- D. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- E. High caloric food
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications Explanation: ***Bupropion***
- **Bupropion** is contraindicated in patients with **anorexia nervosa** or **bulimia nervosa** due to the increased risk of **seizures**.
- Patients with eating disorders often have electrolyte imbalances and metabolic derangements, which further lower the seizure threshold.
*Olanzapine*
- **Olanzapine**, an atypical antipsychotic, can be used in patients with anorexia nervosa to help with **weight gain** and reduce rigid thinking patterns.
- It is particularly useful when significant **anxiety** or **psychotic features** are present, which can exacerbate the eating disorder.
*Cognitive-behavioral therapy*
- **Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)** is a cornerstone of treatment for eating disorders, including anorexia nervosa.
- It helps patients identify and change distorted thoughts and behaviors related to food, weight, and body image.
*Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors*
- **SSRIs** may be used in anorexia nervosa, primarily after **weight restoration**, to address co-occurring **depression** or **anxiety disorders**.
- They are generally not effective for acute weight gain but can prevent relapse and treat underlying mood disturbances.
*High caloric food*
- Providing **high-caloric food** and nutritional rehabilitation is essential in managing anorexia nervosa to reverse the state of **malnutrition**.
- This must be done carefully to avoid **refeeding syndrome**, a potentially fatal shift in fluid and electrolytes that can occur with rapid refeeding.
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 3: A 64-year-old woman has progressively worsening abdominal pain 5 hours after an open valve replacement with cardiopulmonary bypass. The pain is crampy and associated with an urge to defecate. The patient reports having had 2 bloody bowel movements in the last hour. Her operation was complicated by significant intraoperative blood loss, which prolonged the operation and necessitated 2 transfusions of red blood cells. She has hypercholesterolemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. The patient received prophylactic perioperative antibiotics and opioid pain management during recovery. Her temperature is 37.9°C (98.9°F), pulse is 95/min, and blood pressure is 115/69 mm Hg. Examination shows a soft abdomen with mild tenderness to palpation in the left quadrants but no rebound tenderness or guarding. Bowel sounds are decreased. Rectal examination shows blood on the examining finger. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Embolization of superior mesenteric artery
- B. Atherosclerotic narrowing of the intestinal vessels
- C. Small outpouchings in the sigmoid wall
- D. Infection with Clostridioides difficile
- E. Decreased blood flow to the splenic flexure (Correct Answer)
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications Explanation: ***Decreased blood flow to the splenic flexure***
- This patient's symptoms are highly suggestive of **ischemic colitis**, which often affects the **splenic flexure** due to its "watershed" area vulnerability. **Cardiopulmonary bypass** and significant **intraoperative blood loss** (leading to hypotension and hypoperfusion) are major risk factors for this condition.
- The presentation with **crampy abdominal pain**, **urgent defecation**, and **bloody bowel movements** shortly after cardiac surgery points to colonic ischemia.
*Embolization of superior mesenteric artery*
- While an acute **SMA embolism** could cause severe abdominal pain and bloody stools, it typically presents with **more diffuse and severe abdominal tenderness**, often with marked tenderness disproportionate to examination findings early on, and rapid progression to peritonitis.
- The patient's history of valvular disease and hypercholesterolemia increases the risk of embolization, but the **mild tenderness confined to left quadrants** and decreased bowel sounds are less typical of an acute SMA occlusion.
*Atherosclerotic narrowing of the intestinal vessels*
- This describes **chronic mesenteric ischemia**, which typically causes **postprandial abdominal pain** (intestinal angina) and weight loss, not acute abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea in the immediate postoperative period.
- While the patient has risk factors for atherosclerosis (hypercholesterolemia, diabetes), the acute onset of symptoms following cardiac surgery points to an acute ischemic event rather than chronic narrowing.
*Small outpouchings in the sigmoid wall*
- This refers to **diverticulitis** or **diverticular bleeding**. While diverticular bleeding can cause painless or painful bleeding, and diverticulitis can cause abdominal pain, the acute onset post-cardiac surgery in the setting of hypoperfusion makes ischemic colitis a more likely diagnosis.
- Diverticulitis typically presents with **localized left lower quadrant pain**, fever, and leukocytosis, but the systemic context of recent cardiac surgery and hypoperfusion strongly favors ischemia.
*Infection with Clostridioides difficile*
- **_Clostridioides difficile_ infection** typically causes **watery diarrhea**, often after antibiotic use, and usually takes several days to develop symptoms after exposure or antibiotic initiation.
- Although the patient received perioperative antibiotics, the onset of symptoms within hours of surgery and the presence of **frank bloody stools** are less characteristic of _C. difficile_ infection, which is more commonly associated with non-bloody diarrhea.
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 4: A 2-month-old girl is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. She was born at 32 weeks' gestation and weighed 1616 g (3 lb 9 oz); she currently weighs 2466 g (5 lb 7 oz). She is exclusively breastfed and receives vitamin D supplementation. Physical examination shows no abnormalities apart from low height and weight. This patient is at increased risk for which of the following complications?
- A. Iron deficiency anemia (Correct Answer)
- B. Hemorrhage
- C. Scurvy
- D. Subacute combined degeneration
- E. Intussusception
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications Explanation: ***Iron deficiency anemia***
- Preterm infants have **lower iron stores** at birth due to reduced placental transfer in the third trimester.
- Their rapid growth rate and exclusive breastfeeding (breast milk has low iron content) further increase their risk of **iron deficiency anemia**.
*Hemorrhage*
- While preterm infants are at higher risk for certain hemorrhages (e.g., intraventricular hemorrhage), this typically occurs in the **immediate neonatal period** and risk significantly decreases by 2 months of age.
- Hemorrhage is not a common long-term complication unique to a 2-month-old preterm infant without additional risk factors.
*Scurvy*
- Scurvy is caused by **vitamin C deficiency**, which is typically not a concern in breastfed infants as breast milk provides adequate vitamin C.
- The primary deficiency risk addressed by supplementation in breastfed infants is vitamin D, not vitamin C.
*Subacute combined degeneration*
- This condition is caused by **vitamin B12 deficiency**, leading to demyelination of the spinal cord.
- While possible in infants of vegan mothers, it is unlikely in a breastfed infant without specific dietary restrictions in the mother.
*Intussusception*
- Intussusception is a condition where one segment of the intestine telescopes into another, usually occurring between **3 months and 3 years of age**.
- It is not specifically linked to prematurity or low birth weight as an increased long-term risk.
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 5: A 52-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of upper abdominal pain and nausea that occurs about 3 hours after eating and at night. These symptoms improve with eating. After eating, he often has a feeling of fullness and bloating. He has had several episodes of dark stools over the past month. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years and drinks 2 alcoholic beverages daily. He takes no medications. His temperature is 36.4°C (97.5°F), pulse is 80/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. Abdominal examination shows epigastric tenderness with no guarding or rebound. Bowel sounds are normal. Which of the following treatments is most appropriate to prevent further complications of the disease in this patient?
- A. Intravenous vitamin B12 supplementation
- B. Truncal vagotomy
- C. Amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and omeprazole (Correct Answer)
- D. Fundoplication, hiatoplasty, and gastropexy
- E. Distal gastrectomy with gastroduodenostomy
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications Explanation: ***Amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and omeprazole***
- This patient's symptoms (epigastric pain 3 hours after eating and at night, improvement with eating, dark stools) are highly suggestive of a **duodenal ulcer complicated by upper gastrointestinal bleeding**. The most common cause of duodenal ulcers is *H. pylori* infection.
- The recommended first-line treatment for *H. pylori* infection involves a triple therapy regimen, including two antibiotics (like **amoxicillin and clarithromycin**) to eradicate the bacteria and a **proton pump inhibitor (omeprazole)** to reduce acid production and promote ulcer healing.
*Intravenous vitamin B12 supplementation*
- This treatment is appropriate for **vitamin B12 deficiency**, which can occur in conditions like atrophic gastritis, pernicious anemia, or following gastric resections, but is not indicated for acute peptic ulcer disease and wouldn't address the primary pathology.
- There is no clinical indication in the patient's presentation (e.g., neurological symptoms, macrocytic anemia) to suggest a deficiency in vitamin B12.
*Truncal vagotomy*
- **Truncal vagotomy** is a surgical procedure that was historically performed to reduce gastric acid secretion by cutting the vagus nerve. It is rarely used now due to the effectiveness of medical therapies for peptic ulcer disease.
- This invasive surgical option is generally reserved for refractory cases of peptic ulcer disease not responsive to medical management, or when complications like uncontrolled bleeding or perforation necessitate surgical intervention.
*Fundoplication, hiatoplasty, and gastropexy*
- These surgical procedures are primarily used to treat **gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)** and **hiatal hernia**, not peptic ulcer disease.
- Fundoplication wraps the stomach fundus around the lower esophagus to reinforce the lower esophageal sphincter, addressing reflux symptoms which are not the primary complaint here.
*Distal gastrectomy with gastroduodenostomy*
- **Distal gastrectomy** is a major surgical procedure involving the removal of the distal part of the stomach. It is typically reserved for severe complications of peptic ulcer disease (e.g., perforation, obstruction, recurrent bleeding unresponsive to other treatments) or gastric cancer.
- While it might be considered in extreme cases of complicated peptic ulcer, it is not the initial or most appropriate treatment for preventing further complications in a patient who has yet to receive standard anti-*H. pylori* therapy.
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 6: Eight hours after undergoing an open right hemicolectomy and a colostomy for colon cancer, a 52-year-old man has wet and bloody surgical dressings. He has had episodes of blood in his stools during the past 6 months, which led to the detection of colon cancer. He has hypertension and ischemic heart disease. His younger brother died of a bleeding disorder at the age of 16. The patient has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 36 years and drinks three to four beers daily. Prior to admission, his medications included aspirin, metoprolol, enalapril, and simvastatin. Aspirin was stopped 7 days prior to the scheduled surgery. He appears uncomfortable. His temperature is 36°C (96.8°F), pulse is 98/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 118/72 mm Hg. Examination shows a soft abdomen with a 14-cm midline incision that has severe oozing of blood from its margins. The colostomy bag has some blood collected within. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 12.3 g/dL
Leukocyte count 11,200/mm3
Platelet count 210,000/mm3
Bleeding time 4 minutes
Prothrombin time 15 seconds (INR=1.1)
Activated partial thromboplastin time 36 seconds
Serum
Urea nitrogen 30 mg/dL
Glucose 96 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.1 mg/dL
AST 48 U/L
ALT 34 U/L
γ-Glutamyltransferase 70 U/L (N= 5–50 U/L)
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's bleeding?
- A. Factor VIII deficiency
- B. Liver dysfunction
- C. Erosion of blood vessels
- D. Insufficient mechanical hemostasis (Correct Answer)
- E. Platelet dysfunction
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications Explanation: ***Insufficient mechanical hemostasis***
- The patient's **coagulation studies are within normal limits** (normal PT, aPTT, bleeding time, and platelet count), ruling out most common intrinsic bleeding disorders.
- Given the timing (8 hours post-surgery) and the nature of bleeding (oozing from incision margins and colostomy site), **inadequate surgical closure or ligature** is the most probable cause.
*Factor VIII deficiency*
- This would present with a **prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)**, which is normal in this patient (36 seconds). His brother's death from a bleeding disorder is a red herring.
- Congenital factor deficiencies typically manifest earlier in life and cause more severe, spontaneous bleeding, not just post-operative oozing with normal coagulation factors.
*Liver dysfunction*
- Severe liver dysfunction would typically lead to **prolonged PT and aPTT** due to impaired synthesis of clotting factors.
- While the patient has elevated GGT, indicating some liver stress likely from alcohol, his AST and ALT are only mildly elevated, and his coagulation tests are normal.
*Erosion of blood vessels*
- This is less likely to cause widespread oozing and would typically present as a more significant, **pulsatile hemorrhage** or hematoma.
- While possible in a surgical field, the lack of significant hemodynamic compromise and normal coagulation points away from a major vessel erosion.
*Platelet dysfunction*
- This would typically result in a **prolonged bleeding time**, which is normal in this patient (4 minutes).
- Although the patient was on aspirin, it was stopped 7 days prior to surgery, which is typically sufficient for platelet function to recover.
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 7: A 42-year-old woman comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. She has generalized fatigue and has had difficulties doing her household duties for the past 3 months. She has eczema and gastroesophageal reflux disease. She has a history of using intravenous methamphetamine in her youth but has not used illicit drugs in 23 years. Her medications include topical clobetasol and pantoprazole. She is 160 cm (5 ft 3 in) tall and weighs 105 kg (231 lb); BMI is 42 kg/m2. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 95/min, and blood pressure is 145/90 mm Hg. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Cardiac examination shows no abnormalities. Pelvic examination shows a normal vagina and cervix. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 13.1 g/dL
Leukocyte count 7,800/mm3
Platelet count 312,000/mm3
Serum
Na+ 141 mEq/L
K+ 4.6 mEq/L
Cl- 98 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 12 mg/dL
Fasting glucose 110 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.8 mg/dL
Total cholesterol 269 mg/dL
HDL-cholesterol 55 mg/dL
LDL-cholesterol 160 mg/dL
Triglycerides 320 mg/dL
Urinalysis is within normal limits. An x-ray of the chest shows no abnormalities. She has not lost any weight over the past year despite following supervised weight loss programs, including various diets and exercise regimens. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
- A. Phentermine and topiramate therapy and follow-up in 3 months
- B. Bariatric surgery (Correct Answer)
- C. Liposuction
- D. Behavioral therapy
- E. Metformin and statin therapy and follow-up in 3 months
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications Explanation: ***Bariatric surgery***
- This patient has **severe obesity** (BMI of 42 kg/m²) with obesity-related comorbidities including **hypertension** (BP 145/90 mm Hg), **dyslipidemia** (elevated cholesterol and triglycerides), and **pre-diabetes** (fasting glucose 110 mg/dL), and has failed multiple supervised weight loss programs. **Bariatric surgery** is indicated for patients with BMI ≥ 40 kg/m² or BMI ≥ 35 kg/m² with obesity-related comorbidities who have failed at least 6 months of supervised weight loss.
- It is the most effective treatment for sustained weight loss in patients with **severe obesity**, leading to significant improvement or resolution of comorbidities.
*Phentermine and topiramate therapy and follow-up in 3 months*
- While medication can aid weight loss, this patient's **BMI of 42 kg/m²** signifies severe obesity, where medication alone is often insufficient for sustained and significant weight reduction.
- **Pharmacotherapy** is typically considered for BMI ≥ 30 kg/m² or BMI ≥ 27 kg/m² with comorbidities, but for class III obesity (BMI ≥ 40 kg/m²), bariatric surgery generally provides superior and more lasting outcomes.
*Liposuction*
- **Liposuction** is primarily a cosmetic procedure for localized fat removal and is not an effective treatment for generalized severe obesity or weight loss, nor does it address the metabolic complications of obesity.
- It does not lead to sustained weight loss or improvement in obesity-related comorbidities like **hypertension** and **dyslipidemia**.
*Behavioral therapy*
- The patient has already attempted multiple supervised weight loss programs, including various diets and exercise regimens, suggesting that **behavioral therapy** alone has not been effective for sustained weight loss in her case.
- While beneficial as part of a comprehensive approach, it is unlikely to achieve the significant and sustained weight loss required for a patient with **severe obesity** that has failed prior conventional methods.
*Metformin and statin therapy and follow-up in 3 months*
- **Metformin** and **statin therapy** target specific comorbidities (pre-diabetes/insulin resistance and dyslipidemia, respectively) but do not address the underlying **severe obesity**.
- While these medications are important for managing aspects of her metabolic syndrome, they are not a primary treatment for weight loss and will not lead to significant weight reduction in a patient with a **BMI of 42 kg/m²**.
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 8: Four days after undergoing a craniotomy and evacuation of a subdural hematoma, a 56-year-old man has severe pain and swelling of his right leg. He has chills and nausea. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease, and was started on hemodialysis 2 years ago. Prior to admission, his medications were insulin, enalapril, atorvastatin, and sevelamer. His temperature is 38.3°C (101°F), pulse is 110/min, and blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg. Examination shows a swollen, warm, and erythematous right calf. Dorsiflexion of the right foot causes severe pain in the right calf. The peripheral pulses are palpated bilaterally. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.1 g/dL
Leukocyte count 11,800/mm3
Platelet count 230,000/mm3
Serum
Glucose 87 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.9 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in treatment?
- A. Urokinase therapy
- B. Iliac stenting
- C. Warfarin therapy
- D. Unfractionated heparin therapy (Correct Answer)
- E. Inferior vena cava filter
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications Explanation: ***Unfractionated heparin therapy***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **deep vein thrombosis (DVT)**, including unilateral leg pain, swelling, warmth, erythema, and a positive Homan's sign (pain on dorsiflexion). The recent craniotomy places him at high risk for DVT.
- **Unfractionated heparin is the anticoagulant of choice** for this patient due to TWO critical factors:
1. **Recent craniotomy (4 days ago)**: Requires a rapidly reversible anticoagulant in case of intracranial bleeding; UFH can be reversed with protamine sulfate
2. **Chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis**: Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) is contraindicated in severe renal failure (CrCl <30 mL/min) as it is renally eliminated and increases bleeding risk. UFH is not renally cleared and can be monitored with aPTT.
*Urokinase therapy*
- **Urokinase is a thrombolytic agent** used to dissolve existing clots, primarily in cases of massive pulmonary embolism or severe DVT with limb-threatening ischemia (phlegmasia cerulea dolens).
- Given the patient's **recent craniotomy and subdural hematoma evacuation**, thrombolytic therapy is **absolutely contraindicated** due to very high risk of intracranial hemorrhage. Recent neurosurgery is a contraindication for at least 2-4 weeks.
*Iliac stenting*
- **Iliac vein stenting** is a procedure typically used to treat chronic **iliac vein compression** (e.g., May-Thurner syndrome) or chronic post-thrombotic obstruction.
- This is an **acute DVT presentation** (4 days post-op) with no indication of chronic iliac vein compression or obstruction. Stenting has no role in acute DVT management.
*Warfarin therapy*
- **Warfarin is an oral anticoagulant** used for long-term DVT treatment but has a **delayed onset of action** (requires 5-7 days to reach therapeutic INR).
- It is **not suitable for acute initial treatment** of DVT, especially in a patient requiring rapid anticoagulation. Warfarin must be overlapped with parenteral anticoagulation (heparin) initially.
- Additionally, warfarin dosing is complex in dialysis patients due to altered vitamin K metabolism.
*Inferior vena cava filter*
- An **IVC filter** is indicated for patients with DVT who have an **absolute contraindication to anticoagulation** (e.g., active bleeding, recent hemorrhagic stroke) or who develop recurrent thromboembolism despite adequate anticoagulation.
- This patient **does not have a contraindication to anticoagulation**. While he had recent neurosurgery, unfractionated heparin is safe to use with careful monitoring and is rapidly reversible if needed.
- IVC filters have significant complications (thrombosis, filter migration, IVC perforation) and should be avoided when anticoagulation is feasible.
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 9: A 37-year-old man presents to the physician. He has been overweight since childhood. He has not succeeded in losing weight despite following different diet and exercise programs over the past several years. He has had diabetes mellitus for 2 years and severe gastroesophageal reflux disease for 9 years. His medications include metformin, aspirin, and pantoprazole. His blood pressure is 142/94 mm Hg, pulse is 76/min, and respiratory rate is 14/min. His BMI is 36.5 kg/m2. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin A1C 6.6%
Serum
Fasting glucose 132 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most appropriate surgical management?
- A. No surgical management at this time
- B. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding
- C. Biliopancreatic diversion and duodenal switch (BPD-DS)
- D. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy
- E. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (Correct Answer)
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications Explanation: ***Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass***
- This patient meets criteria for bariatric surgery with a **BMI of 36.5 kg/m2** along with significant **comorbidities** such as **type 2 diabetes** and **severe GERD**.
- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is particularly effective for **diabetes remission** and is the most effective bariatric procedure for **resolving GERD**, making it the most appropriate choice given his symptoms.
*No surgical management at this time*
- The patient has a high BMI (36.5 kg/m2) with multiple obesity-related comorbidities including **diabetes mellitus** and **severe GERD** that have not improved with lifestyle changes and medication.
- Delaying surgical management would allow his obesity and related conditions to potentially worsen, despite his efforts to lose weight through diet and exercise.
*Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding*
- This procedure typically results in **less weight loss** compared to other bariatric surgeries and is less effective at resolving comorbidities like diabetes and GERD.
- It carries a higher rate of **long-term complications** such as band erosion or slippage, and would not address the patient's severe GERD effectively.
*Biliopancreatic diversion and duodenal switch (BPD-DS)*
- While BPD-DS leads to the most significant weight loss and diabetes remission, it is associated with a **higher risk of surgical complications** and **severe nutritional deficiencies**.
- Given the patient's BMI and comorbidities, a less aggressive procedure like Roux-en-Y gastric bypass offers a better risk-benefit profile, especially for GERD.
*Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy*
- Sleeve gastrectomy is an effective weight-loss procedure, but it can **worsen or induce GERD** in some patients due to changes in gastric anatomy and pressure.
- As the patient has severe GERD, this procedure would not be the optimal choice and could exacerbate his symptoms.
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications US Medical PG Question 10: A 69-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of a 1-week history of recurring black stools. On questioning, he reports fatigue and loss of appetite over the last 3 months. Twenty years ago, he underwent a partial gastrectomy for peptic ulcer disease. The patient's father died of metastatic colon cancer at the age of 57 years. He is 163 cm (5 ft 4 in) tall and weighs 55 kg (121 lb); BMI is 20.8 kg/m2. He appears chronically ill. His temperature is 36.5°C (97.7°F), pulse is 105/min, and blood pressure is 115/70 mm Hg. The conjunctiva appear pale. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. The abdomen is soft and nontender. There is a well-healed scar on the upper abdomen. His hemoglobin concentration is 10.5 g/dL and his mean corpuscular volume is 101 μm3. An upper endoscopy shows a large nodular mass on the anterior wall of the lesser curvature of the gastric stump. Biopsy samples are obtained, showing polypoid, glandular formation of irregular-shaped and fused gastric cells with intraluminal mucus, demonstrating an infiltrative growth. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Abdominopelvic CT scan (Correct Answer)
- B. Stool antigen test for H. pylori
- C. Laparoscopy
- D. Vitamin B12 assessment
- E. Treatment with PPI, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin
Bariatric surgery procedures and complications Explanation: ***Abdominopelvic CT scan***
- The biopsy findings of **polypoid, glandular formation of irregular-shaped and fused gastric cells with intraluminal mucus, demonstrating an infiltrative growth** are highly suggestive of **gastric adenocarcinoma**. An abdominopelvic CT scan is crucial for **staging** the cancer, assessing for **local invasion**, **lymph node involvement**, and **distant metastasis**.
- Given the history of **partial gastrectomy** (a risk factor for stump cancer), the macroscopic appearance on endoscopy, and the histological findings, further staging with a CT scan is essential to guide subsequent management, such as surgical planning or chemotherapy.
*Stool antigen test for H. pylori*
- While *H. pylori* is a risk factor for gastric cancer, the patient already has a **large nodular mass** and **biopsy-proven adenocarcinoma**. Testing for *H. pylori* at this stage would not change the immediate management and is **not the most appropriate next step** for a confirmed malignancy.
- Eradication therapy for *H. pylori* is typically indicated for **early-stage gastric cancer** (e.g., MALT lymphoma) or **pre-malignant lesions**, but not as an initial step for advanced or confirmed adenocarcinoma where staging is paramount.
*Laparoscopy*
- **Laparoscopy** is often performed after initial imaging (like CT) to confirm resectability, detect **peritoneal metastasis** that may not be visible on CT, and obtain samples for cytology. However, it is generally done **after CT staging** as CT provides a broader initial assessment of disease extent.
- Therefore, while laparoscopy may be a subsequent step, it is **not the most appropriate *next* step** before comprehensive imaging is completed.
*Vitamin B12 assessment*
- The patient's history of **partial gastrectomy** can lead to **vitamin B12 deficiency** due to the loss of intrinsic factor-producing parietal cells and altered absorption. The mild **macrocytic anemia** (MCV 101 μm3) supports this possibility.
- However, while important, addressing vitamin B12 deficiency is **secondary** to the immediate concern of **staging and managing the life-threatening gastric adenocarcinoma**. The primary focus must be on the cancer.
*Treatment with PPI, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin*
- This regimen is **triple therapy for *H. pylori* eradication**. As discussed, while *H. pylori* is a risk factor, the patient already has biopsy-proven gastric adenocarcinoma, and testing/treating *H. pylori* is **not the most appropriate immediate step** in this context.
- This treatment would not address the confirmed gastric cancer and would **delay definitive management** aimed at the malignancy.
More Bariatric surgery procedures and complications US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.