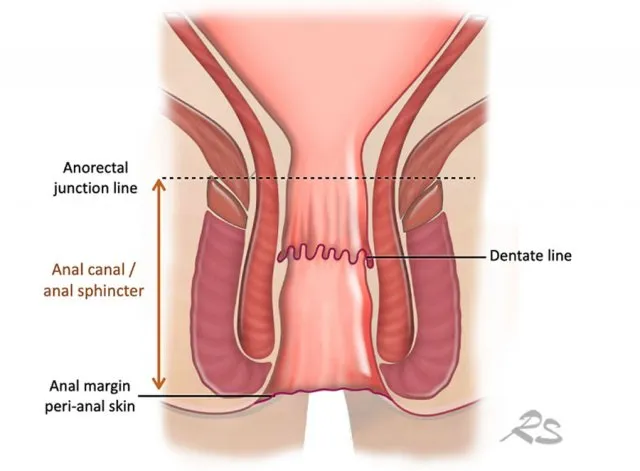
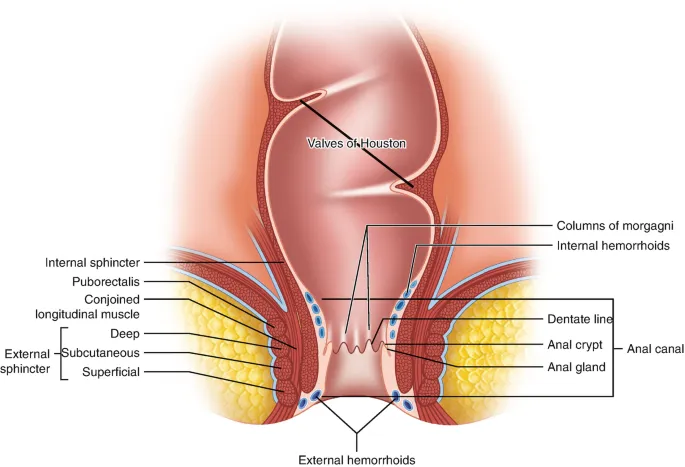
Anorectal procedures US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Anorectal procedures. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Anorectal procedures US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old woman presents to the office with complaints of intense anal pain every time she has a bowel movement. The pain has been present for the past 4 weeks, and it is dull and throbbing in nature. It is associated with mild bright red bleeding from the rectum that is aggravated during defecation. She has no relevant past medical history. When asked about her sexual history, she reports practicing anal intercourse. The vital signs include heart rate 98/min, respiratory rate 16/min, temperature 37.6°C (99.7°F), and blood pressure 110/66 mm Hg. On physical examination, the anal sphincter tone is markedly increased, and it's impossible to introduce the finger due to severe pain. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Local anal trauma (Correct Answer)
- B. Rectal prolapse and paradoxical contraction of the puborectalis muscle
- C. Inflammatory bowel disease
- D. Anorectal abscess
- E. Hemorrhoidal disease
Anorectal procedures Explanation: ***Local anal trauma***
- The patient's history of **anal intercourse**, severe **anal pain** during bowel movements, **bright red bleeding**, and a markedly **increased anal sphincter tone** with inability to perform a DRE due to pain are highly indicative of an **anal fissure** caused by local trauma.
- The dull, throbbing pain suggests associated spasm of the internal anal sphincter, a common complication of anal fissures.
*Rectal prolapse and paradoxical contraction of the puborectalis muscle*
- **Rectal prolapse** typically presents with a sensation of a mass protruding from the anus and difficulty with bowel movements, not usually intense, sharp pain and bright red bleeding.
- **Paradoxical contraction of the puborectalis muscle** (anismus) causes difficult defecation and straining but is not typically associated with acute, severe pain and bright red bleeding as primary symptoms.
*Inflammatory bowel disease*
- While IBD can cause rectal bleeding and anal pain (e.g., in Crohn's disease with perianal fistulas or fissures), the presentation here is acute and highly suggestive of a mechanical cause, without other systemic symptoms of IBD like diarrhea, weight loss, or abdominal pain.
- The **isolated acute anal pain** and bleeding linked to defecation and anal intercourse are less typical for an initial presentation of IBD without other associated symptoms.
*Anorectal abscess*
- Anorectal abscesses typically present with severe, constant, throbbing **perianal pain** that is often worse when sitting, and may be accompanied by fever, chills, and localized swelling or erythema, which are not described here.
- While an abscess might cause throbbing pain, the association with **defecation-induced pain** and **bright red bleeding** from a visible source like an anal fissure is less characteristic.
*Hemorrhoidal disease*
- Hemorrhoids often cause **painless bright red bleeding** during defecation or can cause itching and discomfort. **Thrombosed external hemorrhoids** can cause acute, severe pain but usually present with a palpable, tender nodule.
- The description of **intense, sharp anal pain** during bowel movements, increased sphincter tone, and inability to perform a digital rectal exam are more consistent with an anal fissure than typical hemorrhoidal disease.
Anorectal procedures US Medical PG Question 2: A 28-year-old woman comes to the physician with a history of bright red blood in her stools for 3 days. She has defecated once per day. She does not have fever, pain on defecation, or abdominal pain. She was treated for a urinary tract infection with levofloxacin around 3 months ago. Menses occur at regular intervals of 28–30 days and lasts 3–4 days. Her father died of colon cancer 4 years ago. Her only medication is an iron supplement. She is 162 cm (5 ft 4 in) tall and weighs 101.2 kg (223 lbs); BMI is 38.3 kg/m2. Her temperature is 36.5°C (97.7°F), pulse is 89/min, and blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg. Rectal examination shows anal skin tags. Anoscopy shows multiple enlarged bluish veins above the dentate line at 7 and 11 o'clock positions. When asked to exhale through a closed nostril a mass prolapses but spontaneously reduces when breathing normally. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Infrared coagulation
- B. Propranolol therapy
- C. Topical diltiazem
- D. Hemorrhoidectomy
- E. Docusate therapy (Correct Answer)
Anorectal procedures Explanation: ***Docusate therapy***
- The patient presents with symptoms and signs consistent with **grade II internal hemorrhoids** (prolapses with straining but spontaneously reduces) and a history of constipation (implied by iron supplementation and obesity).
- **Conservative management with stool softeners** like docusate is the first-line treatment for grade II internal hemorrhoids, promoting easier bowel movements and reducing straining, which exacerbates hemorrhoids.
- Other conservative measures include increased dietary fiber and adequate hydration.
*Infrared coagulation*
- This is a **procedural treatment** sometimes used for grade I and II internal hemorrhoids that are **refractory to conservative management**.
- It is not the most appropriate initial step. Given the patient's presentation, **conservative management should be attempted first** before considering procedural interventions.
*Propranolol therapy*
- **Propranolol** is a beta-blocker used to manage **portal hypertension** and prevent variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis.
- There is **no indication of portal hypertension** or liver disease in this patient (normal vital signs, no stigmata of chronic liver disease).
- This medication is not used in the management of hemorrhoids.
*Topical diltiazem*
- **Topical diltiazem** is a calcium channel blocker used to treat **anal fissures** by relaxing the internal anal sphincter and improving blood flow to promote healing.
- The patient's symptoms (bright red blood, **no pain on defecation**) are not consistent with an anal fissure, which typically presents with severe pain during and after bowel movements.
*Hemorrhoidectomy*
- **Hemorrhoidectomy** is a surgical procedure typically reserved for **severe (grade III or IV)** internal hemorrhoids or those unresponsive to less invasive treatments.
- The patient's hemorrhoids are grade II, which are likely to respond to conservative management, making surgery an overly aggressive initial approach.
Anorectal procedures US Medical PG Question 3: A 45-year-old woman comes to the office with a 2-week history of rectal bleeding that occurs every day with her bowel movements. She denies any pain during defecation. Apart from this, she does not have any other complaints. Her past medical history is insignificant except for 5 normal vaginal deliveries. Her vitals are a heart rate of 72/min, a respiratory rate of 15/min, a temperature of 36.7°C (98.1°F), and a blood pressure of 115/85 mm Hg. On rectovaginal examination, there is a palpable, non-tender, prolapsed mass that can be pushed back by the examiner's finger into the anal sphincter. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Rectal ulcer
- B. Anal fissure
- C. Hemorrhoids (Correct Answer)
- D. Proctitis
- E. Anorectal fistula
Anorectal procedures Explanation: ***Hemorrhoids***
- The presentation of **painless rectal bleeding** with bowel movements and a **palpable, prolapsed, reducible mass** is classic for hemorrhoids, especially common in multiparous women.
- The absence of pain and the ability to reduce the prolapsed mass are key differentiating features from other perianal conditions.
*Rectal ulcer*
- Rectal ulcers typically present with **painful defecation** and may cause blood in the stool, but are not usually associated with a reducible prolapsed mass.
- They are often associated with other inflammatory conditions or trauma, which are not described here.
*Anal fissure*
- Anal fissures are characterized by **severe pain during and after defecation** due to a tear in the anal canal lining, and the bleeding is usually bright red and minimal.
- The primary symptom is pain, which this patient explicitly denies.
*Proctitis*
- Proctitis involves **inflammation of the rectal lining**, leading to symptoms like tenesmus, urgency, and bloody or purulent discharge, often with abdominal pain.
- It does not typically present with a palpable, prolapsed, reducible anal mass.
*Anorectal fistula*
- Anorectal fistulas are abnormal tracts between the anal canal or rectum and the perianal skin, usually causing **pain, swelling, and purulent discharge**.
- While bleeding can occur, the primary symptom is drainage, and they do not present as a reducible prolapsed mass.
Anorectal procedures US Medical PG Question 4: A 34-year-old woman with no significant prior medical history presents to the clinic with several days of bloody stool. She also complains of constipation and straining, but she has no other symptoms. She has no family history of colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Her vital signs are as follows: blood pressure is 121/81 mm Hg, heart rate is 77/min, and respiratory rate is 15/min. There is no abdominal discomfort on physical exam, and a digital rectal exam reveals bright red blood. Of the following, which is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Colorectal cancer
- B. Ulcerative colitis
- C. Anal fissure
- D. External hemorrhoids
- E. Internal hemorrhoids (Correct Answer)
Anorectal procedures Explanation: ***Internal hemorrhoids***
- **Painless bright red blood** per rectum, especially with **constipation and straining**, is highly characteristic of internal hemorrhoids.
- Internal hemorrhoids are located **above the dentate line**, making them typically painless, and they often prolapse during defecation, causing bleeding.
*Colorectal cancer*
- While colorectal cancer can cause bloody stool, it is less likely in a **34-year-old woman with no family history** and no other systemic symptoms like weight loss or abdominal pain.
- The bright red blood associated with straining points away from an upper GI bleed, which is more typical of many colorectal cancers.
*Ulcerative colitis*
- Ulcerative colitis typically presents with bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and tenesmus, which are **not mentioned** in this patient's history.
- It is a chronic inflammatory condition, and the isolated symptom of bright red blood with constipation is not classic for UC.
*Anal fissure*
- An anal fissure would cause **severe pain during defecation** due to a tear in the anal canal, which is absent in this patient.
- While an anal fissure can cause bright red blood, the lack of pain makes it less likely than hemorrhoids.
*External hemorrhoids*
- **External hemorrhoids are usually painful or itchy** and located below the dentate line.
- They also can cause bleeding, but the absence of pain and bright red blood suggests internal hemorrhoids which are more likely to bleed painlessly.
Anorectal procedures US Medical PG Question 5: A 38-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of severe pain while passing stools. The stools are covered with bright red blood. He has been avoiding defecation because of the pain. Last year, he was hospitalized for pilonidal sinus surgery. He has had chronic lower back pain ever since he had an accident at his workplace 10 years ago. The patient's father was diagnosed with colon cancer at the age of 62. Current medications include oxycodone and gabapentin. He is 163 cm (5 ft 4 in) tall and weighs 100 kg (220 lb); BMI is 37.6 kg/m2. Vital signs are within normal limits. The abdomen is soft and nontender. Digital rectal examination was not performed because of severe pain. His hemoglobin is 16.3 mg/dL and his leukocyte count is 8300/mm3. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Anal sphincterotomy
- B. Colonoscopy
- C. Botulinum toxin injection
- D. Sitz baths and topical nifedipine (Correct Answer)
- E. Tract curettage
Anorectal procedures Explanation: ***Sitz baths and topical nifedipine***
- The patient's presentation of severe pain with defecation, bright red blood on stools, and avoidance of defecation is highly suggestive of an **anal fissure**.
- **Sitz baths** provide symptomatic relief by promoting muscle relaxation and increasing blood flow, while **topical nifedipine** acts as a calcium channel blocker to relax the internal anal sphincter, reducing pain and promoting healing.
*Anal sphincterotomy*
- This is a surgical procedure typically reserved for **chronic, refractory anal fissures** that have failed conservative management.
- Performing it as a first-line treatment is **premature** and carries higher risks compared to less invasive options.
*Colonoscopy*
- While the patient has a family history of colon cancer, the clinical presentation with **severe anal pain** and **bright red blood** primarily points to an anal fissure.
- A colonoscopy is generally indicated for evaluating suspicion of malignancy or other colonic pathology, not as an initial step for acute, localized anal pain attributed to a likely fissure.
*Botulinum toxin injection*
- **Botulinum toxin injection** is a treatment for anal fissures, similar to calcium channel blockers, by relaxing the internal anal sphincter.
- It is typically considered when topical treatments have failed, but before surgical intervention, making it not the very first step in management.
*Tract curettage*
- **Tract curettage** is a procedure primarily used for treating **anal fistulas** or **pilonidal cysts/sinuses**, which are different conditions from an anal fissure.
- The patient had pilonidal sinus surgery previously, but his current symptoms are consistent with an anal fissure, not a recurrence of pilonidal disease or an anal fistula.
Anorectal procedures US Medical PG Question 6: An institutionalized 65-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of abdominal pain and distension for 12 hours. The pain was acute in onset and is a cramping-type pain associated with nausea, vomiting, and constipation. He has a history of chronic constipation and has used laxatives for years. There is no history of inflammatory bowel disease in his family. He has not been hospitalized recently. There is no recent history of weight loss or change in bowel habits. On physical examination, the patient appears ill. The abdomen is distended with tenderness mainly in the left lower quadrant and is tympanic on percussion. The blood pressure is 110/79 mm Hg, heart rate is 100/min, the respiratory rate is 20/min, and the temperature is 37.2°C (99.0°F). The CBC shows an elevated white blood cell count. The plain abdominal X-ray is shown in the accompanying image. What is the most likely cause of his condition?
- A. Sigmoid volvulus (Correct Answer)
- B. Intussusception
- C. Acute diverticulitis
- D. Toxic megacolon
- E. Colon cancer
Anorectal procedures Explanation: ***Sigmoid volvulus***
- The patient’s symptoms of acute **abdominal pain**, distension, and cramping strongly indicate **sigmoid volvulus**, often seen in chronic constipation and institutionalized patients.
- Physical examination revealing **tenderness in the left lower quadrant** and a tympanic abdomen supports the diagnosis of bowel obstruction typically caused by **volvulus**.
*Intussusception*
- Generally presents with **currant jelly stools** and is more common in children; the acute symptoms here are less typical.
- It often involves a **lead point** or associated conditions like **polyps** or tumors, which are not indicated in this case.
*Acute diverticulitis*
- Usually associated with **localized pain** in the left lower quadrant but would present with fever and changes in bowel habits, which the patient lacks.
- Typically shows **peritoneal signs** and may have complications like abscess or perforation, not indicated here.
*Toxic megacolon*
- Commonly associated with underlying **inflammatory bowel disease** or infections, not indicated in this patient with no recent history of **IBD**.
- Symptoms would include severe **diarrhea** and abdominal pain, which do not fit the current acute cramping and constipation pattern.
*Colon cancer*
- While it can cause abdominal symptoms, it presents more insidiously with **weight loss** or **change in bowel habits**, none of which are reported here.
- The acute presentation and findings do not align with a malignancy, which would often be chronic in nature.
Anorectal procedures US Medical PG Question 7: The following image shows \qquad and the test being performed is \qquad ?
- A. Meckel's Diverticulum, Technetium scan (Correct Answer)
- B. Carcinoid Tumor, Octreo-scan
- C. Extra-adrenal Pheochromocytoma, PET DOPA scan
- D. Adrenal Pheochromocytoma, MIBG scan
- E. Intestinal Lymphoma, PET-CT scan
Anorectal procedures Explanation: ***Meckel's Diverticulum, Technetium scan***
- The image on the left shows a **true diverticulum** of the small intestine, consistent with a **Meckel's diverticulum**, which is a remnant of the vitelline duct. The arrow indicates the diverticulum.
- The images on the right show a **Technetium-99m pertechnetate scan**, demonstrating focal uptake (indicated by the arrows) in the lower abdomen, consistent with **ectopic gastric mucosa** typically found in a Meckel's diverticulum.
*Carcinoid Tumor, Octreo-scan*
- A **carcinoid tumor** is a neuroendocrine tumor, and while it can occur in the small bowel, its appearance on gross examination would be different from the diverticulum shown.
- An **OctreoScan** (using somatostatin analogs) is used to detect neuroendocrine tumors like carcinoids due to their somatostatin receptors, but the scan image does not show a pattern consistent with this.
*Extra-adrenal Pheochromocytoma, PET DOPA scan*
- An **extra-adrenal pheochromocytoma** is a tumor of chromaffin cells outside the adrenal gland, and it would not appear as an intestinal diverticulum.
- A **PET DOPA scan** (using 18F-DOPA) is used to localize pheochromocytomas, but the imaging pattern shown is not characteristic of this type of scan for such a tumor.
*Adrenal Pheochromocytoma, MIBG scan*
- An **adrenal pheochromocytoma** is a tumor of the adrenal gland, which is located in the retroperitoneum, completely distinct from the intestinal structure shown on the left.
- An **MIBG scan** (using meta-iodobenzylguanidine) is used to localize pheochromocytomas because MIBG is selectively taken up by chromaffin cells, but the images do not represent an MIBG scan or an adrenal pathology.
*Intestinal Lymphoma, PET-CT scan*
- **Intestinal lymphoma** can occur in the small bowel but would typically present as a mass lesion or infiltrative process, not as an isolated diverticulum.
- A **PET-CT scan** using fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) is used for staging and evaluating lymphoma due to increased glucose metabolism in malignant cells, but the imaging pattern shown does not demonstrate the diffuse FDG uptake characteristic of PET-CT.
Anorectal procedures US Medical PG Question 8: All the following statements regarding this condition are true except:
- A. It is remnant of vitello intestinal duct
- B. Broad-base of this defect should be amputated at its base (Correct Answer)
- C. This condition can be a lead point for ileoileal or ileocolic intussusception
- D. This condition is mostly asymptomatic
- E. It is the most common congenital anomaly of the gastrointestinal tract
Anorectal procedures Explanation: ***Broad-base of this defect should be amputated at its base***
- This statement is incorrect. While a broad-based diverticulum (like Meckel's diverticulum shown) may require surgical resection, it should not be simply amputated at its base. Resection should involve removing the diverticulum along with a small segment of the adjacent ileum to reduce the risk of recurrence or complications due to heterotopic mucosa.
- Simple amputation at a broad base can lead to **retained heterotopic mucosa**, increasing the risk of subsequent complications such as ulceration, bleeding, or perforation.
*It is remnant of vitello intestinal duct*
- This statement is correct. The image displays a **Meckel's diverticulum**, which is a **true diverticulum** representing a persistent portion of the embryonic **vitelline duct** (also known as the omphalomesenteric duct).
- This duct normally connects the developing midgut to the yolk sac during fetal development and typically obliterates by the seventh week of gestation.
*This condition can be a lead point for ileoileal or ileocolic intussusception*
- This statement is correct. A Meckel's diverticulum can act as a **lead point** for **intussusception**, where one segment of the intestine telescopes into an adjacent segment.
- The diverticulum's mobility and potential for invagination make it a common cause of intussusception, especially in children, leading to bowel obstruction.
*This condition is mostly asymptomatic*
- This statement is correct. Meckel's diverticulum is typically **asymptomatic** in a majority of individuals who have it.
- While it can cause complications like bleeding, inflammation (diverticulitis), obstruction, or perforation, these complications occur in only a small percentage of affected individuals, demonstrating its generally silent nature.
*It is the most common congenital anomaly of the gastrointestinal tract*
- This statement is correct. Meckel's diverticulum is indeed the **most common congenital anomaly of the gastrointestinal tract**, occurring in approximately **2% of the population**.
- It follows the **"rule of 2s"**: affects 2% of population, located approximately 2 feet from the ileocecal valve, is typically 2 inches long, and only 2% become symptomatic.
Anorectal procedures US Medical PG Question 9: A 34-year-old male patient complains of sudden severe epigastric pain along with vomiting, tenderness, guarding. On examination there is abdominal rigidity and tachycardia. He admits to taking NSAIDs for pain. The radiological examination of the patient is given below. All statements given below are true except?
- A. Tenderness on per-rectal examination
- B. Blumberg sign is positive
- C. Dullness over flanks is observed
- D. Pain often radiates to groin (Correct Answer)
- E. Obliteration of liver dullness on percussion
Anorectal procedures Explanation: ***Pain often radiates to groin***
- The clinical presentation (sudden severe epigastric pain, vomiting, tenderness, guarding, rigidity, tachycardia, NSAID use) and the radiological imaging showing **free air under the diaphragm** are highly suggestive of **perforated viscus**, likely a perforated peptic ulcer.
- Pain from a perforated ulcer typically **radiates to the shoulder** (due to diaphragmatic irritation) or generalizes throughout the abdomen, but **not typically to the groin**.
*Tenderness on per-rectal examination*
- **Tenderness on per-rectal examination** can be present in cases of generalized peritonitis, as the inflammation can extend to the pelvic peritoneum.
- This finding is consistent with the diffuse inflammation caused by a perforated viscus.
*Blumberg sign is positive*
- **Blumberg sign**, also known as **rebound tenderness**, is a classic sign of **peritoneal irritation** or peritonitis.
- Given the severe abdominal pain, guarding, and rigidity, peritonitis is highly likely in this patient, making a positive Blumberg sign expected.
*Dullness over flanks is observed*
- **Dullness on percussion over the flanks** indicates the presence of **fluid** in the peritoneal cavity (ascites).
- In a perforated viscus, gastric or intestinal contents, along with inflammatory exudates, can accumulate in the dependent areas of the abdomen, leading to dullness in the flanks.
Anorectal procedures US Medical PG Question 10: Identify the tube shown in the image:
- A. Ryle's tube
- B. Malecot's catheter
- C. Sengstaken-Blakemore catheter (Correct Answer)
- D. Foley's catheter
- E. Minnesota tube
Anorectal procedures Explanation: ***Sengstaken-Blakemore catheter***
- This catheter is identifiable by its **triple lumen** and **two inflatable balloons** (one esophageal, one gastric), designed to compress bleeding esophageal varices.
- The image clearly displays these characteristic balloons and multiple ports, distinguishing it from other tubes.
*Minnesota tube*
- A Minnesota tube is similar to the Sengstaken-Blakemore catheter but has **four lumens** instead of three, with an additional **esophageal aspiration port** above the esophageal balloon.
- While structurally similar, the specific lumen configuration visible in the image is consistent with the Sengstaken-Blakemore design.
*Ryle's tube*
- A Ryle's tube is a simple **nasogastric tube** with a single lumen, primarily used for feeding or gastric decompression.
- It does not feature the complex balloon system seen in the image.
*Malecot's catheter*
- A Malecot's catheter is a **self-retaining catheter** with a mushroom-shaped tip, typically used for drainage (e.g., nephrostomy).
- Its design is simple and lacks the inflatable balloons and multiple lumens characteristic of the depicted device.
*Foley's catheter*
- A Foley's catheter is a **urinary catheter** with a single inflatable balloon for retention in the bladder and two lumens (one for drainage, one for balloon inflation).
- While it has an inflatable balloon, its overall structure and intended use are distinct from the esophageal-gastric balloon system shown.
More Anorectal procedures US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.