Gastrointestinal Surgery

On this page
🔪 The Gastrointestinal Surgeon's Arsenal: Mastering the Abdominal Theater
Gastrointestinal surgery demands more than technical skill-it requires pattern recognition that distinguishes surgical emergencies from medical mimics, decision algorithms that balance intervention against observation, and an understanding of how cutting into one organ reverberates through entire physiologic systems. You'll master the frameworks that transform anatomic knowledge into operative judgment, learning when a scalpel saves lives and when restraint does. Through systematic approaches to the surgical abdomen, you'll build the discriminating mind that sees beyond symptoms to underlying pathology, integrating minimally invasive techniques with time-tested open approaches. This is where anatomy, physiology, and clinical reasoning converge into decisive action.
📌 Remember: STOMACH - Surgical Technique Optimizes Mortality And Complications Healing - Every GI procedure requires understanding of 4 key principles: vascular supply preservation, tension-free anastomoses, adequate margins, and contamination control
The surgical approach hierarchy follows anatomical complexity:
-
Upper GI Procedures (Mortality: 1-5%)
- Esophageal resections: Ivor Lewis, McKeown, transhiatal
- Gastric procedures: subtotal gastrectomy, total gastrectomy, sleeve gastrectomy
- Lymph node dissection: D1 (perigastric) vs D2 (extended)
- Margin requirements: ≥5cm proximal, ≥2cm distal for adenocarcinoma
-
Hepatobiliary Operations (Mortality: 2-8%)
- Liver resections: anatomic vs non-anatomic
- Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple): 18-25% morbidity rate
- Blood loss average: 800-1200mL
- Operating time: 4-7 hours
⭐ Clinical Pearl: The "Critical View of Safety" during laparoscopic cholecystectomy requires identification of 3 structures: hepatocystic triangle cleared of tissue, 2 arteries only entering gallbladder, and liver bed clearly visible. Achieving this view reduces bile duct injury rates from 0.6% to 0.3%.
- Colorectal Procedures (Mortality: 1-4%)
- Right hemicolectomy: ileocolic, right colic, middle colic vessel ligation
- Low anterior resection: total mesorectal excision (TME) technique
- Anastomotic leak rates: 5-15% for rectal anastomoses
- Protective ileostomy reduces clinical leak impact by 67%
💡 Master This: Surgical margins determine oncologic outcomes - ≥2cm for colon cancer, ≥1cm circumferential for rectal cancer. Positive margins increase local recurrence from 5% to 25% and reduce 5-year survival by 15-20%.
| Procedure Category | Mortality Rate | Major Morbidity | Length of Stay | Key Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esophagectomy | 3-5% | 40-50% | 10-14 days | Anastomotic leak, pneumonia |
| Whipple | 2-4% | 35-45% | 8-12 days | Pancreatic fistula, DGE |
| Liver Resection | 1-3% | 20-30% | 5-8 days | Bleeding, liver failure |
| Colectomy | 1-2% | 15-25% | 4-7 days | Anastomotic leak, SSI |
| Bariatric Surgery | 0.1-0.5% | 5-10% | 1-2 days | Leak, bleeding, obstruction |
Understanding tissue planes and fascial anatomy enables precise dissection with minimal blood loss. The "holy plane" of TME maintains circumferential margin integrity while preserving autonomic nerves for functional outcomes.
Connect these foundational principles through Minimally Invasive Mastery to understand how laparoscopic and robotic approaches transform traditional open techniques.
🔪 The Gastrointestinal Surgeon's Arsenal: Mastering the Abdominal Theater
🤖 Minimally Invasive Mastery: The Precision Revolution
📌 Remember: PORTS - Position Optimally Reduces Tissue Stress - Trocar placement follows the "baseball diamond" configuration: camera at umbilicus, working ports 8-10cm apart at 60-90 degree angles for optimal triangulation
The pneumoperitoneum physiology creates unique challenges:
-
CO₂ Insufflation Parameters
- Pressure: 12-15 mmHg (vs atmospheric 760 mmHg)
- Flow rate: 1-2 L/min for initial insufflation
- Absorption rate: 200-400 mL/min through peritoneum
- Peak serum CO₂: 45-60 mmHg (normal 35-45 mmHg)
- Respiratory compensation: increased minute ventilation by 20-30%
-
Hemodynamic Changes
- Cardiac output: decreased 20-30% due to venous compression
- Systemic vascular resistance: increased 15-25%
- Renal blood flow: reduced 25-40% with oliguria risk
- Trendelenburg position: additional 10-15% cardiac output reduction
- Reverse Trendelenburg: improved venous return but reduced cerebral perfusion
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Robotic surgery provides 7 degrees of freedom vs 4 degrees for laparoscopic instruments, with tremor filtration and motion scaling (3:1 to 5:1 ratios). This precision reduces conversion rates for complex procedures like low anterior resection from 8-12% to 3-5%.
- Advanced Laparoscopic Techniques
- Single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS): cosmetic advantage but increased difficulty
- Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES): experimental applications
- Fluorescence-guided surgery: indocyanine green for perfusion assessment
- Anastomotic leak reduction: 40-50% with perfusion guidance
- Lymph node identification: enhanced detection of sentinel nodes
💡 Master This: Energy devices determine tissue effects - monopolar electrocautery (cutting/coagulation), bipolar devices (precise hemostasis), ultrasonic scalpels (protein denaturation at 55-100°C), and advanced bipolar (LigaSure) with feedback-controlled energy delivery for vessels up to 7mm diameter.
| Technology | Advantages | Limitations | Learning Curve | Cost Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Laparoscopy | Proven, versatile | 2D vision, tremor | 20-30 cases | 1x baseline |
| 3D Laparoscopy | Depth perception | Fatigue, weight | 10-15 cases | 1.5x baseline |
| Robotic Surgery | Precision, ergonomics | Cost, setup time | 50-75 cases | 3-4x baseline |
| Fluorescence | Real-time perfusion | Equipment needs | 5-10 cases | 1.2x baseline |
| SILS | Single scar | Instrument collision | 40-50 cases | 1.3x baseline |
Conversion criteria to open surgery include uncontrolled bleeding (>500mL/hour), inability to progress after 2 hours, unclear anatomy with injury risk, or hemodynamic instability. Conversion rates vary: cholecystectomy 2-5%, colectomy 5-15%, esophagectomy 10-20%.
Master these minimally invasive principles through Pattern Recognition Frameworks to develop systematic approaches for complex surgical decision-making.
🤖 Minimally Invasive Mastery: The Precision Revolution
🎯 Pattern Recognition Frameworks: The Surgical Decision Matrix
Surgical pattern recognition follows the "See-Think-Act" paradigm, where clinical presentation patterns trigger systematic evaluation algorithms leading to evidence-based interventions. Master surgeons recognize >95% of surgical scenarios within 30 seconds of clinical presentation.
📌 Remember: DECIDE - Define problem Establish criteria Consider alternatives Identify solutions Develop action Evaluate outcome - Every surgical decision requires 6-step systematic analysis with quantifiable decision points
Emergency Surgery Recognition Patterns:
-
Acute Abdomen Triage (See X, Think Y)
- Rigid abdomen + hypotension → Think perforation (90% specificity)
- RLQ pain + fever + leukocytosis >15,000 → Think appendicitis (85% sensitivity)
- Epigastric pain + amylase >1000 → Think pancreatitis (95% specificity)
- Ranson's criteria ≥3 → severe pancreatitis (mortality 15-20%)
- APACHE II >8 → ICU monitoring required
- CT severity index >6 → necrotizing pancreatitis risk
-
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Patterns
- Hematemesis + melena → upper GI source (95% accuracy)
- Hematochezia + hemodynamic stability → lower GI source (80% accuracy)
- Shock index >1.0 → massive bleeding requiring immediate intervention
- Blood loss estimation: Class III (30-40% loss) = tachycardia + hypotension
- Transfusion trigger: hemoglobin <7 g/dL in stable patients
- Massive transfusion protocol: >10 units PRBC in 24 hours
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Pneumoperitoneum on upright chest X-ray has 85% sensitivity for perforation, but CT scan increases sensitivity to >95%. Free fluid without free air suggests ischemia or early perforation requiring serial examinations every 4-6 hours.
Elective Surgery Selection Criteria:
- Oncologic Resection Patterns
- T1-T2 lesions + no nodal involvement → minimally invasive approach (equivalent oncologic outcomes)
- T3-T4 lesions + adjacent organ involvement → multivisceral resection (R0 resection priority)
- Metastatic disease + symptomatic primary → palliative resection vs bypass
- Performance status ≥2 → poor surgical candidate (mortality >10%)
- Life expectancy <6 months → non-operative management preferred
- Oligometastatic disease → consider aggressive resection (5-year survival 20-40%)
💡 Master This: Physiologic scoring systems predict surgical risk - ASA class, Charlson comorbidity index, and frailty scores combine to estimate 30-day mortality. ASA III patients have 3-5x higher mortality than ASA I-II, while frailty scores >5 increase complications by 200-300%.
| Clinical Scenario | Recognition Pattern | Decision Threshold | Action Required | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Cholangitis | Charcot's triad + fever | Bilirubin >4 mg/dL | ERCP within 24h | >90% resolution |
| Bowel Obstruction | Distension + no flatus | CT: transition point | Conservative 48h | 70% resolution |
| Anastomotic Leak | Fever + abdominal pain | POD 5-7 onset | CT with contrast | 85% detection |
| Bleeding Ulcer | Hematemesis + melena | Forrest Ia-IIb | Endoscopic therapy | >95% hemostasis |
| Incarcerated Hernia | Irreducible + pain | >6 hours duration | Emergent repair | >98% success |
Risk Stratification Algorithms guide perioperative management:
-
Cardiac Risk Assessment (Revised Cardiac Risk Index)
- High-risk surgery + ≥2 risk factors → cardiology consultation
- Functional capacity <4 METs → stress testing consideration
- Active cardiac conditions → delay elective surgery
-
Pulmonary Risk Factors
- COPD + FEV1 <1.5L → increased pneumonia risk (15-25%)
- Smoking within 8 weeks → double complication rate
- Upper abdominal surgery → 50% reduction in vital capacity
Connect these recognition patterns through Systematic Discrimination to master the subtle differences between similar clinical presentations.
🎯 Pattern Recognition Frameworks: The Surgical Decision Matrix
🔬 Systematic Discrimination: The Differential Surgeon's Mind
📌 Remember: COMPARE - Clinical Onset Morphology Pattern Associated Risk Evidence - Every differential requires 6-parameter analysis with specific threshold values for diagnostic certainty
Acute Abdominal Pain Discrimination:
- Right Lower Quadrant Pain Syndromes
-
Appendicitis: Alvarado score ≥7 (sensitivity 85%, specificity 76%)
- Migration pattern: periumbilical → RLQ in 12-24 hours
- Laboratory: WBC 10,000-18,000 with left shift >75%
- CT findings: appendiceal wall thickening >2mm, periappendiceal fat stranding
-
Cecal Diverticulitis: Asian predominance (80% vs 5% Western)
- Age distribution: younger patients (mean age 40 vs appendicitis 28)
- CT findings: cecal wall thickening, pericolic fat stranding
- Conservative success: 85-90% with antibiotics alone
-
Crohn's Terminal Ileitis: chronic symptoms >3 months (vs acute appendicitis)
- Laboratory: elevated CRP, low albumin <3.5 g/dL
- CT findings: terminal ileal thickening >3mm, mesenteric lymphadenopathy
- Endoscopic confirmation: cobblestone mucosa, skip lesions
-
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Appendiceal perforation occurs in 20-30% of cases >48 hours duration, increasing morbidity 5-fold and length of stay from 1-2 days to 5-7 days. Pediatric patients have higher perforation rates (35-40%) due to delayed diagnosis.
Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding Discrimination:
- Peptic Ulcer vs Variceal Bleeding
-
Peptic Ulcer Disease: H. pylori positive in 60-70%, NSAID use in 20-30%
- Endoscopic stigmata: Forrest classification predicts rebleeding risk
- Forrest Ia (spurting): 90% rebleed without intervention
- Forrest IIa (visible vessel): 50% rebleed risk
- Forrest IIb (adherent clot): 25% rebleed risk
-
Esophageal Varices: Portal hypertension with HVPG >12 mmHg
- Child-Pugh Class C: mortality 30-50% per bleeding episode
- MELD score >18: 6-week mortality >20%
- Variceal size: large varices (>5mm) have 30% annual bleeding risk
-
| Discriminating Feature | Peptic Ulcer | Variceal Bleeding | Mallory-Weiss | Boerhaave |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onset Pattern | Gradual | Sudden massive | Post-vomiting | Post-retching |
| Hemodynamic Impact | Variable | Severe | Mild-moderate | Severe |
| Chest Pain | Rare | Rare | Occasional | Severe |
| Pneumomediastinum | Never | Never | Rare | Pathognomonic |
| Mortality Risk | 2-5% | 15-30% | <1% | 20-40% |
- Small Bowel vs Large Bowel Obstruction
-
Small Bowel: crampy pain every 4-5 minutes, early vomiting
- CT findings: dilated loops >3cm, air-fluid levels
- Conservative management: successful 70-80% if partial obstruction
- Surgical timing: complete obstruction requires operation within 24-48 hours
-
Large Bowel: constant pain, late vomiting, marked distension
- Cecal diameter >9cm: perforation risk requires immediate decompression
- Sigmoid volvulus: coffee bean sign on plain radiographs
- Endoscopic detorsion: successful 85-90% for sigmoid volvulus
-
💡 Master This: Closed-loop obstruction creates surgical emergency - competent ileocecal valve with large bowel obstruction causes cecal distension with perforation risk when diameter >12cm. Mortality increases from 5% to 30% with perforation.
Inflammatory vs Infectious Discrimination:
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease vs Infectious Colitis
-
Ulcerative Colitis: continuous involvement, rectal sparing rare
- Laboratory: p-ANCA positive in 60-70%
- Endoscopy: friable mucosa, loss of vascular pattern
- Histology: crypt abscesses, surface epithelial damage
-
Crohn's Disease: skip lesions, transmural inflammation
- Laboratory: ASCA positive in 50-60%
- Endoscopy: cobblestone appearance, linear ulcerations
- Complications: strictures 30%, fistulas 20%, abscesses 15%
-
Connect these discrimination skills through Treatment Algorithms to master evidence-based surgical intervention strategies.
🔬 Systematic Discrimination: The Differential Surgeon's Mind
⚖️ Treatment Algorithms: The Evidence-Based Surgical Playbook
📌 Remember: PROTOCOL - Patient Risk Outcome Timing Options Complications Objectives Long-term - Every algorithm requires 7-factor analysis with quantified decision thresholds for optimal outcomes
Emergency Surgery Treatment Algorithms:
- Acute Cholangitis Management (Tokyo Guidelines 2018)
-
Grade I (mild): antibiotics alone, elective ERCP within 72 hours
- Success rate: 85-90% with conservative management
- Antibiotic choice: piperacillin-tazobactam or ciprofloxacin + metronidazole
-
Grade II (moderate): urgent ERCP within 24 hours
- Biliary drainage success: >95% with endoscopic approach
- Stone extraction: complete clearance in 80-85% of cases
-
Grade III (severe): immediate resuscitation + emergent drainage
- Mortality without drainage: >50% within 48 hours
- Percutaneous drainage: alternative when ERCP unavailable
- Surgical drainage: last resort with mortality 15-25%
-
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Mirizzi syndrome complicates 2-3% of cholecystectomies, where impacted cystic artery stone causes common hepatic duct stricture. Type II-IV lesions require hepaticojejunostomy with success rates >90% and morbidity 15-20%.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding Treatment Protocols:
-
Upper GI Bleeding Algorithm
-
Hemodynamic instability: 2 large-bore IVs, type and crossmatch 6 units
- Massive transfusion protocol: 1:1:1 ratio (PRBC:FFP:platelets)
- Tranexamic acid: reduces mortality 15% in massive bleeding
-
Endoscopic intervention timing:
- High-risk patients: endoscopy within 12 hours (mortality benefit)
- Low-risk patients: endoscopy within 24 hours (adequate outcomes)
- Rockall score ≥8: mortality >40%, consider surgery early
-
-
Lower GI Bleeding Management
- Hemodynamically stable: colonoscopy after prep (diagnostic yield 85-95%)
- Ongoing bleeding: CT angiography if bleeding rate >0.3 mL/min
- Angiographic embolization: success 85-95%, rebleeding 10-20%
- Surgical intervention: segmental resection vs subtotal colectomy
- Blind subtotal colectomy: mortality 10-15%, avoid if possible
| Bleeding Severity | Hemoglobin Drop | Transfusion Need | Intervention Timing | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | <2 g/dL | None | Outpatient | >95% |
| Moderate | 2-4 g/dL | 1-2 units | 24-48 hours | 85-90% |
| Severe | >4 g/dL | >4 units | <12 hours | 70-80% |
| Massive | >6 g/dL | >6 units | Immediate | 50-70% |
- Colorectal Cancer Management
-
Stage I-II: surgical resection alone (5-year survival 85-95%)
-
Stage III: surgery + adjuvant chemotherapy (5-year survival 65-75%)
- FOLFOX regimen: oxaliplatin + 5-FU + leucovorin for 6 months
- Capecitabine monotherapy: alternative for elderly patients
-
Stage IV: multidisciplinary approach with selective resection
- Resectable metastases: 5-year survival 40-50% with complete resection
- Unresectable disease: palliative chemotherapy (median survival 24-30 months)
-
💡 Master This: Neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer (T3-T4 or N+) includes chemoradiation followed by surgery 6-8 weeks later. Pathologic complete response occurs in 15-25% and improves 5-year survival from 75% to >90%.
Emergency Bowel Obstruction Protocol:
Adhesive Small Bowel Obstruction management follows conservative trial for 24-48 hours with success rates 70-80% for partial obstruction. Complete obstruction requires surgical intervention within 24 hours to prevent bowel necrosis and perforation.
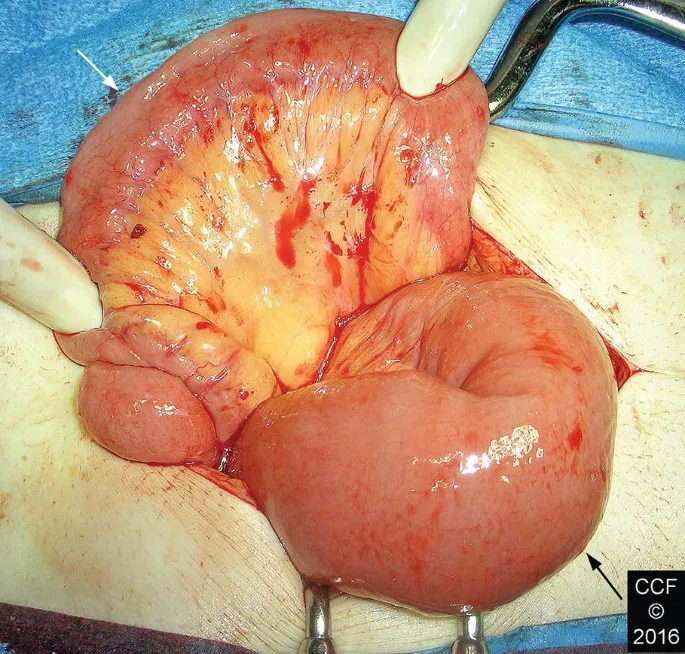
Connect these evidence-based algorithms through Multi-System Integration to understand complex interactions between surgical interventions and physiologic responses.
⚖️ Treatment Algorithms: The Evidence-Based Surgical Playbook
🔗 Multi-System Integration: The Physiologic Symphony
📌 Remember: SYSTEMS - Surgical Yields Systemic Trauma Evoking Multiple Stress - Every major operation triggers 6 physiologic cascades: inflammatory, coagulation, cardiovascular, pulmonary, renal, and metabolic responses requiring integrated management
Cardiovascular-Gastrointestinal Integration:
-
Hemodynamic Response Patterns
-
Hypovolemic shock: blood loss >20% causes compensatory tachycardia
- Class I (0-15% loss): normal vital signs, minimal intervention
- Class II (15-30% loss): tachycardia >100, crystalloid resuscitation
- Class III (30-40% loss): hypotension, blood transfusion required
- Class IV (>40% loss): profound shock, massive transfusion protocol
-
Cardiac output optimization: goal-directed therapy improves outcomes
- Stroke volume variation <13%: adequate preload
- Central venous pressure: poor predictor of fluid responsiveness
- Passive leg raise test: >10% stroke volume increase predicts fluid responsiveness
-
-
Splanchnic Circulation Dynamics
- Mesenteric blood flow: reduces 50-70% during major surgery
- Anastomotic healing: requires adequate perfusion (>30 mmHg tissue oxygen)
- Vasopressor effects: norepinephrine preferred over dopamine for splanchnic preservation
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols reduce length of stay by 2-3 days and complications by 25-30% through multimodal optimization: preoperative carbohydrate loading, goal-directed fluid therapy, multimodal analgesia, and early mobilization.
Pulmonary-Surgical Integration:
-
Respiratory Complications Prevention
- Upper abdominal surgery: 50% reduction in functional residual capacity
- Diaphragmatic dysfunction: persists 7-10 days postoperatively
- Pneumonia risk factors: age >70, smoking, COPD, prolonged surgery >3 hours
- Incentive spirometry: reduces pneumonia 40-50% when used hourly
- Continuous positive airway pressure: prevents atelectasis in high-risk patients
-
Ventilatory Management Strategies
- Protective ventilation: tidal volume 6-8 mL/kg, PEEP 5-10 cmH₂O
- Recruitment maneuvers: prevent atelectasis during prolonged procedures
- Extubation criteria: spontaneous breathing trial with pressure support ≤8 cmH₂O
Renal-Metabolic Integration:
- Acute Kidney Injury Prevention
- Perioperative AKI: occurs 5-15% of major surgery patients
- Risk factors: age >65, diabetes, hypertension, contrast exposure
- Fluid optimization: maintains renal perfusion without fluid overload
- Nephrotoxin avoidance: NSAIDs, aminoglycosides, contrast agents
- Biomarker monitoring: NGAL, cystatin C for early detection
| System | Normal Response | Pathologic Response | Intervention | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Mild tachycardia | Shock, arrhythmias | Fluid/vasopressors | >90% |
| Pulmonary | Reduced FRC | Pneumonia, ARDS | Lung protection | 85-90% |
| Renal | Oliguria <24h | AKI, dialysis need | Fluid optimization | 80-85% |
| GI | Ileus 24-48h | Prolonged ileus | Early feeding | 75-80% |
| Immune | SIRS response | Sepsis, organ failure | Source control | 70-85% |
-
Metabolic Response to Surgery
- Hypermetabolic state: energy expenditure increases 20-30%
- Protein catabolism: muscle breakdown 150-200 g/day
- Glucose intolerance: stress hyperglycemia in 80-90% of patients
- Target glucose: 140-180 mg/dL in critically ill patients
- Insulin therapy: reduces infection risk 25-30% with tight control
-
Early Enteral Nutrition Benefits
- Gut barrier function: maintains intestinal integrity
- Immune function: preserves gut-associated lymphoid tissue
- Anastomotic healing: improves collagen synthesis and tensile strength
- Feeding initiation: within 24 hours when hemodynamically stable
- Feeding advancement: goal rate 24-48 hours postoperatively
- Complications reduction: pneumonia 40%, wound infections 30%
💡 Master This: Gut-brain axis dysfunction after major surgery causes postoperative ileus lasting 3-5 days. Multimodal management includes early feeding, prokinetic agents (metoclopramide), peripheral opioid antagonists (alvimopan), and chewing gum to stimulate vagal tone.
Coagulation-Surgical Integration:
- Hemostatic Balance Management
- Surgical trauma: activates coagulation cascade and fibrinolysis
- Massive transfusion: dilutional coagulopathy after >1 blood volume replacement
- Thromboembolic prophylaxis: mechanical + pharmacologic reduces VTE 60-70%
- Sequential compression devices: start intraoperatively
- Pharmacologic prophylaxis: enoxaparin 40 mg daily or heparin 5000 units TID
- Extended prophylaxis: 4 weeks for cancer surgery patients
Connect these multi-system concepts through Rapid Mastery Tools to develop practical frameworks for immediate clinical application.
🔗 Multi-System Integration: The Physiologic Symphony
🎯 Rapid Mastery Tools: The Surgical Command Center
📌 Remember: MASTER - Memorize Algorithms Systematize Thresholds Execute Rapidly - Surgical expertise requires 6 core competencies: pattern recognition, threshold memorization, algorithm execution, complication anticipation, resource optimization, and outcome prediction
Essential Surgical Arsenal - Critical Numbers:
-
Hemodynamic Thresholds
- Shock index >1.0: massive bleeding requiring immediate intervention
- Mean arterial pressure <65 mmHg: organ hypoperfusion threshold
- Central venous pressure 8-12 mmHg: optimal preload range
- Cardiac index <2.2 L/min/m²: inadequate cardiac output
- Mixed venous oxygen saturation <70%: tissue hypoxia indicator
-
Laboratory Decision Points
- Hemoglobin <7 g/dL: transfusion threshold for stable patients
- Platelet count <50,000: bleeding risk for major surgery
- INR >1.5: coagulopathy requiring correction
- Creatinine increase >0.3 mg/dL: acute kidney injury definition
- Lactate >4 mmol/L: severe tissue hypoxia requiring immediate action
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Damage control surgery principles apply when physiologic exhaustion occurs: hypothermia <35°C, acidosis pH <7.2, coagulopathy INR >1.5. Abbreviated surgery with planned reoperation reduces mortality from 60% to 30% in severely injured patients.
Rapid Assessment Frameworks:
-
AMPLE History (Emergency Surgery)
- Allergies: drug allergies affecting anesthetic choice
- Medications: anticoagulants, steroids, cardiac drugs
- Past medical history: cardiac, pulmonary, renal disease
- Last meal: aspiration risk assessment
- Events: mechanism of injury or symptom onset
-
SBAR Communication (Surgical Handoffs)
- Situation: patient condition and immediate concerns
- Background: relevant history and current medications
- Assessment: clinical findings and working diagnosis
- Recommendation: proposed plan and urgency level
| Emergency Scenario | Recognition Time | Decision Time | Action Time | Success Window |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemorrhagic Shock | <30 seconds | <60 seconds | <5 minutes | Golden hour |
| Bowel Perforation | <2 minutes | <5 minutes | <30 minutes | 6-8 hours |
| Anastomotic Leak | <5 minutes | <15 minutes | <2 hours | 24-48 hours |
| Pulmonary Embolism | <1 minute | <3 minutes | <15 minutes | 2-4 hours |
| Septic Shock | <3 minutes | <10 minutes | <1 hour | 6 hours |
-
Surgical Site Infection Prevention (Bundle Approach)
- Antibiotic prophylaxis: within 60 minutes of skin incision
- Skin preparation: chlorhexidine-alcohol superior to povidone-iodine
- Normothermia: maintain >36°C throughout procedure
- Glucose control: <180 mg/dL in perioperative period
- Hair removal: clippers only, avoid razors
-
Venous Thromboembolism Prevention
- Risk assessment: Caprini score or Rogers score
- Mechanical prophylaxis: sequential compression devices for all patients
- Pharmacologic prophylaxis: enoxaparin 40 mg daily for moderate-high risk
- Extended prophylaxis: 4 weeks for cancer surgery and major procedures
💡 Master This: Surgical timeout verification prevents wrong-site surgery (1 in 112,000 procedures) through universal protocol: patient identity, surgical site marking, procedure verification, implant confirmation, and antibiotic timing checked by entire surgical team.
Postoperative Monitoring Priorities:
-
First 24 Hours Critical Parameters
- Hourly vital signs: early warning score calculation
- Urine output: >0.5 mL/kg/hour indicates adequate perfusion
- Pain scores: <4/10 with multimodal analgesia
- Nausea/vomiting: prophylaxis reduces PONV 60-70%
- Surgical site: bleeding, hematoma, infection signs
-
Early Warning Score Triggers
- Respiratory rate >24 or <8: respiratory compromise
- Oxygen saturation <92%: hypoxemia requiring intervention
- Systolic BP <90 or >200: hemodynamic instability
- Heart rate >130 or <40: cardiac issues
- Temperature >38.5°C: infection or inflammatory response
Resource Optimization Matrix:
-
Operating Room Efficiency
- Turnover time: <30 minutes between cases
- First case start: within 15 minutes of scheduled time
- Equipment availability: >95% for scheduled procedures
- Cancellation rate: <5% for elective surgery
-
ICU Utilization Criteria
- Planned ICU: major hepatobiliary, esophagectomy, Whipple procedures
- Unplanned ICU: hemodynamic instability, respiratory failure, major complications
- Step-down criteria: stable vital signs >12 hours, minimal vasopressor support
This comprehensive surgical command center provides the rapid-access tools necessary for expert-level decision-making in high-stakes gastrointestinal surgery, enabling optimal patient outcomes through systematic excellence.
🎯 Rapid Mastery Tools: The Surgical Command Center
Practice Questions: Gastrointestinal Surgery
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 27-year-old female has a history of periodic bloody diarrhea over several years. Colonoscopy shows sigmoid colon inflammation, and the patient complains of joint pain in her knees and ankles. You suspect inflammatory bowel disease. Which of the following would suggest a diagnosis of Crohn disease:













