Massive transfusion protocols US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Massive transfusion protocols. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Massive transfusion protocols US Medical PG Question 1: A 36-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department 20 minutes after being involved in a high-speed motor vehicle collision. On arrival, she is unconscious. Her pulse is 140/min, respirations are 12/min and shallow, and blood pressure is 76/55 mm Hg. 0.9% saline infusion is begun. A focused assessment with sonography shows blood in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. Her hemoglobin concentration is 7.6 g/dL and hematocrit is 22%. The surgeon decided to move the patient to the operating room for an emergent explorative laparotomy. Packed red blood cell transfusion is ordered prior to surgery. However, a friend of the patient asks for the transfusion to be held as the patient is a Jehovah's Witness. The patient has no advance directive and there is no documentation showing her refusal of blood transfusions. The patient's husband and children cannot be contacted. Which of the following is the most appropriate next best step in management?
- A. Administer hydroxyethyl starch
- B. Transfusion of packed red blood cells (Correct Answer)
- C. Consult hospital ethics committee
- D. Administer high-dose iron dextran
Massive transfusion protocols Explanation: ***Transfusion of packed red blood cells***
- This patient is in **hemorrhagic shock** (tachycardia, hypotension, low hemoglobin, and hematocrit with evidence of active bleeding), requiring emergent blood transfusion to prevent irreversible organ damage and death.
- In an **emergency setting** with an **unconscious patient** and **no documented refusal** of blood products, the principle of **presumed consent** for life-saving treatment takes precedence, especially when next of kin cannot be reached.
*Administer hydroxyethyl starch*
- **Colloids** like hydroxyethyl starch can temporarily increase intravascular volume but do not provide oxygen-carrying capacity, which is critically needed for a patient with severe anemia and hemorrhagic shock.
- While useful for volume expansion, it is **not a substitute for blood products** in severe bleeding and can have adverse effects such as kidney injury.
*Consult hospital ethics committee*
- Consulting an ethics committee is appropriate for **complex ethical dilemmas** when there is time for deliberation and the patient's life is not in immediate danger.
- In this acute, life-threatening emergency, **delaying treatment** to consult an ethics committee would jeopardize the patient's life and is not appropriate.
*Administer high-dose iron dextran*
- **Iron dextran** is used to treat iron-deficiency anemia and works by supporting red blood cell production over several days to weeks.
- It is **ineffective in acute hemorrhagic shock** where immediate restoration of oxygen-carrying capacity is required.
Massive transfusion protocols US Medical PG Question 2: A 35-year-old patient is brought into the emergency department post motor vehicle crash. Stabilization of the patient in the trauma bay requires endotracheal intubation. The patient has a laceration on the femoral artery from shrapnel and seems to have lost large quantities of blood. The patient is transfused with 13 units of packed red blood cells. His vitals are T 96.5, HR 150, BP 90/40. Even with the direct pressure on the femoral artery, the patient continues to bleed. Results of labs drawn within the last hour are pending. Which of the following is most likely to stop the bleeding in this patient?
- A. Normal saline
- B. Fresh frozen plasma and platelets (Correct Answer)
- C. Whole blood
- D. Dextrose
- E. Cryoprecipitate
Massive transfusion protocols Explanation: ***Fresh frozen plasma and platelets***
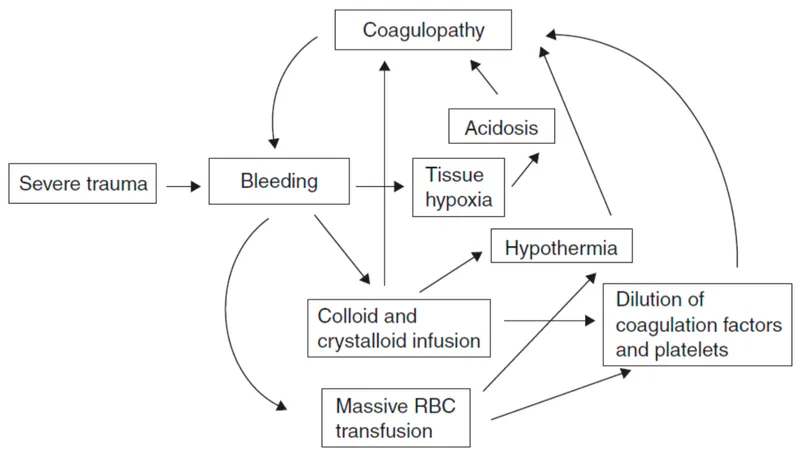
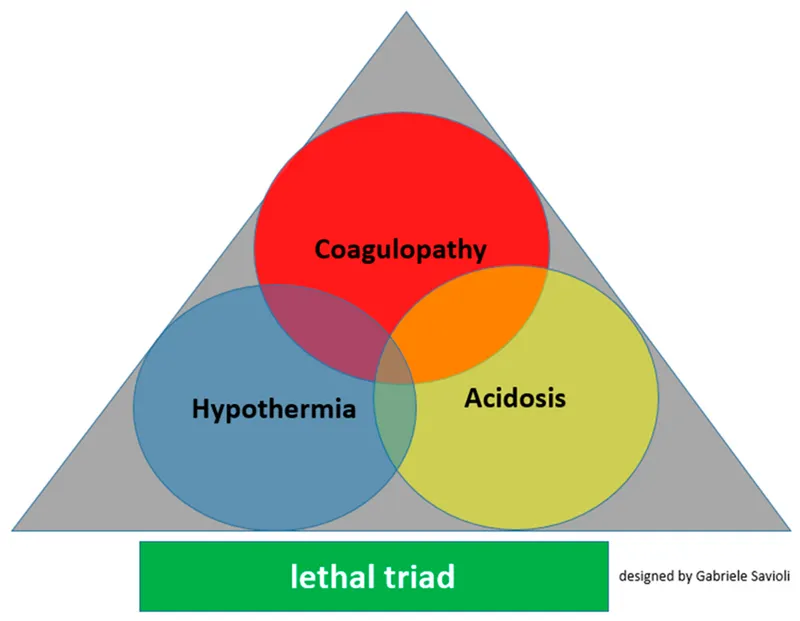
- This patient is experiencing **dilutional coagulopathy** due to massive transfusion of packed red blood cells, which lack clotting factors and platelets.
- **Fresh frozen plasma (FFP)** provides essential clotting factors, while **platelets** directly address thrombocytopenia, both crucial for **hemostasis**.
- This represents **standard component therapy** readily available in emergency departments.
*Normal saline*
- Administering normal saline would further dilute the remaining clotting factors and platelets, potentially **worsening the coagulopathy**.
- While essential for **volume resuscitation**, it does not provide any clotting components needed to stop bleeding.
*Whole blood*
- While **whole blood** contains red blood cells, plasma, and platelets in physiologic ratios, it is **not readily available** in most civilian trauma centers.
- Modern practice uses **component therapy** (FFP + platelets + PRBCs) which is more widely accessible and allows for targeted resuscitation.
- Low-titer O whole blood programs exist in some centers but are not universally available.
*Dextrose*
- **Dextrose solutions** primarily provide free water and glucose, used for hydration and hypoglycemia.
- It has **no hemostatic properties** and would further dilute clotting factors, exacerbating the bleeding.
*Cryoprecipitate*
- **Cryoprecipitate** is rich in **fibrinogen, factor VIII, factor XIII, and von Willebrand factor**.
- While useful for specific factor deficiencies or when fibrinogen is critically low in massive transfusions, it **does not replace all clotting factors or platelets** comprehensively as FFP and platelets would.
- Typically used as **adjunctive therapy** when fibrinogen levels are known to be low.
Massive transfusion protocols US Medical PG Question 3: A 33-year-old pilot is transported to the emergency department after she was involved in a cargo plane crash during a military training exercise in South Korea. She is conscious but confused. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. Physical examination shows numerous lacerations and ecchymoses over the face, trunk, and upper extremities. The lower extremities are cool to the touch. There is continued bleeding despite the application of firm pressure to the sites of injury. The first physiologic response to develop in this patient was most likely which of the following?
- A. Increased respiratory rate
- B. Increased capillary refill time
- C. Decreased systolic blood pressure
- D. Decreased urine output
- E. Increased heart rate (Correct Answer)
Massive transfusion protocols Explanation: ***Increased heart rate***
- **Tachycardia** is often the first physiological response to **hypovolemia** (due to hemorrhage, such as that stemming from multiple lacerations). The heart attempts to compensate for reduced circulating blood volume by increasing its pumping rate.
- This sympathetic nervous system response aims to maintain **cardiac output** and tissue perfusion as **blood pressure** and **venous return** start to fall.
*Increased respiratory rate*
- An increased respiratory rate, or **tachypnea**, typically occurs later as the body attempts to compensate for decreased oxygen delivery and metabolic acidosis that can result from sustained hypoperfusion and shock.
- While significant, it usually follows the initial hemodynamic adjustments of the heart.
*Increased capillary refill time*
- **Increased capillary refill time** indicates impaired peripheral perfusion and is a sign of more significant **hypovolemic shock**, often occurring after initial compensatory mechanisms have been activated.
- This reflects **peripheral vasoconstriction**, a later compensatory mechanism, rather than the very first physiological response.
*Decreased systolic blood pressure*
- **Decreased systolic blood pressure** (hypotension) is a later sign of shock and indicates a failure of the body's compensatory mechanisms to maintain adequate blood volume and perfusion, often reflecting a loss of more than 30-40% of blood volume.
- The body initially tries to maintain blood pressure through increased heart rate and vasoconstriction before it drops.
*Decreased urine output*
- **Decreased urine output** (oliguria) is a renal compensatory mechanism in response to reduced renal perfusion and increased antidiuretic hormone (ADH) release, aiming to conserve fluid.
- This response takes time to manifest and is not typically the very first physiological change after acute blood loss.
Massive transfusion protocols US Medical PG Question 4: A 67-year-old man with a history of chronic alcoholism presents to the emergency department after a suicide attempt. The patient was found in his apartment by his grandson with wrist lacerations. He was rushed to the emergency department and was resuscitated en route. The patient has a past medical history of ischemic heart disease and depression. His pulse is barely palpable and he is not responding to questions coherently. His temperature is 98.2°F (36.8°C), blood pressure is 107/48 mmHg, pulse is 160/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. After fluid resuscitation and wound care, his blood pressure improves to 127/55 mmHg. On physical exam, the patient complains of numbness surrounding his mouth and pain in the location of the lacerations of his wrists. Which of the following best describes the laboratory findings in this patient?
- A. Hyperkalemia
- B. Increased free iron
- C. No lab abnormalities
- D. Hypomagnesemia (Correct Answer)
- E. Hypocalcemia
Massive transfusion protocols Explanation: ***Hypomagnesemia***
- **Chronic alcoholism** is a significant risk factor for hypomagnesemia due to decreased dietary intake, increased renal excretion, and gastrointestinal losses.
- Clinical signs such as **numbness around the mouth** (circumoral paresthesia), **tachycardia**, and **agitation/confusion** can be manifestations of severe hypomagnesemia, which can also predispose to arrhythmias.
*Hyperkalemia*
- While electrolyte imbalances are common in alcoholism, **hyperkalemia** is less typical in this acute presentation unless associated with other complications like **renal failure** or certain medications.
- The patient's symptoms (numbness, tachycardia) are not classic for hyperkalemia; hyperkalemia often presents with **muscle weakness** or **cardiac arrhythmias** (peaked T waves, widened QRS).
*Increased free iron*
- **Increased free iron** is typically associated with conditions like **hemochromatosis** or acute iron poisoning, neither of which is suggested by the patient's history or symptoms.
- Chronic alcoholism can lead to iron overload in some cases, but this is usually chronic and does not manifest acutely with these neurological or cardiac symptoms.
*No lab abnormalities*
- Given the patient's history of **chronic alcoholism**, presentation with **tachycardia**, altered mental status, and circumoral paresthesia, it is highly unlikely that there would be no laboratory abnormalities.
- Alcoholism frequently leads to significant **electrolyte disturbances** and nutritional deficiencies, making "no lab abnormalities" an improbable finding.
*Hypocalcemia*
- While **hypocalcemia** can cause circumoral paresthesia, it is often secondary to **hypomagnesemia** in alcoholic patients.
- **Hypocalcemia** also typically presents with stronger signs of neuromuscular irritability like **tetany**, **Chvostek's sign**, or **Trousseau's sign**, which are not explicitly mentioned.
Massive transfusion protocols US Medical PG Question 5: A 69-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department because of fatigue and lethargy for 5 days. She has also had weakness and nausea for the last 3 days. She has sarcoidosis, major depressive disorder, and hypertension. She had a stroke 5 years ago. Current medications include aspirin, nifedipine, prednisolone, fluoxetine, and rosuvastatin, but she has not taken any of her medications for 7 days due to international travel. Her temperature is 36.1°C (96.9°F), pulse is 95/min, and blood pressure is 85/65 mm Hg. She is lethargic but oriented. Examination shows no other abnormalities. Her hemoglobin concentration is 13.4 g/dL and leukocyte count is 9,600/mm3. Both serum cortisol and ACTH levels are decreased. This patient is most likely to have which of the following additional laboratory abnormalities?
- A. Hyperglycemia
- B. Hyperkalemia
- C. Hyponatremia (Correct Answer)
- D. Hypokalemia
- E. Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis
Massive transfusion protocols Explanation: ***Hyponatremia***
- This patient has **secondary adrenal insufficiency** due to **HPA axis suppression** from chronic prednisolone use, precipitated by abrupt withdrawal after 7 days without medication.
- **Both decreased cortisol and ACTH** confirm secondary (central) adrenal insufficiency, distinguishing it from primary adrenal insufficiency where ACTH would be elevated.
- **Hyponatremia** develops due to **cortisol deficiency** impairing free water excretion, leading to dilutional hyponatremia—a hallmark laboratory finding in adrenal insufficiency.
- Clinical features include **fatigue, lethargy, hypotension, nausea, and weakness**, consistent with adrenal crisis.
*Hyperglycemia*
- While **glucocorticoids** cause hyperglycemia, **cortisol deficiency** in adrenal insufficiency leads to **impaired gluconeogenesis** and a tendency toward **hypoglycemia**, not hyperglycemia.
- The patient's presentation with hypotension and weakness is consistent with adrenal crisis, not hyperglycemia.
*Hyperkalemia*
- **Hyperkalemia** is characteristic of **primary adrenal insufficiency** (Addison's disease) due to **aldosterone deficiency** affecting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
- In **secondary adrenal insufficiency**, the hypothalamic-pituitary axis is suppressed but the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system remains intact**, so aldosterone secretion is preserved and significant hyperkalemia does not occur.
*Hypokalemia*
- **Hypokalemia** is not a typical feature of adrenal insufficiency and is more commonly associated with diuretic use, primary hyperaldosteronism, or other conditions not present in this case.
- The patient's condition reflects cortisol deficiency with preserved aldosterone function.
*Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis*
- **Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis** occurs in conditions like **renal tubular acidosis** or **diarrhea**, but is not a direct or common consequence of secondary adrenal insufficiency.
- The acute presentation with hypotension and electrolyte disturbance (hyponatremia) is the primary metabolic derangement in this case.
Massive transfusion protocols US Medical PG Question 6: A 55-year-old man with known coronary artery disease presents to the ED with epigastric pain, worsening fatigue, and melena. He takes aspirin and rosuvastatin, but took ibuprofen over the past two weeks for lower back pain. He denies nausea, vomiting, hematemesis, chest pain, fever, and weight loss. Sitting blood pressure is 100/70 mmHg and pulse is 90/min, but standing blood pressure is 85/60 mmHg and pulse is 110/min. Airway is patent. His hands feel cold and clammy. Abdominal exam confirms epigastric pain, but no rebound tenderness or guarding. Despite 2 liters of lactated Ringer's, the blood pressure and pulse have not changed. What hemoglobin (Hb) threshold should be considered if packed red blood cell (pRBC) transfusion is ordered in this patient?
- A. < 10
- B. threshold does not matter
- C. < 9
- D. < 7
- E. < 8 (Correct Answer)
Massive transfusion protocols Explanation: ***< 8***
- This patient presents with signs of **hemodynamic instability** (orthostasis, cold extremities, persistent hypotension despite fluid resuscitation) and active upper gastrointestinal bleeding (melena, epigastric pain, recent NSAID use).
- In patients with **hemodynamic instability** due to acute blood loss, the transfusion threshold is generally higher, at **Hb < 8 g/dL**, to ensure adequate oxygen delivery, especially in the setting of coronary artery disease.
*< 10*
- A transfusion threshold of **Hb < 10 g/dL** is typically reserved for patients with more severe conditions like **unstable angina**, active myocardial ischemia, or when severe symptoms of anemia persist despite an Hb > 8 g/dL.
- While this patient has coronary artery disease, his immediate need for transfusion is driven by acute blood loss and instability, not solely anemic angina.
*threshold does not matter*
- This statement is incorrect as transfusion decisions are based on specific **hemoglobin thresholds** and clinical context to optimize patient outcomes and avoid unnecessary transfusions.
- Ignoring thresholds could lead to either undertransfusion (risking organ damage) or overtransfusion (risking complications like TACO or TRALI).
*< 9*
- An Hb threshold of **< 9 g/dL** might be considered in some scenarios of acute bleeding, but with clear signs of **hemodynamic instability** and severe symptoms, an Hb of 8 g/dL or less is a more commonly accepted trigger.
- The combination of ongoing bleeding, significant orthostasis, and cold extremities points to a more urgent need for correction.
*< 7*
- A transfusion threshold of **Hb < 7 g/dL** is generally applied to hemodynamically stable patients without significant comorbidities, as demonstrated in the TRICC trial.
- This patient is **hemodynamically unstable** and has significant comorbidity (coronary artery disease), warranting a higher transfusion threshold.
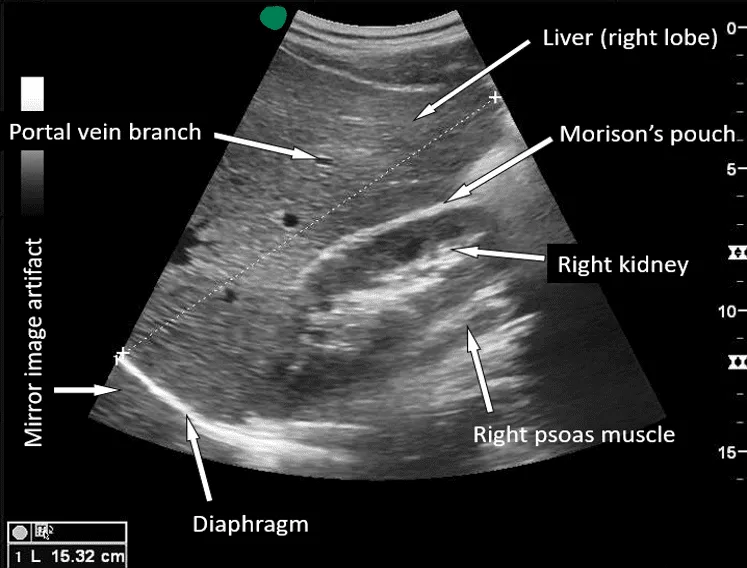
Massive transfusion protocols US Medical PG Question 7: A 27-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by emergency medical services. The patient was an unrestrained passenger in a head-on collision that occurred 15 minutes ago and is currently unresponsive. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 60/33 mmHg, pulse is 180/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 95% on room air. A FAST exam demonstrates fluid in Morrison’s pouch. Laboratory values are drawn upon presentation to the ED and sent off. The patient is started on IV fluids and an initial trauma survey is started. Twenty minutes later, his blood pressure is 95/65 mmHg, and his pulse is 110/min. The patient is further stabilized and is scheduled for emergency surgery. Which of the following best represents this patient’s most likely initial laboratory values?
- A. Hemoglobin: 10 g/dL, Hematocrit: 30%, MCV: 110 µm^3
- B. Hemoglobin: 19 g/dL, Hematocrit: 55%, MCV: 95 µm^3
- C. Hemoglobin: 7 g/dL, Hematocrit: 21%, MCV: 75 µm^3
- D. Hemoglobin: 11 g/dL, Hematocrit: 33%, MCV: 88 µm^3 (Correct Answer)
- E. Hemoglobin: 15 g/dL, Hematocrit: 45%, MCV: 90 µm^3
Massive transfusion protocols Explanation: ***Hemoglobin: 11 g/dL, Hematocrit: 33%, MCV: 88 µm^3***
- The patient experienced significant trauma and is experiencing **hemorrhagic shock**, as evidenced by his initial **hypotension** (BP 60/33 mmHg), **tachycardia** (pulse 180/min), and positive **FAST exam** for fluid in Morrison's pouch, indicating intra-abdominal bleeding.
- The initial hemoglobin and hematocrit could be mildly decreased due to acute blood loss, but significant drops are often *not immediately apparent* as plasma volume has not yet moved into the intravascular compartment to dilute the remaining red blood cells. A hemoglobin of 11 g/dL and hematocrit of 33% are consistent with **acute blood loss** before significant hemodilution occurs. MCV of 88 µm^3 is within the normal range for **normocytic anemia** seen in acute hemorrhage.
*Hemoglobin: 10 g/dL, Hematocrit: 30%, MCV: 110 µm^3*
- While a hemoglobin of 10 g/dL and hematocrit of 30% are consistent with anemia due to blood loss, an **MCV of 110 µm^3** (macrocytic) is not typically seen in acute hemorrhage.
- Macrocytic anemia usually results from conditions like **B12 or folate deficiency**, alcoholism, or liver disease, which are not suggested by the acute traumatic scenario.
*Hemoglobin: 19 g/dL, Hematocrit: 55%, MCV: 95 µm^3*
- This indicates **polycythemia** (abnormally high red blood cell count), which is the opposite of what would be expected in a patient experiencing acute hemorrhagic shock.
- These values would suggest conditions like **polycythemia vera** or severe dehydration, which are not relevant in this acute trauma setting.
*Hemoglobin: 7 g/dL, Hematocrit: 21%, MCV: 75 µm^3*
- While a hemoglobin of 7 g/dL and hematocrit of 21% represent significant anemia consistent with major blood loss, these values are typically seen *later* as **hemodilution** occurs, or in cases of chronic blood loss.
- An **MCV of 75 µm^3** (microcytic) is generally indicative of **iron deficiency anemia** or thalassemia, which develops over time and is not characteristic of acute traumatic blood loss.
*Hemoglobin: 15 g/dL, Hematocrit: 45%, MCV: 90 µm^3*
- These values are within the **normal range** for hemoglobin and hematocrit, which would not be expected in a patient presenting with signs of **hemorrhagic shock** and a positive FAST exam indicating significant internal bleeding.
- This would suggest either very minor blood loss or that the values were taken before any bleeding had occurred or before hemodilution had a chance to manifest.
Massive transfusion protocols US Medical PG Question 8: A 24-year-old male is brought in by fire rescue after being the restrained driver in a motor vehicle accident. There was a prolonged extraction. At the scene, the patient was GCS 13. The patient was boarded and transported. In the trauma bay, vitals are T 97.2°F, HR 132 bpm, BP 145/90 mmHg, RR 22/min, and O2 Sat 100%. ABCs are intact with a GCS of 15, and on secondary survey you note the following (Figure F). FAST exam is positive at Morrison's pouch. Abdominal exam shows exquisite tenderness to palpation with rebound and guarding. Which of the following radiographs is most likely to be present in this patient?
- A. Radiograph C (Correct Answer)
- B. Radiograph B
- C. Radiograph D
- D. Radiograph A
- E. Radiograph E
Massive transfusion protocols Explanation: ***Radiograph C***
- This radiograph displays a **ruptured spleen** with significant intrasplenic and perisplenic hemorrhage, depicted by contrast extravasation and fluid collection. The patient's presentation with a positive **FAST exam at Morrison's pouch**, exquisite abdominal tenderness, rebound, and guarding strongly indicates significant **intra-abdominal bleeding**, which is consistent with active hemorrhage from a ruptured organ like the spleen.
- The patient's **tachycardia (HR 132 bpm)** despite stable blood pressure suggests compensated shock due to blood loss, further supporting the presence of a severe hemorrhagic injury.
- Splenic injury is one of the most common solid organ injuries in blunt abdominal trauma from motor vehicle accidents.
*Radiograph B*
- This radiograph depicts a **pelvic fracture**, which can cause significant blood loss but does not directly explain the positive FAST exam at **Morrison's pouch**, which specifically indicates fluid in the hepatorenal recess of the peritoneal cavity.
- While pelvic fractures are common in motor vehicle accidents, the abdominal findings of exquisite tenderness, rebound, and guarding point more towards an **intra-abdominal organ injury** with peritoneal irritation rather than solely a pelvic injury.
- Pelvic hematomas are typically **retroperitoneal** and would not cause peritoneal signs.
*Radiograph D*
- This radiograph shows a **renal injury** with hemorrhage, which accounts for retroperitoneal bleeding. However, renal injuries typically do not result in a positive FAST exam at **Morrison's pouch** because the fluid tends to collect in the retroperitoneum rather than the peritoneal cavity.
- While significant, renal hemorrhage would not fully explain the diffuse **peritoneal signs** like rebound and guarding across the abdomen.
- The kidneys are retroperitoneal organs, so isolated renal injuries do not typically cause hemoperitoneum.
*Radiograph A*
- This radiograph shows a **liver laceration**, which can cause a positive FAST exam and intra-abdominal hemorrhage. Liver injuries are also common in blunt abdominal trauma.
- However, in the context of this patient's presentation, **splenic rupture** is more likely given the specific clinical findings. Morrison's pouch (hepatorenal recess) can collect blood from either liver or splenic injuries due to gravitational flow.
- The degree of peritoneal irritation and hemodynamic changes suggest a more extensive hemorrhagic injury pattern consistent with splenic rupture.
*Radiograph E*
- This radiograph shows a **bowel injury** that might demonstrate free air or bowel wall thickening. While bowel injuries can occur in trauma, they typically present with **pneumoperitoneum** (free air) rather than the fluid collection seen on FAST exam.
- Primary hemorrhage from hollow viscus injury is less common and less severe than solid organ injuries.
- The combination of **hemodynamic instability markers** (tachycardia) and clear peritoneal signs with positive FAST for fluid points more definitively to a significant solid organ injury with active bleeding rather than hollow viscus injury.
Massive transfusion protocols US Medical PG Question 9: A 35-year-old man arrives at the emergency department within minutes after a head-on motor vehicle accident. He suffered from blunt abdominal trauma, several lacerations to his face as well as lacerations to his upper and lower extremities. The patient is afebrile, blood pressure is 45/25 mmHg and pulse is 160/minute. A CBC is obtained and is most likely to demonstrate which of the following?
- A. Hb 17 g/dL, Hct 20%
- B. Hb 15 g/dL, Hct 45% (Correct Answer)
- C. Hb 5 g/dL, Hct 30%
- D. Hb 20 g/dL, Hct 60%
- E. Hb 5 g/dL, Hct 20%
Massive transfusion protocols Explanation: ***Hb 15 g/dL, Hct 45%***
- This option represents **normal hemoglobin and hematocrit values**, which are expected in the **initial minutes following acute hemorrhage**.
- In acute blood loss, **whole blood is lost** (both RBCs and plasma together), so the **concentration of RBCs remains unchanged** initially.
- **Hemodilution has not yet occurred**, as there hasn't been enough time for fluid shifts from the extravascular to the intravascular space to dilute the blood.
- This is a **critical teaching point**: early CBC values can be **falsely reassuring** and don't reflect the severity of hemorrhagic shock.
*Hb 17 g/dL, Hct 20%*
- This option shows a **medically implausible combination** - the normal Hb:Hct ratio is approximately **1:3**, so an Hb of 17 g/dL should correspond to an Hct of approximately 51%, not 20%.
- This combination cannot occur physiologically and does not represent any stage of acute blood loss.
*Hb 5 g/dL, Hct 30%*
- This shows an **incorrect Hb:Hct ratio** (6:1 instead of the expected 3:1) - if Hb is 5 g/dL, the Hct should be approximately 15%, not 30%.
- While severe anemia can occur with massive blood loss, this would only be apparent **hours after injury** once hemodilution from fluid shifts occurs, not within minutes.
- The implausible ratio makes this medically incorrect.
*Hb 20 g/dL, Hct 60%*
- These values represent **polycythemia** (abnormally high red blood cell counts), which is the opposite of what would be expected after acute traumatic blood loss.
- The Hb:Hct ratio is appropriate (1:3), but the elevated values suggest chronic hypoxemia, dehydration, or myeloproliferative disorders - not acute hemorrhage.
*Hb 5 g/dL, Hct 20%*
- This shows an **incorrect Hb:Hct ratio** (4:1 instead of the expected 3:1) - if Hb is 5 g/dL, the Hct should be approximately 15%, not 20%.
- Even if we accept these as severe anemia values, they would only be seen **several hours after injury** when sufficient time has passed for fluid shifts and hemodilution to occur, not within minutes of the trauma.
Massive transfusion protocols US Medical PG Question 10: A 58-year-old cirrhotic man with ascites undergoes large volume paracentesis (6 liters removed). Four hours later, he becomes hypotensive (BP 80/50 mmHg) and tachycardic (HR 115/min). Labs show: Cr 2.1 mg/dL (baseline 1.0), Na+ 128 mEq/L, Hct 38%. What is the most appropriate immediate management?
- A. 5% albumin 6-8 grams per liter of ascites removed (Correct Answer)
- B. Normal saline bolus 2 liters
- C. Octreotide and midodrine for hepatorenal syndrome
- D. Vasopressors to maintain blood pressure
- E. Re-infusion of filtered ascitic fluid
Massive transfusion protocols Explanation: ***5% albumin 6-8 grams per liter of ascites removed***
- This patient is experiencing **post-paracentesis circulatory dysfunction (PPCD)**, characterized by hypotension and **acute kidney injury** (doubled creatinine) following a large volume paracentesis (>5L).
- Administration of **intravenous albumin** is the gold standard treatement to expand the **effective arterial blood volume** and prevent further deterioration into hepatorenal syndrome.
*Normal saline bolus 2 liters*
- In cirrhotic patients, **crystalloids** are less effective as they rapidly redistribute into the **interstitial space** (third-spacing) and can worsen ascites/edema.
- Saline does not provide the **oncotic pressure** required to counteract the splanchnic vasodilation typical of PPCD.
*Octreotide and midodrine for hepatorenal syndrome*
- While these agents are used for **Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS)**, the immediate priority in post-procedure hypotension is **volume expansion** to correct the circulatory dysfunction.
- These medications are typically reserved for patients who do not respond to **volume expansion with albumin** or meet specific criteria for type 1 HRS.
*Vasopressors to maintain blood pressure*
- Vasopressors like **norepinephrine** are generally considered after fluid resuscitation with **albumin** has failed to restore hemodynamic stability.
- Using pressors alone ignores the underlying **intravascular volume deficit** caused by the fluid shift after paracentesis.
*Re-infusion of filtered ascitic fluid*
- This is not a standard or recommended clinical practice due to risks of **infection**, **coagulopathy**, and lack of evidence for efficacy.
- The specific requirement in this pathology is **concentrated albumin** to maintain oncotic pressure, which ascitic fluid does not provide efficiently.
More Massive transfusion protocols US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.