Fluid and electrolyte management

On this page
💧 The Fluid Command Center: Mastering Your Body's Hydraulic System
You'll master the art and science of fluid and electrolyte management by understanding how your body maintains its delicate hydraulic balance, recognizing subtle signs of imbalance before they become critical, and deploying precise replacement strategies tailored to each clinical scenario. This lesson builds your confidence from foundational physiology through advanced critical care integration, transforming abstract lab values and vital signs into actionable clinical decisions that directly impact patient outcomes.
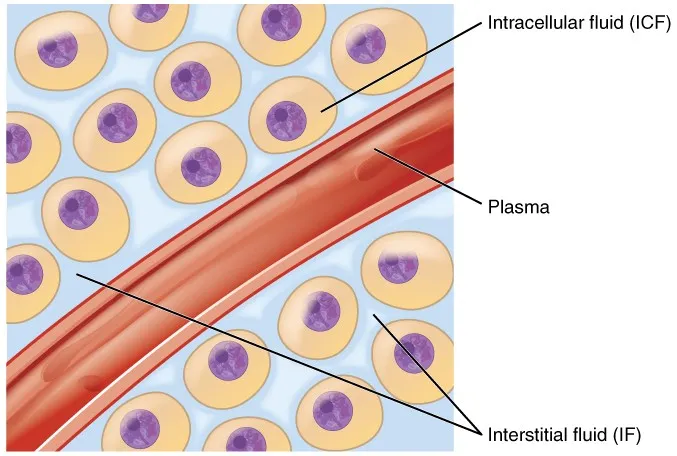
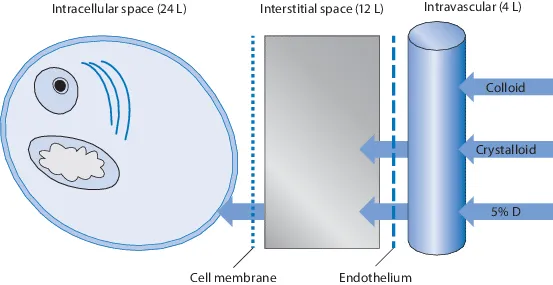
The human body operates as a sophisticated hydraulic system where 60% of total body weight consists of water in a 70kg adult (42 liters total). This fluid distributes across three critical compartments: intracellular fluid (28L, 67%), interstitial fluid (11L, 26%), and plasma volume (3L, 7%). Each compartment maintains distinct electrolyte compositions that determine cellular function and hemodynamic stability.
📌 Remember: "60-40-20 Rule" - 60% total body water, 40% intracellular, 20% extracellular (with 15% interstitial, 5% plasma)
- Intracellular Compartment (ICF)
- Volume: 28 liters in 70kg adult
- Primary cation: K+ (140 mEq/L)
- Primary anion: Phosphate and proteins
- Maintains cellular metabolism
- Controls enzyme function
- Extracellular Compartment (ECF)
- Interstitial fluid: 11 liters
- Na+ concentration: 145 mEq/L
- Cl- concentration: 110 mEq/L
- Plasma volume: 3 liters
- Contains 7g/dL proteins
- Oncotic pressure: 25 mmHg
- Interstitial fluid: 11 liters
| Compartment | Volume (L) | Na+ (mEq/L) | K+ (mEq/L) | Cl- (mEq/L) | Protein (g/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | 3 | 140 | 4 | 105 | 7.0 |
| Interstitial | 11 | 145 | 4 | 115 | 0.2 |
| Intracellular | 28 | 10 | 140 | 10 | 16.0 |
💡 Master This: Starling forces govern fluid movement - hydrostatic pressure (32 mmHg arterial, 15 mmHg venous) pushes fluid out while oncotic pressure (25 mmHg) pulls fluid back into vessels
Normal fluid turnover reaches 2.5 liters daily through insensible losses (800mL respiratory, 400mL skin), urine output (1500mL), and stool (200mL). During stress, these losses can increase 5-fold, demanding precise replacement strategies to maintain the delicate balance that keeps every cell functioning optimally.
Connect these foundational compartments through Electrolyte Equilibrium to understand how ion gradients drive every physiological process.
💧 The Fluid Command Center: Mastering Your Body's Hydraulic System
⚡ Electrolyte Equilibrium: The Ion Orchestra in Perfect Harmony
📌 Remember: "SODIUM BRAIN, POTASSIUM HEART" - Na+ disorders cause neurological symptoms, K+ disorders cause cardiac arrhythmias
- Sodium Disorders (Normal: 135-145 mEq/L)
- Hyponatremia (<135 mEq/L)
- Mild (130-134): Usually asymptomatic
- Moderate (125-129): Nausea, confusion
- Severe (<125): Seizures, coma, mortality 50%
- Hypernatremia (>145 mEq/L)
- Cellular shrinkage occurs with >2% volume loss
- Mortality rate: 15% when Na+ >160 mEq/L
- Hyponatremia (<135 mEq/L)
- Potassium Disorders (Normal: 3.5-5.0 mEq/L)
- Hypokalemia (<3.5 mEq/L)
- ECG changes: U-waves appear at <3.0 mEq/L
- Paralysis risk: <2.5 mEq/L
- Hyperkalemia (>5.5 mEq/L)
- Peaked T-waves: >6.0 mEq/L
- Cardiac arrest risk: >7.0 mEq/L
- Hypokalemia (<3.5 mEq/L)
| Electrolyte | Normal Range | Mild Abnormal | Severe Abnormal | Life-Threatening |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 135-145 | 130-134 / 146-150 | 125-129 / 151-160 | <125 / >160 |
| Potassium (mEq/L) | 3.5-5.0 | 3.0-3.4 / 5.1-5.5 | 2.5-2.9 / 5.6-6.5 | <2.5 / >6.5 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 8.5-10.5 | 7.5-8.4 / 10.6-11.5 | 7.0-7.4 / 11.6-13.0 | <7.0 / >13.0 |
| Magnesium (mEq/L) | 1.5-2.5 | 1.2-1.4 / 2.6-3.0 | 1.0-1.1 / 3.1-4.0 | <1.0 / >4.0 |
💡 Master This: Calcium exists in 3 forms - ionized (50%), protein-bound (40%), complexed (10%) - only ionized calcium is physiologically active, requiring pH correction for accurate interpretation
Calcium disorders manifest as neuromuscular excitability changes. Hypocalcemia (<8.5 mg/dL) produces Chvostek's sign (facial twitching) and Trousseau's sign (carpopedal spasm), while hypercalcemia (>10.5 mg/dL) causes "stones, bones, groans, and psychiatric overtones" with QT shortening on ECG.
Magnesium serves as the "forgotten electrolyte" despite being essential for >300 enzymatic reactions. Hypomagnesemia (<1.5 mEq/L) prevents correction of other electrolyte abnormalities and increases digoxin toxicity risk by 3-fold.
Connect these electrolyte principles through Assessment Mastery to develop systematic evaluation skills for complex fluid disorders.
⚡ Electrolyte Equilibrium: The Ion Orchestra in Perfect Harmony
🔍 Assessment Mastery: Reading the Body's Fluid Status Like a Master Detective
📌 Remember: "DRY SKIN WET LUNGS" - Dehydration shows skin tenting >3 seconds, dry mucous membranes; Overload shows crackles, JVD >8cm, peripheral edema
- Physical Examination Hierarchy
- Skin Assessment
- Skin turgor: Normal <2 seconds, dehydration >3 seconds
- Mucous membranes: Dry indicates >5% volume loss
- Capillary refill: Normal <2 seconds, prolonged >3 seconds
- Cardiovascular Signs
- Jugular venous pressure: Normal 6-8cm H2O
- Orthostatic vitals: >20 mmHg systolic drop indicates volume depletion
- Heart rate increase: >20 bpm standing suggests hypovolemia
- Pulmonary Assessment
- Crackles: Bilateral suggests volume overload
- Pleural effusions: Indicate fluid retention
- Skin Assessment
- Laboratory Markers
- BUN/Creatinine ratio: >20:1 suggests prerenal azotemia
- Urine specific gravity: >1.020 indicates concentration
- Fractional excretion of sodium: <1% suggests volume depletion
| Assessment Tool | Normal Value | Hypovolemia | Hypervolemia | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JVP (cm H2O) | 6-8 | <6 | >12 | 85% | 90% |
| Skin Turgor (sec) | <2 | >3 | <2 | 75% | 85% |
| BUN/Cr Ratio | 10-20 | >20 | 10-15 | 80% | 70% |
| IVC Diameter (cm) | 1.5-2.5 | <1.5 | >2.5 | 90% | 85% |
| CVP (mmHg) | 2-8 | <2 | >12 | 95% | 95% |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | |||||
| flowchart TD |
Start["<b>📋 Clinical Assessment</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Initial evaluation</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Patient history</span>"]
Exam{"<b>🩺 Physical Exam</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Bedside findings</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Vital signs</span>"}
%% Hypovolemia Path
Turgor["<b>💧 Skin Turgor</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Delayed >3 sec</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Poor elasticity</span>"]
JVP_Low["<b>🩸 Low JVP</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• JVP < 6 cm</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Flat neck veins</span>"]
Ortho["<b>📉 Orthostatics</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• BP drop on stand</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• ⬆️ HR response</span>"]
HypoCond["<b>⚠️ Hypovolemia</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Likely volume loss</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Low intravascular</span>"]
VolumeRx["<b>💊 Replacement</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• IV crystalloids</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Restore perfusion</span>"]
%% Hypervolemia Path
Crackles["<b>🫁 Crackles</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Lung auscultation</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Pulmonary edema</span>"]
JVP_High["<b>🩸 High JVP</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• JVP > 12 cm</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Distended veins</span>"]
Edema["<b>🦵 Peripheral Edema</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Pitting edema</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Dependent swelling</span>"]
HyperCond["<b>⚠️ Hypervolemia</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Likely overload</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Fluid excess</span>"]
DiuresisRx["<b>💊 Diuresis</b><br><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Loop diuretics</span><span style='display:block; text-align:left; color:#555'>• Fluid restriction</span>"]
%% Connections
Start --> Exam
Exam --> Turgor
Exam --> JVP_Low
Exam --> Ortho
Exam --> Crackles
Exam --> JVP_High
Exam --> Edema
Turgor --> HypoCond
JVP_Low --> HypoCond
Ortho --> HypoCond
HypoCond --> VolumeRx
Crackles --> HyperCond
JVP_High --> HyperCond
Edema --> HyperCond
HyperCond --> DiuresisRx
%% Styles
style Start fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E
style Exam fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E
style Turgor fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C
style JVP_Low fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C
style Ortho fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C
style Crackles fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C
style JVP_High fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C
style Edema fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C
style HypoCond fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C
style HyperCond fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C
style VolumeRx fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534
style DiuresisRx fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534
> ⭐ **Clinical Pearl**: **IVC ultrasound** provides **90% accuracy** for volume status - **diameter <1.5cm** with **>50% collapse** indicates **hypovolemia**, **>2.5cm** with **<25% collapse** suggests **hypervolemia**
> 💡 **Master This**: **Central venous pressure** remains the **gold standard** for volume assessment - **CVP <5 mmHg** indicates **volume depletion**, **>12 mmHg** suggests **volume overload** or **cardiac dysfunction**
**Advanced monitoring** includes **pulse pressure variation** (**>13%** indicates **fluid responsiveness**), **stroke volume variation** (**>10%** suggests **preload dependence**), and **passive leg raise test** (**>10% cardiac output increase** predicts **fluid responsiveness** with **85% accuracy**).
**Point-of-care ultrasound** revolutionizes bedside assessment. **B-lines** on lung ultrasound indicate **pulmonary edema**, while **IVC collapsibility index** **>50%** suggests **volume depletion**. These tools provide **real-time feedback** for fluid management decisions.
Connect assessment skills through **Replacement Strategies** to master evidence-based fluid and electrolyte correction protocols.
🔍 Assessment Mastery: Reading the Body's Fluid Status Like a Master Detective
🎯 Replacement Strategies: Precision Targeting for Optimal Outcomes
📌 Remember: "4-2-1 RULE" - Maintenance fluids 4mL/kg/hr first 10kg, 2mL/kg/hr next 10kg, 1mL/kg/hr remaining weight
- Crystalloid Solutions
- Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl)
- Osmolality: 308 mOsm/L
- Sodium content: 154 mEq/L
- Chloride content: 154 mEq/L
- Risk: Hyperchloremic acidosis with >2L administration
- Lactated Ringer's
- Osmolality: 273 mOsm/L
- Sodium: 130 mEq/L, Potassium: 4 mEq/L
- Lactate: 28 mEq/L (metabolized to bicarbonate)
- Contraindicated in liver failure (impaired lactate metabolism)
- Plasmalyte-A
- Balanced electrolyte composition
- Acetate and gluconate as buffers
- Lower chloride content (98 mEq/L)
- Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl)
- Colloid Solutions
- 5% Albumin
- Oncotic pressure: 20 mmHg
- Volume expansion: 1:1 ratio
- Half-life: 16-24 hours
- 25% Albumin
- Volume expansion: 1:3-4 ratio
- Used for hypoproteinemia with edema
- 5% Albumin
| Solution Type | Volume Distribution | Intravascular Retention | Duration (hours) | Cost Factor | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Saline | 25% intravascular | 25% | 2-4 | 1x | Hyperchloremic acidosis |
| Lactated Ringer's | 25% intravascular | 25% | 2-4 | 1.2x | Hyperlactatemia |
| 5% Albumin | 100% intravascular | 80% | 16-24 | 25x | Anaphylaxis (rare) |
| Hetastarch | 100% intravascular | 60% | 8-12 | 15x | Coagulopathy |
| Gelatin | 100% intravascular | 40% | 4-6 | 10x | Allergic reactions |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | |||||
| flowchart TD |
Start["💧 Fluid Deficit
• Identify loss• Clinical assessment"]
Type{"📋 Deficit Type
• Volume status• Electrolyte balance"}
Vol["🧮 Calculate Deficit
• Assess weight loss• Determine severity"]
Elec["🧪 Specific Replacement
• Electrolyte labs• Correct ions"]
Mild["🩺 Mild Clincal
• 3-5% = 20mL/kg• Stable hemodynamics"]
Mod["🩺 Moderate Clinical
• 6-9% = 40mL/kg• Poor skin turgor"]
Sev["⚠️ Severe Clinical
• >10% = 60mL/kg• Reassurance signs"]
Na["💊 Sodium Deficit
• 0.6 x wt x change• Monitor CNS"]
K["💊 Potassium Deficit
• 10-20 mEq/hr max• ECG monitoring"]
MildTime["✅ Mild Timing
• Replace over 24h• Gradual fix"]
ModTime["✅ Mod Timing
• Replace over 12h• Monitor output"]
SevTime["✅ Sev Timing
• Replace 6-8 hours• Urgent care"]
Start --> Type Type -->|Volume| Vol Type -->|Electrolyte| Elec
Vol --> Mild Vol --> Mod Vol --> Sev
Elec --> Na Elec --> K
Mild --> MildTime Mod --> ModTime Sev --> SevTime
style Start fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style Type fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style Vol fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style Elec fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style Mild fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style Mod fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style Sev fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style Na fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style K fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style MildTime fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252 style ModTime fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252 style SevTime fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252
> ⭐ **Clinical Pearl**: **Balanced crystalloids** reduce **acute kidney injury** by **15%** and **mortality** by **11%** compared to **normal saline** in critically ill patients (SMART trial, **n=15,802**)
> 💡 **Master This**: **Sodium deficit calculation** = **0.6 × weight (kg) × (desired Na+ - current Na+)** - replace **50%** in first **24 hours**, remainder over **48 hours** to prevent **cerebral edema**
**Electrolyte replacement protocols** require careful attention to **maximum infusion rates**. **Potassium** replacement should not exceed **20 mEq/hr** via peripheral IV or **40 mEq/hr** via central line. **Magnesium** replacement typically requires **2-4g** over **4-6 hours** for severe deficiency.
**Hypertonic saline (3%)** administration for **severe hyponatremia** follows strict protocols: **1-2 mL/kg/hr** to raise **sodium** by **1-2 mEq/L/hr**, with **maximum correction** of **8 mEq/L** in **24 hours** to prevent **osmotic demyelination syndrome**.
Connect replacement strategies through **Monitoring Protocols** to ensure safe and effective fluid management outcomes.
🎯 Replacement Strategies: Precision Targeting for Optimal Outcomes
📊 Monitoring Protocols: The Clinical Dashboard for Fluid Management Excellence
📌 Remember: "MONITOR TRIO" - Urine output >0.5mL/kg/hr, MAP >65 mmHg, CVP 8-12 mmHg indicate adequate fluid resuscitation
- Hemodynamic Monitoring
- Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
- Target: >65 mmHg for organ perfusion
- Calculation: (SBP + 2×DBP) ÷ 3
- Autoregulation maintained MAP 60-150 mmHg
- Central Venous Pressure (CVP)
- Normal range: 2-8 mmHg
- Fluid responsive: CVP <8 mmHg
- Volume overload: CVP >12 mmHg
- Pulse Pressure Variation (PPV)
- Normal: <10% variation
- Fluid responsive: >13% variation
- Requires: Mechanical ventilation, tidal volume >8mL/kg
- Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
- Laboratory Monitoring
- Electrolyte panels: Every 6-12 hours during active replacement
- Arterial blood gas: pH, lactate, base deficit
- Renal function: Creatinine, BUN, urine electrolytes
- Clinical Endpoints
- Urine output: >0.5 mL/kg/hr adults, >1 mL/kg/hr children
- Mental status: Alert, oriented
- Skin perfusion: Warm, dry, capillary refill <2 seconds
| Parameter | Normal Range | Target Range | Frequency | Action Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAP (mmHg) | 70-100 | >65 | Continuous | <60 |
| CVP (mmHg) | 2-8 | 8-12 | Hourly | <5 or >15 |
| Urine Output (mL/kg/hr) | >0.5 | >0.5 | Hourly | <0.3 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | <2 | <2 | q6h | >4 |
| ScvO2 (%) | >70 | >70 | q6h | <65 |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | ||||
| flowchart TD |
Start["👁️ Monitoring
• Follow protocol• Review status"]
Hemo["📋 Hemo Status
• Vital signs• Monitor data"]
MAP["🔬 MAP Goal
• Targets >65 mmHg• Mean arterial BP"]
CVP["🔬 CVP Goal
• Range 8-12 mmHg• Venous pressure"]
PPV["🔬 PPV Goal
• Target < 13%• Pulse pressure"]
Perf["📋 Perfusion?
• Screen clinical• Organ function"]
Cont["✅ Continue
• Maintain therapy• Stable status"]
Assess["📋 Assess Fluid
• Responsiveness• Clinical screen"]
PLR["🔬 PLR Test
• Passive leg raise• Dynamic check"]
COInc["📋 CO ⬆️ >10%?
• Cardiac output• Positive response"]
Bolus["💊 Fluid Bolus
• Administer fluid• Vol expansion"]
Vaso["💊 Vasopressors
• Start support• Med management"]
Reassess["👁️ Reassess
• Check in 30 min• Repeat cycle"]
Start --> Hemo Hemo --> MAP Hemo --> CVP Hemo --> PPV MAP --> Perf CVP --> Perf PPV --> Perf
Perf -->|Yes| Cont Perf -->|No| Assess Assess --> PLR PLR --> COInc
COInc -->|Yes| Bolus COInc -->|No| Vaso
Bolus --> Reassess Vaso --> Reassess
style Start fill:#EEFAFF, stroke:#DAF3FF, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#0369A1 style Hemo fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style MAP fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style CVP fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style PPV fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style Perf fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style Cont fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252 style Assess fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style PLR fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style COInc fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style Bolus fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style Vaso fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style Reassess fill:#EEFAFF, stroke:#DAF3FF, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#0369A1
> ⭐ **Clinical Pearl**: **Positive fluid balance** **>1L** by **day 3** increases **ICU mortality** by **60%** - aggressive **de-resuscitation** improves outcomes once **shock resolves**
> 💡 **Master This**: **Passive leg raise test** predicts **fluid responsiveness** with **85% accuracy** - **>10% increase** in **cardiac output** or **stroke volume** indicates **preload dependence**
**Advanced monitoring** incorporates **goal-directed therapy** protocols using **esophageal Doppler**, **pulse contour analysis**, or **bioreactance** to optimize **stroke volume** and **cardiac output**. These technologies reduce **complications** by **25%** and **hospital length of stay** by **1.5 days**.
**Fluid balance tracking** requires meticulous **input/output** documentation. **Cumulative positive balance** correlates with **increased mortality**, **prolonged mechanical ventilation**, and **delayed wound healing**. **Daily weights** provide the most accurate assessment of **net fluid balance** (**1kg = 1L fluid**).
Connect monitoring protocols through **Advanced Integration** to master complex fluid management in challenging clinical scenarios.
📊 Monitoring Protocols: The Clinical Dashboard for Fluid Management Excellence
🔗 Advanced Integration: Mastering Complex Fluid Scenarios in Critical Care
📌 Remember: "SEPSIS TRIAD" - Capillary leak causes third-spacing, vasodilation requires vasopressors, myocardial depression needs inotropes
- Sepsis-Associated Fluid Management
- Initial resuscitation: 30 mL/kg crystalloid within 3 hours
- Capillary leak peaks at 6-12 hours, resolves by 48-72 hours
- Fluid extravasation: 50-70% of administered crystalloid
- Albumin consideration: Albumin 20g if albumin <2.5 g/dL
- ALBIOS study: 28-day mortality reduction in severe sepsis
- Cost-effectiveness: $50,000 per QALY gained
- Cardiac Surgery Fluid Management
- Cardiopulmonary bypass causes systemic inflammation
- Capillary leak increases fluid requirements by 200-300%
- Restrictive strategy: <1L positive balance day 1
- Goal-directed therapy: SVV <10%, PPV <13%
- Acute Kidney Injury Considerations
- Fluid overload worsens AKI outcomes
- Furosemide stress test: 2mg/kg - urine <200mL/2hr predicts severe AKI
- Renal replacement therapy: Consider if fluid overload >10% baseline weight
| Clinical Scenario | Initial Fluid | Target CVP | Vasopressor Threshold | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Septic Shock | 30 mL/kg crystalloid | 8-12 mmHg | MAP <65 after fluids | Albumin if <2.5 g/dL |
| Cardiogenic Shock | 250-500 mL bolus | 12-15 mmHg | Immediate if hypotensive | Inotropes primary |
| Hemorrhagic Shock | Permissive hypotension | 8-10 mmHg | SBP >90 mmHg | Blood products 1:1:1 |
| Burn Resuscitation | Parkland formula | 12-15 mmHg | MAP <65 mmHg | Colloids after 24h |
| Post-cardiac Surgery | Restrictive approach | 8-12 mmHg | MAP <70 mmHg | GDT protocols |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | ||||
| flowchart TD |
Start["💧 Fluid Scenario
• Complex case• Critical care"]
Patho{"🩺 Pathophysiology
• Primary cause• Check status"}
DistShock["⚠️ Distributive
• High-vol resus• Fill the tank"]
DistCryst["💊 Crystalloid
• 30 mL/kg dose• IV administration"]
DistResp{"📋 Adequate?
• Assess response• Check BP/perfus"}
DistPress["💊 Vasopressors
• Add pressors• Support MAP"]
DistMaint["👁️ Maintenance
• Stable phase• Titrate fluids"]
CardShock["⚠️ Cardiogenic
• Restrict fluids• Avoid overload"]
CardTest["🔬 Fluid Challenge
• 250-500 mL dose• Small test dose"]
CardImp{"📋 Improvement?
• Hemodynamics• Cardiac output"}
CardIno["💊 Inotropes
• Vasopressors• Contractility"]
CardCaut["👁️ Cautious Fluid
• Additional dose• Close monitoring"]
HypoShock["⚠️ Hypovolemic
• Rapid replace• Restore volume"]
HypoSrc["🔬 Find Source
• Identify bleed• Imaging/Exam"]
HypoCtrl["⚠️ Source Control
• Stop the loss• Surgical/Interv"]
HypoResus["✅ Balanced Resus
• Final outcome• Hemostasis"]
Start --> Patho Patho -->|Distributive| DistShock Patho -->|Cardiogenic| CardShock Patho -->|Hypovolemic| HypoShock
DistShock --> DistCryst DistCryst --> DistResp DistResp -->|No| DistPress DistResp -->|Yes| DistMaint
CardShock --> CardTest CardTest --> CardImp CardImp -->|No| CardIno CardImp -->|Yes| CardCaut
HypoShock --> HypoSrc HypoSrc --> HypoCtrl HypoCtrl --> HypoResus
style Start fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style Patho fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style DistShock fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style CardShock fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style HypoShock fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style DistCryst fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style CardTest fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style HypoSrc fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style DistResp fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style CardImp fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style DistPress fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style CardIno fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style HypoCtrl fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style DistMaint fill:#EEFAFF, stroke:#DAF3FF, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#0369A1 style CardCaut fill:#EEFAFF, stroke:#DAF3FF, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#0369A1 style HypoResus fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252
> ⭐ **Clinical Pearl**: **Fluid creep** phenomenon - **burn patients** receive **150-200%** of **Parkland formula** due to **liberal fluid administration**, increasing **compartment syndrome** risk by **300%**
> 💡 **Master This**: **De-resuscitation phase** begins when **shock resolves** - **negative fluid balance** of **500-1000 mL/day** improves **ventilator-free days** and **reduces mortality** by **15%**
**Pharmacological interactions** significantly impact fluid management. **ACE inhibitors** and **ARBs** impair **autoregulation**, requiring **higher MAP targets** (**>75 mmHg**). **Diuretics** in **AKI** may worsen outcomes unless **fluid overload** exceeds **10%** baseline weight.
**Biomarker-guided therapy** incorporates **BNP/NT-proBNP** for **volume status** assessment. **BNP >400 pg/mL** suggests **volume overload**, while **<100 pg/mL** indicates **volume depletion** with **85% accuracy**. **Procalcitonin** levels guide **antibiotic duration** and **fluid strategy** in **sepsis**.
Connect advanced integration through **Clinical Mastery Arsenal** to develop rapid-reference tools for expert fluid management.
🔗 Advanced Integration: Mastering Complex Fluid Scenarios in Critical Care
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Your Rapid-Reference Toolkit for Fluid Excellence
📌 Remember: "FLUID FIVE" - Volume, Rate, Type, Electrolytes, Monitoring - master these 5 elements for every fluid decision
- Essential Calculation Arsenal
- Maintenance fluids: 4-2-1 rule (4 mL/kg/hr first 10kg, 2 mL/kg/hr next 10kg, 1 mL/kg/hr remaining)
- Sodium deficit: 0.6 × weight × (target Na - current Na)
- Free water deficit: 0.6 × weight × [(current Na ÷ 140) - 1]
- Anion gap: Na - (Cl + HCO3) (normal 8-12)
- Osmolality: 2(Na) + glucose/18 + BUN/2.8 (normal 280-295)
- Critical Thresholds
- Shock indicators: MAP <65, lactate >2, urine <0.5 mL/kg/hr
- Fluid responsiveness: PPV >13%, SVV >10%, PLR >10% CO increase
- Electrolyte emergencies: Na <125 or >160, K >6.5, Ca <7.0
- Emergency Protocols
- Septic shock: 30 mL/kg within 3 hours
- Hemorrhagic shock: Permissive hypotension SBP 80-90
- Severe hyponatremia: 3% saline 1-2 mL/kg/hr
| Clinical Situation | First-Line Fluid | Volume/Rate | Target Parameter | Time Frame |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Septic Shock | Crystalloid | 30 mL/kg | MAP >65 mmHg | 3 hours |
| Hemorrhagic Shock | Blood products | 1:1:1 ratio | SBP >90 mmHg | 1 hour |
| Severe Dehydration | Isotonic crystalloid | 20 mL/kg bolus | Normal perfusion | 1-2 hours |
| Hypernatremia | 0.45% saline | 1-2 mL/kg/hr | Na decrease 1-2/hr | 24-48 hours |
| Severe Hyponatremia | 3% saline | 1-2 mL/kg/hr | Na increase 1-2/hr | 24 hours |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | ||||
| flowchart TD |
Start["🚨 Fluid Emergency
• Critical state• Urgent action"]
Hemo["📋 Hemodynamics
• Vitals assessment• Clinical status"]
Rapid["⚠️ Rapid Assessment
• Quick evaluation• Identify shock"]
Elec["🔬 Electrolytes
• Lab assessment• Check levels"]
Targeted["💊 Targeted Replace
• Specific deficit• Controlled dose"]
Shock["🩺 Shock Type
• Classification• Pathophysiology"]
Distrib["💊 Distributive
• 30 mL/kg fluid• Crystalloid bolus"]
Hypo["💊 Hypovolemic
• Source control• Rapid replacement"]
Cardio["💊 Cardiogenic
• Inotrope support• Minimal fluid"]
Reassess["👁️ Reassess
• Check in 30 min• Evaluate response"]
Goals["📋 Goals Met?
• Clinical targets• Hemodynamics"]
Maint["✅ Maintenance
• Stable phase• Routine care"]
Escalate["⚠️ Escalate Therapy
• Increase support• Specialist consult"]
Start --> Hemo Hemo -->|Shock Present| Rapid Hemo -->|Stable| Elec Elec --> Targeted Rapid --> Shock Shock -->|Distributive| Distrib Shock -->|Hypovolemic| Hypo Shock -->|Cardiogenic| Cardio Distrib --> Reassess Hypo --> Reassess Cardio --> Reassess Reassess --> Goals Goals -->|Yes| Maint Goals -->|No| Escalate
style Start fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style Hemo fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style Rapid fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C style Elec fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style Targeted fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style Shock fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style Distrib fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style Hypo fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style Cardio fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style Reassess fill:#EEFAFF, stroke:#DAF3FF, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#0369A1 style Goals fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style Maint fill:#F6F5F5, stroke:#E7E6E6, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#525252 style Escalate fill:#FDF4F3, stroke:#FCE6E4, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#B91C1C
> ⭐ **Clinical Pearl**: **Rule of 15s** for **hypoglycemia** applies to **hyponatremia** - **15 mL/kg** of **3% saline** raises **sodium** by **15 mEq/L** over **15 minutes** for **seizures**
> 💡 **Master This**: **Fluid challenge test** - **250-500 mL** over **15 minutes** with **hemodynamic monitoring** - **>10% stroke volume increase** predicts **fluid responsiveness** with **90% accuracy**
**Quality metrics** for fluid management include **time to initial resuscitation** (**<1 hour**), **appropriate fluid choice** (**balanced crystalloids** preferred), **electrolyte correction rate** (**Na change 1-2 mEq/L/hr**), and **fluid balance optimization** (**negative balance** post-resuscitation).
**Technology integration** enhances decision-making through **electronic calculators**, **smart pumps** with **dose limits**, **automated alerts** for **electrolyte abnormalities**, and **trending displays** for **fluid balance**. These tools reduce **medication errors** by **75%** and improve **protocol compliance** to **>95%**.
Master these tools through **deliberate practice**, **simulation training**, and **systematic application**. Every patient encounter becomes an opportunity to refine your fluid management expertise, building the clinical judgment that distinguishes expert practitioners from novices.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Your Rapid-Reference Toolkit for Fluid Excellence
Practice Questions: Fluid and electrolyte management
Test your understanding with these related questions
A physician at an internal medicine ward notices that several of his patients have hyponatremia without any associated symptoms. Severe hyponatremia, often defined as < 120 mEq/L, is associated with altered mental status, coma, and seizures, and warrants treatment with hypertonic saline. Because some patients are chronically hyponatremic, with serum levels < 120 mEq/L, but remain asymptomatic, the physician is considering decreasing the cutoff for severe hyponatremia to < 115 mEq/L. Changing the cutoff to < 115 mEq/L would affect the validity of serum sodium in predicting severe hyponatremia requiring hypertonic saline in which of the following ways?













