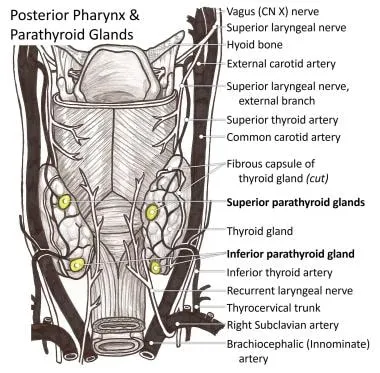
Radioguided parathyroidectomy US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Radioguided parathyroidectomy. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Radioguided parathyroidectomy US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old man undergoes a parathyroidectomy given recurrent episodes of dehydration and kidney stones caused by hypercalcemia secondary to an elevated PTH level. He is recovering on the surgical floor on day 3. His temperature is 97.6°F (36.4°C), blood pressure is 122/81 mmHg, pulse is 84/min, respirations are 12/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. The patient is complaining of perioral numbness currently. What is the most appropriate management of this patient?
- A. Potassium
- B. TSH level
- C. Vitamin D
- D. Observation
- E. Calcium gluconate (Correct Answer)
Radioguided parathyroidectomy Explanation: ***Calcium gluconate***
- The patient's presentation of **perioral numbness** following a parathyroidectomy, especially given a history of hypercalcemia, is highly suggestive of **hypocalcemia**.
- **Calcium gluconate** is indicated for acute symptomatic hypocalcemia to rapidly raise serum calcium levels and alleviate symptoms.
*Potassium*
- There is no clinical indication for **potassium** supplementation; the symptom of perioral numbness is not associated with potassium imbalance.
- Parathyroidectomy and hypercalcemia primarily affect calcium and phosphate metabolism, not typically potassium.
*TSH level*
- A **TSH level** is used to assess thyroid function, which is generally not directly affected by parathyroidectomy unless thyroid tissue was incidentally damaged.
- The symptoms presented do not suggest a thyroid dysfunction.
*Vitamin D*
- While **vitamin D** is crucial for calcium absorption and might be used in chronic management of hypocalcemia, it would not provide the immediate relief needed for acute symptomatic hypocalcemia.
- Acute symptoms like perioral numbness require a rapid elevation of serum calcium.
*Observation*
- **Observation** is inappropriate given the patient's symptomatic presentation of **perioral numbness**, which indicates acute and potentially worsening hypocalcemia.
- Untreated symptomatic hypocalcemia can progress to more severe complications such as seizures, arrhythmias, and laryngospasm.
Radioguided parathyroidectomy US Medical PG Question 2: A 35-year-old man comes to the physician for evaluation of a neck mass and hoarseness. He has no history of major medical illness. Physical examination shows a 2.5-cm fixed, irregular thyroid nodule. His serum calcitonin concentration is elevated. The nodule is most likely comprised of cells that are embryologically derived from which of the following structures?
- A. Second branchial pouch
- B. Fourth branchial arch
- C. Surface ectoderm
- D. Third branchial pouch
- E. Neural crest cells (Correct Answer)
Radioguided parathyroidectomy Explanation: ***Neural crest cells***
- The elevated **serum calcitonin** in the presence of a thyroid nodule is highly suggestive of **medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC)**.
- **MTC** originates from the **parafollicular C cells** of the thyroid, which are embryologically derived from **neural crest cells** that migrate to the **ultimobranchial body** (from the 4th/5th pharyngeal pouch) during development and subsequently integrate into the thyroid gland.
- This is the definitive embryological origin of calcitonin-producing C cells.
*Second branchial pouch*
- The second branchial pouch typically gives rise to the **palatine tonsil crypts** and **tonsillar fossa**.
- It is not associated with the development of the **parafollicular C cells** or thyroid malignancies.
*Fourth branchial arch*
- The fourth branchial arch gives rise to the **superior laryngeal nerve** and associated laryngeal cartilages.
- While the **ultimobranchial body** (from the 4th/5th pharyngeal pouch) does contribute C cells to the thyroid, these cells themselves are derived from **neural crest cells** that migrate to this structure, not from the pouch itself.
- Therefore, the embryological origin is neural crest, not the branchial arch/pouch.
*Surface ectoderm*
- Surface ectoderm forms structures such as the **epidermis of the skin**, **hair**, **nails**, and **lens of the eye**.
- It does not contribute to the development of the **C cells** or the thyroid gland.
*Third branchial pouch*
- The third branchial pouch gives rise to the **inferior parathyroid glands** and the majority of the **thymus**.
- While it contributes to endocrine tissues, it does not form the **parafollicular C cells** of the thyroid.
Radioguided parathyroidectomy US Medical PG Question 3: A 50-year-old man undergoes parathyroidectomy for treatment-resistant hyperparathyroidism. The procedure is complicated by brisk bleeding from the superior thyroid artery near the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. To stop the bleeding, the artery is ligated at its origin. Which of the following is most likely the origin of the artery that was injured in this patient?
- A. Thyrocervical trunk
- B. Ascending pharyngeal artery
- C. Internal carotid artery
- D. Subclavian artery
- E. External carotid artery (Correct Answer)
Radioguided parathyroidectomy Explanation: ***External carotid artery***
- The **superior thyroid artery** is the first branch to arise from the **external carotid artery** in the neck.
- Ligation of this artery at its origin is a common surgical maneuver to control bleeding during thyroid or parathyroid surgery.
*Thyrocervical trunk*
- The **thyrocervical trunk** is a branch of the **subclavian artery** and gives rise to the inferior thyroid artery, not the superior thyroid artery.
- Injury to the superior thyroid artery would not necessitate ligation of a vessel originating from the thyrocervical trunk.
*Ascending pharyngeal artery*
- The **ascending pharyngeal artery** is a small artery that branches from the **external carotid artery** but supplies the pharynx, not the thyroid gland.
- It is not typically implicated in bleeding during parathyroidectomy or in relation to the superior laryngeal nerve.
*Internal carotid artery*
- The **internal carotid artery** primarily supplies the brain and does not have branches in the neck that supply the thyroid or parathyroid glands.
- It arises from the common carotid artery but does not give off the superior thyroid artery.
*Subclavian artery*
- The **subclavian artery** gives rise to the **thyrocervical trunk**, which then supplies the inferior thyroid artery, but not directly the superior thyroid artery.
- The superior thyroid artery originates higher up from the external carotid artery.
Radioguided parathyroidectomy US Medical PG Question 4: A 48-year-old female complains of tingling sensation in her fingertips as well as the skin around her mouth which woke her up from sleep. She is in the postoperative floor as she just underwent a complete thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid cancer. Her temperature is 37° C (98.6° F), respirations are 15/min, pulse is 67/min, and blood pressure is 122/88 mm Hg. While recording the blood pressure, spasm of the muscles of the hand and forearm is seen. What is the next best step in the management of this patient?
- A. No treatment is necessary, this is expected following surgery
- B. Magnesium replacement
- C. Albumin infusion
- D. Calcium replacement (Correct Answer)
- E. Propylthiouracil
Radioguided parathyroidectomy Explanation: ***Calcium replacement***
- The patient's symptoms of **perioral tingling**, **fingertip paresthesias**, and **carpopedal spasm** (Chvostek's or Trousseau's sign when blood pressure cuff is inflated) are classic signs of **hypocalcemia**, a common complication following total thyroidectomy due to inadvertent parathyroid gland removal or damage.
- **Immediate calcium replacement** is crucial to prevent life-threatening complications such as laryngospasm and cardiac arrhythmias.
*No treatment is necessary, this is expected following surgery*
- While potential complications can arise after surgery, **symptomatic hypocalcemia** is not an expected or benign finding and requires prompt intervention.
- Ignoring these symptoms could lead to severe consequences, including **respiratory distress** and **cardiac arrest**.
*Magnesium replacement*
- Although **hypomagnesemia** can sometimes cause symptoms similar to hypocalcemia or exacerbate it, the classic presentation described here points primarily to calcium deficiency.
- While magnesium levels should be checked if calcium replacement is not fully effective, **calcium replacement** is the immediate priority for symptomatic hypocalcemia.
*Albumin infusion*
- **Albumin infusion** is primarily used to address low serum albumin levels, typically in states of significant fluid shifts, malnutrition, or ascites, to help maintain oncotic pressure.
- There is no indication of hypoalbuminemia or related issues in this patient's presentation; it would not address the underlying hypocalcemia.
*Propylthiouracil*
- **Propylthiouracil (PTU)** is an antithyroid medication used to treat hyperthyroidism by inhibiting thyroid hormone synthesis.
- The patient has just undergone a **total thyroidectomy** and has symptoms of **hypocalcemia**, not hyperthyroidism; therefore, PTU is completely inappropriate.
Radioguided parathyroidectomy US Medical PG Question 5: Three hours after undergoing a total right hip replacement, a 71-year-old woman has tingling around the lips and numbness in her fingertips. Her surgery was complicated by unintentional laceration of the right femoral artery that resulted in profuse bleeding. She appears uncomfortable. Examination shows an adducted thumb, extended fingers, and flexed metacarpophalangeal joints and wrists. Tapping on the cheeks leads to contraction of the facial muscles. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Acute kidney injury
- B. Parathyroid ischemia
- C. Intravascular hemolysis
- D. Calcium chelation (Correct Answer)
- E. Metabolic acidosis
Radioguided parathyroidectomy Explanation: ***Calcium chelation***
- The patient exhibits symptoms of **hypocalcemia**, including perioral tingling, fingertip numbness, **Trousseau sign** (adducted thumb, extended fingers, flexed metacarpophalangeal joints and wrists), and **Chvostek's sign** (facial muscle contraction upon tapping the cheek).
- Her significant blood loss and subsequent transfusion likely involved large volumes of **citrated blood products** (e.g., packed red blood cells), where citrate acts as an **anticoagulant** by chelating calcium, leading to transient hypocalcemia.
*Acute kidney injury*
- While acute kidney injury can cause electrolyte imbalances, it typically leads to **hyperphosphatemia**, not necessarily acute symptomatic hypocalcemia presenting within hours of surgery in this manner.
- The patient's immediate post-operative presentation points away from kidney injury being the primary cause of these acute neurological symptoms.
*Parathyroid ischemia*
- **Parathyroid ischemia** could cause hypocalcemia due to reduced parathyroid hormone production, but it is typically associated with **neck surgeries** (e.g., thyroidectomy) and not directly with hip replacement or arterial laceration.
- The onset of symptoms within hours of surgery is too rapid for parathyroid ischemia to fully manifest, as the half-life of PTH is short, but the subsequent drop in calcium would take longer to become clinically significant.
*Intravascular hemolysis*
- **Intravascular hemolysis** can occur due to transfusion reactions or other causes, leading to symptoms like fever, chills, and hemoglobinuria.
- It does not directly cause the specific neurological signs of hypocalcemia described (Trousseau's and Chvostek's signs).
*Metabolic acidosis*
- **Metabolic acidosis** can alter calcium binding to albumin, leading to an **increase in ionized calcium** (the physiologically active form), rather than a decrease.
- While acidosis can occur after massive blood loss and shock, it would not explain the classic signs of hypocalcemia.
Radioguided parathyroidectomy US Medical PG Question 6: A 55-year-old man presents to the physician with tiredness, lethargy, bone pain, and colicky right abdominal pain for 1 month. He has no comorbidities. He does not have any significant past medical history. His height is 176 cm (5 ft 7 in), weight is 88 kg (194 lb), and his BMI is 28.47 kg/m2. The physical examination is normal, except for mild right lumbar region tenderness. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 13.5 g/dL
Serum TSH 2.2 mU/L
Serum calcium 12.3 mg/dL
Serum phosphorus 1.1 mg/dL
Serum sodium 136 mEq/L
Serum potassium 3.5 mEq/L
Serum creatinine 1.1 mg/dL
Urine calcium Elevated
An ultrasound of the abdomen reveals a single stone in the right ureter without hydroureteronephrosis. Clinically, no evidence of malignancy was observed. An X-ray of the long bones reveals diffuse osteopenia with subperiosteal bone resorption. The serum parathyroid hormone level is tested and it is grossly elevated. What is the most appropriate next step in his management?
- A. Ultrasound of the neck only
- B. CT scan of the neck
- C. 99mTc sestamibi scan with ultrasound of the neck (Correct Answer)
- D. Bone scan (DEXA)
- E. Sestamibi scan only
Radioguided parathyroidectomy Explanation: ***99mTc sestamibi scan with ultrasound of the neck***
- The patient presents with **hypercalcemia**, **hypophosphatemia**, elevated **PTH**, **nephrolithiasis**, and **osteopenia with subperiosteal bone resorption**. These are classic signs of **primary hyperparathyroidism**.
- A **99mTc sestamibi scan** helps localize abnormally functioning parathyroid tissue (adenoma), while an **ultrasound of the neck** provides anatomical detail, guiding surgical planning for parathyroidectomy.
*Ultrasound of the neck only*
- While an ultrasound can identify some parathyroid adenomas, its sensitivity can be limited, especially for smaller or ectopically located glands.
- It does not assess the functional activity or metabolic uptake, which is crucial for identifying the hyperfunctioning gland.
*CT scan of the neck*
- A CT scan can help identify parathyroid adenomas, particularly in cases where ultrasound is inconclusive, but it involves radiation exposure.
- It is generally considered a second-line imaging modality for parathyroid localization after sestamibi scan and ultrasound, or in cases of ectopic adenomas.
*Bone scan (DEXA)*
- A **DEXA scan** measures **bone mineral density** and would confirm the severity of osteopenia or osteoporosis, which is expected in hyperparathyroidism.
- However, it does not localize the source of the excess PTH, which is the immediate goal for surgical planning.
*Sestamibi scan only*
- A **sestamibi scan** is excellent for localizing hyperfunctioning parathyroid tissue but may lack precise anatomical resolution for surgical planning.
- Combining it with an **ultrasound of the neck** provides both functional and anatomical information, optimizing surgical success.
Radioguided parathyroidectomy US Medical PG Question 7: A 68-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of difficulty swallowing pieces of meat and choking frequently during meal times. He also sometimes regurgitates foul-smelling, undigested food particles. Examination shows a 3 x 3 cm soft cystic, immobile mass in the upper third of the left side of his neck anterior to the left sternocleidomastoid muscle that becomes prominent when he coughs. A barium swallow shows an accumulation of contrast on the lateral aspect of the neck at the C5 level. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause for this patient's condition?
- A. Remnant of the embryological omphalomesenteric duct
- B. Inadequate relaxation of lower esophageal sphincter
- C. Remnant of the thyroglossal duct
- D. Increased intrapharyngeal pressure (Correct Answer)
- E. Remnant of the second branchial cleft
Radioguided parathyroidectomy Explanation: ***Increased intrapharyngeal pressure***
- The symptoms of **dysphagia**, **regurgitation of undigested food**, and a **neck mass prominent with coughing** are classic for a **Zenker's diverticulum**, which results from increased intrapharyngeal pressure causing herniation of mucosa through Killian's triangle.
- The barium swallow showing **contrast accumulation** and the location of the mass further support this diagnosis, as Zenker's diverticula are pseudo-diverticula caused by pulsion from high pressure during swallowing.
*Remnant of the embryological omphalomesenteric duct*
- An **omphalomesenteric duct remnant** typically presents as a **Meckel's diverticulum** in the small intestine or an umbilical fistula, not as a neck mass with swallowing difficulties.
- This embryological anomaly is related to the midgut development and has no connection to pharyngeal issues.
*Inadequate relaxation of lower esophageal sphincter*
- **Inadequate relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter** (LES) is characteristic of **achalasia**, which causes dysphagia and regurgitation, but typically of *fermented* rather than *undigested* food, and does not present with a palpable neck mass as described.
- Achalasia involves the distal esophagus and does not lead to a pharyngeal outpouching.
*Remnant of the thyroglossal duct*
- A **thyroglossal duct cyst** is a midline neck mass that moves with swallowing and tongue protrusion, which is not consistent with the lateral, pulsion-type mass that becomes prominent with coughing.
- While it can be found in the upper third of the neck, its embryological origin and presentation differ significantly from a Zenker's diverticulum.
*Remnant of the second branchial cleft*
- A **second branchial cleft cyst** is typically a lateral neck mass, often located anterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, but it is congenital and does not typically present with progressive dysphagia and regurgitation of undigested food in adulthood, nor does it typically become prominent with coughing due to increased intrapharyngeal pressure.
- These cysts are usually asymptomatic unless infected and are not directly related to swallowing mechanics.
Radioguided parathyroidectomy US Medical PG Question 8: A 67-year-old woman with tertiary hyperparathyroidism and end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis has persistent hypercalcemia (calcium 12.8 mg/dL) despite maximal medical management with cinacalcet and vitamin D restriction. She has severe pruritus, calciphylaxis, and vascular calcifications. All four parathyroid glands are enlarged on imaging. Evaluate the optimal surgical strategy considering her complex medical status and need for ongoing dialysis access.
- A. Single adenoma resection guided by sestamibi
- B. Subtotal parathyroidectomy (3.5 gland resection)
- C. Total parathyroidectomy without autotransplantation
- D. Total parathyroidectomy with forearm autotransplantation (Correct Answer)
- E. Medical management escalation with denosumab
Radioguided parathyroidectomy Explanation: ***Total parathyroidectomy with forearm autotransplantation***
- In **tertiary hyperparathyroidism** with four-gland enlargement, this procedure provides definitive treatment while allowing for easier access if **recurrent hyperplasia** occurs.
- Placing the tissue in the **forearm** avoids risky neck re-explorations in the future and is the standard for patients who may remain on long-term dialysis.
*Single adenoma resection guided by sestamibi*
- This approach is inappropriate because **tertiary hyperparathyroidism** involves **multiglandular hyperplasia**, not a single solitary adenoma.
- Imaging with **sestamibi** is less reliable in renal patients, and leaving three hyperplastic glands would lead to surgical failure.
*Subtotal parathyroidectomy (3.5 gland resection)*
- While a valid option for some, it carries a higher risk of **persistent hypercalcemia** or recurrence within the neck remnant compared to total resection.
- In patients with **calciphylaxis** and severe symptoms, many surgeons prefer total resection to ensure immediate clearance of excess **parathyroid hormone**.
*Total parathyroidectomy without autotransplantation*
- This technique leads to permanent **hypoparathyroidism**, which is difficult to manage and can result in **adynamic bone disease**.
- It is generally reserved for patients who are not candidates for future transplantation and have severe, life-threatening **hypercalcemia** where no hormonal replacement is desired.
*Medical management escalation with denosumab*
- The patient has already failed **maximal medical management** including **cinacalcet**, and her severe **calciphylaxis** is a surgical emergency.
- **Denosumab** does not address the underlying autonomous parathyroid hyperplasia and is not a definitive treatment for **tertiary hyperparathyroidism**.
Radioguided parathyroidectomy US Medical PG Question 9: A 30-year-old man presents with a 6 cm adrenal mass discovered incidentally. Biochemical workup shows elevated 24-hour urine metanephrines and plasma free metanephrines. He also has elevated serum calcium, PTH, and a pancreatic head mass on CT. Genetic testing confirms MEN 2B syndrome. Evaluate the management priorities and sequencing of interventions.
- A. Simultaneous thyroidectomy and bilateral adrenalectomy
- B. Medical management of pheochromocytoma then parathyroidectomy
- C. Immediate thyroidectomy followed by staged procedures
- D. Adrenalectomy first, then thyroidectomy, then other tumors (Correct Answer)
- E. Pancreatic surgery first due to mass effect
Radioguided parathyroidectomy Explanation: ***Adrenalectomy first, then thyroidectomy, then other tumors***
- Prioritizing **pheochromocytoma** resection is critical to avoid a life-threatening **hypertensive crisis** during subsequent surgeries.
- Adequate medical preparation with **alpha-blockade** followed by beta-blockade is mandatory before any surgical intervention in these patients.
*Simultaneous thyroidectomy and bilateral adrenalectomy*
- Simultaneous procedures significantly increase **perioperative risk** and operative time without ensuring hemodynamic stability during the thyroid portion.
- Managing the **catecholamine surge** from a pheochromocytoma is safer when performed as a separate, initial stage.
*Medical management of pheochromocytoma then parathyroidectomy*
- While **alpha-blockade** is necessary, the question asks for the sequence of surgical interventions, where adrenalectomy must precede other operations.
- This patient presents with features suggestive of **MEN 2B**, which classically does not include hyperparathyroidism, unlike **MEN 1** or **MEN 2A**.
*Immediate thyroidectomy followed by staged procedures*
- Performing a **thyroidectomy** first is contraindicated because the stress of surgery and anesthesia can trigger a **pheochromocytoma crisis**.
- Even if medullary thyroid carcinoma is aggressive, the risk of immediate **intraoperative death** from pheochromocytoma takes precedence.
*Pancreatic surgery first due to mass effect*
- Although a **pancreatic head mass** is present (suggestive of MEN 1 overlap or separate pathology), it is not the immediate life-threatening priority.
- Operating on the pancreas before controlling and removing the **pheochromocytoma** exposes the patient to severe hemodynamic instability.
Radioguided parathyroidectomy US Medical PG Question 10: A 38-year-old woman with primary hyperparathyroidism (calcium 11.8 mg/dL, PTH 185 pg/mL) has negative sestamibi scan and ultrasound. She desires surgical cure and has no medical contraindications. She has a Z-score of -2.8 on DEXA scan and a history of recurrent kidney stones. Evaluate the surgical approach and expected outcomes.
- A. Defer surgery until localization studies are positive
- B. Bilateral neck exploration with identification of all four glands (Correct Answer)
- C. Minimally invasive parathyroidectomy of the largest gland
- D. Medical management with cinacalcet and bisphosphonates
- E. Intraoperative PTH-guided focused exploration
Radioguided parathyroidectomy Explanation: ***Bilateral neck exploration with identification of all four glands***
- When **preoperative localization** studies (Sestamibi and Ultrasound) are negative, a **bilateral neck exploration** is the gold standard to identify the source of primary hyperparathyroidism.
- This patient has clear indications for surgery including **nephrolithiasis**, a **Z-score of -2.8** (osteoporosis), and symptomatic hypercalcemia, making surgical intervention necessary despite negative imaging.
*Defer surgery until localization studies are positive*
- **Negative imaging** does not rule out primary hyperparathyroidism or contraindicate surgery when biochemical evidence is clear.
- Deferring treatment would risk further **bone loss** and recurrent **kidney stones** in a patient who already meets surgical criteria.
*Minimally invasive parathyroidectomy of the largest gland*
- **Minimally invasive parathyroidectomy (MIP)** requires precise preoperative localization to guide the surgeon to a specific quadrant.
- Attempting MIP without localization increases the risk of **surgical failure** and missing ectopic or multiglandular disease.
*Medical management with cinacalcet and bisphosphonates*
- **Medical management** is generally reserved for patients who are not surgical candidates or those who refuse surgery.
- While cinacalcet lowers **PTH** and calcium, it does not provide a **permanent cure** for the underlying adenoma or hyperplasia and is not the first-line choice for a young, fit patient.
*Intraoperative PTH-guided focused exploration*
- **Focused exploration** relies on knowing which side to explore first; without imaging, there is no target for a "focused" approach.
- While **intraoperative PTH** (ioPTH) monitoring is a useful adjunct to confirm cure, it does not replace the need for a comprehensive **bilateral search** when imaging is nonlocalizing.
More Radioguided parathyroidectomy US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.