Adrenalectomy approaches US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Adrenalectomy approaches. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Adrenalectomy approaches US Medical PG Question 1: A 34-year-old woman is recovering in the post-operative unit following a laparoscopic procedure for chronic endometriosis. She had initially presented with complaints of painful menstrual cramps that kept her bedridden most of the day. She also mentioned to her gynecologist that she had been diagnosed with endometriosis 4 years ago, and she could not find a medication or alternative therapeutic measure that helped. Her medical history was significant for surgery she had 6 years ago to remove tumors she had above her kidneys, after which she was prescribed hydrocortisone. An hour after the laparoscopic procedure, she calls the nurse because she is having difficulty breathing. The nurse records her vital signs include: blood pressure 85/55 mm Hg, respirations 20/min, and pulse 115/min. The patient suddenly loses consciousness. Intravenous fluids are started immediately. She gains consciousness, but her blood pressure is unchanged. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the hypotension?
- A. Bleeding profusely through the surgical site
- B. Improper supplementation of steroids (Correct Answer)
- C. Infection involving the suture line
- D. High doses of anesthetic drugs
- E. Loss of fluids during the procedure
Adrenalectomy approaches Explanation: ***Improper supplementation of steroids***
- The patient's history of **bilateral adrenalectomy (tumors above kidneys)** for which she was prescribed **hydrocortisone** indicates **adrenal insufficiency**. Stressful events like surgery require an increased dose of steroids, and improper supplementation can lead to an **adrenal crisis**.
- The symptoms of **hypotension, tachycardia, and loss of consciousness** are characteristic of an **adrenal crisis (acute adrenal insufficiency)**, which occurs when the body lacks sufficient cortisol during stress.
*Bleeding profusely through the surgical site*
- While **hemorrhage** can cause hypotension and tachycardia, the patient regained consciousness with IV fluids but her **blood pressure remained unchanged**, which is less typical for isolated blood loss if volume is restored without addressing the underlying cause.
- There is no direct mention of visible bleeding, the prompt only states the patient lost consciousness and her blood pressure is unchanged.
*Infection involving the suture line*
- **Surgical site infections** typically manifest several days post-op, presenting with **fever, erythema, and purulent drainage**, not acute hypotension and loss of consciousness an hour after surgery.
- The immediate post-operative timeline and systemic symptoms are not consistent with a localized wound infection as the primary cause of this acute decline.
*High doses of anesthetic drugs*
- Anesthetic drugs can cause **vasodilation and hypotension**. However, their effects are usually transient and would likely resolve more completely with IV fluids, especially an hour after a laparoscopic procedure.
- If it was due to anesthetic drugs, the patient's blood pressure would likely normalize with fluid administration once the effects of the anesthetic began to wear off, which is not the case here.
*Loss of fluids during the procedure*
- **Fluid loss** during surgery can cause hypotension, but intravenous fluids were administered, and the patient regained consciousness.
- If fluid loss were the sole cause, resolving consciousness and maintaining low blood pressure typically indicates the fluid loss was not completely compensated, but the primary cause for the persistent hypotension is not just volume.
Adrenalectomy approaches US Medical PG Question 2: During a thyroidectomy, a surgeon must carefully identify and preserve the parathyroid glands. These glands are most commonly located posterior to which part of the thyroid gland?
- A. Superior poles
- B. Inferior poles (Correct Answer)
- C. Pyramidal lobe
- D. Middle third
Adrenalectomy approaches Explanation: Detailed anatomical knowledge is crucial during thyroidectomy to ensure preservation of vital structures [1].
***Inferior poles***
- The **inferior parathyroid glands** (parathyroid IV) are most commonly located posterior to the **inferior poles** of the thyroid gland [1].
- While they are more variable in position than superior glands and can descend into the thymus or mediastinum, the **most common location** is still posterior to the inferior poles [1].
- During thyroidectomy, these glands are frequently encountered in the inferior pole region and must be carefully preserved [1].
*Superior poles*
- The **superior parathyroid glands** (parathyroid III) are typically found at the **middle-to-upper third** of the thyroid, near the cricothyroid junction, rather than directly at the superior poles.
- While their position is more constant than inferior glands, they are not specifically located at the superior poles themselves.
*Pyramidal lobe*
- The **pyramidal lobe** is an embryological remnant extending superiorly from the thyroid isthmus.
- It is not associated with parathyroid gland location, as parathyroids are distinct endocrine structures located on the posterior thyroid surface.
*Middle third*
- The **superior parathyroid glands** are often found near the middle third of the thyroid posteriorly.
- However, when considering all four parathyroid glands (both superior and inferior pairs), the **inferior glands** at the inferior poles represent the most common overall location pattern.
Adrenalectomy approaches US Medical PG Question 3: An endocrine surgeon wants to evaluate the risk of multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type 2 syndromes in patients who experienced surgical hypertension during pheochromocytoma resection. She conducts a case-control study that identifies patients who experienced surgical hypertension and subsequently compares them to the control group with regard to the number of patients with underlying MEN type 2 syndromes. The odds ratio of MEN type 2 syndromes in patients with surgical hypertension during pheochromocytoma removal was 3.4 (p < 0.01). Given the rare disease assumption, this odds ratio can be interpreted as an approximation of the relative risk. The surgeon concludes that the risk of surgical hypertension during pheochromocytoma removal is 3.4 times greater in patients with MEN type 2 syndromes than in patients without MEN syndromes. This conclusion is best supported by which of the following assumptions?
- A. The case-control study used a large sample size
- B. The relationship between MEN syndromes and surgical hypertension is not due to random error
- C. Pheochromocytoma is common in MEN type 2 syndromes
- D. The 95% confidence interval for the odds ratio does not include 1.0
- E. Surgical hypertension associated with pheochromocytoma is rare (Correct Answer)
Adrenalectomy approaches Explanation: ***Surgical hypertension associated with pheochromocytoma is rare***
- The phrase "given the **rare disease assumption**" is critical here, as it allows the **odds ratio** to approximate the **relative risk**. This assumption is valid when the outcome (surgical hypertension) is rare in the general population.
- If the outcome is rare, the odds ratio provides a good estimate of how many times more likely the outcome is in the exposed group compared to the unexposed group.
*The case-control study used a large sample size*
- A large sample size increases the **precision** of the estimate and the **statistical power** but does not inherently allow an odds ratio to be interpreted as a relative risk.
- While important for reliable results, sample size alone doesn't validate the "rare disease assumption."
*The relationship between MEN syndromes and surgical hypertension is not due to random error*
- This statement refers to the **statistical significance** of the findings (p < 0.01), indicating the observed effect is unlikely due to chance.
- It does not, however, relate to the specific condition under which an odds ratio approximates a relative risk.
*Pheochromocytoma is common in MEN type 2 syndromes*
- This statement addresses the prevalence of pheochromocytoma in patients with MEN type 2, not the rarity of the outcome (surgical hypertension) in the general population.
- While pheochromocytoma is indeed a feature of MEN2, this fact alone doesn't validate the rare disease assumption regarding surgical hypertension.
*The 95% confidence interval for the odds ratio does not include 1.0*
- This indicates **statistical significance**, meaning the odds ratio is significantly different from 1, suggesting an association between the exposure and the outcome.
- It does not provide the basis for interpreting the odds ratio as a relative risk under the rare disease assumption.
Adrenalectomy approaches US Medical PG Question 4: A 47-year-old woman complains of weight gain and irregular menses for the past 2 years. She has gained 13 kg (28.6 lb) and feels that most of the weight gain is in her abdomen and face. She has type 2 diabetes and hypertension for 1 year, and they are difficult to control with medications. Vital signs include a temperature of 36.9°C (98.4°F), blood pressure of 160/100 mm Hg, and pulse of 95/min. The patient's late-night salivary cortisol is elevated. Morning plasma ACTH is high. Brain magnetic resonance imaging shows a 2 cm pituitary adenoma. Which of the following is the optimal therapy for this patient?
- A. Unilateral adrenalectomy
- B. Bilateral adrenalectomy
- C. Pituitary radiotherapy
- D. Medical therapy
- E. Transsphenoidal pituitary adenomectomy (Correct Answer)
Adrenalectomy approaches Explanation: ***Transsphenoidal pituitary adenomectomy***
- This patient presents with **Cushing's disease**, characterized by **elevated late-night salivary cortisol** and **high morning plasma ACTH**, coupled with a **pituitary adenoma** on MRI. **Transsphenoidal pituitary adenomectomy** is the first-line and most effective treatment for Cushing's disease, offering the highest chance of remission by directly removing the adenoma.
- Successful surgical removal of the tumor can quickly normalize **ACTH** and **cortisol** levels, leading to significant improvement in symptoms like **weight gain**, **hypertension**, **diabetes**, and **menstrual irregularities**.
*Unilateral adrenalectomy*
- This procedure treats **adrenal adenomas** causing Cushing's syndrome (primary adrenal hypercortisolism), which is characterized by **low or undetectable ACTH levels**. This patient has **high ACTH**, indicating a pituitary source.
- Performing a unilateral adrenalectomy in this case would not address the underlying **pituitary tumor** and would not cure Cushing's disease.
*Bilateral adrenalectomy*
- This is a treatment for severe, refractory Cushing's disease, or as a palliative measure, when **pituitary surgery** has failed or is contraindicated.
- While it effectively removes the source of **cortisol**, it leads to **adrenal insufficiency**, requiring lifelong corticosteroid replacement, and carries the risk of **Nelson's Syndrome** (rapid pituitary tumor growth due to loss of negative feedback).
*Pituitary radiotherapy*
- **Pituitary radiotherapy** is a secondary treatment option, typically used when **transsphenoidal surgery** fails to achieve remission, or if there is residual tumor.
- It has a slower onset of action (months to years) compared to surgery, and the patient's severe symptoms require more immediate control.
*Medical therapy*
- **Medical therapies** (e.g., **ketoconazole**, **mifepristone**, **pasireotide**) are often used as bridging therapy before surgery, when surgery is contraindicated, or for patients with persistent disease after surgery.
- They help control **hypercortisolism** but do not cure the underlying **pituitary adenoma**, making **surgical removal** the preferred definitive treatment.
Adrenalectomy approaches US Medical PG Question 5: A 30-year-old man comes to the physician after receiving a high blood pressure reading of 160/90 mm Hg at an annual employee health check-up. During the past few months, the patient has had occasional headaches and mild abdominal pain, both of which were relieved with ibuprofen. He has also had several episodes of heart palpitations. He has no history of serious illness. His mother and father both have hypertension. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the past 10 years and drinks one glass of wine daily. He occasionally smokes marijuana. He appears pale. His temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F), pulse is 103/min, and blood pressure is 164/102 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 15.3 g/dL
Leukocyte count 7,900/mm3
Platelet count 223,000/mm3
Serum
Na+ 138 mEq/L
K+ 4.6 mEq/L
Cl- 103 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 14 mg/dL
Glucose 90 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.9 mg/dL
Plasma metanephrines 1.2 nmol/L (N < 0.5 nmol/L)
Urine toxicology screening is positive for tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). Renal doppler shows no abnormalities. A CT scan of the abdomen shows a mass in the left adrenal gland. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
- A. Resection of adrenal mass
- B. Phenoxybenzamine (Correct Answer)
- C. Propranolol
- D. Metoprolol
- E. MIBG therapy
Adrenalectomy approaches Explanation: ***Phenoxybenzamine***
- The patient's presentation with **hypertension**, **palpitations**, and significantly elevated **plasma metanephrines** (1.2 nmol/L vs. normal < 0.5 nmol/L), along with an **adrenal mass**, strongly suggests a **pheochromocytoma**.
- **Alpha-blockade** with phenoxybenzamine is the crucial first step to control blood pressure and prevent a **hypertensive crisis** during subsequent surgical resection.
*Resection of adrenal mass*
- While surgical resection is the **definitive treatment** for pheochromocytoma, it should **not be performed before adequate alpha-blockade**.
- **Unprepared surgery** can lead to a fatal hypertensive crisis due to uncontrolled catecholamine release during manipulation of the tumor.
*Propranolol*
- Propranolol is a **non-selective beta-blocker** and should **not be initiated before alpha-blockade** in pheochromocytoma.
- Blocking beta-adrenergic receptors can lead to **unopposed alpha-adrenergic vasoconstriction**, potentially worsening hypertension and causing a crisis.
*Metoprolol*
- Metoprolol is a **selective beta-1 blocker** and, like other beta-blockers, should **not be used before alpha-blockade** in pheochromocytoma.
- While it may have fewer peripheral vasoconstrictive effects than non-selective beta-blockers, the risk of unopposed alpha-stimulation remains significant.
*MIBG therapy*
- **Metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) therapy** is a form of **radiotherapy** used for metastatic or inoperable pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma.
- It is **not the initial management** for a resectable adrenal mass in a patient with a newly diagnosed pheochromocytoma.
Adrenalectomy approaches US Medical PG Question 6: A 33-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a pounding headache for the past 3 hours. The pain is 8 out of 10 in intensity, does not radiate, and is not relieved by ibuprofen. He also has associated dizziness, blurring of vision, and palpitations. He has had similar episodes over the last 6 months but none this severe. He has not had fever, weight change, or loss of appetite. He underwent an appendectomy at the age of 18. His father died of renal cancer. He is diaphoretic. His temperature is 36.8°C (98.4°F), pulse is 112/min, and blood pressure is 220/130 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 14.8 g/dL
Leukocyte count 9600/mm3
Platelet count 345,000/mm3
Serum
Glucose 112 mg/dL
Na+ 137 mEq/L
K+ 4.2 mEq/L
Cl- 105 mEq/L
Creatinine 1.0 mg/dL
Urine dipstick shows no abnormalities. Which of the following findings on imaging is the most likely explanation for this patient's symptoms?
- A. Paravertebral mass
- B. Adrenal medullary mass (Correct Answer)
- C. Intracranial hemorrhage
- D. Renal cortical mass
- E. Meningeal mass
Adrenalectomy approaches Explanation: ***Adrenal medullary mass***
- The patient's symptoms (pounding headache, palpitations, diaphoresis, dizziness, blurred vision) along with severe **hypertension** (220/130 mmHg) and tachycardia (112/min) are classic for a **pheochromocytoma**, which is typically an adrenal medullary tumor.
- The episodic nature of the symptoms over 6 months and the patient's father dying of **renal cancer** (suggesting a potential familial syndrome like VHL or MEN2, which can include pheochromocytoma) further support this diagnosis.
*Paravertebral mass*
- While pheochromocytomas can sometimes be **extra-adrenal** (paragangliomas) and located in the paravertebral regions, an "adrenal medullary mass" is the most common and direct explanation for these symptoms.
- A paravertebral mass without the context of catecholamine excess would typically present with symptoms related to **compression** or local invasion, not systemic paroxysmal symptoms of hypertension, headache, and palpitations.
*Intracranial hemorrhage*
- An intracranial hemorrhage can cause severe headache and neurological symptoms, but it is less likely to cause a prolonged history of episodic symptoms with associated **palpitations and diaphoresis**.
- While severe hypertension can be a cause or consequence of hemorrhage, the constellation of symptoms strongly points towards **catecholamine excess**.
*Renal cortical mass*
- A renal cortical mass, such as a **renal cell carcinoma**, typically presents with hematuria, flank pain, or an abdominal mass.
- It usually does not cause paroxysmal headaches, palpitations, and severe, episodic hypertension unless it's an extremely rare instance of a renin-producing tumor, which wouldn't cause the other adrenergic symptoms.
*Meningeal mass*
- A meningeal mass (e.g., meningioma) typically causes symptoms related to **mass effect** on the brain or spinal cord, such as seizures, focal neurological deficits, or chronic headache.
- It would not explain the prominent **adrenergic symptoms** like palpitations and diaphoresis, or the severe, episodic hypertension.
Adrenalectomy approaches US Medical PG Question 7: Immediately after undergoing a right total knee replacement, a 69-year-old woman has severe abdominal pain, non-bloody emesis, and confusion. She has a history of Hashimoto thyroiditis that is well-controlled with levothyroxine and hyperlipidemia that is controlled by diet. She underwent bunion removal surgery from her right foot 10 years ago. Her temperature is 39°C (102.2°F), pulse is 120/min, and blood pressure is 60/30 mm Hg. Abdominal examination shows a diffusely tender abdomen with normal bowel sounds. She is confused and oriented to person but not place or time. Laboratory studies are pending. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. High-dose hydrocortisone
- B. Exploratory laparotomy
- C. CT angiogram of the abdomen
- D. Noncontrast CT of the head
- E. Intravenous isotonic saline infusion (Correct Answer)
Adrenalectomy approaches Explanation: ***Intravenous isotonic saline infusion***
- The patient presents with **shock** (BP 60/30 mm Hg, pulse 120/min, confusion), which is immediately life-threatening and requires urgent intervention.
- **IV fluid resuscitation** is the **first priority** in any shock state to restore intravascular volume, improve tissue perfusion, and stabilize hemodynamics.
- While this patient has features concerning for **acute adrenal crisis** (Hashimoto thyroiditis with possible polyglandular autoimmune syndrome, post-surgical stress, fever, hypotension, confusion), **fluid resuscitation must be initiated immediately** before or concurrent with other therapies.
- In practice, **high-dose hydrocortisone should be given simultaneously** with fluids, but restoring circulating volume is the foundational first step.
*High-dose hydrocortisone*
- This patient has **Hashimoto thyroiditis** and presents with shock after major surgery (a known precipitant), raising strong suspicion for **acute adrenal crisis**.
- Patients with autoimmune thyroid disease can have concurrent **autoimmune adrenal insufficiency** (Schmidt syndrome/APS-2).
- **Hydrocortisone is critical** and should be given immediately (typically 100 mg IV), but **not before addressing the shock state** with fluid resuscitation.
- This would be the appropriate **second step** or given concurrently with fluids.
*Exploratory laparotomy*
- While the patient has **severe abdominal pain** and **diffuse tenderness**, the overall presentation (fever, hypotension, post-op state) suggests **medical shock** rather than a surgical emergency.
- **Normal bowel sounds** make mechanical obstruction or perforation less likely.
- Surgery is inappropriate until the patient is hemodynamically stabilized and a surgical cause is confirmed.
*CT angiogram of the abdomen*
- This could evaluate for **mesenteric ischemia**, but the patient is **too unstable** for imaging.
- The clinical picture better fits **adrenal crisis** or **septic shock** rather than vascular catastrophe.
- **Delaying resuscitation** for imaging in a patient with severe hypotension would be harmful.
*Noncontrast CT of the head*
- The patient's **confusion** is most likely due to **hypoperfusion** and **shock** rather than a primary intracranial process.
- **Altered mental status** is a common manifestation of shock and adrenal crisis.
- Cerebral perfusion depends on adequate systemic blood pressure, making **circulatory stabilization the priority**.
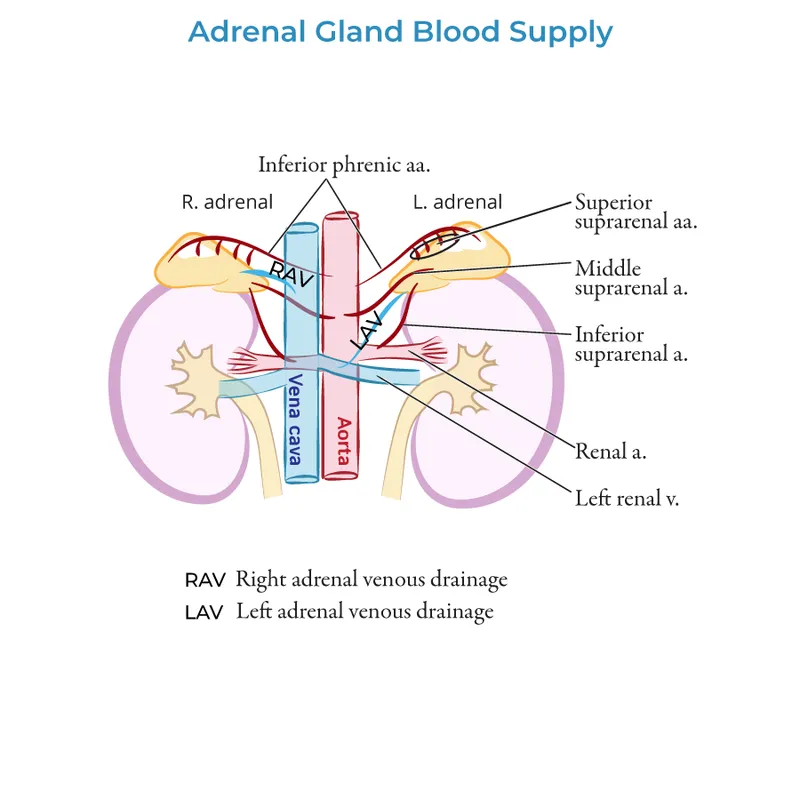
Adrenalectomy approaches US Medical PG Question 8: A researcher is investigating the blood supply of the adrenal gland. While performing an autopsy on a patient who died from unrelated causes, he identifies a vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the inferior aspect of the right adrenal gland. Which of the following vessels most likely gave rise to the vessel in question?
- A. Inferior phrenic artery
- B. Abdominal aorta
- C. Renal artery (Correct Answer)
- D. Superior mesenteric artery
- E. Common iliac artery
Adrenalectomy approaches Explanation: ***Renal artery***
- The **inferior suprarenal artery**, which supplies the inferior part of the adrenal gland, typically arises from the **renal artery**.
- The adrenal glands receive a rich blood supply from three main arterial sources: superior, middle, and inferior suprarenal arteries.
*Inferior phrenic artery*
- The **superior suprarenal arteries** typically arise from the **inferior phrenic arteries** and supply the superior aspect of the adrenal glands.
- While critical for adrenal blood supply, they do not typically contribute to the inferior aspect directly.
*Abdominal aorta*
- The **middle suprarenal artery** usually arises directly from the **abdominal aorta**.
- This vessel supplies the central part of the adrenal gland, but not primarily the inferior aspect.
*Superior mesenteric artery*
- The **superior mesenteric artery** primarily supplies structures of the midgut (e.g., small intestine, ascending colon) and does not typically give rise to vessels supplying the adrenal glands.
- It is located inferior to the origin of the renal arteries and the adrenal glands.
*Common iliac artery*
- The **common iliac arteries** supply the lower limbs and pelvic organs, originating from the abdominal aorta bifurcation.
- These arteries are located much too far inferior to supply the adrenal glands, which are retroperitoneal structures in the upper abdomen.
Adrenalectomy approaches US Medical PG Question 9: A 27-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance following a motor vehicle accident 1 hour prior. He appears agitated. His blood pressure is 85/60 mm Hg, the pulse is 110/min, and the respiratory rate is 19/min. Physical examination shows bruising of the left flank and fracture of the left lower thoracic bones. Strict bed rest and monitoring with intravenous fluids is initiated. Urinalysis shows numerous RBCs. A contrast-enhanced CT scan shows normal enhancement of the right kidney. The left renal artery is only visible in the proximal section with a small amount of extravasated blood around the left kidney. The left kidney shows no enhancement. Imaging of the spleen shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Immediate surgical exploration (Correct Answer)
- B. Observation with delayed repair
- C. Conservative management
- D. Renal artery embolization
- E. Renal artery embolization with delayed nephrectomy
Adrenalectomy approaches Explanation: ***Immediate surgical exploration***
- The patient presents with signs of **hemodynamic instability** (BP 85/60, pulse 110/min, agitation) and imaging findings consistent with **left renal artery avulsion** and devascularization (no enhancement of the left kidney, visible only proximally, extravasated blood). These findings necessitate immediate surgical intervention to control hemorrhage and assess kidney viability.
- The goal is to revascularize the kidney if possible, perform a nephrectomy if the kidney is unsalvageable, and manage hemorrhage to stabilize the patient.
*Observation with delayed repair*
- This approach is typically reserved for **hemodynamically stable** patients with renal injuries, especially lower-grade injuries that do not involve complete vessel avulsion or ongoing significant hemorrhage.
- Delaying intervention in a hemodynamically unstable patient with a presumed renal artery avulsion can lead to further decompensation, irreversible kidney damage, and increased mortality.
*Conservative management*
- **Conservative management** is appropriate for hemodynamically stable patients with minor renal injuries, such as contusions or small lacerations, or for very selected cases of more severe injuries that have spontaneously tamponaded and are not causing significant clinical compromise.
- The patient's **hemodynamic instability** and direct evidence of renal artery injury preclude conservative management in this case.
*Renal artery embolization*
- **Renal artery embolization** is a highly effective, minimally invasive technique for controlling bleeding from renal injuries. However, it is primarily indicated for **hemodynamically stable patients** with contained hemorrhage or specific pseudoaneurysms/AV fistulas.
- In a hemodynamically unstable patient with a complete renal artery avulsion and non-perfused kidney, embolization is unlikely to revascularize the kidney and may even hinder subsequent surgical repair if revascularization is deemed possible. Furthermore, it might not be sufficient to control diffuse or extensive bleeding associated with avulsion.
*Renal artery embolization with delayed nephrectomy*
- While embolization can precede nephrectomy in certain scenarios for better hemorrhage control, it is not the primary immediate step in a **hemodynamically unstable** patient with renal artery avulsion and a non-enhancing kidney.
- The primary concern is the patient's instability, which requires immediate surgical control, and delaying nephrectomy after embolization often isn't feasible if the kidney is completely devascularized and the patient is unstable. The decision for nephrectomy typically occurs during the initial surgical exploration.
Adrenalectomy approaches US Medical PG Question 10: A 67-year-old woman with tertiary hyperparathyroidism and end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis has persistent hypercalcemia (calcium 12.8 mg/dL) despite maximal medical management with cinacalcet and vitamin D restriction. She has severe pruritus, calciphylaxis, and vascular calcifications. All four parathyroid glands are enlarged on imaging. Evaluate the optimal surgical strategy considering her complex medical status and need for ongoing dialysis access.
- A. Single adenoma resection guided by sestamibi
- B. Subtotal parathyroidectomy (3.5 gland resection)
- C. Total parathyroidectomy without autotransplantation
- D. Total parathyroidectomy with forearm autotransplantation (Correct Answer)
- E. Medical management escalation with denosumab
Adrenalectomy approaches Explanation: ***Total parathyroidectomy with forearm autotransplantation***
- In **tertiary hyperparathyroidism** with four-gland enlargement, this procedure provides definitive treatment while allowing for easier access if **recurrent hyperplasia** occurs.
- Placing the tissue in the **forearm** avoids risky neck re-explorations in the future and is the standard for patients who may remain on long-term dialysis.
*Single adenoma resection guided by sestamibi*
- This approach is inappropriate because **tertiary hyperparathyroidism** involves **multiglandular hyperplasia**, not a single solitary adenoma.
- Imaging with **sestamibi** is less reliable in renal patients, and leaving three hyperplastic glands would lead to surgical failure.
*Subtotal parathyroidectomy (3.5 gland resection)*
- While a valid option for some, it carries a higher risk of **persistent hypercalcemia** or recurrence within the neck remnant compared to total resection.
- In patients with **calciphylaxis** and severe symptoms, many surgeons prefer total resection to ensure immediate clearance of excess **parathyroid hormone**.
*Total parathyroidectomy without autotransplantation*
- This technique leads to permanent **hypoparathyroidism**, which is difficult to manage and can result in **adynamic bone disease**.
- It is generally reserved for patients who are not candidates for future transplantation and have severe, life-threatening **hypercalcemia** where no hormonal replacement is desired.
*Medical management escalation with denosumab*
- The patient has already failed **maximal medical management** including **cinacalcet**, and her severe **calciphylaxis** is a surgical emergency.
- **Denosumab** does not address the underlying autonomous parathyroid hyperplasia and is not a definitive treatment for **tertiary hyperparathyroidism**.
More Adrenalectomy approaches US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.