Endocrine Surgery

On this page
🏥 The Endocrine Surgeon's Operating Theater: Precision Medicine at Its Peak
Endocrine surgery demands a unique fusion of anatomical precision, biochemical insight, and pattern recognition where millimeters matter and hormonal consequences ripple through every organ system. You'll master the decision frameworks that guide thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pancreatic interventions, learning to interpret diagnostic patterns that distinguish observation from operation. Through systematic exploration of surgical anatomy, preoperative testing strategies, and evidence-based protocols, you'll build the integrated thinking required to navigate these high-stakes procedures where technical excellence meets endocrine physiology in real time.
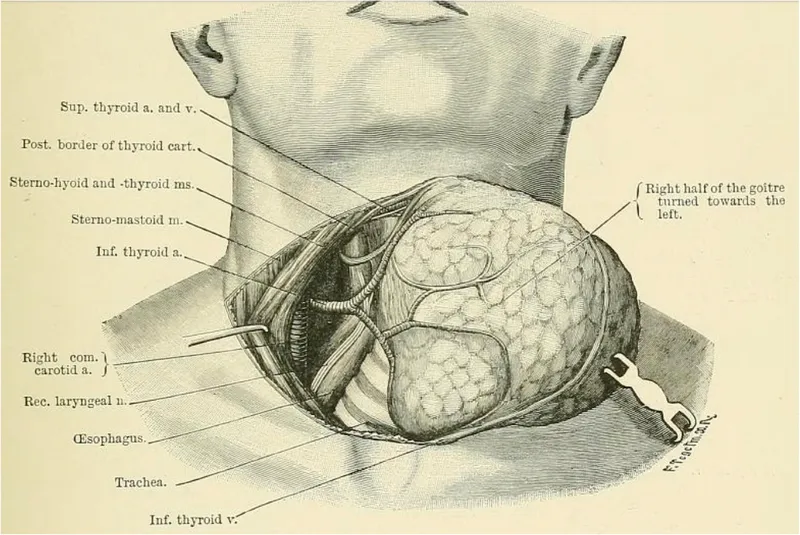
📌 Remember: ENDOCRINE - Essential glands, Nerve protection, Delicate dissection, Optimal timing, Calcium monitoring, Replacement therapy, Intraoperative decisions, Nodule evaluation, Emergency management
The endocrine surgical landscape encompasses five major gland systems: thyroid (25-30g), parathyroids (30-50mg each), adrenals (4-6g each), pancreatic islets, and pituitary. Each requires distinct surgical approaches, with complication rates ranging from <1% for routine thyroidectomy to 15-20% for complex pheochromocytoma resections.
-
Thyroid Surgery Volume
- Annual procedures: 150,000+ in US
- Cancer cases: 25-30% of total
- Papillary: 85% of thyroid cancers
- Follicular: 10% of cases
- Medullary: 3-4% requiring specialized approach
- Anaplastic: <2% with 6-month median survival
-
Critical Success Metrics
- Recurrent laryngeal nerve preservation: >98%
- Permanent hypoparathyroidism: <2%
- Operative mortality: <0.1% for benign disease
- Increases to 2-5% for pheochromocytoma
- Reaches 10-15% for emergency procedures
| Gland System | Weight/Size | Key Nerves at Risk | Major Complication | Replacement Needs | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thyroid | 15-25g | RLN, External branch SLN | Voice changes (5-10%) | Levothyroxine (100% total) | >95% |
| Parathyroid | 30-50mg each | RLN proximity | Hypocalcemia (15-30%) | Calcitriol + Calcium | 90-95% |
| Adrenal | 4-6g | Splenic vessels | Hemorrhage (5-8%) | Hydrocortisone (unilateral: 0%) | >90% |
| Pheochromocytoma | Variable | Major vessels | Hypertensive crisis (20%) | None if unilateral | 85-90% |
| Pancreatic Islets | Microscopic | Pancreatic duct | Diabetes (variable) | Insulin (depends on extent) | 70-80% |
💡 Master This: Endocrine surgery success depends on three pillars: anatomical preservation (nerve integrity), physiological replacement (hormone balance), and oncological adequacy (complete resection). Master the anatomy, and you prevent 90% of complications.
Understanding endocrine surgical principles unlocks the logic behind every procedural decision, from preoperative hormone optimization to postoperative monitoring protocols. This foundation enables surgeons to navigate the complex interplay between anatomical precision and physiological consequences that defines modern endocrine surgery.
🏥 The Endocrine Surgeon's Operating Theater: Precision Medicine at Its Peak
⚔️ The Surgical Battlefield: Navigating Endocrine Anatomy Under Fire
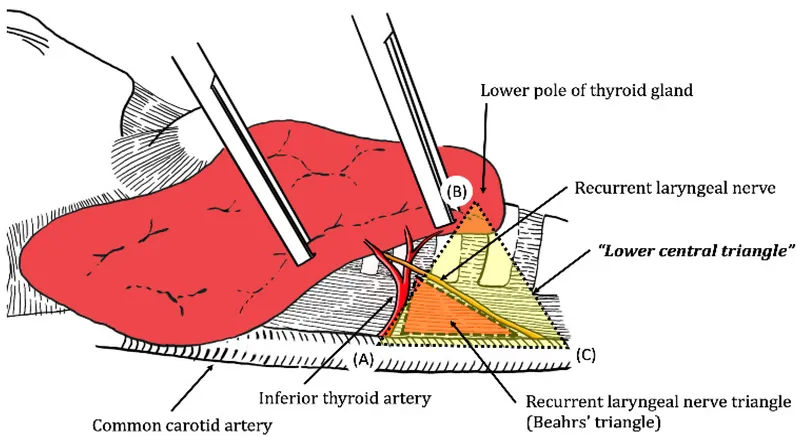
📌 Remember: RLN PROTECTION - Recurrent course variable, Ligament of Berry danger zone, Nerve stimulator essential, Parathyroid blood supply, Right nerve more anterior, Oblique course left side, Traction injury prevention, Electrocautery minimal, Careful dissection, Thorough identification, Intraoperative monitoring, Optimal visualization, No blind clamping
The recurrent laryngeal nerve anatomy varies significantly: right RLN recurs around subclavian artery (shorter course), while left RLN loops around aortic arch (longer, more predictable path). Non-recurrent laryngeal nerves occur in 0.5-1% of patients, typically right-sided with aberrant subclavian artery.
-
Critical Anatomical Relationships
- RLN to inferior thyroid artery: 3 possible relationships
- Nerve anterior to artery: 25%
- Nerve posterior to artery: 65%
- Nerve between branches: 10%
- Ligament of Berry: highest risk zone for RLN injury
- Contains 85% of RLN injuries
- Requires meticulous capsular dissection
- Electrocautery contraindicated within 2mm
- RLN to inferior thyroid artery: 3 possible relationships
-
Parathyroid Gland Locations
- Superior parathyroids: more consistent location
- Posterior-superior thyroid pole: 80%
- Retroesophageal: 15%
- Intrathyroidal: <5%
- Inferior parathyroids: highly variable
- Inferior pole region: 50%
- Thyrothymic ligament: 25%
- Mediastinal: 15%
- Intrathyroidal: 10%
- Superior parathyroids: more consistent location
| Anatomical Structure | Location Variability | Injury Risk | Identification Method | Protection Strategy | Complication Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right RLN | High (non-recurrent 1%) | Moderate | Nerve stimulator | Capsular dissection | 2-5% temporary |
| Left RLN | Low (predictable course) | Lower | Visual + stimulator | Tracheoesophageal groove | 1-3% temporary |
| Superior Parathyroid | Low (80% consistent) | Moderate | Color + size | Preserve blood supply | 5-10% devascularization |
| Inferior Parathyroid | Very High (50% variable) | High | Systematic search | Autotransplantation | 15-20% inadvertent removal |
| External Branch SLN | Moderate | High | Cricothyroid stimulation | High ligation avoidance | 10-15% injury |
💡 Master This: Anatomical preservation trumps speed in endocrine surgery. Every structure has backup identification methods: visual landmarks, nerve stimulation, and systematic exploration patterns. When in doubt, preserve and identify later.
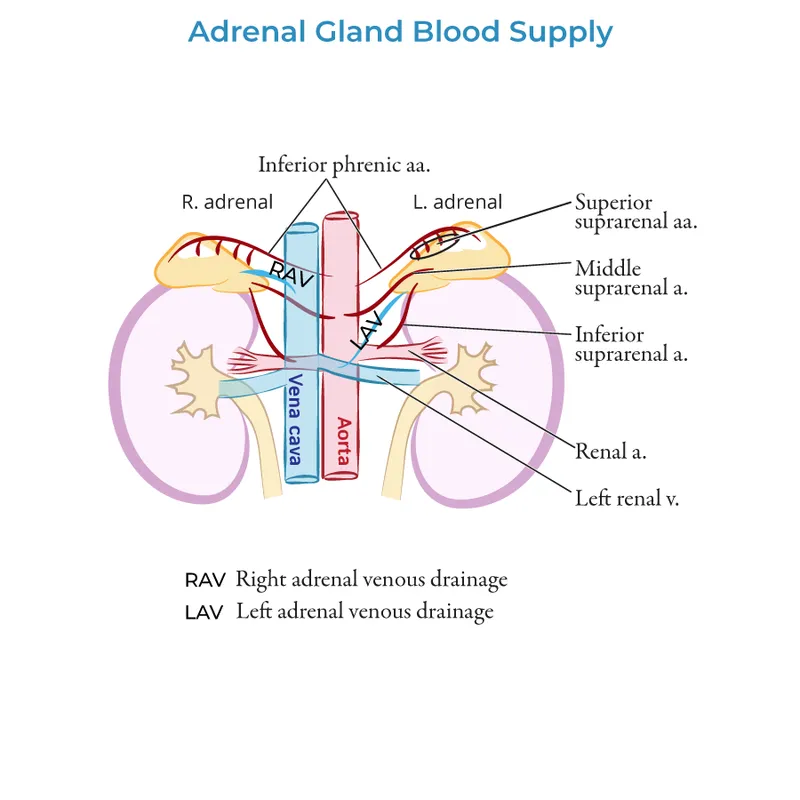
The adrenal surgical anatomy presents different challenges: right adrenal sits posterior to IVC, requiring careful retraction, while left adrenal relates to splenic vessels and pancreatic tail. Pheochromocytomas can be highly vascular with friable capsules, making gentle handling essential to prevent catecholamine release.
⚔️ The Surgical Battlefield: Navigating Endocrine Anatomy Under Fire
🎯 The Decision Matrix: Pattern Recognition in Endocrine Pathology
-
Thyroid Nodule Surgical Indications
- Size thresholds for FNA biopsy:
- TIRADS 5 (high suspicion): >1.0 cm
- TIRADS 4 (intermediate): >1.5 cm
- TIRADS 3 (low suspicion): >2.5 cm
- TIRADS 2 (benign): >5.0 cm (compressive symptoms)
- Bethesda classification surgical triggers:
- Bethesda VI (malignant): 100% surgical
- Bethesda V (suspicious): 95-99% malignant
- Bethesda IV (follicular neoplasm): 25-30% malignant
- Bethesda III (AUS/FLUS): 10-15% malignant
- Size thresholds for FNA biopsy:
-
Hyperparathyroidism Surgical Criteria
- Asymptomatic primary HPT (meet any one):
- Serum calcium >1.0 mg/dL above normal
- 24-hour urine calcium >400 mg
- Creatinine clearance <60 mL/min
- Bone density T-score <-2.5 at any site
- Age <50 years
- Symptomatic disease: 100% surgical regardless of levels
- Asymptomatic primary HPT (meet any one):
📌 Remember: PHEO PREP - Phenoxybenzamine 10-14 days, Heart rate control with beta-blockers, Expanded blood volume, Operative day monitoring, Pressors available, Rapid response team, Emergency protocols, Postoperative ICU monitoring
| Clinical Scenario | Key Threshold | Surgical Urgency | Preop Requirements | Success Rate | Major Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxic Multinodular Goiter | TSH <0.1 + symptoms | Elective | Euthyroid state | >95% | Thyroid storm (2-3%) |
| Graves Disease | Failed medical Rx | Semi-urgent | Beta-blockade + iodine | >90% | Thyrotoxic crisis (5%) |
| Pheochromocytoma | Catecholamines >3x normal | Urgent | Alpha-blockade 10-14 days | 85-90% | Hypertensive crisis (20%) |
| Primary Hyperparathyroidism | Calcium >12 mg/dL | Urgent | Hydration + bisphosphonates | >95% | Cardiac arrhythmias (5%) |
| Medullary Thyroid Cancer | Calcitonin >100 pg/mL | Semi-urgent | Genetic testing | 80-85% | Persistent disease (20%) |
-
Adrenal Mass Surgical Indications
- Size criteria: >4 cm diameter (malignancy risk >25%)
- Functional status: Any functional tumor regardless of size
- Growth rate: >1 cm/year on serial imaging
- Imaging characteristics: >10 HU on non-contrast CT
- Young age: <40 years with >3 cm mass
-
MEN Syndrome Surgical Timing
- MEN 1: Parathyroid surgery first (easiest, lowest morbidity)
- MEN 2A: Thyroidectomy by age 5 (RET codon dependent)
- MEN 2B: Thyroidectomy by age 1 (aggressive MTC)
- Pheochromocytoma: Always first in MEN 2 (prevent crisis)
💡 Master This: Pattern recognition in endocrine surgery means knowing the numbers: calcium levels, hormone thresholds, size criteria, and timing windows. Every decision has quantitative triggers that eliminate guesswork and optimize outcomes.
The surgical decision matrix integrates biochemical markers, imaging characteristics, patient factors, and disease progression into clear action plans. Master these algorithms, and complex cases become systematic protocols with predictable success rates.
🎯 The Decision Matrix: Pattern Recognition in Endocrine Pathology
🔬 The Diagnostic Arsenal: Precision Testing for Surgical Planning
- Thyroid Diagnostic Hierarchy
- First-line screening: TSH (sensitivity >95% for dysfunction)
- TSH <0.1: 99% specificity for hyperthyroidism
- TSH >10: 95% specificity for hypothyroidism
- Structural assessment: High-resolution ultrasound
- Sensitivity 95% for >5mm nodules
- TIRADS classification predicts malignancy risk
- Doppler flow assesses vascularity patterns
- Cytological diagnosis: Ultrasound-guided FNA
- Bethesda VI: 97-99% malignant
- Bethesda V: 95-99% malignant
- Bethesda IV: 25-30% malignant
- Non-diagnostic rate: <10% with on-site cytology
- First-line screening: TSH (sensitivity >95% for dysfunction)
📌 Remember: THYROID WORKUP - TSH first always, High-resolution ultrasound, Yield from FNA biopsy, Repeat if non-diagnostic, Oncogene testing available, Iodine uptake if hyperthyroid, Doppler for vascularity
| Diagnostic Test | Sensitivity | Specificity | Clinical Application | Cost Factor | Turnaround Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thyroid US | 95% (>5mm nodules) | 85% (malignancy features) | First-line imaging | Low ($200-300) | Same day |
| Thyroid FNA | 90-95% (adequate sample) | 99% (malignant cytology) | Tissue diagnosis | Moderate ($400-600) | 3-5 days |
| Sestamibi Scan | 85-90% (single adenoma) | 95% (parathyroid localization) | Parathyroid imaging | High ($800-1200) | 1-2 days |
| 4D-CT Parathyroid | 90-95% (ectopic glands) | 90% (adenoma detection) | Failed sestamibi | High ($1000-1500) | Same day |
| Genetic Testing | >99% (known mutations) | >99% (mutation detection) | MEN syndromes | Very High ($2000-5000) | 2-4 weeks |
- Biochemical confirmation first: PTH >65 pg/mL with elevated calcium
- First-line imaging: Sestamibi scan (85-90% sensitivity)
- Second-line: 4D-CT or MRI for negative sestamibi
- Intraoperative tools: PTH monitoring (>50% drop confirms cure)
- Ectopic locations: 15-20% require extended exploration
- Pheochromocytoma Biochemical Testing
- 24-hour urine catecholamines: Gold standard (>95% sensitivity)
- Norepinephrine >170 mcg/24hr (normal <85)
- Epinephrine >35 mcg/24hr (normal <25)
- Plasma metanephrines: Highest sensitivity (>99%)
- Normetanephrine >180 pg/mL (normal <90)
- Metanephrine >120 pg/mL (normal <50)
- False positive rate: 10-15% (medications, stress, diet)
- 24-hour urine catecholamines: Gold standard (>95% sensitivity)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Intraoperative PTH monitoring has >95% accuracy for cure prediction. PTH drop >50% at 10 minutes post-excision indicates successful removal of all hyperfunctioning tissue. Failure to drop mandates continued exploration.
-
Advanced Molecular Diagnostics
- Thyroid molecular testing (Bethesda III-IV):
- Afirma Gene Expression Classifier: 90% sensitivity
- ThyroSeq v3: 94% sensitivity, 82% specificity
- Reduces unnecessary surgery by 15-30%
- RET proto-oncogene testing (MEN 2):
- Codon 634 mutations: Highest risk (>95% MTC by age 10)
- Codon 918 mutations: MEN 2B (100% MTC risk)
- Prophylactic thyroidectomy timing based on specific codon
- Thyroid molecular testing (Bethesda III-IV):
-
Functional Imaging Integration
- PET-CT with 68Ga-DOTATATE: Neuroendocrine tumors
- Sensitivity >90% for well-differentiated NETs
- Changes management in 25-30% of cases
- 18F-FDG PET: Aggressive thyroid cancers
- Negative radioiodine scan with elevated thyroglobulin
- Sensitivity 85% for recurrent disease
- PET-CT with 68Ga-DOTATATE: Neuroendocrine tumors
💡 Master This: Diagnostic precision drives surgical success. Layer biochemical confirmation, anatomical localization, and functional assessment to create comprehensive surgical plans. Every test has specific indications, limitations, and decision thresholds that guide operative strategy.
The diagnostic arsenal transforms clinical suspicion into surgical certainty through systematic testing algorithms. Master the sequence, understand the thresholds, and integrate results to achieve optimal patient outcomes with minimal unnecessary procedures.
🔬 The Diagnostic Arsenal: Precision Testing for Surgical Planning
⚡ The Treatment Protocols: Evidence-Based Surgical Excellence
-
Thyroid Cancer Treatment Algorithms
- Papillary thyroid cancer (85% of cases):
- <1 cm, unifocal, no LN: Lobectomy (95% cure rate)
- >1 cm or multifocal: Total thyroidectomy (98% cure rate)
- Central LN dissection: Prophylactic for >4 cm tumors
- Lateral LN dissection: Therapeutic only (proven metastases)
- Follicular thyroid cancer (10% of cases):
- Minimally invasive: Lobectomy acceptable (90% cure)
- Widely invasive: Total thyroidectomy mandatory (85% cure)
- Vascular invasion: High-risk category (70% 10-year survival)
- Papillary thyroid cancer (85% of cases):
-
Hyperparathyroidism Surgical Approaches
- Single adenoma (85% of cases):
- Minimally invasive parathyroidectomy (95% cure rate)
- Operative time: 30-45 minutes
- Length of stay: Outpatient or 23-hour observation
- Multigland disease (15% of cases):
- Bilateral neck exploration (90% cure rate)
- 3.5 gland parathyroidectomy with autotransplantation
- Operative time: 90-120 minutes
- Single adenoma (85% of cases):
📌 Remember: PARATHYROID SURGERY - PTH monitoring essential, Adenomal localization, Rapid PTH assay, Autotransplantation option, Thorough exploration, Hypocalcemia prevention, Yield >50% PTH drop, Recurrence <5%, Outpatient feasible, Intraoperative decisions, Devascularization avoidance
| Procedure Type | Cure Rate | Complication Rate | Hospital Stay | Return to Work | Long-term Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thyroid Lobectomy | 95% (low-risk PTC) | RLN injury <2% | Outpatient | 1-2 weeks | Annual US + Tg |
| Total Thyroidectomy | 98% (appropriate cases) | Hypocalcemia 15-30% | 23 hours | 2-3 weeks | Suppressed TSH + Tg |
| Minimally Invasive Parathyroidectomy | 95% (single adenoma) | Failure <5% | Outpatient | 3-5 days | Calcium + PTH 6 months |
| Bilateral Parathyroid Exploration | 90% (multigland disease) | Permanent hypocalcemia 5-10% | 1-2 days | 1-2 weeks | Lifelong calcium monitoring |
| Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy | >95% (benign disease) | Conversion rate 5% | 1-2 days | 2-3 weeks | Annual imaging 5 years |
- Preoperative optimization (mandatory):
- Phenoxybenzamine: 10 mg BID, increase every 2-3 days
- Target: Seated BP <140/90, standing BP >90/60
- Duration: Minimum 10-14 days before surgery
- Beta-blockade: Only after alpha-blockade (prevent crisis)
- Intraoperative management:
- Arterial line + central venous access
- Nicardipine or clevidipine for hypertensive episodes
- Phenylephrine for post-resection hypotension
- Avoid histamine-releasing drugs (morphine, atracurium)
- Adrenal Surgery Outcomes
- Laparoscopic approach (gold standard for <6 cm masses):
- Conversion rate: <5% in experienced hands
- Operative time: 90-120 minutes
- Blood loss: <100 mL average
- Length of stay: 1-2 days vs 4-5 days open
- Open approach indications:
- Size >6 cm (malignancy concern)
- Suspected malignancy on imaging
- Previous extensive abdominal surgery
- Inability to tolerate pneumoperitoneum
- Laparoscopic approach (gold standard for <6 cm masses):
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Radioactive iodine therapy after total thyroidectomy improves disease-free survival by 15-20% in intermediate-risk patients. Stimulated thyroglobulin <1 ng/mL at 6-12 months predicts excellent prognosis (>95% disease-free at 10 years).
- Postoperative Management Protocols
- Thyroidectomy monitoring:
- Calcium levels: Every 6 hours for 24-48 hours
- Symptomatic hypocalcemia: Calcium gluconate 1-2 ampules IV
- Severe symptoms: Calcitriol 0.25-0.5 mcg BID
- Voice assessment: Laryngoscopy if voice changes
- Parathyroidectomy follow-up:
- Calcium + PTH: 1 week, 6 months, annually
- Bone density: 1-2 years post-surgery
- Kidney function: Annual creatinine and 24-hour urine calcium
- Thyroidectomy monitoring:
💡 Master This: Evidence-based protocols eliminate decision uncertainty and optimize outcomes. Every procedure has defined success metrics, complication thresholds, and monitoring requirements. Follow the algorithms, track the numbers, and achieve predictable excellence.
The treatment protocol mastery transforms complex surgical decisions into systematic approaches with quantifiable results. Understanding these frameworks enables consistent high-quality care across all endocrine surgical scenarios.
⚡ The Treatment Protocols: Evidence-Based Surgical Excellence
🌐 The Integration Network: Multi-System Endocrine Mastery
-
Thyroid-Parathyroid Surgical Integration
- Simultaneous procedures in MEN 1 syndrome:
- Parathyroidectomy first: Easier identification before thyroid manipulation
- Success rate: 90-95% for both procedures
- Complication risk: Additive (hypocalcemia 25-35%)
- Calcium homeostasis post-thyroidectomy:
- Transient hypocalcemia: 15-30% of patients
- Permanent hypoparathyroidism: <2% in experienced hands
- Vitamin D deficiency: Exacerbates hypocalcemia (check 25-OH vitamin D)
- Simultaneous procedures in MEN 1 syndrome:
-
Adrenal-Pituitary Axis Considerations
- Bilateral adrenalectomy consequences:
- Immediate steroid dependence: Hydrocortisone 15-20 mg daily
- Mineralocorticoid replacement: Fludrocortisone 0.1 mg daily
- Stress dosing protocols: Triple dose during illness/surgery
- Nelson syndrome risk: 10-15% develop pituitary adenomas
- Unilateral adrenalectomy recovery:
- Contralateral suppression: 6-12 months recovery time
- Stress testing: ACTH stimulation at 6 months
- No replacement needed: If contralateral gland normal
- Bilateral adrenalectomy consequences:
📌 Remember: MEN SYNDROMES - Multiple glands affected, Endocrine tumor clusters, Neoplasia inheritance patterns, Surgical timing critical, Young age presentation, Needs genetic counseling, Dominant inheritance, RET gene mutations, Organ-specific protocols, Monitoring lifelong, Early intervention, Screening family members
| MEN Syndrome | Primary Manifestations | Surgical Sequence | Screening Protocol | Genetic Testing | Family Counseling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEN 1 | HPT (95%), Pancreatic NET (40%), Pituitary (30%) | Parathyroid → Pancreas → Pituitary | Annual biochemical + imaging | MEN1 gene (85% detection) | 50% inheritance risk |
| MEN 2A | MTC (95%), Pheo (50%), HPT (20%) | Pheo → Thyroid → Parathyroid | Annual calcitonin + catecholamines | RET proto-oncogene (>95% detection) | 50% inheritance risk |
| MEN 2B | MTC (100%), Pheo (50%), Marfanoid | Pheo → Thyroid (age 1) | Intensive early screening | RET codon 918 (>99% detection) | 50% inheritance risk |
- Insulinoma management:
- Preoperative localization: EUS (90% sensitivity)
- Intraoperative ultrasound: >95% detection rate
- Enucleation vs resection: Distance from main duct (>2-3 mm)
- Cure rate: >95% for benign insulinomas
- Gastrinoma (Zollinger-Ellison):
- Duodenal primary: 60% of cases (small, multiple)
- Pancreatic location: 25% of cases (larger, single)
- Lymph node metastases: 60% at presentation
- Cure rate: 60-70% (due to occult metastases)
- Thyroid Cancer Multi-System Effects
- RAI therapy systemic impacts:
- Salivary gland dysfunction: 30-40% of patients
- Lacrimal gland effects: Dry eyes in 20%
- Gonadal effects: Temporary fertility reduction
- Secondary malignancy risk: <1% increase
- TSH suppression consequences:
- Cardiovascular effects: Atrial fibrillation risk (2-3x increase)
- Bone density loss: 1-2% annually in postmenopausal women
- Target TSH levels: <0.1 (high risk), 0.1-0.5 (intermediate), 0.5-2.0 (low risk)
- RAI therapy systemic impacts:
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Pheochromocytoma must be resected first in MEN 2 patients before any other procedure. Undiagnosed pheo during thyroidectomy can cause fatal hypertensive crisis. Always screen with 24-hour urine catecholamines or plasma metanephrines.
- Advanced Integration Strategies
- Simultaneous bilateral procedures:
- Bilateral adrenalectomy: Requires lifelong steroid replacement
- Total parathyroidectomy: Autotransplantation to forearm muscle
- Completion thyroidectomy: Higher RLN injury risk (5-8%)
- Staged procedure planning:
- Interval between stages: 6-12 weeks optimal
- Functional assessment: Between procedures essential
- Complication management: Before next intervention
- Simultaneous bilateral procedures:
💡 Master This: Multi-system endocrine surgery requires orchestra conductor thinking-understanding how each intervention affects the entire hormonal symphony. Sequence matters, timing is critical, and system-wide monitoring prevents cascade complications.
The integration network mastery elevates endocrine surgical practice from technical procedures to comprehensive endocrine care where every decision considers system-wide implications and long-term hormonal balance.
🌐 The Integration Network: Multi-System Endocrine Mastery
🏆 The Mastery Toolkit: Rapid Excellence Framework
- Essential Numbers Arsenal
- Calcium thresholds: <8.0 mg/dL symptomatic, <7.0 mg/dL severe
- PTH monitoring: >50% drop at 10 minutes confirms cure
- RLN injury rates: <2% temporary, <0.5% permanent (expert level)
- Thyroid cancer cure: >95% for T1-T2 disease
- Pheochromocytoma prep: 10-14 days alpha-blockade minimum
- Adrenal size threshold: >4 cm surgical consideration
- MEN 2B thyroidectomy: By age 1 (aggressive MTC)
📌 Remember: SURGICAL EXCELLENCE - Systematic approach always, Understand anatomy completely, Recognize complications early, Gentle tissue handling, Intraoperative monitoring, Clear communication, Anticipate problems, Learn from outcomes, Evidence-based decisions, Xcellence through repetition, Continuous improvement, Ethical patient care, Lifelong learning, Leadership development, Educate others, Never compromise safety, Celebrate team success, Empathy for patients
| Competency Domain | Novice Level | Proficient Level | Expert Level | Master Level | Assessment Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomical Knowledge | Basic landmarks | Variant recognition | Pathological distortion | Teaching others | Oral examination |
| Technical Skills | >4 hours operative time | 2-3 hours standard | <2 hours complex cases | <90 minutes routine | Direct observation |
| Complication Management | Recognition | Basic management | Prevention strategies | System improvement | Case review |
| Decision Making | Algorithm following | Adaptation | Innovation | Protocol development | Outcome analysis |
| Patient Communication | Information delivery | Shared decision making | Complex counseling | Mentoring others | Patient feedback |
- Thyroid nodule assessment: TIRADS score in <30 seconds
- Parathyroid localization: Sestamibi interpretation accuracy >90%
- Pheochromocytoma signs: Triad recognition + biochemical correlation
- MEN syndrome features: Genetic pattern + screening protocols
- Complication recognition: Early warning signs + intervention thresholds
- Performance Benchmarks
- Operative time targets:
- Thyroid lobectomy: <90 minutes
- Total thyroidectomy: <120 minutes
- Parathyroidectomy: <60 minutes (single adenoma)
- Laparoscopic adrenalectomy: <90 minutes
- Complication rate goals:
- RLN injury: <2% temporary, <0.5% permanent
- Hypocalcemia: <15% temporary, <2% permanent
- Bleeding requiring reoperation: <1%
- Infection rate: <2%
- Operative time targets:
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Deliberate practice with immediate feedback accelerates skill acquisition by 10x. Video review of every case, outcome tracking, and mentor feedback create rapid improvement cycles. Track your numbers and compare to benchmarks.
-
Clinical Decision Commandments
- "Calcium first, surgery second" - Optimize biochemistry before operative intervention
- "When in doubt, preserve" - Anatomical structures over speed
- "Numbers don't lie" - Quantitative thresholds guide all decisions
- "Prepare for the worst" - Pheochromocytoma protocols prevent disasters
- "Family matters" - Genetic counseling for hereditary syndromes
- "Monitor everything" - Intraoperative and postoperative surveillance
- "Learn from every case" - Outcome analysis drives improvement
-
Emergency Response Protocols
- Thyroid storm management:
- Propranolol 1-2 mg IV every 5 minutes
- Methimazole 20-30 mg PO every 6 hours
- Hydrocortisone 100 mg IV every 8 hours
- Cooling measures + fluid resuscitation
- Hypocalcemic crisis:
- Calcium gluconate 1-2 ampules IV immediately
- Calcitriol 0.5-1.0 mcg PO BID
- Magnesium replacement if <1.8 mg/dL
- Cardiac monitoring for arrhythmias
- Thyroid storm management:
💡 Master This: Surgical mastery combines technical excellence, clinical judgment, and system thinking. Track your outcomes, learn from complications, and continuously refine your decision-making algorithms. Excellence is measurable, reproducible, and teachable.
The mastery toolkit provides systematic frameworks for achieving surgical excellence through deliberate practice, outcome measurement, and continuous improvement. Master these tools, and transform from competent surgeon to endocrine surgery expert with predictable, superior results.
🏆 The Mastery Toolkit: Rapid Excellence Framework
Practice Questions: Endocrine Surgery
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 50-year-old woman comes to the physician because of palpitations and irritability. Over the past 4 months, she has had several episodes of heart racing and skipping beats that lasted between 30 seconds and several hours. She has also been arguing with her husband more, often about the temperature being too warm. The patient has also lost 8.8-kg (19.4-lb) over the past 4 months, despite being less strict with her diet. She has mild asthma treated with inhaled bronchodilators. Her pulse is 102/min and blood pressure is 148/98 mm Hg. On physical examination, the skin is warm and moist. A mass is palpated in the anterior neck area. On laboratory studies, thyroid stimulating hormone is undetectable and there are antibodies against the thyrotropin-receptor. Thyroid scintigraphy shows diffusely increased iodine uptake. Two weeks later, a single oral dose of radioactive iodine is administered. This patient will most likely require which of the following in the long-term?













