Breast Surgery

On this page
🏗️ Breast Surgery: The Architectural Foundation
Breast surgery demands you master anatomy that shifts with hormones and age, recognize malignant patterns hidden among benign mimics, and navigate treatment decisions where oncologic precision meets reconstructive artistry and patient autonomy. You'll build a framework that integrates imaging interpretation, genetic risk stratification, surgical technique selection, and multidisciplinary coordination to transform complex presentations into confident clinical action. This lesson equips you to distinguish the urgent from the routine, balance breast conservation against survival, and synthesize pathology reports with staging systems to guide care that respects both evidence and individual values.
Essential Anatomical Architecture
The breast's structural organization follows predictable patterns that guide surgical approaches:
-
Mammary Ridge Development
- Embryonic milk line extends from axilla to groin
- Normal breast development: 4th-6th intercostal space
- Accessory tissue occurs in 2-5% of population
- Most common: axillary tail of Spence
- Clinical significance: can undergo malignant transformation
-
Ductal System Organization
- 15-20 major lactiferous ducts converge at nipple
- Each duct drains 10-100 alveolar clusters
- Terminal duct lobular units (TDLUs): 85% of breast cancers originate here
- Estrogen-sensitive proliferation zones
- Maximum density in upper outer quadrant
📌 Remember: TAIL for breast boundaries - Third rib (superior), Anterior axillary line (lateral), Inframammary fold (inferior), Lateral sternal border (medial)
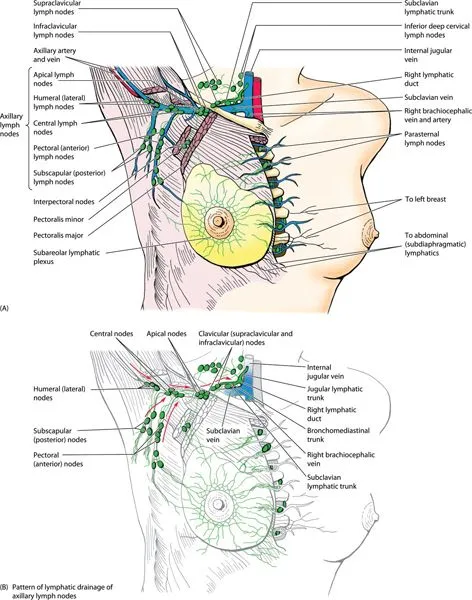
Lymphatic Drainage Mastery
Understanding lymphatic flow patterns determines surgical staging and treatment decisions:
| Drainage Route | Percentage | Primary Nodes | Clinical Significance | |---|---|---|---|---| | Axillary | 75% | Levels I-III | Primary staging site | | Internal mammary | 20% | Parasternal | Often missed, affects prognosis | | Posterior intercostal | 3% | Posterior mediastinal | Rare but aggressive spread | | Contralateral | 1% | Opposite breast | Advanced disease marker | | Supraclavicular | 1% | Level IV | Stage III disease |* Axillary Level Classification
- Level I: Lateral to pectoralis minor (10-40 nodes)
- Level II: Behind pectoralis minor (1-10 nodes)
- Level III: Medial to pectoralis minor (1-5 nodes)
- Rotter's nodes: between pectoralis major/minor
- Clinical significance: Level III involvement = N2 disease
⭐ Clinical Pearl: 97% of breast lymphatic drainage flows to axillary nodes first, making sentinel lymph node biopsy accurate for staging in T1-T2 tumors without clinical adenopathy
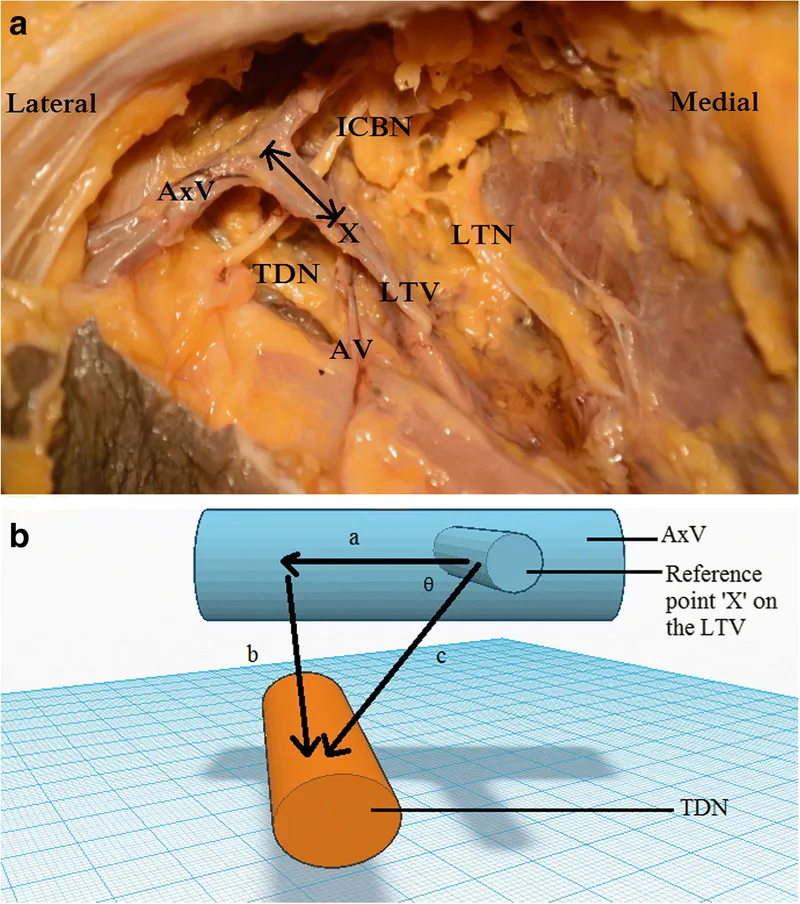
Neurovascular Territory Mapping
Surgical success depends on preserving critical neurovascular structures:
-
Arterial Supply Network
- Internal mammary artery: 60% of medial breast perfusion
- Lateral thoracic artery: 30% of lateral breast supply
- Intercostal perforators: 10% additional supply
- Perforator mapping critical for reconstruction planning
- 2nd-4th intercostal perforators most reliable
-
Venous Drainage Patterns
- Superficial system: 70% of drainage
- Deep system: 30% via internal mammary veins
- Batson's plexus: vertebral metastasis pathway
- Clinical correlation: explains bone metastasis pattern
💡 Master This: The long thoracic nerve (nerve to serratus anterior) runs 2cm posterior to the midaxillary line - injury causes winged scapula in 2-5% of axillary dissections
Critical Surgical Landmarks
- Anatomical Boundaries for Dissection
- Latissimus dorsi: posterior boundary
- Pectoralis major: anterior boundary
- Axillary vein: superior boundary (never dissect above)
- Intercostobrachial nerve: T2 lateral cutaneous branch
- Sacrifice causes numbness in 15-20% of patients
- Preservation possible in 80% of cases with careful technique
📌 Remember: SALT for axillary nerve injuries - Serratus anterior (long thoracic), Axillary nerve, Latissimus dorsi (thoracodorsal), Thoracic nerve (medial pectoral)
Understanding these anatomical relationships transforms surgical decision-making from memorized steps to logical, anatomy-based interventions that optimize outcomes while minimizing complications.
🏗️ Breast Surgery: The Architectural Foundation
⚙️ Breast Surgery: The Physiological Command Center
Hormonal Orchestration Mechanisms
The breast responds to sophisticated hormonal control systems that determine both physiological function and pathological risk:
-
Estrogen Signaling Pathways
- Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα): 75% of breast cancers express this receptor
- Estrogen receptor beta (ERβ): protective effects, decreased in malignancy
- Peak estrogen exposure: 400-500 pg/mL during ovulation
- Stimulates ductal elongation and branching
- Increases cell proliferation by 200-300% during luteal phase
- Lifetime estrogen exposure correlates with cancer risk
-
Progesterone Response Systems
- Progesterone receptor (PR): marker of functional estrogen pathway
- Peak levels: 15-20 ng/mL during luteal phase
- Stimulates alveolar development and differentiation
- Anti-proliferative effects on ductal epithelium
- PR-positive tumors have better prognosis than PR-negative
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Triple-negative breast cancer (ER-/PR-/HER2-) represents 15-20% of cases but accounts for disproportionate mortality due to lack of targeted therapy options
Cellular Proliferation Control Systems
Understanding cell cycle regulation reveals how normal breast tissue transforms into malignancy:
- Cell Cycle Checkpoint Control
- p53 tumor suppressor: mutated in 50-80% of breast cancers
- BRCA1/BRCA2: DNA repair genes, 5-10% of hereditary cases
- HER2/neu amplification: 15-20% of breast cancers
- Drives aggressive proliferation
- Target for trastuzumab therapy
- HER2-positive tumors: higher recurrence without treatment
💡 Master This: Ki-67 proliferation index >20% indicates aggressive tumor biology and predicts response to chemotherapy in hormone receptor-positive disease
Immune Surveillance Networks
The breast maintains sophisticated immune monitoring systems that influence both cancer development and treatment response:
- Tumor Microenvironment Dynamics
- Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs): >50% predicts better outcomes
- Macrophage polarization: M1 (anti-tumor) vs M2 (pro-tumor)
- PD-L1 expression: 10-15% of triple-negative cancers
- Target for immunotherapy
- Pembrolizumab approved for PD-L1 positive metastatic disease
| Immune Marker | Normal Range | Cancer Significance | Treatment Implications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD8+ T cells | 15-25% | Higher = better prognosis | Predicts immunotherapy response |
| Regulatory T cells | 5-10% | Higher = worse prognosis | Immunosuppressive environment |
| NK cells | 10-20% | Decreased in cancer | Adoptive transfer potential |
| Dendritic cells | 2-5% | Maturation impaired | Vaccine development target |
| Myeloid cells | Variable | M2 polarization = poor outcome | Repolarization strategies |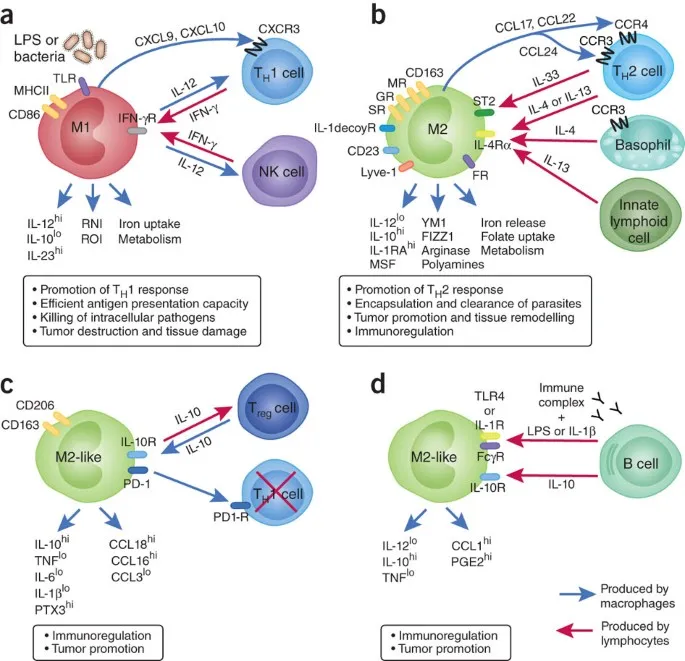
📌 Remember: TILS for immune prognostic factors - Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, Interferon signaling, Lymphocyte activation, Stromal immune response
Metabolic Reprogramming Pathways
Cancer cells undergo fundamental metabolic changes that create therapeutic vulnerabilities:
-
Warburg Effect Implementation
- Glucose uptake increased 10-20 fold in cancer cells
- Lactate production despite oxygen availability
- PET scan sensitivity: 85-95% for tumors >1cm
- SUV max >2.5 suggests malignancy
- False negatives: lobular carcinoma, low-grade tumors
-
Lipid Metabolism Alterations
- Fatty acid synthase overexpression in 90% of breast cancers
- Cholesterol metabolism dysregulation
- Obesity increases risk by 20-40% in postmenopausal women
- Aromatase activity in adipose tissue
- Insulin resistance promotes tumor growth
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Metformin use in diabetic patients with breast cancer shows 25-30% reduction in cancer-specific mortality through AMPK pathway activation and mTOR inhibition
These physiological control mechanisms reveal how normal breast function becomes dysregulated in disease states, providing the foundation for understanding both preventive strategies and therapeutic interventions that target specific molecular pathways.
⚙️ Breast Surgery: The Physiological Command Center
🎯 Breast Surgery: The Clinical Pattern Recognition Matrix
Clinical Presentation Pattern Recognition
Master clinicians recognize specific presentation patterns that immediately narrow differential diagnoses:
-
Age-Stratified Presentation Patterns
- <30 years: Fibroadenoma (68%), phyllodes tumor (2%)
- 30-50 years: Invasive ductal carcinoma (45%), DCIS (25%)
- >50 years: Invasive carcinoma (85%), inflammatory cancer (3%)
- Bilateral cancer: 5-10% synchronous, 0.5-1% annual metachronous risk
- Male breast cancer: 1% of all cases, BRCA2 association
-
Physical Examination Red Flags
- Skin dimpling: Cooper's ligament involvement suggests T2-T3 disease
- Peau d'orange: dermal lymphatic obstruction, inflammatory vs locally advanced
- Nipple retraction: central duct involvement, subareolar cancer location
- Bloody discharge: 10-15% cancer risk in postmenopausal women
- Unilateral discharge: higher suspicion than bilateral
📌 Remember: BREAST examination sequence - Bilateral inspection, Regional lymph nodes, Examination supine, Assess nipple discharge, Systematic palpation, Thorough documentation
Imaging Pattern Integration Framework
Systematic imaging interpretation creates reproducible diagnostic accuracy:
| Imaging Modality | Sensitivity | Specificity | Best Use Case | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mammography | 85-90% | 90-95% | Screening >40 years | Dense breast tissue |
| Ultrasound | 95-99% | 80-85% | Palpable masses | Operator dependent |
| MRI | 95-99% | 70-80% | High-risk screening | High false positive rate |
| Tomosynthesis | 90-95% | 92-97% | Dense breasts | Limited availability |
| PET-CT | 85-95% | 90-95% | Metastatic staging | Poor for small lesions |
- BI-RADS 0: Incomplete assessment, recall rate 8-12%
- BI-RADS 1-2: Benign, routine screening in 1-2 years
- BI-RADS 3: Probably benign, <2% cancer risk, 6-month follow-up
- BI-RADS 4: Suspicious, 2-95% cancer risk, tissue sampling required
- 4A: 2-10% cancer risk
- 4B: 10-50% cancer risk
- 4C: 50-95% cancer risk
- BI-RADS 5: Highly suspicious, >95% cancer risk
- BI-RADS 6: Known malignancy
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Concordance assessment is critical - if imaging shows BI-RADS 4-5 but pathology shows benign results, surgical consultation required due to sampling error risk of 2-10%
Histological Pattern Recognition
Understanding tissue patterns guides surgical planning and adjuvant therapy decisions:
-
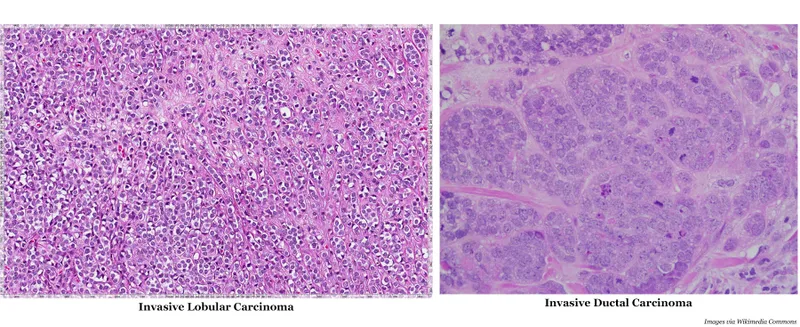
Invasive Carcinoma Subtypes
- Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC): 75-80% of invasive cancers
- Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC): 10-15%, multifocal in 20-40%
- Special types: 10-15% (tubular, mucinous, papillary)
- Better prognosis than IDC
- Tubular carcinoma: >99% 10-year survival if node-negative
-
In Situ Carcinoma Management
- DCIS: 20-25% of screen-detected cancers
- High-grade DCIS: 25-30% risk of invasive cancer at 10 years without treatment
- Low-grade DCIS: 5-10% risk of invasive cancer at 10 years
- Van Nuys Prognostic Index: guides treatment decisions
- Oncotype DX DCIS: recurrence score helps select patients for radiation
💡 Master This: Lymphovascular invasion (LVI) presence increases local recurrence risk by 2-3 fold and distant metastasis risk by 1.5-2 fold, influencing decisions about adjuvant chemotherapy in node-negative disease
Molecular Subtype Classification
Modern breast surgery integrates molecular characteristics that determine both prognosis and treatment selection:
- Intrinsic Molecular Subtypes
- Luminal A: ER+/PR+/HER2-/Ki67 <20% (40% of cases)
- Luminal B: ER+/HER2-/Ki67 ≥20% or ER+/HER2+ (20% of cases)
- HER2-enriched: ER-/PR-/HER2+ (15% of cases)
- Triple-negative: ER-/PR-/HER2- (15% of cases)
- BRCA1-associated: 70% are triple-negative
- Basal-like: 80% of triple-negative cancers
📌 Remember: LUMPS for molecular classification - Luminal A (best prognosis), Unspecified (luminal B), Malignant HER2+ (targeted therapy), Poor prognosis (triple-negative), Special testing (BRCA)
These pattern recognition frameworks transform complex clinical scenarios into systematic approaches that ensure appropriate surgical intervention while avoiding both under-treatment and over-treatment of breast disease.
🎯 Breast Surgery: The Clinical Pattern Recognition Matrix
🔬 Breast Surgery: The Diagnostic Discrimination Engine
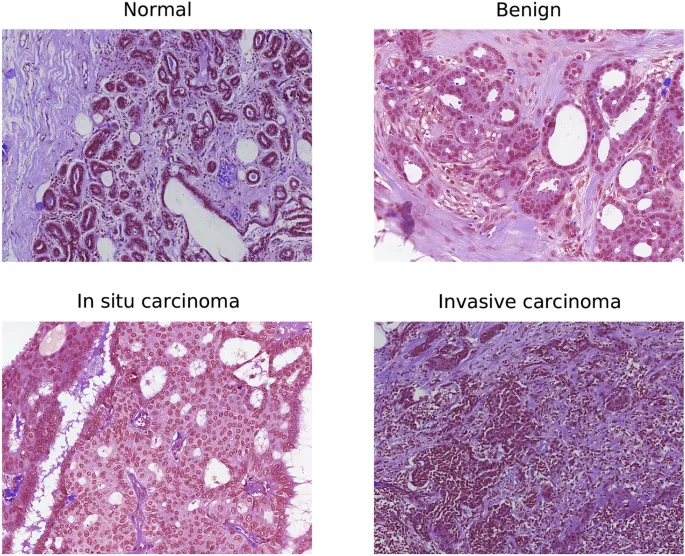
Benign vs Malignant Discrimination Matrix
Systematic comparison of key differentiating features enables accurate clinical decision-making:
| Feature | Benign Lesions | High-Risk Lesions | Invasive Cancer | Management Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth Pattern | Well-circumscribed | Atypical proliferation | Infiltrative borders | Surgical margins |
| Imaging Characteristics | Round/oval masses | Variable enhancement | Spiculated/irregular | Biopsy approach |
| Hormone Sensitivity | Cyclical changes | Increased ER expression | Variable receptor status | Medical therapy |
| Age Distribution | Younger patients | Perimenopausal | All ages, peak 50-70 | Screening protocols |
| Recurrence Risk | <1% malignant transformation | 15-25% cancer risk | 100% without treatment | Follow-up intensity |
- Simple fibroadenoma: <1% malignant transformation risk
- Complex fibroadenoma: 3-4% cancer risk, requires excision
- Giant fibroadenoma: >5cm, phyllodes tumor consideration
- Core biopsy concordance: 95% accuracy for diagnosis
- Observation acceptable if <2cm and imaging-pathology concordant
- Atypical Hyperplasia Risk Stratification
- Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH): 4-5 fold increased cancer risk
- Atypical lobular hyperplasia (ALH): 4-5 fold increased cancer risk
- Flat epithelial atypia (FEA): 2-3 fold increased cancer risk
- Upgrade rate to DCIS/invasive cancer: 10-20% for ADH
- Surgical excision recommended for atypical lesions on core biopsy
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Papillary lesions on core biopsy have 15-25% upgrade rate to malignancy at surgical excision, making complete removal mandatory regardless of imaging concordance
High-Risk Lesion Management Algorithm
Understanding which lesions require surgical intervention versus observation prevents both over-treatment and missed cancers:
- Lobular Carcinoma In Situ (LCIS) Management
- Classical LCIS: marker of increased risk, not precursor
- Pleomorphic LCIS: precursor lesion, requires excision
- Cancer risk: 1-2% per year, bilateral risk
- Chemoprevention: tamoxifen reduces risk by 50%
- Prophylactic mastectomy: >90% risk reduction in high-risk patients
💡 Master This: Concordance triangle - clinical findings, imaging characteristics, and pathology results must all align; discordance in any component mandates surgical consultation and possible re-biopsy
Invasive Cancer Subtype Discrimination
Different invasive cancer subtypes require tailored surgical approaches and have distinct prognostic implications:
-
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Variants
- Grade 1: Well-differentiated, >95% 10-year survival if node-negative
- Grade 2: Moderately differentiated, 85-90% 10-year survival
- Grade 3: Poorly differentiated, 70-80% 10-year survival
- Nottingham grading: tubule formation + nuclear pleomorphism + mitotic rate
- Ki-67 proliferation index: <20% vs ≥20% affects chemotherapy decisions
-
Special Type Carcinomas
- Invasive lobular carcinoma: multifocal in 20-40%, MRI recommended
- Tubular carcinoma: excellent prognosis, chemotherapy rarely indicated
- Mucinous carcinoma: favorable prognosis if pure (>90% mucin)
- Mixed mucinous: worse prognosis, treated as IDC
- Micropapillary carcinoma: high lymphatic invasion risk
| Cancer Subtype | 5-Year Survival | Multifocality Risk | Chemotherapy Indication | Surgical Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tubular | >95% | Low (5-10%) | Rarely indicated | Wide excision sufficient |
| Mucinous (pure) | 90-95% | Low (10-15%) | Age-dependent | Standard margins |
| Invasive lobular | 85-90% | High (20-40%) | Standard criteria | Consider MRI |
| Micropapillary | 70-80% | High (30-50%) | Usually indicated | Aggressive surgery |
| Inflammatory | 40-50% | N/A (diffuse) | Always indicated | Neoadjuvant approach |
Margin Assessment and Re-excision Criteria
Understanding margin adequacy prevents both local recurrence and unnecessary re-operations:
-
Invasive Cancer Margin Standards
- "No ink on tumor": adequate margin for invasive cancer
- Close margins (<2mm): acceptable if no ink on tumor
- Positive margins: re-excision vs mastectomy decision
- Re-excision rate: 15-25% in breast conservation
- Cavity shave margins: reduce re-excision by 50%
-
DCIS Margin Requirements
- ≥2mm margins: standard recommendation for DCIS
- <2mm margins: increased local recurrence risk
- Positive margins: always requires re-excision
- Radiation therapy: reduces local recurrence by 50-60%
- Tamoxifen: additional 30-40% reduction in ER-positive DCIS
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Oncoplastic techniques allow wider excisions while maintaining cosmetic outcomes, reducing re-excision rates from 20-25% to <10% in experienced hands
These discrimination frameworks enable surgeons to make evidence-based decisions that optimize oncologic outcomes while minimizing patient morbidity and psychological distress from over-treatment.
🔬 Breast Surgery: The Diagnostic Discrimination Engine
⚖️ Breast Surgery: The Treatment Decision Engine
Surgical Treatment Algorithm Framework
Systematic treatment selection optimizes outcomes while minimizing over-treatment:
-
Breast Conservation Therapy Criteria
- Tumor-to-breast ratio: <20% for acceptable cosmesis
- Multifocal disease: relative contraindication, MRI evaluation
- Prior radiation: absolute contraindication to re-irradiation
- Pregnancy: radiation contraindicated, timing considerations
- BRCA mutation: not contraindication to conservation
- Young age (<40 years): higher local recurrence but survival equivalent
-
Mastectomy Indications
- Inflammatory breast cancer: neoadjuvant therapy → mastectomy
- Multicentric disease: >5cm separation between tumor foci
- Extensive DCIS: >4cm or multicentric
- Positive margins: after reasonable re-excision attempts
- Prophylactic contralateral: 5-10% reduction in overall mortality
- Risk-reducing: >90% reduction in BRCA carriers
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy converts 30-40% of mastectomy candidates to breast conservation eligibility while providing in vivo chemosensitivity assessment
Reconstruction Decision Matrix
Reconstruction timing and technique selection requires integration of multiple patient and treatment factors:
| Reconstruction Type | Success Rate | Complications | Best Candidates | Contraindications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immediate Implant | 85-90% | 15-20% | Non-smokers, no radiation | Active smoking, radiation |
| Delayed Implant | 90-95% | 10-15% | Post-radiation patients | Insufficient tissue |
| Autologous (DIEP) | 95-98% | 20-25% | Adequate donor tissue | Vascular disease |
| Latissimus Dorsi | 90-95% | 15-20% | Failed implant reconstruction | Prior back surgery |
| No Reconstruction | N/A | 0% | Patient preference | None |
- Oncologic safety: no delay in adjuvant therapy initiation
- Radiation effects: increased complications (30-40% vs 15-20%)
- Nipple-sparing mastectomy: selected patients with favorable tumor location
- Contraindications: nipple involvement, inflammatory cancer
- Oncologic safety: equivalent to skin-sparing mastectomy
- Autologous Reconstruction Advantages
- Natural feel: superior to implant-based
- Radiation tolerance: better outcomes than implants
- Longevity: lifetime solution without replacement
- DIEP flap: gold standard for autologous reconstruction
- Operative time: 6-8 hours, microsurgical expertise required
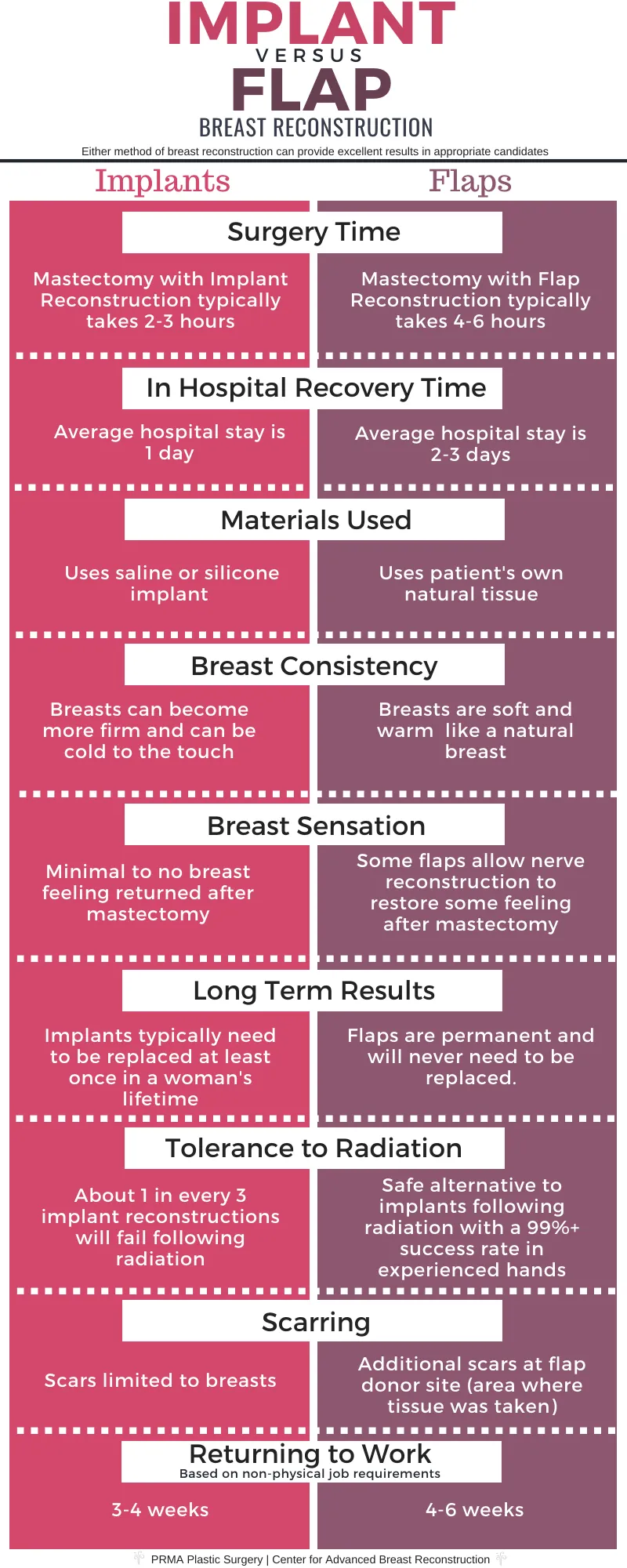
💡 Master This: Radiation therapy increases implant complications by 2-3 fold, making autologous reconstruction preferred in patients requiring post-mastectomy radiation
Adjuvant Therapy Integration
Surgical decisions must integrate with systemic therapy planning to optimize overall treatment outcomes:
-
Chemotherapy Timing Considerations
- Adjuvant chemotherapy: start within 6-8 weeks of surgery
- Neoadjuvant approach: T2-T3 tumors, triple-negative, HER2-positive
- Pathologic complete response (pCR): excellent prognosis marker
- Triple-negative: pCR in 30-40% with standard regimens
- HER2-positive: pCR in 40-60% with dual HER2 blockade
-
Radiation Therapy Coordination
- Breast conservation: radiation mandatory for local control
- Post-mastectomy radiation: T3-T4, ≥4 positive nodes, positive margins
- Reconstruction timing: delayed preferred if radiation planned
- Hypofractionated radiation: 3 weeks vs 6 weeks, equivalent efficacy
- Partial breast irradiation: selected patients with favorable characteristics
| Treatment Sequence | Indication | Timeline | Outcome Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery → Chemo → Radiation | Standard adjuvant | 6-8 weeks between | Baseline approach |
| Chemo → Surgery → Radiation | Neoadjuvant candidates | 3-4 months pre-op | Downstaging, pCR assessment |
| Surgery → Radiation → Chemo | Elderly, comorbidities | Immediate post-op | Reduced systemic toxicity |
| Chemo → Surgery → Chemo | Dose-dense protocols | Split chemotherapy | Investigational approaches |
Quality Metrics and Outcome Optimization
Evidence-based quality measures guide treatment decisions and institutional performance:
-
Surgical Quality Indicators
- Re-excision rate: <20% for breast conservation
- Surgical site infection: <5% for clean procedures
- 30-day readmission: <5% for elective surgery
- Time to adjuvant therapy: <8 weeks from surgery
- Positive margin rate: <10% institutional benchmark
- Sentinel node identification: >95% success rate
-
Long-term Outcome Measures
- Local recurrence: <5% at 10 years for early-stage disease
- Overall survival: >90% for node-negative disease
- Disease-free survival: >85% for node-positive disease
- Patient satisfaction: >90% with treatment decisions
- Cosmetic outcomes: >80% good-excellent ratings
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Multidisciplinary team coordination improves treatment adherence by 15-20% and reduces time to treatment initiation by 25-30% compared to sequential consultations
These treatment frameworks ensure that surgical decisions align with evidence-based guidelines while maintaining flexibility for individual patient circumstances and preferences.
⚖️ Breast Surgery: The Treatment Decision Engine
🔗 Breast Surgery: The Multi-System Integration Hub
Genetic-Surgical Integration Framework
Understanding hereditary cancer syndromes transforms surgical decision-making from reactive to predictive medicine:
-
BRCA1/BRCA2 Mutation Management
- BRCA1 carriers: 55-65% lifetime breast cancer risk, 39% ovarian cancer risk
- BRCA2 carriers: 45% lifetime breast cancer risk, 11-17% ovarian cancer risk
- Male BRCA2 carriers: 6% breast cancer risk, increased prostate cancer
- Risk-reducing mastectomy: >90% breast cancer risk reduction
- Risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy: 80-90% ovarian cancer reduction
- Timing considerations: childbearing completion, age 35-40 for ovarian surgery
-
Emerging Genetic Syndromes
- TP53 (Li-Fraumeni): >90% lifetime cancer risk, radiation avoidance
- PALB2: 35% lifetime breast cancer risk, moderate penetrance
- ATM: 15-20% lifetime breast cancer risk, radiation sensitivity
- Multigene panel testing: 5-10% additional pathogenic variants beyond BRCA
- Variants of uncertain significance: 40-50% of panel results
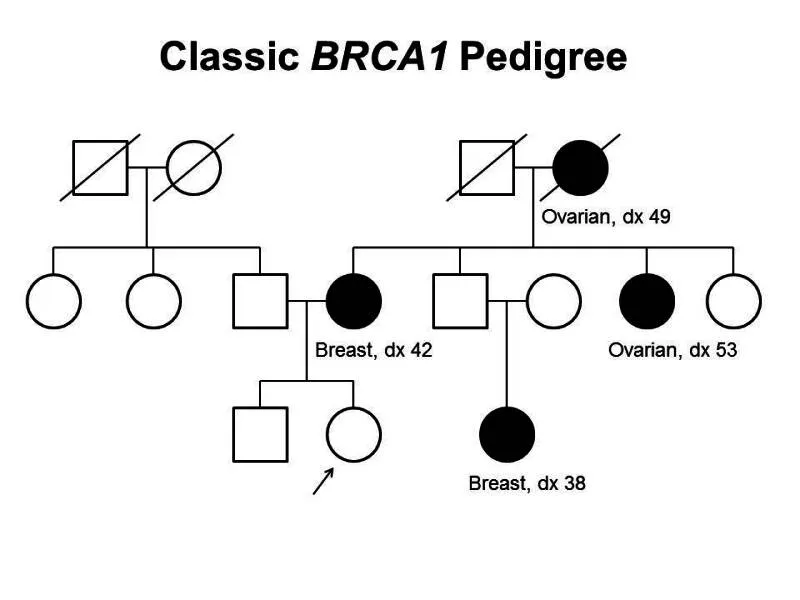
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Radiation therapy in TP53 mutation carriers increases second malignancy risk by 5-10 fold, making mastectomy preferred over breast conservation in Li-Fraumeni syndrome
Fertility Preservation Integration
Coordinating cancer treatment with reproductive planning requires sophisticated timing and technique integration:
-
Fertility Preservation Options
- Embryo cryopreservation: highest success rates, requires partner/donor
- Oocyte cryopreservation: single women, 2-week stimulation protocol
- Ovarian tissue cryopreservation: prepubertal patients, experimental
- GnRH agonists: ovarian suppression during chemotherapy
- Success rates: 30-40% live birth rate per transfer
-
Treatment Timing Coordination
- Fertility consultation: within 48-72 hours of diagnosis
- Ovarian stimulation: 10-14 days, can start any cycle day
- Treatment delay: <4 weeks acceptable for fertility preservation
- Letrozole protocols: estrogen-sensitive cancers, equivalent outcomes
- Emergency protocols: random start, minimal delay
| Age Group | Fertility Priority | Recommended Approach | Success Rates | Time Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <25 years | High | Oocyte + tissue preservation | 60-70% | 2-3 weeks |
| 25-35 years | Moderate-High | Oocyte cryopreservation | 40-50% | 2 weeks |
| 35-40 years | Moderate | Embryo preferred | 20-30% | 2-3 weeks |
| >40 years | Low | Case-by-case | <10% | Individual decision |
💡 Master This: Chemotherapy-induced amenorrhea occurs in >90% of women >40 years and 20-30% of women <30 years, making fertility preservation counseling mandatory for all reproductive-age patients
Reconstructive-Oncologic Integration
Coordinating reconstruction with oncologic treatment requires understanding how each component affects the others:
-
Radiation-Reconstruction Interactions
- Implant-based reconstruction: 30-40% complication rate with radiation
- Autologous reconstruction: 10-15% complication rate with radiation
- Timing optimization: radiation → 6-12 months → reconstruction
- Tissue expander complications: capsular contracture (40-60%), infection (15-20%)
- Autologous flap tolerance: better cosmetic outcomes after radiation
-
Oncoplastic Surgery Integration
- Volume displacement: local tissue rearrangement, <20% volume loss
- Volume replacement: contralateral reduction, symmetry procedures
- Margin optimization: wider excisions with maintained cosmesis
- Re-excision reduction: from 20-25% to <10%
- Patient satisfaction: >90% with oncoplastic techniques
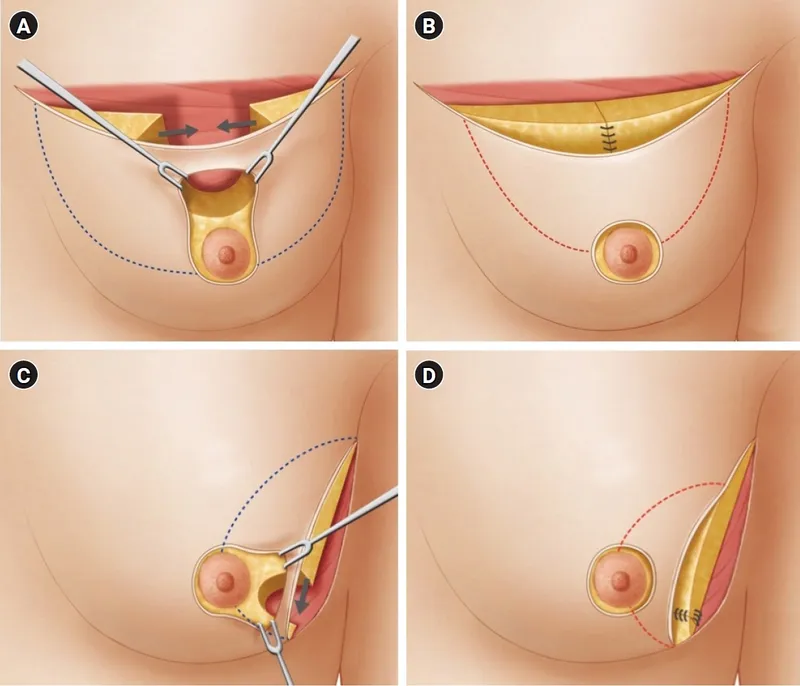
📌 Remember: RADIO for reconstruction planning - Radiation effects, Autologous preferred, Delayed if uncertain, Immediate if no radiation, Oncoplastic alternatives
Survivorship Care Integration
Long-term survivorship planning begins at diagnosis and continues throughout treatment:
-
Surveillance Protocol Development
- Physical examination: every 3-6 months for 3 years, then annually
- Mammography: annually, 6 months after radiation completion
- Advanced imaging: not recommended for routine surveillance
- Genetic carriers: MRI screening annually starting age 25-30
- High-risk lesions: enhanced surveillance protocols
-
Late Effects Management
- Lymphedema: 15-20% incidence after axillary dissection
- Cardiac toxicity: anthracycline and trastuzumab monitoring
- Bone health: aromatase inhibitor effects, DEXA screening
- Cognitive effects: chemobrain in 20-30% of patients
- Sexual health: hormonal therapy effects, counseling resources
| Survivorship Issue | Incidence | Monitoring Schedule | Intervention Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lymphedema | 15-20% | Annual assessment | Physical therapy, compression |
| Cardiac dysfunction | 5-10% | ECHO/MUGA q6-12mo | Cardio-oncology referral |
| Bone loss | 20-30% | DEXA q1-2 years | Bisphosphonates, calcium |
| Cognitive changes | 20-30% | Symptom assessment | Cognitive rehabilitation |
| Sexual dysfunction | 40-60% | Annual screening | Counseling, medical therapy |
These integration frameworks ensure that breast surgery serves as the coordinating center for comprehensive cancer care that addresses not only immediate treatment needs but also long-term survivorship and quality of life optimization.
🔗 Breast Surgery: The Multi-System Integration Hub
🎯 Breast Surgery: The Clinical Mastery Arsenal
Essential Clinical Thresholds Arsenal
Master these critical numerical thresholds that guide every major breast surgery decision:
-
Diagnostic Thresholds
- BI-RADS 4A: 2-10% cancer risk → core biopsy
- BI-RADS 4B: 10-50% cancer risk → 14-gauge core
- BI-RADS 4C: 50-95% cancer risk → surgical consultation
- Upgrade risk ADH: 10-20% → mandatory excision
- Papillary lesions: 15-25% upgrade → complete removal
-
Surgical Decision Thresholds
- Tumor-to-breast ratio: >20% → mastectomy consideration
- Margin adequacy invasive: no ink on tumor = adequate
- Margin adequacy DCIS: ≥2mm = standard
- Re-excision rate: <20% = quality benchmark
- Lymphedema risk: 15-20% after axillary dissection
📌 Remember: MARGINS for surgical adequacy - Malignant (no ink), Atypical (2mm DCIS), Re-excision (<20%), Guidelines (evidence-based), Invasive (clear), Negative predictive value, Standard protocols
Rapid Assessment Framework
The 60-Second Breast Surgery Assessment:
-
Clinical Evaluation (15 seconds)
- Age group: <30 (benign likely), 30-50 (mixed), >50 (cancer concern)
- Physical findings: mobile vs fixed, skin changes, lymphadenopathy
- Family history: BRCA risk factors, multiple primaries
-
Imaging Integration (15 seconds)
- BI-RADS category: determines next step
- Concordance assessment: clinical-imaging-pathology alignment
- Multifocal/multicentric: MRI consideration
-
Pathology Correlation (15 seconds)
- Benign concordant: routine follow-up
- High-risk lesions: surgical excision
- Malignant: staging and treatment planning
-
Treatment Planning (15 seconds)
- Conservation candidate: tumor size, location, patient preference
- Systemic therapy: neoadjuvant vs adjuvant approach
- Reconstruction: immediate vs delayed based on radiation
⭐ Clinical Pearl: The 4-Question Breast Surgery Framework - (1) What is it? (diagnosis), (2) Where is it? (staging), (3) How aggressive? (biology), (4) What does patient want? (shared decision-making)
High-Yield Clinical Correlations
| Clinical Scenario | Key Finding | Immediate Action | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bloody nipple discharge | Unilateral, single duct | Ductography/MRI | 85-90% diagnostic yield |
| Palpable mass + negative imaging | <30 years old | Ultrasound-guided biopsy | 95% sensitivity |
| BRCA+ patient | Risk-reducing surgery | Genetic counseling | >90% risk reduction |
| Positive margins | Invasive cancer | Re-excision vs mastectomy | 80-85% clear margins |
| Lymphedema symptoms | Post-axillary dissection | Physical therapy referral | 70-80% improvement |
Inflammatory Breast Cancer Recognition:
- Skin erythema >1/3 breast surface
- Peau d'orange appearance
- Rapid onset <6 months
- Pathologic confirmation: dermal lymphatic invasion → Immediate oncology referral + neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Pregnancy-Associated Breast Cancer:
- Any trimester: core biopsy safe
- Chemotherapy: safe after 1st trimester
- Radiation: contraindicated during pregnancy
- Surgery: safe in any trimester → Multidisciplinary coordination essential
💡 Master This: URGENT breast surgery scenarios - Unilateral bloody discharge, Rapid skin changes, Genetic high-risk, Enlarged lymph nodes, New mass in pregnancy, Triple assessment discordance
Quality Optimization Checklist
Pre-operative Optimization:
- Imaging concordance verified
- Genetic counseling if indicated (<50 years, family history)
- Fertility preservation discussed (reproductive age)
- Reconstruction options reviewed
- Multidisciplinary team input obtained
Intraoperative Excellence:
- Specimen orientation confirmed
- Margin assessment performed
- Sentinel node identification >95%
- Hemostasis achieved
- Cosmetic outcome optimized
Post-operative Monitoring:
- Pathology review within 48 hours
- Adjuvant therapy planning within 2 weeks
- Complication surveillance established
- Survivorship planning initiated
- Quality metrics tracked
📌 Remember: EXCELLENCE in breast surgery - Evidence-based decisions, Xcellent communication, Coordinated care, Ethical practice, Lifelong learning, Low complications, Empathetic approach, Navigate complexity, Continuous improvement, Exceptional outcomes
This clinical mastery arsenal provides the systematic framework and rapid-reference tools necessary for delivering consistently excellent breast surgical care across the full spectrum of benign and malignant breast disease.
🎯 Breast Surgery: The Clinical Mastery Arsenal
Practice Questions: Breast Surgery
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 33-year-old woman comes to the physician 1 week after noticing a lump in her right breast. Fifteen years ago, she was diagnosed with osteosarcoma of her left distal femur. Her father died of an adrenocortical carcinoma at the age of 41 years. Examination shows a 2-cm, firm, immobile mass in the lower outer quadrant of the right breast. A core needle biopsy of the mass shows adenocarcinoma. Genetic analysis in this patient is most likely to show a defect in which of the following genes?













