Anesthesia and Perioperative medicine

On this page
🎯 The Anesthesia Command Center: Mastering Perioperative Excellence
Anesthesia transforms surgery from an ordeal into a controlled, reversible state where pain vanishes, muscles relax, and consciousness fades-all while you maintain the patient's physiological tightrope between life and death. You'll master how anesthetic agents work at molecular levels, build vigilance through monitoring protocols that catch deterioration before disaster strikes, and develop rapid-fire crisis recognition skills that turn emergencies into managed events. This lesson integrates pharmacology, physiology, and systems thinking to forge your command of the perioperative period, where every decision cascades through multiple organ systems and timing separates excellent outcomes from catastrophe.
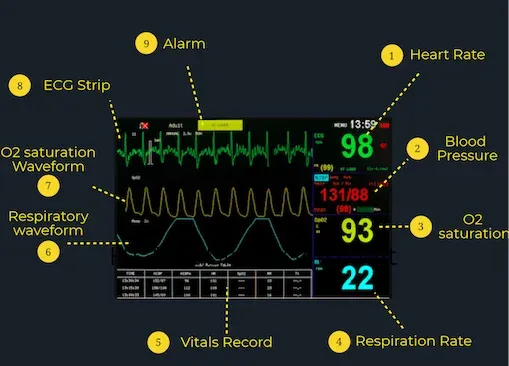
Anesthesia represents one of medicine's most dynamic specialties, requiring real-time integration of pharmacology, physiology, and pathology. Every anesthetic encounter demands mastery of drug interactions, airway management, hemodynamic control, and complication recognition. The perioperative period extends this responsibility from preoperative optimization through postoperative recovery, creating a continuum of care where clinical decisions directly impact morbidity and mortality.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Perioperative complications occur in 15-20% of surgical patients, with cardiovascular events accounting for 40% of perioperative mortality in non-cardiac surgery.
Modern anesthesia practice integrates evidence-based protocols with individualized patient care, utilizing advanced monitoring technologies and targeted drug delivery systems. Understanding the fundamental principles of anesthetic pharmacology, physiological monitoring, and complication management provides the foundation for safe perioperative care across all surgical specialties.
💡 Master This: The MAC (Minimum Alveolar Concentration) concept quantifies anesthetic potency - 1 MAC prevents movement in 50% of patients during surgical incision, with most procedures requiring 1.2-1.3 MAC for adequate anesthesia.
Connect these foundational principles through systematic exploration of anesthetic mechanisms to understand how molecular actions translate into clinical effects.
🎯 The Anesthesia Command Center: Mastering Perioperative Excellence
🧠 Anesthetic Mechanisms: The Molecular Orchestra
📌 Remember: GABA-NMDA - General Anesthetics Block Awareness through NMDA Modulation, Depressing Arousal pathways.
| Anesthetic Agent | Primary Mechanism | Onset Time | Duration | MAC/EC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sevoflurane | GABA-A enhancement | 2-3 minutes | 5-10 minutes | 2.0% |
| Propofol | GABA-A potentiation | 30-60 seconds | 5-15 minutes | 3-5 μg/mL |
| Etomidate | GABA-A selective | 15-30 seconds | 3-8 minutes | 0.3 μg/mL |
| Ketamine | NMDA antagonism | 1-2 minutes | 10-20 minutes | 0.5-2 mg/kg |
| Midazolam | GABA-A benzodiazepine | 2-5 minutes | 30-60 minutes | 150-300 ng/mL |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Ketamine provides dissociative anesthesia through NMDA receptor antagonism, maintaining cardiovascular stability and spontaneous ventilation - ideal for hemodynamically unstable patients.
-
Inhalational Anesthetics
- Sevoflurane: Blood:gas coefficient 0.65 - rapid onset/offset
- Desflurane: Blood:gas coefficient 0.42 - fastest emergence
- Requires heated vaporizer due to boiling point 23.5°C
- Causes airway irritation at concentrations >6%
- Isoflurane: Blood:gas coefficient 1.4 - intermediate kinetics
- Coronary steal phenomenon at concentrations >1.5 MAC
-
Intravenous Anesthetics
- Propofol: Context-sensitive half-time 10-40 minutes
- Redistribution half-life 2-8 minutes explains rapid awakening
- Pain on injection in 60-80% of patients
- Etomidate: Minimal cardiovascular depression
- Adrenal suppression lasting 6-24 hours post-injection
- Myoclonus in 30-60% of patients
- Propofol: Context-sensitive half-time 10-40 minutes
💡 Master This: Context-sensitive half-time increases with infusion duration for all IV anesthetics except remifentanil, which maintains 3-5 minute offset regardless of infusion length due to ester hydrolysis.
Understanding these molecular mechanisms through systematic monitoring approaches reveals how anesthetic depth correlates with measurable physiological parameters.
🧠 Anesthetic Mechanisms: The Molecular Orchestra
📊 Monitoring Mastery: The Vigilance Protocol
The ASA Standard Monitors establish minimum monitoring requirements: pulse oximetry, capnography, ECG, blood pressure, and temperature. Advanced monitoring includes processed EEG (BIS, entropy), neuromuscular blockade (TOF), and cardiac output measurement for high-risk procedures.
📌 Remember: PECT-BNT - Pulse oximetry, ECG, Capnography, Temperature, Blood pressure, Neuromuscular, Train-of-four monitoring essentials.
| Monitor Type | Parameter | Normal Range | Critical Values | Response Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulse Oximetry | SpO2 | 97-100% | <90% | 10-30 seconds |
| Capnography | ETCO2 | 35-45 mmHg | <20 or >60 mmHg | 1-3 breaths |
| Blood Pressure | MAP | 65-100 mmHg | <60 or >110 mmHg | 1-5 minutes |
| BIS Monitor | Consciousness | 40-60 | <30 or >70 | 5-15 seconds |
| TOF Ratio | NMB Recovery | >0.9 | <0.7 | Real-time |
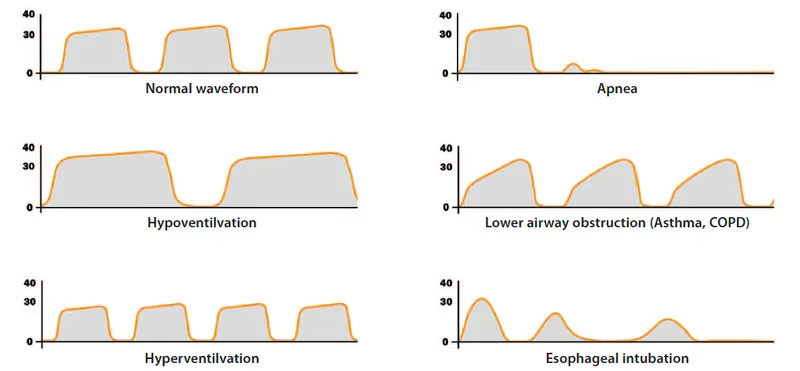
- Sudden decrease to zero: Esophageal intubation or complete airway obstruction
- Gradual decrease: Hypovolemia, decreased cardiac output, or pulmonary embolism
- Gradual increase: Malignant hyperthermia, inadequate ventilation, or CO2 rebreathing
- Biphasic waveform: Partial airway obstruction or bronchospasm
⭐ Clinical Pearl: BIS values 40-60 correlate with adequate anesthetic depth for surgery, while values <30 indicate burst suppression and potential overdose.
-
Processed EEG Monitoring
- BIS (Bispectral Index): 0-100 scale with 40-60 target range
- Values >70 suggest awareness risk
- Values <30 indicate burst suppression
- Entropy monitoring: State Entropy (SE) and Response Entropy (RE)
- SE-RE difference >10 suggests inadequate analgesia
- BIS (Bispectral Index): 0-100 scale with 40-60 target range
-
Neuromuscular Monitoring
- Train-of-Four (TOF) ratio: >0.9 required for safe extubation
- TOF count 0: Intense blockade (100% block)
- TOF count 1-3: Deep blockade (90-99% block)
- TOF ratio 0.7-0.9: Moderate residual blockade
- Post-tetanic count: Assesses deep neuromuscular blockade
- Train-of-Four (TOF) ratio: >0.9 required for safe extubation
💡 Master This: Pulse oximetry lag time averages 20-30 seconds from lung to finger, making capnography the earliest indicator of ventilation problems during anesthesia.
These monitoring principles through pattern recognition frameworks enable rapid identification of perioperative complications.
📊 Monitoring Mastery: The Vigilance Protocol
🚨 Crisis Recognition: The Emergency Response Matrix
Anesthesia emergencies follow predictable patterns with specific diagnostic criteria and treatment algorithms. The "Can't Intubate, Can't Oxygenate" scenario represents the ultimate airway emergency, requiring surgical airway within 3-5 minutes to prevent hypoxic brain injury.
📌 Remember: COVER ABCD - Cardiovascular, Oxygenation, Ventilation, Equipment, Rx drugs, Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Drugs for crisis management.
| Emergency | Key Signs | Time to Action | Primary Treatment | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
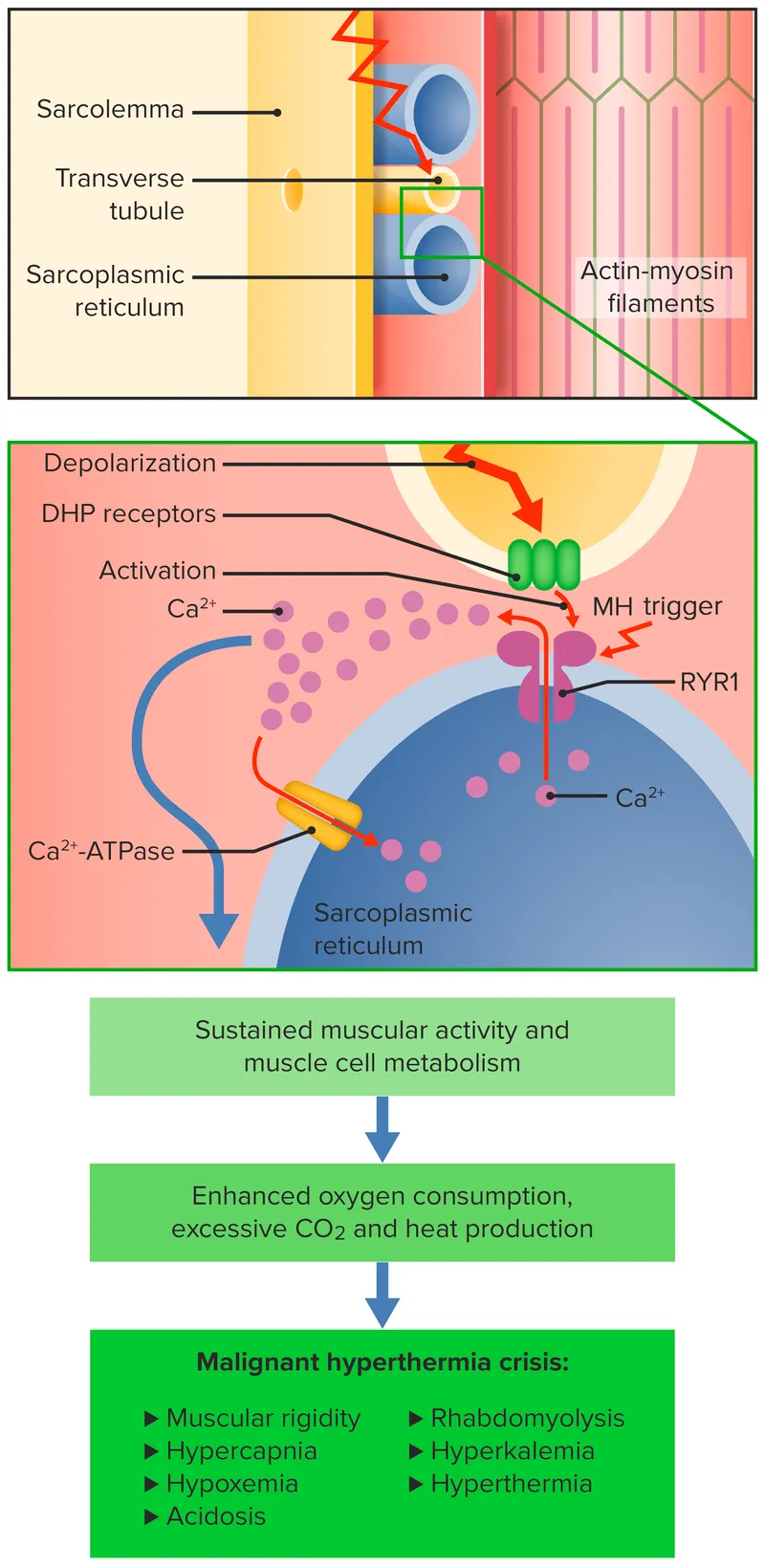
| Malignant Hyperthermia | ETCO2 >55 mmHg | <5 minutes | Dantrolene 2.5 mg/kg | 95% survival |
| Anaphylaxis | Hypotension + rash | <2 minutes | Epinephrine 0.5-1 mg | 90% recovery |
| Air Embolism | Mill wheel murmur | <1 minute | Left lateral position | 70% survival |
| LAST | CNS/cardiac toxicity | <3 minutes | Lipid emulsion 20% | 85% recovery |
| Aspiration | Witnessed/suspected | Immediate | Suction + positioning | Variable |
- ETCO2 increase >55 mmHg (earliest and most sensitive)
- Tachycardia >150 bpm in adults
- Masseter muscle rigidity following succinylcholine
- Temperature increase >2°C/hour (late sign)
- Mixed acidosis with pH <7.25
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity (LAST) requires lipid emulsion 20% at 1.5 mL/kg bolus followed by 0.25 mL/kg/min infusion - never exceed 12 mL/kg total dose.
-
Airway Emergencies
- "Can't Intubate, Can't Oxygenate": Surgical airway within 3-5 minutes
- Cricothyrotomy preferred over tracheostomy in emergency
- Success rate >95% when performed correctly
- Aspiration: Head-down position and immediate suction
- Bronchoscopy within 24 hours if particulate matter suspected
- Steroid therapy contraindicated - increases infection risk
- "Can't Intubate, Can't Oxygenate": Surgical airway within 3-5 minutes
-
Cardiovascular Emergencies
- Anaphylaxis: Epinephrine 0.5-1 mg IV every 3-5 minutes
- Fluid resuscitation 25-50 mL/kg for distributive shock
- H1 and H2 antihistamines as adjunctive therapy
- Air Embolism: Left lateral Trendelenburg position
- 100% oxygen and attempt aspiration via central line
- Hyperbaric oxygen if neurological symptoms persist
- Anaphylaxis: Epinephrine 0.5-1 mg IV every 3-5 minutes
💡 Master This: Dantrolene dosing for MH crisis: 2.5 mg/kg IV bolus, repeat every 3 minutes until symptoms resolve - average total dose 8-10 mg/kg.
Crisis recognition through systematic treatment algorithms enables evidence-based therapeutic interventions.
🚨 Crisis Recognition: The Emergency Response Matrix
💊 Therapeutic Algorithms: The Treatment Decision Tree
Anesthetic technique selection depends on surgical requirements, patient comorbidities, and postoperative pain management goals. Regional anesthesia reduces opioid consumption by 40-60% and decreases PONV by 30-50% compared to general anesthesia alone.
📌 Remember: SOAP-ME - Surgery type, Optimization status, Airway assessment, Pain management, Monitoring needs, Emergence plan for anesthetic selection.
| Technique | Indications | Contraindications | Success Rate | Complication Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spinal Anesthesia | Surgery <3 hours | Coagulopathy | 95-98% | 0.1-0.5% |
| Epidural | Labor, thoracic surgery | Infection at site | 90-95% | 0.5-1% |
| Brachial Plexus | Upper extremity | Contralateral pneumothorax | 85-95% | 1-3% |
| Femoral Block | Knee surgery | Anticoagulation | 90-95% | <1% |
| TAP Block | Abdominal surgery | Peritonitis | 80-90% | <0.5% |
- TIVA Protocols
- Propofol induction: 1-2.5 mg/kg over 30-60 seconds
- Maintenance: 4-12 mg/kg/hr titrated to BIS 40-60
- Context-sensitive half-time: 10-40 minutes depending on duration
- Remifentanil: 0.5-1 μg/kg bolus, 0.1-0.5 μg/kg/min infusion
- Offset within 5-10 minutes regardless of infusion duration
- Requires multimodal analgesia for postoperative pain
- Propofol induction: 1-2.5 mg/kg over 30-60 seconds
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols reduce hospital length of stay by 1-3 days and complications by 30-50% through multimodal optimization.
-
Regional Anesthesia Dosing
- Bupivacaine 0.25-0.5%: Maximum 2.5 mg/kg without epinephrine
- Duration 4-8 hours for motor block, 6-12 hours for sensory
- Cardiotoxicity risk at doses >3 mg/kg
- Lidocaine 1-2%: Maximum 4.5 mg/kg without epinephrine
- Onset 5-15 minutes, duration 1-3 hours
- Add epinephrine 1:200,000 increases maximum dose to 7 mg/kg
- Bupivacaine 0.25-0.5%: Maximum 2.5 mg/kg without epinephrine
-
Emergence Optimization
- Sugammadex: 2-4 mg/kg for moderate block reversal
- 16 mg/kg for immediate reversal of rocuronium
- Contraindicated in severe renal impairment (CrCl <30)
- Multimodal analgesia: Acetaminophen 1g + ketorolac 30mg
- Reduces opioid requirements by 25-40%
- Improves patient satisfaction scores by 15-25%
- Sugammadex: 2-4 mg/kg for moderate block reversal
💡 Master This: Neuraxial anesthesia reduces perioperative mortality by 30% in high-risk patients undergoing major surgery, particularly cardiac and vascular procedures.
Treatment algorithms through advanced integration concepts reveal how multiple anesthetic modalities work synergistically.
💊 Therapeutic Algorithms: The Treatment Decision Tree
🔄 Perioperative Integration: The Systems Approach
Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols demonstrate how systematic integration improves outcomes across 20+ evidence-based interventions. ERAS implementation reduces complications by 30-50%, length of stay by 1-3 days, and healthcare costs by 15-25%.
📌 Remember: PREPARE-PERFORM-RECOVER - Preoperative optimization, Risk stratification, Education, Pain management, Anesthesia planning, Regional techniques, Early mobilization for Perioperative Excellence, Rapid Functional recovery, Optimal Resource utilization, Multimodal approach.
| Phase | Key Interventions | Timeline | Outcome Metrics | Evidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative | Risk assessment, optimization | 2-4 weeks | Complication reduction 20-30% | Level I |
| Intraoperative | Goal-directed therapy | Real-time | Fluid balance optimization | Level I |
| Postoperative | Early mobilization | 2-6 hours | LOS reduction 1-3 days | Level I |
| Recovery | Multimodal analgesia | 24-72 hours | Opioid reduction 40-60% | Level I |
| Follow-up | Complication surveillance | 30 days | Readmission reduction 15-25% | Level II |
-
Cardiovascular Optimization
- Beta-blocker therapy: Continue chronic medications, avoid new initiation
- Perioperative MI risk increases 2-3 fold with acute withdrawal
- New beta-blockers increase stroke risk by 73% (POISE trial)
- Statin therapy: High-intensity statins reduce cardiac events by 25-35%
- Atorvastatin 80mg or rosuvastatin 40mg starting 2 weeks preoperatively
- Pleiotropic effects include anti-inflammatory and plaque stabilization
- Beta-blocker therapy: Continue chronic medications, avoid new initiation
-
Pulmonary Optimization
- Incentive spirometry: 10 breaths every hour reduces pneumonia by 50%
- Preoperative training improves compliance and effectiveness
- Combined with CPAP for OSA patients reduces complications by 60%
- Smoking cessation: ≥4 weeks required for ciliary function recovery
- Nicotine replacement maintains cessation during perioperative stress
- Varenicline or bupropion for long-term success
- Incentive spirometry: 10 breaths every hour reduces pneumonia by 50%
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Goal-directed fluid therapy using stroke volume variation reduces complications by 25% and hospital stay by 1.2 days compared to liberal fluid strategies.
- Intraoperative Integration
- Hemodynamic optimization: MAP >65 mmHg and SVV <13%
- Fluid responsiveness predicted by SVV, PPV, or PLR test
- Vasopressor preference: Norepinephrine over phenylephrine for cardiac output
- Temperature management: Normothermia 36-37°C throughout procedure
- Forced-air warming reduces SSI risk by 60%
- Hypothermia <36°C increases bleeding by 16% and infection by 19%
- Hemodynamic optimization: MAP >65 mmHg and SVV <13%
💡 Master This: Opioid-sparing anesthesia using regional blocks + multimodal analgesia reduces chronic pain development by 40-50% and opioid dependence by 60-70%.
Integration principles through rapid mastery frameworks create comprehensive clinical decision-making tools.
🔄 Perioperative Integration: The Systems Approach
⚡ Clinical Command Arsenal: The Mastery Toolkit
The Essential Arsenal consolidates high-yield clinical data into rapid-reference formats for immediate application. Master these core numbers and decision trees to achieve expert-level clinical performance across all anesthetic encounters.
📌 Remember: FAST-SAFE-SMART - Fundamental dosing, Airway algorithms, Safety protocols, Timing parameters, Systemic monitoring, Anesthetic depth, Fluid management, Emergency responses for Speedy Mastery, Accurate Recognition, Targeted interventions.
| Critical Parameter | Normal Range | Action Threshold | Emergency Response | Time Window |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETCO2 | 35-45 mmHg | <20 or >60 mmHg | Check airway/circulation | <30 seconds |
| SpO2 | 97-100% | <90% | Increase FiO2, check airway | <60 seconds |
| MAP | 65-100 mmHg | <60 or >110 mmHg | Fluid/vasopressor/vasodilator | <2 minutes |
| BIS | 40-60 | <30 or >70 | Adjust anesthetic depth | <1 minute |
| Temperature | 36-37°C | <35 or >38.5°C | Warming/cooling measures | <5 minutes |
-
Malignant Hyperthermia
- Dantrolene: 2.5 mg/kg IV every 3 minutes until resolution
- Average total dose: 8-10 mg/kg
- Continue 1-3 mg/kg q6h for 24-48 hours
- Cooling measures: Ice packs, cold saline, cooling blankets
- Dantrolene: 2.5 mg/kg IV every 3 minutes until resolution
-
Anaphylaxis Protocol
- Epinephrine: 0.5-1 mg IV (1:10,000) every 3-5 minutes
- Infusion: 0.1-1 μg/kg/min for refractory cases
- Fluid resuscitation: 25-50 mL/kg crystalloid
- Adjunctive therapy: H1/H2 blockers, steroids, bronchodilators
- Epinephrine: 0.5-1 mg IV (1:10,000) every 3-5 minutes
-
Local Anesthetic Toxicity
- Lipid emulsion 20%: 1.5 mL/kg bolus over 1 minute
- Infusion: 0.25 mL/kg/min for 10 minutes
- Maximum total dose: 12 mL/kg over 30 minutes
- Lipid emulsion 20%: 1.5 mL/kg bolus over 1 minute
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Rapid sequence induction timing: Preoxygenation 3-5 minutes → Propofol 1-2.5 mg/kg → Succinylcholine 1-1.5 mg/kg → Intubation at 45-60 seconds.
Airway Management Hierarchy:
- Bag-mask ventilation - First-line for oxygenation
- Supraglottic airway - LMA for rescue ventilation
- Endotracheal intubation - Definitive airway control
- Surgical airway - Cricothyrotomy for CICO scenario
Regional Anesthesia Quick Reference:
- Spinal anesthesia: Bupivacaine 10-15 mg for lower extremity/abdomen
- Epidural: Test dose 3 mL lidocaine 1.5% with epinephrine 1:200,000
- Brachial plexus: 20-30 mL bupivacaine 0.25-0.5% for upper extremity
- Femoral block: 15-20 mL bupivacaine 0.25% for knee surgery
💡 Master This: Context-sensitive half-times at 3 hours: Propofol 23 minutes, Midazolam 65 minutes, Fentanyl 45 minutes, Remifentanil 5 minutes - choose agents based on emergence requirements.
Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting (PONV) Prevention:
- High-risk patients (≥3 risk factors): Multimodal prophylaxis
- Ondansetron 4-8 mg + Dexamethasone 4-8 mg + Droperidol 0.625-1.25 mg
- TIVA preferred over volatile anesthetics for PONV reduction
Master these clinical command tools to achieve expert-level anesthetic practice with rapid decision-making capabilities and optimal patient outcomes across all perioperative scenarios.
⚡ Clinical Command Arsenal: The Mastery Toolkit
Practice Questions: Anesthesia and Perioperative medicine
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 4-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother after cutting his buttock on a piece of broken glass. There is a 5-cm curvilinear laceration over the patient's right buttock. His vital signs are unremarkable. The decision to repair the laceration is made. Which of the following will offer the longest anesthesia for the laceration repair?













