Abdominal emergencies

On this page
🚨 Emergency Command Center: The Acute Abdomen Arsenal
The acute abdomen transforms your emergency department into a high-stakes diagnostic arena where minutes determine whether a patient walks out or rolls to the operating room. You'll master the pathophysiological cascades that turn appendicitis into sepsis, recognize the clinical patterns that distinguish surgical catastrophe from medical mimicry, and deploy the diagnostic and therapeutic tools that save lives before peritonitis wins. This lesson builds your systematic approach to abdominal emergencies-from initial presentation through definitive intervention-integrating anatomy, physiology, and clinical reasoning into the split-second decisions that define emergency medicine.
📌 Remember: VOMIT - Vascular, Obstruction, Metabolic, Infection, Trauma - covers 85% of abdominal emergencies requiring immediate intervention
The acute abdomen represents a constellation of conditions where time = tissue. Delayed recognition increases mortality by 12-15% per hour in conditions like mesenteric ischemia, while early intervention in appendicitis reduces perforation rates from 25% to <5%.
| Emergency Type | Golden Hour | Mortality Untreated | Key Discriminator | Immediate Action | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesenteric Ischemia | 6 hours | 90% | Pain out of proportion | Vascular surgery | 85% if <6h |
| AAA Rupture | 30 minutes | 95% | Pulsatile mass + shock | OR immediately | 50% if unstable |
| Perforated Viscus | 4-6 hours | 40-60% | Free air + peritonitis | Surgical repair | 90% if early |
| Strangulated Bowel | 6-8 hours | 25-30% | Closed loop + ischemia | Bowel resection | 95% if viable |
| Necrotizing Pancreatitis | 24-48 hours | 15-20% | SIRS + organ failure | ICU + debridement | 80% with MDT |
- Hemodynamic Instability Triggers
- Systolic BP <90 mmHg or >20% drop from baseline
- Heart rate >120 bpm with poor response to fluids
- Lactate >4 mmol/L suggesting tissue hypoperfusion
- Mesenteric ischemia: lactate >6 mmol/L in 80%
- Septic shock: lactate >2 mmol/L with organ dysfunction
- Hemorrhagic shock: lactate correlates with blood loss >30%
💡 Master This: Every abdominal emergency follows the "Rule of Sixes" - 6 hours for ischemia, 6 liters for resuscitation, 6 units for massive transfusion, and 6 systems for multiorgan failure assessment
The foundation of emergency abdominal care rests on recognizing that surgical emergencies account for 15-20% of ED presentations but represent 60% of preventable deaths. This knowledge transforms your approach from reactive to predictive, enabling life-saving interventions before irreversible damage occurs.
Connect this foundational understanding through systematic assessment patterns to master the diagnostic frameworks that separate surgical from medical emergencies.
🚨 Emergency Command Center: The Acute Abdomen Arsenal
⚡ Pathophysiological Cascade: The Inflammatory Storm
📌 Remember: SIRS-MODS - Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome leads to Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome in 20-30% of severe abdominal emergencies within 24-48 hours

The inflammatory response follows a biphasic pattern: initial pro-inflammatory surge (0-6 hours) followed by compensatory anti-inflammatory response (6-24 hours). Understanding this timeline predicts clinical deterioration and guides intervention windows.
-
Phase 1: Tissue Injury Response (0-2 hours)
- Local mediator release: TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 within 30 minutes
- Complement activation: C3a, C5a triggering mast cell degranulation
- Coagulation cascade: Factor XII activation leading to DIC risk
- Platelet count drops >50% in severe cases
- PT/PTT elevation >1.5x normal indicates consumption
- D-dimer >500 ng/mL suggests ongoing fibrinolysis
-
Phase 2: Systemic Amplification (2-6 hours)
- Endothelial dysfunction: NO dysregulation causing vasodilation
- Capillary leak: albumin extravasation >50% in severe cases
- Metabolic acidosis: lactate >4 mmol/L from tissue hypoperfusion
- Base deficit >-6 mEq/L indicates significant fluid losses
- Anion gap >16 mEq/L suggests metabolic derangement
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Procalcitonin >2 ng/mL distinguishes bacterial peritonitis from sterile inflammation with 85% sensitivity, guiding antibiotic decisions in unclear cases
| Mediator | Peak Time | Half-Life | Clinical Effect | Threshold | Intervention Window |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | 2-4 hours | 20 minutes | Fever, hypotension | >50 pg/mL | 0-6 hours |
| IL-6 | 4-8 hours | 4-6 hours | Acute phase response | >100 pg/mL | 6-12 hours |
| Procalcitonin | 6-12 hours | 24 hours | Bacterial infection | >2 ng/mL | 12-24 hours |
| Lactate | 1-3 hours | 60 minutes | Tissue hypoperfusion | >4 mmol/L | 0-3 hours |
| CRP | 12-24 hours | 48 hours | Inflammation marker | >150 mg/L | 24-48 hours |
- Organ-Specific Dysfunction Patterns
- Cardiovascular: Distributive shock with SVR <800 dynes·sec/cm⁵
- Pulmonary: ARDS development in 15-25% with PaO₂/FiO₂ <300
- Renal: AKI in 30-40% with creatinine >1.5x baseline
- Oliguria <0.5 mL/kg/hr for >6 hours
- NGAL >150 ng/mL predicts AKI 12-24 hours before creatinine
- Hepatic: Bilirubin >2 mg/dL and ALT >2x normal
- Hematologic: Platelet count <100,000 or >50% drop
Understanding these pathophysiological cascades through pattern recognition frameworks enables rapid identification of patients requiring immediate intervention versus those suitable for observation.
⚡ Pathophysiological Cascade: The Inflammatory Storm
🎯 Recognition Mastery: The Clinical Pattern Matrix
📌 Remember: OPQRST-AAA - Onset, Provocation, Quality, Radiation, Severity, Timing - plus Associated symptoms, Alleviating factors, Aggravating factors - captures 95% of diagnostic information in the first 3 minutes
The "Rule of Threes" governs abdominal emergency recognition: 3 minutes for initial assessment, 3 key findings for diagnosis, 3 hours for definitive management, and 3 systems (cardiovascular, GI, genitourinary) for complications.
- High-Acuity Pattern Recognition
- Immediate Threat Patterns (minutes to hours)
- AAA rupture: Triad present in only 50% - hypotension, back pain, pulsatile mass
- Mesenteric ischemia: Pain out of proportion in 75%, lactate >6 mmol/L
- Perforated viscus: Free air on imaging 85%, rigid abdomen 70%
- Urgent Patterns (hours to 12 hours)
- Strangulated hernia: Irreducible mass 100%, bowel sounds absent 80%
- Acute cholangitis: Charcot's triad in 70%, Reynolds pentad in severe cases
- Necrotizing pancreatitis: SIRS criteria >2 in 90% of severe cases
- Immediate Threat Patterns (minutes to hours)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: The "pain migration pattern" - periumbilical to RLQ in appendicitis (65%), epigastric to RUQ in cholecystitis (80%) - provides diagnostic accuracy >85% when combined with laboratory findings
| Clinical Pattern | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Key Discriminator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murphy's Sign | 65% | 87% | 70% | 84% | Inspiratory arrest on palpation |
| Rovsing's Sign | 68% | 58% | 45% | 78% | RLQ pain with LLQ palpation |
| Psoas Sign | 16% | 95% | 80% | 50% | Pain with hip extension |
| Obturator Sign | 8% | 94% | 60% | 50% | Pain with hip rotation |
| Grey Turner's | 3% | 99% | 85% | 65% | Flank ecchymosis |
- Age-Stratified Pattern Recognition
- Pediatric (<18 years): Appendicitis 35%, intussusception 15%, testicular torsion 10%
- Alvarado Score >7 has 85% sensitivity in children >5 years
- Ultrasound first approach reduces radiation by 60%
- Adult (18-65 years): Appendicitis 25%, cholecystitis 20%, diverticulitis 15%
- CT accuracy >95% for most conditions
- Laboratory markers more reliable than physical exam
- Elderly (>65 years): Diverticulitis 30%, cholecystitis 25%, bowel obstruction 20%
- Atypical presentations in 60% of cases
- Delayed diagnosis increases mortality 2-3x
- Pediatric (<18 years): Appendicitis 35%, intussusception 15%, testicular torsion 10%
The pattern recognition matrix enables rapid categorization of patients into surgical, medical, or observation pathways within 15 minutes of presentation, optimizing resource utilization and patient outcomes.
Connect these recognition patterns through systematic diagnostic algorithms to master the evidence-based approaches that ensure no life-threatening condition is missed.
🎯 Recognition Mastery: The Clinical Pattern Matrix
🔬 Diagnostic Precision: The Investigation Arsenal
📌 Remember: LABS-CT-OR - Laboratory markers guide urgency, CT provides anatomical detail, OR confirms diagnosis - but clinical suspicion drives the sequence and timing of investigations
The diagnostic approach follows Bayesian principles: pre-test probability determines test selection, while post-test probability guides management decisions. Understanding these relationships prevents both over-investigation and missed diagnoses.
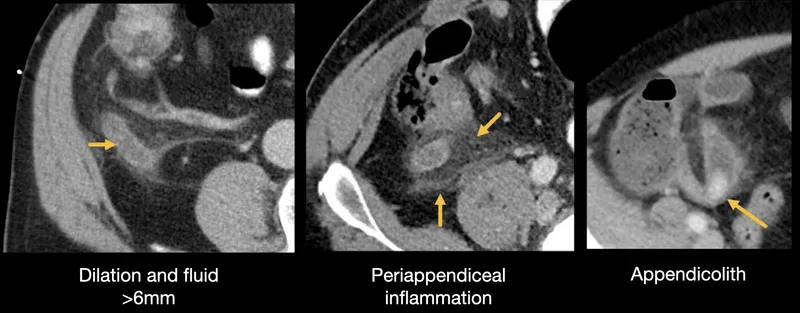
- Laboratory Investigation Hierarchy
- Immediate Priority (within 15 minutes)
- CBC: WBC >15,000 suggests bacterial infection (80% sensitivity)
- BMP: Creatinine for surgical risk, glucose for DKA mimics
- Lactate: >4 mmol/L indicates tissue hypoperfusion requiring urgent intervention
- Secondary Priority (within 30 minutes)
- Liver enzymes: ALT >150 suggests hepatobiliary pathology
- Lipase: >3x normal confirms pancreatitis (85% sensitivity)
- Urinalysis: >5 RBC/hpf suggests urological cause
- Specialized Markers (within 60 minutes)
- Procalcitonin: >2 ng/mL distinguishes bacterial from viral (90% specificity)
- D-dimer: >500 ng/mL suggests thrombotic complications
- Troponin: Elevated in 15% of severe abdominal emergencies
- Immediate Priority (within 15 minutes)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Lactate clearance >20% within 2 hours predicts survival in abdominal sepsis with 85% accuracy, making serial measurements more valuable than absolute values
| Investigation | Sensitivity | Specificity | Time to Result | Cost Factor | Radiation Dose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound | 85-95% | 95-99% | <15 minutes | 1x | None |
| CT Abdomen | 95-98% | 90-95% | 30-45 minutes | 10x | 10-15 mSv |
| MRI | 90-95% | 95-98% | 45-60 minutes | 20x | None |
| Diagnostic Laparoscopy | 98-100% | 95-98% | 60-90 minutes | 100x | Minimal |
| ERCP | 90-95% | 95-98% | 60-120 minutes | 50x | 5-10 mSv |
| %%{init: {'flowchart': {'htmlLabels': true}}}%% | |||||
| flowchart TD |
Start["🩺 Clinical Suspicion
• Initial evaluation• Patient assessment"]
Prob["📋 Probability?
• Assess risk level• Pre-test probability"]
High["🔬 Targeted Imaging
• High risk >80%• Specific modality"]
ConfirmHigh["📋 Confirm Diagnosis?
• Review scan results• Assess findings"]
Mod["🔬 CT Abd/Pelvis
• Mod risk 20-80%• Contrast CT study"]
DiagMod["📋 Diagnostic?
• Evaluate imaging• Clear result?"]
Low["🔬 Conservative Labs
• Low risk <20%• Minimal testing"]
Rx["💊 Treatment
• Start therapy• Clinical management"]
Broaden["🩺 Broaden Invest.
• Expand search• Rule out others"]
Equiv["👁️ MRI or Repeat CT
• Equivocal result• Further imaging"]
Start --> Prob Prob -->|>80%| High Prob -->|20-80%| Mod Prob -->|<20%| Low
High --> ConfirmHigh ConfirmHigh -->|Yes| Rx ConfirmHigh -->|No| Broaden
Mod --> DiagMod DiagMod -->|Yes| Rx DiagMod -->|No| Broaden DiagMod -->|Equivocal| Equiv
style Start fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style Prob fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style High fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style ConfirmHigh fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style Mod fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style DiagMod fill:#FEF8EC, stroke:#FBECCA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#854D0E style Low fill:#FFF7ED, stroke:#FFEED5, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#C2410C style Rx fill:#F1FCF5, stroke:#BEF4D8, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#166534 style Broaden fill:#F7F5FD, stroke:#F0EDFA, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#6B21A8 style Equiv fill:#EEFAFF, stroke:#DAF3FF, stroke-width:1.5px, rx:12, ry:12, color:#0369A1
> 💡 **Master This**: The **"Rule of 90s"** - investigations should have **>90%** sensitivity for ruling out dangerous conditions and **>90%** specificity for confirming surgical indications to minimize false positives and negatives
* **Imaging Strategy by Clinical Scenario**
- **Hemodynamically Unstable**
+ **FAST exam**: **95%** sensitive for free fluid, **<5 minutes**
+ **Portable chest X-ray**: **85%** sensitive for pneumoperitoneum
+ **Bedside ultrasound**: **90%** sensitive for AAA **>5 cm**
- **Stable with Peritonitis**
+ **CT with IV contrast**: **95%** accuracy for perforation
+ **Upright chest X-ray**: **75%** sensitive for free air
+ **Water-soluble contrast study**: **90%** sensitive for leak
- **Stable without Peritonitis**
+ **Ultrasound first**: **85%** sensitive for cholecystitis, appendicitis
+ **CT if ultrasound negative**: **98%** sensitivity for most pathology
+ **MRI for pregnant patients**: **90%** sensitivity, no radiation
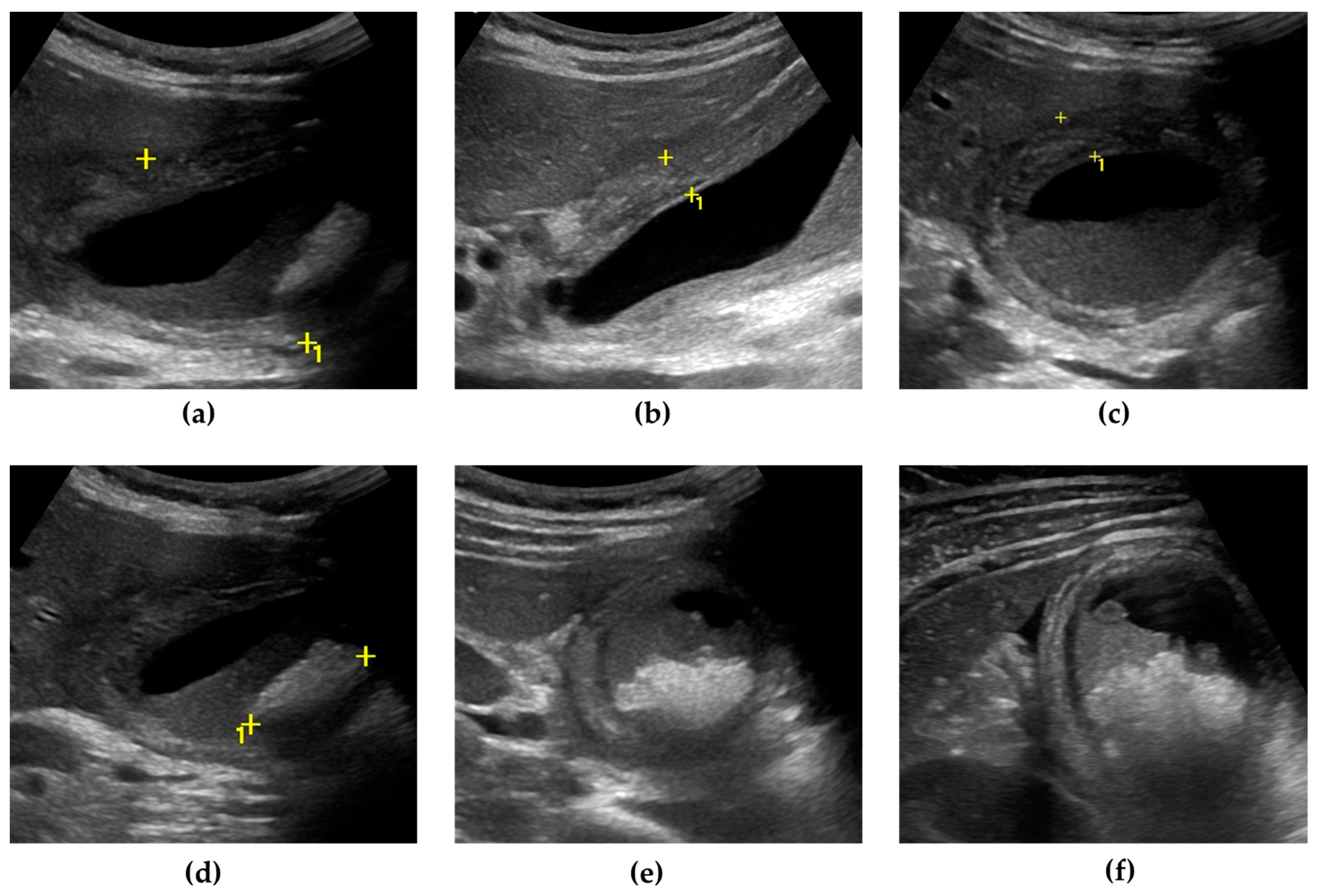
* **Advanced Diagnostic Techniques**
- **CT Angiography**: **95%** sensitive for mesenteric ischemia, **<30 minutes**
- **MRCP**: **90%** sensitive for choledocholithiasis, no contrast needed
- **Nuclear medicine**: **HIDA scan** **95%** specific for acute cholecystitis
+ **Technetium-99m** uptake patterns distinguish acute from chronic
+ **Morphine augmentation** increases sensitivity to **98%**
The diagnostic arsenal enables **evidence-based** decision-making that balances **speed**, **accuracy**, and **resource utilization** while maintaining **patient safety** as the primary objective.
Connect these diagnostic frameworks through evidence-based treatment algorithms to master the therapeutic interventions that optimize patient outcomes.
🔬 Diagnostic Precision: The Investigation Arsenal
⚕️ Treatment Command: The Intervention Matrix
📌 Remember: ABC-STOP - Airway, Breathing, Circulation first, then Surgical control, Temperature management, Output monitoring, Pain control - addresses 95% of immediate life threats
The treatment matrix follows damage control principles: stop the bleeding, control contamination, restore physiology, then definitive repair. This sequence prevents the "lethal triad" of hypothermia, acidosis, and coagulopathy that kills 60% of patients who develop all three.
- Resuscitation Protocol Hierarchy
- Phase 1: Immediate Stabilization (0-15 minutes)
- Fluid resuscitation: 20 mL/kg crystalloid bolus, reassess
- Blood pressure support: MAP >65 mmHg target
- Oxygen delivery: SpO₂ >94%, consider intubation if GCS <8
- Phase 2: Source Control (15-60 minutes)
- Surgical consultation: <30 minutes for unstable patients
- Antibiotic therapy: <1 hour for suspected infection
- Pain management: Multimodal approach, avoid masking peritonitis
- Phase 3: Definitive Management (1-6 hours)
- Operative intervention: <6 hours for ischemic conditions
- ICU management: Organ support as needed
- Monitoring protocols: Serial assessments every 2-4 hours
- Phase 1: Immediate Stabilization (0-15 minutes)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Permissive hypotension (SBP 80-90 mmHg) in penetrating trauma reduces bleeding by 40% until surgical control, but maintain MAP >65 mmHg in blunt trauma and elderly patients
| Intervention | Time Window | Success Rate | Complication Rate | Resource Intensity | Evidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emergency Laparotomy | <2 hours | 85-90% | 15-25% | High | Level I |
| Laparoscopic Repair | <6 hours | 90-95% | 5-10% | Moderate | Level I |
| Endoscopic Intervention | <12 hours | 80-85% | <5% | Low | Level II |
| Percutaneous Drainage | <24 hours | 75-80% | 10-15% | Low | Level II |
| Medical Management | Variable | 60-70% | <5% | Low | Level III |
-
Condition-Specific Treatment Algorithms
- Hemorrhagic Shock Management
- Massive transfusion protocol: 1:1:1 ratio (RBC:FFP:Platelets)
- Tranexamic acid: 1g IV within 3 hours reduces mortality 15%
- Factor VIIa: Consider if pH >7.2 and temperature >35°C
- Septic Shock Protocol
- Fluid resuscitation: 30 mL/kg within 3 hours
- Vasopressors: Norepinephrine first-line, target MAP >65 mmHg
- Source control: <12 hours for optimal outcomes
- Bowel Obstruction Management
- Decompression: NG tube reduces aspiration risk 80%
- Fluid replacement: 3-5 L deficit common in small bowel obstruction
- Surgical timing: <24 hours for strangulation, 48-72 hours for simple
- Hemorrhagic Shock Management
-
Advanced Intervention Strategies
- Minimally Invasive Approaches
- Laparoscopic surgery: 50% reduction in wound complications
- Robotic assistance: 30% improvement in precision for complex cases
- NOTES procedures: Reduced morbidity in selected patients
- Interventional Radiology
- Embolization: 90% success rate for GI bleeding
- Stent placement: 85% success for malignant obstruction
- Drainage procedures: 80% success for abscess management
- Minimally Invasive Approaches
The intervention matrix enables coordinated care that optimizes patient outcomes while minimizing morbidity and resource utilization through evidence-based protocols.
Connect these treatment strategies through advanced integration concepts to master the multisystem approach required for complex abdominal emergencies.
⚕️ Treatment Command: The Intervention Matrix
🌐 Systems Integration: The Multiorgan Orchestra
📌 Remember: HEART-LUNG-KIDNEY-BRAIN - the four critical systems that determine survival in abdominal emergencies, with cardiovascular compromise leading to pulmonary edema, renal failure, and neurological dysfunction in 60% of severe cases
The "domino effect" in abdominal emergencies follows predictable patterns: hypovolemia leads to renal hypoperfusion, triggering RAAS activation, causing sodium retention and pulmonary edema, ultimately resulting in respiratory failure in 25-30% of severe cases.
- Cardiovascular-Abdominal Integration
- Hemodynamic Monitoring Targets
- Central venous pressure: 8-12 mmHg optimal, >15 mmHg suggests fluid overload
- Cardiac output: Maintain >4 L/min or cardiac index >2.5 L/min/m²
- Mixed venous oxygen saturation: >70% indicates adequate oxygen delivery
- Fluid Management Strategies
- Crystalloid resuscitation: 30 mL/kg initial, then 250-500 mL boluses
- Colloid therapy: Albumin if serum level <2.5 g/dL
- Blood products: Hemoglobin >7 g/dL target, >9 g/dL if cardiac disease
- Hemodynamic Monitoring Targets
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Pulse pressure variation >13% during mechanical ventilation predicts fluid responsiveness with 85% accuracy, preventing both under-resuscitation and fluid overload complications
| System | Primary Effect | Secondary Effect | Monitoring Parameter | Intervention Threshold | Target Goal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Hypovolemia | Decreased perfusion | MAP | <65 mmHg | 65-75 mmHg |
| Pulmonary | V/Q mismatch | Hypoxemia | PaO₂/FiO₂ | <300 | >300 |
| Renal | Hypoperfusion | Acute kidney injury | Creatinine | >1.5x baseline | <1.2 mg/dL |
| Hepatic | Hypoperfusion | Synthetic dysfunction | INR | >1.5 | <1.3 |
| Neurological | Hypoperfusion | Delirium | GCS | <13 | 15 |
- Respiratory-Abdominal Interactions
- Mechanical Ventilation Considerations
- Tidal volume: 6-8 mL/kg ideal body weight prevents VILI
- PEEP optimization: 5-10 cmH₂O improves oxygenation without compromising venous return
- Plateau pressure: <30 cmH₂O prevents barotrauma
- Abdominal Compartment Effects
- Intra-abdominal pressure >20 mmHg reduces FRC by 50%
- Diaphragmatic elevation increases work of breathing by 40%
- Venous return decreases 25% for every 10 mmHg IAP increase
- Mechanical Ventilation Considerations

-
Renal-Hepatic-Abdominal Triangle
- Hepatorenal Syndrome Risk
- Creatinine >1.5 mg/dL with bilirubin >3 mg/dL indicates 30% mortality risk
- Urine sodium <10 mEq/L suggests prerenal etiology
- Fractional excretion of sodium <1% confirms volume depletion
- Metabolic Consequences
- Lactate clearance: >20% in 6 hours predicts survival
- Base deficit: >-6 mEq/L indicates significant tissue debt
- Anion gap: >16 mEq/L suggests metabolic acidosis
- Hepatorenal Syndrome Risk
-
Neuroendocrine Stress Response
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis
- Cortisol levels: >25 μg/dL normal stress response
- Relative adrenal insufficiency: <9 μg/dL increase after cosyntropin
- Vasopressor dependency: May require hydrocortisone 200-300 mg/day
- Sympathetic Nervous System
- Catecholamine surge: Norepinephrine >1000 pg/mL in severe stress
- Heart rate variability: Decreased indicates autonomic dysfunction
- Temperature regulation: Hypothermia <36°C or hyperthermia >38.5°C
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis
The systems integration approach enables holistic management that addresses primary pathology while preventing secondary organ dysfunction, optimizing both short-term survival and long-term functional outcomes.
Connect this multisystem understanding through rapid mastery frameworks to develop the clinical expertise tools needed for immediate application in emergency settings.
🌐 Systems Integration: The Multiorgan Orchestra
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Emergency Physician's Toolkit
📌 Remember: FAST-TRACK - First impression, Assessment systematic, Stabilize immediately, Triage appropriately, Treat definitively, Reassess frequently, Adjust continuously, Communicate clearly, Keep learning - the 9-step mastery cycle used by top 10% of emergency physicians
The "Expert's Edge" comes from pattern libraries built through deliberate practice: recognizing subtle signs that predict deterioration, knowing when to deviate from protocols, and maintaining situational awareness across multiple patients simultaneously.
- The 5-Minute Assessment Protocol
- Minute 1: Global Impression
- Appearance: Toxic vs well-appearing determines urgency
- Vital signs: Shock index >1.0 indicates significant volume loss
- Pain behavior: Writhing suggests colic, stillness suggests peritonitis
- Minutes 2-3: Focused History
- SOCRATES: Site, Onset, Character, Radiation, Associated symptoms, Timing, Exacerbating factors, Severity
- Red flag symptoms: Syncope, hematemesis, melena, fever >38.5°C
- Minutes 4-5: Targeted Examination
- Inspection: Distension, scars, hernias, skin changes
- Auscultation: Bowel sounds - absent suggests ileus, high-pitched suggests obstruction
- Palpation: Start away from pain, watch face not hands
- Minute 1: Global Impression
⭐ Clinical Pearl: The "Rule of Faces" - patients with surgical emergencies have characteristic facial expressions: anxious (ischemia), grimacing (perforation), pale and sweaty (hemorrhage) - 85% diagnostic accuracy when combined with vital signs
| Clinical Tool | Time Required | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Clinical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIRS Criteria | <2 minutes | 80% | 85% | 75% | Sepsis screening |
| Alvarado Score | <3 minutes | 85% | 80% | 90% | Appendicitis probability |
| Ranson Criteria | 48 hours | 90% | 85% | 95% | Pancreatitis severity |
| APACHE II | <5 minutes | 85% | 80% | 90% | ICU mortality prediction |
| SOFA Score | <3 minutes | 80% | 75% | 85% | Organ dysfunction |
- The Expert's Decision Matrix
- High-Stakes Decisions (life vs death)
- Operate now: Unstable with surgical pathology - 100% indication
- Resuscitate first: Unstable but unclear pathology - stabilize then reassess
- Observe closely: Stable with equivocal findings - serial exams every 2-4 hours
- Resource Allocation Decisions
- ICU admission: SOFA score >6 or vasopressor requirement
- OR priority: Emergency (<1 hour), urgent (<6 hours), elective (<24 hours)
- Consultant involvement: Immediate for unstable, urgent for surgical candidates
- High-Stakes Decisions (life vs death)
-
Communication Excellence Framework
- SBAR Handoffs: Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation
- Situation: "65-year-old male with acute abdominal pain"
- Background: "3-hour onset, peritoneal signs, lactate 4.2"
- Assessment: "Likely perforated viscus, hemodynamically stable"
- Recommendation: "Needs emergency surgery consultation"
- Family Communication: Empathy + Information + Expectations
- Acknowledge emotions: "I can see you're worried"
- Provide updates: "Here's what we know so far"
- Set expectations: "The next step is..."
- SBAR Handoffs: Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation
-
Quality Metrics for Mastery
- Time-Based Metrics
- Door-to-assessment: <10 minutes for all patients
- Door-to-CT: <60 minutes for stable patients
- Door-to-OR: <90 minutes for surgical emergencies
- Outcome Metrics
- Diagnostic accuracy: >90% for common conditions
- Complication rates: <5% for medical management
- Patient satisfaction: >95% for communication scores
- Time-Based Metrics
The clinical mastery arsenal provides systematic frameworks that ensure consistent excellence while maintaining the flexibility needed for complex cases and unusual presentations.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Emergency Physician's Toolkit
Practice Questions: Abdominal emergencies
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 68-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department with intense abdominal pain for the past 2 hours. She has had 1 episode of bloody diarrhea recently. She has an 18-year history of diabetes mellitus. She was diagnosed with hypertension and ischemic heart disease 6 years ago. She is fully alert and oriented. Her temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F), blood pressure is 145/90 mm Hg, pulse is 78/min, and respirations are 14/min. Abdominal examination shows mild generalized abdominal tenderness without guarding or rebound tenderness. An abdominal plain X-ray shows no abnormalities. Abdominal CT reveals colonic wall thickening and pericolonic fat stranding in the splenic curvature. Bowel rest, intravenous hydration, and IV antibiotics are initiated. Which of the following is the most important diagnostic evaluation at this time?













