Medication-assisted treatment US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Medication-assisted treatment. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Medication-assisted treatment US Medical PG Question 1: A 42-year-old man is discovered unconscious by local police while patrolling in a park. He is unresponsive to stimulation. Syringes were found scattered around him. His heart rate is 70/min and respiratory rate is 6/min. Physical examination reveals a disheveled man with track marks on both arms. His glasgow coma scale is 8. Pupillary examination reveals miosis. An ambulance is called and a reversing agent is administered. Which of the following is most accurate regarding the reversal agent most likely administered to this patient?
- A. Works on dopamine receptors
- B. Has a short half-life
- C. Can be given per oral
- D. Results in acute withdrawal (Correct Answer)
- E. Is a non-competitive inhibitor
Medication-assisted treatment Explanation: ***Results in acute withdrawal***
- The patient's presentation (unconscious, track marks, miosis, bradypnea) is characteristic of **opioid overdose**. The reversal agent, **naloxone**, rapidly displaces opioids from their receptors, leading to an abrupt onset of withdrawal symptoms.
- **Acute opioid withdrawal** can manifest with symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle cramps, and agitation, as the body suddenly lacks the opioid-induced suppression.
- This is the **most clinically significant** characteristic of naloxone in the acute overdose setting, as it explains the immediate physiological response patients experience.
*Works on dopamine receptors*
- **Naloxone** primarily acts as an **opioid receptor antagonist**, particularly at the mu-opioid receptor.
- It does not significantly interact with or exert its primary effects through **dopamine receptors**.
*Has a short half-life*
- While this statement is **factually true** (naloxone has a half-life of 30-81 minutes), it describes a **pharmacokinetic property** rather than a characteristic of its reversal mechanism.
- The question asks about the reversal agent in the context of immediate administration, where the **acute precipitation of withdrawal** is the most defining and immediate clinical consequence.
- The short half-life is clinically relevant for monitoring (patients may re-sedate), but it is not the most accurate statement regarding what happens when the reversal agent is administered.
*Can be given per oral*
- Although **naloxone** can be administered orally, its **bioavailability via the oral route is very low** (less than 3%) due to extensive first-pass metabolism.
- For acute overdose reversal, it is typically administered via intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, or intranasal routes for rapid and effective absorption.
*Is a non-competitive inhibitor*
- **Naloxone** is a **competitive antagonist** of opioid receptors, meaning it competes with opioids for binding sites.
- It does not bind to an allosteric site to reduce the opioid's efficiency (non-competitive inhibition); rather, it directly blocks the receptor.
Medication-assisted treatment US Medical PG Question 2: A 44-year-old man presents to the clinic worried about his risk for bladder cancer. His best friend who worked with him as a painter for the past 20-years died recently after being diagnosed with transitional cell carcinoma. He is worried that their long and heavy cigarette smoking history might have contributed to his death. He also reports that he has been feeling down since his friend's death 2 months ago and has not been eating or sleeping as usual. He took time off from work but now is running past due on some of his bills. He feels like he is moving a lot slower than usual. He would like to stop smoking but feels like it's impossible with just his willpower. What side-effect is most likely if this patient were started on his appropriate pharmacotherapy?
- A. Can decrease seizure threshold (Correct Answer)
- B. Can treat overdose with sodium bicarbonate
- C. Can cause restlessness at initiation or termination
- D. Can cause sedation and weight gain
- E. Can worsen uncontrolled hypertension
Medication-assisted treatment Explanation: ***Can decrease seizure threshold***
- The patient exhibits symptoms consistent with **major depressive disorder** (anhedonia, sleep/appetite disturbance, psychomotor retardation) and co-occurring **nicotine dependence**.
- **Bupropion** is an appropriate pharmacotherapy as it treats both depression and aids in smoking cessation, but it carries a dose-dependent risk of **lowering the seizure threshold**.
*Can treat overdose with sodium bicarbonate*
- This statement is characteristic of **tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) overdose**, which leads to cardiac arrhythmias that can be mitigated by sodium bicarbonate.
- Bupropion overdose is associated with seizures, blurred vision, and hallucinations, not typically managed with sodium bicarbonate for cardiac effects.
*Can cause restlessness at initiation or termination*
- This side effect is more commonly associated with **akathisia from antipsychotics** or sometimes **selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)** during initiation or withdrawal.
- While bupropion can cause agitation, "restlessness" in this context as a primary differentiating side effect for initiation/termination is less specific than the seizure risk.
*Can cause sedation and weight gain*
- **Sedation and weight gain** are common side effects of many antidepressants, particularly older TCAs and some newer atypical antidepressants like **mirtazapine**.
- Bupropion is known for being **non-sedating** and can actually cause **weight loss**, making this option incorrect.
*Can worsen uncontrolled hypertension*
- While bupropion can cause a **mild increase in blood pressure**, sustained treatment with **MAOIs** (monoamine oxidase inhibitors) or **SNRIs** (serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors) are more significantly associated with worsening uncontrolled hypertension.
- The risk of seizure threshold lowering is a more distinct and clinically relevant side effect for bupropion compared to hypertension exacerbation.
Medication-assisted treatment US Medical PG Question 3: A 27-year-old homeless man presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain and vomiting. He has a known history of intravenous drug use and has been admitted to the hospital several times before. On physical examination his temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 130/85 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 19/min, and pulse oximetry is 99% on room air. The patient is in obvious discomfort. There is increased salivation and lacrimation. Pupils are reactive to light and 5 mm bilaterally. Cardiopulmonary exam is unremarkable. There is diffuse abdominal tenderness to palpation with no rebound or guarding. Which of the following interventions would have prevented this patient’s current condition?
- A. Naltrexone
- B. Buprenorphine (Correct Answer)
- C. Lorazepam
- D. Naloxone
- E. Bupropion
Medication-assisted treatment Explanation: ***Buprenorphine***
- This patient is presenting with symptoms consistent with **opioid withdrawal** (abdominal pain, vomiting, increased salivation, lacrimation). **Buprenorphine** is used for **opioid dependence treatment** as it's a **partial opioid agonist** that helps manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings, thus preventing acute withdrawal episodes.
- By stabilizing opioid receptors, buprenorphine, often combined with naloxone (Suboxone), reduces the risk of relapse and prevents the cycle of **intravenous drug use** that leads to withdrawal.
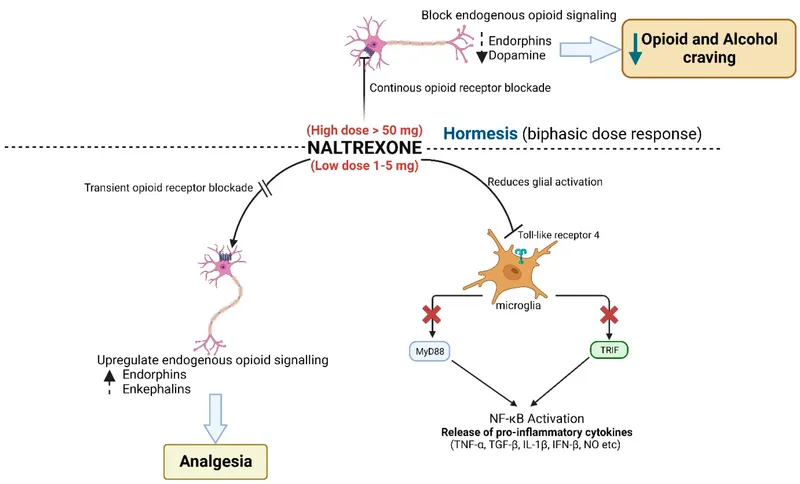
*Naltrexone*
- **Naltrexone** is an **opioid antagonist** used to prevent relapse in individuals who have achieved abstinence from opioids. It blocks the effects of opioids.
- However, administering naltrexone to someone actively using opioids or in withdrawal would precipitate or worsen withdrawal symptoms, making it unsuitable for preventing this acute presentation.
*Lorazepam*
- **Lorazepam** is a **benzodiazepine** primarily used to treat **anxiety**, **insomnia**, and **seizures**, and it is often used in **alcohol withdrawal**.
- While it can help manage some anxiety associated with opioid withdrawal, it does not address the underlying opioid dependence or prevent the physical symptoms of withdrawal itself, nor does it prevent the underlying cause of withdrawal which is abstinence from opioids.
*Naloxone*
- **Naloxone** is a potent, short-acting **opioid antagonist** used to **reverse opioid overdose** by rapidly displacing opioids from receptors.
- It would not prevent withdrawal; in fact, administering naloxone to an opioid-dependent individual would acutely precipitate severe withdrawal.
*Bupropion*
- **Bupropion** is an **antidepressant** that also aids in **smoking cessation**. It works by inhibiting the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine.
- It has no role in the prevention or treatment of opioid withdrawal and would not have altered this patient's current condition.
Medication-assisted treatment US Medical PG Question 4: A 25-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after his girlfriend discovered him at home in a minimally responsive state. He has a history of drinking alcohol excessively and using illicit drugs. On arrival, he does not respond to commands but withdraws all extremities to pain. His pulse is 90/min, respirations are 8/min, and blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry while receiving bag-valve-mask ventilation shows an oxygen saturation of 95%. Examination shows cool, dry skin, with scattered track marks on his arms and legs. The pupils are pinpoint and react sluggishly to light. His serum blood glucose level is 80 mg/dL. The most appropriate next step in management is intravenous administration of which of the following?
- A. Fomepizole
- B. Naltrexone
- C. Methadone
- D. Naloxone (Correct Answer)
- E. Phentolamine
Medication-assisted treatment Explanation: ***Naloxone***
- The patient presents with classic signs of **opioid overdose**: altered mental status, **respiratory depression** (8/min), and **pinpoint pupils**.
- **Naloxone** is an opioid antagonist that rapidly reverses the effects of opioid toxicity and is the most appropriate first-line treatment in this scenario.
*Fomepizole*
- This medication is used as an antidote for **methanol** and **ethylene glycol poisoning**, which typically present with metabolic acidosis and renal failure, not pinpoint pupils and respiratory depression.
- There are no clinical signs in this patient indicative of methanol or ethylene glycol ingestion.
*Naltrexone*
- **Naltrexone** is an opioid antagonist used for long-term management of opioid use disorder or alcohol dependence, but it is not used in acute overdose resuscitation due to its slower onset and formulation (oral or long-acting injectable).
- Its primary role is to prevent relapse, not to reverse acute respiratory depression.
*Methadone*
- **Methadone** is a long-acting opioid agonist used for opioid replacement therapy and chronic pain management.
- Administering methadone would worsen the patient's opioid-induced respiratory depression and central nervous system depression.
*Phentolamine*
- **Phentolamine** is an alpha-adrenergic blocker used to treat hypertensive crises, particularly those caused by pheochromocytoma or extravasation of vasopressors.
- It has no role in managing opioid overdose and could lead to hypotension in this patient.
Medication-assisted treatment US Medical PG Question 5: A 14-year-old teenager is brought to the physician by her mother who seems extremely concerned that her daughter is unable to sleep at night and has become increasingly irritated and aggressive. She has been noticing changes in her daughter's behavior recently. She had no idea what was going on until she found pills hidden in her daughter's room a week ago. Her daughter confessed that she tried these drugs once with her friends and started using them since then. Her mother threw away all the pills and prevented her daughter from seeing her friends. This is when she started to notice her daughter tear often and sweat. She is seeking a quick and effective treatment for her daughter. Which drug was the teenager most likely using?
- A. Atomoxetine
- B. Naloxone
- C. Marijuana
- D. Oxycodone (Correct Answer)
- E. Cocaine
Medication-assisted treatment Explanation: ***Oxycodone***
- The patient's symptoms of **irritability**, **aggression**, inability to sleep, tearing, and sweating after the mother disposing of her pills are consistent with **opioid withdrawal**.
- **Oxycodone** is a potent opioid analgesic that can lead to significant physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms upon cessation.
*Atomoxetine*
- **Atomoxetine** is a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor used for **ADHD**; it does not typically cause these withdrawal symptoms.
- Discontinuation of atomoxetine usually does not result in the severe physiological withdrawal syndrome described.
*Naloxone*
- **Naloxone** is an **opioid antagonist** used to reverse opioid overdose, not a drug of abuse that would cause these withdrawal symptoms.
- Its mechanism of action involves blocking opioid receptors, which would precipitate withdrawal if given to an opioid-dependent individual but is not itself abused in this manner.
*Marijuana*
- **Marijuana withdrawal** can cause irritability and sleep disturbances, but typically does not involve physical symptoms like significant tearing and sweating.
- Marijuana is an illicit drug, and withdrawal is generally less severe than opioid withdrawal.
*Cocaine*
- **Cocaine withdrawal** is primarily psychological, characterized by **dysphoria**, fatigue, and intense cravings, without the prominent physical symptoms like tearing and sweating seen here.
- While cocaine abuse is strongly associated with aggression and irritability, the specific physical withdrawal symptoms point away from it.
Medication-assisted treatment US Medical PG Question 6: A 33-year-old woman presents with anxiety, poor sleep, and occasional handshaking and sweating for the past 10 months. She says that the best remedy for her symptoms is a “glass of a good cognac” after work. She describes herself as a “moderate drinker”. However, on a more detailed assessment, the patient confesses that she drinks 1–2 drinks per working day and 3–5 drinks on days-off when she is partying. She was once involved in a car accident while being drunk. She works as a financial assistant and describes her job as “demanding”. She is divorced and lives with her 15-year-old daughter. She says that she often hears from her daughter that she should stop drinking. She realizes that the scope of the problem might be larger than she perceives, but she has never tried stopping drinking. She does not feel hopeless, but sometimes she feels guilty because of her behavior. She does not smoke and does not report illicit drugs use. Which of the following medications would be a proper part of the management of this patient?
- A. Topiramate
- B. Naltrexone (Correct Answer)
- C. Amitriptyline
- D. Gabapentin
- E. Disulfiram
Medication-assisted treatment Explanation: ***Naltrexone***
- This patient exhibits symptoms consistent with **alcohol use disorder**, including increased tolerance, problematic use despite negative consequences (car accident, daughter's concern), and use to alleviate withdrawal-like symptoms (anxiety, poor sleep, handshaking, sweating). **Naltrexone** helps reduce **craving and pleasurable effects of alcohol** by blocking opioid receptors.
- Given that she has never tried stopping and does not endorse severe withdrawal symptoms requiring inpatient detoxification typically, naltrexone is a suitable first-line pharmacotherapy for **alcohol use disorder** in this context.
*Topiramate*
- While **topiramate** can be used as an off-label treatment for alcohol use disorder, particularly in reducing heavy drinking and cravings, it is generally considered a second-line option.
- Its side effect profile can be more notable (e.g., cognitive slowing, paresthesias) compared to naltrexone, and it's less commonly chosen as an initial monotherapy when other options are available.
*Amitriptyline*
- **Amitriptyline** is a tricyclic antidepressant primarily used for **depression** and some **neuropathic pain** conditions.
- It is not indicated for the treatment of **alcohol use disorder** and could potentially worsen some symptoms or interact with alcohol.
*Gabapentin*
- **Gabapentin** is sometimes used off-label for **alcohol use disorder**, particularly for managing withdrawal symptoms, reducing cravings, and improving sleep.
- However, for a patient who has never attempted cessation and is not in acute withdrawal, but rather is seeking to reduce problematic drinking, naltrexone is generally preferred as a first-line agent.
*Disulfiram*
- **Disulfiram** works by causing an unpleasant physical reaction (nausea, vomiting, flushing, palpitations) when alcohol is consumed.
- It requires strong patient motivation and adherence, as the patient must avoid all alcohol. Given her current struggle with moderation and no prior attempts at abstinence, beginning with disulfiram, which relies on aversive conditioning, might be challenging and is often reserved for highly motivated patients or those who have failed other treatments.
Medication-assisted treatment US Medical PG Question 7: A 21-year-old female presents to her psychiatrist for ongoing management of major depressive disorder. She has previously tried cognitive behavioral therapy as well as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, but neither treatment has been very effective. She also states that she has been smoking two packs per day for the last three months and would like to stop smoking. Based on these concerns, her psychiatrist prescribes a medication that addresses both depression and smoking cessation. Which of the following if present, would be a contraindication for the drug that was most likely prescribed in this case?
- A. Patient works as a wine taster
- B. Patient is bulimic (Correct Answer)
- C. Patient is elderly
- D. Patient also takes monoamine oxidase inhibitors
- E. Patient is pregnant
Medication-assisted treatment Explanation: ***Patient is bulimic***
- The drug prescribed is **bupropion**, which is effective for both **major depressive disorder** and **smoking cessation**.
- **Bupropion is absolutely contraindicated** in patients with **bulimia nervosa** or **anorexia nervosa** due to a significantly **increased risk of seizures**.
- Patients with eating disorders have **electrolyte imbalances** and **metabolic disturbances** that increase seizure susceptibility, and bupropion lowers the seizure threshold.
- This is an **FDA black box warning** and represents an absolute contraindication.
*Patient also takes monoamine oxidase inhibitors*
- While caution is required, **MAOI use is not an absolute contraindication** to bupropion.
- A **washout period of 14 days** after stopping an MAOI is required before starting bupropion.
- Unlike with SSRIs (where MAOI co-administration can cause serotonin syndrome), bupropion primarily affects **dopamine** and **norepinephrine** reuptake, making the interaction less severe.
- This represents a **relative contraindication** requiring proper timing, not an absolute contraindication.
*Patient works as a wine taster*
- Working as a **wine taster** does not pose a medical **contraindication** to **bupropion**.
- While excessive alcohol use should be avoided (increases seizure risk), occupational exposure to small amounts of alcohol is not a contraindication.
*Patient is elderly*
- **Bupropion** can be safely used in **elderly patients** with appropriate dose adjustments.
- It may be preferable to other antidepressants due to favorable side-effect profile: less **sedation**, **anticholinergic effects**, and **orthostatic hypotension**.
- Age alone is not a contraindication.
*Patient is pregnant*
- **Bupropion** is **Pregnancy Category C** (now classified as having no adequate human studies).
- While generally avoided unless benefits outweigh risks, it is not an absolute contraindication.
- Many pregnant women with depression and nicotine dependence may appropriately receive bupropion after careful risk-benefit assessment.
Medication-assisted treatment US Medical PG Question 8: A 17-year-old girl is brought to the physician for the evaluation of fatigue for the past 6 months. During this period, she has had a 5-kg (11-lbs) weight loss. She states that she has no friends. When she is not in school, she spends most of her time in bed. She has no history of serious illness. Her mother has major depressive disorder. She appears pale and thin. She is at 25th percentile for height, 10th percentile for weight, and 20th percentile for BMI; her BMI is 19.0. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 65/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. Examination shows dry skin, brittle nails, and calluses on the knuckles. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 12.3 g/dL
Serum
Na+ 133 mEq/L
Cl- 90 mEq/L
K+ 3.2 mEq/L
HCO3- 30 mEq/L
Ca+2 7.8 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Anemia
- B. Major depressive disorder
- C. Milk-alkali syndrome
- D. Bulimia nervosa
- E. Anorexia nervosa (Correct Answer)
Medication-assisted treatment Explanation: ***Anorexia nervosa***
- The patient presents with **significant weight loss**, **fatigue**, social withdrawal, and physical signs such as **dry skin**, **brittle nails**, and **bradycardia**, all consistent with anorexia nervosa.
- While not explicitly stated, the **calluses on the knuckles (Russell's sign)** often indicate self-induced vomiting, which is a common compensatory behavior in eating disorders, even those primarily restrictive like anorexia nervosa.
*Anemia*
- While the patient appears pale, her **hemoglobin level of 12.3 g/dL** is within the normal range for a female, ruling out anemia as the primary diagnosis.
- Pallor in this context is more likely due to **poor nutrition** and overall debilitation associated with an eating disorder.
*Major depressive disorder*
- The patient exhibits symptoms like **fatigue**, weight loss, and social withdrawal, which can be seen in major depressive disorder, and her mother has a history of it.
- However, the additional physical findings (dry skin, brittle nails, bradycardia, **calluses on knuckles**) and the specific pattern of **weight loss** points more strongly towards an eating disorder.
*Milk-alkali syndrome*
- This syndrome is characterized by **hypercalcemia** (Ca+2 > 10.5 mg/dL), metabolic alkalosis (increased HCO3-), and often **renal insufficiency**, usually due to excessive intake of calcium and absorbable alkali.
- The patient's **hypocalcemia (Ca+2 7.8 mg/dL)** and slightly elevated HCO3- (30 mEq/L) are inconsistent with milk-alkali syndrome.
*Bulimia nervosa*
- Bulimia nervosa is characterized by **recurrent episodes of binge eating** followed by compensatory behaviors such as purging (self-induced vomiting, laxative abuse). The presence of **Russell's sign** (calluses on knuckles) suggests purging.
- However, patients with bulimia nervosa typically maintain a **normal body weight or are overweight**, unlike this patient who has significant weight loss and a BMI at the 20th percentile, which makes anorexia nervosa with purging subtype more likely.
Medication-assisted treatment US Medical PG Question 9: A 21-year-old woman presents into the clinic worried that she might be pregnant. Her last menstrual period was 4 months ago and recalls that she did have unprotected sex with her boyfriend, despite not having sexual desire. They have since broken up, and she would like to do a pregnancy test. She appears very emaciated but is physically active. She says that she spends a few hours in the gym almost every day but would spend longer if she was to stray from her diet so that she does not gain any weight. Her calculated BMI is 17 kg/m2, and her urine pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following additional findings would most likely be present in this patient?
- A. Hypocholesterolemia
- B. Orthostasis (Correct Answer)
- C. Primary amenorrhea
- D. Hypokalemic alkalosis
- E. Increased LH and FSH
Medication-assisted treatment Explanation: ***Orthostasis***
- This patient's presentation is highly suggestive of **anorexia nervosa** (BMI 17 kg/m2, amenorrhea, excessive exercise, fear of weight gain despite emaciation, and lack of sexual desire). **Orthostasis** (a drop in blood pressure upon standing) is a common finding due to **dehydration** and **volume depletion** often present in patients with anorexia nervosa.
- **Bradycardia** and **hypotension** (which contributes to orthostasis) are frequent cardiovascular complications of anorexia nervosa as the body attempts to conserve energy.
*Hypocholesterolemia*
- Patients with anorexia nervosa more commonly present with **hypercholesterolemia**, not hypocholesterolemia.
- This paradox is thought to be due to **decreased cholesterol degradation** and **impaired metabolism** in the setting of severe caloric restriction.
*Primary amenorrhea*
- The patient's last menstrual period was 4 months ago, indicating she has experienced menstruation in the past. Therefore, her amenorrhea is **secondary** (cessation of menses for 3 consecutive months in a woman who has previously menstruated), not primary (absence of menses by age 15 or within 5 years of thelarche).
- The **hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis dysfunction** due to low body weight and nutritional deficiency leads to secondary amenorrhea in anorexia nervosa.
*Hypokalemic alkalosis*
- **Hypokalemic alkalosis** is typically associated with **purging behaviors** like vomiting or laxative abuse, which are characteristic of the bulimia nervosa subtype or the binge-eating/purging subtype of anorexia nervosa.
- While this patient's exercise is excessive, there is no direct evidence of purging in the provided vignette; her symptoms more strongly point towards the **restrictive subtype** of anorexia nervosa, where metabolic alkalosis is less common unless purging is also occurring.
*Increased LH and FSH*
- In anorexia nervosa, the severe caloric restriction and low body fat lead to **hypothalamic dysfunction**, specifically affecting the release of **gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)**.
- This results in **decreased production of LH and FSH** from the pituitary gland, leading to hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, which explains the amenorrhea.
Medication-assisted treatment US Medical PG Question 10: An 18-year-old female visits your obstetrics clinic for her first prenatal checkup. It's her first month of pregnancy and other than morning sickness, she is feeling well. Upon inquiring about her past medical history, the patient admits that she used to be very fearful of weight gain and often used laxatives to lose weight. After getting therapy for this condition, she regained her normal body weight but continues to struggle with the disease occasionally. Given this history, how could her past condition affect the pregnancy?
- A. Bradycardia in newborn
- B. Seizure for mother
- C. Postpartum depression for mother (Correct Answer)
- D. Down syndrome in newborn
- E. Anemia in newborn
Medication-assisted treatment Explanation: ***Postpartum depression for mother***
- A history of **eating disorders** significantly increases the risk of **postpartum depression** and anxiety due to psychological vulnerabilities and potential nutritional deficiencies.
- The stress of pregnancy, childbirth, and motherhood can trigger a relapse or worsen existing psychiatric conditions, making **postpartum depression** a common complication.
*Bradycardia in newborn*
- **Bradycardia** in a newborn is typically associated with conditions like fetal distress during labor, congenital heart defects, or hypoxia, not directly with a mother's past eating disorder history.
- While an eating disorder can affect maternal health, it's not a primary direct cause of neonatal **bradycardia**.
*Seizure for mother*
- **Seizures** in pregnant women are commonly linked to severe preeclampsia/eclampsia, epilepsy, or other neurological conditions.
- A past history of eating disorders does not directly predispose a mother to **seizures** during pregnancy or postpartum unless accompanied by severe electrolyte imbalances, which are usually managed.
*Down syndrome in newborn*
- **Down syndrome** is a genetic condition caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 (Trisomy 21) and is primarily associated with advanced maternal age.
- There is no established causal link between a maternal history of **eating disorders** and the occurrence of **Down syndrome** in the newborn.
*Anemia in newborn*
- **Anemia** in a newborn can result from various factors such as maternal **anemia**, blood loss during delivery, or hemolytic disease.
- While maternal eating disorders can cause nutritional deficiencies, including maternal **anemia**, this does not directly result in **anemia** in the newborn unless those deficiencies are severe and uncorrected, or if other, more direct causes are present.
More Medication-assisted treatment US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.