Substance use disorders

On this page
🧠 The Addiction Spectrum: Decoding Substance Use Disorders
Substance use disorders represent one of medicine's most complex challenges, where neurochemistry, behavior, and social context collide to create patterns of harm that affect millions worldwide. You'll learn how addiction commandeers reward circuitry at the molecular level, master the clinical signatures that distinguish intoxication from withdrawal across drug classes, and build a systematic approach to evidence-based treatment that integrates pharmacotherapy with psychosocial support. This lesson equips you to recognize these disorders early, differentiate substance-specific presentations, and deploy interventions that transform lives by addressing both the biological hijacking and the recovery ecosystem patients need to heal.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-5) revolutionized addiction classification by eliminating the abuse/dependence distinction, creating a unified 11-criteria spectrum ranging from mild (2-3 criteria) to severe (6+ criteria) substance use disorders. This dimensional approach captures 85% of clinical presentations more accurately than previous categorical systems.
📌 Remember: IMPAIRED CONTROL - Impaired control, More than intended, Persistent desire, Activities given up, Interpersonal problems, Role obligations neglected, Environmentally hazardous use, Despite consequences
⭐ Clinical Pearl: The 4 C's framework - Craving, Control loss, Compulsive use, and Continued use despite Consequences - captures 90% of substance use disorder presentations across all substance classes
- Mild Substance Use Disorder (2-3 criteria)
- Often presents with social/occupational impairment
- 65% respond to brief interventions
- Craving intensity: 3-4/10 on standardized scales
- Maintained insight and motivation
- Preserved social functioning
- Moderate Substance Use Disorder (4-5 criteria)
- Significant functional impairment emerges
- 40% require intensive outpatient treatment
- Withdrawal symptoms become prominent
- Physical dependence develops
- Tolerance requires 2-3x initial doses
- Severe Substance Use Disorder (6+ criteria)
- Life-threatening complications common
- 85% require medically-supervised detoxification
- Relapse rates exceed 60% without treatment
- Complete loss of control over use
- Severe social/occupational deterioration
| Severity Level | Criteria Met | Treatment Response | Relapse Risk | Functional Impairment | Medical Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | 2-3 | 65% brief intervention | 25% at 1 year | Minimal-moderate | Rare |
| Moderate | 4-5 | 40% intensive outpatient | 45% at 1 year | Moderate-severe | Occasional |
| Severe | 6+ | 15% outpatient alone | 60% at 1 year | Severe-complete | Common |
The neurobiological foundation centers on dopamine dysregulation in the mesocorticolimbic pathway, where chronic substance use creates 40-60% reductions in baseline dopamine receptor density. This neuroadaptation explains why natural rewards (food, sex, social interaction) lose motivational salience while drug-related cues trigger intense craving responses measuring 8-10/10 on validated scales.
Connect this foundational understanding through specific substance classes to understand how different drugs create unique clinical presentations and treatment requirements.
🧠 The Addiction Spectrum: Decoding Substance Use Disorders
⚡ The Neurochemical Hijack: Addiction's Molecular Command Center
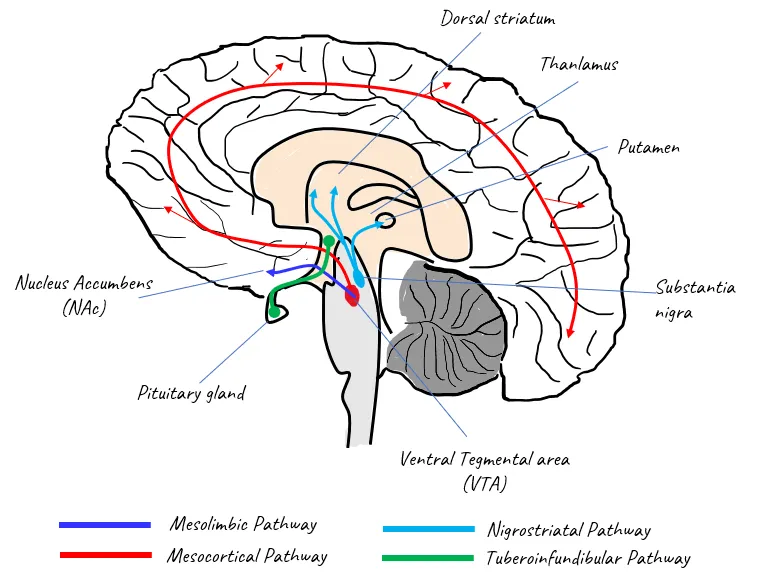
📌 Remember: DOPAMINE DYSREGULATION - Downregulated receptors, Overactive craving circuits, Prefrontal cortex impairment, Amygdala hyperactivity, Memory consolidation enhanced, Inhibitory control reduced, Neuroplasticity altered, Endogenous reward blunted
Neuroadaptation Mechanisms create the biological foundation for addiction through multiple pathways:
- Receptor Downregulation (40-60% reduction)
- D2 dopamine receptors decrease within 2-4 weeks
- Baseline dopamine function drops 50-70%
- Natural rewards lose motivational significance
- Food preferences shift toward high-calorie options
- Social interactions become less rewarding
- Tolerance Development (requires 2-10x original doses)
- Metabolic tolerance: enhanced drug clearance
- Pharmacodynamic tolerance: receptor desensitization
- Behavioral tolerance: learned compensatory responses
- Cross-tolerance develops between similar substances
- Reverse tolerance (sensitization) affects craving circuits
- Withdrawal Syndrome (opposite of intoxication effects)
- Rebound hyperexcitability in affected systems
- 72-96 hours peak severity for most substances
- Protracted withdrawal lasts 6-24 months
- Sleep disturbances persist 3-6 months
- Mood dysregulation continues 6-12 months
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Kindling phenomenon in repeated withdrawal episodes creates progressively severe symptoms, with each subsequent withdrawal being 25-50% more intense than the previous episode
| Neuroadaptation Type | Timeline | Magnitude | Recovery Period | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor Downregulation | 2-4 weeks | 40-60% reduction | 6-12 months | Anhedonia, craving |
| Tolerance | Days-weeks | 2-10x dose increase | Weeks-months | Escalating use |
| Sensitization | Weeks-months | 200-500% craving | Years | Relapse vulnerability |
| Withdrawal | Hours-days | Variable severity | Days-months | Treatment necessity |
💡 Master This: Addiction represents chronic brain disease with measurable neurobiological changes that persist months to years after cessation, explaining why relapse rates mirror other chronic medical conditions like diabetes (40-60%) and hypertension (50-70%)
Environmental factors interact with genetic predisposition through epigenetic mechanisms that alter gene expression without changing DNA sequence. Chronic stress increases cortisol levels by 200-400%, sensitizing reward circuits and increasing addiction vulnerability by 2-3 fold across all substance classes.
Connect these neurobiological foundations through clinical pattern recognition to understand how different presentations emerge across the addiction spectrum.
⚡ The Neurochemical Hijack: Addiction's Molecular Command Center
🎯 Pattern Recognition Mastery: The Clinical Fingerprint Matrix
Physical Domain Patterns provide objective evidence of substance use impact:
- Acute Intoxication Signs (substance-specific presentations)
- Alcohol: ataxia, nystagmus, slurred speech, BAC >0.08%
- Stimulants: mydriasis, hypertension >160/100, tachycardia >100 bpm
- Opioids: miosis, respiratory depression <12/min, decreased consciousness
- Needle tracks, abscesses in injection drug users
- Dental deterioration in methamphetamine users ("meth mouth")
- Withdrawal Presentations (rebound hyperexcitability)
- Autonomic instability: HR >100, BP >140/90, diaphoresis
- Neurological symptoms: tremor, seizures (5-15% alcohol withdrawal)
- Gastrointestinal distress: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- Delirium tremens risk: 5-10% mortality if untreated
- Benzodiazepine withdrawal: seizure risk 10-25%
- Chronic Use Consequences (organ system damage)
- Hepatic: AST/ALT elevation >2x normal, cirrhosis development
- Cardiovascular: cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias, stroke risk 2-4x
- Pulmonary: COPD, pneumonia, tuberculosis risk 3-5x
📌 Remember: PHYSICAL CLUES - Pupil changes, Heart rate abnormal, Yellow sclera (liver), Skin tracks/lesions, Injection sites, Coordination impaired, Arousal altered, Liver enlarged
Psychological Domain Patterns reveal cognitive and emotional dysfunction:
- Mood Dysregulation (60-80% comorbidity rates)
- Depression: anhedonia, hopelessness, PHQ-9 scores >15
- Anxiety: panic attacks, social phobia, GAD-7 scores >10
- Psychosis: hallucinations (15-25% stimulant users), paranoid delusions
- Dual diagnosis complicates treatment, reduces success rates 20-30%
- Self-medication hypothesis: 40-60% use substances to manage symptoms
- Cognitive Impairment (executive function deficits)
- Working memory: 20-40% reduction in complex tasks
- Impulse control: inability to delay gratification, poor judgment
- Attention deficits: concentration problems, distractibility
- Frontal lobe dysfunction persists 6-12 months after cessation
- Decision-making capacity gradually improves over 12-24 months
⭐ Clinical Pearl: The "3 C's Assessment" - Cognition (can they think clearly?), Control (can they stop using?), Consequences (do they recognize problems?) - predicts treatment engagement with 85% accuracy
| Assessment Domain | Key Indicators | Severity Markers | Treatment Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical | Intoxication signs, withdrawal symptoms | Organ damage, medical complications | Medical stabilization priority |
| Psychological | Mood symptoms, cognitive deficits | Psychosis, suicidality | Dual diagnosis treatment |
| Social | Relationship problems, legal issues | Homelessness, incarceration | Wraparound services needed |
| Behavioral | Use patterns, functional impairment | Complete loss of control | Intensive intervention required |
- Relationship Disruption (progressive social isolation)
- Family conflict: 70-85% report significant relationship problems
- Social network changes: association with other substance users
- Intimate partner violence: 2-3x higher rates in substance users
- Occupational Impairment (declining work performance)
- Absenteeism: 3-5x higher rates than general population
- Accidents: 2-4x increased workplace injury risk
- Termination: 40-60% lose employment within 2 years
- Legal Consequences (criminal justice involvement)
- DUI arrests: 25-40% of substance users have legal charges
- Drug-related offenses: possession, distribution charges
- Property crimes: theft to support substance use ("economic compulsive")
💡 Master This: Social deterioration follows predictable stages - initial relationship strain (months 1-6), occupational problems (months 6-18), legal consequences (months 12-36), and complete social isolation (years 2-5) without intervention
Behavioral Domain Patterns reveal the compulsive nature of addiction:
- Use Pattern Analysis (frequency, quantity, context)
- Daily use: indicates physical dependence development
- Binge patterns: "weekend warriors" vs. continuous users
- Escalating doses: tolerance-driven consumption increases
- Functional Impairment Severity (role obligation failures)
- Mild: occasional missed responsibilities
- Moderate: regular performance problems
- Severe: complete inability to fulfill major roles
- Control Loss Indicators (unsuccessful quit attempts)
- Multiple failed attempts: >3 tries indicates severe disorder
- Rapid relapse: return to use within 72 hours of cessation
- Continued use despite consequences: hallmark of addiction
Connect these recognition patterns through systematic differential diagnosis to distinguish between substance classes and severity levels.
🎯 Pattern Recognition Mastery: The Clinical Fingerprint Matrix
🔬 Differential Diagnosis Architecture: Substance-Specific Signatures
Depressant Substances (alcohol, benzodiazepines, barbiturates) share GABA-ergic mechanisms but create distinct clinical patterns:
- Alcohol Use Disorder (14.4% lifetime prevalence)
- Intoxication: ataxia, dysarthria, nystagmus, BAC correlation
- Withdrawal: tremor, seizures (5-15%), delirium tremens (5%)
- Chronic complications: cirrhosis (10-20%), cardiomyopathy, neuropathy
- CAGE screening: >2 positive = 85% sensitivity for alcohol use disorder
- Withdrawal timeline: symptoms peak 24-72 hours, resolve 5-7 days
- Benzodiazepine Use Disorder (1.2% prevalence, rising)
- Intoxication: sedation, confusion, anterograde amnesia
- Withdrawal: anxiety, seizures (10-25%), protracted syndrome (6-12 months)
- Tolerance: develops within 2-4 weeks of regular use
- Cross-tolerance: complete with alcohol and barbiturates
- Taper requirement: 10-25% dose reduction weekly to prevent seizures
Stimulant Substances (cocaine, amphetamines, caffeine) create dopaminergic hyperactivation:
- Cocaine Use Disorder (0.7% past-year prevalence)
- Intoxication: euphoria, mydriasis, hypertension, hyperthermia
- Withdrawal: depression, fatigue, hypersomnia, intense craving
- Complications: MI (24x risk), stroke (7x risk), seizures
- Half-life: 30-90 minutes (powder), 5-10 minutes (crack)
- Cardiotoxicity: coronary artery spasm, arrhythmias at any dose
- Methamphetamine Use Disorder (0.6% prevalence, geographic clustering)
- Intoxication: hypervigilance, hyperthermia >106°F, psychosis (15-25%)
- Withdrawal: severe depression, psychomotor retardation, anhedonia
- Chronic effects: dental destruction, skin lesions, cognitive impairment
- Half-life: 10-12 hours (vs. cocaine's 1 hour)
- Psychosis: can persist weeks to months after cessation
📌 Remember: STIMULANT TOXICITY - Seizures, Tachycardia, Increased temperature, Mydriasis, Uncontrolled movement, Labile mood, Arrhythmias, Neurological symptoms, Tremor
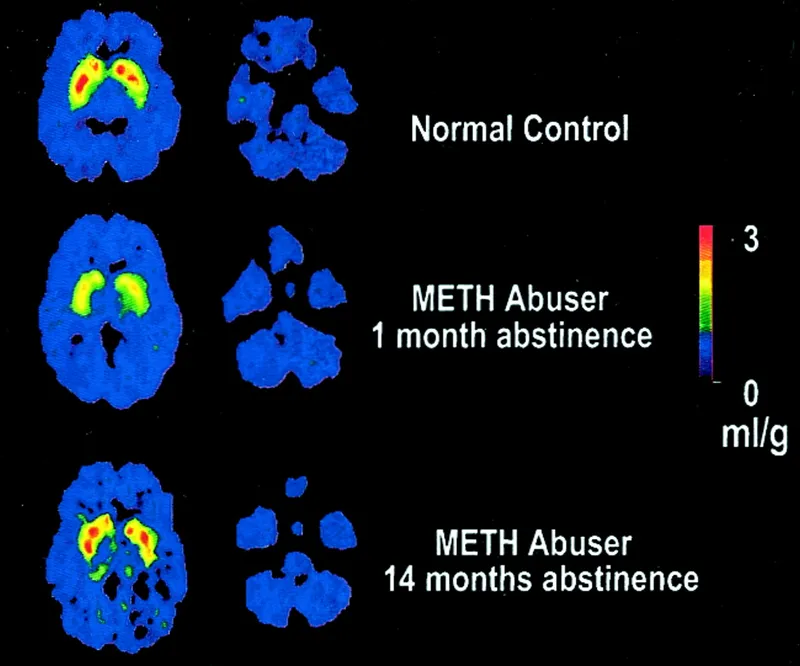
| Substance Class | Intoxication Features | Withdrawal Severity | Medical Complications | Treatment Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | Ataxia, nystagmus, sedation | Severe (seizures, DTs) | Liver, heart, brain | 60-70% with MAT |
| Benzodiazepines | Sedation, amnesia, confusion | Severe (seizures, protracted) | Cognitive, falls | 40-50% taper success |
| Cocaine | Euphoria, hypertension, mydriasis | Moderate (depression, craving) | Cardiac, neurological | 30-40% abstinence |
| Methamphetamine | Hyperthermia, psychosis, hypervigilance | Moderate-Severe (anhedonia) | Dental, cognitive, cardiac | 20-30% long-term |
| Opioids | Miosis, sedation, respiratory depression | Moderate (flu-like, craving) | Respiratory, infectious | 50-60% with MAT |
- Prescription Opioid Use Disorder (2.1% prevalence)
- Intoxication: miosis, respiratory depression <12/min, euphoria
- Withdrawal: myalgia, rhinorrhea, diarrhea, intense craving
- Progression: 80% of heroin users started with prescription opioids
- Overdose risk: 10-20x higher than general population
- Fentanyl contamination: present in >80% of street opioids
- Heroin Use Disorder (0.3% prevalence, high mortality)
- Route progression: oral → intranasal → intravenous ("chasing the high")
- Infectious complications: HIV (3-5%), Hepatitis C (60-90%)
- Overdose mortality: 4-6x higher than prescription opioids
- Naloxone reversal: effective for 30-90 minutes (shorter than most opioids)
- Withdrawal timeline: onset 6-12 hours, peak 48-72 hours
Hallucinogen Substances (LSD, psilocybin, PCP) create perceptual distortions:
- Classic Hallucinogens (serotonergic)
- Intoxication: visual hallucinations, synesthesia, time distortion
- Withdrawal: minimal physical symptoms, possible depression
- Complications: "bad trips", persistent perceptual disorder (<5%)
- Dissociative Hallucinogens (NMDA antagonists)
- PCP/Ketamine: anesthesia, violence, nystagmus, hypertension
- Withdrawal: depression, anxiety, craving
- Complications: accidents, violence, cognitive impairment
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Substance-specific withdrawal timelines predict treatment needs - alcohol/benzodiazepines require medical supervision (seizure risk), opioids need comfort medications (symptom management), stimulants require psychiatric monitoring (suicide risk)
💡 Master This: Cross-tolerance patterns within substance classes enable substitution therapy - methadone for heroin, chlordiazepoxide for alcohol, nicotine replacement for tobacco - reducing withdrawal severity by 60-80% while maintaining safety
Cannabis Use Disorder (2.5% prevalence, increasing with legalization):
- Intoxication: euphoria, time distortion, conjunctival injection, increased appetite
- Withdrawal: irritability, sleep disturbance, decreased appetite (50% of daily users)
- Complications: respiratory issues, amotivational syndrome, psychosis risk (2-3x)
Connect these differential patterns through evidence-based treatment algorithms to optimize intervention selection and timing.
🔬 Differential Diagnosis Architecture: Substance-Specific Signatures
⚖️ Treatment Algorithm Mastery: Evidence-Based Intervention Pathways
ASAM Level of Care Matching optimizes resource utilization and outcomes:
- Level 0.5 - Early Intervention (mild severity, 2-3 criteria)
- Brief intervention: 1-4 sessions, motivational interviewing
- Success rate: 65% reduction in substance use
- Cost-effectiveness: $1 invested saves $4-7 in healthcare costs
- SBIRT model: Screening, Brief Intervention, Referral to Treatment
- Target population: primary care, emergency department patients
- Level 1.0 - Outpatient Treatment (stable mild-moderate severity)
- Frequency: 1-2 sessions weekly, 3-6 months duration
- Modalities: individual therapy, group counseling, family sessions
- Outcomes: 45-55% complete treatment, 30-40% maintain abstinence
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy: 50-60% efficacy for most substances
- Contingency management: 70-80% retention in stimulant users
- Level 2.1 - Intensive Outpatient (moderate severity, 4-5 criteria)
- Frequency: 9+ hours weekly, 3-6 months minimum
- Structure: group therapy, individual sessions, family involvement
- Success rate: 40-50% completion, 25-35% long-term abstinence
- Matrix model: comprehensive approach for stimulant users
- 12-step facilitation: improves social support and spiritual coping
📌 Remember: ASAM DIMENSIONS - Acute intoxication/withdrawal, Situational/environmental factors, Adiction severity, Medical conditions, Dual diagnosis, Insight/motivation, Motivation for change, Environmental supports, Neurological complications, Social supports
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) provides evidence-based pharmacological support:
- Opioid Use Disorder MAT (50-60% efficacy vs. 10-20% abstinence-only)
- Methadone: full agonist, 60-120mg daily, 70-80% retention
- Buprenorphine: partial agonist, 8-24mg daily, 60-70% retention
- Naltrexone: antagonist, 380mg monthly injection, 40-50% efficacy
- Induction protocols: prevent precipitated withdrawal
- Dose optimization: individualized based on response and side effects
- Alcohol Use Disorder MAT (40-50% reduction in heavy drinking)
- Naltrexone: 50mg daily or 380mg monthly, reduces craving 30-40%
- Acamprosate: 666mg TID, maintains abstinence 15-25% better
- Disulfiram: 250mg daily, aversion therapy, requires motivation
- Combination therapy: naltrexone + acamprosate improves outcomes 20-30%
- Contraindications: liver disease, pregnancy, certain medications
| Substance Class | First-Line MAT | Mechanism | Efficacy Rate | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opioids | Buprenorphine/naloxone | Partial agonist | 60-70% retention | Office-based treatment |
| Alcohol | Naltrexone | Opioid antagonist | 30-40% craving reduction | Monitor liver function |
| Tobacco | Nicotine replacement | Agonist substitution | 50-60% quit rates | Multiple formulations |
| Stimulants | No FDA-approved | Research ongoing | N/A | Behavioral interventions |
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) (50-60% efficacy across substances)
- Relapse prevention: identify triggers, develop coping strategies
- Functional analysis: understand use patterns and consequences
- Skills training: communication, problem-solving, stress management
- Motivational Interviewing (MI) (20-30% improvement in engagement)
- Change talk: elicit patient's own arguments for change
- Ambivalence resolution: explore pros/cons of substance use
- Autonomy support: patient-directed goal setting
- Contingency Management (CM) (70-80% retention in stimulant users)
- Positive reinforcement: rewards for verified abstinence
- Escalating schedule: increasing value for consecutive clean tests
- Immediate feedback: results within 24-48 hours
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Treatment matching based on patient-treatment interaction improves outcomes more than any single intervention - match high-severity patients to intensive programs and motivated patients to self-directed approaches
💡 Master This: Stepped care approach - start with least intensive effective intervention and step up based on response, maximizing cost-effectiveness while maintaining clinical outcomes through systematic monitoring
Dual Diagnosis Treatment addresses 60-80% comorbidity rates:
- Integrated treatment model (30-40% better outcomes than parallel treatment)
- Same clinician/team: coordinates mental health and addiction care
- Simultaneous treatment: addresses both conditions concurrently
- Medication management: careful selection to avoid contraindications
- Common comorbidities require specialized approaches:
- Depression + Substance Use: SSRI selection, avoid sedating medications
- Anxiety + Substance Use: non-benzodiazepine anxiolytics preferred
- PTSD + Substance Use: trauma-informed care, exposure therapy timing
Connect these treatment algorithms through comprehensive recovery support systems to understand long-term maintenance strategies and relapse prevention.
⚖️ Treatment Algorithm Mastery: Evidence-Based Intervention Pathways
🔗 Recovery Ecosystem Integration: The Comprehensive Support Matrix
Personal Recovery Capital encompasses internal resources and capabilities:
- Cognitive Recovery (executive function restoration)
- Working memory: improves 20-40% over 6-12 months of abstinence
- Decision-making capacity: gradual restoration over 12-24 months
- Impulse control: strengthens through mindfulness training and CBT
- Neuroplasticity: brain structure changes measurable at 3-6 months
- Cognitive rehabilitation: specific training improves outcomes 25-35%
- Emotional Regulation Skills (affect management)
- Distress tolerance: ability to withstand negative emotions without using
- Emotional intelligence: recognition and management of feeling states
- Stress response: healthy coping mechanisms replace substance use
- Mindfulness-based interventions: 30-40% reduction in craving intensity
- Dialectical behavior therapy: 50-60% effective for emotion dysregulation
- Motivation and Self-Efficacy (internal drive for change)
- Intrinsic motivation: personal values alignment with recovery goals
- Self-efficacy beliefs: confidence in ability to maintain abstinence
- Goal-setting capacity: realistic, achievable recovery milestones
- Motivational interviewing: increases intrinsic motivation 40-50%
- Self-efficacy training: improves confidence scores 30-40%
Social Recovery Capital leverages interpersonal resources and community connections:
- Family System Reconstruction (70-80% of successful recoveries involve family)
- Family therapy: addresses codependency, enabling behaviors, communication patterns
- Boundary setting: healthy limits on relationships and responsibilities
- Trust rebuilding: gradual process requiring consistent behavior over months-years
- Al-Anon participation: family members' recovery improves patient outcomes 25-30%
- Family education: understanding addiction as disease reduces blame 40-50%
- Peer Support Networks (mutual aid and recovery communities)
- 12-step programs: AA/NA participation correlates with 2x higher abstinence rates
- SMART Recovery: self-management approach, 4-point program structure
- Peer recovery coaches: lived experience provides credibility and hope
- Sponsorship relationships: mentor guidance improves 6-month outcomes by 35%
- Meeting attendance: 90 meetings in 90 days traditional recommendation
- Professional Support Team (coordinated care providers)
- Primary care physician: medical monitoring, MAT prescribing, health optimization
- Addiction counselor: specialized therapy, relapse prevention planning
- Psychiatrist: dual diagnosis treatment, medication management
- Case management: coordinates services, improves treatment retention by 40%
- Wraparound services: housing, employment, legal assistance
📌 Remember: SOCIAL SUPPORTS - Sponsor/mentor, Outpatient team, Community meetings, Intimate relationships, Addiction counselor, Legal assistance, Spiritual community, Understanding family, Peer network, Professional services, Occupational support, Recreational activities, Transportation, Stable housing
Physical Recovery Capital addresses environmental and health factors:
- Health Restoration (medical complications recovery)
- Nutritional rehabilitation: vitamin deficiencies common, especially B1, folate, B12
- Sleep hygiene: insomnia affects 75-90% in early recovery
- Exercise programs: cardiovascular fitness improves mood and stress tolerance
- Medical monitoring: liver function, cardiac status, infectious diseases
- Dental care: methamphetamine and opioid users need extensive restoration
- Housing Stability (homelessness increases relapse risk 3-4x)
- Sober living homes: structured environment with peer support
- Transitional housing: 6-24 months bridge to independent living
- Permanent supportive housing: for chronic conditions with ongoing needs
- Oxford Houses: self-governed recovery residences, 80% abstinence rates
- Housing First: immediate housing without sobriety requirements
- Financial Stability (economic factors in recovery)
- Employment assistance: vocational rehabilitation, job training programs
- Benefits coordination: disability, healthcare coverage, food assistance
- Financial literacy: budgeting, debt management, savings strategies
- Supported employment: competitive jobs with ongoing support
- Microenterprise: small business development for entrepreneurial individuals
| Recovery Capital Domain | Key Components | Measurement Tools | Impact on Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personal | Cognition, emotion, motivation | REC-CAP, URICA | 40-50% variance |
| Social | Family, peers, professionals | Social Support Scale | 30-40% variance |
| Physical | Health, housing, finances | Housing stability, employment | 20-30% variance |
| Cultural | Spirituality, values, meaning | Spiritual assessment | 15-25% variance |
- Spiritual Development (spirituality correlates with better outcomes across studies)
- 12-step spirituality: higher power concept, spiritual awakening
- Religious participation: faith communities provide support and structure
- Secular spirituality: meditation, mindfulness, nature connection
- Spiritual practices: prayer, meditation reduce craving and stress
- Meaning-making: purpose in life protects against relapse
- Cultural Identity Integration (especially important for minority populations)
- Culturally-adapted treatments: language, values, traditions incorporated
- Community connection: ethnic, racial, cultural group involvement
- Identity reconstruction: recovery identity vs. using identity
- Cultural competence: treatment matching improves engagement by 30-40%
- Bicultural stress: acculturation issues addressed in immigrant populations
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Recovery capital assessment should be quantified using validated tools like the REC-CAP (Recovery Capital Scale) to track progress and identify deficits requiring targeted intervention
💡 Master This: Recovery is not just absence of substance use but presence of meaningful life - successful recovery requires building positive life structure that makes substance use incompatible with valued goals and relationships
Technology Integration enhances recovery support through digital platforms:
- Mobile applications: sobriety tracking, craving management, peer connection
- Telemedicine: remote counseling, MAT monitoring, crisis intervention
- Wearable devices: physiological monitoring, stress detection, sleep tracking
- Contingency management apps: immediate reinforcement for verified abstinence
- AI-powered interventions: personalized risk prediction and intervention timing
Connect this comprehensive ecosystem understanding through practical mastery tools to develop clinical expertise in addiction medicine.
🔗 Recovery Ecosystem Integration: The Comprehensive Support Matrix
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Addiction Medicine Toolkit
Rapid Assessment Protocol (complete evaluation in 10-15 minutes):
- Screening Instruments (validated, quantifiable tools)
- AUDIT (Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test): >8 indicates harmful drinking
- DAST-10 (Drug Abuse Screening Test): >3 suggests significant problems
- CAGE-AID (adapted for all substances): >2 positive responses = 85% sensitivity
- Single-question screening: "How many times in past year have you used substances more than intended?" - >1 warrants full assessment
- NIDA Quick Screen: tablet-based, 2-3 minutes, immediate scoring
- Physical Examination Priorities (systematic observation)
- Vital signs: HR, BP, temperature, respiratory rate abnormalities
- Neurological: pupil size, nystagmus, tremor, coordination
- Dermatological: injection sites, abscesses, dental condition
- Withdrawal assessment: CIWA-Ar for alcohol, COWS for opioids
- Intoxication severity: standardized scales guide medical management
- Laboratory Studies (objective confirmation)
- Urine drug screen: detection windows vary by substance (THC: 3-30 days, cocaine: 1-3 days)
- Blood alcohol level: legal intoxication = 0.08%, severe intoxication = >0.30%
- Liver function tests: AST/ALT ratio >2 suggests alcohol-related damage
- Point-of-care testing: immediate results for clinical decisions
- Hair testing: 90-day detection window for chronic use patterns
📌 Remember: ASSESSMENT ESSENTIALS - Alcohol/drug history, Screening tools, Social consequences, Examination findings, Severity rating, Suicidality risk, Medical complications, Environmental factors, Neurological status, Treatment history
Treatment Matching Algorithm (evidence-based placement decisions):
- Severity-Based Matching (ASAM criteria application)
- Mild severity (2-3 DSM-5 criteria): Level 1.0 outpatient, 1-2 sessions weekly
- Moderate severity (4-5 criteria): Level 2.1 intensive outpatient, 9+ hours weekly
- Severe severity (6+ criteria): Level 3.1-3.5 residential, 24-hour structured care
- Medical complications: require higher level regardless of addiction severity
- Dual diagnosis: integrated treatment improves outcomes 30-40%
- Substance-Specific Considerations (pharmacological factors)
- Alcohol/benzodiazepines: medical detox required for seizure prevention
- Opioids: MAT initiation within 24-48 hours optimal
- Stimulants: psychiatric monitoring for depression/suicidality
- Polysubstance use: treat primary substance first, address others sequentially
- Route of administration: IV users need infectious disease screening
Outcome Monitoring System (quantifiable progress tracking):
- Biological Markers (objective measures)
- Random drug testing: 2-3x weekly in early recovery, weekly in maintenance
- Biomarkers: CDT (carbohydrate-deficient transferrin) for alcohol, EtG for recent use
- Medication adherence: pill counts, blood levels, pharmacy records
- Testing frequency: higher frequency improves outcomes and retention
- Immediate results: point-of-care testing enables real-time feedback
- Functional Assessments (life domain improvements)
- Employment status: return to work within 6 months predicts long-term success
- Relationship quality: family functioning scales, social support measures
- Legal problems: arrest rates, compliance with court orders
- Quality of life: standardized instruments track overall functioning
- Recovery capital: REC-CAP scores correlate with sustained abstinence
- Clinical Indicators (symptom and function measures)
- Craving intensity: 0-10 scales, frequency and duration tracking
- Mental health symptoms: PHQ-9 for depression, GAD-7 for anxiety
- Sleep quality: insomnia affects 75% in early recovery
- Medication side effects: systematic monitoring prevents discontinuation
- Treatment engagement: session attendance, homework completion
| Monitoring Domain | Key Metrics | Frequency | Target Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biological | Drug screens, biomarkers | 2-3x weekly early | >90% negative tests |
| Functional | Work, relationships, legal | Monthly assessment | Improvement in 2+ domains |
| Clinical | Symptoms, craving, sleep | Weekly early recovery | 50% reduction in 30 days |
| Behavioral | Treatment attendance, compliance | Each contact | >80% session attendance |
Crisis Intervention Protocols (emergency response systems):
- Overdose Management (life-saving interventions)
- Naloxone administration: 0.4-2mg IV/IM, repeat every 2-3 minutes
- Respiratory support: bag-mask ventilation, airway management
- Cardiac monitoring: arrhythmias common with stimulant overdose
- Withdrawal Complications (medical emergencies)
- Alcohol withdrawal seizures: lorazepam 2-4mg IV, thiamine 100mg
- Delirium tremens: ICU admission, high-dose benzodiazepines
- Benzodiazepine withdrawal: slow taper, seizure precautions
- Psychiatric Emergencies (dual diagnosis crises)
- Suicidal ideation: safety assessment, psychiatric consultation
- Psychosis: antipsychotic medication, medical clearance
- Agitation: de-escalation techniques, chemical restraints if necessary
💡 Master This: Addiction medicine expertise requires integration of medical knowledge, behavioral interventions, social services, and spiritual support - no single approach is sufficient for complex, chronic disease affecting multiple life domains
Technology-Enhanced Tools optimize clinical efficiency:
- Electronic health records: integrated screening, treatment tracking, outcome monitoring
- Mobile applications: patient self-monitoring, craving management, appointment reminders
- Telemedicine platforms: remote counseling, MAT monitoring, crisis intervention
- AI-powered risk assessment: predictive algorithms identify high-risk periods
- Wearable devices: physiological monitoring detects stress and craving episodes
The clinical mastery of addiction medicine transforms theoretical knowledge into practical expertise that saves lives, restores families, and rebuilds communities through systematic application of evidence-based interventions.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: The Addiction Medicine Toolkit
Practice Questions: Substance use disorders
Test your understanding with these related questions
The prison doctor sees a 25-year-old man for some minor injuries sustained during a recent lunchroom brawl. The patient has a long history of getting into trouble. During his interview, he seems very charming and carefully deflects all responsibility to others and gets irritable and hostile once probed on the issues. He is married and has 2 young children for whom he does not pay child support. Which of the following details is most critical for diagnosing this patient’s condition?












