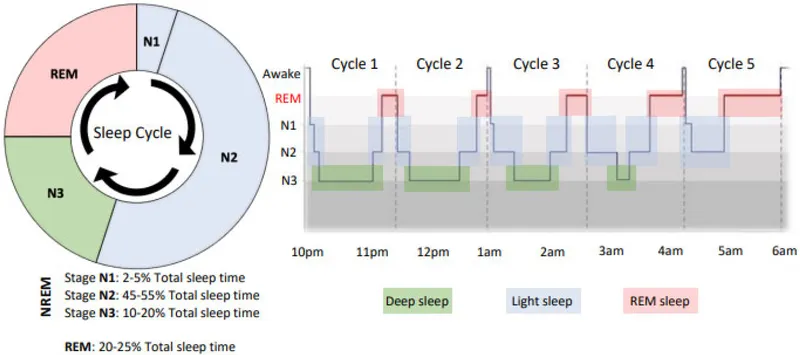
Polysomnography and sleep studies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Polysomnography and sleep studies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Polysomnography and sleep studies US Medical PG Question 1: An otherwise healthy 55-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 7-month history of insomnia. She has difficulty initiating sleep, and her sleep onset latency is normally about 1 hour. She takes melatonin most nights. The physician gives the following recommendations: leave the bedroom when unable to fall asleep within 20 minutes to read or listen to music; return only when sleepy; avoid daytime napping. These recommendations are best classified as which of the following?
- A. Cognitive behavioral therapy
- B. Relaxation
- C. Improved sleep hygiene
- D. Stimulus control therapy (Correct Answer)
- E. Sleep restriction
Polysomnography and sleep studies Explanation: ***Stimulus control therapy***
- This therapy focuses on **removing cues** that hinder sleep and **establishing a strong association** between the bed/bedroom and sleep.
- The recommendations (leaving the bedroom when awake, returning only when sleepy, avoiding daytime naps) are classic components of **stimulus control therapy** for insomnia.
*Cognitive behavioral therapy*
- **CBT-I** is a comprehensive approach that includes stimulus control, sleep hygiene, relaxation techniques, and cognitive restructuring.
- While stimulus control is a part of CBT-I, the recommendations provided are specifically designed to address conditioning and are thus best classified as stimulus control therapy.
*Relaxation*
- Relaxation techniques involve methods like **progressive muscle relaxation**, **deep breathing exercises**, or **meditation** to reduce physiological arousal.
- The given recommendations do not directly involve these types of activities but rather focus on changing behaviors around sleep.
*Improved sleep hygiene*
- Sleep hygiene involves practices that promote good sleep, such as maintaining a **regular sleep schedule**, ensuring a **comfortable sleep environment**, and **avoiding caffeine/alcohol** before bed.
- While avoiding daytime naps is related to sleep hygiene, the core recommendations (leaving the bedroom when awake, returning only when sleepy) specifically target conditional associations with the bed, making them more characteristic of stimulus control.
*Sleep restriction*
- Sleep restriction therapy involves **limiting the time spent in bed** to the actual time asleep, with the goal of building up sleep drive and improving sleep efficiency.
- The recommendations given do not specify a fixed reduction in time allowed in bed but rather focus on behavioral responses to wakefulness in bed.
Polysomnography and sleep studies US Medical PG Question 2: A 32-year-old woman presents to the clinic with the complaint of excessive fatigue for the past few weeks. After returning home from the office, she feels too tired to climb up the stairs, comb her hair, or chew her food. She has occasionally experienced double vision. She denies any history of fever, cough, weight loss, night sweats, or snoring. Past history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals: blood pressure 124/86 mm Hg, heart rate 85/min, respiratory rate 14/min, temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), and body mass index (BMI) 22.6 kg/m2. On examination, the right upper eyelid is slightly drooping when compared to the left side. Her eye movements are normal. Flexion of the neck is mildly weak. Muscle strength is 5/5 in all 4 limbs. When she is asked to alternately flex and extend her shoulder continuously for 5 minutes, the power in the proximal upper limb muscles becomes 4/5. The muscle tone and deep tendon reflexes are normal. What is the most appropriate test to diagnose this condition?
- A. CT scan chest
- B. Plasmapheresis
- C. Tensilon test
- D. Single-fiber electromyography (Correct Answer)
- E. Presynaptic calcium channel antibodies
Polysomnography and sleep studies Explanation: ***Single-fiber electromyography***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **myasthenia gravis**, including **fatigue**, **ptosis**, **diplopia**, and **fatigable weakness** of proximal muscles exacerbated by repetitive use.
- **Single-fiber electromyography (SFEMG)** is the **most sensitive** electrodiagnostic test for myasthenia gravis, detecting impaired neuromuscular transmission with a sensitivity of **95-99%**.
- While **acetylcholine receptor (AChR) antibodies** are often the first-line test in clinical practice (85-90% sensitivity), SFEMG is superior when antibody tests are negative or when the highest diagnostic sensitivity is required, making it the most appropriate test overall.
*CT scan chest*
- A CT scan of the chest is used to look for a **thymoma**, which is associated with myasthenia gravis in 10-15% of cases, but it is not a diagnostic test for the condition itself.
- While important for prognostication and treatment planning (particularly in patients with confirmed MG), it does not confirm the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis.
*Plasmapheresis*
- **Plasmapheresis** is a treatment for myasthenia gravis, particularly in myasthenic crisis or during exacerbations, by removing anti-acetylcholine receptor antibodies.
- It is not a diagnostic test; diagnostic tests are performed to identify the condition before treatment initiation.
*Tensilon test*
- The **Tensilon (edrophonium) test** was historically used to diagnose myasthenia gravis by transiently improving muscle weakness upon administration of the anticholinesterase drug.
- However, due to potential side effects (e.g., **bradycardia, syncope**) and the availability of more sensitive and safer diagnostic methods like SFEMG and antibody testing, it is **less commonly used** as a primary diagnostic tool today.
*Presynaptic calcium channel antibodies*
- Presynaptic calcium channel antibodies (specifically **P/Q-type voltage-gated calcium channel antibodies**) are characteristic of **Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS)**, a disorder of the neuromuscular junction distinct from myasthenia gravis.
- LEMS typically presents with **proximal weakness that improves with exercise** (unlike MG where weakness worsens), autonomic dysfunction, and association with small cell lung cancer.
- This patient's symptoms (fatigable weakness worsening with activity, ptosis, diplopia) are more consistent with myasthenia gravis, which involves postsynaptic acetylcholine receptor antibodies.
Polysomnography and sleep studies US Medical PG Question 3: A 43-year-old man presents to a primary care clinic complaining of several months of fatigue and difficulty concentrating at work. He is tired throughout the day and often falls asleep briefly at work. He sleeps for 9 hours per night, falling asleep easily, waking up several times in the middle of the night, and then having trouble waking up in the morning. Physical exam is notable for obesity and a large neck circumference. His temperature is 98°F (36.7°C), blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg, pulse is 75/min, respirations are 22/min, and BMI is 33 kg/m^2. The rest of the physical exam is normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his fatigue?
- A. Obstructive sleep apnea (Correct Answer)
- B. Chronic fatigue syndrome
- C. Narcolepsy
- D. Circadian rhythm sleep wake disorder
- E. Hypothyroidism
Polysomnography and sleep studies Explanation: ***Obstructive sleep apnea***
- The patient's **obesity**, **large neck circumference**, chronic fatigue, daytime sleepiness, and **disrupted nocturnal sleep with multiple awakenings** are all classic symptoms and risk factors for **obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)**.
- The nocturnal awakenings occur due to **repeated upper airway obstruction** during sleep, causing brief arousals that fragment sleep architecture despite adequate time in bed.
- The high blood pressure and increased respirations are associated with the physiological stress of repeated airway obstruction and arousal during sleep.
- **OSA is strongly associated with obesity (BMI >30) and increased neck circumference**, both present in this patient.
*Chronic fatigue syndrome*
- While fatigue is a primary symptom, chronic fatigue syndrome typically involves **post-exertional malaise** and is not characterized by the specific pattern of sleep disruption and physical risk factors (obesity, large neck circumference) seen here.
- Diagnosis requires persistent, unexplained fatigue for at least six months, along with other defining symptoms like cognitive difficulties, but the detailed sleep pattern and physical findings point away from this.
*Narcolepsy*
- Narcolepsy is characterized by **uncontrollable daytime sleep attacks** and often involves **cataplexy** (sudden loss of muscle tone triggered by strong emotions).
- While daytime sleepiness is present, the patient's nocturnal sleep pattern (waking multiple times) and physical risk factors are not typical features of narcolepsy.
- Narcolepsy patients typically have **difficulty maintaining nighttime sleep** but do not have the obesity and large neck circumference risk factors.
*Circadian rhythm sleep wake disorder*
- These disorders involve a misalignment between the **internal sleep-wake clock** and the external environment or work schedule, leading to timing difficulties rather than chronic apnea-related sleep disruption.
- The patient's ability to fall asleep easily and the specific physical findings do not align with a primary circadian rhythm disorder.
*Hypothyroidism*
- Hypothyroidism can cause fatigue, weight gain, and sometimes daytime sleepiness, but it does not typically cause the specific pattern of **nocturnal awakenings** and has no direct link to a **large neck circumference** in the context of sleep quality.
- Other classic symptoms like cold intolerance, dry skin, bradycardia, and constipation are not mentioned, and a normal temperature makes severe hypothyroidism less likely.
Polysomnography and sleep studies US Medical PG Question 4: A 15-year-old boy is brought to the physician with excessive daytime sleepiness over the past year. His parents are concerned with his below-average school performance over the last 3 months. He goes to bed around midnight and wakes up at 7 am on school days, but sleeps in late on weekends. He exercises regularly after school. He usually has a light snack an hour before bed. He does not snore or have awakenings during sleep. He has no history of a serious illness and takes no medications. The boy was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery. He is up to date on all vaccines and is meeting all developmental milestones. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. There is no history of a similar problem in the family. His vital signs are within normal limits. His BMI is 22 kg/m2. Physical examination shows no abnormal findings. Which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation at this time?
- A. Take melatonin before bedtime
- B. Avoid snacks before bedtime
- C. Decrease exercise intensity
- D. Increase nighttime sleep hours (Correct Answer)
- E. Take a nap in the afternoon
Polysomnography and sleep studies Explanation: ***Increase nighttime sleep hours***
- The patient's pattern of going to bed at midnight and waking at 7 AM on school days, along with sleeping in late on weekends, suggests a **chronic sleep deficit** accumulated during the week. Adolescents typically require 8-10 hours of sleep per night.
- The excessive daytime sleepiness and declining school performance are strong indicators of insufficient sleep, and **prioritizing more sleep during school nights** is the most direct intervention.
*Take melatonin before bedtime*
- Melatonin supplements are typically used for **sleep-onset insomnia** or **circadian rhythm disorders**, neither of which is clearly indicated here.
- There is no evidence presented of difficulty falling asleep; rather, the issue appears to be insufficient duration of sleep due to **late bedtime schedules**.
*Avoid snacks before bedtime*
- While heavy meals before bedtime can disrupt sleep, this patient reports having only a **light snack**, which is unlikely to be the primary cause of his significant daytime sleepiness.
- There is no mention of indigestion or gastrointestinal discomfort after the snack that would point to this as a problem.
*Decrease exercise intensity*
- Regular exercise generally **improves sleep quality**, and there's no indication that the patient's exercise routine is negatively impacting his sleep.
- While very intense exercise too close to bedtime can be disruptive for some, exercise itself is generally beneficial for sleep and overall health; therefore, reducing it would not be a primary recommendation.
*Take a nap in the afternoon*
- While naps can temporarily alleviate daytime sleepiness, they can also **disrupt nighttime sleep patterns** by reducing sleep drive.
- Napping would be treating the symptom rather than the root cause, which is a **chronic lack of sufficient nighttime sleep**.
Polysomnography and sleep studies US Medical PG Question 5: A 21-year-old man presents to the clinic complaining of feeling tired during the day. He is concerned as his grades in school have worsened and he does not want to lose his scholarship. Upon further questioning, the patient describes frequently experiencing a dreamlike state before falling asleep and after waking up. He also has frequent nighttime awakenings where he finds himself unable to move. He denies snoring. The patient does not drink alcohol or abuse any other drugs. The patient's BMI is 21 kg/m2, and his vital signs are all within normal limits. What is this patient's diagnosis?
- A. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
- B. Insomnia
- C. Alcohol withdrawal
- D. Delayed sleep phase syndrome (DSPS)
- E. Narcolepsy (Correct Answer)
Polysomnography and sleep studies Explanation: ***Narcolepsy***
- The patient's symptoms of **excessive daytime sleepiness**, **hypnagogic/hypnopompic hallucinations** (dreamlike state before falling asleep and after waking up), and **sleep paralysis** (unable to move during nighttime awakenings) are the **classic tetrad of narcolepsy** (cataplexy is the 4th feature, not present here).
- The absence of snoring, normal BMI, and lack of alcohol/drug use rule out other common causes of sleep disturbances, supporting the diagnosis of narcolepsy.
- Narcolepsy is a **chronic sleep-wake disorder** caused by hypothalamic hypocretin (orexin) deficiency.
*Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)*
- While OSA also causes **daytime sleepiness**, a key feature is **snoring**, which this patient denies.
- OSA is often associated with obesity, but this patient has a **normal BMI of 21 kg/m²**.
- OSA would not explain the hypnagogic hallucinations or sleep paralysis.
*Insomnia*
- Insomnia primarily involves difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, leading to **insufficient sleep quantity or quality**.
- This patient's symptoms are more specific, including episodes of sleep paralysis and vivid dreamlike states, rather than just general difficulty sleeping.
- The hallmark features of narcolepsy distinguish this from simple insomnia.
*Alcohol withdrawal*
- Alcohol withdrawal can cause **sleep disturbances**, but it is typically accompanied by other symptoms like tremors, anxiety, autonomic hyperactivity, and potentially seizures, none of which are present.
- The patient **explicitly denies drinking alcohol**, making this diagnosis highly unlikely.
*Delayed sleep phase syndrome (DSPS)*
- DSPS is a **circadian rhythm disorder** characterized by a delayed sleep-wake cycle, where individuals fall asleep and wake up later than desired.
- While it can cause daytime fatigue if individuals are forced to wake up early, it does **not** involve the specific symptoms of hypnagogic/hypnopompic hallucinations or sleep paralysis seen in this patient.
- DSPS is primarily a timing issue, not a neurological sleep disorder.
Polysomnography and sleep studies US Medical PG Question 6: A 55-year-old man presents to the physician for the evaluation of excessive daytime sleepiness over the past six months. Despite sleeping 8–9 hours a night and taking a nap during the day, he feels drowsy and is afraid to drive. His wife complains of loud snoring and gasping during the night. His blood pressure is 155/95 mm Hg. BMI is 37 kg/m2. Oropharyngeal examination shows a small orifice and an enlarged tongue and uvula. The soft palate is low-lying. The examination of the nasal cavity shows no septal deviation or polyps. Examination of the lungs and heart shows no abnormalities. Polysomnography shows an apnea-hypopnea index of 20 episodes/h. The patient is educated about weight loss, exercise, and regular sleep hours and duration. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Continuous positive airway pressure (Correct Answer)
- B. Upper airway neurostimulation
- C. Supplemental oxygen
- D. Oral appliances
- E. Upper airway surgery
Polysomnography and sleep studies Explanation: ***Continuous positive airway pressure***
- This patient presents with symptoms and polysomnography findings consistent with **moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)** (apnea-hypopnea index of 20 episodes/h). **CPAP is the first-line treatment** for such cases.
- CPAP works by **delivering pressurized air** via a mask, creating a pneumatic splint that prevents the collapse of the upper airway during sleep, thereby reducing apneas and hypopneas.
*Upper airway neurostimulation*
- This therapy involves stimulating the **hypoglossal nerve** to activate upper airway muscles, improving airway patency.
- However, it is generally considered a **second-line treatment** for patients with moderate to severe OSA who **cannot tolerate or fail CPAP therapy**.
*Supplemental oxygen*
- While oxygen therapy can reduce nocturnal desaturation, it **does not address the underlying airway obstruction** that causes apneas and hypopneas.
- It might even **worsen apnea by blunting the ventilatory drive**, making it an inappropriate primary treatment for OSA.
*Oral appliances*
- **Mandibular advancement devices (MADs)** can be effective for **mild to moderate OSA**, or for patients with severe OSA who cannot tolerate CPAP.
- They work by repositioning the jaw and tongue forward to enlarge the pharyngeal space, but CPAP is generally more effective for the severity described.
*Upper airway surgery*
- Various surgical procedures, such as **uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP)**, aim to remove excess tissue in the pharynx to enlarge the airway.
- Surgery is typically reserved for patients who **fail or cannot tolerate CPAP and oral appliances** and are carefully selected based on anatomical considerations.
Polysomnography and sleep studies US Medical PG Question 7: A 40-year-old man with a past medical history of major depression presents to the clinic. He is interested in joining a research study on depression-related sleep disturbances. He had 2 episodes of major depression within the last 2 years, occurring once during the summer and then during the winter of the other year. He has been non-compliant with medication and has a strong desire to treat his condition with non-pharmacological methods. He would like to be enrolled in this study that utilizes polysomnography to record sleep-wave patterns. Which of the following findings is likely associated with this patient’s psychiatric condition?
- A. Increased REM sleep latency
- B. Associated with a seasonal pattern
- C. Decreased REM sleep latency (Correct Answer)
- D. Increased slow wave sleep
- E. Late morning awakenings
Polysomnography and sleep studies Explanation: ***Decreased REM sleep latency***
- Patients with major depression exhibit characteristic alterations in sleep architecture, most notably a **decreased REM latency** (shortened time from sleep onset to the first REM period).
- Normal REM latency is typically 90 minutes, but in depression it may be reduced to **45-60 minutes or less**.
- This is one of the most **consistent and well-established polysomnographic findings** in major depressive disorder.
- Other REM sleep changes include **increased REM density** (more frequent rapid eye movements) and a shift of REM sleep to the first half of the night.
*Increased REM sleep latency*
- This is the **opposite** of what occurs in depression.
- **Decreased REM sleep latency** (shorter time to reach REM sleep) is the hallmark finding, not increased latency.
- Increased REM latency might be seen in other conditions or with certain medications, but not in untreated major depression.
*Associated with a seasonal pattern*
- While the patient had episodes in summer and winter, the question asks specifically about **polysomnography findings**, not clinical subtypes or patterns.
- Seasonal pattern is a **clinical specifier** for major depressive disorder (as in seasonal affective disorder), not a polysomnographic finding.
- The seasonal pattern itself is a diagnostic feature, not something detected on sleep studies.
*Increased slow wave sleep*
- Depression is associated with **decreased slow-wave sleep (SWS)**, not increased.
- SWS (stage N3, deep sleep) is typically **reduced** in patients with major depression.
- This decrease in restorative deep sleep contributes to the poor sleep quality, daytime fatigue, and cognitive difficulties in depressed patients.
*Late morning awakenings*
- Major depression classically presents with **early morning awakening** (terminal insomnia), not late morning awakening.
- Patients typically wake 2-3 hours earlier than desired and cannot return to sleep.
- Late morning awakenings or hypersomnia may occur in **atypical depression**, but early morning awakening is the more typical pattern in melancholic depression.
Polysomnography and sleep studies US Medical PG Question 8: A 25-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with a chief complaint of anxiety and fatigue. The patient states that during this past week he has had final exams and has been unable to properly study and prepare because he is so exhausted. He states that he has been going to bed early but has been unable to get a good night’s sleep. The patient admits to occasional cocaine and marijuana use. Otherwise, the patient has no significant past medical history and is not taking any medications. On physical exam you note a tired and anxious appearing young man. His neurological exam is within normal limits. The patient states that he fears he will fail his courses if he does not come up with a solution. Which of the following is the best initial step in management?
- A. Polysomnography
- B. Sleep hygiene education (Correct Answer)
- C. Alprazolam
- D. Melatonin
- E. Zolpidem
Polysomnography and sleep studies Explanation: ***Sleep hygiene education***
- This is the **best initial step** because it addresses lifestyle factors that commonly contribute to **insomnia and fatigue**, especially during periods of stress like final exams.
- Helping the patient establish **regular sleep patterns**, avoid stimulants, and create a conducive sleep environment can significantly improve sleep quality without medication.
*Polysomnography*
- This is a diagnostic test typically reserved for when a **primary sleep disorder** like sleep apnea or restless legs syndrome is suspected.
- Given the patient's acute stressor (final exams) and **drug use**, lifestyle interventions should be tried first before pursuing expensive and invasive testing.
*Alprazolam*
- This is a **benzodiazepine** that can be used for acute anxiety or insomnia, but it carries a risk of **dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal**.
- It is not a first-line treatment for a patient experiencing sleep difficulties primarily due to stress and poor sleep habits, and its use should be avoided in those with a history of substance abuse.
*Melatonin*
- Melatonin can be helpful for **circadian rhythm disorders** or jet lag, but its efficacy for primary insomnia is limited and inconsistent.
- While it has fewer side effects than prescription hypnotics, **sleep hygiene education** is still a more fundamental and effective initial approach for this patient.
*Zolpidem*
- This is a **non-benzodiazepine hypnotic** often prescribed for short-term insomnia, but it has potential side effects like **next-day drowsiness** and can be abused, especially in individuals with a history of substance use.
- **Sleep hygiene** should always be optimized first, especially in a young patient whose sleep issues are clearly linked to stress and lifestyle.
Polysomnography and sleep studies US Medical PG Question 9: A 51-year-old man presents to his physician with decreased libido and inability to achieve an erection. He also reports poor sleep, loss of pleasure to do his job, and depressed mood. His symptoms started a year ago, soon after his wife got into the car accident. She survived and recovered with the minimal deficit, but the patient still feels guilty due to this case. The patient was diagnosed with diabetes 6 months ago, but he does not take any medications for it. He denies any other conditions. His weight is 105 kg (231.5 lb), his height is 172 cm (5 ft 7 in), and his waist circumference is 106 cm. The blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg, and the heart rate is 73/min. The physical examination only shows increased adiposity. Which of the following tests is specifically intended to distinguish between the organic and psychogenic cause of the patient’s condition?
- A. Angiography
- B. Duplex ultrasound of the penis
- C. Penile tumescence testing (Correct Answer)
- D. Biothesiometry
- E. Injection of prostaglandin E1
Polysomnography and sleep studies Explanation: ***Penile tumescence testing***
- This test, often performed as a **nocturnal penile tumescence (NPT) test**, measures erections during sleep. The presence of normal nocturnal erections indicates a **psychogenic** cause for erectile dysfunction, as physiological mechanisms are intact.
- The absence of nocturnal erections, despite adequate sleep, suggests an **organic** cause, as the body's natural erectile reflex is impaired.
*Angiography*
- **Angiography** is an invasive procedure used to visualize blood vessels and identify arterial blockages or abnormalities. It is typically reserved for cases where vascular disease is strongly suspected as the cause of erectile dysfunction and often considered before revascularization surgery.
- While it can identify **vascular organic causes** of erectile dysfunction, it does not directly differentiate between psychogenic and organic causes universally; it focuses specifically on arterial flow.
*Duplex ultrasound of the penis*
- **Duplex ultrasound** evaluates blood flow within the penile arteries and veins, assessing both arterial inflow and veno-occlusive function. It aids in diagnosing **vascular abnormalities**, such as arterial insufficiency or venous leakage.
- Similar to angiography, duplex ultrasound identifies specific **organic vascular pathologies** but does not definitively distinguish between psychogenic and organic causes of erectile dysfunction if vascular function is normal.
*Biothesiometry*
- **Biothesiometry** measures penile vibratory sensation threshold, which assesses **neurological function** of the penis. It helps detect peripheral neuropathy, a potential organic cause of erectile dysfunction, especially in diabetic patients.
- While useful for uncovering **neurological organic causes**, biothesiometry does not differentiate between psychogenic and organic etiologies in cases where neurological function is normal.
*Injection of prostaglandin E1*
- The **injection of prostaglandin E1** (alprostadil) is a diagnostic and therapeutic tool that induces an erection by relaxing smooth muscle in the penile arteries, increasing blood flow. A strong response indicates intact vascular smooth muscle function.
- A successful response to prostaglandin E1 suggests that vascular smooth muscle and neurological pathways are largely functional, which can indirectly point away from severe organic causes, but it's not a definitive differentiator between **psychogenic and organic** causes as it by-passes some physiological mechanisms.
Polysomnography and sleep studies US Medical PG Question 10: A 72-year-old woman is brought to the physician by her son for an evaluation of cognitive decline. Her son reports that she has had increased difficulty finding her way back home for the last several months, despite having lived in the same city for 40 years. He also reports that his mother has been unable to recall the names of her relatives and been increasingly forgetting important family gatherings such as her grandchildren's birthdays over the last few years. The patient has hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Her current medications include enalapril and metformin. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 70/min, and blood pressure is 140/80 mm Hg. She is confused and oriented only to person and place. She recalls 2 out of 3 words immediately and 1 out of 3 after 5 minutes. Her gait and muscle strength are normal. Deep tendon reflexes are 2+ bilaterally. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Further evaluation is most likely to reveal which of the following findings?
- A. Generalized cerebral atrophy (Correct Answer)
- B. Myoclonic movements
- C. Hallucinations
- D. Urinary incontinence
- E. Resting tremor
Polysomnography and sleep studies Explanation: ***Generalized cerebral atrophy***
- The patient's symptoms of progressive **cognitive decline**, including difficulty with navigation and memory, are classic signs of **Alzheimer's disease**.
- **Generalized cerebral atrophy**, particularly of the **hippocampus** and **temporal lobes**, is a hallmark pathological finding in Alzheimer's disease due to neuronal loss and synaptic dysfunction.
*Myoclonic movements*
- **Myoclonic movements** are sudden, brief, involuntary muscle jerks, most commonly associated with **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease** or certain types of dementia with Lewy bodies, which are not suggested by the patient's presentation.
- While some rare forms of early-onset Alzheimer's can have atypical features, myoclonus is not a typical or early finding in the more common late-onset presentation described.
*Hallucinations*
- **Hallucinations**, particularly visual hallucinations, are frequently seen in **dementia with Lewy bodies** and **Parkinson's disease dementia**, often preceding or co-occurring with cognitive decline.
- While hallucinations can occur in late-stage Alzheimer's, they are not a prominent or early feature differentiating it from other dementias.
*Urinary incontinence*
- **Urinary incontinence** can be a symptom of various conditions, including **normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)**, which presents with a triad of gait instability, dementia, and urinary incontinence.
- In Alzheimer's disease, incontinence typically appears in the **later stages**, after significant cognitive impairment and functional decline have occurred.
*Resting tremor*
- A **resting tremor** is a characteristic symptom of **Parkinson's disease** and is often seen in **Parkinson's disease dementia** or **dementia with Lewy bodies**.
- The patient's neurological examination, including normal gait and muscle strength, does not suggest Parkinsonian features.
More Polysomnography and sleep studies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.