Neuroimaging findings US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Neuroimaging findings. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Neuroimaging findings US Medical PG Question 1: A 21-year-old man presents to the emergency room requesting surgery to remove "microchips," which he believes were implanted in his brain by "Russian spies" 6 months ago to control his thoughts. He also reports hearing the "spies" talk to each other through embedded "microspeakers." You notice that his hair appears unwashed and some of his clothes are on backward. Urine toxicology is negative for illicit drugs. Which of the following additional findings are you most likely to see in this patient during the course of his illness?
- A. Anhedonia, guilty rumination, and insomnia
- B. Grandiose delusions, racing thoughts, and pressured speech
- C. Asociality, flat affect, and alogia (Correct Answer)
- D. Amnesia, multiple personality states, and de-realization
- E. Intrusive thoughts, ritualized behaviors, and anxious mood
Neuroimaging findings Explanation: ***Asociality, flat affect, and alogia***
- This patient exhibits **delusions (persecutory, control)** and **auditory hallucinations**, classic positive symptoms of **schizophrenia**. The question asks about findings "during the course of his illness," which points to the **typical progression of schizophrenia**: patients initially present with **positive symptoms** (as seen in this case) and **over time develop negative symptoms** such as **asociality** (lack of motivation to engage in social interaction), **flat affect** (reduced emotional expression), and **alogia** (poverty of speech).
- The disorganized appearance (unwashed hair, clothes on backward) already demonstrates **disorganized behavior**, part of the schizophrenia spectrum. Negative symptoms typically emerge or worsen as the illness progresses, representing the most likely additional findings.
*Anhedonia, guilty rumination, and insomnia*
- While **anhedonia** and **insomnia** can be seen in schizophrenia, their presence alongside prominent **guilty rumination** would more strongly suggest a **depressive disorder with psychotic features**, rather than primary schizophrenia, especially with the patient's specific, classic psychotic symptoms.
- The primary symptoms described (delusions of control, auditory hallucinations) are more characteristic of primary psychotic disorders, and guilty rumination is not a typical feature of schizophrenia progression.
*Grandiose delusions, racing thoughts, and pressured speech*
- These symptoms are hallmark features of **mania** or a **manic episode with psychotic features**. While psychotic features can occur in bipolar disorder with mania, the patient's specific delusions of being controlled by spies and hearing voices discussing him are more typical of schizophrenia.
- The absence of information about elevated mood, increased energy, or decreased need for sleep also makes mania less likely compared to schizophrenia.
*Amnesia, multiple personality states, and de-realization*
- These symptoms are characteristic of **dissociative disorders**. **Amnesia** and **multiple personality states** (now known as identity alteration in dissociative identity disorder) involve disturbances in memory and identity.
- **De-realization** involves feelings of unreality regarding one's surroundings. None of these align with the patient's primary presentation of well-formed delusions and hallucinations characteristic of a psychotic disorder.
*Intrusive thoughts, ritualized behaviors, and anxious mood*
- These are core features of **obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)**. The patient's symptoms are clearly defined as delusions (fixed false beliefs) and hallucinations (perceptions without external stimuli), which are distinct from the ego-dystonic intrusive thoughts and ritualistic compulsions of OCD.
- While anxiety may be present in psychotic disorders, the primary presentation here is not dominated by OCD-like symptoms, and these would not be expected to develop as part of schizophrenia's natural course.
Neuroimaging findings US Medical PG Question 2: A 67-year-old female is brought to the emergency room by her son for unusual behavior. She moved into her son’s house three years ago after her husband passed away. The son reports that when he returned home from work earlier in the day, he found his mother minimally responsive. She regained consciousness soon after his arrival and did not recall the event. The son also reports that for the past two years, his mother has had trouble remembering names and addresses. She still goes shopping on her own and cooks regularly. Her past medical history is notable for major depressive disorder, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. She takes clomipramine, glyburide, lisinopril, and hydrochlorothiazide. She recently saw her primary care provider who adjusted some of her medication dosages. Her temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 135/75 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 18/min. On examination, she is easily distractible with disorganized speech. She does not recognize her son and thinks that her intravenous line is a rope. She says she feels fine and would like to go home. Brain imaging would likely reveal which of the following?
- A. Caudate nucleus atrophy
- B. Mesial temporal lobe atrophy
- C. Multiple ischemic sites and microhemorrhages
- D. Normal cerebrum (Correct Answer)
- E. Focal atrophy of the frontal and temporal cortices
Neuroimaging findings Explanation: ***Normal cerebrum***
- The patient's presentation with acute onset confusion, fluctuating consciousness, inattention, disorganized thinking, and perceptual disturbances (misidentifying an IV line as a rope) is highly suggestive of **delirium**.
- Given her history of recent medication changes (especially **clomipramine**, a tricyclic antidepressant with anticholinergic properties) and comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, depression), she is at high risk for medication-induced or metabolic delirium.
- **Delirium is a functional disturbance** without structural brain lesions; brain imaging is typically performed to rule out other causes but would show **no acute abnormalities** in uncomplicated delirium.
*Mesial temporal lobe atrophy*
- This finding is characteristic of **Alzheimer's disease** and would be associated with a more progressive, insidious cognitive decline rather than an acute confusional state with fluctuations.
- While she has some long-standing memory issues, her acute presentation of profound disorientation and perceptual disturbances is not typical for an acute exacerbation of Alzheimer's itself, which causes mostly specific memory and cognitive decline.
*Focal atrophy of the frontal and temporal cortices*
- This pattern is more characteristic of **frontotemporal dementia** (FTD), which typically presents with prominent behavioral changes (disinhibition, apathy) or language difficulties.
- The patient's acute fluctuating mental status is not a primary feature of FTD, which follows a more gradual, progressive course.
*Caudate nucleus atrophy*
- **Caudate nucleus atrophy** is a hallmark feature of **Huntington's disease**, a genetic neurodegenerative disorder characterized by involuntary movements (chorea), psychiatric symptoms, and cognitive decline.
- Her symptoms of acute delirium and chronic memory loss do not align with the typical presentation of Huntington's disease.
*Multiple ischemic sites and microhemorrhages*
- This pattern is indicative of **vascular dementia** or multi-infarct dementia, characterized by a stepwise decline in cognitive function with focal neurological deficits.
- While her comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension) increase her risk for vascular disease, her acute fluctuating delirium is more consistent with a metabolic or medication-induced cause rather than acute widespread ischemic events.
Neuroimaging findings US Medical PG Question 3: A 24-year-old woman is brought to the hospital by her mother because she has "not been herself" for the past 3 months. The patient says she hears voices in her head. The mother said that when she is talking to her daughter she can’t seem to make out what she is saying; it is as if her thoughts are disorganized. When talking with the patient, you notice a lack of energy and an apathetic affect. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
- A. Major depressive disorder
- B. Schizophrenia
- C. Brief psychotic disorder
- D. Schizotypal disorder
- E. Schizophreniform disorder (Correct Answer)
Neuroimaging findings Explanation: ***Schizophreniform disorder***
- The patient exhibits core **psychotic symptoms** (hearing voices, disorganized thoughts) for a duration of **3 months**, which is characteristic of schizophreniform disorder (symptoms lasting **1 to 6 months**).
- Her **lack of energy** and **apathetic affect** align with the negative symptoms commonly seen in psychotic disorders.
*Major depressive disorder*
- While **lack of energy** and **apathetic affect** can be present, the prominent **hallucinations** (hearing voices) and **disorganized thoughts** are not primary features of major depressive disorder.
- A diagnosis of depression alone would not fully account for her psychotic symptoms.
*Schizophrenia*
- Schizophrenia requires symptoms to be present for **at least 6 months**, including at least one month of **active phase symptoms**. This patient's symptoms have only been present for 3 months.
- While the symptoms are consistent with schizophrenia, the **duration criterion** has not yet been met.
*Brief psychotic disorder*
- Brief psychotic disorder is characterized by psychotic symptoms lasting **less than 1 month**. This patient's symptoms have been ongoing for 3 months.
- The chronicity of symptoms makes this diagnosis unlikely.
*Schizotypal disorder*
- Schizotypal disorder is a **personality disorder** characterized by peculiar thoughts and behaviors, but typically **without overt psychotic episodes** or pronounced disorganized speech/hallucinations as described.
- While there may be odd beliefs or ideas of reference, the clear **auditory hallucinations** and **thought disorder** in this case point to a more severe psychotic condition.
Neuroimaging findings US Medical PG Question 4: A 75-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with her son because she is convinced that people are stealing from her. Her son claims she has been misplacing her medications and money throughout the house. She recently lost her husband to old age and has become reclusive and no longer wants people to visit. Physical examination is unremarkable and the patient is oriented to person, time, and place. A mini-mental status examination (MMSE) is performed and she has difficulty recalling words after 5 minutes and also has problems with serial subtraction. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Histrionic personality disorder
- B. Schizophrenia
- C. Delirium
- D. Schizoid personality disorder
- E. Dementia (Correct Answer)
Neuroimaging findings Explanation: ***Dementia***
- The patient has **primary cognitive impairment** evidenced by MMSE deficits (poor delayed recall, impaired serial subtraction) and functional decline (misplacing items).
- Her **delusions of theft are secondary to dementia**, a common behavioral and psychological symptom of dementia (BPSD), particularly in Alzheimer's disease.
- The **insidious onset** in a 75-year-old with progressive memory decline points to a neurodegenerative process.
- Orientation remains intact in early-to-moderate dementia, which doesn't rule out the diagnosis.
- The stressor (husband's death) may have unmasked or accelerated symptom recognition but doesn't explain the cognitive deficits.
*Histrionic personality disorder*
- Characterized by **excessive emotionality** and **attention-seeking behavior**, which are not evident in this presentation.
- Personality disorders are lifelong patterns, not new-onset conditions in elderly patients with cognitive decline.
- Does not explain the objective cognitive deficits on MMSE.
*Schizophrenia*
- Schizophrenia typically has onset in **late adolescence to early adulthood**, not at age 75.
- While late-onset schizophrenia exists, the **prominent cognitive impairment** (memory, executive function) as the PRIMARY feature points toward dementia rather than a primary psychotic disorder.
- Schizophrenia would show more pervasive psychotic symptoms without the specific pattern of memory and executive dysfunction seen here.
*Delirium*
- Delirium has **acute onset** (hours to days) with **fluctuating consciousness** and altered attention.
- This patient is **oriented to person, time, and place** and has a gradual, progressive course (misplacing items over time).
- No mention of acute medical illness, medication changes, or rapid cognitive fluctuation.
*Schizoid personality disorder*
- A lifelong pattern of **social detachment** and restricted emotional expression, not a new condition in late life.
- Does not explain the cognitive impairment, memory deficits, or delusional beliefs.
- The patient's reclusiveness is reactive to recent loss and concerns about theft, not a longstanding personality trait.
Neuroimaging findings US Medical PG Question 5: A 20-year-old male is brought to a psychiatrist by his parents for bizarre behavior. His parents report that over the past two semesters in school, his personality and behavior have changed noticeably. He refuses to leave his room because he believes people are spying on him. He hears voices that are persecutory and is convinced that people at school have chips implanted in their brains to spy on him. Screenings for depression and mania are negative. His past medical history is unremarkable. His family history is notable for a maternal uncle with bipolar disorder. He does not drink alcohol or smoke. His temperature is 98.8°F (37.1°C), blood pressure is 115/70 mmHg, pulse is 85/min, and respirations are 18/min. On examination, he appears to be responding to internal stimuli. Which of the following pathways is primarily responsible for these symptoms?
- A. Papez circuit
- B. Mesocortical pathway
- C. Nigrostriatal pathway
- D. Tuberoinfundibular pathway
- E. Mesolimbic pathway (Correct Answer)
Neuroimaging findings Explanation: ***Mesolimbic pathway***
- The **mesolimbic pathway** is primarily associated with the **positive symptoms of psychosis**, such as **hallucinations and delusions**, due to **dopamine hyperactivity**.
- The patient's **persecutory delusions, auditory hallucinations, and paranoia** are hallmark positive symptoms seen in conditions like schizophrenia, which are mediated by this pathway.
*Papez circuit*
- The **Papez circuit** is involved in **emotion and memory**, connecting structures like the hippocampus and cingulate gyrus.
- Dysregulation of this circuit would more likely manifest as deficits in memory or emotional regulation rather than the prominent psychotic features described.
*Mesocortical pathway*
- The **mesocortical pathway** projects to the **prefrontal cortex** and is implicated in **negative symptoms** (e.g., apathy, flat affect) and **cognitive deficits** (e.g., executive dysfunction) of psychosis, often due to **dopamine hypoactivity**.
- While cognitive and negative symptoms can co-occur in psychotic disorders, they are not the primary, most striking symptoms described here.
*Nigrostriatal pathway*
- The **nigrostriatal pathway** is crucial for **motor control**, connecting the substantia nigra to the striatum.
- Dysfunction in this pathway leads to **extrapyramidal symptoms** (e.g., tremors, rigidity, dyskinesia), which are not present in this patient's presentation.
*Tuberoinfundibular pathway*
- The **tuberoinfundibular pathway** connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland and regulates **prolactin secretion**.
- Its primary role is in neuroendocrine function, and its dysfunction would lead to **hyperprolactinemia** and related symptoms, not the psychotic features described.
Neuroimaging findings US Medical PG Question 6: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Neuroimaging findings Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Neuroimaging findings US Medical PG Question 7: A 72-year-old woman is brought to the physician by her son for an evaluation of cognitive decline. Her son reports that she has had increased difficulty finding her way back home for the last several months, despite having lived in the same city for 40 years. He also reports that his mother has been unable to recall the names of her relatives and been increasingly forgetting important family gatherings such as her grandchildren's birthdays over the last few years. The patient has hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Her current medications include enalapril and metformin. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 70/min, and blood pressure is 140/80 mm Hg. She is confused and oriented only to person and place. She recalls 2 out of 3 words immediately and 1 out of 3 after 5 minutes. Her gait and muscle strength are normal. Deep tendon reflexes are 2+ bilaterally. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Further evaluation is most likely to reveal which of the following findings?
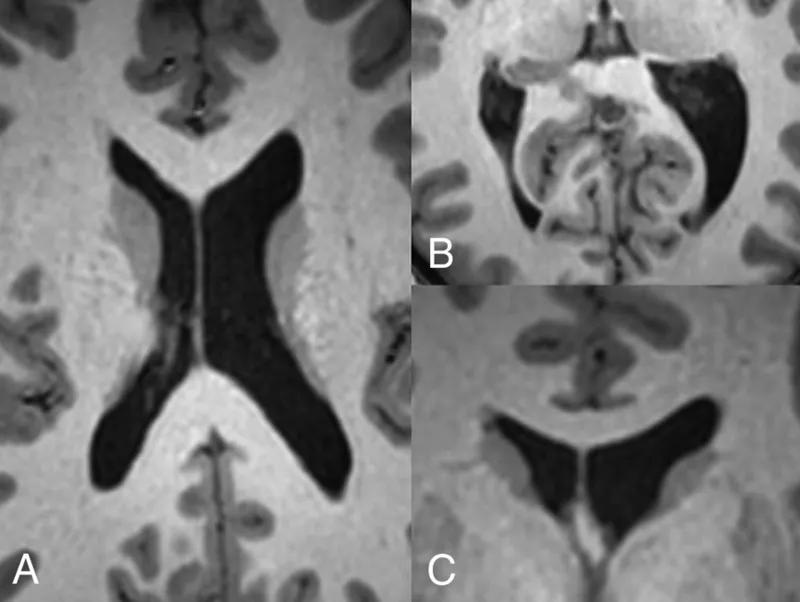
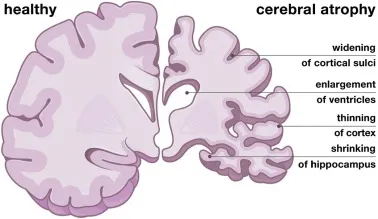
- A. Generalized cerebral atrophy (Correct Answer)
- B. Myoclonic movements
- C. Hallucinations
- D. Urinary incontinence
- E. Resting tremor
Neuroimaging findings Explanation: ***Generalized cerebral atrophy***
- The patient's symptoms of progressive **cognitive decline**, including difficulty with navigation and memory, are classic signs of **Alzheimer's disease**.
- **Generalized cerebral atrophy**, particularly of the **hippocampus** and **temporal lobes**, is a hallmark pathological finding in Alzheimer's disease due to neuronal loss and synaptic dysfunction.
*Myoclonic movements*
- **Myoclonic movements** are sudden, brief, involuntary muscle jerks, most commonly associated with **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease** or certain types of dementia with Lewy bodies, which are not suggested by the patient's presentation.
- While some rare forms of early-onset Alzheimer's can have atypical features, myoclonus is not a typical or early finding in the more common late-onset presentation described.
*Hallucinations*
- **Hallucinations**, particularly visual hallucinations, are frequently seen in **dementia with Lewy bodies** and **Parkinson's disease dementia**, often preceding or co-occurring with cognitive decline.
- While hallucinations can occur in late-stage Alzheimer's, they are not a prominent or early feature differentiating it from other dementias.
*Urinary incontinence*
- **Urinary incontinence** can be a symptom of various conditions, including **normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH)**, which presents with a triad of gait instability, dementia, and urinary incontinence.
- In Alzheimer's disease, incontinence typically appears in the **later stages**, after significant cognitive impairment and functional decline have occurred.
*Resting tremor*
- A **resting tremor** is a characteristic symptom of **Parkinson's disease** and is often seen in **Parkinson's disease dementia** or **dementia with Lewy bodies**.
- The patient's neurological examination, including normal gait and muscle strength, does not suggest Parkinsonian features.
Neuroimaging findings US Medical PG Question 8: A 68-year-old man, accompanied by his wife, presents to his physician with cognitive decline and hallucinations. The patient’s wife tells that his cognitive impairment progressed gradually over the past 6 years, and first began with problems counting and attention. The hallucinations began approximately a year ago. The patient describes them as realistic and non-frightening; most often, he sees his cat accompanying him everywhere he goes. The patient’s wife also notes frequent episodes of staring spells in her husband and prolonged daytime napping. The blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg with the orthostatic change to 110/60 mm Hg, heart rate is 75/min, respiratory rate is 13/min, and the temperature is 36.6°C (97.8°F). The patient is alert and responsive, but he is disoriented to time and place. He is pale and hypomimic. The cardiac, lung, and abdominal examinations are within normal limits for the patient’s age. The neurological examination is significant for a bilateral symmetrical cogwheel rigidity in the upper extremities. What would you most likely see on additional radiological investigations?
- A. Multiple lacunar infarcts on MRI
- B. Marked hippocampal atrophy on MRI
- C. Hypoperfusion and hypometabolism in frontal lobes on SPECT
- D. Decreased perfusion and dopaminergic activity in occipital lobes on PET (Correct Answer)
- E. Pontine 'hot-cross bun' sign on MRI
Neuroimaging findings Explanation: ***Decreased perfusion and dopaminergic activity in occipital lobes on PET***
- This finding is characteristic of **dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB)**, which is strongly suggested by the patient's presentation with **cognitive fluctuations**, **visual hallucinations** (non-frightening, realistic), **parkinsonism** (cogwheel rigidity), and **REM sleep behavior disorder** (daytime napping/staring spells could be a manifestation). PET scans in DLB often show reduced occipital lobe uptake.
- The combination of **parkinsonism** (cogwheel rigidity) and **visual hallucinations** preceding or appearing early in the course of cognitive decline is a hallmark of DLB, which differentiates it from other dementias.
*Multiple lacunar infarcts on MRI*
- While lacunar infarcts can cause cognitive decline (**vascular dementia**), the clinical picture of prominent, well-formed visual hallucinations, parkinsonism, and cognitive fluctuations is less typical for purely vascular dementia.
- Vascular dementia usually presents with a step-wise decline in cognition and focal neurological deficits, which are not the primary features here.
*Marked hippocampal atrophy on MRI*
- **Hippocampal atrophy** is a hallmark of **Alzheimer's disease**, which typically presents with insidious memory loss as the primary symptom.
- The prominent early visual hallucinations and parkinsonism are not typical initial features of Alzheimer's disease.
*Hypoperfusion and hypometabolism in frontal lobes on SPECT*
- **Frontal lobe hypoperfusion/hypometabolism** on SPECT/PET is characteristic of **frontotemporal dementia (FTD)**.
- FTD typically presents with early behavioral changes or language deficits, not prominent visual hallucinations, parkinsonism, or significant cognitive fluctuations in the way seen in this patient.
*Pontine 'hot-cross bun' sign on MRI*
- The **'hot-cross bun' sign** on MRI is pathognomonic for **multiple system atrophy (MSA)**, specifically the **MSA-C subtype (cerebellar)**.
- While MSA can cause parkinsonism and autonomic dysfunction, it typically does not feature prominent visual hallucinations or significant cognitive decline as early and striking features as seen in this patient.
Neuroimaging findings US Medical PG Question 9: A 24-year-old man and his mother arrive for a psychiatric evaluation. She is concerned about his health and behavior ever since he dropped out of graduate school and moved back home 8 months ago. He is always very anxious and preoccupied with thoughts of school and getting a job. He also seems to behave very oddly at times such as wearing his winter jacket in summer. He says that he hears voices but he can not understand what they are saying. When prompted he describes a plot to have him killed with poison seeping from the walls. Today, his heart rate is 90/min, respiratory rate is 17/min, blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F). On physical exam, he appears gaunt and anxious. His heart has a regular rate and rhythm and his lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. CMP, CBC, and TSH are normal. A urine toxicology test is negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Schizophrenia (Correct Answer)
- B. Substance-induced psychosis
- C. Schizophreniform disorder
- D. Schizoaffective disorder
- E. Brief psychotic disorder
Neuroimaging findings Explanation: ***Schizophrenia***
- The patient presents with **delusions** ("plot to have him killed"), **hallucinations** ("hears voices"), **disorganized thinking** (preoccupied with school and job but no progress made, wearing winter jacket in summer can be a sign of disorganized behavior), and **negative symptoms** (appears gaunt and anxious, social withdrawal, drop out of school). These symptoms have been present since he dropped out of graduate school 8 months ago, indicating a **duration of at least 6 months**.
- The combination of these symptoms persisting for over 6 months, impacting his functioning, and absence of other medical or substance-related causes, is diagnostic of **schizophrenia**.
*Substance-induced psychosis*
- The **urine toxicology test is negative**, ruling out recent substance use as the cause of his psychotic symptoms.
- The **chronicity** of symptoms (8 months) is less typical for acute substance-induced psychosis, which generally resolves more quickly after the substance is cleared.
*Schizophreniform disorder*
- Schizophreniform disorder involves the same symptoms as schizophrenia but with a **duration of at least 1 month but less than 6 months**.
- The patient's symptoms have been present for **8 months**, exceeding the criteria for schizophreniform disorder.
*Schizoaffective disorder*
- Schizoaffective disorder requires the presence of a **major mood episode** (depressive or manic) concurrent with criteria A of schizophrenia. Additionally, **delusions or hallucinations for at least 2 weeks** must occur in the absence of a major mood episode at some point during the illness.
- While the patient appears anxious, there is **no clear evidence of a persistent major depressive or manic episode** that would qualify for schizoaffective disorder.
*Brief psychotic disorder*
- Brief psychotic disorder is characterized by psychotic symptoms lasting **more than 1 day but less than 1 month**.
- The patient's symptoms have been ongoing for **8 months**, far exceeding the duration for brief psychotic disorder.
Neuroimaging findings US Medical PG Question 10: A 27-year-old woman comes to the physician because she has been hearing voices in her apartment during the past year. She also reports that she has been receiving warning messages in newspaper articles during this period. She thinks that “someone is trying to kill her”. She avoids meeting her family and friends because they do not believe her. She does not use illicit drugs. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Mental status examination shows a normal affect. Which of the following is the most appropriate long-term treatment?
- A. Lithium carbonate
- B. Fluphenazine
- C. Clozapine
- D. Quetiapine (Correct Answer)
- E. Midazolam
Neuroimaging findings Explanation: ***Quetiapine***
- This patient presents with **psychotic symptoms** (auditory hallucinations, delusions of persecution and reference) lasting over a year, consistent with **schizophrenia**.
- **Quetiapine** is a **second-generation antipsychotic** (atypical antipsychotic) commonly used as a long-term treatment for schizophrenia due to its efficacy in managing positive and negative symptoms and typically favorable side effect profile compared to first-generation agents.
*Lithium carbonate*
- **Lithium** is primarily used as a **mood stabilizer** for bipolar disorder, particularly for managing manic and mixed episodes.
- While it can have some antipsychotic effects, it is not the first-line long-term treatment for **schizophrenia** with prominent psychotic symptoms.
*Fluphenazine*
- **Fluphenazine** is a **first-generation antipsychotic** (typical antipsychotic) and is effective for positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
- However, it has a higher risk of **extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS)** and **tardive dyskinesia** compared to second-generation antipsychotics, making second-generation agents often preferred for long-term treatment.
*Clozapine*
- **Clozapine** is a highly effective **second-generation antipsychotic** for **treatment-resistant schizophrenia** but is not a first-line agent for initial treatment due to significant side effects.
- Its use is limited by the risk of **agranulocytosis**, requiring regular blood monitoring, and other serious side effects like myocarditis and seizures.
*Midazolam*
- **Midazolam** is a **benzodiazepine** used for acute sedation, anxiety, or insomnia due to its rapid onset and short duration of action.
- It has no role in the long-term treatment of **psychotic disorders** like schizophrenia.
More Neuroimaging findings US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.