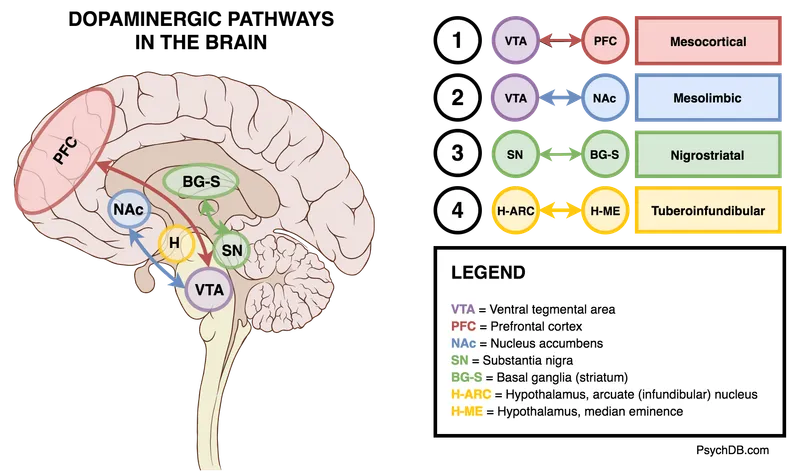
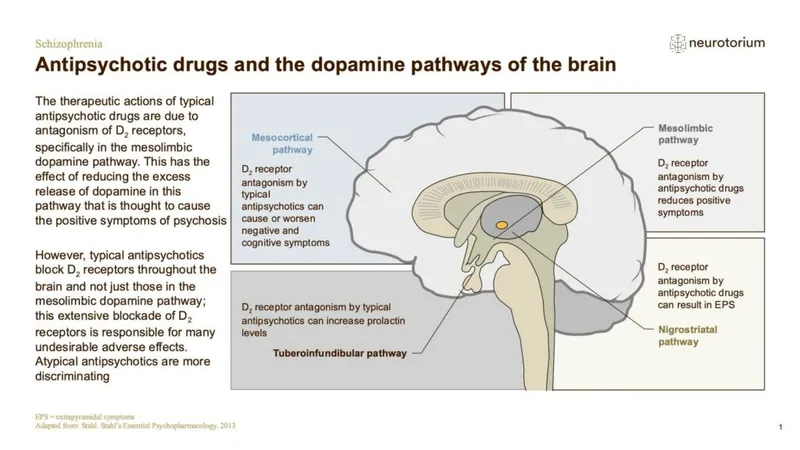
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Antipsychotic mechanisms of action. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old obese man is evaluated in a locked psychiatric facility. He was admitted to the unit after he was caught running through traffic naked while tearing out his hair. His urine toxicology screening was negative for illicit substances and after careful evaluation and additional history, provided by his parents, he was diagnosed with schizophrenia and was treated with aripiprazole. His symptoms did not improve after several dosage adjustments and he was placed on haloperidol, but this left him too lethargic and slow and he was placed on loxapine. After several dosage adjustments today, he is still quite confused. He describes giant spiders and robots that torture him in his room. He describes an incessant voice screaming at him to run away. He also strongly dislikes his current medication and would like to try something else. Which of the following is indicated in this patient?
- A. Haloperidol
- B. Olanzapine
- C. Chlorpromazine
- D. Fluphenazine
- E. Clozapine (Correct Answer)
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action Explanation: ***Clozapine***
- This patient has **treatment-resistant schizophrenia**, indicated by a lack of response to multiple trials of antipsychotics, including aripiprazole (atypical), haloperidol (typical), and loxapine (atypical).
- **Clozapine** is the only antipsychotic proven effective for treatment-resistant schizophrenia, significantly reducing psychotic symptoms and suicidality.
*Haloperidol*
- Haloperidol is a **first-generation antipsychotic** that the patient has already tried and found to be too sedating and slow.
- Continuing with haloperidol would likely result in persistent side effects and inadequate symptom control given his prior negative experience.
*Olanzapine*
- Olanzapine is a **second-generation atypical antipsychotic**; however, it is not typically indicated as a first-line treatment for treatment-resistant schizophrenia after failure of multiple agents.
- While effective for schizophrenia, it would be less effective than clozapine in a patient who has failed several previous antipsychotic trials.
*Chlorpromazine*
- Chlorpromazine is a **first-generation antipsychotic** that carries a higher risk of sedation, extrapyramidal symptoms, and anticholinergic side effects.
- It is unlikely to be more effective than haloperidol, which the patient already found too sedating and slow, and would not be the preferred choice for treatment-resistant schizophrenia.
*Fluphenazine*
- Fluphenazine is a **first-generation antipsychotic** with potent dopamine D2 receptor blockade, often leading to significant extrapyramidal side effects.
- Like other first-generation antipsychotics, it is not indicated as the next step for treatment-resistant schizophrenia after failure of multiple trials.
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action US Medical PG Question 2: A 35-year-old woman comes to the physician accompanied by her husband after he started noticing strange behavior. He first noticed her talking to herself 8 months ago. For the past 6 months, she has refused to eat any packaged foods out of fear that the government is trying to poison her. She has no significant past medical history. She smoked marijuana in college but has not smoked any since. She appears restless. Mental status examination shows a flat affect. Her speech is clear, but her thought process is disorganized with many loose associations. The patient is diagnosed with schizophrenia and started on olanzapine. This patient is most likely to experience which of the following adverse effects?
- A. Dyslipidemia (Correct Answer)
- B. Diabetes insipidus
- C. Agranulocytosis
- D. Myoglobinuria
- E. Seizures
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action Explanation: ***Dyslipidemia***
- **Olanzapine** is a **second-generation antipsychotic** commonly associated with significant **metabolic side effects**, including **weight gain**, **dyslipidemia**, and **insulin resistance**.
- These metabolic disturbances increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
*Diabetes insipidus*
- This is a rare side effect, not typically associated with **olanzapine** or other **second-generation antipsychotics**.
- **Lithium** is an antimanic agent that can cause **nephrogenic diabetes insipidus**, but it is not relevant here.
*Agranulocytosis*
- While a serious side effect of some antipsychotics, **agranulocytosis** is most notably associated with **clozapine**,
- **Olanzapine** has a much lower risk of causing **agranulocytosis** compared to clozapine.
*Myoglobinuria*
- **Myoglobinuria** is associated with conditions like significant muscle damage (e.g., rhabdomyolysis).
- It is not a direct or common adverse effect of **olanzapine** therapy.
*Seizures*
- While some antipsychotics can lower the **seizure threshold**, **olanzapine** generally has a relatively low risk of inducing seizures.
- The risk is higher with certain other antipsychotics, particularly at high doses, or in patients with pre-existing seizure disorders.
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action US Medical PG Question 3: A 31-year-old woman is brought to the physician because of increasing restlessness over the past 2 weeks. She reports that she continuously paces around the house and is unable to sit still for more than 10 minutes at a time. During this period, she has had multiple episodes of anxiety with chest tightness and shortness of breath. She was diagnosed with a psychotic illness 2 months ago. Her current medications include haloperidol and a multivitamin. She appears agitated. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. The examination was interrupted multiple times when she became restless and began to walk around the room. To reduce the likelihood of the patient developing her current symptoms, a drug with which of the following mechanisms of action should have been prescribed instead of her current medication?
- A. H2 receptor antagonism
- B. 5-HT2A receptor antagonism (Correct Answer)
- C. α2 receptor antagonism
- D. NMDA receptor antagonism
- E. GABA receptor antagonism
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action Explanation: ***5-HT2A receptor antagonism***
- The patient is experiencing **akathisia**, a common extrapyramidal side effect of **typical antipsychotics** like haloperidol, characterized by subjective or objective motor restlessness.
- Atypical antipsychotics, which exert their antipsychotic effects primarily through **5-HT2A receptor antagonism** along with D2 receptor antagonism, have a lower propensity to cause extrapyramidal symptoms, including akathisia, compared to typical antipsychotics.
*H2 receptor antagonism*
- **H2 receptor antagonists** are primarily used to reduce gastric acid secretion in conditions like peptic ulcer disease and GERD.
- They have no direct role in treating psychosis or preventing extrapyramidal side effects.
*α2 receptor antagonism*
- **Alpha-2 receptor antagonists** (e.g., mirtazapine) are typically used as antidepressants; their mechanism involves increasing norepinephrine and serotonin release.
- This mechanism is not directly therapeutic for psychosis and would not prevent akathisia caused by D2 receptor blockade.
*NMDA receptor antagonism*
- **NMDA receptor antagonists** (e.g., ketamine, memantine) are studied for various neurological and psychiatric conditions, but their primary use is not in typical psychosis treatment, nor do they prevent akathisia from antipsychotics.
- Instead, NMDA receptor hypofunction is hypothesized in schizophrenia, and antagonism could potentially worsen psychotic symptoms.
*GABA receptor antagonism*
- **GABA receptor antagonists** (e.g., flumazenil) block the effects of inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA and can cause seizures and increased anxiety, which would be detrimental in a patient with psychosis and anxiety.
- Medications that *enhance* GABAergic transmission (e.g., benzodiazepines) are sometimes used to treat acute akathisia or anxiety, but long-term antagonism would be contra-indicated.
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action US Medical PG Question 4: A 26-year-old man is brought to the hospital by his wife who complains that her husband has been behaving oddly for the past few hours. The patient’s wife says that she has known him for only 4 months. The wife is unable to give any past medical history. The patient’s speech is difficult to follow, and he seems very distracted. After 15 minutes, he becomes agitated and starts to bang his head on a nearby pillar. He is admitted to the psychiatric ward and is given an emergency medication, after which he calms down. In the next 2 days, he continues to become agitated at times and required 2 more doses of the same drug. On the 4th day of admission, he appears very weak, confused, and does not respond to questions appropriately. His vital signs include: temperature 40.0°C (104.0°F), blood pressure 160/95 mm Hg, and pulse 114/min. On physical examination, he is profusely diaphoretic. He is unable to stand upright or even get up from his bed. Which of the following is the mechanism of action of the drug which most likely caused this patient’s current condition?
- A. Skeletal muscle relaxation
- B. Agonistic effect on dopamine receptors
- C. Serotonin reuptake inhibition
- D. Histamine H2 receptor blocking
- E. Dopamine receptor blocking (Correct Answer)
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action Explanation: ***Dopamine receptor blocking***
- The patient's presentation with **fever, altered mental status, muscle rigidity**, and **autonomic instability** (tachycardia, hypertension, diaphoresis) after receiving antipsychotic medication strongly suggests **neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)**.
- NMS is caused by a severe decrease in **dopaminergic activity**, primarily due to the blockade of **D2 dopamine receptors** in the basal ganglia and hypothalamus by antipsychotics.
- The classic tetrad of NMS includes: **hyperthermia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status**, and **autonomic instability**.
*Skeletal muscle relaxation*
- While agitation might be treated with benzodiazepines, which cause muscle relaxation, this mechanism does not explain the **severe rigidity, hyperthermia**, and **autonomic dysfunction** seen in the patient.
- **Muscle rigidity** (lead-pipe rigidity) is a hallmark of the patient's current condition, contradicting the idea of muscle relaxation.
*Agonistic effect on dopamine receptors*
- An agonistic effect on dopamine receptors would typically lead to symptoms similar to **psychosis** or **mania**, not the severe rigidity and hypodopaminergic state observed in NMS.
- This mechanism would counteract the effects of antipsychotics and would not cause NMS.
*Serotonin reuptake inhibition*
- This is the mechanism of action for **SSRIs**, and an excess of serotonin can lead to **serotonin syndrome**, which shares some features with NMS but typically includes **hyperreflexia** and **myoclonus**, rather than lead-pipe rigidity.
- The context of treating acute psychosis with an emergency medication points more towards an antipsychotic, not an antidepressant.
*Histamine H2 receptor blocking*
- **Histamine H2 receptor blockers** are used to treat conditions like **acid reflux** and **peptic ulcers**; they have no direct neurological effects that would cause NMS.
- This mechanism is entirely irrelevant to the patient's psychiatric symptoms and subsequent severe adverse reaction.
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action US Medical PG Question 5: A 44-year-old man presents to his psychiatrist for a follow-up appointment. He is currently being treated for schizophrenia. He states that he is doing well but has experienced some odd movement of his face recently. The patient's sister is with him and states that he has been more reclusive lately and holding what seems to be conversations despite nobody being in his room with him. She has not noticed improvement in his symptoms despite changes in his medications that the psychiatrist has made at the last 3 appointments. His temperature is 99.3°F (37.4°C), blood pressure is 157/88 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam is notable for rhythmic movements of the patient's mouth and tongue. Which of the following is a side effect of the next best step in management?
- A. Anxiolysis
- B. Dry mouth and dry eyes
- C. QT prolongation on EKG
- D. Infection (Correct Answer)
- E. Worsening of psychotic symptoms
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action Explanation: ***Infection***
- The patient has **tardive dyskinesia** and **persistent psychotic symptoms** despite changes in medications. The next best step is to switch to **clozapine**.
- **Clozapine** can cause **agranulocytosis**, which increases the risk of serious infections and requires regular monitoring of white blood cell counts.
*Anxiolysis*
- While some antipsychotics can have anxiolytic effects, it is not the primary side effect or the most concerning one for the "next best step" in this context.
- The patient's primary issues are persistent psychosis and tardive dyskinesia, not anxiety that would be specifically targeted as the main side effect.
*Dry mouth and dry eyes*
- These are common **anticholinergic side effects** associated with many antipsychotics, including clozapine, but they are generally less severe and life-threatening compared to the risk of agranulocytosis.
- While unpleasant, they are not the most significant or defining side effect of the "next best step" in managing this patient's complex presentation.
*QT prolongation on EKG*
- **QT prolongation** is a known cardiac side effect of several antipsychotics, including clozapine.
- However, the risk of **agranulocytosis** with **clozapine** is arguably the most critical and distinct side effect requiring stringent monitoring, making it the "next best step" related answer.
*Worsening of psychotic symptoms*
- The "next best step" would be directed at *improving* psychotic symptoms, not worsening them. **Clozapine** is specifically indicated for **treatment-resistant schizophrenia**.
- Worsening psychosis would indicate treatment failure or an adverse reaction, not a typical side effect of the intended beneficial action.
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action US Medical PG Question 6: A 30-year-old male presents to a local clinic with a complaint of a stiff neck. The patient is known to be sporadic with follow-up appointments but was last seen recently for a regular depot injection. He initially presented with complaints of paranoid delusions and auditory hallucinations that lasted for 7 months and caused significant social and financial deterioration. He was brought into the clinic by his older brother, who provides social support. Because of the patient's tendency to be non-compliant with medications, the patient was placed on a specific drug to mitigate this pattern. Which of the following medications is responsible for the patient's movement disorder?
- A. Thioridazine
- B. Clozapine
- C. Haloperidol (Correct Answer)
- D. Olanzapine
- E. Benztropine
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action Explanation: ***Haloperidol***
- The patient's history of **paranoid delusions** and **auditory hallucinations** lasting 7 months, along with significant social and financial deterioration, is consistent with **schizophrenia**.
- Given the patient's **non-compliance** and lack of social support, he was likely prescribed a **long-acting injectable antipsychotic**. **Haloperidol decanoate** is a first-generation antipsychotic often used in this scenario, known for its higher risk of **extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS)** like a **stiff neck (dystonia)** compared to second-generation agents.
*Thioridazine*
- **Thioridazine** is a **first-generation antipsychotic** but is associated with a **lower incidence of EPS** compared to other high-potency typical antipsychotics like haloperidol.
- It also carries significant risks of **cardiac arrhythmias (QT prolongation)** and **retinal toxicity**, making it a less common choice for long-term management, especially with compliance issues.
*Clozapine*
- **Clozapine** is an atypical (second-generation) antipsychotic known for its efficacy in **treatment-resistant schizophrenia** and a very **low risk of EPS**.
- However, it requires **weekly blood monitoring** due to the risk of **agranulocytosis**, which makes it unsuitable for a patient with compliance issues and lack of social support.
*Olanzapine*
- **Olanzapine** is a **second-generation antipsychotic** that is available as a **long-acting injection**. While it can cause some EPS, the risk is generally **lower than with haloperidol**.
- It is more commonly associated with **metabolic side effects** such as weight gain, hyperglycemia, and dyslipidemia, rather than severe acute dystonia as the primary concern.
*Benztropine*
- **Benztropine** is an **anticholinergic medication** used to **treat the EPS induced by antipsychotics**, such as dystonia and parkinsonism.
- If a patient is experiencing a stiff neck due to an antipsychotic, benztropine would be a treatment for the side effect, not the cause of it.
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action US Medical PG Question 7: A 16-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother because she is worried about his behavior. Yesterday, he was expelled from school for repeatedly skipping classes. Over the past 2 months, he was suspended 3 times for bullying and aggressive behavior towards his peers and teachers. Once, his neighbor found him smoking cigarettes in his backyard. In the past, he consistently maintained an A grade average and had been a regular attendee of youth group events at their local church. The mother first noticed this change in behavior 3 months ago, around the time at which his father moved out after discovering his wife was having an affair. Which of the following defense mechanisms best describes the change in this patient's behavior?
- A. Projection
- B. Passive aggression
- C. Regression
- D. Suppression
- E. Acting out (Correct Answer)
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action Explanation: ***Acting out***
- This defense mechanism involves **engaging in destructive or inappropriate behaviors** to cope with emotional distress, often
**unconsciously** expressing unmet needs or feelings.
- The patient's sudden and significant shift from a well-behaved, high-achieving student to one who skips classes, engages in bullying, and smokes cigarettes can be seen as an expression of his emotional turmoil following his parents' separation.
*Projection*
- **Projection** is an attributional defense mechanism in which a person **attributes their own unacceptable thoughts or feelings to
another person**.
- While the patient is exhibiting negative behaviors, he is not explicitly attributing his own internal conflicts or feelings onto others; rather, he is demonstrating them through his actions.
*Passive aggression*
- **Passive aggression** is characterized by expressing negative feelings indirectly, often through **procrastination, stubbornness, or
inefficiency**, rather than direct confrontation.
- The patient's behaviors, such as bullying and skipping classes, are more overt and direct expressions of anger and distress, not indirect resistance.
*Regression*
- **Regression** involves reverting to **earlier, less mature behaviors or coping mechanisms** in response to stress.
- While some of his behaviors could be seen as less mature, the primary mechanism at play here is the direct, behavioral expression of conflict, rather than a return to an earlier developmental stage of coping, such as thumb-sucking or bed-wetting.
*Suppression*
- **Suppression** is a **conscious, deliberate effort to push unwanted thoughts or feelings out of awareness**.
- The patient's behaviors are likely an unconscious or preconscious response to his distress; he is not actively trying to forget or ignore his problems but rather demonstrating his distress through his actions.
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action US Medical PG Question 8: An investigator is studying a drug that acts on the thyroid hormone pathway. Levels of serum free T3 and T4 in healthy participants are measured before and after administration of the drug. After administration, there is a decrease in the average serum free T3 level, while the average serum free T4 level is increased compared to initial serum studies. Inhibition of which of the following is the most likely mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Thyroid-stimulating hormone
- B. Follicular iodotyrosine deiodinase
- C. Follicular thyroid peroxidase
- D. Peripheral 5'-deiodinase (Correct Answer)
- E. Follicular thyroid proteases
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action Explanation: ***Peripheral 5'-deiodinase***
- Inhibition of **peripheral 5'-deiodinase** would decrease the conversion of **T4 to T3** in the periphery, resulting in lower **free T3** and higher **free T4** levels.
- This enzyme is crucial for activating T4 into the more potent T3, and its blockade explains the observed changes in hormone levels.
*Thyroid-stimulating hormone*
- Inhibition of **TSH** would lead to a decrease in the production and release of both **T3 and T4** from the thyroid gland.
- This contradicts the observed increase in **free T4** levels.
*Follicular iodotyrosine deiodinase*
- This enzyme is involved in recycling iodine from **monoiodotyrosine (MIT)** and **diiodotyrosine (DIT)** within the thyroid follicular cells, which is important for efficient thyroid hormone synthesis.
- Its inhibition would primarily affect iodine availability and synthesis, not directly lead to increased T4 and decreased T3 in the periphery.
*Follicular thyroid peroxidase*
- **Thyroid peroxidase (TPO)** is critical for the **iodination of tyrosine residues** on thyroglobulin and the **coupling of MIT and DIT** to form T3 and T4.
- Inhibition of TPO would decrease the synthesis of both **T3 and T4**, contrary to the observed increase in **free T4**.
*Follicular thyroid proteases*
- **Thyroid proteases** cleave thyroglobulin to release mature **T3 and T4** into the bloodstream.
- Inhibition of these proteases would lead to a decrease in the release of both **T3 and T4**, which does not align with the observed increase in **free T4**.
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action US Medical PG Question 9: An 18-year-old boy presents to the clinic with shortness of breath and fever for the last 2 days. He also has a cough for the same duration. He is asthmatic and uses inhaled albuterol for symptom relief when required. He used albuterol today 3 times at 10-minute intervals but has not had relief of his symptoms. On physical examination, his temperature is 38.3°C (101.0°F), pulse is 130/min, blood pressure is 116/80 mm Hg, and respirations are 28/min. Auscultation of the chest reveals bilateral crackles. Considering that he has already taken inhaled albuterol and has tachycardia, the physician nebulizes him with inhaled ipratropium bromide, which significantly improves his symptoms. Which of the following is the mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of vagally-mediated contraction of bronchial smooth muscles (Correct Answer)
- B. Inhibition of degranulation of mast cells
- C. Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4, leading to prevention of release of cytokines and chemokines
- D. Inhibition of adenosine receptors in the respiratory tract
- E. Stimulation of β2-adrenergic receptors in bronchial smooth muscle
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action Explanation: ***Inhibition of vagally-mediated contraction of bronchial smooth muscles***
- Ipratropium bromide is a **short-acting muscarinic antagonist (SAMA)** that blocks M3 muscarinic receptors on bronchial smooth muscle
- This action **inhibits acetylcholine's effect**, leading to bronchodilation by preventing vagally-mediated bronchoconstriction
- Particularly useful as an **adjunct to β2-agonists** in acute asthma exacerbations and COPD
*Inhibition of degranulation of mast cells*
- This is the mechanism of action of **mast cell stabilizers** like cromolyn sodium and nedocromil
- These drugs are used for **asthma prophylaxis**, not acute symptom relief
- They prevent the release of inflammatory mediators like histamine from mast cells
*Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4, leading to prevention of release of cytokines and chemokines*
- This is the mechanism of action of **phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitors** such as roflumilast
- Primarily used in **severe COPD** to reduce inflammation
- PDE4 inhibition increases intracellular cAMP, which has anti-inflammatory effects
*Inhibition of adenosine receptors in the respiratory tract*
- This is the mechanism of action of **methylxanthines** like theophylline and aminophylline
- Blocking adenosine receptors provides bronchodilation and reduces inflammation
- Now considered **second-line therapy** due to narrow therapeutic index
*Stimulation of β2-adrenergic receptors in bronchial smooth muscle*
- This is the mechanism of action of **β2-agonists** like albuterol (already used by this patient)
- Not the mechanism of ipratropium, which is an **anticholinergic** agent
- The patient had already received albuterol without adequate relief, prompting the addition of ipratropium
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action US Medical PG Question 10: An 83-year-old man is being seen in the hospital for confusion. The patient was admitted 4 days ago for pneumonia. He has been improving on ceftriaxone and azithromycin. Then 2 nights ago he had an episode of confusion. He was unsure where he was and attempted to leave. He was calmed down by nurses with redirection. He had a chest radiograph that was stable from admission, a normal EKG, and a normal urinalysis. This morning he was alert and oriented. Then this evening he became confused and agitated again. The patient has a history of benign prostatic hyperplasia, severe dementia, and osteoarthritis. He takes tamsulosin in addition to the newly started antibiotics. Upon physical examination, the patient is alert but orientated only to name. He tries to get up, falls back onto the bed, and grabs his right knee. He states, “I need to get to work. My boss is waiting, but my knee hurts.” He tries to walk again, threatens the nurse who stops him, and throws a plate at the wall. In addition to reorientation, which of the following is the next best step in management?
- A. Morphine
- B. Lorazepam
- C. Haloperidol (Correct Answer)
- D. Rivastigmine
- E. Physical restraints
Antipsychotic mechanisms of action Explanation: ***Haloperidol***
- The patient exhibits **delirium** with acute agitation, threatening behavior, and violent actions (throwing objects), representing an **imminent safety risk** to himself and staff.
- After **non-pharmacological interventions** (reorientation) have failed, **low-dose haloperidol** is appropriate for managing **severe agitation** in delirium when there is risk of harm.
- While antipsychotics have an FDA black box warning for increased mortality in elderly patients with dementia and recent evidence questions their efficacy in delirium, they remain indicated for **acute agitation with safety concerns** as a short-term intervention.
- Haloperidol is preferred over atypical antipsychotics in acute hospital settings due to availability in parenteral forms and lower anticholinergic burden.
*Morphine*
- While the patient mentions knee pain (likely from osteoarthritis), his **primary issue** is acute agitation and delirium, not pain management.
- **Opioids** can worsen delirium and confusion in elderly patients through anticholinergic effects and sedation.
- Pain should be addressed, but not as the primary intervention for violent, agitated behavior.
*Lorazepam*
- **Benzodiazepines** are generally **contraindicated in delirium** as they worsen confusion, increase fall risk, and can cause paradoxical agitation in elderly patients.
- The **only exceptions** are delirium from alcohol or benzodiazepine withdrawal, or seizures—none of which apply to this patient.
- Lorazepam would likely exacerbate rather than improve this patient's mental status.
*Rivastigmine*
- **Rivastigmine** is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor for chronic management of **dementia symptoms**, not acute delirium.
- It has **no role** in managing acute behavioral disturbances and takes weeks to show any effect.
- Studies have not shown benefit of cholinesterase inhibitors in preventing or treating delirium.
*Physical restraints*
- Physical restraints should be used only as a **last resort** when pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions have failed and there is immediate, serious risk of harm.
- Restraints can **increase agitation**, cause injuries, lead to delirium worsening, and are associated with increased morbidity and mortality.
- They do not address the underlying cause and should be avoided when other options are available.
More Antipsychotic mechanisms of action US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.