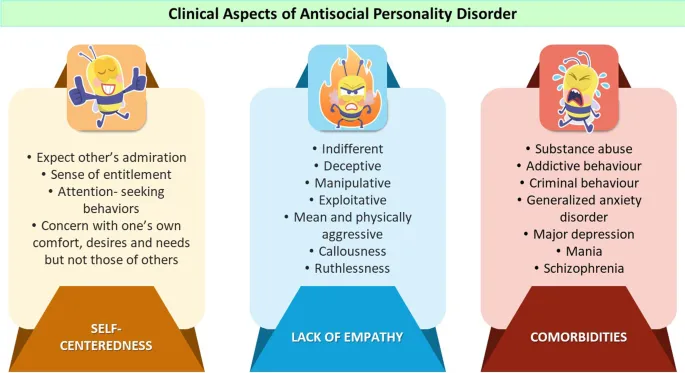
Antisocial personality disorder US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Antisocial personality disorder. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Antisocial personality disorder US Medical PG Question 1: An 8-year-old boy is brought in by his mother who is concerned about her child’s behavior. She says his teachers have complained about him bullying other students at school, starting fights, and stealing other children’s lunch money. She also says that a neighbor down the street called her 6 months ago and reported that the patient had entered her yard and started viciously kicking her dog. He has no significant past medical history. He is in the 90th percentile for height and weight and has been meeting all developmental milestones. The patient is afebrile and his vital signs are within normal limits. Which of the following adult personality disorders does this patient’s diagnosis most likely predict?
- A. Paranoid personality disorder
- B. Schizotypal personality disorder
- C. Schizoid personality disorder
- D. Avoidant personality disorder
- E. Antisocial personality disorder (Correct Answer)
Antisocial personality disorder Explanation: ***Antisocial personality disorder***
- The patient's presentation with a consistent pattern of violating the rights of others, including **bullying**, **fighting**, **stealing**, and **animal cruelty**, is highly indicative of **conduct disorder**.
- **Conduct disorder** in childhood is the most common precursor to developing **antisocial personality disorder** in adulthood.
*Paranoid personality disorder*
- This disorder is characterized by a pervasive **distrust and suspicion of others**, interpreting their motives as malicious, which is not indicated by the patient's behavior.
- While they may be hostile, their actions typically stem from perceived threats rather than direct aggression or disregard for others' rights as seen here.
*Schizotypal personality disorder*
- Individuals with schizotypal personality disorder exhibit **odd beliefs**, **magical thinking**, and **eccentric behavior** or appearance.
- They also tend to have **social anxiety** and difficulty forming close relationships, which doesn't align with the presented externalizing behaviors.
*Schizoid personality disorder*
- This disorder is characterized by a pervasive pattern of **detachment from social relationships** and a restricted range of emotional expression.
- There is no evidence of social withdrawal or uninterest in relationships; instead, the patient is actively engaging in harmful social interactions.
*Avoidant personality disorder*
- This disorder involves extreme **social inhibition**, feelings of inadequacy, and hypersensitivity to **negative evaluation**.
- The patient’s aggressive and non-compliant behaviors are contrary to the withdrawn and fearful nature seen in avoidant personality disorder.
Antisocial personality disorder US Medical PG Question 2: A 23-year-old man presents to an outpatient psychiatrist complaining of anxiety and a persistent feeling that “something terrible will happen to my family.” He describes 1 year of vague, disturbing thoughts about his family members contracting a “horrible disease” or dying in an accident. He believes that he can prevent these outcomes by washing his hands of “the contaminants” any time that he touches something and by performing praying and counting rituals each time that he has unwanted, disturbing thoughts. The thoughts and rituals have become more frequent recently, making it impossible for him to work, and he expresses feeling deeply embarrassed by them. Which of the following is the most effective treatment for this patient's disorder?
- A. Psychodynamic psychotherapy and citalopram
- B. Cognitive behavioral therapy and haloperidol
- C. Cognitive behavioral therapy and clonazepam
- D. Cognitive behavioral therapy and fluoxetine (Correct Answer)
- E. Psychodynamic psychotherapy and aripiprazole
Antisocial personality disorder Explanation: ***Cognitive behavioral therapy and fluoxetine***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)**, characterized by intrusive, distressing thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) performed to neutralize the anxiety.
- **Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)**, specifically Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP), is the most effective psychotherapy for OCD, and **SSRIs** like fluoxetine are the first-line pharmacotherapy.
*Psychodynamic psychotherapy and citalopram*
- While citalopram (an SSRI) is an appropriate pharmacological treatment for OCD, **psychodynamic psychotherapy** is generally not considered first-line or most effective for OCD due to its focus on unconscious conflicts rather than direct symptom reduction.
- This approach may not provide the structured, symptom-focused interventions needed to manage obsessions and compulsions effectively.
*Cognitive behavioral therapy and haloperidol*
- **CBT** is an excellent choice, but **haloperidol**, an antipsychotic, is not a first-line treatment for OCD; it is primarily used for psychotic disorders or as an augmentation strategy in severe, treatment-resistant OCD, which is not indicated here.
- Using an antipsychotic as a primary treatment for OCD without a clear indication of psychosis or severe non-response to SSRIs is inappropriate and can lead to unnecessary side effects.
*Cognitive behavioral therapy and clonazepam*
- **CBT** is appropriate, but **clonazepam**, a benzodiazepine, is generally not recommended as a monotherapy or primary adjunctive treatment for OCD due to its *sedative side effects*, *potential for dependence*, and *lack of efficacy* in addressing the core symptoms of OCD.
- Benzodiazepines may be used for short-term anxiety relief but do not treat the underlying obsessive-compulsive processes.
*Psychodynamic psychotherapy and aripiprazole*
- **Psychodynamic psychotherapy** is not the most effective approach for OCD.
- **Aripiprazole**, an atypical antipsychotic, is typically used as an augmentation strategy for *treatment-resistant OCD* when initial SSRI trials have failed, not as a first-line medication, and this patient's case does not describe treatment resistance.
Antisocial personality disorder US Medical PG Question 3: A 26-year-old woman thinks poorly of herself and is extremely sensitive to criticism. She is socially inhibited and has never had a romantic relationship, although she desires one. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Schizoid personality disorder
- B. Paranoid personality disorder
- C. Depression
- D. Dysthymia
- E. Avoidant personality disorder (Correct Answer)
Antisocial personality disorder Explanation: ***Avoidant personality disorder***
- Characterized by **social inhibition**, feelings of **inadequacy**, and **hypersensitivity to negative evaluation**, leading to avoidance of social interactions despite a desire for connection.
- The patient's self-perception, sensitivity to criticism, and absence of romantic relationships are classic signs.
*Schizoid personality disorder*
- Individuals with schizoid personality disorder exhibit a pervasive pattern of **detachment from social relationships** and a restricted range of emotional expression.
- Unlike avoidant personality disorder, they typically **do not desire social connection** and are indifferent to criticism or praise.
*Paranoid personality disorder*
- Marked by pervasive **distrust and suspiciousness of others**, interpreting their motives as malevolent.
- This patient's symptoms are more focused on self-perception and social anxiety rather than paranoid ideation.
*Depression*
- Depression involves a sustained period of **low mood**, loss of interest or pleasure, and other vegetative symptoms, which are not explicitly described as the primary, long-standing issue here.
- While feelings of worthlessness can occur in depression, the chronic, pervasive social inhibition and desire for relationships point away from a primary depressive episode as the sole diagnosis.
*Dysthymia*
- Dysthymia, or persistent depressive disorder, is characterized by a chronically depressed mood for at least two years, but it usually includes more pervasive depressive symptoms like low energy and anhedonia.
- While it can involve poor self-esteem, it doesn't fully explain the specific pattern of social avoidance and hypersensitivity to criticism, especially the patient's desire for social connection, which is often dampened in dysthymia.
Antisocial personality disorder US Medical PG Question 4: A 10-year-old child is sent to the school psychologist in May because he refuses to comply with the class rules. His teacher says this has been going on since school started back in August. He gets upset at the teacher regularly when he is told to complete a homework assignment in class. Sometimes he refuses to complete them altogether. Several of his teachers have reported that he intentionally creates noises in class to interrupt the class. He tells the psychologist that the teacher and his classmates are at fault. What is the most appropriate treatment?
- A. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (Correct Answer)
- B. Interpersonal therapy
- C. Administration of lithium
- D. Motivational interviewing
- E. Administration of clozapine
Antisocial personality disorder Explanation: ***Cognitive-behavioral therapy***
- This child exhibits symptoms consistent with **Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)**, including persistent refusal to comply with rules, anger outbursts, and blaming others. **CBT** is a highly effective treatment for ODD, teaching children coping skills, anger management, and problem-solving.
- CBT helps children identify and change **maladaptive thought patterns** and behaviors, which is crucial for managing the defiant and argumentative behaviors seen in ODD.
*Interpersonal therapy*
- **Interpersonal therapy (IPT)** primarily focuses on improving interpersonal relationships and communication patterns, often used for depression or eating disorders.
- While improved relationships might be a secondary benefit, IPT does not directly target the core **defiant behaviors** and **anger management** issues central to ODD.
*Administration of lithium*
- **Lithium** is a mood stabilizer primarily used in the treatment of **bipolar disorder** and severe mood dysregulation.
- There is no indication from the provided symptoms (defiance, anger, blaming others) that the child is experiencing a mood disorder that would warrant lithium.
*Motivational interviewing*
- **Motivational interviewing** is a counseling approach that helps individuals resolve ambivalence to change, often used in substance abuse or health behavior change.
- While it can be useful in encouraging willingness to engage in therapy, it is not a direct therapeutic modality for addressing the specific **behavioral challenges** and **underlying cognitive distortions** of ODD.
*Administration of clozapine*
- **Clozapine** is an antipsychotic medication reserved for severe mental illnesses like **treatment-resistant schizophrenia** due to its significant side effects.
- The child's symptoms of defiance and rule-breaking are not indicative of a psychotic disorder requiring antipsychotic medication.
Antisocial personality disorder US Medical PG Question 5: A 23-year-old woman presents to the emergency room for a self-inflicted laceration of her distal volar forearm. The patient states that she knew her husband was having sexual thoughts about the woman from the grocery store, prompting her decision to cut her own wrist. In the emergency department the bleeding is stopped and the patient is currently medically stable. When interviewing the patient, she is teary and apologizes for her behavior. She is grateful to you for her care and regrets her actions. Of note, the patient has presented to the emergency department before for a similar reason when she was struggling with online dating. The patient states that she struggles with her romantic relationship though she deeply desires them. On physical exam you note a frightened young woman who is wearing a revealing dress that prominently displays her breasts. You tell the patient that she will have to stay in the psychiatric emergency department for the night which makes her furious. Which of the following personality disorders is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Borderline (Correct Answer)
- B. Dependent
- C. Antisocial
- D. Histrionic
- E. Avoidant
Antisocial personality disorder Explanation: ***Borderline***
- The patient exhibits **impulsivity** (self-harm), **unstable relationships**, fear of abandonment (husband's "sexual thoughts"), and rapid mood shifts (tearful apology followed by fury), which are characteristic of Borderline Personality Disorder.
- Recurrent self-harm and previous presentations for similar reasons (struggling with online dating) highlight a pattern of **unstable self-image** and coping mechanisms.
*Dependent*
- While individuals with Dependent Personality Disorder desire relationships, their primary feature is an excessive need to be cared for, leading to **submissive behavior** and fear of separation, rather than the dramatic impulsivity and anger seen in the patient.
- The patient's fury and self-harm suggest a more volatile and emotionally dysregulated presentation than typically associated with dependency.
*Antisocial*
- Antisocial Personality Disorder involves a pervasive pattern of **disregard for and violation of the rights of others**, often involving deceitfulness, impulsivity, and lack of remorse. The patient's apology and regret for her actions are inconsistent with this diagnosis.
- There is no evidence of habitual law-breaking, exploitation of others, or a general callous disregard for others' feelings, which are core features of antisocial personality.
*Histrionic*
- Histrionic Personality Disorder is characterized by excessive **emotionality** and **attention-seeking behavior**, often through provocative actions (like dressing revealingly). However, the patient's severe self-harm, unstable relationships, intense abandonment fears, and rapid mood swings are more indicative of borderline personality.
- While the revealing dress might suggest some histrionic traits, the overarching presentation of chronic relationship instability, impulsivity, and self-mutilation points more strongly to Borderline Personality Disorder.
*Avoidant*
- Avoidant Personality Disorder involves extreme **social inhibition**, feelings of inadequacy, and hypersensitivity to negative evaluation, leading to avoidance of social interactions despite a desire for intimacy.
- The patient's active pursuit of relationships, even if unstable, and her dramatic, impulsive behaviors are inconsistent with the core features of social avoidance and timidity seen in Avoidant Personality Disorder.
Antisocial personality disorder US Medical PG Question 6: A 15-year-old boy is referred to a child psychologist because of worsening behavior and constant disruption in class. He has received multiple reprimands in the past 6 months for not doing the homework his teacher assigned, and he refuses to listen to the classroom instructions. Additionally, his teachers say he is very argumentative and blames other children for not letting him do his work. He was previously well behaved and one of the top students in his class. He denies any recent major life events or changes at home. His past medical history is noncontributory. His vital signs are all within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- B. Antisocial personality disorder
- C. Conduct disorder
- D. Oppositional defiant disorder (Correct Answer)
- E. Major depressive disorder
Antisocial personality disorder Explanation: ***Oppositional defiant disorder***
- This patient's symptoms of **argumentativeness**, **defiance**, and **blaming others**, combined with his previous good behavior and denial of major life events, are classic signs of **oppositional defiant disorder (ODD)**.
- ODD involves a pattern of angry/irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behavior, or vindictiveness lasting at least 6 months, clearly distinguishing it from a temporary behavioral issue.
*Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder*
- While **ADHD** can cause inattention and difficulty following instructions, it typically presents earlier in childhood and is characterized by **hyperactivity**, **impulsivity**, and **inattention** that would have likely been prominent before recently.
- The patient's primary symptoms here are an argumentative and defiant attitude rather than core symptoms of inattention or hyperactivity that began recently.
*Antisocial personality disorder*
- This disorder is typically diagnosed in **adulthood (18 years or older)**, although symptoms of **conduct disorder** must be present before age 15. The patient is currently 15.
- **Antisocial personality disorder** involves a pervasive pattern of disregard for and violation of the rights of others, which is more severe than the defiance seen in this case.
*Conduct disorder*
- **Conduct disorder** involves a more severe pattern of behavior, including aggression towards people or animals, destruction of property, deceitfulness or theft, and serious violations of rules, which is not described in this patient.
- The behaviors in this patient (argumentativeness, defiance) are less severe than the behaviors associated with conduct disorder.
*Major depressive disorder*
- Although behavioral changes can occur in **depression**, this patient does not exhibit other common symptoms such as **anhedonia**, changes in sleep or appetite, or persistent sadness, which would be expected with **major depressive disorder**.
- His behaviors are primarily externalizing and defiant rather than indicating an internal state of sadness or loss of interest.
Antisocial personality disorder US Medical PG Question 7: A 16-year-old boy is brought in to a psychiatrist's office by his mother for increasingly concerning erratic behavior. Her son has recently entered a new relationship, and he constantly voices beliefs that his girlfriend is cheating on him. He ended his last relationship after voicing the same beliefs about his last partner. During the visit, the patient reports that these beliefs are justified, since everyone at school is “out to get him.” He says that even his teachers are against him, based on their criticism of his schoolwork. His mother adds that her son has always held grudges against people and has always taken comments very personally. The patient has no psychiatric history and is in otherwise good health. What condition is this patient genetically predisposed for?
- A. Antisocial personality disorder
- B. Major depressive disorder
- C. Narcolepsy
- D. Substance use disorder
- E. Schizophrenia (Correct Answer)
Antisocial personality disorder Explanation: ***Schizophrenia***
- The patient's symptoms of **pervasive distrust**, **suspiciousness**, beliefs that others are "out to get him," and taking comments personally are characteristic of **paranoid personality disorder**.
- **Paranoid personality disorder (PPD)** is considered part of the **schizotypal spectrum** or **cluster A personality disorders**, and individuals with PPD have a higher genetic predisposition to develop **schizophrenia** and other psychotic disorders.
*Antisocial personality disorder*
- This disorder is characterized by **disregard for and violation of the rights of others**, impulsivity, and lack of remorse, which are not the primary features described here.
- While individuals with this disorder may exhibit manipulative behavior, their core issue is not paranoid ideation but rather a pattern of social irresponsibility and law-breaking.
*Major depressive disorder*
- This condition is characterized by **persistent sadness**, loss of interest or pleasure, and other vegetative symptoms, which are not present in this patient's presentation.
- The patient's primary symptoms revolve around **paranoia and suspiciousness**, not mood disturbances.
*Narcolepsy*
- Narcolepsy is a **neurological condition** characterized by overwhelming daytime sleepiness and sudden attacks of sleep.
- This diagnosis is entirely unrelated to the patient's psychological symptoms of paranoia and distrust.
*Substance use disorder*
- While substance use can sometimes induce paranoid thinking, the patient's long-standing history of **grudges** and taking comments personally, even prior to potential substance exposure (implied by no psychiatric history mentioned for substance abuse), suggests a more ingrained personality trait rather than solely substance-induced paranoia.
- There is **no information provided about substance use**, making this a less likely primary condition or genetic predisposition.
Antisocial personality disorder US Medical PG Question 8: A 27-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for exposure to toxic materials. The patient states that when he left for work this morning he was certain that he had closed the door to his pantry. However, upon returning home, he saw that the door to his pantry was wide open. The patient is certain that his neighbors have been tampering with his food and potentially poisoned him. He further states that he has known, ever since they have moved in, that they have been trying to break into his house and steal his things. He has tried multiple times to get them evicted from the building to no avail. It is for this reason that he is certain that they are trying to get their revenge upon him. The physician performs a physical exam and tells the patient that he thinks there is nothing to be concerned about, but that he should call him or come into the office if he experiences any symptoms. The patient is outraged at this news and requests a competent doctor who is not colluding with his enemies. He storms out of the office angrily, stating that he deserves the best in medical care, not this. Which of the following is the most likely personality disorder that this patient is suffering from?
- A. Intermittent explosive disorder
- B. Paranoid personality disorder (Correct Answer)
- C. Schizoid personality disorder
- D. Narcissistic personality disorder
- E. Borderline personality disorder
Antisocial personality disorder Explanation: ***Paranoid personality disorder***
- This patient exhibits a pervasive distrust and **suspiciousness of others**, interpreting their motives as malevolent.
- His belief that his neighbors are tampering with his food, trying to break into his house, and that the doctor is colluding with them demonstrates **unwarranted suspicion and paranoid ideation**.
- **Note:** The intensity and fixed nature of these beliefs suggest they may cross into delusional territory, which would indicate **delusional disorder (persecutory type)** rather than a personality disorder. However, among the personality disorder options listed, paranoid personality disorder best fits the presentation of pervasive distrust and suspiciousness.
*Intermittent explosive disorder*
- This disorder is characterized by recurrent **behavioral outbursts** representing a failure to control aggressive impulses.
- While the patient exhibited anger, his primary issue is **pervasive paranoia** rather than episodic impulsive aggression.
*Schizoid personality disorder*
- Individuals with schizoid personality disorder typically display a pervasive pattern of **detachment from social relationships** and a restricted range of emotional expression.
- This patient is actively engaged, albeit negatively, with others and expresses strong emotions, which differs from the emotional aloofness of schizoid personality disorder.
*Narcissistic personality disorder*
- This disorder is characterized by a pervasive pattern of **grandiosity**, a need for admiration, and a lack of empathy; symptoms include sense of entitlement and arrogance.
- While the patient states he \"deserves the best in medical care,\" his primary features are **suspicion and distrust**, not grandiosity or a focus on self-importance.
*Borderline personality disorder*
- This disorder is marked by a pervasive pattern of **instability in interpersonal relationships**, self-image, affects, and impulsivity.
- The patient's presentation lacks the impulsivity, self-harm behaviors, or frantic efforts to avoid abandonment seen in **borderline personality disorder**.
Antisocial personality disorder US Medical PG Question 9: A 14-year-old male is brought to your psychiatric clinic after he was caught stealing his peers’ belongings multiple times by his teacher. He is a straight-A student with many friends and is an outstanding football player. He describes his family as very loving and gets along with his older siblings. He also states that he has no ill will towards anyone he stole from in class. Although never caught, he admits that he would often steal things in stores or locker rooms when no one was looking in order to satisfy an intense impulse. Which of the following is the best diagnosis for this patient?
- A. Kleptomania (Correct Answer)
- B. Antisocial Personality Disorder
- C. Conduct disorder
- D. Schizophrenia
- E. Manic episode
Antisocial personality disorder Explanation: ***Kleptomania***
- The patient's presentation of stealing for an **intense impulse** rather than for financial gain or to express anger, along with an absence of other behavioral issues, aligns with the diagnostic criteria for **kleptomania**.
- The patient describes feeling no ill will towards those he stole from, suggesting the stealing is driven by a compulsive urge rather than malicious intent or antisocial behavior.
*Antisocial Personality Disorder*
- This disorder is characterized by a pervasive pattern of **disregard for and violation of the rights of others**, beginning in childhood or early adolescence, and extending into adulthood.
- The patient's good academic standing, many friends, loving family, and lack of ill will towards his victims do not fit the typical pattern of deceitfulness, impulsivity, irritability, or aggression seen in **antisocial personality disorder**.
*Conduct disorder*
- **Conduct disorder** involves a repetitive and persistent pattern of behavior in which the basic rights of others or major age-appropriate societal norms or rules are violated.
- While stealing is a feature, a diagnosis of conduct disorder requires a broader pattern of aggressive, destructive, deceitful, or rule-violating behaviors, which are not present in this patient's otherwise well-adjusted life (e.g., good student, many friends, loving family).
*Schizophrenia*
- **Schizophrenia** is a severe mental disorder characterized by thought disorders, delusions, hallucinations, and grossly disorganized behavior, which are not present in this patient.
- The patient's symptoms are solely focused on impulse-driven stealing and do not include any psychotic features.
*Manic episode*
- A **manic episode** involves a distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood and abnormally and persistently increased goal-directed activity or energy.
- While impulsivity can be a feature of mania, the patient's presentation lacks other hallmark symptoms such as decreased need for sleep, grandiosity, flight of ideas, or increased talkativeness, and the stealing is described as an isolated intense impulse rather than part of a broader mood disturbance.
Antisocial personality disorder US Medical PG Question 10: A 24-year-old man comes to the physician with a wound on his forearm. He says that he injured himself by absentmindedly walking into a glass door. He does not have health insurance. He has had 5 jobs in the past 8 months. He quit each job after 3–4 weeks because he found the work beneath him. He was imprisoned 6 years ago for credit card fraud. He was released from prison on parole a year ago. He was expelled from school at the age of 13 years for stealing school property and threatening to assault a teacher. He has fathered 6 children with 4 women. He says that he does not provide child support because he needs the money for his own personal expenses. The patient's vital signs are within normal limits. Examination of the forearm shows a 6 cm long, 0.5 cm deep wound with neat edges on the dorsal surface of the left forearm. There are bruises on the left shoulder, back, and the proximal phalanges of the right hand. On mental status examination, the patient is alert and calm. His mood is described as cheerful. His thought process, thought content, and speech are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Antisocial personality disorder (Correct Answer)
- B. Intermittent explosive disorder
- C. Oppositional defiant disorder
- D. Narcissistic personality disorder
- E. Conduct disorder
Antisocial personality disorder Explanation: **Antisocial personality disorder**
- The patient exhibits a pervasive pattern of **disregard for and violation of the rights of others**, including impulsive behavior, chronic unemployment, criminal history (**credit card fraud, parole violation**), and lack of remorse for not supporting his children. These behaviors are hallmarks of **antisocial personality disorder**.
- The history of behavioral problems starting at age 13 with **stealing and threatening a teacher** (a pattern consistent with childhood conduct disorder transforming into antisocial personality disorder in adulthood) further supports this diagnosis.
*Intermittent explosive disorder*
- Characterized by recurrent behavioral outbursts representing a failure to control aggressive impulses, often involving verbal aggression or physical aggression toward property, animals, or other individuals.
- While the patient has a history of aggression (threatening a teacher), the primary features in the vignette are more consistent with a pervasive pattern of disregard for others' rights and law-breaking, not solely explosive outbursts.
*Oppositional defiant disorder*
- Characterized by a pattern of angry/irritable mood, argumentative/defiant behavior, or vindictiveness lasting at least 6 months, typically seen in childhood and adolescence.
- The patient's behaviors, such as credit card fraud, chronic unemployment, multiple children with different partners, and lack of child support, extend far beyond just oppositional defiance and involve serious violations of societal norms and laws.
*Narcissistic personality disorder*
- Involves a pervasive pattern of grandiosity, a need for admiration, and a lack of empathy; the patient's statement about work being "beneath him" hints at grandiosity.
- However, the prominent features of **criminality, impulsivity, and disregard for others' rights** are more consistent with antisocial personality disorder than narcissistic personality disorder.
*Conduct disorder*
- This is a diagnostic category for persistent patterns of behavior in childhood and adolescence where the basic rights of others or major age-appropriate societal norms or rules are violated.
- While the patient's history at age 13 (stealing, threatening a teacher) would likely meet criteria for **conduct disorder**, this diagnosis is for individuals under 18. At 24 years old, the adult equivalent is antisocial personality disorder.
More Antisocial personality disorder US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.