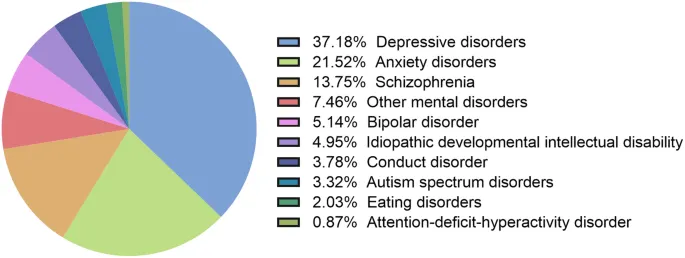
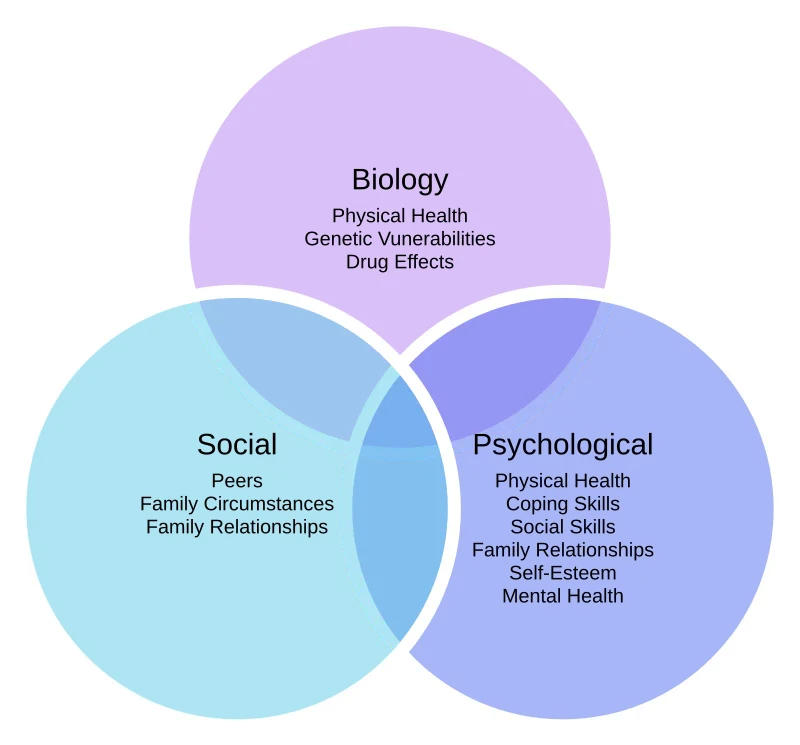
Mood disorder epidemiology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Mood disorder epidemiology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Mood disorder epidemiology US Medical PG Question 1: A researcher is investigating whether there is an association between the use of social media in teenagers and bipolar disorder. In order to study this potential relationship, she collects data from people who have bipolar disorder and matched controls without the disorder. She then asks how much on average these individuals used social media in the 3 years prior to their diagnosis. This continuous data is divided into 2 groups: those who used more than 2 hours per day and those who used less than 2 hours per day. She finds that out of 1000 subjects, 500 had bipolar disorder of which 300 used social media more than 2 hours per day. She also finds that 400 subjects who did not have the disorder also did not use social media more than 2 hours per day. Which of the following is the odds ratio for development of bipolar disorder after being exposed to more social media?
- A. 1.5
- B. 6 (Correct Answer)
- C. 0.17
- D. 0.67
Mood disorder epidemiology Explanation: ***6***
- To calculate the odds ratio, we first construct a 2x2 table [1]:
- Bipolar Disorder (Cases): 500
- No Bipolar Disorder (Controls): 500 (1000 total subjects - 500 cases)
- Cases exposed to more social media (>2 hrs/day): 300
- Cases not exposed to more social media (≤2 hrs/day): 200 (500 - 300)
- Controls not exposed to more social media (≤2 hrs/day): 400
- Controls exposed to more social media (>2 hrs/day): 100 (500 - 400)
- The odds ratio (OR) is calculated as (odds of exposure in cases) / (odds of exposure in controls) = (300/200) / (100/400) = 1.5 / 0.25 = **6** [1].
*1.5*
- This value represents the **odds of exposure** (more than 2 hours of social media) in individuals with bipolar disorder (300 cases exposed / 200 cases unexposed = 1.5).
- It is not the odds ratio, which compares these odds to the odds of exposure in the control group.
*0.17*
- This value is close to the reciprocal of 6 (1/6 ≈ 0.166), suggesting a potential miscalculation or an inverted odds ratio.
- An odds ratio of 0.17 would imply a protective effect (lower odds of bipolar disorder with more social media), which is contrary to the calculation and typical interpretation in this context.
*0.67*
- This value is the reciprocal of 1.5 (1/1.5 ≈ 0.67) which represents the odds of *not* being exposed in cases (200/300).
- It does not represent the correct odds ratio, which compares the odds of exposure in cases to the odds of exposure in controls.
Mood disorder epidemiology US Medical PG Question 2: A 19-year-old woman is brought to the physician by her parents because of irritable mood that started 5 days ago. Since then, she has been staying up late at night working on a secret project. She is energetic despite sleeping less than 4 hours per day. Her parents report that she seems easily distracted. She is usually very responsible, but this week she spent her paycheck on supplies for her project. She has never had similar symptoms before. In the past, she has had episodes where she felt too fatigued to go to school and slept until 2 pm every day for 2 weeks at a time. During those times, her parents noticed that she cried excessively, was very indecisive, and expressed feelings of worthlessness. Two months ago, she had an asthma exacerbation and was treated with bronchodilators and steroids. She tried cocaine once in high school but has not used it since. Vital signs are within normal limits. On mental status examination, she is irritable but cooperative. Her speech is pressured and her thought process is linear. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Major depressive disorder
- B. Bipolar I disorder
- C. Bipolar II disorder (Correct Answer)
- D. Schizoaffective disorder
- E. Substance abuse
Mood disorder epidemiology Explanation: ***Bipolar II disorder***
- This patient exhibits symptoms consistent with both **hypomania** (increased energy, decreased need for sleep, irritability, distractibility, spending sprees) and past episodes of **major depression** (fatigue, hypersomnia, crying, indecisiveness, worthlessness). The key distinction for Bipolar II is the presence of at least one hypomanic episode and one major depressive episode, without a full manic episode.
- The current symptoms of increased energy and decreased need for sleep for 5 days, along with a significant change in behavior (spending paycheck on a "secret project"), indicate a level of impairment consistent with hypomania, rather than a full-blown mania as the thought process is described as linear.
*Major depressive disorder*
- While the patient has a history of depressive episodes, the current presentation with **elevated mood, increased energy, and decreased need for sleep** is inconsistent with a unipolar depressive episode.
- Major depressive disorder does not involve periods of elevated or irritable mood or increased activity.
*Bipolar I disorder*
- Bipolar I disorder requires the occurrence of at least one **manic episode**. While the patient's current symptoms are suggestive of a mood elevation, they do not meet the criteria for full mania, which typically involves severe impairment, psychotic features, or hospitalization.
- The patient's speech is pressured but her thought process is described as **linear**, which is less typical for a full manic episode where **flight of ideas** or **tangential/disorganized thinking** might be present.
*Schizoaffective disorder*
- Schizoaffective disorder involves a period of uninterrupted illness during which there is a **major mood episode (depressive or manic) concurrent with symptoms of schizophrenia**, such as delusions or hallucinations.
- The patient's symptoms are primarily mood-related, and there is no mention of psychotic symptoms independent of the mood disturbance.
*Substance abuse*
- Although the patient used cocaine once in high school, there is no evidence of recent substance use that would explain the current symptoms. The symptoms are sustained over days and include a history of recurrent mood disturbances.
- While the patient received steroid treatment 2 months ago (which can precipitate mood episodes), the timing and clinical presentation are more consistent with a primary mood disorder rather than a substance/medication-induced disorder.
Mood disorder epidemiology US Medical PG Question 3: A 30-year-old woman comes to the physician because of difficulty sleeping. She is afraid of falling asleep and gets up earlier than desired. Four months ago, she was the driver in a car accident that resulted in the death of her unborn child. She has vivid nightmares of the event and reports that she frequently re-experiences the accident. She blames herself for the death of her child, has stopped working as an accountant, avoids driving in cars, and has withdrawn from her parents and close friends. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Acute stress disorder
- B. Normal grief
- C. Major depressive disorder
- D. Adjustment disorder
- E. Post-traumatic stress disorder (Correct Answer)
Mood disorder epidemiology Explanation: ***Post-traumatic stress disorder***
- The patient's symptoms, including **re-experiencing the trauma** (nightmares, flashbacks), avoidance behaviors (avoiding driving, withdrawing from social interactions), and negative alterations in cognition and mood (difficulty sleeping, self-blame), persisting for **four months** after a traumatic event, are characteristic of PTSD.
- The severity and chronicity of these symptoms, significantly impacting her daily functioning, align with the diagnostic criteria for PTSD.
*Acute stress disorder*
- This diagnosis also involves exposure to a traumatic event and similar symptoms (intrusive thoughts, negative mood, avoidance) but is diagnosed only when symptoms last for a minimum of **3 days and a maximum of 1 month** after the trauma.
- Since the patient's symptoms have persisted for **four months**, acute stress disorder is ruled out.
*Normal grief*
- While grief is a natural response to loss, the patient's symptoms extend beyond typical grief, involving specific **trauma-related re-experiencing** and **avoidance behaviors** that are not primarily focused on the deceased, but rather on the traumatic event itself.
- Normal grief typically does not involve the severe, persistent avoidance and intrusive symptoms of a traumatic nature seen here.
*Major depressive disorder*
- Although the patient exhibits symptoms that could overlap with depression (difficulty sleeping, withdrawal, loss of interest), the primary driver of her symptoms is the **traumatic event** and its associated re-experiencing and avoidance.
- A diagnosis of MDD would be considered if the depressive symptoms are paramount and not better explained by the trauma response, but in this case, the **trauma-specific symptoms** are central.
*Adjustment disorder*
- This disorder is characterized by the development of emotional or behavioral symptoms in response to an identifiable stressor, occurring within **3 months of the stressor**.
- While a traumatic event could be a stressor, adjustment disorder is diagnosed when the symptoms **do not meet the criteria for another specific mental disorder**, like PTSD, and are generally less severe and pervasive than what is described in this patient.
Mood disorder epidemiology US Medical PG Question 4: A 27-year-old woman visits a psychiatrist expressing her feelings of sadness which are present on most days of the week. She says that she has been feeling this way for about 2 to 3 years. During her first pregnancy 3 years ago, the fetus died in utero, and the pregnancy was terminated at 21 weeks. Ever since then, she hasn’t been able to sleep well at night and has difficulty concentrating on her tasks most of the time. However, for the past month, she has found it more difficult to cope. She says she has no will to have another child as she still feels guilty and responsible for the previous pregnancy. Over the past few days, she has completely lost her appetite and only eats once or twice a day. She doesn’t recall a single day in the last 3 years where she has not felt this way. The patient denies any past or current smoking, alcohol, or recreational drug use. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Persistent depressive disorder (Correct Answer)
- B. Bipolar disorder
- C. Schizoaffective disorder
- D. Cyclothymia
- E. Major depressive disorder
Mood disorder epidemiology Explanation: ***Persistent depressive disorder***
- The patient exhibits classic symptoms of **persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia)**: chronic depressed mood for **at least two years**, accompanied by other depressive symptoms like **insomnia**, **difficulty concentrating**, and changes in appetite.
- The duration of her symptoms (2-3 years) and the consistent feeling of sadness support this diagnosis, fitting the diagnostic criteria for **dysthymia**.
*Bipolar disorder*
- Bipolar disorder involves distinct episodes of **mania or hypomania** alternating with depressive episodes.
- The patient's history does not indicate any periods of elevated mood, increased energy, or decreased need for sleep, which are characteristic of **bipolar disorder**.
*Schizoaffective disorder*
- Schizoaffective disorder is characterized by a combination of **mood symptoms** (like depression or mania) and **psychotic symptoms** (like delusions or hallucinations) occurring simultaneously or in distinct episodes.
- This patient presents with no evidence of **psychotic symptoms** such as hallucinations or delusions.
*Cyclothymia*
- Cyclothymia is a milder, chronic form of **bipolar disorder** involving numerous periods of **hypomanic symptoms** and numerous periods of **depressive symptoms** for at least two years.
- The patient's presentation lacks any history of **hypomanic episodes**, making cyclothymia an unlikely diagnosis.
*Major depressive disorder*
- While the patient is experiencing a **major depressive episode** currently (as suggested by increased severity in the last month and complete loss of appetite), the underlying chronic nature of her symptoms (2-3 years) and the fact that she has not been symptom-free for more than two months indicate **persistent depressive disorder**.
- A diagnosis of **major depressive disorder** would typically be given if the symptoms were acute (less than 2 years) and severe, without the chronic, pervasive depressive state described.
Mood disorder epidemiology US Medical PG Question 5: A 45-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with complaints of muscle pains, poor sleep, and daytime fatigue. When asked about stressors she states that she "panics" about her job, marriage, children, and finances. When asked to clarify what the "panics" entail, she states that it involves severe worrying. She has had these symptoms since she last saw you one year ago. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Generalized anxiety disorder (Correct Answer)
- B. Social phobia
- C. Adjustment disorder
- D. Obsessive-compulsive disorder
- E. Panic disorder
Mood disorder epidemiology Explanation: ***Generalized anxiety disorder***
- This patient presents with **chronic, excessive, and uncontrollable worry** about multiple life circumstances (job, marriage, children, finances), fulfilling the core diagnostic criterion for GAD.
- The associated symptoms of **muscle pains**, **poor sleep**, and **daytime fatigue** are common physical manifestations of GAD, and the duration of symptoms for over a year supports the diagnosis.
*Social phobia*
- **Social phobia**, or social anxiety disorder, involves intense fear and anxiety in **social situations** where one might be scrutinized or judged.
- The patient's reported worries are broad and not limited to social interactions, making social phobia less likely.
*Adjustment disorder*
- **Adjustment disorder** is characterized by emotional or behavioral symptoms developing within **three months of an identifiable stressor**, not diffuse chronic worry.
- The symptoms in adjustment disorder typically resolve within **six months** after the stressor or its consequences have ended, whereas this patient's symptoms are chronic and pervasive.
*Obsessive-compulsive disorder*
- **Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)** involves recurrent, intrusive **obsessions** (thoughts, urges, images) and/or **compulsions** (repetitive behaviors or mental acts) performed to reduce anxiety.
- While the patient experiences severe worrying, there's no mention of specific obsessions or compulsive behaviors aimed at neutralizing those anxieties.
*Panic disorder*
- **Panic disorder** is characterized by recurrent, unexpected **panic attacks**—sudden surges of intense fear or discomfort accompanied by physical and cognitive symptoms.
- While the patient uses the term "panics," she clarifies it involves "severe worrying," not discrete, intense, and short-lived panic attacks.
Mood disorder epidemiology US Medical PG Question 6: A mental health volunteer is interviewing locals as part of a community outreach program. A 46-year-old man discloses that he has felt sad for as long as he can remember. He feels as though his life is cursed and if something terrible can happen to him, it usually will. He has difficulty making decisions and feels hopeless. He also feels that he has had worsening suicidal ideations, guilt from past problems, decreased energy, and poor concentration over the past 2 weeks. He is otherwise getting enough sleep and able to hold a job. Which of the following statement best describes this patient's condition?
- A. The patient may have symptoms of mania or psychosis.
- B. The patient is likely to show anhedonia.
- C. The patient likely has paranoid personality disorder.
- D. The patient has double depression. (Correct Answer)
- E. The patient should be started on an SSRI.
Mood disorder epidemiology Explanation: ***The patient has double depression.***
- The patient describes **chronic low-grade depressive symptoms** ("felt sad for as long as he can remember," "life is cursed," "difficulty making decisions," "hopeless") consistent with **persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia)**, which requires at least 2 years of symptoms.
- The recent worsening of symptoms over the past two weeks, including "worsening suicidal ideations, guilt from past problems, decreased energy, and poor concentration," indicates an additional **major depressive episode (MDE) superimposed on dysthymia**, a condition known as **double depression**.
- This patient currently meets criteria for both conditions simultaneously, not just at risk for developing them.
*The patient may have symptoms of mania or psychosis.*
- There are no symptoms mentioned that suggest **mania**, such as elevated mood, increased energy, decreased need for sleep, grandiosity, or racing thoughts.
- While suicidal ideation is present, there is no evidence of **psychotic features** like hallucinations or delusions.
*The patient is likely to show anhedonia.*
- **Anhedonia** (inability to feel pleasure) is a common symptom of depression and may well be present in this patient.
- However, the patient's presentation specifically highlights the pattern of **chronic dysthymia with a superimposed major depressive episode**, making **double depression** a more precise, comprehensive, and diagnostically specific description of his current condition.
- While anhedonia might be present, it is a symptom rather than a diagnostic formulation.
*The patient likely has paranoid personality disorder.*
- **Paranoid personality disorder** is characterized by pervasive distrust and suspicion of others, interpreting their motives as malevolent, without sufficient basis.
- The patient's feelings of being "cursed" and that "something terrible can happen" reflect **depressive pessimism and negative cognitive distortions**, not paranoid ideation about others' intentions.
- This is consistent with the hopelessness seen in depression.
*The patient should be started on an SSRI.*
- While an **SSRI (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor)** combined with psychotherapy would likely be appropriate treatment for double depression, making a specific treatment recommendation is premature without comprehensive clinical assessment.
- The question asks for the **best statement describing the patient's condition** (diagnosis), not for treatment recommendations.
Mood disorder epidemiology US Medical PG Question 7: An investigator is studying the relationship between suicide and unemployment using data from a national health registry that encompasses 10,000 people who died by suicide, as well as 100,000 matched controls. The investigator finds that unemployment was associated with an increased risk of death by suicide (odds ratio = 3.02; p < 0.001). Among patients with a significant psychiatric history, there was no relationship between suicide and unemployment (p = 0.282). Likewise, no relationship was found between the two variables among patients without a psychiatric history (p = 0.32). These results are best explained by which of the following?
- A. Selection bias
- B. Matching
- C. Effect modification
- D. Confounding (Correct Answer)
- E. Stratification
Mood disorder epidemiology Explanation: ***Confounding***
- **Confounding** occurs when an observed association between an exposure (unemployment) and an outcome (suicide) is actually due to an unmeasured third variable (psychiatric history) that is associated with both the exposure and the outcome.
- The finding that the association disappears or changes significantly when stratified by psychiatric history (p > 0.05 in both groups) indicates that **psychiatric history** was confounding the initial association.
*Selection bias*
- **Selection bias** occurs when the way participants are selected or retained in a study leads to a systematic difference between the study population and the target population, or between exposure and outcome groups.
- While this study uses a national registry, the description does not suggest a problem with how individuals were selected or that this bias explains the observed pattern.
*Matching*
- **Matching** is a technique used to control for confounding during study design by ensuring that cases and controls are similar with respect to potential confounders.
- While the study mentions "matched controls," the issue described (initial association disappearing after stratification) points to an uncontrolled confounder, not the mechanism of matching itself as the explanation for the results.
*Effect modification*
- **Effect modification** occurs when the relationship between an exposure and an outcome differs depending on the level of a third variable (the effect modifier).
- If **effect modification** were present, we would expect to see a significant association in at least one of the stratified groups, but the magnitude or direction of the association would vary. Here, the association essentially disappears in both strata.
*Stratification*
- **Stratification** is a method used to analyze data by separating participants into different subgroups based on a third variable, often to address confounding or examine effect modification.
- While stratification was performed in this study (by psychiatric history), it is the *method* used to reveal the problem, not the explanation for why the initial association was observed or why it disappeared.
Mood disorder epidemiology US Medical PG Question 8: A 24-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for a wellness exam. She currently has no acute concerns but has been feeling hopeless, has a poor appetite, difficulty with concentration, and trouble with sleep. She says that she has poor self-esteem and that her symptoms have been occurring for the past 3 years. She has had moments where she felt better, but it lasted a few weeks out of the year. She currently lives alone and does not pursue romantic relationships because she feels she is not attractive. She has a past medical history of asthma. Her mother is alive and healthy. Her father committed suicide and suffered from major depressive disorder. On physical exam, the patient has a gloomy demeanor and appears restless and anxious. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Major depressive disorder
- B. Cyclothymia
- C. Persistent depressive disorder (Correct Answer)
- D. Seasonal affective disorder
- E. Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder
Mood disorder epidemiology Explanation: ***Persistent depressive disorder***
- The patient exhibits chronic symptoms of depression (poor appetite, poor self-esteem, difficulty with concentration, trouble with sleep, hopelessness) lasting for at least **2 years**, with symptom-free periods lasting no more than **2 months**.
- Her long-standing symptoms (3 years) and the intermittent improvement, but never full resolution for extended periods, are characteristic of **persistent depressive disorder** (formerly dysthymia).
*Major depressive disorder*
- While the patient has many symptoms of depression, **major depressive disorder** is characterized by distinct episodes of at least 2 weeks, with significant functional impairment. The chronic, fluctuating course over 3 years is less typical.
- The presence of depressive symptoms for 3 years, with only brief periods of improvement, points away from episodic major depressive disorder alone and more towards a chronic form.
*Cyclothymia*
- **Cyclothymia** involves numerous periods of hypomanic symptoms and numerous periods of depressive symptoms for at least 2 years, with periods of stability lasting no more than 2 months. The patient describes only depressive symptoms, not hypomanic episodes.
- There is no mention of elevated mood, increased energy, or decreased need for sleep, which are characteristic of **hypomanic episodes** in cyclothymia.
*Seasonal affective disorder*
- **Seasonal affective disorder** is a type of depressive disorder that occurs during a specific season (most commonly winter) and resolves during other seasons; the patient's symptoms are year-round and chronic.
- The patient's symptoms are not described as tied to a particular season, making this diagnosis less likely.
*Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder*
- Predominantly diagnosed in **children and adolescents**, this disorder is characterized by severe recurrent temper outbursts and persistently irritable or angry mood between outbursts.
- The patient's age (24 years old) and the absence of temper outbursts make this diagnosis inappropriate.
Mood disorder epidemiology US Medical PG Question 9: A 38-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up visit. She has a 2-year history of depressed mood and fatigue accompanied by early morning awakening. One week ago, she started feeling a decrease in her need for sleep and now feels rested after about 5 hours of sleep per night. She had two similar episodes that occurred 6 months ago and a year ago, respectively. She reports increased energy and libido. She has a 4-kg (8.8-lb) weight loss over the past month. She does not feel the need to eat and says she derives her energy ""from the universe"". She enjoys her work as a librarian. She started taking fluoxetine 3 months ago. On mental exam, she is alert and oriented to time and place; she is irritable. She does not have auditory or visual hallucinations. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Delusional disorder
- B. Cyclothymic disorder
- C. Schizoaffective disorder
- D. Bipolar II disorder (Correct Answer)
- E. Medication-induced bipolar disorder
Mood disorder epidemiology Explanation: ***Bipolar II disorder***
- The patient meets criteria for **Bipolar II disorder**: at least one **hypomanic episode** (current presentation) and at least one **major depressive episode** (2-year history with recurrent episodes).
- Current hypomanic features include: **decreased need for sleep** (feels rested after 5 hours), **increased energy and libido**, **significant weight loss** (4 kg in one month), **irritability**, and grandiose thinking ("derives energy from the universe").
- She has had **recurrent depressive episodes** over 2 years (episodes 1 year ago and 6 months ago), fulfilling the major depressive episode requirement.
- While the hypomania emerged after starting **fluoxetine**, antidepressants commonly **unmask underlying bipolar disorder** rather than cause a separate medication-induced condition. The diagnosis remains **Bipolar II disorder** per DSM-5-TR when there is evidence of an underlying mood disorder pattern.
*Medication-induced bipolar disorder*
- Substance/medication-induced bipolar disorder requires that symptoms occur **exclusively during substance use** without evidence of an independent bipolar disorder.
- This patient's **recurrent pattern** of mood episodes (multiple depressive episodes over 2 years) suggests an **underlying bipolar disorder** that was unmasked by antidepressant treatment, not a purely medication-induced condition.
- The temporal relationship with fluoxetine is significant but represents **antidepressant-induced switching** in bipolar disorder, not a separate diagnostic entity.
*Delusional disorder*
- Requires **non-bizarre delusions** persisting for at least one month as the predominant feature, without prominent mood symptoms.
- This patient's primary presentation is a **mood episode** (hypomania) with the "universe" comment being part of her elevated/expansive mood rather than a fixed, systematized delusion.
- Functioning remains relatively intact (still enjoys her work).
*Cyclothymic disorder*
- Involves numerous periods of **hypomanic and depressive symptoms** for at least 2 years, but symptoms never meet full criteria for hypomanic or major depressive episodes.
- This patient has **full hypomanic and major depressive episodes**, making Bipolar II disorder the more appropriate diagnosis.
- The severity of her current symptoms (significant sleep reduction, 4-kg weight loss, marked functional changes) exceeds cyclothymic disorder.
*Schizoaffective disorder*
- Requires a **major mood episode** concurrent with **criterion A symptoms of schizophrenia** (delusions, hallucinations) for at least 2 weeks, plus psychotic symptoms without mood symptoms for at least 2 weeks.
- This patient has **no hallucinations** and no clear psychotic symptoms independent of her mood state.
- Her elevated mood fully accounts for her presentation.
Mood disorder epidemiology US Medical PG Question 10: A 28-year-old woman presents with depressed mood lasting for most days of the week for the past month. She also mentions that she has lost her appetite for the past 3 weeks. She adds that her job performance has significantly deteriorated because of these symptoms, and she feels like she will have to quit her job soon. Upon asking about her hobbies, she says that she used to enjoy dancing and music but does not have any desire to do them anymore. The patient’s husband says that she has had many sleepless nights last month. The patient denies any history of smoking, alcohol intake, or use of illicit substances. No significant past medical history. Physical examination is unremarkable. Routine laboratory tests are all within normal limits. Which of the following clinical features must be present, in addition to this patient’s current symptoms, to confirm the diagnosis of a major depressive episode?
- A. Intense fear of losing control
- B. Lack of concentration (Correct Answer)
- C. Weight loss
- D. Anterograde amnesia
- E. Nightmares
Mood disorder epidemiology Explanation: ***Lack of concentration***
- The diagnostic criteria for a **major depressive episode** (DSM-5) require at least **5 out of 9 cardinal symptoms** present for at least 2 weeks, with at least one being either **depressed mood** or **anhedonia**.
- This patient currently has **4 symptoms**: (1) depressed mood, (2) anhedonia (loss of interest in dancing/music), (3) appetite disturbance (loss of appetite), and (4) sleep disturbance (insomnia).
- To meet diagnostic criteria, she needs **one more symptom** from the remaining options: fatigue, feelings of worthlessness/guilt, **diminished ability to concentrate or indecisiveness**, psychomotor changes, or suicidal ideation.
- **Lack of concentration** is one of the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria and would bring her total to 5 symptoms, confirming the diagnosis.
*Intense fear of losing control*
- This symptom is characteristic of **panic disorder** or anxiety disorders, where individuals experience sudden, intense episodes of fear with accompanying physical and cognitive symptoms.
- While anxiety can co-occur with depression, intense fear of losing control is **not a DSM-5 diagnostic criterion** for major depressive episode.
*Weight loss*
- The patient already has **loss of appetite**, which satisfies the weight/appetite criterion for major depressive episode.
- **Weight loss and appetite changes are part of the same diagnostic criterion**, not separate ones. Therefore, weight loss would not add an additional criterion to reach the required 5 symptoms.
- While clinically significant weight loss can occur in depression, it would not provide the "additional" criterion needed in this case.
*Anterograde amnesia*
- **Anterograde amnesia** (inability to form new memories) is associated with neurological conditions such as **hippocampal damage**, **Korsakoff syndrome**, or **traumatic brain injury**.
- It is **not a DSM-5 diagnostic criterion** for major depressive episode, though some cognitive impairment (concentration difficulties) may occur.
*Nightmares*
- The patient already has **insomnia** (sleep disturbance), which is one of the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria.
- While nightmares may occur in depression, they are not a separate diagnostic criterion and would not add to the symptom count since sleep disturbance is already present.
More Mood disorder epidemiology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.