Lysosomal Storage Diseases US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Lysosomal Storage Diseases. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
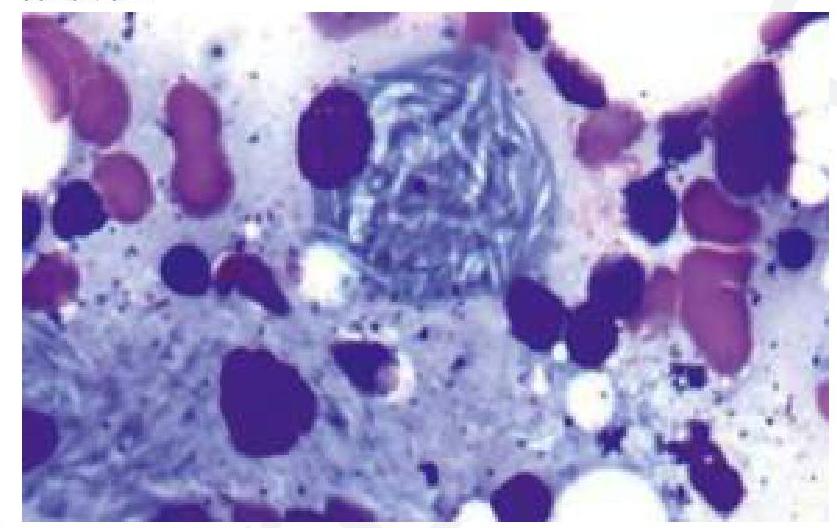
Lysosomal Storage Diseases US Medical PG Question 1: A child presents with bone pain and hepatosplenomegaly, indicative of Gaucher's disease. A trephine biopsy and aspirate show the following finding. Which of the following is the most likely enzyme deficient in this condition?
- A. Hexosaminidase
- B. Glucocerebrosidase (Correct Answer)
- C. Sphingomyelinase
- D. Alpha 1,4-glucosidase
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Explanation: ***Correct: Glucocerebrosidase***
- The clinical presentation of **bone pain**, **hepatosplenomegaly**, and the characteristic histological finding of **lipid-laden macrophages** (Gaucher cells) with a **crinkled paper** appearance in the bone marrow aspirate are highly suggestive of **Gaucher's disease**.
- **Gaucher's disease** is caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme **glucocerebrosidase**, leading to the accumulation of **glucocerebroside**.
*Incorrect: Hexosaminidase*
- Deficiency of **hexosaminidase A** is associated with **Tay-Sachs disease**, which presents with neurological degeneration but typically **lacks hepatosplenomegaly** and bone pain.
- The histological findings in Tay-Sachs disease would show neuronal storage of **GM2 gangliosides**, not Gaucher cells.
*Incorrect: Sphingomyelinase*
- Deficiency of **sphingomyelinase** causes **Niemann-Pick disease**, characterized by hepatosplenomegaly, neurological involvement, and interstitial lung disease, but the storage cells (foam cells) have a **foamy appearance** due to sphingomyelin accumulation, not the "crinkled paper" appearance of Gaucher cells.
- While there is organomegaly, the distinct **histological features** in the image rule out Niemann-Pick disease.
*Incorrect: Alpha 1,4-glucosidase*
- Deficiency of **alpha 1,4-glucosidase** (acid maltase) causes **Pompe disease** (Glycogen Storage Disease Type II), which primarily affects muscle and liver with **glycogen accumulation**.
- Pompe disease does not typically present with the same type of **bone pain** or the characteristic **Gaucher cells** seen in the image.
Lysosomal Storage Diseases US Medical PG Question 2: Which one of the following diseases is classified as an autosomal dominant disorder?
- A. Hemochromatosis
- B. Phenylketonuria
- C. Maturity onset diabetes of the young (Correct Answer)
- D. Glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Explanation: ***Maturity onset diabetes of the young***
- **Maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY)** is a genetically heterogeneous group of single-gene disorders characterized by beta-cell dysfunction and impaired insulin secretion, typically inherited in an **autosomal dominant pattern** [1].
- A single copy of the mutated gene is sufficient to cause the condition, leading to diabetes usually before the age of 25, often without obesity or autoantibodies [1].
*Hemochromatosis*
- **Hemochromatosis** is typically inherited in an **autosomal recessive pattern**, meaning two copies of the mutated gene (e.g., *HFE* gene) are required for the disease to manifest.
- It leads to excessive iron absorption and tissue iron overload.
*Phenylketonuria*
- **Phenylketonuria (PKU)** is an **autosomal recessive disorder** caused by a deficiency in the enzyme **phenylalanine hydroxylase**, necessitating two mutated gene copies for the disease to occur.
- This leads to the accumulation of phenylalanine, causing neurological damage if untreated.
*Glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency*
- **Glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency** is an **X-linked recessive disorder**, meaning the gene is located on the X chromosome and typically affects males more severely.
- Females can be carriers, and hemizygous males (having only one X chromosome) will express the disorder if they inherit the mutated gene.
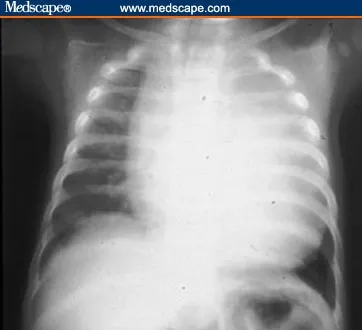
Lysosomal Storage Diseases US Medical PG Question 3: A patient presents with an X-ray showing cardiomegaly, along with symptoms of hypotonia, macroglossia, hepatomegaly, and floppy baby syndrome. The X ray of the infant is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Pompe's disease (Correct Answer)
- B. Ebstein anomaly
- C. Transposition of great arteries
- D. Von Gierke's disease
- E. Congenital hypothyroidism
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Explanation: ***Pompe's disease***
- Pompe's disease (Type II glycogen storage disease) is characterized by a deficiency of **alpha-glucosidase**, leading to **glycogen accumulation** in lysosomes.
- This accumulation results in **cardiomegaly**, **hypotonia** ("floppy baby"), **hepatomegaly**, and **macroglossia**, which perfectly match the clinical presentation.
*Ebstein anomaly*
- This is a congenital heart defect involving the **tricuspid valve**, leading to its displacement into the right ventricle.
- While it causes cardiomegaly, it does not typically present with the systemic features like **hypotonia, macroglossia, or hepatomegaly** described.
*Transposition of great arteries*
- This is a complex congenital heart defect where the **aorta and pulmonary artery are switched**, resulting in two separate circulatory systems.
- It causes severe cyanosis and cardiomegaly but does not explain the widespread glycogen storage symptoms such as **hypotonia** or **hepatomegaly**.
*Von Gierke's disease*
- **Von Gierke's disease** (Type I glycogen storage disease) is caused by a deficiency of **glucose-6-phosphatase**.
- It primarily affects the **liver and kidneys**, causing severe hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, and **nephromegaly**, but typically not significant cardiomegaly or profound hypotonia.
*Congenital hypothyroidism*
- Can present with **macroglossia, hypotonia, and hepatomegaly** similar to Pompe's disease.
- However, the **massive cardiomegaly** seen on X-ray is not typical of hypothyroidism, and other features like prolonged jaundice, constipation, and umbilical hernia would be more prominent.
Lysosomal Storage Diseases US Medical PG Question 4: Lysosomal transport defect is seen in which of the following conditions?
- A. Cystinosis (Correct Answer)
- B. Gaucher's disease
- C. Metachromatic leukodystrophy
- D. Tay-Sachs disease
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Explanation: ***Cystinosis***
- Cystinosis is characterized by **lysosomal transport defects** leading to the accumulation of cystine within lysosomes.
- This condition results in **multisystemic involvement**, primarily affecting the kidneys and eyes, due to the inability to effectively transport cystine out of the lysosomes.
*Metachromatic leukosytrophy*
- Caused by deficiency of the **enzyme arylsulfatase A**, leading to sulfatide accumulation in lysosomes [1].
- It primarily affects the **nervous system** and is not primarily linked to a defect in lysosomal transport.
*Goucher's disease*
- Results from a deficiency of the enzyme **glucocerebrosidase**, leading to glucocerebroside accumulation [1].
- It mainly affects the **spleen, liver, and bone marrow**, rather than a generalized lysosomal transport defect.
*Tay Sach's disease*
- Caused by a deficiency in the **enzyme hexosaminidase A**, leading to GM2 ganglioside accumulation in neurones [1].
- This condition primarily affects the **nervous system** and does not involve a defect in lysosomal transport [1].
**References:**
[1] Kumar V, Abbas AK, et al.. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 9th ed. Genetic Disorders, pp. 159-164.
Lysosomal Storage Diseases US Medical PG Question 5: Which of the following statements about Niemann-Pick disease is false?
- A. Due to deficiency of sphingomyelinase.
- B. CNS symptoms are present in type A.
- C. Type B Niemann-Pick disease is characterized by severe neurological symptoms. (Correct Answer)
- D. Histiocytes show PAS positive inclusions, and Type A is more severe.
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Explanation: ***Type B Niemann-Pick disease is characterized by severe neurological symptoms.***
- This statement is **false** because **Type B Niemann-Pick disease** generally presents with **visceral involvement** (e.g., hepatosplenomegaly, lung disease) with **minimal to no neurological symptoms**.
- **Severe neurological symptoms** are characteristic of **Type A Niemann-Pick disease**, which involves widespread CNS degeneration and a more rapidly progressive course.
*Due to deficiency of sphingomyelinase.*
- This statement is **true**.
- Niemann-Pick disease (Types A and B) is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme **acid sphingomyelinase**, leading to the accumulation of sphingomyelin within lysosomes, particularly in macrophages.
*CNS symptoms are present in type A.*
- This statement is **true**.
- **Type A Niemann-Pick disease** is the most severe form and is characterized by significant **neurodegeneration** in addition to visceral involvement.
- Patients typically present with **developmental regression**, **ataxia**, and **spasticity** due to extensive sphingomyelin deposition in the central nervous system.
*Histiocytes show PAS positive inclusions, and Type A is more severe.*
- This statement is **true**.
- The characteristic "foam cells" (lipid-laden macrophages/histiocytes) found in tissues of Niemann-Pick patients stain positive with **periodic acid–Schiff (PAS)** due to accumulated sphingomyelin.
- **Type A Niemann-Pick disease** is indeed the most severe form, with a rapidly progressive course and early fatality, usually by early childhood.
Lysosomal Storage Diseases US Medical PG Question 6: A 10-month-old child with coarse facies is referred for developmental delay. On examination, hepatosplenomegaly was noted. WBC N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase activity was absent. The X-ray is shown below. What is the diagnosis?
- A. I cell disease (Correct Answer)
- B. MPS type II
- C. Proteus syndrome
- D. Larsen syndrome
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Explanation: ***I cell disease***
- **I-cell disease** (Mucolipidosis II) is characterized by **coarse facial features**, developmental delay, hepatosplenomegaly, and **skeletal abnormalities** (dysostosis multiplex) seen on X-ray, which are consistent with the image.
- The absence of **N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase (GlcNAc-1-phosphotransferase)** activity leads to misrouting of lysosomal enzymes, resulting in accumulation of mucolipids within cells.
*MPS type II*
- **MPS type II** (Hunter syndrome) also presents with coarse facies, developmental delay, and hepatosplenomegaly, and can show skeletal abnormalities.
- However, the enzymatic defect is in **iduronate sulfatase**, not GlcNAc-1-phosphotransferase, and the clinical course tends to be slightly milder than I-cell disease, particularly in early infancy.
*Proteus syndrome*
- **Proteus syndrome** is characterized by **overgrowth of tissues**, asymmetric growth, and various tumors, not by the specific metabolic defect or typical pattern of skeletal changes described.
- It does not involve absent GlcNAc-1-phosphotransferase activity.
*Larsen syndrome*
- **Larsen syndrome** primarily involves **skeletal abnormalities**, such as joint dislocations (especially knees, hips, and elbows), flattened facial appearance, and clubfoot.
- It does not feature the same metabolic defect (absent GlcNAc-1-phosphotransferase activity) or the prominent coarse facial features and hepatosplenomegaly seen in the patient.
Lysosomal Storage Diseases US Medical PG Question 7: An 8-month-old infant is brought in with poor feeding, lethargy, hypotonia, and hepatomegaly. Labs reveal hypoglycemia and metabolic acidosis. Which condition is most likely?
- A. Hereditary fructose intolerance
- B. Galactosemia
- C. Pompe disease
- D. Von Gierke disease (Correct Answer)
- E. Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Explanation: ***Von Gierke disease***
- **Type I glycogen storage disease** (GSD I) typically presents in infancy with **hypoglycemia** (due to impaired glucose release from glycogen), **hepatomegaly** (due to glycogen accumulation), and **lactic acidosis**.
- Other common findings include **hyperlipidemia** and **hyperuricemia**, while **hypotonia** and **poor feeding** are generalized symptoms stemming from metabolic derangements.
*Hereditary fructose intolerance*
- This condition presents when **fructose** is introduced into the diet, typically after 4-6 months of age, with symptoms like **nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain**, and **hepatomegaly**.
- While it can cause **hypoglycemia** and **metabolic acidosis**, the profound **hypotonia** and general metabolic collapse described in an 8-month-old on a typical diet makes GSD I more likely initially.
*Galactosemia*
- Symptoms usually appear within days or weeks of birth upon the initiation of **milk feeding**, including **vomiting, lethargy, poor feeding, jaundice, hepatomegaly**, and **cataracts**.
- While it causes **hypoglycemia** and can lead to acidosis and hypotonia, the age of presentation and lack of specific mention of jaundice or cataracts makes it a less precise fit.
*Pompe disease*
- Also known as **glycogen storage disease type II**, it is characterized by the accumulation of glycogen in **lysosomes**, primarily affecting muscles.
- The infantile form presents with severe **cardiomyopathy**, **muscle weakness**, and **hypotonia**, but **hypoglycemia** and **hepatomegaly** are not its primary or most prominent features.
*Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency*
- A **fatty acid oxidation disorder** that presents with episodic **hypoglycemia** (particularly during fasting or illness), **lethargy**, and **hepatomegaly**.
- Key distinguishing features include **hypoketotic hypoglycemia** and elevated **dicarboxylic acids** on urine organic acids, but the **lactic acidosis** and overall metabolic profile are more consistent with GSD I.
Lysosomal Storage Diseases US Medical PG Question 8: A 7-month-old boy is brought to the pediatrician by his parents due to progressively worsening weakness for the last three months. The parents also describe the boy as having an exaggerated response when startled as well as diminishing response to visual stimuli. At birth, the boy was healthy and remained as such for the first few months of life. The mother says pregnancy was unremarkable, and the boy was born at 39 weeks with no complications during delivery. He is up to date on his vaccinations. The boy's grandparents immigrated from an eastern European country. Physical examination reveals hyperreflexia. Abdominal examination reveals no abnormalities. On fundoscopy, the following is seen. Which of the following is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Arylsulfatase A
- B. β-Glucosidase
- C. α-Galactosidase
- D. Hexosaminidase B
- E. Hexosaminidase A (Correct Answer)
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Explanation: ***Hexosaminidase A***
- Deficiency of **Hexosaminidase A** leads to **Tay-Sachs disease**, characterized by deterioration in motor and cognitive functions, aligning with the symptoms of weakness and abnormal responses.
- The condition is associated with a **cherry-red spot** on the retina, often observed in patients, further confirming the diagnosis.
- **Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry** is a key risk factor, consistent with the patient's eastern European heritage.
*Arylsulfatase A*
- Deficiency causes **metachromatic leukodystrophy**, which typically presents with **ataxia** and loss of previously attained skills, but not the exaggerated startle response noted in this case.
- The condition is not commonly associated with the specific visual and neurologic symptoms observed in the patient.
*β-Glucosidase*
- Deficiency leads to **Gaucher's disease**, which presents with splenomegaly, bone pain, and anemia, rather than the neurological symptoms seen here.
- The symptoms do not match the **progressive weakness** and startle reflex changes described.
*α-Galactosidase*
- Lack of this enzyme results in **Fabry disease**, which mainly causes pain episodes, skin lesions, and organ dysfunction, especially renal involvement.
- Neurological symptoms described here do not fit the typical presentation seen in Fabry disease.
*Hexosaminidase B*
- Deficiency causes **Sandhoff disease**, which presents similarly to Tay-Sachs with developmental regression and cherry-red spot.
- However, Sandhoff disease typically includes **hepatosplenomegaly**, which is notably absent in this patient on abdominal examination.
- The normal abdominal findings help distinguish this from Hexosaminidase A deficiency.
Lysosomal Storage Diseases US Medical PG Question 9: An 11-year-old boy was brought to the outpatient clinic with intention tremor and poor scholastic performance. His sister has similar complaints. On examination, hepatomegaly is seen. The eye finding is shown in the image. What is the probable diagnosis?
- A. Glutaric aciduria
- B. Wilson's disease (Correct Answer)
- C. Hepatitis A
- D. Huntington's chorea
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Explanation: ***Wilson's disease***
- The combination of **intention tremor**, **poor scholastic performance** (indicating neurological involvement), **hepatomegaly**, and the **eye finding** (Kayser-Fleischer ring seen in the image) points strongly to Wilson's disease. The sister having similar complaints suggests an **autosomal recessive** inheritance pattern, consistent with Wilson's disease.
- The image shows **Kayser-Fleischer ring**, a golden-brown ring at the corneal limbus due to **copper deposition in Descemet's membrane**, which is pathognomonic for Wilson's disease with neurological involvement.
- Wilson's disease is caused by mutations in the **ATP7B gene**, leading to impaired copper excretion and accumulation in the liver, brain, and cornea.
*Glutaric aciduria*
- This is a rare **autosomal recessive metabolic disorder** that primarily affects the brain, leading to **dystonia** and **developmental delay**.
- While it can cause neurological symptoms, it typically does not present with **hepatomegaly** or **Kayser-Fleischer rings** as prominent features.
*Hepatitis A*
- **Hepatitis A** is an acute viral infection of the liver, causing symptoms like fever, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and **jaundice**.
- However, it typically does not cause **intention tremor**, **poor scholastic performance**, or have a familial pattern suggesting an inherited neurological disorder. It also does not cause Kayser-Fleischer rings.
*Huntington's chorea*
- **Huntington's chorea** is an **autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder** characterized by **chorea**, psychiatric symptoms, and cognitive decline, typically manifesting in adulthood.
- It does not present with **hepatomegaly** or **Kayser-Fleischer rings** at this age and is not associated with the constellation of liver and neurological symptoms described.
Lysosomal Storage Diseases US Medical PG Question 10: A neonate presents with the clinical features shown in the image below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Down syndrome
- B. Congenital hypothyroidism (Correct Answer)
- C. Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome
- D. Turner syndrome
Lysosomal Storage Diseases Explanation: ***Congenital hypothyroidism***
- The image shows a neonate with **macroglossia** (large tongue), **umbilical hernia**, and possibly **puffy eyelids** and **dull facies**, all characteristic signs of congenital hypothyroidism.
- Other features often include **hypotonia**, **feeding difficulties**, **prolonged jaundice**, and **constipation**.
*Down syndrome*
- While Down syndrome can present with **hypotonia** and some shared features, the characteristic **epicanthal folds**, **simian crease**, **brushfield spots**, and flattened facial profile are not clearly evident.
- Macroglossia is common but other features like an umbilical hernia would be less specific.
*Ellis-Van Creveld syndrome*
- This syndrome is characterized by **chondroectodermal dysplasia**, typically presenting with **polydactyly**, **short-limbed dwarfism**, **nail dysplasia**, and **cardiac defects**.
- These distinct skeletal and ectodermal abnormalities are not visible in the presented image.
*Turner syndrome*
- Turner syndrome (XO karyotype) primarily affects females and is characterized by **short stature**, **webbed neck**, **lymphedema of hands and feet**, and **cardiac anomalies** (e.g., coarctation of the aorta).
- The features shown in the image, such as macroglossia and umbilical hernia, are not typical of Turner syndrome.
More Lysosomal Storage Diseases US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.