Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism US Medical PG Question 1: History of dislike for sweet food items is typically present in:
- A. Glycogen storage disease
- B. Diabetes mellitus
- C. Galactosemia
- D. Hereditary fructose intolerance (Correct Answer)
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism Explanation: ***Hereditary fructose intolerance***
- Patients with hereditary fructose intolerance develop severe symptoms like **nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and hypoglycemia** after ingesting fructose, leading to an aversive response and **dislike for sweet food items**.
- This aversion is a protective mechanism, as avoiding fructose-containing foods (including many sweets) prevents the accumulation of toxic metabolites due to a deficiency in **hepatic aldolase B**.
*Glycogen storage disease*
- While glycogen storage diseases can cause hypoglycemia, they typically do not lead to a specific **aversion to sweet foods**.
- The primary defect is in **glycogen synthesis or breakdown**, leading to symptoms like hepatomegaly, muscle weakness, and exercise intolerance.
*Diabetes mellitus*
- Patients with diabetes mellitus often have a **craving for sweet foods** due to uncontrolled blood glucose levels and insulin resistance, rather than a dislike.
- The condition is characterized by **hyperglycemia** and may involve polydipsia, polyuria, and polyphagia.
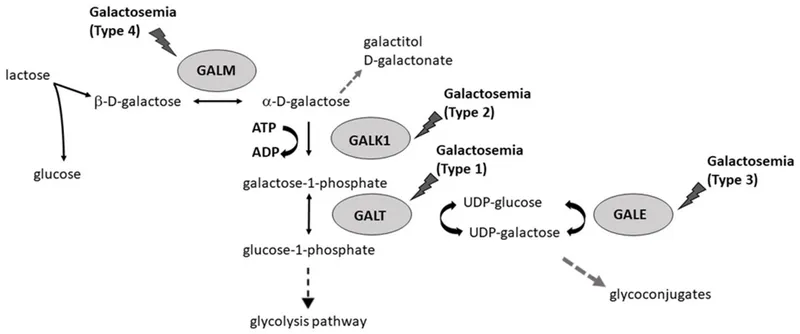
*Galactosemia*
- Galactosemia involves an inability to metabolize galactose, leading to symptoms such as **vomiting, lethargy, and jaundice** upon milk ingestion [1].
- While patients will avoid milk, their aversion is not generally to all sweet foods, as sweet foods do not always contain galactose [1].
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism US Medical PG Question 2: An 8-month-old infant is brought in with poor feeding, lethargy, hypotonia, and hepatomegaly. Labs reveal hypoglycemia and metabolic acidosis. Which condition is most likely?
- A. Hereditary fructose intolerance
- B. Galactosemia
- C. Pompe disease
- D. Von Gierke disease (Correct Answer)
- E. Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism Explanation: ***Von Gierke disease***
- **Type I glycogen storage disease** (GSD I) typically presents in infancy with **hypoglycemia** (due to impaired glucose release from glycogen), **hepatomegaly** (due to glycogen accumulation), and **lactic acidosis**.
- Other common findings include **hyperlipidemia** and **hyperuricemia**, while **hypotonia** and **poor feeding** are generalized symptoms stemming from metabolic derangements.
*Hereditary fructose intolerance*
- This condition presents when **fructose** is introduced into the diet, typically after 4-6 months of age, with symptoms like **nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain**, and **hepatomegaly**.
- While it can cause **hypoglycemia** and **metabolic acidosis**, the profound **hypotonia** and general metabolic collapse described in an 8-month-old on a typical diet makes GSD I more likely initially.
*Galactosemia*
- Symptoms usually appear within days or weeks of birth upon the initiation of **milk feeding**, including **vomiting, lethargy, poor feeding, jaundice, hepatomegaly**, and **cataracts**.
- While it causes **hypoglycemia** and can lead to acidosis and hypotonia, the age of presentation and lack of specific mention of jaundice or cataracts makes it a less precise fit.
*Pompe disease*
- Also known as **glycogen storage disease type II**, it is characterized by the accumulation of glycogen in **lysosomes**, primarily affecting muscles.
- The infantile form presents with severe **cardiomyopathy**, **muscle weakness**, and **hypotonia**, but **hypoglycemia** and **hepatomegaly** are not its primary or most prominent features.
*Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency*
- A **fatty acid oxidation disorder** that presents with episodic **hypoglycemia** (particularly during fasting or illness), **lethargy**, and **hepatomegaly**.
- Key distinguishing features include **hypoketotic hypoglycemia** and elevated **dicarboxylic acids** on urine organic acids, but the **lactic acidosis** and overall metabolic profile are more consistent with GSD I.
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism US Medical PG Question 3: A cataract formation in both eyes was discovered in a 1-year-old child during a routine well-child visit, with blood tests showing elevated galactose and galactitol levels. To determine which enzyme might be defective in the child, which intracellular metabolite should be measured?
- A. Galactose
- B. Fructose
- C. Glucose
- D. Galactose-1-phosphate (Correct Answer)
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism Explanation: ***Galactose-1-phosphate***
- An elevation of **galactose-1-phosphate** in a patient with cataracts and elevated galactose and galactitol levels points to a deficiency in **galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase (GALT)**, indicating **classic galactosemia**.
- The accumulation of **galactose-1-phosphate** is toxic and underlies the severe symptoms of classic galactosemia, including cataracts, liver damage, and intellectual disability.
- Measuring this metabolite specifically identifies GALT deficiency and distinguishes it from other enzyme defects in galactose metabolism.
*Galactose*
- Elevated **galactose** is observed in **galactosemia**, but measuring galactose itself doesn't differentiate between the different enzyme deficiencies (e.g., GALT vs. GALK deficiency).
- While elevated, it's the downstream metabolites like **galactose-1-phosphate** that are more specific for diagnosing the enzyme defect in classic galactosemia.
*Fructose*
- **Fructose** metabolism is distinct from galactose metabolism, and its levels would not be directly affected by defects in galactose-metabolizing enzymes.
- Elevated fructose would suggest a different metabolic disorder, such as **hereditary fructose intolerance**, which has different clinical presentations.
*Glucose*
- **Glucose** levels are not specific for diagnosing enzyme defects in galactose metabolism.
- While hypoglycemia can occur in severe galactosemia, measuring glucose doesn't identify which specific enzyme is deficient and is not the primary diagnostic metabolite.
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism US Medical PG Question 4: Which glycogen storage disease also presents as a lysosomal storage disease?
- A. Von Gierke's disease
- B. McArdle's disease
- C. Andersen's disease
- D. Pompe's disease (Correct Answer)
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism Explanation: ***Pompe's disease***
- Also known as **glycogen storage disease type II**, it is caused by a deficiency of **acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA)**, a *lysosomal enzyme*.
- This deficiency leads to the accumulation of **glycogen in lysosomes**, particularly affecting muscle tissue, thereby earning its classification as both a glycogen storage disease and a lysosomal storage disease.
*Von Gierke's disease*
- This is **glycogen storage disease type I** and is due to a deficiency in **glucose-6-phosphatase**.
- It primarily affects the **liver and kidneys**, causing severe **hypoglycemia** and **lactic acidosis**, but it is not classified as a lysosomal storage disease.
*McArdle's disease*
- This is **glycogen storage disease type V**, caused by a deficiency in **muscle glycogen phosphorylase (myophosphorylase)**.
- It manifests as **exercise intolerance** and muscle pain, but it does not involve lysosomal enzyme defects or glycogen accumulation in lysosomes.
*Andersen's disease*
- This is **glycogen storage disease type IV**, caused by a deficiency in the **glycogen branching enzyme**.
- It leads to the formation of **abnormal glycogen structures**, primarily affecting the liver and causing early liver failure, but it is not a lysosomal storage disorder.
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism US Medical PG Question 5: A 9-month-old girl is brought to the physician because of a 1-month history of poor feeding and irritability. She is at the 15th percentile for height and 5th percentile for weight. Examination shows hypotonia and wasting of skeletal muscles. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. There is hepatomegaly. Her serum glucose is 61 mg/dL, creatinine kinase is 100 U/L, and lactic acid is within the reference range. Urine ketone bodies are elevated. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphatase
- B. Muscle phosphorylase
- C. Acid alpha-glucosidase
- D. Glycogen debrancher (Correct Answer)
- E. Glucocerebrosidase
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism Explanation: ***Glycogen debrancher***
- The patient's symptoms of **hepatomegaly**, **hypoglycemia**, **poor feeding**, **growth failure**, and **elevated urine ketones** in the presence of normal lactic acid suggest Type III glycogen storage disease (Cori disease), caused by a deficiency in **glycogen debrancher enzyme**.
- **Muscle wasting** and **hypotonia** are also consistent with Type III GSD, as the debranching enzyme is present in both liver and muscle.
*Glucose-6-phosphatase*
- Deficiency in **glucose-6-phosphatase** (Type I GSD, Von Gierke disease) also presents with **hepatomegaly** and **hypoglycemia**.
- However, Type I GSD is characterized by **lactic acidosis**, which is explicitly stated as normal in this patient, and **hyperlipidemia**, which is not mentioned.
*Muscle phosphorylase*
- Deficiency in **muscle phosphorylase** (Type V GSD, McArdle disease) primarily affects skeletal muscle, causing **exercise intolerance** and **muscle pain**.
- It does not typically present with **hypoglycemia**, **hepatomegaly**, or **growth failure** in infancy.
*Acid alpha-glucosidase*
- Deficiency in **acid alpha-glucosidase** (Type II GSD, Pompe disease) causes accumulation of glycogen in lysosomes, leading to severe **cardiomyopathy**, **hypotonia**, and **muscle weakness**.
- While hypotonia is present, the absence of **cardiomegaly** and significant **liver involvement** makes this diagnosis less likely.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- Deficiency in **glucocerebrosidase** causes Gaucher disease, a lysosomal storage disorder, not a glycogen storage disorder.
- Symptoms include **hepatosplenomegaly**, **bone crises**, and neurological symptoms, but not **hypoglycemia** or isolated muscle wasting directly related to glycogen metabolism.
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism US Medical PG Question 6: A 4-year-old boy is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. He started walking at 20 months of age. He can use a cup to drink but cannot use silverware. He speaks in 2-word sentences and can build a tower of 4 blocks. He can scribble but cannot draw a circle. He is above the 99th percentile for height and at the 15th percentile for weight. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows bilateral inferior lens dislocation. His fingers are long and slender. He has a high-arched palate. The thumb and 5th finger overlap when he grips a wrist with the opposite hand. The skin over the neck can be extended and stretched easily. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Hypoxanthine-guanine-phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency
- B. Galactokinase deficiency
- C. Fibrillin 1 deficiency
- D. Cystathionine synthase deficiency (Correct Answer)
- E. Type V collagen deficiency
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism Explanation: ***Cystathionine synthase deficiency***
- The combination of **inferior lens dislocation**, **marfanoid habitus** (tall stature, long slender fingers, high-arched palate), **developmental delay** (late walking, speech delay), and **hyperelastic skin** is highly suggestive of **homocystinuria** due to cystathionine synthase deficiency.
- **Homocystinuria** is an autosomal recessive disorder causing accumulation of **homocysteine**, leading to multisystem involvement.
*Hypoxanthine-guanine-phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency*
- This deficiency causes **Lesch-Nyhan syndrome**, characterized by **gout, intellectual disability, choreoathetosis, and self-mutilation**.
- It does not present with lens dislocation or marfanoid features.
*Galactokinase deficiency*
- This is a rare form of **galactosemia** primarily causing **cataracts**.
- It does not explain the developmental delay, marfanoid features, or lens dislocation.
*Fibrillin 1 deficiency*
- This causes **Marfan syndrome**, which shares features like **tall stature, long slender fingers, high-arched palate, and lens dislocation**.
- However, in Marfan syndrome, lens dislocation is typically **superior**, while in this case, it is **inferior**, pointing towards homocystinuria.
*Type V collagen deficiency*
- This can be associated with **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome**, which features **hyperelastic skin** and joint hypermobility.
- However, it does not typically cause lens dislocation or the specific marfanoid habitus described, and developmental delay is not a primary feature.
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism US Medical PG Question 7: A 52-year-old man is admitted directly from the clinic for a serum glucose of 980 mg/dL. He has had type 2 diabetes for 16 years, for which he was prescribed metformin and glimepiride; however, he reports not having followed his prescription due to its high cost. For the past 12 days, he has had excess urination, and has lost 6 kg in weight. He has also noted a progressively worsening cough productive of greenish-brown sputum for approximately 20 days. His temperature is 38.9°C (102.02°F), blood pressure is 97/62 mm Hg, pulse is 97/minute and respiratory rate is 26/minute. On physical examination, he is somnolent, his eyes are sunken, and there are crackles at the left lung base.
Lab results are shown:
Arterial pH: 7.33
Serum sodium: 130 mEq/L
Serum potassium: 3 mEq/L
Serum osmolality: 325 mOsm/kg
Serum beta-hydroxybutyrate: negative
Urinalysis: trace ketones
Intravenous normal saline infusion is started. Which of the following is the best next step in this patient?
- A. Adding sodium bicarbonate infusion
- B. Starting basal-bolus insulin
- C. Adding dopamine infusion
- D. Adding potassium to the intravenous fluids (Correct Answer)
- E. Starting regular insulin infusion
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism Explanation: ***Adding potassium to the intravenous fluids***
- This patient presents with **hypokalemia** (serum potassium 3 mEq/L) and is receiving aggressive fluid resuscitation, which will further dilute his potassium and drive potassium into cells, potentially worsening the hypokalemia. **Potassium replacement** is critical to prevent cardiac arrhythmias.
- While fluids and insulin will be necessary, **correcting potassium** should be initiated early, especially with symptoms of hypokalemia or if the level is <3.3 mEq/L, to prevent serious complications and before starting insulin.
*Adding sodium bicarbonate infusion*
- The patient's arterial pH of 7.33 indicates only **mild acidosis**, likely due to hypovolemic lactic acidosis or other underlying issues, but not severe enough to warrant bicarbonate infusion.
- Additionally, his serum beta-hydroxybutyrate is negative and ketones are only trace, ruling out **diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)**, which is typically the primary indication for bicarbonate in diabetic emergencies.
*Starting basal-bolus insulin*
- The patient requires insulin for his **hyperglycemia**, but **basal-bolus insulin** is usually started once the patient is stable, able to eat, and out of the acute hyperosmolar state.
- In this emergency setting, **intravenous regular insulin infusion** is preferred for precise titration and rapid glucose control.
*Adding dopamine infusion*
- Dopamine is a **vasopressor** used to support blood pressure in cases of **hypotensive shock** refractory to fluid resuscitation.
- While the patient is hypotensive (BP 97/62 mm Hg), his primary problem is severe dehydration, so initial management focuses on **fluid resuscitation** with normal saline rather than immediate pressors.
*Starting regular insulin infusion*
- While **regular insulin infusion** is appropriate for managing severe hyperglycemia in hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS), it should be initiated **after initial fluid resuscitation** and after ensuring potassium is ≥3.3 mEq/L.
- Administering insulin without adequate potassium replacement could precipitate severe and life-threatening **hypokalemia**, as insulin drives potassium into cells.
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism US Medical PG Question 8: The lac operon allows E. coli to effectively utilize lactose when it is available, and not to produce unnecessary proteins. Which of the following genes is constitutively expressed and results in the repression of the lac operon?
- A. LacY
- B. LacI (Correct Answer)
- C. LacZ
- D. CAP
- E. LacA
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism Explanation: ***LacI***
- The **LacI gene** encodes the **Lac repressor protein**, which is constitutively expressed (always produced) and binds to the operator region of the lac operon.
- When bound, the **Lac repressor** blocks RNA polymerase from transcribing the structural genes (LacZ, LacY, LacA), thereby repressing the operon in the absence of lactose.
*LacY*
- The **LacY gene** encodes **lactose permease**, an enzyme responsible for transporting lactose into the bacterial cell.
- Its expression is regulated by the lac operon and is not constitutively expressed; rather, it is induced in the presence of lactose.
*LacZ*
- The **LacZ gene** encodes **beta-galactosidase**, the enzyme that breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose.
- Like LacY, its expression is part of the lac operon and is induced when lactose is available, not expressed constitutively.
*CAP*
- **CAP (Catabolite Activator Protein)** is a regulatory protein that, when bound to cAMP, activates transcription of the lac operon when glucose is absent.
- While essential for lac operon regulation, CAP is not a gene whose constitutive expression leads to repression of the operon.
*LacA*
- The **LacA gene** encodes **thiogalactoside transacetylase**, an enzyme with a less clear role in lactose metabolism but is part of the lac operon.
- Its expression is also regulated and induced along with LacZ and LacY, not constitutively expressed to repress the operon.
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism US Medical PG Question 9: An investigator is studying the metabolism of an experimental drug that is known to have first order kinetics. Immediately after administering an intravenous dose of the drug to a patient, the serum concentration is 60 U/L. 3 hours later, the serum concentration of the drug is 30 U/L. 9 hours after administration, the serum concentration of the drug is most likely to be which of the following?
- A. 5 U/L
- B. 0 U/L
- C. 15 U/L
- D. 7.5 U/L (Correct Answer)
- E. 3.75 U/L
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism Explanation: ***7.5 U/L***
- The drug follows **first-order kinetics**, meaning a constant fraction of the drug is eliminated per unit time, resulting in a constant **half-life**.
- The concentration halved from 60 U/L to 30 U/L in 3 hours, indicating a **half-life of 3 hours**. Thus, after another 3 hours (total 6 hours), the concentration would be 15 U/L, and after yet another 3 hours (total 9 hours), it would be **7.5 U/L**.
*5 U/L*
- This answer suggests a slower rate of elimination than calculated for first-order kinetics with a 3-hour half-life.
- If the half-life were longer than 3 hours, then 5 U/L might be a plausible concentration at 9 hours.
*0 U/L*
- For drugs following **first-order kinetics**, the concentration approaches zero asymptotically and never truly reaches zero within a finite timeframe, unless the total elimination has significantly exceeded multiple half-lives.
- This answer indicates complete elimination, which is incorrect for a drug still undergoing elimination after 9 hours.
*15 U/L*
- This would be the concentration at 6 hours (two half-lives) after administration, not 9 hours (three half-lives).
- It would occur if only two half-life periods had passed instead of three.
*3.75 U/L*
- This value represents the concentration after a fourth half-life (12 hours), not three half-lives (9 hours).
- This would be the concentration after 12 hours had passed from the initial administration.
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism US Medical PG Question 10: A 4-year-old girl presents to the emergency department after persistent vomiting and complaints that her abdomen hurts. Her parents came home to their daughter like this while she was at home being watched by the babysitter. The child is otherwise healthy. Family history is notable for depression, suicide, neuropathic pain, diabetes, hypertension, cancer, and angina. The child is now minimally responsive and confused. Her temperature is 100°F (37.8°C), blood pressure is 100/60 mmHg, pulse is 140/min, respirations are 22/min, and oxygen saturation is 100% on room air. Physical exam is notable for a confused girl who is vomiting bloody emesis into a basin. Laboratory studies are ordered as seen below.
Serum:
Na+: 140 mEq/L
Cl-: 101 mEq/L
K+: 3.9 mEq/L
HCO3-: 11 mEq/L
BUN: 20 mg/dL
Glucose: 99 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.0 mg/dL
Radiography is notable for a few radiopaque objects in the stomach. Urine and serum toxicology are pending. Which of the following is the most likely intoxication?
- A. Lead
- B. Iron (Correct Answer)
- C. Aspirin
- D. Acetaminophen
- E. Nortriptyline
Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism Explanation: ***Iron***
- The combination of **gastrointestinal symptoms** (vomiting, bloody emesis), **metabolic acidosis** (HCO3- of 11 mEq/L), and **radiopaque objects** on imaging is highly suggestive of iron intoxication. Iron tablets are often radiopaque.
- Iron toxicity can rapidly progress to severe systemic effects, including **hypovolemic shock**, **acidosis**, and **organ damage**, consistent with the child's declining mental status and vital signs (tachycardia, tachypnea).
*Lead*
- Lead poisoning typically presents with more **chronic symptoms** affecting the neurological, hematopoietic, and gastrointestinal systems, rather than acute severe gastroenteritis and rapid deterioration.
- While lead is radiopaque, lead poisoning is less commonly associated with the acute, severe presentation including **bloody emesis** and **metabolic acidosis** seen here.
*Aspirin*
- Aspirin (salicylate) overdose causes an initial **respiratory alkalosis** followed by a **metabolic acidosis** with an increased anion gap. While metabolic acidosis is present, the radiopaque findings are not typical of aspirin.
- Gastrointestinal effects can include vomiting, but **bloody emesis** and visible radiopaque tablets are less characteristic of aspirin compared to iron.
*Acetaminophen*
- Acetaminophen overdose primarily causes **hepatic toxicity**, which manifests 1-3 days after ingestion with elevated liver enzymes.
- It does not cause the **radiopaque findings** or the immediate, severe gastrointestinal irritation and profound metabolic acidosis seen in this case.
*Nortriptyline*
- Nortriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA). TCA overdose typically presents with **cardiac toxicity** (QRS widening, arrhythmias), **anticholinergic effects** (dilated pupils, dry skin, hyperthermia), and central nervous system depression, seizures, or coma.
- While it can cause CNS depression and confusion, it does not typically lead to **bloody emesis**, profound **metabolic acidosis**, or **radiopaque tablets** on X-ray.
More Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.