Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism US Medical PG Question 1: Which amino acids accumulate in maple syrup urine disease?
- A. Valine
- B. Leucine
- C. Isoleucine
- D. All branched-chain amino acids (Correct Answer)
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism Explanation: ***All branched-chain amino acids***
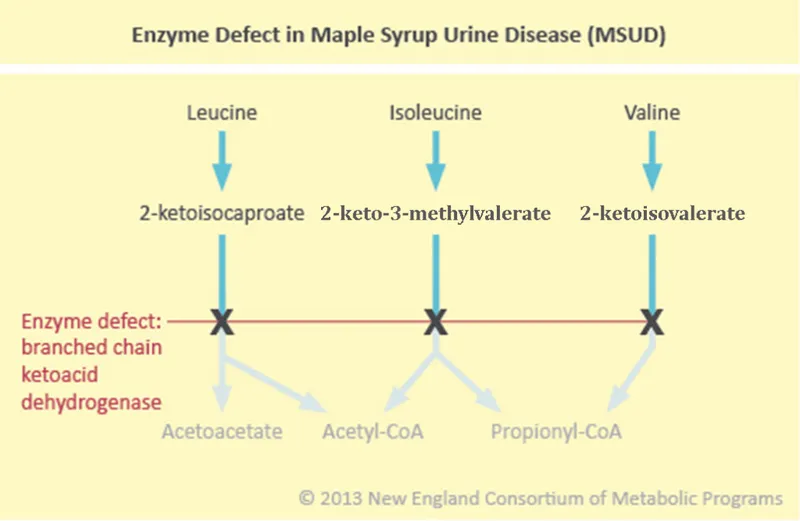
- Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is characterized by a deficiency in the **branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex**, which is responsible for the breakdown of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs).
- This deficiency leads to the accumulation of **leucine, isoleucine, and valine**, along with their corresponding alpha-keto acids, in the blood and urine.
- The distinctive **maple syrup odor** in the urine is caused by the accumulation of branched-chain keto acids derived from all three BCAAs.
*Leucine*
- While leucine is one of the BCAAs that accumulates in MSUD, it is not the *only* amino acid involved.
- The accumulation of **leucine** is particularly associated with the severe neurological symptoms seen in MSUD, as it is the most neurotoxic of the three BCAAs.
*Valine*
- Valine is another BCAA that accumulates due to the metabolic block in MSUD.
- However, the disease involves the accumulation of all three BCAAs, not just valine in isolation.
*Isoleucine*
- Isoleucine is the third BCAA that accumulates in MSUD due to the defective enzyme.
- Like leucine and valine, isoleucine and its corresponding keto acid accumulate in blood and urine when the branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex is deficient.
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism US Medical PG Question 2: A young boy with a thin build and long fingers presents with diminished vision. On examination, subluxation of the lens is observed, and cystathionine synthase deficiency is detected. Which amino acid should the patient be supplemented with?
- A. Tyrosine
- B. Serine
- C. Cysteine (Correct Answer)
- D. Methionine
- E. Glycine
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism Explanation: ***Cysteine***
- In **cystathionine synthase deficiency** (homocystinuria), the body cannot convert **homocysteine to cystathionine**, and subsequently to **cysteine**.
- **Cysteine** therefore becomes an **essential amino acid** in these patients and must be supplemented.
*Tyrosine*
- **Tyrosine** is a non-essential amino acid synthesized from **phenylalanine**, and its deficiency is not directly related to cystathionine synthase deficiency.
- It is not involved in the **methionine or homocysteine metabolic pathway** that is disrupted in homocystinuria.
*Serine*
- **Serine** is a substrate for the **cystathionine synthase enzyme**, which combines with **homocysteine** to form **cystathionine**.
- Supplementation with serine alone would not bypass the enzyme deficiency or provide the essential product, **cysteine**.
*Methionine*
- **Methionine** is the precursor to **homocysteine**, and in cystathionine synthase deficiency, there's often an accumulation of methionine and homocysteine.
- Therefore, **methionine restriction** is typically part of the treatment, not supplementation.
*Glycine*
- **Glycine** is involved in one-carbon metabolism but is not directly involved in the **transsulfuration pathway** affected by cystathionine synthase deficiency.
- Glycine supplementation would not address the inability to synthesize **cysteine** from homocysteine.
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism US Medical PG Question 3: An infant is brought by his parents with complaints that his urine turns black on standing. Which of the following metabolic disorders is likely?
- A. Phenylketonuria
- B. Alkaptonuria (Correct Answer)
- C. Homocystinuria
- D. Maple syrup urine disease
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism Explanation: ***Alkaptonuria***
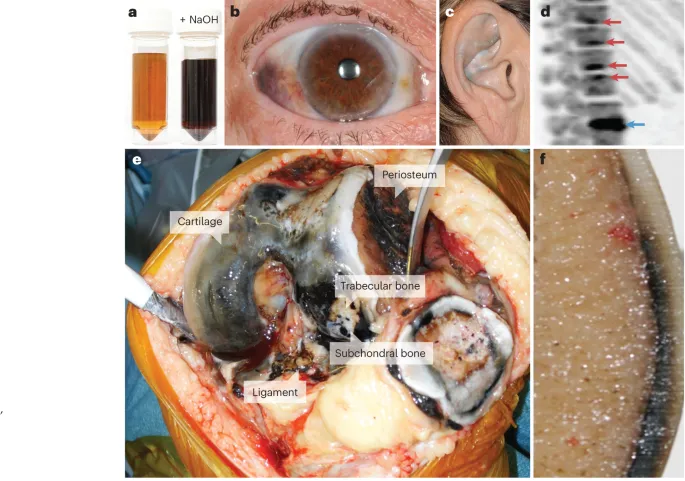
- **Alkaptonuria** is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by a deficiency of **homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase**, an enzyme involved in the metabolism of tyrosine.
- The accumulation of **homogentisic acid** in tissues and urine causes the urine to turn black on standing due to oxidation.
*Phenylketonuria*
- **Phenylketonuria (PKU)** is caused by a deficiency of **phenylalanine hydroxylase**, leading to the accumulation of phenylalanine.
- While it can manifest with intellectual disability and neurological symptoms, it does not typically cause the urine to turn black.
*Homocystinuria*
- **Homocystinuria** is a disorder of methionine metabolism, typically due to a deficiency of **cystathionine beta-synthase**.
- It is characterized by intellectual disability, skeletal abnormalities, and lens dislocation, but not black urine.
*Maple syrup urine disease*
- **Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)** results from a deficiency of **branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex**, leading to the accumulation of branched-chain amino acids.
- The distinguishing feature is urine that smells like maple syrup, not turning black.
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism US Medical PG Question 4: A 35-year-old man presents to the physician with arthritic pain in both knees along with back pain. He states that the pain has been present for months. The patient is afebrile, and his slightly swollen knee joints are neither hot nor tender to palpation; however the pain does restrict his motion. The cartilage of his ears appears slightly darker than normal. No tophi are present. A urine specimen is taken for analysis of uric acid content and turns black in the laboratory while standing. What is the most likely diagnosis at this point?
- A. Alkaptonuria (Correct Answer)
- B. Ankylosing spondylitis
- C. Maple syrup urine disease
- D. Phenylketonuria
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism Explanation: ### Alkaptonuria
- The key diagnostic features are **arthritic pain in the knees and back**, **darkening of ear cartilage (ochronosis)** [1], and **urine turning black on standing** due to the oxidation of homogentisic acid.
- This is an **autosomal recessive disorder** caused by a deficiency of **homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase**, leading to the accumulation of homogentisic acid.
### Ankylosing spondylitis
- Characterized by **chronic inflammatory back pain and stiffness** that improves with exercise, often associated with sacroiliitis.
- While back pain is present, the absence of findings like **HLA-B27 positivity** (not mentioned) and the specific urine and cartilage findings make it less likely.
### Maple syrup urine disease
- This is a metabolic disorder affecting the metabolism of **branched-chain amino acids** (leucine, isoleucine, valine), leading to a characteristic **sweet-smelling urine**.
- It typically presents in infancy with severe neurological symptoms and feeding difficulties, not with arthritic pain and dark urine.
### Phenylketonuria
- Caused by a deficiency of **phenylalanine hydroxylase**, leading to the accumulation of phenylalanine.
- Presents with severe intellectual disability, seizures, and a musty odor in urine if untreated, without the specific arthritic or ochronotic findings seen here.
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism US Medical PG Question 5: An investigator is studying the activity level of several different enzymes in human subjects from various demographic groups. An elevated level of activity of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase is found in one of the study subjects. This patient is most likely to have which of the following conditions?
- A. Phenylketonuria
- B. Homocystinuria
- C. Gout (Correct Answer)
- D. Alkaptonuria
- E. Maple syrup urine disease
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism Explanation: ***Gout***
- **Elevated phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) synthetase activity** leads to increased production of PRPP, a precursor for **purine biosynthesis**.
- Increased purine synthesis results in overproduction of **uric acid**, which can precipitate as monosodium urate crystals in joints, causing **gout**.
*Phenylketonuria*
- Caused by a deficiency in **phenylalanine hydroxylase**, leading to an accumulation of **phenylalanine**.
- Not directly related to increased PRPP synthetase activity or purine metabolism.
*Homocystinuria*
- Primarily due to a deficiency in **cystathionine beta-synthase**, leading to elevated levels of **homocysteine**.
- This condition involves methionine metabolism, not purine metabolism or PRPP synthetase.
*Alkaptonuria*
- Results from a deficiency in **homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase**, causing the accumulation of **homogentisic acid**.
- It is an inborn error of tyrosine metabolism and is unrelated to PRPP synthetase activity.
*Maple syrup urine disease*
- Caused by a deficiency in the **branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex**, leading to accumulation of **leucine, isoleucine, and valine**.
- This condition affects branched-chain amino acid metabolism, not purine metabolism.
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism US Medical PG Question 6: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of sudden-onset abdominal pain that began 1 hour ago. Three days ago, he was diagnosed with a urinary tract infection and was treated with nitrofurantoin. There is no personal history of serious illness. His parents emigrated from Kenya before he was born. Examination shows diffuse abdominal tenderness, mild splenomegaly, and scleral icterus. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 9.8 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume 88 μm3
Reticulocyte count 3.1%
Serum
Bilirubin
Total 3.8 mg/dL
Direct 0.6 mg/dL
Haptoglobin 16 mg/dL (N=41–165 mg/dL)
Lactate dehydrogenase 179 U/L
Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Defective red blood cell membrane proteins
- B. Lead poisoning
- C. Defect in orotic acid metabolism
- D. Absent hemoglobin beta chain
- E. Enzyme deficiency in red blood cells (Correct Answer)
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism Explanation: ***Enzyme deficiency in red blood cells***
- The patient's symptoms (abdominal pain, scleral icterus, mild splenomegaly, anemia, elevated reticulocyte count, increased unconjugated bilirubin, low haptoglobin, and elevated LDH) are consistent with **hemolytic anemia**. The recent use of **nitrofurantoin**, an oxidative stressor, in a patient of African descent, strongly suggests a diagnosis of **Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency**.
- G6PD deficiency is an **X-linked recessive** inherited enzyme defect causing red blood cells to be susceptible to oxidative damage, leading to hemolysis when exposed to certain drugs (like nitrofurantoin) or infections.
*Defective red blood cell membrane proteins*
- This describes conditions like **hereditary spherocytosis** or **hereditary elliptocytosis**. While these cause hemolytic anemia, the acute onset triggered by a drug (nitrofurantoin) is less typical.
- Hereditary spherocytosis is characterized by **microspherocytes** on a peripheral smear and is usually diagnosed earlier in life or has a chronic course, often without an acute precipitating drug.
*Lead poisoning*
- Lead poisoning typically causes **microcytic anemia** with **basophilic stippling** and neurological symptoms, not the type of hemolytic anemia and jaundice described.
- It does not present as an acute hemolytic crisis triggered by an oxidative drug.
*Defect in orotic acid metabolism*
- This can lead to conditions like **hereditary orotic aciduria**, which presents with **megaloblastic anemia** (without B12 or folate deficiency) and developmental delay.
- It is not associated with acute hemolytic episodes triggered by oxidative drugs or the specific lab findings seen here.
*Absent hemoglobin beta chain*
- This refers to **beta-thalassemia major**, which causes **microcytic hypochromic anemia** that is typically chronic and presents early in childhood with severe anemia requiring regular transfusions.
- Beta-thalassemia does not present as an acute hemolytic crisis triggered by nitrofurantoin, and the MCV in this patient is normal (88 μm³), not microcytic.
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism US Medical PG Question 7: A 3-day-old female infant presents with poor feeding, lethargy, vomiting after feeding, and seizures. Labs revealed ketoacidosis and elevated hydroxypropionic acid levels. Upon administration of parenteral glucose and protein devoid of valine, isoleucine, methionine, and threonine, and carnitine, the infant began to recover. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this infant?
- A. Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase
- B. Propionyl-CoA carboxylase (Correct Answer)
- C. Cystathionine synthase
- D. Phenylalanine hydroxylase
- E. Homogentisate oxidase
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism Explanation: ***Propionyl-CoA carboxylase***
- The presence of **ketoacidosis** and elevated **hydroxypropionic acid** levels is characteristic of propionic acidemia, which is caused by a deficiency in **propionyl-CoA carboxylase**.
- The therapeutic benefit from a diet restricted in **valine, methionine, threonine**, and **isoleucine** (precursors of propionyl-CoA) along with carnitine supplementation further supports this diagnosis.
*Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase*
- A deficiency in this enzyme leads to **Maple Syrup Urine Disease**, characterized by elevated **branched-chain ketoacids** and associated with a distinctive sweet odor in urine.
- While it causes neurotoxicity and poor feeding, the specific finding of elevated **hydroxypropionic acid** points away from this diagnosis.
*Cystathionine synthase*
- Deficiency in **cystathionine synthase** causes **homocystinuria**, leading to elevated **homocysteine** levels.
- Symptoms include developmental delay, ectopia lentis, and skeletal abnormalities, but not typically elevated **hydroxypropionic acid** or severe neonatal ketoacidosis in this manner.
*Phenylalanine hydroxylase*
- This enzyme is deficient in **phenylketonuria (PKU)**, resulting in high levels of **phenylalanine** and its metabolites.
- PKU is typically associated with intellectual disability, seizures, and a musty odor, but not ketoacidosis or elevated **hydroxypropionic acid**.
*Homogentisate oxidase*
- A deficiency in this enzyme causes **alkaptonuria**, characterized by the accumulation of **homogentisic acid**.
- This condition is usually benign in infancy, primarily manifesting as dark urine upon standing and later developing into ochronosis and arthritis, without acute neonatal ketoacidosis or elevated **hydroxypropionic acid**.
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism US Medical PG Question 8: A 4-year-old boy is brought to a pediatrician by his parents for a consultation after his teacher complained about his inability to focus or make friends at school. They mention that the boy does not interact well with others at home, school, or daycare. On physical examination, his vital signs are stable with normal weight, height, and head circumference for his age and sex. His general examination and neurologic examination are completely normal. A recent audiological evaluation shows normal hearing, and intellectual disability has been ruled out by a clinical psychologist. Which of the following investigations is indicated as part of his diagnostic evaluation at present?
- A. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain
- B. Electroencephalography
- C. No further testing is needed
- D. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scanning of head
- E. Autism spectrum disorder screening and developmental assessment (Correct Answer)
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism Explanation: ***Autism spectrum disorder screening and developmental assessment***
- The clinical presentation (inability to focus, difficulty making friends, poor social interaction across multiple settings) is **highly suggestive of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)**.
- After ruling out **hearing impairment and intellectual disability**, the next appropriate step is **formal ASD screening using validated tools** such as the **Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT)**, **Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS)**, or **Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R)**.
- According to **AAP guidelines**, when developmental concerns suggestive of ASD are identified, formal screening and comprehensive developmental assessment are **essential components of the diagnostic evaluation**.
- ASD diagnosis is primarily **clinical**, based on standardized screening tools and developmental assessments, not neuroimaging or electrophysiological studies.
*No further testing is needed*
- This is **incorrect** because the patient has not yet undergone **formal ASD-specific screening and developmental assessment**.
- While hearing and intellectual disability have been ruled out, **diagnostic confirmation of ASD** requires structured evaluation using validated assessment tools.
- Simply observing symptoms without formal screening is inadequate for establishing an ASD diagnosis.
*Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain*
- Brain MRI is **not routinely indicated** for ASD diagnosis as it typically shows **normal findings** in children with ASD.
- Neuroimaging is reserved for cases with **focal neurological signs, regression, or atypical features** suggesting structural abnormalities.
- This patient has a **normal neurological examination**, making MRI unnecessary.
*Electroencephalography*
- EEG is indicated only when there is suspicion of **seizure disorder** or other specific neurological conditions.
- The patient has a **normal neurological examination** with no seizure-like symptoms, making EEG unnecessary at this stage.
*Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scanning of head*
- PET scans are **not part of routine ASD diagnostic workup** and are typically used in research settings or for evaluating specific metabolic or neoplastic conditions.
- The **radiation exposure and invasiveness** make PET scanning inappropriate for initial diagnostic evaluation in a child with developmental concerns.
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism US Medical PG Question 9: A 4-year-old boy is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. He started walking at 20 months of age. He can use a cup to drink but cannot use silverware. He speaks in 2-word sentences and can build a tower of 4 blocks. He can scribble but cannot draw a circle. He is above the 99th percentile for height and at the 15th percentile for weight. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows bilateral inferior lens dislocation. His fingers are long and slender. He has a high-arched palate. The thumb and 5th finger overlap when he grips a wrist with the opposite hand. The skin over the neck can be extended and stretched easily. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Hypoxanthine-guanine-phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency
- B. Galactokinase deficiency
- C. Fibrillin 1 deficiency
- D. Cystathionine synthase deficiency (Correct Answer)
- E. Type V collagen deficiency
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism Explanation: ***Cystathionine synthase deficiency***
- The combination of **inferior lens dislocation**, **marfanoid habitus** (tall stature, long slender fingers, high-arched palate), **developmental delay** (late walking, speech delay), and **hyperelastic skin** is highly suggestive of **homocystinuria** due to cystathionine synthase deficiency.
- **Homocystinuria** is an autosomal recessive disorder causing accumulation of **homocysteine**, leading to multisystem involvement.
*Hypoxanthine-guanine-phosphoribosyl transferase deficiency*
- This deficiency causes **Lesch-Nyhan syndrome**, characterized by **gout, intellectual disability, choreoathetosis, and self-mutilation**.
- It does not present with lens dislocation or marfanoid features.
*Galactokinase deficiency*
- This is a rare form of **galactosemia** primarily causing **cataracts**.
- It does not explain the developmental delay, marfanoid features, or lens dislocation.
*Fibrillin 1 deficiency*
- This causes **Marfan syndrome**, which shares features like **tall stature, long slender fingers, high-arched palate, and lens dislocation**.
- However, in Marfan syndrome, lens dislocation is typically **superior**, while in this case, it is **inferior**, pointing towards homocystinuria.
*Type V collagen deficiency*
- This can be associated with **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome**, which features **hyperelastic skin** and joint hypermobility.
- However, it does not typically cause lens dislocation or the specific marfanoid habitus described, and developmental delay is not a primary feature.
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism US Medical PG Question 10: A previously healthy 24-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 30 minutes after an episode of loss of consciousness. He was standing in line at a bus stop when he suddenly became tense, fell down, and lost consciousness; this was followed by 4 minutes of violent jerky movements of his arms and legs. He was confused after the episode. He has no recollection of the event or its immediate aftermath. On arrival, he is alert and oriented to time, place, and person. His temperature is 37.7°C (99.4°F), pulse is 98/min, and blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg. Physical examination shows blood in the mouth. Neurologic examination shows no focal findings. A CT scan of the head shows no abnormalities. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following laboratory findings?
- A. Increased serum sodium
- B. Reduced serum creatine kinase
- C. Reduced serum bicarbonate (Correct Answer)
- D. Increased serum magnesium
- E. Increased serum calcium
Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism Explanation: ***Reduced serum bicarbonate***
- The patient's presentation with sudden loss of consciousness, tonic-clonic movements, postictal confusion, and tongue biting is classic for a **generalized tonic-clonic seizure**
- Prolonged intense muscle activity during the seizure leads to **anaerobic metabolism** and **lactic acidosis**
- The accumulated lactic acid consumes bicarbonate as a buffer, resulting in **reduced serum bicarbonate** and metabolic acidosis
- This is typically transient and resolves within hours as lactate is cleared
*Increased serum sodium*
- Seizures do not typically cause **hypernatremia** as a direct consequence
- While severe hyponatremia can precipitate seizures, the seizure itself does not increase sodium levels
- Serum sodium is generally unchanged immediately post-seizure
*Reduced serum creatine kinase*
- The violent muscle contractions during a **tonic-clonic seizure** cause **rhabdomyolysis** (muscle breakdown)
- This results in a significant **increase in serum creatine kinase (CK)**, not a reduction
- Elevated CK is a common and expected finding after generalized tonic-clonic seizures and may peak 24-48 hours post-seizure
*Increased serum magnesium*
- There is no physiological mechanism by which a seizure would cause **hypermagnesemia**
- Magnesium levels are typically unaffected by seizure activity
- Note: Low magnesium can be a cause of seizures, but the seizure itself doesn't increase magnesium
*Increased serum calcium*
- **Serum calcium** levels are not directly affected by the acute seizure event
- While severe **hypocalcemia** can precipitate seizures, a seizure does not cause hypercalcemia
- Calcium homeostasis remains stable during and after typical seizures
More Disorders of Amino Acid Metabolism US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.