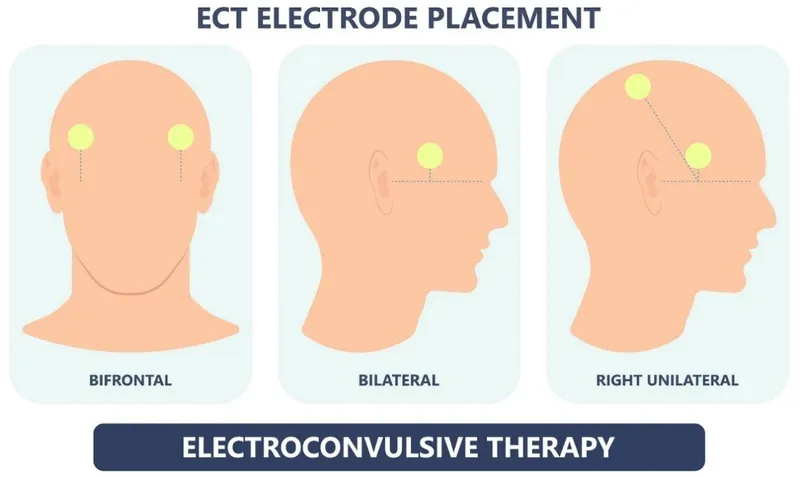
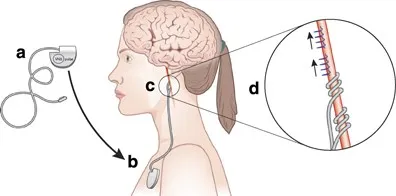
ECT and neuromodulation therapies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for ECT and neuromodulation therapies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
ECT and neuromodulation therapies US Medical PG Question 1: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of spells of unresponsiveness and upward rolling of the eyes for 2 months. The episodes start abruptly and last a few seconds. During that time he does not hear anyone’s voice or make any purposeful movements. When the episodes end, he continues what he was doing before the spell. He does not lose his posture or fall to the ground. Episodes occur multiple times during the day. Physical examination shows no abnormal findings. An EEG following hyperventilation shows 3 Hz spike-and-slow-wave discharges. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy at this time?
- A. No pharmacotherapy at this time
- B. Ethosuximide (Correct Answer)
- C. Sodium valproate
- D. Oxcarbazepine
- E. Lamotrigine
ECT and neuromodulation therapies Explanation: ***Ethosuximide***
- The described clinical picture (brief unresponsiveness, eye-rolling, continuing activity afterward, frequent daily episodes, normal physical exam, and 3-Hz spike-and-slow-wave discharges on EEG during hyperventilation) is classic for **childhood absence epilepsy**.
- **Ethosuximide** is the first-line and most effective treatment specifically for absence seizures due to its selective action on T-type calcium channels in the thalamus, which are implicated in the generation of absence seizures.
*No pharmacotherapy at this time*
- Leaving childhood absence epilepsy untreated can lead to significant impairments in learning, attention, and cognitive development due to the frequent, brief interruptions in consciousness.
- Given the clear diagnostic criteria including characteristic EEG findings and frequent episodes, initiating appropriate pharmacotherapy is medically indicated and crucial for the child's well-being.
*Sodium valproate*
- While **sodium valproate** is effective against absence seizures and has a broader spectrum of action against other seizure types, it is often considered a second-line agent for absence epilepsy due to potential side effects.
- Its use may be preferred if there are co-occurring generalized tonic-clonic seizures or if ethosuximide is not tolerated or effective, but for isolated absence seizures, ethosuximide has a better side effect profile.
*Oxcarbazepine*
- **Oxcarbazepine** is a sodium channel blocker primarily used for focal (partial onset) seizures and secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures.
- It is generally ineffective and can sometimes *worsen* absence seizures, making it an inappropriate choice for this diagnosis.
*Lamotrigine*
- **Lamotrigine** is a broad-spectrum antiepileptic drug effective for various seizure types, including focal, generalized tonic-clonic, and some forms of atypical absence seizures.
- While it can be used for absence seizures, it is generally considered a second-line or add-on therapy, especially when ethosuximide or valproate are ineffective or not tolerated, or if there are co-existing seizure types. It is not the most appropriate first-line choice for classic childhood absence epilepsy.
ECT and neuromodulation therapies US Medical PG Question 2: A 23-year-old woman is admitted to the inpatient psychiatry unit after her boyfriend reported she was “acting funny and refusing to talk.” The patient’s boyfriend states that he came home from work and found the patient sitting up in bed staring at the wall. When he said her name or waved his hand in front of her, she did not respond. When he tried to move her, she would remain in whatever position she was placed. The patient’s temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 122/79 mmHg, pulse is 68/min, and respirations are 12/min with an oxygen saturation of 98% O2 on room air. During the physical exam, the patient is lying on the bed with her left arm raised and pointing at the ceiling. She resists any attempt to change her position. The patient remains mute and ignores any external stimuli. The patient’s medical history is significant for depression. She was recently switched from phenelzine to fluoxetine. Which of the following is the best initial therapy?
- A. Electroconvulsive therapy
- B. Lorazepam (Correct Answer)
- C. Haloperidol
- D. Cyproheptadine
- E. Benztropine
ECT and neuromodulation therapies Explanation: **Lorazepam**
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **catatonia**, including **mutism**, **waxy flexibility**, and **posturing**, following a medication change from phenelzine (MAOI) to fluoxetine (SSRI), which could potentially precipitate catatonia or serotonin syndrome.
- **Benzodiazepines**, particularly lorazepam, are the **first-line treatment** for catatonia, often showing a rapid and dramatic response.
*Electroconvulsive therapy*
- While **ECT** is a highly effective treatment for severe catatonia, especially when unresponsive to benzodiazepines, it is typically considered a **second-line intervention** or for cases involving medical instability.
- Given the strong initial efficacy and safety profile of benzodiazepines, they are preferred as the first step before proceeding to ECT.
*Haloperidol*
- **Antipsychotics** like haloperidol are generally **contraindicated** in catatonia, as they can sometimes worsen the symptoms or even induce **neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)**, which shares some features with severe catatonia.
- NMS is a serious condition with high mortality, and introducing an antipsychotic in a catatonic patient could be dangerous.
*Cyproheptadine*
- **Cyproheptadine** is a **serotonin antagonist** used primarily in the treatment of **serotonin syndrome**, which involves symptoms like hyperthermia, agitation, and hyperreflexia.
- While the medication change could raise suspicion for serotonin syndrome, the clinical picture of **waxy flexibility, mutism, and posturing** is much more indicative of catatonia, for which cyproheptadine is not an effective treatment.
*Benztropine*
- **Benztropine** is an **anticholinergic medication** primarily used to treat **extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS)** caused by antipsychotics, such as **dystonia** or **parkinsonism**.
- The patient's symptoms are not indicative of EPS, and benztropine has no role in the treatment of catatonia.
ECT and neuromodulation therapies US Medical PG Question 3: A 24-year-old male comes into the psychiatric clinic complaining of consistent sadness. He endorses feelings of worthlessness, anxiety, and anhedonia for the past couple months but denies feeling suicidal. He further denies any past episodes of feeling overly energetic with racing thoughts. Confident of the diagnosis, you recommend frequent talk therapy along with a long-term prescription of a known first-line medication for this disorder. What is the drug and what are some of the most frequently encountered side effects?
- A. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; hypomania, suicidal thoughts
- B. Tricyclic antidepressants; hypomania, suicidal thoughts
- C. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; anorgasmia, insomnia (Correct Answer)
- D. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors; Orthostatic hypotension, weight gain
- E. Tricyclic antidepressants; Orthostatic hypotension, anticholinergic effects
ECT and neuromodulation therapies Explanation: ***Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; anorgasmia, insomnia***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **major depressive disorder**, including persistent sadness, worthlessness, anxiety, and anhedonia, without any history of manic or hypomanic episodes. **SSRIs** are considered first-line pharmacotherapy for this condition.
- Common side effects of SSRIs include **sexual dysfunction** (e.g., anorgasmia, decreased libido) and **insomnia** or agitation, especially during the initial weeks of treatment.
*Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; hypomania, suicidal thoughts*
- While SSRIs are the correct drug class, **hypomania** is not a frequent side effect in patients without bipolar disorder. For patients with bipolar disorder, antidepressant monotherapy can induce hypomania or mania, but this patient denies such episodes.
- **Suicidal thoughts** can occur, particularly in young adults, during the initial phase of antidepressant treatment, but it is less common to frame it as a *frequently encountered side effect* in the general population compared to sexual dysfunction or sleep disturbances.
*Tricyclic antidepressants; hypomania, suicidal thoughts*
- **Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)** are generally not first-line due to their less favorable side effect profile compared to SSRIs, including significant anticholinergic effects and cardiovascular risks.
- As with SSRIs, **hypomania** is not a typical frequent side effect in unipolar depression, and while **suicidal thoughts** are a concern with antidepressants, TCAs carry a higher risk of lethality in overdose, making them less preferred initially.
*Monoamine oxidase inhibitors; Orthostatic hypotension, weight gain*
- **Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)** are effective but are typically reserved for **refractory depression** due to their significant drug and food interactions (e.g., tyramine-induced hypertensive crisis).
- While **orthostatic hypotension** and **weight gain** are known side effects of MAOIs, this class is not considered a first-line treatment for major depressive disorder.
*Tricyclic antidepressants; Orthostatic hypotension, anticholinergic effects*
- **TCAs** are indeed associated with side effects such as **orthostatic hypotension** and prominent **anticholinergic effects** (e.g., dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, urinary retention).
- However, because of these more burdensome side effects and higher toxicity in overdose, TCAs are not generally considered the first-line medication choice, especially when SSRIs are available and safer.
ECT and neuromodulation therapies US Medical PG Question 4: A 31-year-old G1P0 woman is brought into the emergency room by the police after a failed suicide attempt. She jumped off a nearby bridge but was quickly rescued by some nearby locals. The height of the bridge was not significant, so the patient did not sustain any injuries. For the 3 weeks before this incident, the patient says she had been particularly down, lacking energy and unable to focus at home or work. She says she no longer enjoys her usual hobbies or favorite meals and is not getting enough sleep. Which of the following is the best course of treatment for this patient?
- A. Bupropion
- B. Paroxetine
- C. Combination of SSRI and SNRI
- D. Phenelzine
- E. Electroconvulsive therapy (Correct Answer)
ECT and neuromodulation therapies Explanation: ***Electroconvulsive therapy***
- This patient presents with **severe depression with suicidal ideation** (a failed suicide attempt), which warrants urgent intervention. **ECT** is highly effective for severe depression, especially when there is an acute suicide risk or psychotic features.
- ECT has a **rapid onset of action** compared to antidepressants, which is crucial for patients at high risk of self-harm, and is considered **safe in pregnancy**.
*Bupropion*
- **Bupropion** is an antidepressant that primarily inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine. While effective for depression, it has a slower onset of action than ECT and may not be sufficient for severe, acute suicidal ideation.
- It is often used for depression with atypical features or for patients who experience sexual side effects with SSRIs, but it is **contraindicated in patients with a history of seizures or eating disorders**.
*Paroxetine*
- **Paroxetine** is an SSRI commonly used for depression and anxiety disorders. Like other antidepressants, it has a delayed onset of action (several weeks) and may not be appropriate for the immediate management of a patient with recent, severe suicidal ideation.
- One of the major concerns with paroxetine in this patient population is that it has a **higher rate of teratogenicity and neonatal complications** compared to other SSRIs, which is relevant given the patient is G1P0.
*Combination of SSRI and SNRI*
- Combining an **SSRI and an SNRI** (e.g., fluoxetine and venlafaxine) is a strategy sometimes used for treatment-resistant depression. However, like monotherapy with these agents, it still has a delayed onset of action.
- The combination also carries a **higher risk of side effects** compared to monotherapy.
*Phenelzine*
- **Phenelzine** is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). MAOIs are effective antidepressants but are typically reserved for **treatment-resistant depression** due to their significant drug-drug and drug-food interactions (e.g., **hypertensive crisis with tyramine-rich foods or sympathomimetics**).
- Given the patient's acute suicidal risk, a treatment with a more rapid and safer profile, such as ECT, would be preferred over initiating an MAOI.
ECT and neuromodulation therapies US Medical PG Question 5: Which neurotransmitter is primarily responsible for parasympathetic effects on heart rate?
- A. Norepinephrine
- B. Dopamine
- C. Acetylcholine (Correct Answer)
- D. Epinephrine
ECT and neuromodulation therapies Explanation: ***Acetylcholine***
- **Acetylcholine** is the primary neurotransmitter released by postganglionic parasympathetic neurons.
- It acts on **muscarinic receptors** (M2 receptors) in the heart to decrease heart rate.
*Norepinephrine*
- **Norepinephrine** is primarily associated with the **sympathetic nervous system**, increasing heart rate and contractility.
- It acts on **beta-1 adrenergic receptors** in the heart.
*Dopamine*
- **Dopamine** is a precursor to norepinephrine and epinephrine, and primarily functions as a neurotransmitter in the **central nervous system** and in regulating renal blood flow.
- While it can have cardiac effects, it is not the primary neurotransmitter for parasympathetic actions on heart rate.
*Epinephrine*
- **Epinephrine** (adrenaline) is a hormone released by the adrenal medulla and a neurotransmitter in the sympathetic nervous system, causing an **increase in heart rate** and contractility.
- It works through **beta-1 adrenergic receptors**, antagonistic to parasympathetic effects.
ECT and neuromodulation therapies US Medical PG Question 6: A 27-year old gentleman presents to the primary care physician with the chief complaint of "feeling down" for the last 6 weeks. He describes trouble falling asleep at night, decreased appetite, and recent feelings of intense guilt regarding the state of his personal relationships. He says that everything "feels slower" than it used to. He endorses having a similar four-week period of feeling this way last year. He denies thoughts of self-harm or harm of others. He also denies racing thoughts or delusions of grandeur. Which of the following would be an INAPPROPRIATE first line treatment for him?
- A. Paroxetine
- B. Electroconvulsive therapy (Correct Answer)
- C. Citalopram
- D. Psychotherapy
- E. Sertraline
ECT and neuromodulation therapies Explanation: ***Electroconvulsive therapy***
- This is generally reserved for **severe depression** that is unresponsive to other treatments or for depression with **psychotic features**, severe suicidality, or catatonia.
- Given the patient's presentation, **ECT** would be an overly aggressive **first-line** treatment choice.
*Paroxetine*
- **Paroxetine** is a **SSRI** and is considered a **first-line antidepressant** for major depressive disorder.
- It works by increasing serotonin levels in the brain to improve mood.
*Citalopram*
- **Citalopram** is an **SSRI** and is also a **first-line treatment option** for major depressive disorder, often well-tolerated.
- It helps regulate mood and alleviate symptoms like those described by the patient.
*Psychotherapy*
- **Psychotherapy**, particularly **cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)** or **interpersonal therapy (IPT)**, is often a **first-line treatment**, either alone or in combination with medication, for depression.
- It can help the patient address negative thought patterns and coping mechanisms.
*Sertraline*
- **Sertraline** is another **SSRI** commonly used as a **first-line agent** for major depressive disorder due to its efficacy and relatively favorable side-effect profile.
- It helps to improve symptoms such as low mood, sleep disturbances, and decreased appetite.
ECT and neuromodulation therapies US Medical PG Question 7: A 38-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for complaints of insomnia. She states that for the last 8 months, she has had difficulty falling asleep. Additionally, she awakens in the middle of the night or early morning and cannot fall back to sleep. When further questioned, she reports decreased appetite with a 12-lb. weight loss in the last 6 months. She was recently demoted at her work as a baker due to trouble focusing and coordinating orders and excess fatigue. She feels she is to blame for her family's current financial status given her demotion. She is given a prescription for fluoxetine at this visit with follow-up 2 weeks later. At the follow-up visit, she reports no improvement in her symptoms despite taking her medication consistently. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Increase dose of current medication
- B. Switch to bupropion
- C. Add lithium
- D. Switch to paroxetine
- E. Continue current medication (Correct Answer)
ECT and neuromodulation therapies Explanation: ***Continue current medication***
- It takes approximately **4-6 weeks** for an antidepressant, such as fluoxetine, to reach its full therapeutic effect and for patients to experience significant symptom improvement.
- Due to the **delayed onset of action**, continuing the medication for a longer period is necessary to assess its efficacy before making changes.
*Increase dose of current medication*
- Increasing the dose after only 2 weeks is premature as the medication has not had sufficient time to reach its **therapeutic plasma concentration** or demonstrate its full effect.
- Adjusting the dose too early could also increase the risk of **side effects** without a clear benefit.
*Switch to bupropion*
- Switching to a different antidepressant like bupropion after just 2 weeks is also premature, as the patient has not had an adequate trial of fluoxetine.
- Bupropion has a different mechanism of action and side effect profile but also requires a similar **onset period** for efficacy.
*Add lithium*
- Lithium is primarily used as a **mood stabilizer** in bipolar disorder or as an augmentation strategy for treatment-resistant depression.
- There is no indication of bipolar disorder, and it's too early to consider her depression as **treatment-resistant** given the short duration of fluoxetine use.
*Switch to paroxetine*
- Switching to another **SSRI** (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor) like paroxetine after only 2 weeks is not appropriate because the initial SSRI has not been given sufficient time to work.
- The patient has not failed therapy with fluoxetine yet, and such a change would unnecessarily prolong the search for an effective treatment.
ECT and neuromodulation therapies US Medical PG Question 8: A 26-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his roommate after he was found attempting to commit suicide. His roommate says that he stopped him before he was about to jump off the balcony. He has been receiving treatment for depression for about a year. 6 months ago, he had come to the hospital reporting decreased interest in his daily activities and inability to concentrate on his work. He had stopped going out or accepting invitations for any social events. He spent several nights tossing and turning in bed. He also expressed guilt for being unable to live up to his parents’ expectations. His psychiatrist started him on fluoxetine. He says that none of the medications have helped even though the dose of his medication was increased on several occasions, and he was also switched to other medications over the course of the past year. He has mentioned having suicidal thoughts due to his inability to cope with daily activities, but this is the first time he has ever attempted it. Which of the following would this patient be a suitable candidate for?
- A. Electroconvulsive therapy (Correct Answer)
- B. Exposure therapy
- C. Cognitive behavioral therapy
- D. Olanzapine
- E. Amitriptyline
ECT and neuromodulation therapies Explanation: ***Electroconvulsive therapy***
- The patient exhibits **severe, treatment-resistant depression with active suicidal ideation and a recent attempt**, making ECT an appropriate and often life-saving intervention.
- ECT is highly effective for severe depression, especially when other treatments have failed and there is an **imminent risk of suicide**.
*Exposure therapy*
- This therapy is primarily used for **anxiety disorders, phobias, and PTSD**, where it helps individuals confront fears.
- It is not indicated for treating severe, persistent depressive episodes or acute suicidal ideation.
*Cognitive behavioral therapy*
- While CBT is effective for depression, this patient's **severe and refractory nature of his depression**, coupled with an active suicide attempt, indicates a need for a more rapid and intensive intervention than CBT alone can provide.
- CBT by itself would generally not be sufficient for a patient with **acute suicidal risk** who has failed multiple pharmacological treatments.
*Olanzapine*
- Olanzapine is an **antipsychotic medication** that can be used as an adjunct in treatment-resistant depression, but it is not typically the first-line augmentation strategy after multiple antidepressant failures and is not as rapidly effective for acute suicidality as ECT.
- Using an atypical antipsychotic like olanzapine alone would not address the immediate, life-threatening risk as effectively as ECT in this severe situation.
*Amitriptyline*
- Amitriptyline is a **tricyclic antidepressant (TCA)**, which is an older class of antidepressants.
- Given the patient has failed multiple prior antidepressant trials and presents with severe, suicidal depression, starting another antidepressant, especially a TCA with its **higher side effect profile and slower onset of action**, would not be appropriate for immediate risk management.
ECT and neuromodulation therapies US Medical PG Question 9: A 29-year-old man is being monitored at the hospital after cutting open his left wrist. He has a long-standing history of unipolar depressive disorder and multiple trials of antidepressants. The patient expresses thoughts of self-harm and does not deny suicidal intent. A course of electroconvulsive therapy is suggested. His medical history is not significant for other organic illness. Which of the following complications of this therapy is this patient at greatest risk for?
- A. Acute kidney injury
- B. Acute coronary syndrome
- C. Anterograde amnesia
- D. Intracranial hemorrhage
- E. Retrograde amnesia (Correct Answer)
ECT and neuromodulation therapies Explanation: ***Retrograde amnesia***
- **Retrograde amnesia**, specifically memory loss for events occurring prior to the treatment, is a common and often transient side effect of **electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)**.
- While generally temporary, it can be distressing for patients and is a significant consideration when recommending ECT, especially in patients with otherwise healthy brains.
*Acute kidney injury*
- **Acute kidney injury (AKI)** is not a typical direct complication of **ECT**.
- While fluid and electrolyte imbalances or certain medications used during ECT (e.g., muscle relaxants) could theoretically impact renal function in predisposed individuals, it is not a primary concern in a patient with no significant history of organic illness.
*Acute coronary syndrome*
- **Acute coronary syndrome (ACS)** is a potential risk associated with the physiological stress of **ECT**, which can include transient **hypertension** and **tachycardia**.
- However, in a 29-year-old with no significant medical history, the risk is considerably lower compared to older patients or those with pre-existing cardiovascular disease.
*Anterograde amnesia*
- **Anterograde amnesia**, the inability to form new memories after the treatment, is typically less common and usually milder than retrograde amnesia following **ECT**.
- While some patients may experience transient difficulty recalling new information immediately post-ECT, it is usually less pronounced than the impact on remote memories.
*Intracranial hemorrhage*
- **Intracranial hemorrhage** is an extremely rare and severe complication of **ECT**, typically associated with pre-existing cerebral vascular abnormalities or uncontrolled hypertension during the procedure.
- In a young patient with no organic illness, the risk of this complication is exceedingly low.
ECT and neuromodulation therapies US Medical PG Question 10: A 73-year-old woman is brought to the physician by her son because of increasing forgetfulness over the past 2 years. Initially, she used to misplace keys and forget her dog's name or her phone number. Now, she often forgets about what she has seen on television or read about the day before. She used to go for a walk every morning but stopped one month ago after she became lost on her way back home. Her son has prevented her from cooking because she has had episodes of leaving the gas stove on after making a meal. She becomes agitated when asked questions directly but is unconcerned when her son reports her history and says he is overprotective of her. She has hypertension, coronary artery disease, and hypercholesterolemia. Current medications include aspirin, enalapril, carvedilol, and atorvastatin. She is alert and oriented to place and person but not to time. Vital signs are within normal limits. Short- and long-term memory deficits are present. Her speech rhythm is normal but is frequently interrupted as she thinks of words to frame her sentences. She makes multiple errors while performing serial sevens. Her clock drawing is impaired and she draws 14 numbers. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Lewy-body dementia
- B. Alzheimer disease (Correct Answer)
- C. Frontotemporal dementia
- D. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
- E. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
ECT and neuromodulation therapies Explanation: **Alzheimer disease**
- The patient's presentation with **progressive memory impairment** (misplacing keys, forgetting recent events), **executive dysfunction** (getting lost, leaving stove on, impaired clock drawing), and **language difficulties** (word-finding pauses) over 2 years is highly characteristic of Alzheimer disease.
- The **insidious onset** and gradual cognitive decline affecting multiple domains, along with relative preservation of motor function initially, are key diagnostic features.
*Lewy-body dementia*
- This condition is often characterized by **fluctuating cognition**, **visual hallucinations**, and **parkinsonism**, none of which are prominent in this patient's presentation.
- While memory impairment can occur, the core features of Lewy body dementia are not described here.
*Frontotemporal dementia*
- **Early behavioral changes** (e.g., disinhibition, apathy) or **prominent language deficits** (e.g., aphasia without initial memory problems) are common in frontotemporal dementia.
- This patient's primary complaint is memory loss, and behavioral changes are reactive rather than disinhibited, making frontotemporal dementia less likely.
*Normal pressure hydrocephalus*
- The classic triad for normal pressure hydrocephalus includes **gait disturbance**, **urinary incontinence**, and **dementia**.
- While dementia is present, there is no mention of gait abnormalities or urinary issues in this patient.
*Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease*
- This is a rapidly progressive and fatal neurodegenerative disorder with a typical course of **weeks to months**, not 2 years.
- It usually presents with **myoclonus**, **ataxia**, and **rapidly progressive dementia**, which are not seen in this case.
More ECT and neuromodulation therapies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.