Depression with melancholic features US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Depression with melancholic features. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Depression with melancholic features US Medical PG Question 1: A 28-year-old woman presents with depressed mood lasting for most days of the week for the past month. She also mentions that she has lost her appetite for the past 3 weeks. She adds that her job performance has significantly deteriorated because of these symptoms, and she feels like she will have to quit her job soon. Upon asking about her hobbies, she says that she used to enjoy dancing and music but does not have any desire to do them anymore. The patient’s husband says that she has had many sleepless nights last month. The patient denies any history of smoking, alcohol intake, or use of illicit substances. No significant past medical history. Physical examination is unremarkable. Routine laboratory tests are all within normal limits. Which of the following clinical features must be present, in addition to this patient’s current symptoms, to confirm the diagnosis of a major depressive episode?
- A. Intense fear of losing control
- B. Lack of concentration (Correct Answer)
- C. Weight loss
- D. Anterograde amnesia
- E. Nightmares
Depression with melancholic features Explanation: ***Lack of concentration***
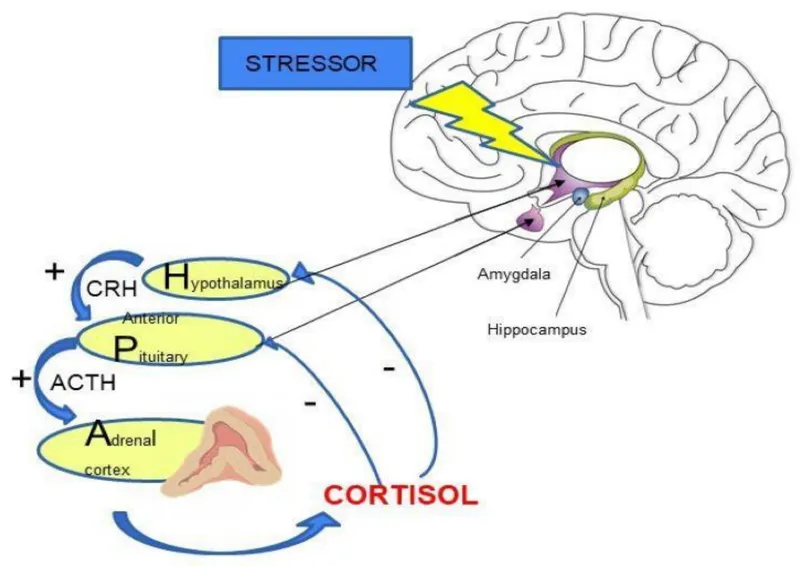
- The diagnostic criteria for a **major depressive episode** (DSM-5) require at least **5 out of 9 cardinal symptoms** present for at least 2 weeks, with at least one being either **depressed mood** or **anhedonia**.
- This patient currently has **4 symptoms**: (1) depressed mood, (2) anhedonia (loss of interest in dancing/music), (3) appetite disturbance (loss of appetite), and (4) sleep disturbance (insomnia).
- To meet diagnostic criteria, she needs **one more symptom** from the remaining options: fatigue, feelings of worthlessness/guilt, **diminished ability to concentrate or indecisiveness**, psychomotor changes, or suicidal ideation.
- **Lack of concentration** is one of the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria and would bring her total to 5 symptoms, confirming the diagnosis.
*Intense fear of losing control*
- This symptom is characteristic of **panic disorder** or anxiety disorders, where individuals experience sudden, intense episodes of fear with accompanying physical and cognitive symptoms.
- While anxiety can co-occur with depression, intense fear of losing control is **not a DSM-5 diagnostic criterion** for major depressive episode.
*Weight loss*
- The patient already has **loss of appetite**, which satisfies the weight/appetite criterion for major depressive episode.
- **Weight loss and appetite changes are part of the same diagnostic criterion**, not separate ones. Therefore, weight loss would not add an additional criterion to reach the required 5 symptoms.
- While clinically significant weight loss can occur in depression, it would not provide the "additional" criterion needed in this case.
*Anterograde amnesia*
- **Anterograde amnesia** (inability to form new memories) is associated with neurological conditions such as **hippocampal damage**, **Korsakoff syndrome**, or **traumatic brain injury**.
- It is **not a DSM-5 diagnostic criterion** for major depressive episode, though some cognitive impairment (concentration difficulties) may occur.
*Nightmares*
- The patient already has **insomnia** (sleep disturbance), which is one of the DSM-5 diagnostic criteria.
- While nightmares may occur in depression, they are not a separate diagnostic criterion and would not add to the symptom count since sleep disturbance is already present.
Depression with melancholic features US Medical PG Question 2: A mental health volunteer is interviewing locals as part of a community outreach program. A 46-year-old man discloses that he has felt sad for as long as he can remember. He feels as though his life is cursed and if something terrible can happen to him, it usually will. He has difficulty making decisions and feels hopeless. He also feels that he has had worsening suicidal ideations, guilt from past problems, decreased energy, and poor concentration over the past 2 weeks. He is otherwise getting enough sleep and able to hold a job. Which of the following statement best describes this patient's condition?
- A. The patient may have symptoms of mania or psychosis.
- B. The patient is likely to show anhedonia.
- C. The patient likely has paranoid personality disorder.
- D. The patient has double depression. (Correct Answer)
- E. The patient should be started on an SSRI.
Depression with melancholic features Explanation: ***The patient has double depression.***
- The patient describes **chronic low-grade depressive symptoms** ("felt sad for as long as he can remember," "life is cursed," "difficulty making decisions," "hopeless") consistent with **persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia)**, which requires at least 2 years of symptoms.
- The recent worsening of symptoms over the past two weeks, including "worsening suicidal ideations, guilt from past problems, decreased energy, and poor concentration," indicates an additional **major depressive episode (MDE) superimposed on dysthymia**, a condition known as **double depression**.
- This patient currently meets criteria for both conditions simultaneously, not just at risk for developing them.
*The patient may have symptoms of mania or psychosis.*
- There are no symptoms mentioned that suggest **mania**, such as elevated mood, increased energy, decreased need for sleep, grandiosity, or racing thoughts.
- While suicidal ideation is present, there is no evidence of **psychotic features** like hallucinations or delusions.
*The patient is likely to show anhedonia.*
- **Anhedonia** (inability to feel pleasure) is a common symptom of depression and may well be present in this patient.
- However, the patient's presentation specifically highlights the pattern of **chronic dysthymia with a superimposed major depressive episode**, making **double depression** a more precise, comprehensive, and diagnostically specific description of his current condition.
- While anhedonia might be present, it is a symptom rather than a diagnostic formulation.
*The patient likely has paranoid personality disorder.*
- **Paranoid personality disorder** is characterized by pervasive distrust and suspicion of others, interpreting their motives as malevolent, without sufficient basis.
- The patient's feelings of being "cursed" and that "something terrible can happen" reflect **depressive pessimism and negative cognitive distortions**, not paranoid ideation about others' intentions.
- This is consistent with the hopelessness seen in depression.
*The patient should be started on an SSRI.*
- While an **SSRI (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor)** combined with psychotherapy would likely be appropriate treatment for double depression, making a specific treatment recommendation is premature without comprehensive clinical assessment.
- The question asks for the **best statement describing the patient's condition** (diagnosis), not for treatment recommendations.
Depression with melancholic features US Medical PG Question 3: A 24-year-old male comes into the psychiatric clinic complaining of consistent sadness. He endorses feelings of worthlessness, anxiety, and anhedonia for the past couple months but denies feeling suicidal. He further denies any past episodes of feeling overly energetic with racing thoughts. Confident of the diagnosis, you recommend frequent talk therapy along with a long-term prescription of a known first-line medication for this disorder. What is the drug and what are some of the most frequently encountered side effects?
- A. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; hypomania, suicidal thoughts
- B. Tricyclic antidepressants; hypomania, suicidal thoughts
- C. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; anorgasmia, insomnia (Correct Answer)
- D. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors; Orthostatic hypotension, weight gain
- E. Tricyclic antidepressants; Orthostatic hypotension, anticholinergic effects
Depression with melancholic features Explanation: ***Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; anorgasmia, insomnia***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **major depressive disorder**, including persistent sadness, worthlessness, anxiety, and anhedonia, without any history of manic or hypomanic episodes. **SSRIs** are considered first-line pharmacotherapy for this condition.
- Common side effects of SSRIs include **sexual dysfunction** (e.g., anorgasmia, decreased libido) and **insomnia** or agitation, especially during the initial weeks of treatment.
*Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; hypomania, suicidal thoughts*
- While SSRIs are the correct drug class, **hypomania** is not a frequent side effect in patients without bipolar disorder. For patients with bipolar disorder, antidepressant monotherapy can induce hypomania or mania, but this patient denies such episodes.
- **Suicidal thoughts** can occur, particularly in young adults, during the initial phase of antidepressant treatment, but it is less common to frame it as a *frequently encountered side effect* in the general population compared to sexual dysfunction or sleep disturbances.
*Tricyclic antidepressants; hypomania, suicidal thoughts*
- **Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)** are generally not first-line due to their less favorable side effect profile compared to SSRIs, including significant anticholinergic effects and cardiovascular risks.
- As with SSRIs, **hypomania** is not a typical frequent side effect in unipolar depression, and while **suicidal thoughts** are a concern with antidepressants, TCAs carry a higher risk of lethality in overdose, making them less preferred initially.
*Monoamine oxidase inhibitors; Orthostatic hypotension, weight gain*
- **Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)** are effective but are typically reserved for **refractory depression** due to their significant drug and food interactions (e.g., tyramine-induced hypertensive crisis).
- While **orthostatic hypotension** and **weight gain** are known side effects of MAOIs, this class is not considered a first-line treatment for major depressive disorder.
*Tricyclic antidepressants; Orthostatic hypotension, anticholinergic effects*
- **TCAs** are indeed associated with side effects such as **orthostatic hypotension** and prominent **anticholinergic effects** (e.g., dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, urinary retention).
- However, because of these more burdensome side effects and higher toxicity in overdose, TCAs are not generally considered the first-line medication choice, especially when SSRIs are available and safer.
Depression with melancholic features US Medical PG Question 4: A 31-year-old G1P0 woman is brought into the emergency room by the police after a failed suicide attempt. She jumped off a nearby bridge but was quickly rescued by some nearby locals. The height of the bridge was not significant, so the patient did not sustain any injuries. For the 3 weeks before this incident, the patient says she had been particularly down, lacking energy and unable to focus at home or work. She says she no longer enjoys her usual hobbies or favorite meals and is not getting enough sleep. Which of the following is the best course of treatment for this patient?
- A. Bupropion
- B. Paroxetine
- C. Combination of SSRI and SNRI
- D. Phenelzine
- E. Electroconvulsive therapy (Correct Answer)
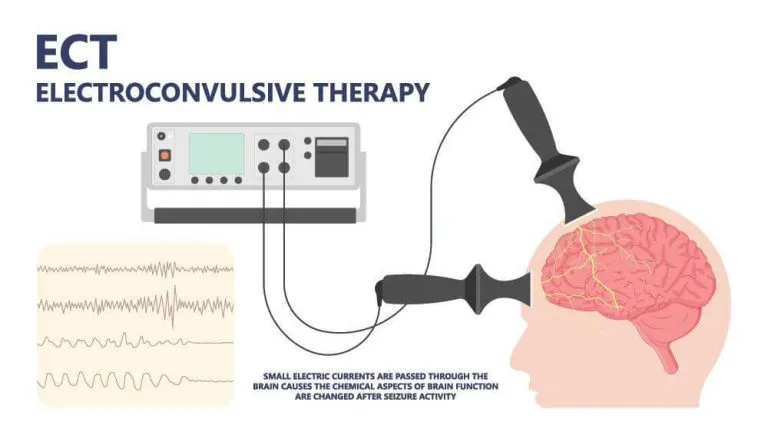
Depression with melancholic features Explanation: ***Electroconvulsive therapy***
- This patient presents with **severe depression with suicidal ideation** (a failed suicide attempt), which warrants urgent intervention. **ECT** is highly effective for severe depression, especially when there is an acute suicide risk or psychotic features.
- ECT has a **rapid onset of action** compared to antidepressants, which is crucial for patients at high risk of self-harm, and is considered **safe in pregnancy**.
*Bupropion*
- **Bupropion** is an antidepressant that primarily inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine. While effective for depression, it has a slower onset of action than ECT and may not be sufficient for severe, acute suicidal ideation.
- It is often used for depression with atypical features or for patients who experience sexual side effects with SSRIs, but it is **contraindicated in patients with a history of seizures or eating disorders**.
*Paroxetine*
- **Paroxetine** is an SSRI commonly used for depression and anxiety disorders. Like other antidepressants, it has a delayed onset of action (several weeks) and may not be appropriate for the immediate management of a patient with recent, severe suicidal ideation.
- One of the major concerns with paroxetine in this patient population is that it has a **higher rate of teratogenicity and neonatal complications** compared to other SSRIs, which is relevant given the patient is G1P0.
*Combination of SSRI and SNRI*
- Combining an **SSRI and an SNRI** (e.g., fluoxetine and venlafaxine) is a strategy sometimes used for treatment-resistant depression. However, like monotherapy with these agents, it still has a delayed onset of action.
- The combination also carries a **higher risk of side effects** compared to monotherapy.
*Phenelzine*
- **Phenelzine** is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). MAOIs are effective antidepressants but are typically reserved for **treatment-resistant depression** due to their significant drug-drug and drug-food interactions (e.g., **hypertensive crisis with tyramine-rich foods or sympathomimetics**).
- Given the patient's acute suicidal risk, a treatment with a more rapid and safer profile, such as ECT, would be preferred over initiating an MAOI.
Depression with melancholic features US Medical PG Question 5: A 34-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 6-week history of depressed mood, loss of interest, and difficulty sleeping. She also has had a 4.5-kg (10-lb) weight loss during this period. She has not been as productive as before at work due to difficulty concentrating. There is no evidence of suicidal ideation. Laboratory studies including thyroid-stimulating hormone are within the reference range. The physician prescribes treatment with escitalopram. This drug targets a neurotransmitter that is produced in which of the following brain structures?
- A. Substantia nigra
- B. Raphe nucleus (Correct Answer)
- C. Nucleus accumbens
- D. Basal nucleus of Meynert
- E. Locus coeruleus
Depression with melancholic features Explanation: ***Raphe nucleus***
- **Escitalopram** is a **selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)**, and the **raphe nuclei** are the primary source of serotonin production in the brain.
- Serotonergic neurons originating from the raphe nuclei project widely throughout the brain, influencing mood, sleep, appetite, and cognition.
*Substantia nigra*
- The **substantia nigra** is primarily associated with **dopamine production**, particularly in the nigrostriatal pathway, which is crucial for motor control.
- Dysfunction in this area is a hallmark of **Parkinson's disease**, not directly targeted by SSRIs for depression.
*Nucleus accumbens*
- The **nucleus accumbens** is a key component of the **reward pathway** and is primarily involved in dopamine and pleasure, not the primary site of serotonin production.
- While dopamine dysfunction can contribute to mood disorders, SSRIs do not directly target dopamine production in this area.
*Basal nucleus of Meynert*
- The **basal nucleus of Meynert** is a major source of **acetylcholine** in the brain, playing a critical role in memory and learning.
- Degeneration of these neurons is associated with **Alzheimer's disease**, and it is not involved in serotonin synthesis.
*Locus coeruleus*
- The **locus coeruleus** is the primary site of **norepinephrine production** in the brain, involved in arousal, attention, and stress responses.
- While norepinephrine is implicated in mood disorders, escitalopram specifically targets **serotonin reuptake**, not norepinephrine synthesis, which occurs in the locus coeruleus.
Depression with melancholic features US Medical PG Question 6: A 27-year old gentleman presents to the primary care physician with the chief complaint of "feeling down" for the last 6 weeks. He describes trouble falling asleep at night, decreased appetite, and recent feelings of intense guilt regarding the state of his personal relationships. He says that everything "feels slower" than it used to. He endorses having a similar four-week period of feeling this way last year. He denies thoughts of self-harm or harm of others. He also denies racing thoughts or delusions of grandeur. Which of the following would be an INAPPROPRIATE first line treatment for him?
- A. Paroxetine
- B. Electroconvulsive therapy (Correct Answer)
- C. Citalopram
- D. Psychotherapy
- E. Sertraline
Depression with melancholic features Explanation: ***Electroconvulsive therapy***
- This is generally reserved for **severe depression** that is unresponsive to other treatments or for depression with **psychotic features**, severe suicidality, or catatonia.
- Given the patient's presentation, **ECT** would be an overly aggressive **first-line** treatment choice.
*Paroxetine*
- **Paroxetine** is a **SSRI** and is considered a **first-line antidepressant** for major depressive disorder.
- It works by increasing serotonin levels in the brain to improve mood.
*Citalopram*
- **Citalopram** is an **SSRI** and is also a **first-line treatment option** for major depressive disorder, often well-tolerated.
- It helps regulate mood and alleviate symptoms like those described by the patient.
*Psychotherapy*
- **Psychotherapy**, particularly **cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)** or **interpersonal therapy (IPT)**, is often a **first-line treatment**, either alone or in combination with medication, for depression.
- It can help the patient address negative thought patterns and coping mechanisms.
*Sertraline*
- **Sertraline** is another **SSRI** commonly used as a **first-line agent** for major depressive disorder due to its efficacy and relatively favorable side-effect profile.
- It helps to improve symptoms such as low mood, sleep disturbances, and decreased appetite.
Depression with melancholic features US Medical PG Question 7: A 17-year-old white female with a history of depression is brought to your office by her parents because they are concerned that she is acting differently. She is quiet and denies any changes in her personality or drug use. After the parents step out so that you can speak alone, she begins crying. She states that school has been very difficult and has been very depressed for the past 2 months. She feels a lot of pressure from her parents and coaches and says she cannot handle it anymore. She says that she has been cutting her wrists for the past week and is planning to commit suicide. She instantly regrets telling you and begs you not to tell her parents. What is the most appropriate course of action?
- A. Prescribe an anti-depressant medication and allow her to return home
- B. Refer her to a psychiatrist
- C. Explain to her that she will have to be hospitalized as she is an acute threat to herself (Correct Answer)
- D. Tell her parents about the situation and allow them to handle it as a family
- E. Prescribe an anti-psychotic medication
Depression with melancholic features Explanation: ***Explain to her that she will have to be hospitalized as she is an acute threat to herself***
- This patient is actively suicidal and engaging in **self-harm (cutting)**, which represents an immediate and serious risk to her life, necessitating **involuntary hospitalization** for her safety.
- In cases of acute suicidality, the ethical principle of **beneficence** (acting in the patient's best interest) and **non-maleficence** (avoiding harm) overrides confidentiality to ensure the patient's immediate safety.
*Prescribe an anti-depressant medication and allow her to return home*
- While an antidepressant may be part of long-term management, simply prescribing medication and sending her home is **inappropriate and dangerous** given her active suicidal ideation and self-harm.
- Antidepressants can have a delayed onset of action (2-4 weeks) and, in some adolescents, may initially increase the risk of **suicidal thoughts**, making close monitoring essential.
*Refer her to a psychiatrist*
- A referral to a psychiatrist is crucial for comprehensive evaluation and long-term treatment, but it does **not address the immediate danger** presented by her active suicidal plans and self-harm.
- An urgent psychiatric consultation or hospitalization is needed first, with a referral following stabilization.
*Tell her parents about the situation and allow them to handle it as a family*
- While parents must be informed, simply delegating the responsibility to them is **insufficient and potentially negligent** given the patient's acute suicidal risk.
- **Medical professionals** have a duty to ensure the safety of a suicidal minor, which often requires a higher level of intervention than parental supervision alone.
*Prescribe an anti-psychotic medication*
- There is **no indication of psychosis** in this patient's presentation; her symptoms are consistent with severe depression and acute suicidality.
- Prescribing an antipsychotic would be **inappropriate** and could cause unnecessary side effects without addressing the underlying depressive disorder or acute suicidal crisis.
Depression with melancholic features US Medical PG Question 8: A 35-year-old banker is brought to a medical clinic by his concerned wife. For the past 3 weeks, he has not been eating well and has had a 10 kg (22 lb) weight loss. He wakes up very early in the mornings and feels extremely despondent. He no longer goes out on the weekends to hang out with his close friends nor does he go on date nights with his wife. He feels guilty for letting his friends and family down recently. He additionally has a history of fibromyalgia and deals with daily pain. What would be the most appropriate treatment plan for this patient?
- A. Amitriptyline
- B. Phenelzine
- C. Venlafaxine (Correct Answer)
- D. Electroconvulsive therapy
- E. Fluoxetine
Depression with melancholic features Explanation: ***Venlafaxine***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **major depressive disorder**, including **anhedonia**, significant **weight loss**, **early morning awakening**, and **feelings of guilt**. His co-occurring **fibromyalgia** makes a **serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI)** like venlafaxine an excellent choice.
- SNRIs are effective for both depression and chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia, as they modulate both **serotonin** and **norepinephrine** pathways, which are implicated in both mood and pain perception.
*Amitriptyline*
- **Amitriptyline** is a **tricyclic antidepressant (TCA)** that can be used for both depression and chronic pain, including fibromyalgia.
- However, TCAs generally have a less favorable side effect profile (e.g., **anticholinergic effects**, **cardiac toxicity in overdose**) compared to SNRIs and SSRIs, making them less of a first-line choice unless other options fail or specific indications are present.
*Phenelzine*
- **Phenelzine** is a **monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)**, typically reserved for **atypical depression** or treatment-resistant depression due to its significant **food and drug interactions** (e.g., **hypertensive crisis** with tyramine-rich foods or sympathomimetics).
- Given this is likely a first-line treatment scenario, an MAOI would not be the most appropriate initial choice.
*Electroconvulsive therapy*
- **Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)** is a highly effective treatment for severe depression, especially with **psychotic features**, **catatonia**, or **severe suicidality**, or in cases of **treatment resistance** where other modalities have failed.
- While the patient has significant symptoms of depression, there is no indication of immediate life-threatening severity (e.g., active suicidal intent with a plan) or treatment resistance to warrant ECT as a first-line option.
*Fluoxetine*
- **Fluoxetine** is a **selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)** and a common first-line treatment for major depressive disorder.
- While it would be effective for the patient's depression, it does not offer the additional specific benefit for **fibromyalgia pain** that an SNRI like venlafaxine provides through dual serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition.
Depression with melancholic features US Medical PG Question 9: A 23-year-old man comes to the physician with a 1-week history of sharp, substernal chest pain that is worse with inspiration and relieved with leaning forward. He has also had nausea and myalgias. His father has coronary artery disease. His temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 110/min, and blood pressure is 130/84 mm Hg. Cardiac examination shows a high-pitched rubbing sound between S1 and S2 that is best heard at the left sternal border. An ECG shows depressed PR interval and diffuse ST elevations. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Dressler syndrome
- B. Acute pericarditis (Correct Answer)
- C. Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
- D. Systemic lupus erythematosus
- E. Acute myocardial infarction
Depression with melancholic features Explanation: ***Acute pericarditis***
- The patient's **sharp, substernal chest pain** that is **worse with inspiration** and **relieved by leaning forward** is a classic presentation of acute pericarditis.
- The **pericardial friction rub** on cardiac examination and **diffuse ST elevations** with a **depressed PR interval** on ECG are highly characteristic findings.
*Dressler syndrome*
- Dressler syndrome is a **late complication of myocardial infarction or cardiac surgery**, typically occurring weeks to months afterward.
- This patient's symptoms developed over a week and are not preceded by such events.
*Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection*
- While *Mycobacterium tuberculosis* can cause pericarditis, it typically presents as **chronic constrictive pericarditis** with effusions and more systemic symptoms like significant fever and night sweats.
- The acute onset and classic ECG findings are less consistent with tuberculous pericarditis.
*Systemic lupus erythematosus*
- SLE can cause pericarditis, but it's usually part of a **multi-system inflammatory picture** with other classic SLE symptoms (e.g., malar rash, arthralgias, renal involvement).
- There are no other features to suggest SLE in this case, and the isolated, acute presentation points more directly to infectious or idiopathic pericarditis.
*Acute myocardial infarction*
- While an MI causes chest pain and ST elevations, the pain is usually described as **crushing or heavy**, not typically pleuritic or relieved by leaning forward.
- **PR depression** is not seen in MI, and the ST elevations are usually localized to specific arterial territories, not diffuse.
Depression with melancholic features US Medical PG Question 10: A 72-year-old man presents to the emergency department because of difficulty breathing and sharp chest pain. The chest pain increases in intensity with lying down, and it radiates to the scapular ridge. Approximately 3 weeks ago, he had an anterior ST-elevation myocardial infarction, which was treated with intravenous alteplase. He was discharged home in a stable condition. Current vital signs include a temperature of 38.1 (100.5°F), blood pressure of 131/91 mm Hg, and pulse of 99/min. On examination, heart sounds are distant and a scratching sound is heard on the left sternal border. ECG reveals widespread concave ST elevations in the precordial leads and PR depressions in leads V2-V6. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient condition?
- A. Recurrent infarction
- B. Myocarditis
- C. Aortic dissection
- D. Dressler’s syndrome (Correct Answer)
- E. Ventricular aneurysm
Depression with melancholic features Explanation: ***Dressler’s syndrome***
- This syndrome, also known as **post-myocardial infarction syndrome**, typically presents weeks to months after an MI and is characterized by pleuritic chest pain, fever, and pericardial friction rub.
- The **widespread ST elevations (concave)** and **PR depressions** on ECG are classic findings of pericarditis, which is the underlying pathology of Dressler's syndrome.
*Recurrent infarction*
- While an MI can cause chest pain, the pain associated with infarction is typically **retrosternal, crushing**, and does not improve with leaning forward or worsen with lying down.
- ECG findings of recurrent MI would show **convex ST elevations** in a specific coronary artery territory, not widespread concave ST elevation.
*Myocarditis*
- Myocarditis can cause chest pain, fever, and ECG changes (including ST elevations), but it is primarily an **inflammation of the heart muscle** often due to viral infection.
- In this case, the **pericardial friction rub** and history of recent MI strongly point towards pericardial inflammation, not primarily myocardial inflammation.
*Aortic dissection*
- Aortic dissection presents with **severe, tearing chest pain** that often radiates to the back, but it typically has an abrupt onset and is not associated with a pericardial friction rub or widespread ST elevations.
- The ECG findings of pericarditis do not support acute aortic dissection.
*Ventricular aneurysm*
- A ventricular aneurysm is a late complication of MI and can lead to symptoms like heart failure or arrhythmias, but it does **not typically cause acute pericarditic chest pain** or associated ECG findings.
- While it can cause persistent ST elevation, it would not be widespread and concave, and it wouldn't be associated with a friction rub.
More Depression with melancholic features US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.
 electrode placement)
electrode placement)
