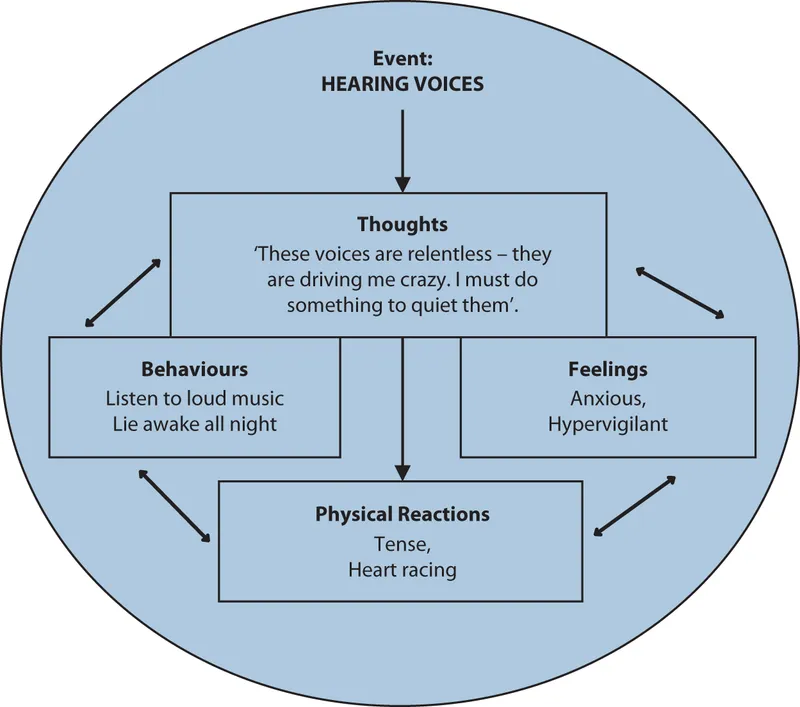
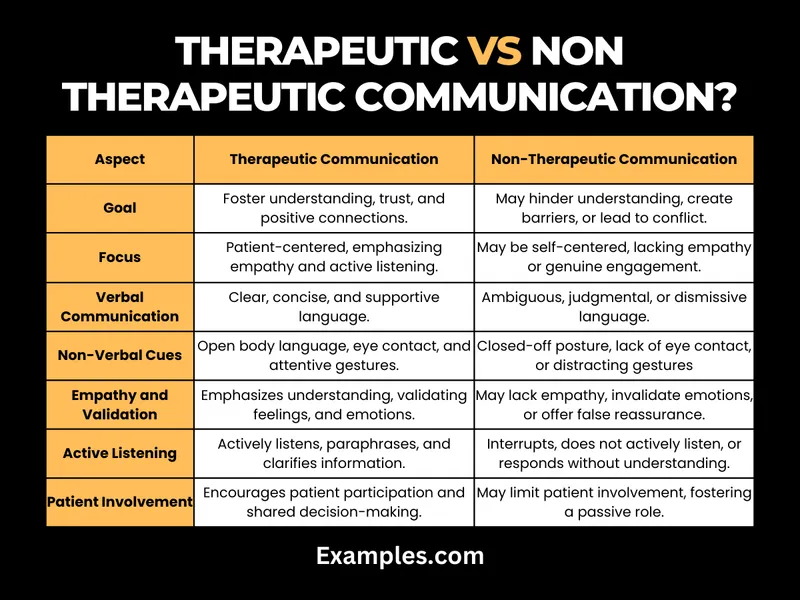
Psychotherapeutic approaches US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Psychotherapeutic approaches. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Psychotherapeutic approaches US Medical PG Question 1: A 23-year-old man presents to an outpatient psychiatrist complaining of anxiety and a persistent feeling that “something terrible will happen to my family.” He describes 1 year of vague, disturbing thoughts about his family members contracting a “horrible disease” or dying in an accident. He believes that he can prevent these outcomes by washing his hands of “the contaminants” any time that he touches something and by performing praying and counting rituals each time that he has unwanted, disturbing thoughts. The thoughts and rituals have become more frequent recently, making it impossible for him to work, and he expresses feeling deeply embarrassed by them. Which of the following is the most effective treatment for this patient's disorder?
- A. Psychodynamic psychotherapy and citalopram
- B. Cognitive behavioral therapy and haloperidol
- C. Cognitive behavioral therapy and clonazepam
- D. Cognitive behavioral therapy and fluoxetine (Correct Answer)
- E. Psychodynamic psychotherapy and aripiprazole
Psychotherapeutic approaches Explanation: ***Cognitive behavioral therapy and fluoxetine***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)**, characterized by intrusive, distressing thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions) performed to neutralize the anxiety.
- **Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)**, specifically Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP), is the most effective psychotherapy for OCD, and **SSRIs** like fluoxetine are the first-line pharmacotherapy.
*Psychodynamic psychotherapy and citalopram*
- While citalopram (an SSRI) is an appropriate pharmacological treatment for OCD, **psychodynamic psychotherapy** is generally not considered first-line or most effective for OCD due to its focus on unconscious conflicts rather than direct symptom reduction.
- This approach may not provide the structured, symptom-focused interventions needed to manage obsessions and compulsions effectively.
*Cognitive behavioral therapy and haloperidol*
- **CBT** is an excellent choice, but **haloperidol**, an antipsychotic, is not a first-line treatment for OCD; it is primarily used for psychotic disorders or as an augmentation strategy in severe, treatment-resistant OCD, which is not indicated here.
- Using an antipsychotic as a primary treatment for OCD without a clear indication of psychosis or severe non-response to SSRIs is inappropriate and can lead to unnecessary side effects.
*Cognitive behavioral therapy and clonazepam*
- **CBT** is appropriate, but **clonazepam**, a benzodiazepine, is generally not recommended as a monotherapy or primary adjunctive treatment for OCD due to its *sedative side effects*, *potential for dependence*, and *lack of efficacy* in addressing the core symptoms of OCD.
- Benzodiazepines may be used for short-term anxiety relief but do not treat the underlying obsessive-compulsive processes.
*Psychodynamic psychotherapy and aripiprazole*
- **Psychodynamic psychotherapy** is not the most effective approach for OCD.
- **Aripiprazole**, an atypical antipsychotic, is typically used as an augmentation strategy for *treatment-resistant OCD* when initial SSRI trials have failed, not as a first-line medication, and this patient's case does not describe treatment resistance.
Psychotherapeutic approaches US Medical PG Question 2: A 20-year-old male is involuntarily admitted to the county psychiatric unit for psychotic behavior over the past three months. The patient's mother explained to the psychiatrist that her son had withdrawn from family and friends, appeared to have no emotions, and had delusions that he was working for the CIA. When he spoke, his sentences did not always seem to have any connection with each other. The mother finally decided to admit her son after he began stating that he "revealed too much information to her and was going to be eliminated by the CIA." Which of the following diagnoses best fits this patient's presentation?
- A. Schizophrenia
- B. Brief psychotic disorder
- C. Schizophreniform disorder (Correct Answer)
- D. Schizoid personality disorder
- E. Schizotypal personality disorder
Psychotherapeutic approaches Explanation: ***Schizophreniform disorder***
- The patient exhibits classic symptoms of **psychosis**, including delusions, disorganized speech, flat affect, and social withdrawal, which are characteristic of schizophrenia spectrum disorders.
- The duration of symptoms (3 months) fits the criteria for **schizophreniform disorder**, which is when psychotic symptoms last between 1 month and 6 months.
*Schizophrenia*
- Schizophrenia requires symptoms to be present for at least **6 months**, including at least 1 month of active-phase symptoms.
- While this patient's symptoms are consistent with psychotic disorder, the **duration criteria** for schizophrenia have not yet been met.
*Brief psychotic disorder*
- Brief psychotic disorder is characterized by symptoms lasting from **1 day to 1 month**, with eventual full return to premorbid functioning.
- The patient's symptoms have persisted for **3 months**, exceeding the maximum duration for brief psychotic disorder.
*Schizoid personality disorder*
- This disorder is characterized by a pervasive pattern of **detachment from social relationships** and a restricted range of emotional expression.
- While the patient exhibits social withdrawal, the presence of **delusions, disorganized speech, and flat affect** indicates a psychotic disorder, not merely a personality disorder.
*Schizotypal personality disorder*
- Schizotypal personality disorder involves pervasive social and interpersonal deficits with **cognitive or perceptual distortions** and eccentric behaviors.
- While it can involve odd beliefs, it does not typically include the prominent, fixed, and systematized **delusions and disorganized speech** seen in this patient's presentation.
Psychotherapeutic approaches US Medical PG Question 3: A 10-year-old child is sent to the school psychologist in May because he refuses to comply with the class rules. His teacher says this has been going on since school started back in August. He gets upset at the teacher regularly when he is told to complete a homework assignment in class. Sometimes he refuses to complete them altogether. Several of his teachers have reported that he intentionally creates noises in class to interrupt the class. He tells the psychologist that the teacher and his classmates are at fault. What is the most appropriate treatment?
- A. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (Correct Answer)
- B. Interpersonal therapy
- C. Administration of lithium
- D. Motivational interviewing
- E. Administration of clozapine
Psychotherapeutic approaches Explanation: ***Cognitive-behavioral therapy***
- This child exhibits symptoms consistent with **Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)**, including persistent refusal to comply with rules, anger outbursts, and blaming others. **CBT** is a highly effective treatment for ODD, teaching children coping skills, anger management, and problem-solving.
- CBT helps children identify and change **maladaptive thought patterns** and behaviors, which is crucial for managing the defiant and argumentative behaviors seen in ODD.
*Interpersonal therapy*
- **Interpersonal therapy (IPT)** primarily focuses on improving interpersonal relationships and communication patterns, often used for depression or eating disorders.
- While improved relationships might be a secondary benefit, IPT does not directly target the core **defiant behaviors** and **anger management** issues central to ODD.
*Administration of lithium*
- **Lithium** is a mood stabilizer primarily used in the treatment of **bipolar disorder** and severe mood dysregulation.
- There is no indication from the provided symptoms (defiance, anger, blaming others) that the child is experiencing a mood disorder that would warrant lithium.
*Motivational interviewing*
- **Motivational interviewing** is a counseling approach that helps individuals resolve ambivalence to change, often used in substance abuse or health behavior change.
- While it can be useful in encouraging willingness to engage in therapy, it is not a direct therapeutic modality for addressing the specific **behavioral challenges** and **underlying cognitive distortions** of ODD.
*Administration of clozapine*
- **Clozapine** is an antipsychotic medication reserved for severe mental illnesses like **treatment-resistant schizophrenia** due to its significant side effects.
- The child's symptoms of defiance and rule-breaking are not indicative of a psychotic disorder requiring antipsychotic medication.
Psychotherapeutic approaches US Medical PG Question 4: A 15-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother for an annual well-child examination. Her mother complains that the patient has a poor diet and spends most of the evening at home texting her friends instead of doing homework. She has been caught smoking cigarettes in the school bathroom several times and appears indifferent to the dean's threats of suspension. Two weeks ago, the patient allowed a friend to pierce her ears with unsterilized safety pins. The mother appeals to the physician to lecture the patient about her behavior and “set her straight.” The patient appears aloof and does not make eye contact. Her grooming is poor. Upon questioning the daughter about her mood, the mother responds “She acts like a rebel. I can't wait until puberty is over.” Which of the following is the most appropriate response?
- A. You should listen to your mother's concerns. You don't want to make poor choices early on or else you might end up on the streets.
- B. Would it be possible for you to step out for a few moments so that I can interview your daughter alone? (Correct Answer)
- C. Let's run a routine urine toxicology screen to make sure your daughter is not doing drugs.
- D. I am very concerned that your daughter is displaying signs of depression, and I'd suggest that she is seen by a psychiatrist.
- E. Your daughter displays normal signs of puberty. Being overly critical of your daughter is not helpful.
Psychotherapeutic approaches Explanation: ***"Would it be possible for you to step out for a few moments so that I can interview your daughter alone?"***
- This approach respects the adolescent's **autonomy** and provides a safe space for her to disclose sensitive information without parental presence.
- Adolescents are more likely to be **candid** about risky behaviors like smoking, substance use, or sexual activity if they feel their privacy is protected.
*"You should listen to your mother's concerns. You don't want to make poor choices early on or else you might end up on the streets."*
- This response is **confrontational** and judgmental, which is likely to alienate the patient and shut down communication.
- It also uses **fear tactics** rather than fostering trust and a therapeutic relationship.
*"Let's run a routine urine toxicology screen to make sure your daughter is not doing drugs."*
- While drug use is a concern given her risky behaviors, immediately suggesting a **toxicology screen** without building rapport can feel accusatory and escalate distrust.
- It's often more effective to establish communication first before moving to definitive testing, especially in a well-child visit where drug use has not been directly admitted.
*"I am very concerned that your daughter is displaying signs of depression, and I'd suggest that she is seen by a psychiatrist."*
- While some of the patient's behaviors (poor grooming, aloofness, indifference) could be consistent with **depression**, immediately jumping to a diagnosis and referral without a direct interview is premature.
- It can also be perceived as labeling and might be rejected by the patient and mother without further exploration.
*"Your daughter displays normal signs of puberty. Being overly critical of your daughter is not helpful."*
- This response dismisses the mother's valid concerns about genuinely **risky behaviors** (smoking, unsterilized piercing, indifference to consequences) as "normal puberty."
- It also implicitly criticizes the mother, which can damage the therapeutic alliance with both the parent and the patient.
Psychotherapeutic approaches US Medical PG Question 5: A 19-year-old male is brought to the emergency department by his roommate for 'strange' behavior over the last 48 hours. The patient states that he is hearing voices speak to him, giving him secret messages and instructions to carry out. He believes that the FBI is following him and spying on his conversations. The patient is concerned that they are listening to these messages and will find out his secrets. The patient's friend does not believe the patient ingested any substance or used any recreational drugs prior to this episode. A negative drug screen is obtained and confirms this. Physical examination does not reveal any abnormalities. Which of the following treatments might best target this patient's symptoms?
- A. Risperidone (Correct Answer)
- B. Psychotherapy
- C. Haloperidol
- D. Chlorpromazine
- E. Sertraline
Psychotherapeutic approaches Explanation: ***Risperidone***
- The patient presents with **auditory hallucinations** and **paranoid delusions**, suggesting an acute psychotic episode, likely the first presentation of **schizophrenia** or a related psychotic disorder.
- **Risperidone** is a second-generation (atypical) antipsychotic, an appropriate first-line treatment for acute psychosis due to its efficacy against both positive and some negative symptoms, with a generally favorable side effect profile compared to first-generation agents.
*Psychotherapy*
- While psychotherapy is a crucial component in the long-term management of psychotic disorders, it is **not sufficient as a monotherapy** for acute psychotic symptoms like prominent hallucinations and delusions, especially in the initial phase.
- Psychotherapy alone would not adequately address the **neurotransmitter imbalances** (e.g., dopamine dysregulation) believed to underlie acute psychosis.
*Haloperidol*
- **Haloperidol** is a first-generation (typical) antipsychotic that is very effective for acute psychosis and severe agitation, primarily by blocking **dopamine D2 receptors**.
- However, first-generation antipsychotics like haloperidol have a **higher risk of extrapyramidal side effects (EPS)**, such as dystonia, akathisia, and parkinsonism, compared to second-generation agents like risperidone, making them generally less preferred for initial treatment unless rapid tranquilization is the main concern or other options are ineffective.
*Chlorpromazine*
- **Chlorpromazine** is another first-generation antipsychotic known for its strong sedative effects and efficacy in treating acute psychosis.
- Similar to haloperidol, it carries a **higher risk of severe side effects**, including **orthostatic hypotension**, sedation, and EPS, making it less favorable as a first-line choice compared to atypical antipsychotics in many acute presentations.
*Sertraline*
- **Sertraline** is a **selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)**, primarily used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
- It has **no significant antipsychotic properties** and would not be effective in treating the patient's acute psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations and delusions.
Psychotherapeutic approaches US Medical PG Question 6: A 16-year-old boy is brought in to a psychiatrist's office by his mother for increasingly concerning erratic behavior. Her son has recently entered a new relationship, and he constantly voices beliefs that his girlfriend is cheating on him. He ended his last relationship after voicing the same beliefs about his last partner. During the visit, the patient reports that these beliefs are justified, since everyone at school is “out to get him.” He says that even his teachers are against him, based on their criticism of his schoolwork. His mother adds that her son has always held grudges against people and has always taken comments very personally. The patient has no psychiatric history and is in otherwise good health. What condition is this patient genetically predisposed for?
- A. Antisocial personality disorder
- B. Major depressive disorder
- C. Narcolepsy
- D. Substance use disorder
- E. Schizophrenia (Correct Answer)
Psychotherapeutic approaches Explanation: ***Schizophrenia***
- The patient's symptoms of **pervasive distrust**, **suspiciousness**, beliefs that others are "out to get him," and taking comments personally are characteristic of **paranoid personality disorder**.
- **Paranoid personality disorder (PPD)** is considered part of the **schizotypal spectrum** or **cluster A personality disorders**, and individuals with PPD have a higher genetic predisposition to develop **schizophrenia** and other psychotic disorders.
*Antisocial personality disorder*
- This disorder is characterized by **disregard for and violation of the rights of others**, impulsivity, and lack of remorse, which are not the primary features described here.
- While individuals with this disorder may exhibit manipulative behavior, their core issue is not paranoid ideation but rather a pattern of social irresponsibility and law-breaking.
*Major depressive disorder*
- This condition is characterized by **persistent sadness**, loss of interest or pleasure, and other vegetative symptoms, which are not present in this patient's presentation.
- The patient's primary symptoms revolve around **paranoia and suspiciousness**, not mood disturbances.
*Narcolepsy*
- Narcolepsy is a **neurological condition** characterized by overwhelming daytime sleepiness and sudden attacks of sleep.
- This diagnosis is entirely unrelated to the patient's psychological symptoms of paranoia and distrust.
*Substance use disorder*
- While substance use can sometimes induce paranoid thinking, the patient's long-standing history of **grudges** and taking comments personally, even prior to potential substance exposure (implied by no psychiatric history mentioned for substance abuse), suggests a more ingrained personality trait rather than solely substance-induced paranoia.
- There is **no information provided about substance use**, making this a less likely primary condition or genetic predisposition.
Psychotherapeutic approaches US Medical PG Question 7: A 23-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a chief complaint of being assaulted on the street. The patient claims that he has been followed by the government for quite some time and that he was assaulted by a government agent but was able to escape. He often hears voices telling him to hide. The patient has an unknown past medical history and admits to smoking marijuana frequently. On physical exam, the patient has no signs of trauma. When interviewing the patient, he is seen conversing with an external party that is not apparent to you. The patient states that he is afraid for his life and that agents are currently pursuing him. What is the best initial response to this patient’s statement?
- A. I think you are safe from the agents here.
- B. You have a mental disorder but don’t worry we will help you.
- C. I don’t think any agents are pursuing you.
- D. What medications are you currently taking?
- E. It sounds like you have been going through some tough experiences lately. (Correct Answer)
Psychotherapeutic approaches Explanation: ***It sounds like you have been going through some tough experiences lately.***
- This response **acknowledges the patient's distress** and experience without validating or refuting their delusional beliefs.
- It helps establish **rapport** and encourages the patient to share more about their symptoms, which is crucial for assessment in a psychiatric emergency.
*I think you are safe from the agents here.*
- While intended to reassure, directly addressing the delusion can be perceived as dismissive and may **escalate the patient's paranoia** or agitation.
- It does not validate their *feelings* of fear, which are real to them, even if the source is delusional.
*You have a mental disorder but don’t worry we will help you.*
- This statement is **confrontational** and judgmental, labeling the patient immediately with a diagnosis.
- This approach can cause the patient to become defensive, shut down, or feel stigmatized, making further assessment and trust-building very difficult in the **initial interaction**.
*I don’t think any agents are pursuing you.*
- Directly **challenging a patient's delusion** is generally unhelpful in acute settings and can lead to increased agitation.
- It invalidates their subjective reality and can make them feel misunderstood or distrustful of the healthcare provider.
*What medications are you currently taking?*
- While important information, asking about medications is too premature as an *initial response* to a patient expressing severe paranoia and fear.
- This question comes across as dismissive of their current emotional state and **prioritizes medical history over emotional support** and rapport-building.
Psychotherapeutic approaches US Medical PG Question 8: A 31-year-old woman comes to the physician because she thinks that her “right wrist is broken.” She says that she has severe pain and that “the bone is sticking out.” She has not had any trauma to the wrist. Her medical records indicate that she was diagnosed with schizophrenia 2 years ago and treated with olanzapine; she has not filled any prescriptions over the past 4 months. Three weeks ago, she stopped going to work because she “did not feel like getting up” in the morning. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination of the right wrist shows no visible injury; there is no warmth, swelling, or erythema. Range of motion is limited by pain. On mental status examination, she has a flat affect. Her speech is pressured and she frequently changes the topic. She has short- and long-term memory deficits. Attention and concentration are poor. There is no evidence of suicidal ideation. Urine toxicology screening is negative. An x-ray of the wrist shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate response to this patient's concerns?
- A. “It seems as though you are having a schizophrenia relapse. If you don't follow my recommendations and take your medications, you will most likely have further and possibly more severe episodes.”
- B. “I cannot see any injury of your wrist and the physical exam as well as the x-ray don't show any injury. I imagine that feeling as if your wrist was broken may be very uncomfortable. Can you tell me more about what it feels like?” (Correct Answer)
- C. I understand your concerns; however, your symptoms seem to be psychological in nature. I would be happy to refer you to a mental health professional.
- D. You are clearly distressed. However, your tests do not suggest a physical problem that can be addressed with medications or surgery. I suggest that we meet and evaluate your symptoms on a regular basis.
- E. I can imagine that you are uncomfortable. That certainly looks painful. Let's take care of this injury first and then we should talk about your problems getting up in the morning.
Psychotherapeutic approaches Explanation: ***“I cannot see any injury of your wrist and the physical exam as well as the x-ray don't show any injury. I imagine that feeling as if your wrist was broken may be very uncomfortable. Can you tell me more about what it feels like?”***
- This response **validates the patient's experience of pain and distress** while gently reorienting them to the objective findings (no physical injury).
- It opens a dialog to explore the **patient's subjective experience** and build trust, which is crucial for addressing underlying psychiatric issues in a patient with schizophrenia.
*“It seems as though you are having a schizophrenia relapse. If you don't follow my recommendations and take your medications, you will most likely have further and possibly more severe episodes.”*
- This statement is **confrontational and judgmental**, potentially alienating the patient and making them less likely to engage in treatment.
- Directly labeling a relapse and warning of future severity without first building rapport can trigger **defensiveness and non-compliance**.
*I understand your concerns; however, your symptoms seem to be psychological in nature. I would be happy to refer you to a mental health professional.*
- While accurate about the psychological nature of symptoms, this response **dismisses the patient's immediate physical complaint** and might make them feel unheard.
- It prematurely jumps to a referral without fully exploring the current presentation or establishing a therapeutic alliance, which can be perceived as the physician "passing the buck."
*I can imagine that you are uncomfortable. That certainly looks painful. Let's take care of this injury first and then we should talk about your problems getting up in the morning.*
- This response **validates a non-existent injury**, reinforcing the patient's delusion and potentially diverting attention from the underlying psychiatric condition.
- Prioritizing a non-existent injury would lead to inappropriate medical interventions and delay necessary psychiatric care.
*You are clearly distressed. However, your tests do not suggest a physical problem that can be addressed with medications or surgery. I suggest that we meet and evaluate your symptoms on a regular basis.*
- While acknowledging distress and the lack of physical pathology, this response is somewhat **vague and lacks a clear plan** for addressing the primary concern of perceived injury.
- "Regular evaluation" without specific intent to explore the psychological component or re-initiate psychiatric treatment may not be sufficient for a patient experiencing a schizophrenia relapse.
Psychotherapeutic approaches US Medical PG Question 9: A 24-year-old woman presents with her husband to a physician with the complaints of fever, cough, and cold for the past 5 days. When the physician asks her if she has taken any medication for her symptoms, she answers, “My husband and I possess great powers to heal sickness. So I tried to cure my symptoms with my power. However, due to some divine cause, it did not work this time, so I thought I should seek medical advice”. Upon asking her husband about this, he says, "I have always had an immense ability to heal others through my powerful thoughts. It is only after I married her that she came to realize the powers within herself.” The physician examines her and prescribes appropriate medications for her symptoms. A year later, the woman presents again to the same physician with a cough and cold for 2 days. The physician asks her why did she not use her ‘power’ this time. She replies, “I separated from my husband 6 months ago, and I no longer believe that I nor my husband had any special power.” The woman denies any hallucinations, mood disturbances, and socio-occupational impairment to date. Which of the following conditions was this patient most likely suffering from?
- A. Brief psychotic disorder
- B. Folie à deux (Correct Answer)
- C. Culture-specific psychosis
- D. Residual phase of schizophrenia
- E. Schizophreniform disorder
Psychotherapeutic approaches Explanation: ***Folie à deux***
- This condition is characterized by a **shared delusional belief** between two or more people who are in a close relationship. One person, typically the dominant partner, has a primary psychotic disorder with delusions, and the other person adopts these delusions.
- In this case, the husband likely initiated the delusional belief about healing powers, which his wife subsequently adopted. Her belief resolved when she separated from him, indicating the **dependent nature** of her delusion.
*Brief psychotic disorder*
- This disorder involves a sudden onset of psychotic symptoms (delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech or behavior) lasting more than one day but less than one month, with eventual full return to premorbid functioning.
- While the patient exhibited a delusional belief, the **shared nature** with her husband and the **resolution upon separation** are more characteristic of folie à deux than an independent brief psychotic episode.
*Culture-specific psychosis*
- This refers to psychotic symptoms and syndromes that are recognized within a particular culture and associated with specific cultural explanations.
- Although some cultures may have beliefs in spiritual healing, the specific scenario of a **delusional belief shared between two individuals** in a close relationship points more directly to folie à deux rather than a broad culture-specific psychosis.
*Residual phase of schizophrenia*
- This phase occurs after an acute episode of schizophrenia, where prominent positive symptoms (delusions, hallucinations) have subsided, but milder negative symptoms (e.g., social withdrawal, blunted affect) or attenuated positive symptoms persist.
- The patient explicitly **denies hallucinations, mood disturbances, and socio-occupational impairment**, and her delusional belief was directly linked to her husband, which does not fit the diagnostic criteria for a residual phase of schizophrenia.
*Schizophreniform disorder*
- This disorder is characterized by symptoms similar to schizophrenia (delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, negative symptoms) but lasts for more than one month and less than six months.
- The patient's presentation does not describe the broad range of symptoms or the duration required for a schizophreniform disorder, and the **resolving nature of her delusion upon separation** is a key differentiating factor.
Psychotherapeutic approaches US Medical PG Question 10: A 44-year-old man is brought to the clinic by his wife insisting that her husband has been acting strange lately. He is a dentist by profession and has no known medical conditions. For the past 6 weeks, he has insisted on listening to the 6 PM news on the radio. He is adamant that the news anchor is referencing his life during the broadcasts. Apart from this, his wife states that her husband is fine. He and his wife deny the use of any prescribed medications or illicit drugs. He is a non-smoker and drinks alcohol only on social occasions. Physical examination and routine laboratory investigations are normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Persecutory delusions
- B. Delusion of control
- C. Erotomanic delusions
- D. Delusion of reference (Correct Answer)
- E. Grandiose delusions
Psychotherapeutic approaches Explanation: ***Delusion of reference***
- This is characterized by the belief that **events, objects, or people in the environment** have a particular and unusual significance, often of a negative or threatening nature, specifically directed at oneself.
- The man's belief that the **news anchor is referencing his life** during broadcasts, despite no actual connection, is a classic presentation of a delusion of reference.
*Persecutory delusions*
- **Persecutory delusions** involve the belief that one is being tormented, followed, tricked, spied on, or ridiculed.
- While the delusion involves external references, it does not explicitly state that the news anchor is actively *harming* or *conspiring against* him, making it less specific than a delusion of reference, which describes the belief that common occurrences refer to oneself.
*Delusion of control*
- This delusion involves the belief that **one's thoughts, feelings, impulses, or actions are not one's own** but are being imposed or controlled by some external force.
- The patient's symptom is about external events referring to him, not about his internal experiences being controlled by an external force.
*Erotomanic delusions*
- This involves the belief that **another person, usually of higher status, is in love with the individual**.
- There is no indication in the scenario that the man believes the news anchor is in love with him.
*Grandiose delusions*
- This is characterized by beliefs of **inflated worth, power, knowledge, identity, or a special relationship to a deity or famous person**.
- The patient's delusion does not involve exaggerated self-importance or a belief in special abilities, but rather a misinterpretation of external communications.
More Psychotherapeutic approaches US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.