Cognitive assessment tools US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Cognitive assessment tools. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
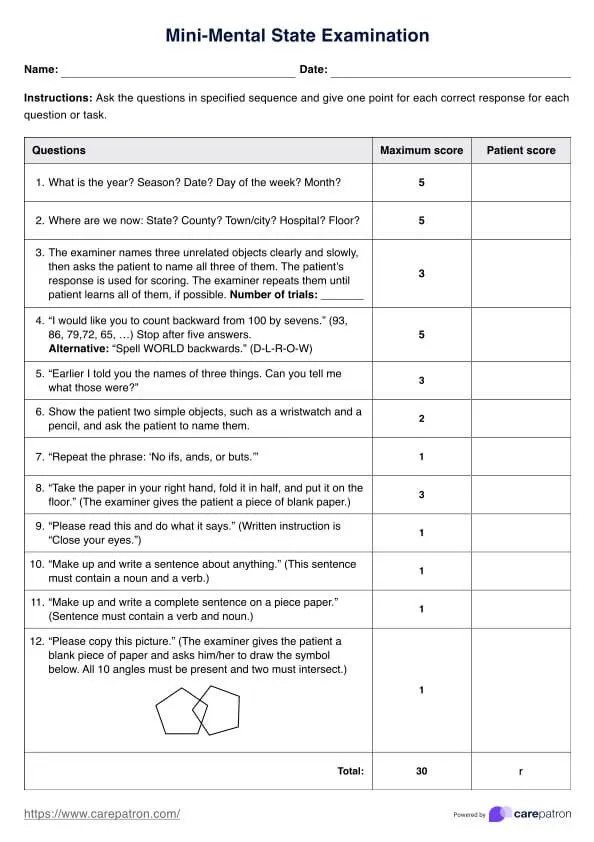
Cognitive assessment tools US Medical PG Question 1: A 72-year-old man is brought to the physician by his wife for memory issues over the last 7 months. The patient's wife feels that he has gradually become more forgetful. He commonly misplaces his car keys and forgets his children's names. He seems to have forgotten how to make dinner and sometimes serves uncooked noodles or raw meat. One night he parked his car in a neighbor's bushes and was found wandering the street. He has a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and COPD. Current medications include atorvastatin, metoprolol, ipratropium, and fluticasone. Vital signs are within normal limits. He is alert and oriented to person and place only. Neurologic examination shows no focal findings. His Mini-Mental State Examination score is 19/30. A complete blood count and serum concentrations of electrolytes, urea nitrogen, creatinine, thyroid-stimulating hormone, liver function tests, vitamin B12 (cobalamin), and folate are within the reference range. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
- A. Electroencephalography
- B. PET scan
- C. MRI of the brain (Correct Answer)
- D. Lumbar puncture
- E. Neuropsychologic testing
Cognitive assessment tools Explanation: ***MRI of the brain***
- An **MRI of the brain** is crucial for evaluating **structural causes of cognitive impairment**, such as tumors, strokes, hydrocephalus, or significant atrophy that might explain the patient's rapidly progressing memory loss and functional decline.
- Given the patient's age, rapidly worsening dementia symptoms, and normal initial lab work, imaging is essential to rule out **reversible or treatable causes** and to characterize the extent of neurodegeneration.
*Electroencephalography*
- **EEG** is primarily used to detect **seizure activity** or to evaluate for rapidly progressive encephalopathies like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, which is not indicated by the patient's presentation.
- The patient's symptoms are consistent with a dementia syndrome, not acute encephalopathy or seizures.
*PET scan*
- A **PET scan** (e.g., FDG-PET or amyloid-PET) can provide information about metabolic activity or amyloid plaques, useful for **differentiating types of dementia** (e.g., Alzheimer's disease).
- However, it is an advanced test typically considered after structural imaging has ruled out other causes and when the diagnosis remains unclear.
*Lumbar puncture*
- **Lumbar puncture** is performed to analyze **cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)** for biomarkers (e.g., tau, Aβ42 levels) to help diagnose specific neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's or to rule out infectious/inflammatory causes.
- It's usually reserved for cases where other investigations are inconclusive or specific conditions are strongly suspected, and structural imaging has been performed.
*Neuropsychologic testing*
- **Neuropsychologic testing** provides a detailed assessment of various cognitive domains and can help to **characterize the pattern and severity of cognitive impairment**.
- While valuable, it is usually performed after initial medical workup and structural imaging to understand the functional impact of any identified brain changes or to further delineate the type of cognitive disorder.
Cognitive assessment tools US Medical PG Question 2: A 24-year-old man presents to the emergency department after a motor vehicle collision. He was in the front seat and unrestrained driver in a head on collision. His temperature is 99.2°F (37.3°C), blood pressure is 90/65 mmHg, pulse is 152/min, respirations are 16/min, and oxygen saturation is 100% on room air. Physical exam is notable for a young man who opens his eyes spontaneously and is looking around. He answers questions with inappropriate responses but discernible words. He withdraws from pain but does not have purposeful movement. Which of the following is this patient's Glasgow coma scale?
- A. 9
- B. 15
- C. 7
- D. 11 (Correct Answer)
- E. 13
Cognitive assessment tools Explanation: ***11***
- **Eye-opening (E)**: The patient opens his eyes spontaneously, scoring **E4**.
- **Verbal response (V)**: He gives inappropriate responses but discernible words, scoring **V3**.
- **Motor response (M)**: He withdraws from pain but does not have purposeful movement, scoring **M4**.
- Therefore, the total Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score is **E4 + V3 + M4 = 11**.
*9*
- This score would imply a lower verbal or motor response, such as **incomprehensible sounds (V2)** or **abnormal flexion (M3)**, which is not consistent with the patient's presentation.
- For example, E4 + V2 + M3 would equal 9.
*15*
- A GCS of 15 indicates **normal neurological function**, meaning the patient would be fully oriented, obey commands, and open eyes spontaneously, which is not the case here.
- This score is for a patient who is fully conscious and responsive.
*7*
- A GCS of 7 suggests a **severe brain injury**, which would typically present with a much poorer response, such as **no verbal response (V1)** or **abnormal extension (M2)**.
- For example, E4 + V1 + M2 would equal 7.
*13*
- This score would mean a higher level of consciousness, such as **confused conversation (V4)** or **localizing pain (M5)**, which is better than the patient's described responses.
- For example, E4 + V4 + M5 would equal 13.
Cognitive assessment tools US Medical PG Question 3: A 13-month-old girl is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. She was born at 38 weeks' gestation. There is no family history of any serious illnesses. She cannot pull herself to stand from a sitting position. She can pick an object between her thumb and index finger but cannot drink from a cup or feed herself using a spoon. She comes when called by name and is willing to play with a ball. She cries if she does not see her parents in the same room as her. She coos “ma” and “ba.” She is at the 50th percentile for height and weight. Physical examination including neurologic examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate assessment of her development?
- A. Fine motor: normal | Gross motor: delayed | Language: normal | Social skills: delayed
- B. Fine motor: normal | Gross motor: delayed | Language: delayed | Social skills: normal (Correct Answer)
- C. Fine motor: delayed | Gross motor: normal | Language: delayed | Social skills: normal
- D. Fine motor: delayed | Gross motor: delayed | Language: normal | Social skills: normal
- E. Fine motor: delayed | Gross motor: normal | Language: normal | Social skills: delayed
Cognitive assessment tools Explanation: ***Fine motor: normal | Gross motor: delayed | Language: delayed | Social skills: normal***
- **Fine motor** is normal because she demonstrates **pincer grasp** (picking up objects between thumb and index finger), which is the key fine motor milestone expected by 9-12 months. The inability to drink from a cup or self-feed with a spoon represents more complex feeding skills that develop later (12-18 months) and are not primary fine motor milestones at 13 months.
- **Gross motor** is delayed because she cannot pull herself to stand, a milestone typically achieved by 9-12 months. At 13 months, she should be cruising along furniture or beginning to walk independently.
- **Language** is delayed because she only coos "ma" and "ba" without meaningful words. By 13 months, children should typically say 1-2 words with meaning (like "mama" or "dada" used specifically) and have varied babbling patterns.
- **Social skills** are normal as she responds to her name, engages in play (willing to play with a ball), and demonstrates appropriate **separation anxiety** when her parents are not in the room—all expected social-emotional milestones for this age.
*Fine motor: normal | Gross motor: delayed | Language: normal | Social skills: delayed*
- Language is delayed, not normal—cooing "ma" and "ba" without meaningful words does not meet the expected milestone of 1-2 words with meaning by 13 months.
- Social skills are normal, not delayed—responding to her name and showing separation anxiety are appropriate for her age.
*Fine motor: delayed | Gross motor: normal | Language: delayed | Social skills: normal*
- Fine motor is normal, not delayed—the presence of **pincer grasp** is the key indicator, and feeding difficulties reflect more complex coordination rather than delayed fine motor development.
- Gross motor is delayed, not normal—inability to pull to stand at 13 months represents a significant delay.
*Fine motor: delayed | Gross motor: delayed | Language: normal | Social skills: normal*
- Fine motor is normal—**pincer grasp** is present and appropriate for age.
- Language is delayed, not normal—she lacks meaningful words expected at 13 months.
*Fine motor: delayed | Gross motor: normal | Language: normal | Social skills: delayed*
- Fine motor is normal—**pincer grasp** is the key milestone and is present.
- Gross motor is delayed, not normal—cannot pull to stand, which should have been achieved months earlier.
- Social skills are normal, not delayed—separation anxiety and responding to name are age-appropriate behaviors.
Cognitive assessment tools US Medical PG Question 4: A 60-year-old woman is brought into the office by her son. Her son states that the patient has been acting inappropriately over the last few years. She has been taking off her clothes in front of visitors and putting objects in her mouth. She has had no emotional response to the death of one of her close friends and was laughing at her funeral. She has almost no memory issues, but sometimes forgets how to use objects such as a telephone. She has no other medical issues and takes no medications. On exam, she has no focal neurological deficits and her mini-mental status exam is 25/30. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Alzheimer's dementia
- B. Pick's disease (Correct Answer)
- C. Normal aging
- D. Vascular dementia
- E. Lewy body dementia
Cognitive assessment tools Explanation: ***Pick's disease***
- The patient's presentation with **disinhibition**, **inappropriate social behavior**, putting objects in her mouth (hyperorality), and **emotional blunting** with preserved memory are classic signs of **frontotemporal dementia (FTD)**, of which Pick's disease is a subtype.
- The relative preservation of memory and visuospatial skills, as indicated by a mini-mental status exam score of 25/30, further supports an FTD diagnosis over Alzheimer's.
*Alzheimer's dementia*
- This typically presents with **prominent memory impairment** (especially **episodic memory**) as an early and defining feature, which is not the case here.
- Behavioral changes in Alzheimer's dementia usually occur later in the disease progression, unlike the early and severe **disinhibition** seen in this patient.
*Normal aging*
- While some cognitive changes can occur with normal aging, such as mild slowing of processing speed or occasional word-finding difficulties, they do not include severe **disinhibition**, **hyperorality**, or marked personality changes.
- Normal aging does not cause significant impairment in daily functioning or inappropriate social behavior.
*Vascular dementia*
- This type of dementia is characterized by a **stepwise decline** in cognitive function, often associated with a history of **strokes** or **cardiovascular risk factors**.
- Its presentation is typically focal neurological deficits and cognitive deficits that correlate with the location of vascular lesions, which are not described in this patient.
*Lewy body dementia*
- Hallmarks of Lewy body dementia include **fluctuating cognition**, **recurrent visual hallucinations**, and **parkinsonism**, none of which are detailed in the patient's presentation.
- While behavioral disturbances can occur, the prominent and early disinhibition and hyperorality seen here are more indicative of frontotemporal dementia.
Cognitive assessment tools US Medical PG Question 5: A research study is comparing 2 novel tests for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The first is a serum blood test, and the second is a novel PET radiotracer that binds to beta-amyloid plaques. The researchers intend to have one group of patients with AD assessed via the novel blood test, and the other group assessed via the novel PET examination. In comparing these 2 trial subsets, the authors of the study may encounter which type of bias?
- A. Selection bias (Correct Answer)
- B. Confounding bias
- C. Recall bias
- D. Measurement bias
- E. Lead-time bias
Cognitive assessment tools Explanation: ***Selection bias***
- This occurs when different patient groups are assigned to different interventions or measurements in a way that creates **systematic differences** between comparison groups.
- In this study, having **separate patient groups** assessed with different diagnostic methods (blood test vs. PET scan) means any differences observed could be due to **differences in the patient populations** rather than differences in test performance.
- To validly compare two diagnostic tests, both tests should ideally be performed on the **same patients** (paired design) or patients should be **randomly assigned** to receive one test or the other, ensuring comparable groups.
- This is a fundamental **study design flaw** that prevents valid comparison of the two diagnostic methods.
*Measurement bias*
- Also called information bias, this occurs when there are systematic errors in how outcomes or exposures are measured.
- While using different measurement tools could introduce measurement variability, the primary issue here is that **different patient populations** are being compared, not just different measurement methods on the same population.
- Measurement bias would be more relevant if the same patients were assessed with both methods but one method was systematically misapplied or measured incorrectly.
*Confounding bias*
- This occurs when an extraneous variable is associated with both the exposure and outcome, distorting the observed relationship.
- While patient characteristics could confound results, the fundamental problem is the **study design itself** (separate groups for separate tests), which is selection bias.
*Recall bias*
- This involves systematic differences in how participants remember or report past events, common in **retrospective case-control studies**.
- Not relevant here, as this involves prospective diagnostic testing, not recollection of past exposures.
*Lead-time bias*
- Occurs in screening studies when earlier detection makes survival appear longer without changing disease outcomes.
- Not applicable to this scenario, which focuses on comparing two diagnostic methods in separate patient groups, not on survival or disease progression timing.
Cognitive assessment tools US Medical PG Question 6: During the selection of subjects for a study on infantile vitamin deficiencies, a child is examined by the lead investigator. She is at the 75th percentile for head circumference and the 80th percentile for length and weight. She can lift her chest and shoulders up when in a prone position, but cannot roll over from a prone position. Her eyes follow objects past the midline. She coos and makes gurgling sounds. When the investigator strokes the sole of her foot, her big toe curls upward and there is fanning of her other toes. She makes a stepping motion when she is held upright and her feet are in contact with the examination table. Which of the following additional skills or behaviors would be expected in a healthy patient of this developmental age?
- A. Cries when separated from her mother
- B. Smiles at her mother (Correct Answer)
- C. Rolls over from her back
- D. Responds to calling of own name
- E. Reaches out for objects
Cognitive assessment tools Explanation: ***Smiles at her mother***
- The child exhibits developmental milestones consistent with a **2-month-old infant**, such as lifting her chest in a prone position, following objects past the midline, cooing, and gurgling. Social smiling typically emerges around **2 months of age**.
- Primitive reflexes like the **Babinski reflex** (big toe curling upward and fanning of other toes) and **stepping reflex** are normally present at this age, supporting the approximate age of 2 months.
*Cries when separated from her mother*
- This behavior suggests **separation anxiety**, which typically develops much later, usually around **8-9 months of age**.
- A 2-month-old infant does not yet have the cognitive understanding or object permanence needed to exhibit true separation anxiety.
*Rolls over from her back*
- Rolling over from the back to the stomach is usually achieved between **4 and 6 months of age**.
- The child in the vignette cannot even roll over from a prone position, indicating she is not yet at the age for rolling from her back.
*Responds to calling of own name*
- Responding to one's own name is a more advanced auditory and cognitive milestone, generally developing between **6 and 9 months of age**.
- At 2 months, infants respond to voices and sounds but do not associate specific words with themselves.
*Reaches out for objects*
- Purposeful reaching and grasping for objects (palmar grasp) typically develops around **4 to 6 months of age**.
- A 2-month-old infant may swat at objects reflexively but does not exhibit coordinated, intentional reaching.
Cognitive assessment tools US Medical PG Question 7: A 4-year-old boy is brought to a pediatrician by his parents for a consultation after his teacher complained about his inability to focus or make friends at school. They mention that the boy does not interact well with others at home, school, or daycare. On physical examination, his vital signs are stable with normal weight, height, and head circumference for his age and sex. His general examination and neurologic examination are completely normal. A recent audiological evaluation shows normal hearing, and intellectual disability has been ruled out by a clinical psychologist. Which of the following investigations is indicated as part of his diagnostic evaluation at present?
- A. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain
- B. Electroencephalography
- C. No further testing is needed
- D. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scanning of head
- E. Autism spectrum disorder screening and developmental assessment (Correct Answer)
Cognitive assessment tools Explanation: ***Autism spectrum disorder screening and developmental assessment***
- The clinical presentation (inability to focus, difficulty making friends, poor social interaction across multiple settings) is **highly suggestive of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)**.
- After ruling out **hearing impairment and intellectual disability**, the next appropriate step is **formal ASD screening using validated tools** such as the **Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT)**, **Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS)**, or **Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R)**.
- According to **AAP guidelines**, when developmental concerns suggestive of ASD are identified, formal screening and comprehensive developmental assessment are **essential components of the diagnostic evaluation**.
- ASD diagnosis is primarily **clinical**, based on standardized screening tools and developmental assessments, not neuroimaging or electrophysiological studies.
*No further testing is needed*
- This is **incorrect** because the patient has not yet undergone **formal ASD-specific screening and developmental assessment**.
- While hearing and intellectual disability have been ruled out, **diagnostic confirmation of ASD** requires structured evaluation using validated assessment tools.
- Simply observing symptoms without formal screening is inadequate for establishing an ASD diagnosis.
*Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain*
- Brain MRI is **not routinely indicated** for ASD diagnosis as it typically shows **normal findings** in children with ASD.
- Neuroimaging is reserved for cases with **focal neurological signs, regression, or atypical features** suggesting structural abnormalities.
- This patient has a **normal neurological examination**, making MRI unnecessary.
*Electroencephalography*
- EEG is indicated only when there is suspicion of **seizure disorder** or other specific neurological conditions.
- The patient has a **normal neurological examination** with no seizure-like symptoms, making EEG unnecessary at this stage.
*Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scanning of head*
- PET scans are **not part of routine ASD diagnostic workup** and are typically used in research settings or for evaluating specific metabolic or neoplastic conditions.
- The **radiation exposure and invasiveness** make PET scanning inappropriate for initial diagnostic evaluation in a child with developmental concerns.
Cognitive assessment tools US Medical PG Question 8: A 3-year-old girl is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. She was born at term and has been healthy since. She can climb up and down the stairs and can pedal a tricycle. She has difficulty using a spoon to feed herself but can copy a line. She speaks in 2- to 3-word sentences that can be understood by most people. She is selfish while playing with children her age and throws tantrums quite often. She cannot put on her own shoes and socks. She does not tolerate separation from her parents. She is at 60th percentile for height and weight. Physical examination including neurologic examination reveals no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate assessment of her development?
- A. Fine motor: Normal | Gross motor: Normal | Language: Delayed | Social skills: Delayed
- B. Fine motor: Delayed | Gross motor: Delayed | Language: Normal | Social skills: Normal
- C. Fine motor: Delayed | Gross motor: Normal | Language: Normal | Social skills: Delayed (Correct Answer)
- D. Fine motor: Normal | Gross motor: Delayed | Language: Normal | Social skills: Delayed
- E. Fine motor: Normal | Gross motor: Delayed | Language: Delayed | Social skills: Normal
Cognitive assessment tools Explanation: ***Fine motor: Delayed | Gross motor: Normal | Language: Normal | Social skills: Delayed***
- The child can copy a line (expected at 3 years) and climb stairs and pedal a tricycle (expected for a 3-year-old), indicating **normal gross motor skills**. However, difficulty using a spoon and putting on shoes/socks suggests **delayed fine motor skills**.
- Speaking in 2- to 3-word sentences understood by most (expected for 2-3 years) indicates **normal language development**. Being selfish and throwing tantrums (normal for 2-3 years) but not tolerating separation (suggests earlier developmental stage for separation anxiety) point to **delayed social skills**.
*Fine motor: Normal | Gross motor: Normal | Language: Delayed | Social skills: Delayed*
- This option incorrectly assesses fine motor skills as normal when the child struggles with tasks like using a spoon and dressing herself.
- While language and social skills are correctly identified as delayed, the overall assessment of fine motor makes this option incorrect.
*Fine motor: Delayed | Gross motor: Delayed | Language: Normal | Social skills: Normal*
- This option incorrectly assesses gross motor skills as delayed, despite the child's ability to climb stairs and pedal a tricycle, which are age-appropriate.
- It also incorrectly assesses social skills as normal, overlooking the persistent separation anxiety and aggressive social play for her age.
*Fine motor: Normal | Gross motor: Delayed | Language: Normal | Social skills: Delayed*
- This option incorrectly describes fine motor skills as normal and gross motor skills as delayed.
- Her ability to pedal a tricycle and climb stairs indicates age-appropriate gross motor development, while her difficulty with a spoon suggests delayed fine motor skills.
*Fine motor: Normal | Gross motor: Delayed | Language: Delayed | Social skills: Normal*
- This option incorrectly states that both fine motor and gross motor skills are affected and also mischaracterizes social skills as normal.
- The child's language development is within the normal range for a 3-year-old, and her social behavior, particularly the separation anxiety, indicates a delay.
Cognitive assessment tools US Medical PG Question 9: A 78-year-old man is brought to the physician by his daughter for a follow-up examination. The daughter noticed that he has gradually become more forgetful and withdrawn over the last year. He frequently misplaces his car keys and forgets the names of his neighbors, whom he has known for 30 years. He has difficulty recalling his address and telephone number. He recently had an episode of urinary and fecal incontinence. Last week, his neighbor found him wandering the parking lot of the grocery store. He has hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He had smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years but quit 18 years ago. His current medications include hydrochlorothiazide and atorvastatin. He appears healthy; BMI is 23 kg/m2. His temperature is 37.2°C (99.0°F), pulse is 86/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 136/84 mm Hg. Mini-mental state examination score is 19/30. He is not bothered by his forgetfulness. Cranial nerves II–XII are intact. He has 5/5 strength and full sensation to light touch in all extremities. His patellar, Achilles, and biceps reflexes are 2+ bilaterally. His gait is steady. MRI scan of the brain shows ventriculomegaly and prominent cerebral sulci. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
- A. Acetazolamide
- B. Sertraline
- C. Memantine
- D. Thiamine
- E. Donepezil (Correct Answer)
Cognitive assessment tools Explanation: ***Donepezil***
- The patient exhibits features consistent with **Alzheimer's disease**, including gradual memory loss, difficulty with daily tasks, episodes of incontinence, and a Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score of 19/30. Donepezil, a **cholinesterase inhibitor**, is a first-line treatment for mild to moderate Alzheimer's to slow cognitive decline.
- The MRI findings of **ventriculomegaly and prominent cerebral sulci** are consistent with general cerebral atrophy often seen in Alzheimer's disease, not hydrocephalus requiring shunting or other specific brain pathologies (normal pressure hydrocephalus would have gait disturbance as a prominent feature, which is absent here).
*Acetazolamide*
- **Acetazolamide** is a **carbonic anhydrase inhibitor** used to treat conditions like glaucoma, altitude sickness, and idiopathic intracranial hypertension.
- There is no indication of elevated intracranial pressure or hydrocephalus that would warrant the use of acetazolamide in this patient.
*Sertraline*
- **Sertraline** is a **selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)** primarily used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
- While depression can coexist with dementia, the primary cognitive symptoms described here are not primarily depressive; therefore, an antidepressant is not the most appropriate initial pharmacotherapy for cognitive decline.
*Memantine*
- **Memantine** is an **NMDA receptor antagonist** used in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease, often in combination with cholinesterase inhibitors or when cholinesterase inhibitors are not tolerated.
- While appropriate for moderate to severe Alzheimer's, **cholinesterase inhibitors** are typically the initial treatment for mild to moderate stages, and the patient's MMSE score of 19/30 often falls into the mild-moderate category where donepezil is usually favored first.
*Thiamine*
- **Thiamine** (vitamin B1) supplementation is primarily used to treat **Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome**, which is associated with chronic alcohol abuse and presents with ataxia, ophthalmoplegia, and confusion, none of which are the primary presenting symptoms here.
- There is no evidence of **nutritional deficiency** or alcohol abuse in this patient to suggest thiamine deficiency as the cause of his cognitive decline.
Cognitive assessment tools US Medical PG Question 10: A 38-year-old male presents for counseling by a psychologist mandated by the court. The patient explains that he does not mean to hit his wife when they are arguing, but something just comes over him that he cannot control. Upon further discussion, the patient reveals that his father was incarcerated several times for physically abusing his mother. Which of the following best describes the behavior seen in this patient?
- A. Acting out (Correct Answer)
- B. Reaction formation
- C. Splitting
- D. Dissociation
- E. Identification
Cognitive assessment tools Explanation: ***Acting out***
- **Acting out** is the defense mechanism where unconscious emotional conflicts or impulses are expressed through actions rather than being consciously felt or verbalized.
- The patient's violent behavior toward his wife represents the direct expression of aggressive impulses through physical action without conscious emotional processing or reflection.
- The key phrase "something just comes over him that he cannot control" demonstrates the hallmark of acting out—expressing feelings through action rather than words or conscious awareness.
- This is a primitive defense mechanism commonly seen in individuals with poor impulse control who cannot tolerate uncomfortable feelings.
*Identification*
- **Identification** involves unconsciously adopting the characteristics, behaviors, or attitudes of another person, typically to reduce anxiety.
- While the patient has a history of witnessing his father's abuse, the question doesn't indicate he is consciously or unconsciously trying to become like his father or modeling himself after him.
- The core issue here is impulsive action (acting out), not identification with the father figure.
*Reaction formation*
- **Reaction formation** occurs when an individual replaces an unacceptable impulse with its opposite behavior.
- This is not present here, as the patient is directly expressing aggression, not replacing it with an opposite behavior like excessive kindness.
*Splitting*
- **Splitting** is viewing people or situations in extreme all-good or all-bad terms, without integrating positive and negative qualities.
- This scenario describes a behavioral pattern, not a distortion in how the patient perceives others.
*Dissociation*
- **Dissociation** involves disruption in consciousness, memory, identity, or perception, with detachment from reality.
- While the patient feels he "cannot control" himself, this describes impulsive acting out rather than true dissociation with memory gaps or detachment from identity.
More Cognitive assessment tools US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.