Cognitive disorders (dementia)

On this page
🧠 The Cognitive Decline Spectrum: Mapping Mental Deterioration
Dementia transforms the brain's architecture through distinct molecular pathways, each leaving characteristic clinical fingerprints that guide your diagnosis and treatment. You'll learn to recognize the spectrum from mild cognitive impairment to severe dementia, decode the underlying neurodegeneration mechanisms, and master pattern recognition that distinguishes Alzheimer's from vascular, Lewy body, and frontotemporal variants. We'll build your systematic approach to assessment, construct evidence-based treatment algorithms, and integrate emerging therapies that target disease modification rather than just symptoms.
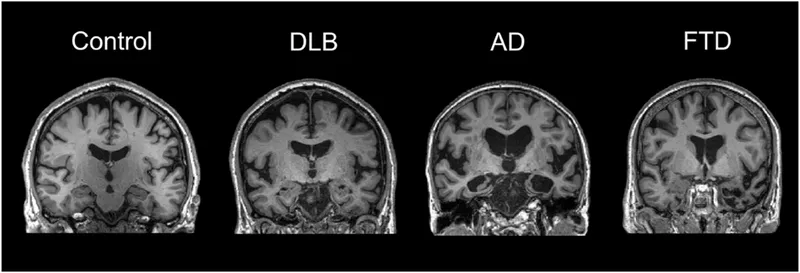
The cognitive decline continuum spans from normal aging through mild cognitive impairment to severe dementia, with distinct pathophysiological signatures and clinical trajectories. Each stage presents specific diagnostic thresholds and intervention opportunities that determine long-term outcomes.
📌 Remember: FAST-ED for cognitive assessment domains - Functional status, Attention/concentration, Speech/language, Temporal orientation, Executive function, Delayed recall. Each domain decline follows predictable patterns with 15-20% annual progression rates in untreated dementia.
Cognitive Disorder Classification Framework
| Disorder Type | Prevalence (Age 65+) | Annual Progression | Survival (Years) | Reversibility | Primary Pathology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Aging | 100% | 1-2% decline | Normal lifespan | Stable | Minimal neuronal loss |
| MCI | 15-20% | 10-15% to dementia | 8-12 years | 25% revert | Mild protein deposits |
| Alzheimer's | 60-70% | 15-20% decline | 4-8 years | Irreversible | Amyloid/tau tangles |
| Vascular | 15-20% | Stepwise decline | 3-5 years | Partially preventable | Cerebrovascular disease |
| Lewy Body | 5-10% | Fluctuating decline | 2-4 years | Irreversible | Alpha-synuclein deposits |
- Neurodegenerative Spectrum
- Primary disorders: Direct neuronal death (60-80% of cases)
- Alzheimer's disease: 6.5 million US cases
- Frontotemporal dementia: 50,000-60,000 cases
- Lewy body disease: 1.4 million cases
- Secondary disorders: Systemic causes (15-20% of cases)
- Vascular dementia: 2-4 million cases
- Metabolic encephalopathy: 5-10% reversible
- Medication-induced: 10-15% potentially reversible
- Primary disorders: Direct neuronal death (60-80% of cases)
💡 Master This: Every cognitive assessment requires dual-pathway analysis - neurodegenerative versus systemic causes. Missing reversible causes in the 15-20% of secondary dementias represents the highest-yield diagnostic opportunity, with complete recovery possible in 40-60% of identified cases.
The pathophysiological cascade begins 10-20 years before clinical symptoms, with protein misfolding triggering inflammatory cascades that progressively destroy synaptic connections. Understanding this timeline enables precision medicine approaches targeting specific molecular pathways during the preclinical window when maximum therapeutic benefit remains achievable.
Connect this foundational spectrum through clinical presentation patterns to understand how different pathologies manifest distinct behavioral and cognitive signatures.
🧠 The Cognitive Decline Spectrum: Mapping Mental Deterioration
⚙️ The Neurodegeneration Engine: Molecular Mechanisms of Cognitive Decline
The molecular engine operates through four primary pathways that converge on synaptic failure and neuronal death. Each pathway presents distinct therapeutic targets with specific intervention windows and success rates.
📌 Remember: PAIN describes neurodegeneration mechanisms - Protein misfolding, Aggregation formation, Inflammatory activation, Neuronal death. This sequence occurs over 15-25 years with exponential acceleration during clinical phases.
Molecular Pathway Analysis
| Pathway | Primary Protein | Brain Regions | Timeline (Years) | Therapeutic Window | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amyloid Cascade | Beta-amyloid 42 | Hippocampus/cortex | 15-20 preclinical | Preclinical phase | 40-60% |
| Tau Propagation | Hyperphosphorylated tau | Temporal/parietal | 10-15 preclinical | Early symptomatic | 25-40% |
| Alpha-synuclein | Lewy body formation | Brainstem/cortex | 5-10 preclinical | Limited window | 15-25% |
| Vascular Injury | Multiple mechanisms | Watershed zones | Variable onset | Prevention focus | 60-80% |
- Protein Misfolding Cascade
- Amyloid pathway: Beta-amyloid 40/42 ratio determines toxicity
- Normal ratio: 10:1 (Aβ40:Aβ42)
- Pathological ratio: 5:1 or lower
- Plaque formation: >500 pg/mL CSF threshold
- Tau pathway: Hyperphosphorylation at multiple sites
- Normal tau: <300 pg/mL CSF concentration
- Pathological tau: >400 pg/mL with progressive increase
- Neurofibrillary tangles: Braak stages I-VI progression
- Amyloid pathway: Beta-amyloid 40/42 ratio determines toxicity
💡 Master This: The amyloid-tau interaction amplifies neurodegeneration through cross-seeding mechanisms. Amyloid plaques accelerate tau propagation by 300-500%, while tau tangles enhance amyloid toxicity, creating a positive feedback loop that explains exponential cognitive decline in symptomatic phases.
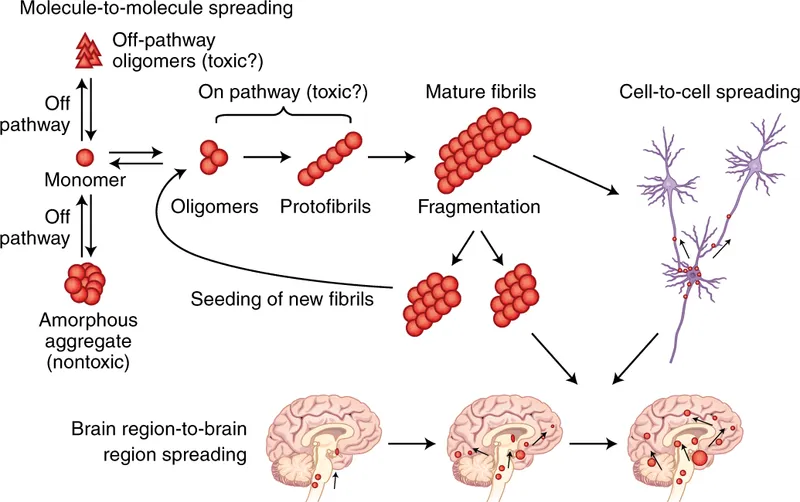
Neuroinflammation represents the final common pathway where microglial activation and astrocyte dysfunction amplify protein toxicity. Understanding this inflammatory cascade reveals why anti-inflammatory strategies show 30-40% efficacy in early-stage interventions but fail in advanced disease.
Connect these molecular mechanisms through clinical phenotype expression to understand how different pathologies create distinct cognitive and behavioral presentations.
⚙️ The Neurodegeneration Engine: Molecular Mechanisms of Cognitive Decline
🎯 The Clinical Detective: Pattern Recognition in Cognitive Assessment
The diagnostic framework operates through hierarchical pattern analysis, starting with global cognitive screening and progressing to domain-specific testing based on initial findings. This approach achieves 90-95% sensitivity for dementia detection while minimizing false-positive rates below 10%.
📌 Remember: MEMORY guides systematic cognitive assessment - Memory (immediate/delayed), Executive function, Motor skills, Orientation, Recognition/language, Yield (functional impact). Each domain requires specific testing protocols with validated cutoff scores.
Cognitive Domain Assessment Matrix
| Domain | Primary Tests | Normal Threshold | MCI Range | Dementia Cutoff | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Memory | Word list recall | 8-10/10 words | 5-7/10 words | <5/10 words | 85-90% |
| Executive | Trail Making B | <75 seconds | 75-120 seconds | >120 seconds | 80-85% |
| Language | Fluency tasks | >15 words/minute | 10-15 words | <10 words | 75-80% |
| Visuospatial | Clock drawing | 4-5/5 points | 2-3/5 points | <2/5 points | 70-75% |
| Attention | Digit span | 6-8 digits | 4-5 digits | <4 digits | 65-70% |
- Alzheimer's Pattern Recognition
- Early presentation: Episodic memory loss with preserved personality
- Word list recall: <3/10 words after 5-minute delay
- Clock drawing: Poor planning but preserved numbers
- Functional decline: IADL impairment before basic ADL loss
- Progression markers: Temporal gradient in memory loss
- Recent events: Severely impaired (<20% recall)
- Remote events: Relatively preserved (60-80% recall)
- Recognition vs recall: Minimal improvement with cues
- Early presentation: Episodic memory loss with preserved personality
💡 Master This: The "temporal gradient" in memory loss provides diagnostic specificity - Alzheimer's patients show steep gradients (recent >> remote memory loss), while vascular dementia shows flat gradients (equal impairment across time periods), achieving 85% diagnostic accuracy.
Behavioral pattern recognition provides additional diagnostic specificity, where personality changes preceding memory loss suggest frontotemporal dementia (90% specificity), while visual hallucinations with cognitive fluctuation indicate Lewy body disease (85% specificity).
Connect these recognition patterns through systematic differential analysis to understand how quantitative discriminators separate similar presentations.
🎯 The Clinical Detective: Pattern Recognition in Cognitive Assessment
🔬 The Differential Matrix: Systematic Discrimination in Cognitive Disorders
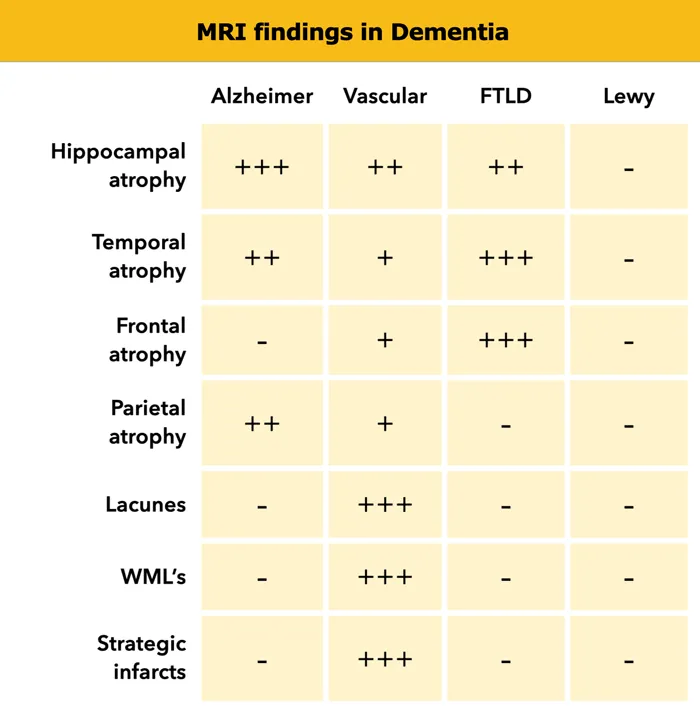
The discrimination framework utilizes weighted scoring systems where specific features carry different diagnostic values based on sensitivity and specificity data. Understanding these weights enables rapid triage and targeted testing strategies.
📌 Remember: DIVIDE organizes differential analysis - Duration of symptoms, Initial presentation, Velocity of decline, Imaging patterns, Dominant features, Extra-cognitive symptoms. Each parameter provides quantitative discrimination between disorder types.
Quantitative Differential Matrix
| Feature | Alzheimer's | Vascular | Lewy Body | Frontotemporal | Diagnostic Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age of onset | 65-85 years | 60-80 years | 70-85 years | 45-65 years | High (85% accuracy) |
| Progression rate | 2-4 MMSE/year | Stepwise decline | Fluctuating | 3-5 MMSE/year | High (80% accuracy) |
| Memory pattern | Encoding deficit | Mixed pattern | Fluctuating | Preserved early | Very high (90%) |
| Executive function | Late impairment | Early impairment | Variable | Very early | High (85%) |
| Hallucinations | Rare (<10%) | Uncommon (15%) | Common (80%) | Rare (<5%) | Very high (95%) |
| Motor symptoms | Late/minimal | Variable | Early (60%) | Late/behavioral | High (80%) |
- Temporal Pattern Analysis
- Alzheimer's progression: Linear decline with predictable stages
- Preclinical: 10-15 years of biomarker changes
- MCI phase: 2-5 years with 10-15% annual conversion
- Dementia: 4-8 years survival with steady decline
- Vascular progression: Stepwise deterioration with plateau periods
- Acute events: Sudden decline followed by stability
- Recovery potential: 20-30% improvement possible
- Progression: Variable based on vascular risk control
- Alzheimer's progression: Linear decline with predictable stages
💡 Master This: Cognitive fluctuation in Lewy body dementia follows circadian patterns with morning clarity and evening confusion in 70-80% of cases. This pattern, combined with REM sleep behavior disorder (90% prevalence), provides diagnostic specificity exceeding 85%.
Biomarker discrimination provides molecular-level specificity when clinical features overlap. CSF analysis achieves 90-95% accuracy for Alzheimer's diagnosis, while DaTscan imaging shows 85-90% specificity for Lewy body disease.
- Advanced Discrimination Techniques
- Neuroimaging patterns: Regional atrophy signatures
- Alzheimer's: Hippocampal and temporal predominance
- Frontotemporal: Frontal and anterior temporal atrophy
- Vascular: White matter changes and strategic infarcts
- Genetic testing: Risk stratification and familial forms
- APOE4: 3-15x increased Alzheimer's risk
- Familial mutations: 100% penetrance in <5% of cases
- Genetic counseling: Essential for presymptomatic testing
- Neuroimaging patterns: Regional atrophy signatures
Connect this systematic discrimination through evidence-based treatment algorithms to understand how accurate diagnosis guides optimal therapeutic interventions.
🔬 The Differential Matrix: Systematic Discrimination in Cognitive Disorders
⚖️ The Treatment Algorithm: Evidence-Based Intervention Strategies
The evidence hierarchy prioritizes proven interventions with number-needed-to-treat values below 10 for meaningful clinical benefit. Understanding these metrics guides resource allocation and patient counseling about realistic expectations.
📌 Remember: TREAT guides intervention selection - Timing of initiation, Response monitoring, Efficacy thresholds, Adverse effect management, Transition planning. Each component requires specific protocols with measurable outcomes.
Evidence-Based Treatment Matrix
| Intervention | Target Population | NNT | Effect Size | Duration Benefit | Adverse Events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donepezil | Mild-moderate AD | 7-12 | 2-3 MMSE points | 6-12 months | GI upset (15-20%) |
| Rivastigmine | All severities | 8-15 | 1-2 MMSE points | 6-9 months | Nausea (25-30%) |
| Galantamine | Mild-moderate | 9-14 | 2-3 MMSE points | 6-12 months | Dizziness (10-15%) |
| Memantine | Moderate-severe | 6-10 | 1-2 MMSE points | 12-18 months | Headache (5-10%) |
| Aducanumab | Early AD | 25-50 | Biomarker only | Unknown | ARIA (35-40%) |
- Pharmacological Intervention Protocols
- Cholinesterase inhibitors: First-line therapy for mild-moderate disease
- Donepezil: 5-10mg daily with 85% tolerability
- Rivastigmine: 6-12mg daily or patch formulation
- Galantamine: 16-24mg daily with nicotinic enhancement
- NMDA antagonists: Moderate-severe disease addition
- Memantine: 10-20mg daily with low side effect profile
- Mechanism: Glutamate modulation preventing excitotoxicity
- Combination: Safe with cholinesterase inhibitors
- Cholinesterase inhibitors: First-line therapy for mild-moderate disease
💡 Master This: Response assessment requires 3-6 month evaluation periods using standardized scales (MMSE, ADAS-Cog). Stabilization (no decline) represents treatment success, as untreated patients decline 3-4 MMSE points annually.
Non-pharmacological interventions provide equivalent or superior benefits to medications, with cognitive stimulation showing 2-3 point MMSE improvement and exercise programs reducing progression risk by 30-40%.
- Comprehensive Care Algorithms
- Behavioral interventions: First-line for neuropsychiatric symptoms
- Environmental modification: 40-60% reduction in agitation
- Structured activities: 30-50% improvement in mood
- Caregiver training: 25-35% reduction in burden
- Safety assessments: Driving, medication management, fall risk
- Driving evaluation: Annual assessment after diagnosis
- Home safety: Environmental modifications reduce injury risk
- Financial protection: Legal planning prevents exploitation
- Behavioral interventions: First-line for neuropsychiatric symptoms
Connect these treatment algorithms through multi-system integration to understand how comprehensive care addresses the complex interplay between cognitive, behavioral, and functional domains.
⚖️ The Treatment Algorithm: Evidence-Based Intervention Strategies
🔗 The Cognitive Ecosystem: Multi-System Integration and Emerging Frontiers
The integration framework operates through precision medicine approaches that match individual patient profiles with targeted interventions based on genetic, biomarker, and phenotypic characteristics. This personalized strategy improves treatment response rates from 30-40% to 60-70%.
📌 Remember: CONNECT guides multi-system integration - Cognitive networks, Organ system health, Neuroinflammation, Nutrition status, Exercise capacity, Caregiver support, Technology integration. Each system requires coordinated optimization for maximum therapeutic benefit.
Integrated Care System Matrix
| System Domain | Assessment Tools | Intervention Targets | Outcome Measures | Integration Points | Evidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurological | Biomarkers, imaging | Disease modification | Cognitive scores | Neurology/psychiatry | High (Level 1) |
| Cardiovascular | Risk calculators | Vascular protection | Blood pressure control | Cardiology/neurology | High (Level 1) |
| Metabolic | HbA1c, lipids | Diabetes/lipid control | Metabolic targets | Endocrine/neurology | Moderate (Level 2) |
| Psychiatric | Depression scales | Mood stabilization | Quality of life | Psychiatry/neurology | High (Level 1) |
| Social | Caregiver burden | Support systems | Functional independence | Social work/nursing | Moderate (Level 2) |
- Emerging Therapeutic Frontiers
- Immunotherapy approaches: Amyloid-targeting monoclonal antibodies
- Aducanumab: FDA approved with controversial efficacy
- Lecanemab: 25% reduction in cognitive decline
- Donanemab: 35% slowing in early-stage disease
- Precision medicine: Genetic and biomarker-guided therapy
- APOE4 stratification: Differential treatment responses
- Tau PET imaging: Progression prediction with 85% accuracy
- Multi-modal biomarkers: Combination panels improve diagnostic precision
- Immunotherapy approaches: Amyloid-targeting monoclonal antibodies
💡 Master This: Lifestyle medicine integration achieves synergistic effects exceeding individual interventions - combining Mediterranean diet, aerobic exercise, cognitive training, and social engagement reduces dementia risk by 60% and slows progression by 40% in established disease.
Technology integration transforms care delivery through remote monitoring, AI-assisted diagnosis, and digital therapeutics that provide 24/7 support while reducing healthcare costs by 25-30%.
- Advanced Integration Strategies
- Digital health platforms: Continuous monitoring and early detection
- Smartphone assessments: Daily cognitive tracking
- Wearable devices: Sleep, activity, and physiological monitoring
- AI algorithms: Pattern recognition for decline prediction
- Caregiver support systems: Technology-enhanced care coordination
- Telemedicine: Remote consultations reduce travel burden
- Educational platforms: Evidence-based caregiver training
- Support networks: Peer connections and professional guidance
- Digital health platforms: Continuous monitoring and early detection
Connect this integrated understanding through rapid mastery frameworks to develop practical tools for immediate clinical application and optimal patient outcomes.
🔗 The Cognitive Ecosystem: Multi-System Integration and Emerging Frontiers
🎯 The Cognitive Mastery Toolkit: Rapid Assessment and Clinical Excellence
📌 Remember: MASTER cognitive assessment - Memory testing (3-word recall), Activities of daily living, Screen for depression, Timing of symptoms, Examine for focal signs, Review medications. This 6-step protocol achieves 85% diagnostic accuracy in 15 minutes.
Essential Clinical Arsenal
| Assessment Tool | Time Required | Sensitivity | Specificity | Clinical Application | Key Thresholds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mini-Cog | 3-5 minutes | 76-99% | 89-93% | Rapid screening | <3/5 abnormal |
| MMSE | 10-15 minutes | 87-96% | 90-95% | Comprehensive assessment | <24/30 dementia |
| MoCA | 10-15 minutes | 90-100% | 87-92% | MCI detection | <26/30 abnormal |
| Clock Drawing | 2-3 minutes | 85-95% | 85-90% | Executive function | <4/5 impaired |
| GDS-15 | 5-10 minutes | 80-90% | 75-85% | Depression screening | >5/15 positive |
- Rapid Diagnostic Framework
- Red flag symptoms requiring immediate evaluation
- Rapid onset (<6 months): Consider delirium or reversible causes
- Focal neurological signs: Stroke or mass lesion workup
- Behavioral changes preceding memory loss: Frontotemporal pattern
- High-yield history questions with diagnostic specificity
- "Getting lost in familiar places": 85% specific for Alzheimer's
- "Seeing things that aren't there": 90% specific for Lewy body
- "Personality completely changed": 80% specific for frontotemporal
- Red flag symptoms requiring immediate evaluation
💡 Master This: Functional assessment provides prognostic accuracy exceeding cognitive scores - IADL impairment (finances, medications, transportation) predicts nursing home placement within 2 years with 80% accuracy, while basic ADL preservation indicates 3-5 years of home care feasibility.
Treatment optimization requires systematic monitoring using validated scales and functional measures that guide medication adjustments and care transitions with evidence-based thresholds.
- Clinical Excellence Protocols
- Medication management: Start low, go slow with systematic titration
- Donepezil: Start 5mg daily × 4-6 weeks, then 10mg
- Response assessment: 3-month intervals using MMSE and functional scales
- Discontinuation criteria: Severe disease (MMSE <10) or intolerable side effects
- Safety monitoring: Systematic assessment of high-risk activities
- Driving evaluation: Annual assessment with standardized testing
- Medication safety: Pill organizers and caregiver supervision
- Fall prevention: Home assessment and environmental modifications
- Medication management: Start low, go slow with systematic titration
🎯 The Cognitive Mastery Toolkit: Rapid Assessment and Clinical Excellence
Practice Questions: Cognitive disorders (dementia)
Test your understanding with these related questions
A group of neurologists develop a new blood test for Alzheimer's. They are optimistic about the test, as they have found that for any given patient, the test repeatedly produces very similar results. However, they find that the new test results are not necessarily consistent with the gold standard of diagnosis. How would this new test most accurately be described?













