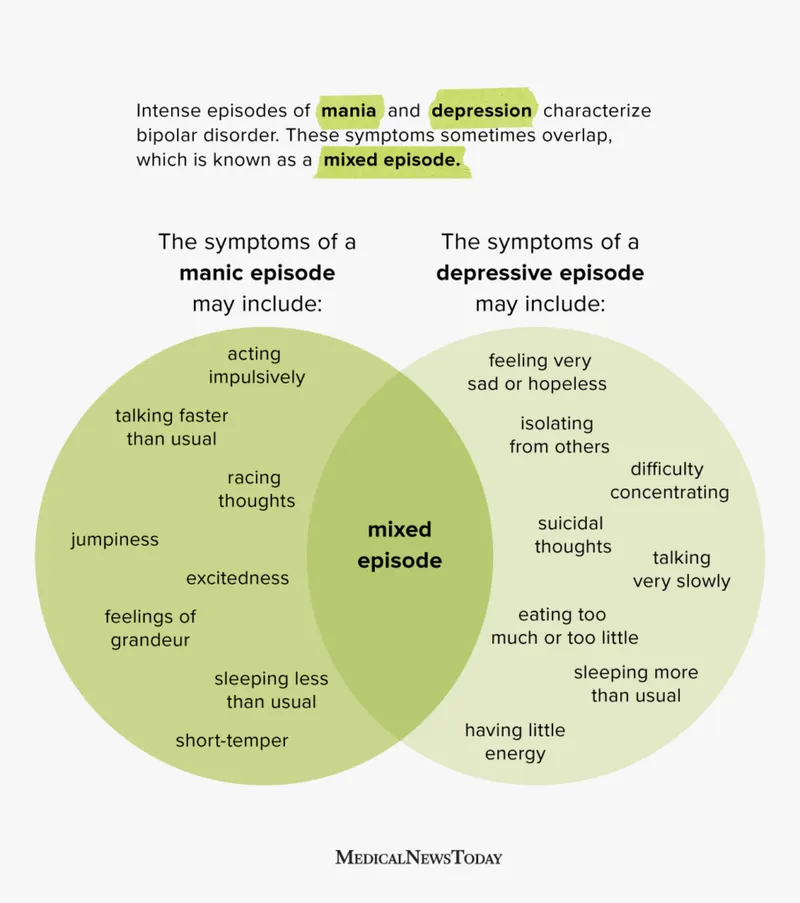
Mixed features specification US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Mixed features specification. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Mixed features specification US Medical PG Question 1: A patient with a history of hypertension and bipolar disorder is seen in your clinic for new-onset tremor, increased urination, and mild dehydration symptoms. Her bipolar disorder has been well-controlled with her current medication regimen. She recently started a new medication for better management of her hypertension. Which of the following medications did she most likely start?
- A. Amlodipine
- B. Lisinopril
- C. Hydrochlorothiazide (Correct Answer)
- D. Furosemide
- E. Metoprolol
Mixed features specification Explanation: ***Hydrochlorothiazide***
- **Thiazide diuretics** are first-line antihypertensive agents that promote **sodium and water excretion**.
- Volume depletion from thiazides **decreases renal lithium clearance**, increasing serum lithium levels and causing **lithium toxicity**.
- Classic lithium toxicity presents with **tremor, polyuria (nephrogenic diabetes insipidus), polydipsia**, and dehydration.
- This represents a critical **drug-drug interaction** between thiazides and lithium.
*Incorrect: Amlodipine*
- **Calcium channel blocker** (dihydropyridine class) commonly used for hypertension.
- Does **not affect lithium levels** or renal clearance.
- Side effects include peripheral edema and reflex tachycardia, not the symptoms described.
*Incorrect: Lisinopril*
- **ACE inhibitor** used as first-line therapy for hypertension.
- Does **not significantly affect lithium clearance** (though ACE inhibitors can have minor effects, they don't typically cause clinically significant lithium toxicity).
- Common side effects include dry cough and hyperkalemia, not tremor or polyuria.
*Incorrect: Furosemide*
- **Loop diuretic** that can cause dehydration and polyuria.
- Could potentially increase lithium levels through volume depletion, but **thiazides are more commonly implicated** in lithium toxicity.
- Furosemide is typically reserved for **resistant hypertension or heart failure**, not as initial therapy.
*Incorrect: Metoprolol*
- **Beta-blocker** used for hypertension management.
- Does **not affect lithium levels** or cause the described symptoms.
- Side effects include bradycardia, fatigue, and bronchospasm in susceptible patients.
Mixed features specification US Medical PG Question 2: A 33-year-old woman is brought to the physician by her husband because of persistent sadness for the past 2 months. During this period, she also has had difficulty sleeping and an increased appetite. She had similar episodes that occurred 2 years ago and 9 months ago that each lasted for 4 months. Between these episodes, she reported feeling very energetic and rested after 3 hours of sleep. She often went for long periods of time without eating. She works as a stock market trader and received a promotion 5 months ago. She regularly attends yoga classes on the weekends with her friends. On mental status examination, she has a blunted affect. She denies suicidal thoughts and illicit drug use. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Major depressive disorder with seasonal pattern
- B. Persistent depressive disorder
- C. Bipolar II disorder (Correct Answer)
- D. Major depressive disorder with atypical features
- E. Cyclothymic disorder
Mixed features specification Explanation: ***Bipolar II disorder***
- The patient exhibits recurrent episodes of **major depression** (sadness, sleep difficulties, increased appetite) interspersed with periods of **hypomania** (energetic, reduced need for sleep, long periods without eating, successful work performance with promotion)
- This pattern is characteristic of **Bipolar II disorder**: major depressive episodes plus at least one hypomanic episode
- No evidence of **frank mania** (e.g., psychosis, severe impairment requiring hospitalization) is present, which distinguishes this from Bipolar I disorder
*Major depressive disorder with seasonal pattern*
- While the patient presents with depressive symptoms, the episodes of **hypomania** (increased energy, decreased need for sleep) rule out unipolar depression
- The history of episodes at various times (2 years ago, 9 months ago, current) does not fit a **seasonal pattern**
- The **hypomanic phases** between depressive episodes are inconsistent with any form of major depressive disorder
*Persistent depressive disorder*
- This condition involves **chronic depressive symptoms** lasting at least 2 years, but typically less severe than major depressive episodes
- The presence of distinct, severe **major depressive episodes** and recurrent **hypomanic periods** contradicts this diagnosis
- Persistent depressive disorder does not include hypomania or mood elevation
*Major depressive disorder with atypical features*
- Atypical features include **increased appetite**, **hypersomnia**, leaden paralysis, interpersonal rejection sensitivity, and mood reactivity
- While increased appetite is present during depressive phases, the alternating periods of **hypomania** exclude this from being major depressive disorder
- Any form of major depressive disorder is ruled out by the presence of hypomanic episodes
*Cyclothymic disorder*
- Cyclothymic disorder involves numerous periods of **hypomanic symptoms** and **depressive symptoms** for at least 2 years, but symptoms do not meet full criteria for major depressive or hypomanic episodes
- This patient explicitly experiences **major depressive episodes** (persistent sadness, neurovegetative symptoms lasting 4 months), which exceed the threshold for cyclothymia
- The severity and duration of depressive episodes make Bipolar II disorder the correct diagnosis
Mixed features specification US Medical PG Question 3: A 24-year-old man is brought to your emergency department under arrest by the local police. The patient was found naked at a busy intersection jumping up and down on top of a car. Interviewing the patient, you discover that he has not slept in 2 days because he does not feel tired. He reports hearing voices. The patient was previously hospitalized 1 year ago with auditory hallucinations, paranoia, and a normal mood. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Schizophrenia
- B. Bipolar disorder
- C. Brief psychotic disorder
- D. Schizotypal disorder
- E. Schizoaffective disorder (Correct Answer)
Mixed features specification Explanation: ***Schizoaffective disorder***
- This patient demonstrates the **hallmark feature** of schizoaffective disorder: **psychotic symptoms occurring both during AND independent of mood episodes**.
- **Current presentation**: Clear **manic episode** (decreased need for sleep, grandiose/disinhibited behavior, psychomotor agitation) with psychotic features (auditory hallucinations).
- **Previous hospitalization**: **Psychotic symptoms (hallucinations, paranoia) in the absence of a mood episode** ("normal mood"), requiring hospitalization for at least 2 weeks - this is the **key diagnostic criterion** for schizoaffective disorder.
- The diagnosis requires an **uninterrupted period of illness** with both psychotic symptoms (meeting Criterion A for schizophrenia) and a major mood episode, PLUS psychotic symptoms for **≥2 weeks without prominent mood symptoms**.
*Bipolar disorder*
- In bipolar disorder with psychotic features, psychotic symptoms occur **exclusively during mood episodes** (manic, hypomanic, or depressive).
- This patient's previous hospitalization with psychosis but **"normal mood"** indicates psychotic symptoms independent of mood episodes, which **rules out** bipolar disorder and points to schizoaffective disorder.
- While the current presentation shows mania with psychosis, the longitudinal course is critical for diagnosis.
*Schizophrenia*
- Schizophrenia involves **continuous psychotic symptoms** without prominent mood episodes dominating the clinical picture.
- This patient has **prominent manic symptoms** (decreased sleep, grandiose behavior, agitation) that are central to the current presentation, making schizophrenia less likely.
- The presence of full mood episodes that occupy a **substantial portion** of the illness duration favors schizoaffective disorder over schizophrenia.
*Brief psychotic disorder*
- Brief psychotic disorder involves psychotic symptoms lasting **<1 month** with full return to baseline functioning.
- This patient has a **recurrent course** with hospitalization 1 year ago, indicating a chronic/recurring condition rather than a brief, self-limited episode.
*Schizotypal disorder*
- This is a **personality disorder** characterized by social deficits, cognitive/perceptual distortions, and eccentric behavior, but **NOT overt psychotic episodes**.
- Does not involve acute psychotic breaks with severe symptoms like hallucinations requiring hospitalization or manic episodes.
Mixed features specification US Medical PG Question 4: A 24-year-old male comes into the psychiatric clinic complaining of consistent sadness. He endorses feelings of worthlessness, anxiety, and anhedonia for the past couple months but denies feeling suicidal. He further denies any past episodes of feeling overly energetic with racing thoughts. Confident of the diagnosis, you recommend frequent talk therapy along with a long-term prescription of a known first-line medication for this disorder. What is the drug and what are some of the most frequently encountered side effects?
- A. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; hypomania, suicidal thoughts
- B. Tricyclic antidepressants; hypomania, suicidal thoughts
- C. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; anorgasmia, insomnia (Correct Answer)
- D. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors; Orthostatic hypotension, weight gain
- E. Tricyclic antidepressants; Orthostatic hypotension, anticholinergic effects
Mixed features specification Explanation: ***Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; anorgasmia, insomnia***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **major depressive disorder**, including persistent sadness, worthlessness, anxiety, and anhedonia, without any history of manic or hypomanic episodes. **SSRIs** are considered first-line pharmacotherapy for this condition.
- Common side effects of SSRIs include **sexual dysfunction** (e.g., anorgasmia, decreased libido) and **insomnia** or agitation, especially during the initial weeks of treatment.
*Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; hypomania, suicidal thoughts*
- While SSRIs are the correct drug class, **hypomania** is not a frequent side effect in patients without bipolar disorder. For patients with bipolar disorder, antidepressant monotherapy can induce hypomania or mania, but this patient denies such episodes.
- **Suicidal thoughts** can occur, particularly in young adults, during the initial phase of antidepressant treatment, but it is less common to frame it as a *frequently encountered side effect* in the general population compared to sexual dysfunction or sleep disturbances.
*Tricyclic antidepressants; hypomania, suicidal thoughts*
- **Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)** are generally not first-line due to their less favorable side effect profile compared to SSRIs, including significant anticholinergic effects and cardiovascular risks.
- As with SSRIs, **hypomania** is not a typical frequent side effect in unipolar depression, and while **suicidal thoughts** are a concern with antidepressants, TCAs carry a higher risk of lethality in overdose, making them less preferred initially.
*Monoamine oxidase inhibitors; Orthostatic hypotension, weight gain*
- **Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)** are effective but are typically reserved for **refractory depression** due to their significant drug and food interactions (e.g., tyramine-induced hypertensive crisis).
- While **orthostatic hypotension** and **weight gain** are known side effects of MAOIs, this class is not considered a first-line treatment for major depressive disorder.
*Tricyclic antidepressants; Orthostatic hypotension, anticholinergic effects*
- **TCAs** are indeed associated with side effects such as **orthostatic hypotension** and prominent **anticholinergic effects** (e.g., dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, urinary retention).
- However, because of these more burdensome side effects and higher toxicity in overdose, TCAs are not generally considered the first-line medication choice, especially when SSRIs are available and safer.
Mixed features specification US Medical PG Question 5: A 57-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by the police after he was found running around a local park naked and screaming late at night. During intake, the patient talks non-stop about the government spying on him and his family, but provides little useful information besides his name and date of birth. Occasionally he refers to himself in the third person. He refuses to eat anything and will only drink clear fluids because he is afraid of being poisoned. A medical records search reveals that the patient has been treated for psychotic behavior and occasional bouts of severe depression for several years. Today, his heart rate is 90/min, respiratory rate is 19/min, blood pressure is 135/85 mm Hg, and temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F). On physical exam, he appears gaunt and anxious. His heart has a regular rate and rhythm and his lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. CMP, CBC, and TSH are normal. A urine toxicology test is negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Schizophrenia
- B. Major depressive disorder
- C. Schizoaffective disorder (Correct Answer)
- D. Brief psychotic disorder
- E. Bipolar 1 disorder
Mixed features specification Explanation: ***Schizoaffective disorder***
- The patient exhibits features of both a **mood disorder** (severe depression) and a **psychotic disorder** (delusions, disorganized behavior, referring to himself in the third person), which are key characteristics of schizoaffective disorder.
- The history of **psychotic behavior** and **severe depression** over several years, with current presentation involving both prominent mood symptoms (agitation, gaunt appearance suggesting poor self-care due to mood) and psychotic features (paranoia, disorganized speech), supports this diagnosis over other psychotic or mood disorders.
*Schizophrenia*
- While the patient exhibits **psychotic symptoms** (delusions, disorganization), the history of "occasional bouts of severe depression" suggests a more prominent and recurring mood component than typically seen in schizophrenia.
- In schizophrenia, mood symptoms are often confined to brief periods relative to the duration of the psychotic illness or are not a prominent and defining feature.
*Major depressive disorder*
- This diagnosis is incorrect because the patient displays clear and pervasive **psychotic symptoms** such as paranoia, disorganized speech, and bizarre behavior (running naked, screaming), which are beyond what is typically seen in major depressive disorder with psychotic features (where psychosis is congruent with the depressive theme).
- The historical pattern of **psychotic behavior** occurring separately from or alongside depressive episodes points away from a primary diagnosis of major depressive disorder.
*Brief psychotic disorder*
- This diagnosis is characterized by psychotic symptoms lasting **less than one month**, with an eventual full return to premorbid functioning.
- The patient's history of **several years** of psychotic behavior and severe depression rules out this acute and time-limited condition.
*Bipolar 1 disorder*
- While bipolar 1 disorder can feature **psychotic symptoms** during manic or depressive episodes, the presentation here emphasizes persistent psychotic features (delusions of being spied on, fear of poisoning) that are not always directly tied to mood episodes or are more enduring than typical for bipolar disorder.
- The long-standing history of both **psychotic and depressive episodes** suggests a more integrated condition of mood and psychosis rather than distinct episodes as seen in bipolar 1 disorder.
Mixed features specification US Medical PG Question 6: A 19-year-old woman presents to an outpatient psychiatrist after 2 weeks of feeling “miserable.” She has been keeping to herself during this time with no desire to socialize with her friends or unable to enjoy her usual hobbies. She also endorses low energy, difficulty concentrating and falling asleep, and decreased appetite. You diagnose a major depressive episode but want to screen for bipolar disorder before starting her on an anti-depressant. Which of the following cluster of symptoms, if previously experienced by this patient, would be most consistent with bipolar I disorder?
- A. Insomnia, anxiety, nightmares, and flashbacks for 6 months
- B. Elevated mood, insomnia, distractibility, and flight of ideas for 5 days
- C. Impulsivity, rapid mood swings, intense anger, self-harming behavior, and splitting for 10 years
- D. Auditory hallucinations, paranoia, and disorganized speech for 2 weeks
- E. Impulsivity, insomnia, increased energy, irritability, and auditory hallucinations for 2 weeks (Correct Answer)
Mixed features specification Explanation: ***Impulsivity, insomnia, increased energy, irritability, and auditory hallucinations for 2 weeks***
- This cluster of symptoms indicates a past **manic episode** with **psychotic features**, characteristic of **Bipolar I disorder**. The duration of 2 weeks meets the diagnostic criteria for a manic episode.
- The presence of **auditory hallucinations** during a manic episode signifies **psychosis**, which is a key differentiator in Bipolar I as opposed to Bipolar II.
*Elevated mood, insomnia, distractibility, and flight of ideas for 5 days*
- While these symptoms suggest a **hypomanic episode**, the duration of 5 days is insufficient to meet the criteria for a manic episode (which requires a minimum of 7 days or hospitalization).
- A hypomanic episode, without psychotic features, indicates **Bipolar II disorder**, not Bipolar I.
*Insomnia, anxiety, nightmares, and flashbacks for 6 months*
- This symptom cluster is highly suggestive of **Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)** due to the presence of nightmares and flashbacks over an extended period.
- These symptoms are not indicative of a manic or hypomanic episode, and thus do not point to bipolar disorder.
*Auditory hallucinations, paranoia, and disorganized speech for 2 weeks*
- This constellation of symptoms suggests a **psychotic disorder** such as **schizophrenia** or **schizophreniform disorder**, especially with auditory hallucinations and disorganized speech dominating the clinical picture.
- While psychosis can occur in bipolar disorder, the question specifically asks for symptoms *consistent with bipolar I*, and these symptoms alone do not describe the characteristic mood disturbance (mania) of bipolar disorder.
*Impulsivity, rapid mood swings, intense anger, self-harming behavior, and splitting for 10 years*
- This pattern of symptoms, particularly the chronic impulsivity, rapid mood swings, intense anger, and splitting, is highly suggestive of **Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)**.
- The chronic nature and specific interpersonal and behavioral challenges are hallmarks of BPD, not primarily a manic or hypomanic episode of bipolar disorder.
Mixed features specification US Medical PG Question 7: A 55-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of fluctuating mood for the past 2 years. He feels great and full of energy for some months when he is very creative with tons of ideas just racing through his mind. He is noted to be very talkative and distracted by his different ideas. During these times, he is very productive and able to accomplish much at work and home. However, these periods are frequently followed by a prolonged depressed mood. During this time, he has low energy, poor concentration, and low self-esteem. The accompanying feeling of hopelessness from these cycling “ups” and “downs” have him eating and sleeping more during the “downs.” He does not remember a period within the last 2 years where he felt “normal.” What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Dysthymic disorder
- B. Bipolar II disorder
- C. Persistent depressive disorder
- D. Bipolar I disorder
- E. Cyclothymic disorder (Correct Answer)
Mixed features specification Explanation: ***Cyclothymic disorder***
- The patient experiences chronic **fluctuating moods**, with numerous periods of **hypomanic symptoms** (elevated energy, racing thoughts, increased productivity) and numerous periods of **depressive symptoms** (low energy, poor concentration, hopelessness) over at least 2 years.
- The symptoms are not severe enough to meet full criteria for a **manic episode**, **hypomanic episode**, or **major depressive episode**, and there has been no period longer than 2 months without symptoms.
*Dysthymic disorder*
- This is the **DSM-IV term** for what is now called **persistent depressive disorder** in DSM-5, involving a **chronic depressed mood** that lasts for at least 2 years.
- It does not include periods of significant elevated mood or hypomania.
- The patient's presentation includes distinct periods of **elevated mood and energy**, which are not characteristic of dysthymic disorder.
*Bipolar II disorder*
- Bipolar II disorder requires at least one **major depressive episode** and at least one **hypomanic episode**.
- While the patient exhibits hypomanic and depressive symptoms, the periods of depression do not meet the full criteria for a **major depressive episode** (e.g., duration, number of symptoms) and the hypomanic symptoms are subsyndromal.
*Persistent depressive disorder*
- This is the **DSM-5 term** for chronic low-grade depression (formerly called dysthymic disorder), characterized by depressed mood for at least 2 years without manic or hypomanic symptoms.
- The patient's history of elevated mood and energy precludes this diagnosis.
*Bipolar I disorder*
- Bipolar I disorder requires at least one **manic episode**, which is characterized by a distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood and abnormally and persistently increased goal-directed activity or energy, lasting at least 1 week and causing significant impairment.
- The patient's "ups" are described as productive and not causing significant impairment or involving psychotic features, indicating **hypomanic symptoms** rather than full mania.
Mixed features specification US Medical PG Question 8: A 23-year-old woman is brought to the physician by her father because of irritability, mood swings, and difficulty sleeping over the past 10 days. A few days ago, she quit her job and spent all of her savings on supplies for a “genius business plan.” She has been energetic despite sleeping only 1–2 hours each night. She was diagnosed with major depressive disorder 2 years ago. Mental status examination shows pressured speech, a labile affect, and flight of ideas. Throughout the examination, she repeatedly states “I feel great, I don't need to be here.” Urine toxicology screening is negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Schizoaffective disorder
- B. Bipolar disorder type II
- C. Bipolar disorder type I (Correct Answer)
- D. Delusional disorder
- E. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Mixed features specification Explanation: ***Bipolar disorder type I***
- The patient's presentation of lasting **elevated mood**, decreased need for sleep, increased energy, pressured speech, flight of ideas, and impulsive behavior (quitting job, spending savings) are hallmark symptoms of a **manic episode**.
- A diagnosis of **Bipolar I Disorder** requires the occurrence of at least one manic episode, which is clearly evident here and distinguishes it from other mood disorders, especially given her prior history of major depressive disorder.
*Schizoaffective disorder*
- This disorder involves a period of illness during which there is an uninterrupted period of major mood episode (depressive or manic) concurrent with symptoms of **schizophrenia**, such as delusions or hallucinations, for at least 2 weeks in the absence of a major mood episode.
- The patient's symptoms are primarily mood-driven and do not include the characteristic psychotic features that persist independently of mood disturbances.
*Bipolar disorder type II*
- Bipolar II Disorder is characterized by at least one major depressive episode and at least one **hypomanic episode**.
- The patient's current symptoms, including significant impairment in social/occupational functioning, are indicative of a **manic episode**, not a hypomanic episode, which by definition does not cause marked impairment or require hospitalization.
*Delusional disorder*
- This disorder is characterized by the presence of **non-bizarre delusions** that last for at least one month, without other prominent psychotic symptoms or significant impairment in functioning.
- While the patient's "genius business plan" might seem delusional, her pervasive mood disturbance, flight of ideas, and significant functional impairment are not consistent with the primary features of delusional disorder.
*Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder*
- ADHD is characterized by a persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with functioning or development, often presenting in childhood.
- While there is some overlap in symptoms like impulsivity and difficulty sleeping, the episodic nature, the extent of **mood disturbance**, grandiosity, and **pressured speech** are more characteristic of a manic episode than ADHD.
Mixed features specification US Medical PG Question 9: A 25-year-old woman is brought to a psychiatrist's office by her husband who states that he is worried about her recent behavior, as it has become more violent. The patient's husband states that his family drove across the country to visit them and that his wife 'threatened his parents with a knife' at dinner last night. Police had to be called to calm her down. He states that she has been acting 'really crazy' for the last 9 months, and the initial behavior that caused him alarm was her admission that his deceased sister was talking to her through a decorative piece of ceramic art in the living room. Initially, he thought she was joking, but soon realized her complaints of 'hearing ghosts' talking to her throughout the house were persisting and 'getting worse'. Over the past 9 months, she has experienced multiple periods of profound sadness, with persistent insomnia and an unintentional weight loss of 12 pounds over several months. She has been complaining of feeling 'worthless' and has had markedly diminished interest in activities for much of this time period. Her general hygiene has also suffered from her recent lack of motivation and she insists that the 'ghosts' are asking her to kill as many people as she can so they won't be alone in the house. Her husband is extremely concerned that she may harm herself or someone else. He states that she currently does not take any medications or illicit drugs as far as he knows. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. The patient herself does not make eye contact or want to speak to the psychiatrist, allowing her husband to speak on her behalf. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Schizophreniform disorder
- B. Schizophrenia
- C. Delusional disorder
- D. Schizoaffective disorder (Correct Answer)
- E. Brief psychotic disorder
Mixed features specification Explanation: ***Schizoaffective disorder***
- This patient exhibits symptoms of both a **major depressive disorder** (multiple periods of profound **sadness**, persistent **insomnia**, **weight loss** over several months, feelings of **worthlessness**, and markedly **diminished interest in activities**) and a **psychotic disorder** (auditory **hallucinations**, command hallucinations, **delusions**, violent behavior).
- The total symptom duration is **9 months**, with **mood symptoms present for the majority of this period**, meeting the key DSM-5 criterion for schizoaffective disorder.
- The patient also demonstrates **psychotic symptoms (hallucinations) that persist throughout**, including periods when mood symptoms may fluctuate, satisfying the requirement for delusions or hallucinations for ≥2 weeks in the absence of a major mood episode.
- The combination of prominent mood episodes concurrent with schizophrenia-spectrum symptoms, with mood symptoms present for the majority of the illness duration, confirms schizoaffective disorder.
*Schizophreniform disorder*
- This disorder involves symptoms characteristic of **schizophrenia** lasting **between 1 and 6 months**.
- The patient's symptoms have been present for **9 months**, exceeding the maximum duration for schizophreniform disorder.
*Schizophrenia*
- Schizophrenia requires persistent psychotic symptoms lasting **at least 6 months**, with at least one month of active-phase symptoms.
- While this patient has psychotic symptoms for 9 months, the **prominent and prolonged depressive symptoms** that are present for the **majority of the illness duration** distinguish this from schizophrenia.
- In schizophrenia, mood symptoms, if present, are **brief relative to the total duration** of the psychotic illness, which is not the case here.
*Delusional disorder*
- Delusional disorder is characterized by **non-bizarre delusions** for at least 1 month, without other prominent psychotic symptoms.
- This patient experiences prominent **auditory hallucinations** ("hearing ghosts," "deceased sister talking to her") and **command hallucinations**, which are not features of delusional disorder.
- The presence of hallucinations rules out this diagnosis.
*Brief psychotic disorder*
- This diagnosis involves sudden onset of psychotic symptoms lasting **more than 1 day but less than 1 month**, with eventual full recovery.
- The patient's symptoms have persisted for **9 months**, far exceeding the duration criterion for brief psychotic disorder.
Mixed features specification US Medical PG Question 10: A 27-year-old woman is brought to the office at the insistence of her fiancé to be evaluated for auditory hallucinations for the past 8 months. The patient’s fiancé tells the physician that the patient often mentions that she can hear her own thoughts speaking aloud to her. The hallucinations have occurred intermittently for at least 1-month periods. Past medical history is significant for hypertension. Her medications include lisinopril and a daily multivitamin both of which she frequently neglects. She lost her security job 7 months ago after failing to report to work on time. The patient’s vital signs include: blood pressure 132/82 mm Hg; pulse 72/min; respiratory rate 18/min, and temperature 36.7°C (98.1°F). On physical examination, the patient has a flat affect and her focus fluctuates from the window to the door. She is disheveled with a foul smell. She has difficulty focusing on the discussion and does not quite understand what is happening around her. A urine toxicology screen is negative. Which of the following is the correct diagnosis for this patient?
- A. Schizoaffective disorder
- B. Schizophrenia (Correct Answer)
- C. Schizoid personality disorder
- D. Schizophreniform disorder
- E. Schizotypal personality disorder
Mixed features specification Explanation: ***Schizophrenia***
- The patient exhibits core symptoms of schizophrenia, including **auditory hallucinations** (hearing thoughts speaking aloud), **disorganized thinking** (difficulty focusing, fluctuating focus), and **negative symptoms** (flat affect, disheveled, foul smell, loss of job due to poor function). These symptoms have been present for **at least 6 months** (8 months of hallucinations, 7 months of job loss), which meets the diagnostic criteria.
- The duration of symptoms (over 6 months) differentiates it from schizophreniform disorder, and the absence of prominent mood episodes rules out schizoaffective disorder.
*Schizoaffective disorder*
- This diagnosis requires a **major mood episode** (depressive or manic) concurrent with Criterion A of schizophrenia, along with a period of **at least 2 weeks of delusions or hallucinations in the absence of prominent mood symptoms**.
- While the patient has some signs of distress (lost job, disorganized), a full major mood episode is not described, and the primary symptoms are clearly psychotic.
*Schizoid personality disorder*
- This is characterized by a pervasive pattern of **detachment from social relationships** and a restricted range of emotional expression, often appearing indifferent to praise or criticism.
- The patient's symptoms are primarily psychotic (hallucinations, disorganized thought), not just social withdrawal or emotional flatness. She doesn't necessarily avoid social contact, but her psychosis interferes with it.
*Schizophreniform disorder*
- This disorder presents with symptoms identical to schizophrenia but with a **duration of at least 1 month but less than 6 months**.
- The patient's symptoms, particularly the auditory hallucinations, have been present for 8 months and are therefore outside the timeframe for schizophreniform disorder.
*Schizotypal personality disorder*
- This disorder involves a pervasive pattern of **social and interpersonal deficits** marked by acute discomfort with, and reduced capacity for, close relationships, as well as **cognitive or perceptual distortions** and eccentric behaviors.
- While there may be some odd beliefs or magical thinking, **full-blown psychotic symptoms like prominent auditory hallucinations** (hearing thoughts speaking aloud) are generally not present as consistently or severely as seen in this patient, who meets criteria for a major psychotic disorder.
More Mixed features specification US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.