Gravity effects on V/Q distribution US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Gravity effects on V/Q distribution. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution US Medical PG Question 1: During a clinical study examining the diffusion of gas between the alveolar compartment and the pulmonary capillary blood, men between the ages of 20 and 50 years are evaluated while they hold a sitting position. After inhaling a water-soluble gas that rapidly combines with hemoglobin, the concentration of the gas in the participant's exhaled air is measured and the diffusion capacity is calculated. Assuming that the concentration of the inhaled gas remains the same, which of the following is most likely to increase the flow of the gas across the alveolar membrane?
- A. Deep exhalation
- B. Entering a cold chamber
- C. Treadmill exercise (Correct Answer)
- D. Standing straight
- E. Assuming a hunched position
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution Explanation: ***Correct: Treadmill exercise***
- **Treadmill exercise** increases cardiac output and pulmonary blood flow, which in turn recruits and distends more **pulmonary capillaries**. This increases the **surface area** available for gas exchange and reduces the diffusion distance, thereby enhancing the flow of gas across the alveolar membrane.
- Exercise also typically leads to deeper and more frequent breaths, increasing the **ventilation-perfusion matching** and overall efficiency of gas exchange.
- According to Fick's law of diffusion (Vgas = A/T × D × ΔP), increasing the surface area (A) directly increases gas flow.
*Incorrect: Deep exhalation*
- **Deep exhalation** would empty the lungs more completely, potentially leading to alveolar collapse in some regions and thus **decreasing the alveolar surface area** available for gas exchange.
- This would also reduce the **driving pressure** for gas diffusion by lowering the alveolar concentration of the inhaled gas.
*Incorrect: Entering a cold chamber*
- Exposure to a **cold chamber** can cause **bronchoconstriction** in some individuals, particularly those with reactive airways, which would increase airway resistance and potentially reduce alveolar ventilation.
- While metabolic rate may slightly increase in the cold, the primary effect on the lungs is unlikely to promote increased gas diffusion in a healthy individual.
*Incorrect: Standing straight*
- **Standing straight** is a normal physiological posture and does not significantly alter the **pulmonary capillary recruitment** or the alveolar surface area in a way that would dramatically increase gas flow compared to a seated position.
- There might be minor gravitational effects on blood flow distribution, but these are generally less impactful than dynamic changes like exercise.
*Incorrect: Assuming a hunched position*
- **Assuming a hunched position** can restrict chest wall expansion and diaphragm movement, leading to **reduced tidal volume** and overall alveolar ventilation.
- This posture, by reducing lung volumes and potentially compressing the lungs, would likely **decrease the effective surface area** for gas exchange and therefore reduce gas flow.
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution US Medical PG Question 2: A 32-year-old woman presents with progressive shortness of breath and a dry cough. She says that her symptoms onset recently after a 12-hour flight. Past medical history is unremarkable. Current medications are oral estrogen/progesterone containing contraceptive pills. Her vital signs include: blood pressure 110/60 mm Hg, pulse 101/min, respiratory rate 22/min, oxygen saturation 88% on room air, and temperature 37.9℃ (100.2℉). Her weight is 94 kg (207.2 lb) and height is 170 cm (5 ft 7 in). On physical examination, she is acrocyanotic. There are significant swelling and warmth over the right calf. There are widespread bilateral rales present. Cardiac auscultation reveals accentuation of the pulmonic component of the second heart sound (P2) and an S3 gallop. Which of the following ventilation/perfusion (V/Q) ratios most likely corresponds to this patient’s condition?
- A. 1.3 (Correct Answer)
- B. 1
- C. 0.8
- D. 0.5
- E. 0.3
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution Explanation: ***1.3***
- This value represents an increased V/Q ratio, or **dead space ventilation**, which is characteristic of a **pulmonary embolism (PE)**. In PE, a portion of the lung is ventilated but not perfused due to the embolism blocking blood flow, leading to wasted ventilation.
- The patient's symptoms (sudden onset dyspnea after a long flight, use of oral contraceptives, calf swelling, hypoxia, and accentuated P2) are highly suggestive of a PE, which is the most likely cause of increased V/Q mismatch.
*1*
- A V/Q ratio of 1 indicates **perfect matching** of ventilation and perfusion, which is an ideal state not typically achieved throughout the entire lung, especially in disease.
- This value would not explain the patient's severe **hypoxia** and overall clinical picture of respiratory distress.
*0.8*
- This is the **average normal V/Q ratio** for the lung as a whole, representing slightly more perfusion than ventilation.
- While it's a normal physiological state, it does not account for the significant V/Q mismatch indicated by the patient's severe hypoxemia (SpO2 88%) and clinical symptoms.
*0.5*
- This value represents a **low V/Q ratio**, indicating relatively more perfusion than ventilation, often seen in conditions like **shunt physiology** (e.g., pneumonia, atelectasis, pulmonary edema).
- While the patient has rales and an S3 gallop suggesting potential pulmonary edema or heart failure secondary to increased right heart strain, the primary pathophysiology in PE is increased V/Q due to unperfused but ventilated lung regions.
*0.3*
- This is a severely **low V/Q ratio**, approaching a **shunt**, where blood passes through the lungs without being adequately oxygenated. This is typical of conditions like **severe pneumonia, ARDS, or significant atelectasis**.
- While PE can cause some degree of bronchoconstriction leading to areas of low V/Q, the predominant and most impactful V/Q mismatch in PE is the high V/Q ratio in areas of unperfused lung.
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution US Medical PG Question 3: An experiment to determine the effects of gravity on blood pressure is conducted on 3 individuals of equal height and blood pressure oriented in different positions in space. Participant A is strapped in a supine position on a bed turned upside down in a vertical orientation with his head towards the floor and his feet towards the ceiling. Participant B is strapped in a supine position on a bed turned downwards in a vertical orientation with his head towards the ceiling and his feet just about touching the floor. Participant C is strapped in a supine position on a bed in a horizontal orientation. Blood pressure readings are then taken at the level of the head, heart, and feet from all 3 participants. Which of these positions will have the lowest recorded blood pressure reading?
- A. Participant B: at the level of the feet
- B. Participant A: at the level of the head
- C. Participant C: at the level of the heart
- D. Participant A: at the level of the feet (Correct Answer)
- E. Participant C: at the level of the feet
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution Explanation: ***Participant A: at the level of the feet***
- In Participant A, the feet are positioned **highest vertically** relative to the heart and are also above the head due to the upside-down vertical orientation. Due to gravity, blood pressure decreases with increasing height above the heart.
- This position would result in the lowest hydrostatic pressure at the feet, leading to the **lowest recorded blood pressure reading**.
*Participant B: at the level of the feet*
- In Participant B, the feet are positioned **below the heart** (towards the floor) in a vertical orientation.
- This position would experience some of the **highest hydrostatic pressure** due to gravity, leading to a high blood pressure reading, not the lowest.
*Participant A: at the level of the head*
- In Participant A, the head is positioned **below the heart** (towards the floor) in an upside-down vertical orientation.
- This position would experience increased hydrostatic pressure, hence a **higher blood pressure** compared to the feet.
*Participant C: at the level of the heart*
- Participant C is in a horizontal position, meaning all body parts are at roughly the same hydrostatic level relative to the heart.
- Blood pressure readings would be **similar across all points** (head, heart, feet) and would reflect the systemic arterial pressure without significant hydrostatic effects, thus not the lowest compared to other extreme positions.
*Participant C: at the level of the feet*
- In Participant C (horizontal), the feet are at approximately the **same hydrostatic level** as the heart.
- The reading at the feet in this position would be close to the **baseline arterial pressure**, not the lowest, as there's minimal hydrostatic gradient.
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution US Medical PG Question 4: A 35-year-old woman volunteers for a study on respiratory physiology. Pressure probes A and B are placed as follows:
Probe A: between the parietal and visceral pleura
Probe B: within the cavity of an alveolus
The probes provide a pressure reading relative to atmospheric pressure. To obtain a baseline reading, she is asked to sit comfortably and breathe normally. Which of the following sets of values will most likely be seen at the end of inspiration?
- A. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg (Correct Answer)
- B. Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- C. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg
- D. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- E. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution Explanation: ***Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg***
- At the **end of inspiration**, the **intrapleural pressure (Probe A)** is at its most negative, typically around -6 to -8 cm H2O (equivalent to -4 to -6 mmHg), reflecting the maximum expansion of the thoracic cavity.
- At the **end of inspiration**, just before exhalation begins, there is **no airflow**, so the **intrapulmonary pressure (Probe B)** equalizes with atmospheric pressure, resulting in a 0 mm Hg reading.
*Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of 0 mm Hg** would indicate a **pneumothorax** since it should always be negative to prevent lung collapse.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** would indicate that **inspiration is still ongoing**, as air would be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapulmonary pressure of 0 mm Hg** is correct at the end of inspiration, an **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is typical for the **end of expiration (Functional Residual Capacity)** during quiet breathing, not the end of inspiration.
- The **intrapleural pressure becomes more negative** during inspiration due to increased thoracic volume, so -4 mm Hg would be insufficient.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is the normal pressure at the **end of expiration**, not the end of inspiration, where it becomes more negative.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** indicates that **inspiration is still in progress**, not at its end, as air would still be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapleural pressure of -6 mm Hg** is consistent with the end of inspiration, an **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** means that **airflow is still occurring into the lungs**.
- At the **very end of inspiration**, just before the start of exhalation, airflow momentarily ceases, and intrapulmonary pressure becomes zero relative to the atmosphere.
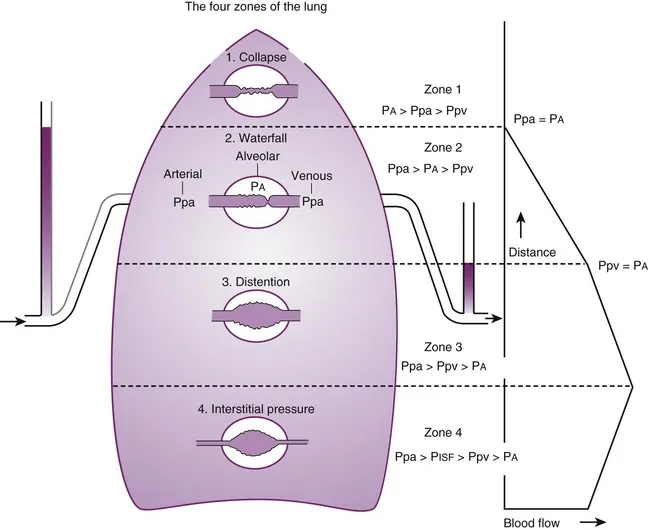
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution US Medical PG Question 5: A 22-year-old man volunteers for a research study on lung function. He has no history of lung disease or allergies and does not smoke. His pulmonary blood flow is measured in the various labeled segments of the lungs while standing. Then the volunteer, still standing, is given very low continuous positive airway pressure and the blood flow measured again. Which of the following sets of findings are most likely to be present in the second measurements relative to the first?
- A. Increased blood flow in zone 2
- B. Reduced blood flow in zone 3
- C. Reduced blood flow in zone 1
- D. Increased blood flow in zone 3
- E. Increased blood flow in zone 1 (Correct Answer)
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution Explanation: ***Increased blood flow in zone 1***
- In healthy standing subjects, **Zone 1** may not exist or is minimal at the apex where alveolar pressure (PA) can exceed arterial pressure (Pa).
- **Very low CPAP** increases alveolar pressure, but when applied at very low levels, it may **recruit collapsed or under-perfused alveoli** by preventing alveolar collapse and improving the pressure gradient.
- The net effect with **very low CPAP** can paradoxically **improve perfusion** in Zone 1 by optimizing alveolar mechanics and reducing vascular resistance through **alveolar recruitment**, particularly in previously under-ventilated apical regions.
*Increased blood flow in zone 2*
- In Zone 2, arterial pressure exceeds alveolar pressure, which exceeds venous pressure (**Pa > PA > Pv**), creating a waterfall effect.
- While CPAP increases alveolar pressure (PA), this would increase the downstream resistance and typically **reduce** the arterial-alveolar pressure gradient (Pa - PA), decreasing flow rather than increasing it.
*Increased blood flow in zone 3*
- **Zone 3** (lung base) normally has the **highest blood flow** where both arterial and venous pressures exceed alveolar pressure (**Pa > Pv > PA**).
- CPAP increases alveolar pressure (PA), which would compress capillaries and **reduce** the pressure gradient, typically decreasing rather than increasing blood flow in this zone.
*Reduced blood flow in zone 1*
- While increasing alveolar pressure with CPAP might be expected to **reduce** Zone 1 perfusion by compressing capillaries, **very low levels of CPAP** can have the opposite effect through **alveolar recruitment** and optimization of lung mechanics.
- The question specifies **very low** CPAP, which is the key—this level improves alveolar patency without significantly compressing capillaries.
*Reduced blood flow in zone 3*
- Zone 3 typically has the highest blood flow due to favorable pressure gradients from gravity.
- CPAP increases PA, which could compress capillaries and reduce the (Pa - PA) gradient, but the **very low level** specified means this effect is minimal and Zone 3 generally maintains adequate perfusion.
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution US Medical PG Question 6: In which of the following pathological states would the oxygen content of the trachea resemble the oxygen content in the affected alveoli?
- A. Emphysema
- B. Exercise
- C. Pulmonary embolism (Correct Answer)
- D. Pulmonary fibrosis
- E. Foreign body obstruction distal to the trachea
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution Explanation: ***Pulmonary embolism***
- A pulmonary embolism blocks **blood flow** to a portion of the lung, creating **dead space ventilation** (high V/Q ratio).
- In the affected alveoli, **no blood perfusion** means no oxygen extraction occurs, so the alveolar oxygen content remains **high and similar to tracheal/inspired air**.
- This is the classic physiological state where ventilation continues but perfusion is absent, preventing gas exchange.
*Foreign body obstruction distal to the trachea*
- A complete obstruction **prevents fresh air** from reaching the affected alveoli.
- The trapped gas undergoes **resorption atelectasis**: oxygen is absorbed into capillary blood, CO2 diffuses in, and alveolar gas equilibrates with **venous blood** composition.
- Alveolar oxygen content becomes **very low**, not similar to tracheal air.
*Emphysema*
- Emphysema involves destruction of **alveolar walls** and enlargement of airspaces with impaired gas exchange.
- While V/Q mismatch occurs, oxygen is still extracted by perfusing blood.
- Alveolar oxygen content is **lower than tracheal air** due to ongoing (though inefficient) gas exchange.
*Exercise*
- During exercise, **oxygen consumption increases** dramatically with enhanced cardiac output and oxygen extraction.
- Alveolar oxygen content is **significantly lower** than tracheal air due to increased oxygen uptake by blood.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- Pulmonary fibrosis causes **thickening of the alveolar-capillary membrane**, impairing oxygen diffusion.
- Despite diffusion limitation, blood still perfuses the alveoli and extracts oxygen.
- Alveolar oxygen content is **lower than tracheal air**, though the A-a gradient is increased.
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution US Medical PG Question 7: A 68-year-old man comes to the emergency room with difficulty in breathing. He was diagnosed with severe obstructive lung disease a few years back. He uses his medication but often has to come to the emergency room for intravenous therapy to help him breathe. He was a smoker for 40 years smoking two packs of cigarettes every day. Which of the following best represents the expected changes in his ventilation, perfusion and V/Q ratio?
- A. Normal ventilation, low or nonexistent perfusion and infinite V/Q ratio
- B. Medium ventilation and perfusion, V/Q that equals 0.8
- C. Higher ventilation and perfusion with lower V/Q ratio
- D. Low ventilation, normal perfusion and low V/Q ratio (Correct Answer)
- E. Lower ventilation and perfusion, but higher V/Q ratio
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution Explanation: ***Low ventilation, normal perfusion and low V/Q ratio***
- In severe **obstructive lung disease** (like COPD), there is airflow limitation, leading to areas of **hypoventilation** in the lungs.
- While ventilation is compromised, blood flow (perfusion) to these areas can remain relatively normal, resulting in a **decreased V/Q ratio**.
*Normal ventilation, low or nonexistent perfusion and infinite V/Q ratio*
- This scenario describes a lung unit with **dead space ventilation**, where there is ventilation but no blood flow (e.g., in a pulmonary embolism).
- The patient's history of **obstructive lung disease** primarily indicates impaired airflow, not a lack of perfusion.
*Medium ventilation and perfusion, V/Q that equals 0.8*
- A **V/Q ratio of 0.8** represents the **ideal normal** ventilation-perfusion matching in a healthy lung.
- The patient has severe obstructive lung disease, which by definition means there is significant mismatch, not normal physiology.
*Higher ventilation and perfusion with lower V/Q ratio*
- While hyperventilation can occur in attempts to compensate, the primary issue in obstructive disease is **impaired ventilation**, not increased ventilation, leading to decreased gas exchange.
- A lower V/Q ratio is expected, but it is driven by **low ventilation**, not higher ventilation and perfusion.
*Lower ventilation and perfusion, but higher V/Q ratio*
- Although both ventilation and perfusion can be affected in severe disease, a **higher V/Q ratio** typically implies areas of increased dead space (more ventilation than perfusion).
- In obstructive disease, the predominant problem is **impaired air entry**, leading to underventilated units with relatively preserved perfusion, thus a **low V/Q ratio**.
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution US Medical PG Question 8: A 21-year-old man is admitted to the intensive care unit for respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation. His minute ventilation is calculated to be 7.0 L/min, and his alveolar ventilation is calculated to be 5.1 L/min. Which of the following is most likely to decrease the difference between minute ventilation and alveolar ventilation?
- A. Increasing the partial pressure of inhaled oxygen
- B. Decreasing the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen
- C. Increasing the respiratory depth
- D. Decreasing the physiologic dead space (Correct Answer)
- E. Increasing the respiratory rate
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution Explanation: ***Decreasing the physiologic dead space***
- The difference between **minute ventilation (VE)** and **alveolar ventilation (VA)** is the **dead space ventilation (VD)**, calculated as: VE - VA = VD
- In this case: 7.0 L/min - 5.1 L/min = 1.9 L/min of dead space ventilation
- Decreasing the **physiologic dead space** directly reduces this difference by allowing a greater proportion of each breath to participate in gas exchange
- This is the most direct way to narrow the gap between VE and VA
*Increasing the partial pressure of inhaled oxygen*
- This intervention primarily affects **oxygenation** by increasing the driving pressure for oxygen diffusion into the blood
- It does not directly change the volume of air participating in alveolar ventilation or reduce dead space ventilation
- The distribution of ventilation between alveolar and dead space remains unchanged
*Decreasing the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen*
- A decrease in hemoglobin affinity for oxygen facilitates **oxygen unloading** to the tissues (rightward shift of the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve)
- This effect is related to **oxygen delivery** and does not alter the proportion of minute ventilation that reaches the alveoli for gas exchange
- Dead space ventilation remains unchanged
*Increasing the respiratory depth*
- Increasing respiratory depth increases **tidal volume (VT)**, which improves the **ratio** of alveolar ventilation to minute ventilation (VA/VE efficiency)
- However, the **absolute difference** (VE - VA) in L/min depends on the **total dead space volume**, which is not changed by increasing tidal volume alone
- While this improves ventilation efficiency, it does not directly reduce the dead space ventilation measured in L/min unless physiologic dead space itself decreases
*Increasing the respiratory rate*
- While increasing respiratory rate increases **minute ventilation (VE)**, it also increases the frequency of ventilating the **dead space** with each breath
- Since dead space ventilation (VD) = respiratory rate × dead space volume, increasing rate while keeping tidal volume constant will proportionally increase both VE and VD
- This can actually widen the absolute gap between VE and VA, making it less efficient
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution US Medical PG Question 9: A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with a 2-day history of cough productive of yellowish sputum. He has had fever, chills, and worsening shortness of breath over this time. He has a 10-year history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He does not drink alcohol or smoke cigarettes. His current medications include atorvastatin, amlodipine, and metoprolol. His temperature is 38.9°C (102.0°F), pulse is 105/min, respirations are 27/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. He appears in mild distress. He has rales over the left lower lung field. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Leukocyte count is 15,000/mm3 (87% segmented neutrophils). Arterial blood gas analysis on room air shows:
pH 7.44
pO2 68 mm Hg
pCO2 28 mm Hg
HCO3- 24 mEq/L
O2 saturation 91%
An x-ray of the chest shows a consolidation in the left lower lobe. Asking the patient to lie down in the left lateral decubitus position would most likely result in which of the following?
- A. Decreased ventilation of the left lung
- B. Worsen the hypocapnia
- C. Increase in A-a gradient (Correct Answer)
- D. Increased perfusion of right lung
- E. Improve the hypoxemia
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution Explanation: ***Increase in A-a gradient***
- Placing the patient in the **left lateral decubitus position** would worsen V/Q mismatch because the **diseased left lung** (with consolidation) would receive increased perfusion due to gravity.
- This increased perfusion to a poorly ventilated area would further impair gas exchange, leading to a larger **alveolar-arterial (A-a) gradient**.
*Decreased ventilation of the left lung*
- While lying on the left side might slightly restrict the expansion of the left lung, the primary issue is the **consolidation** itself, which already severely impairs ventilation.
- The main problem with positioning is not a further decrease in ventilation but rather the **redistribution of blood flow** to an already compromised lung.
*Worsen the hypocapnia*
- The patient has **hypocapnia (pCO2 28 mm Hg)** due to tachypnea as compensation for hypoxemia, indicating increased minute ventilation.
- While worsening the V/Q mismatch will worsen hypoxemia, it's unlikely to directly worsen hypocapnia further; the body would still try to compensate through increased respiratory drive unless the respiratory muscles become fatigued.
*Increased perfusion of right lung*
- In the left lateral decubitus position, **perfusion due to gravity** would increase in the dependent (left) lung, not the non-dependent (right) lung.
- The right lung would experience relatively decreased perfusion compared to the left lung in this position.
*Improve the hypoxemia*
- Lying on the side of the **diseased lung** (left) typically **worsens hypoxemia** because gravity directs more blood flow to the poorly ventilated, consolidated lung.
- To improve hypoxemia, the patient should be positioned with the **healthy lung dependent** (e.g., right lateral decubitus or semi-Fowler's with the right lung lower) to optimize V/Q matching.
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution US Medical PG Question 10: A 52-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with breathlessness for the past 6 hours. She denies cough, nasal congestion or discharge, sneezing, blood in sputum, or palpitation. There is no past history of chronic respiratory or cardiovascular medical conditions, but she mentions that she has been experiencing frequent cramps in her left leg for the past 5 days. She is post-menopausal and has been on hormone replacement therapy for a year now. Her temperature is 38.3°C (100.9°F), the pulse is 116/min, the blood pressure is 136/84 mm Hg, and the respiratory rate is 24/min. Edema and tenderness are present in her left calf region. Auscultation of the chest reveals rales over the left infrascapular and scapular region. The heart sounds are normal and there are no murmurs. Which of the following mechanisms most likely contributed to the pathophysiology of this patient’s condition?
- A. Secretion of vasodilating neurohumoral substances in pulmonary vascular bed
- B. Increased right ventricular preload (Correct Answer)
- C. Decreased physiologic dead space
- D. Alveolar hyperventilation
- E. Decreased alveolar-arterial oxygen tension gradient
Gravity effects on V/Q distribution Explanation: ***Increased right ventricular preload***
- The patient's presentation (acute breathlessness, unilateral leg cramps, calf tenderness and edema, rales) combined with risk factors (post-menopausal, hormone replacement therapy) strongly suggests **pulmonary embolism (PE)** from deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- In PE, thrombus occludes pulmonary vasculature causing **increased pulmonary vascular resistance**, which increases **right ventricular afterload** (the resistance the RV must overcome to eject blood).
- **Note:** While this option states "preload," the primary mechanism is actually increased RV **afterload**. However, this is the most appropriate answer among the given options, as the increased resistance does lead to RV strain and potential backup of blood that can secondarily affect preload.
*Secretion of vasodilating neurohumoral substances in pulmonary vascular bed*
- The primary vascular response in PE is **vasoconstriction**, not vasodilation.
- Hypoxia and mediator release cause **pulmonary vasoconstriction** distal to the embolus, further increasing pulmonary vascular resistance.
*Decreased physiologic dead space*
- In PE, there is **ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch** where lung regions are ventilated but not perfused due to embolic obstruction.
- This actually **increases physiologic dead space** because these areas are ventilated but cannot participate in gas exchange.
*Alveolar hyperventilation*
- Patients with PE often develop **tachypnea and hyperventilation** due to hypoxia, anxiety, and chest discomfort.
- However, this is a **compensatory response** to hypoxemia, not the primary pathophysiological mechanism causing the condition.
*Decreased alveolar-arterial oxygen tension gradient*
- The **A-a gradient is increased in PE** due to V/Q mismatch and shunting, reflecting impaired gas exchange.
- A decreased A-a gradient would indicate efficient gas exchange, which contradicts the hypoxia and breathlessness seen in PE.
More Gravity effects on V/Q distribution US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.