Spirometry interpretation US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Spirometry interpretation. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Spirometry interpretation US Medical PG Question 1: A 62-year-old woman with hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician because of increasing shortness of breath and a dry cough over the past 6 months. She has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes daily for the past 40 years. Chest auscultation shows scattered expiratory wheezes in both lung fields. Spirometry shows an FEV1:FVC ratio of 65% and an FEV1 of 70% of predicted. Her diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) is 42% of predicted. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Pulmonary fibrosis
- B. Bronchial asthma
- C. Emphysema (Correct Answer)
- D. Bronchiectasis
- E. Chronic bronchitis
Spirometry interpretation Explanation: ***Emphysema***
- The patient's history of **40 pack-years of smoking**, combined with **obstructive lung disease (FEV1:FVC ratio of 65%)** and a **markedly reduced DLCO (42% of predicted)**, strongly indicates emphysema.
- **DLCO reduction** is characteristic of emphysema due to the destruction of alveolar-capillary membranes, which impairs gas exchange.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- Pulmonary fibrosis presents with shortness of breath and dry cough, but it is a **restrictive lung disease**, meaning both FEV1 and FVC would be reduced proportionally, leading to a **normal or increased FEV1:FVC ratio**.
- While DLCO is reduced in pulmonary fibrosis, the **obstructive pattern on spirometry** rules out this diagnosis.
*Bronchial asthma*
- Asthma is characterized by **reversible airway obstruction** and often presents with wheezing and shortness of breath.
- However, asthma typically has a **normal DLCO**, as the diffusion capacity of the lung is usually preserved.
*Bronchiectasis*
- Bronchiectasis involves **permanent dilation of the bronchi** and can cause chronic cough, sputum production, and obstructive lung physiology.
- While it can cause some airflow obstruction and reduced DLCO in severe cases, the **primary features often include chronic productive cough** and recurrent infections, and the DLCO reduction is typically less severe than seen in emphysema, unless it's very advanced.
*Chronic bronchitis*
- Chronic bronchitis is defined by a **chronic productive cough** for at least 3 months in each of 2 consecutive years, in a patient for whom other causes have been excluded.
- It causes **obstructive lung disease** and can present with wheezing but typically has a **normal or only slightly reduced DLCO**, as the primary issue is inflammation and mucus production in the airways, not destruction of the alveolar-capillary membrane.
Spirometry interpretation US Medical PG Question 2: A previously healthy 64-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a dry cough and progressively worsening shortness of breath for the past 2 months. She has not had fever, chills, or night sweats. She has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the past 45 years. She appears thin. Examination of the lung shows a prolonged expiratory phase and end-expiratory wheezing. Spirometry shows decreased FEV1:FVC ratio (< 70% predicted), decreased FEV1, and a total lung capacity of 125% of predicted. The diffusion capacity of the lung (DLCO) is decreased. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Bronchiectasis
- B. Interstitial lung disease
- C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Correct Answer)
- D. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- E. Bronchial asthma
Spirometry interpretation Explanation: ***Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease***
- The patient's long history of **smoking (45 pack-years)**, **prolonged expiratory phase**, and **end-expiratory wheezing** are classic signs of airway obstruction.
- Spirometry findings of a **decreased FEV1:FVC ratio** (< 70% predicted), **decreased FEV1**, **increased total lung capacity (TLC)**, and **decreased DLCO** are all highly indicative of **emphysema**, a subtype of COPD.
*Bronchiectasis*
- While it shares symptoms like cough and SOB, **bronchiectasis** is characterized by permanent **dilatation of bronchi** and profuse, chronic **sputum production**, which is not mentioned here.
- Spirometry typically shows **obstructive patterns**, but the marked increase in TLC and decreased DLCO are more specific to emphysema.
*Interstitial lung disease*
- This condition primarily causes a **restrictive lung pattern**, meaning a decreased TLC and normal or increased FEV1:FVC ratio.
- The patient's **increased TLC** and **obstructive spirometry** rule out a purely restrictive process.
*Hypersensitivity pneumonitis*
- This is an inflammatory response to inhaled antigens, often presenting with **recurrent episodes** of fever, chills, and cough, and can lead to restrictive physiology.
- The patient lacks a history of specific **antigen exposure** and presents with an obstructive pattern and increased TLC.
*Bronchial asthma*
- While asthma shares obstructive features like wheezing and a decreased FEV1:FVC ratio, it is characterized by **reversibility** of airway obstruction and typically does not cause a significantly **elevated TLC** or **decreased DLCO** in uncomplicated cases.
- The patient's long smoking history points away from asthma as the primary diagnosis.
Spirometry interpretation US Medical PG Question 3: A 57-year-old man presents to the clinic for a chronic cough over the past 4 months. The patient reports a productive yellow/green cough that is worse at night. He denies any significant precipitating event prior to his symptoms. He denies fever, chest pain, palpitations, weight changes, or abdominal pain, but endorses some difficulty breathing that waxes and wanes. He denies alcohol usage but endorses a 35 pack-year smoking history. A physical examination demonstrates mild wheezes, bibasilar crackles, and mild clubbing of his fingertips. A pulmonary function test is subsequently ordered, and partial results are shown below:
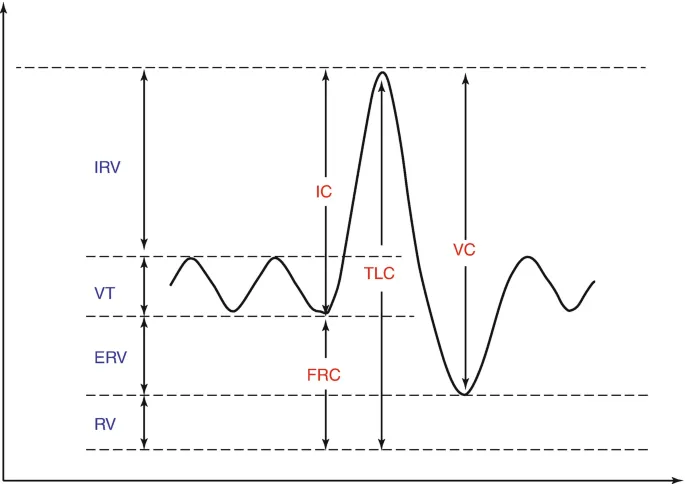
Tidal volume: 500 mL
Residual volume: 1700 mL
Expiratory reserve volume: 1500 mL
Inspiratory reserve volume: 3000 mL
What is the functional residual capacity of this patient?
- A. 4500 mL
- B. 2000 mL
- C. 2200 mL
- D. 3200 mL (Correct Answer)
- E. 3500 mL
Spirometry interpretation Explanation: ***3200 mL***
- The **functional residual capacity (FRC)** is the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal expiration.
- It is calculated as the sum of the **expiratory reserve volume (ERV)** and the **residual volume (RV)**. In this case, 1500 mL (ERV) + 1700 mL (RV) = 3200 mL.
*4500 mL*
- This value represents the sum of the **inspiratory reserve volume (3000 mL)** and the **residual volume (1700 mL)**, which does not correspond to a standard lung volume or capacity.
- It does not logically relate to the definition of functional residual capacity.
*2000 mL*
- This value represents the sum of the **tidal volume (500 mL)** and the **expiratory reserve volume (1500 mL)**, which is incorrect for FRC.
- This would represent the inspiratory capacity minus the inspiratory reserve volume, which is not a standard measurement used in pulmonary function testing.
*2200 mL*
- This value could be obtained by incorrectly adding the **tidal volume (500 mL)** and the **residual volume (1700 mL)**, which is not the correct formula for FRC.
- This calculation represents a miscombination of lung volumes that does not correspond to any standard pulmonary capacity measurement.
*3500 mL*
- This value is the sum of the **tidal volume (500 mL)**, the **expiratory reserve volume (1500 mL)**, and the **residual volume (1700 mL)**.
- This would represent the FRC plus the tidal volume, which is not a standard measurement and does not represent the functional residual capacity.
Spirometry interpretation US Medical PG Question 4: A 69-year-old man presents with progressive malaise, weakness, and confusion. The patient’s wife reports general deterioration over the last 3 days. He suffers from essential hypertension, but this is well controlled with amlodipine. He also has type 2 diabetes mellitus that is treated with metformin. On physical examination, the patient appears severely ill, weak and is unable to speak. His neck veins are distended bilaterally. His skin is mottled and dry with cool extremities, and he is mildly cyanotic. The respiratory rate is 24/min, the pulse is 94/min, the blood pressure is 87/64 mm Hg, and the temperature is 35.5°C (95.9°F). Auscultation yields coarse crackles throughout both lung bases. Which of the following best represents the mechanism of this patient’s condition?
- A. Barrier to cardiac flow
- B. Cardiac pump dysfunction (Correct Answer)
- C. Failure of vasoregulation
- D. Restriction of cardiac filling
- E. Loss of intravascular volume
Spirometry interpretation Explanation: ***Cardiac pump dysfunction***
- The patient exhibits signs of **cardiogenic shock**, including **hypotension** (87/64 mmHg), **tachycardia** (94/min), **crackles** in the lungs (pulmonary edema), **distended neck veins**, and cool, mottled extremities, all indicative of the heart's inability to effectively pump blood.
- The progressive malaise, weakness, and confusion suggest **poor end-organ perfusion** due to severely impaired cardiac output.
*Barrier to cardiac flow*
- This typically refers to conditions like **pulmonary embolism** or **aortic stenosis**, where there's an obstruction to blood flow.
- While pulmonary embolism can cause cardiogenic shock, the diffuse crackles are more suggestive of direct pump failure rather than an acute obstructive event.
*Failure of vasoregulation*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **distributive shock**, such as **septic shock** or anaphylactic shock, where there is widespread vasodilation leading to hypotension.
- **Warm extremities** and a bounding pulse are usually seen in early distributive shock, contrasting with the patient's cool, cyanotic extremities.
*Restriction of cardiac filling*
- This occurs in conditions like **cardiac tamponade** or **constrictive pericarditis**, where external compression or stiffness of the heart limits its ability to fill.
- While neck vein distension can be present, the extensive pulmonary crackles point more to direct pump failure leading to back pressure in the pulmonary circulation, rather than primary filling restriction.
*Loss of intravascular volume*
- This mechanism describes **hypovolemic shock**, which results from significant fluid loss due to hemorrhage, severe dehydration, or burns.
- Patients in hypovolemic shock typically present with **flat neck veins**, increased heart rate, and cool extremities, but generally lack the prominent pulmonary crackles caused by fluid overload from heart failure.
Spirometry interpretation US Medical PG Question 5: A 62-year-old female presents with complaint of chronic productive cough for the last 4 months. She states that she has had 4-5 month periods of similar symptoms over the past several years. She has never smoked, but she reports significant exposure to second-hand smoke in her home. She denies any fevers, reporting only occasional shortness of breath and a persistent cough where she frequently expectorates thick, white sputum. Vital signs are as follows: T 37.1 C, HR 88, BP 136/88, RR 18, O2 sat 94% on room air. Physical exam is significant for bilateral end-expiratory wheezes, a blue tint to the patient's lips and mucous membranes of the mouth, and a barrel chest. Which of the following sets of results would be expected on pulmonary function testing in this patient?
- A. Normal FEV1, Normal FEV1/FVC, Normal TLC, Normal DLCO
- B. Decreased FEV1, Normal FEV1/FVC, Decreased TLC, Decreased DLCO
- C. Decreased FEV1, Decreased FEV1/FVC ratio, Increased TLC, Normal DLCO (Correct Answer)
- D. Decreased FEV1, Increased FEV1/FVC ratio, Decreased TLC, Normal DLCO
- E. Decreased FEV1, Decreased FEV1/FVC ratio, Increased TLC, Decreased DLCO
Spirometry interpretation Explanation: ***Decreased FEV1, Decreased FEV1/FVC ratio, Increased TLC, Normal DLCO***
- This patient presents with **chronic bronchitis**, a form of COPD characterized by **chronic productive cough** with sputum production for at least 3 months in 2 consecutive years. The clinical picture of **cyanosis** ("blue bloater"), **productive cough with thick white sputum**, and **wheezing** points to chronic bronchitis as the predominant pathology.
- COPD is an **obstructive lung disease**, characterized by **decreased FEV1** and **decreased FEV1/FVC ratio** (<0.70).
- **Increased TLC** occurs due to **air trapping** seen in obstructive diseases.
- **Normal DLCO** is characteristic of **chronic bronchitis** where the alveolar-capillary membrane remains relatively intact, unlike in emphysema. Although the patient has a barrel chest (suggesting some hyperinflation), the predominant clinical features favor chronic bronchitis, making normal DLCO the expected finding.
*Normal FEV1, Normal FEV1/FVC, Normal TLC, Normal DLCO*
- This represents **normal pulmonary function**, which is inconsistent with the patient's clinical presentation.
- The **chronic productive cough**, **cyanosis**, **wheezes**, and **barrel chest** clearly indicate underlying obstructive pulmonary disease.
*Decreased FEV1, Normal FEV1/FVC, Decreased TLC, Decreased DLCO*
- This pattern is characteristic of **restrictive lung disease** (decreased TLC with preserved or increased FEV1/FVC ratio).
- A **normal FEV1/FVC ratio** excludes obstructive disease, which is clearly present in this patient based on clinical findings.
- Does not match the obstructive picture presented.
*Decreased FEV1, Increased FEV1/FVC ratio, Decreased TLC, Normal DLCO*
- An **increased FEV1/FVC ratio** with decreased FEV1 is physiologically implausible and not seen in any standard lung disease pattern.
- This would require FVC to be disproportionately more reduced than FEV1, which doesn't occur in typical disease states.
*Decreased FEV1, Decreased FEV1/FVC ratio, Increased TLC, Decreased DLCO*
- This pattern is most consistent with **emphysema-predominant COPD**, where destruction of alveolar-capillary membranes causes **decreased DLCO**.
- While this patient has some features suggestive of emphysema (barrel chest, air trapping), the **predominant clinical picture** of **chronic productive cough**, **cyanosis** ("blue bloater"), and **thick sputum production** points to **chronic bronchitis** as the primary pathology, where DLCO is typically preserved.
- Emphysema patients ("pink puffers") typically present with minimal cough, dyspnea on exertion, and pursed-lip breathing, which are not prominent in this case.
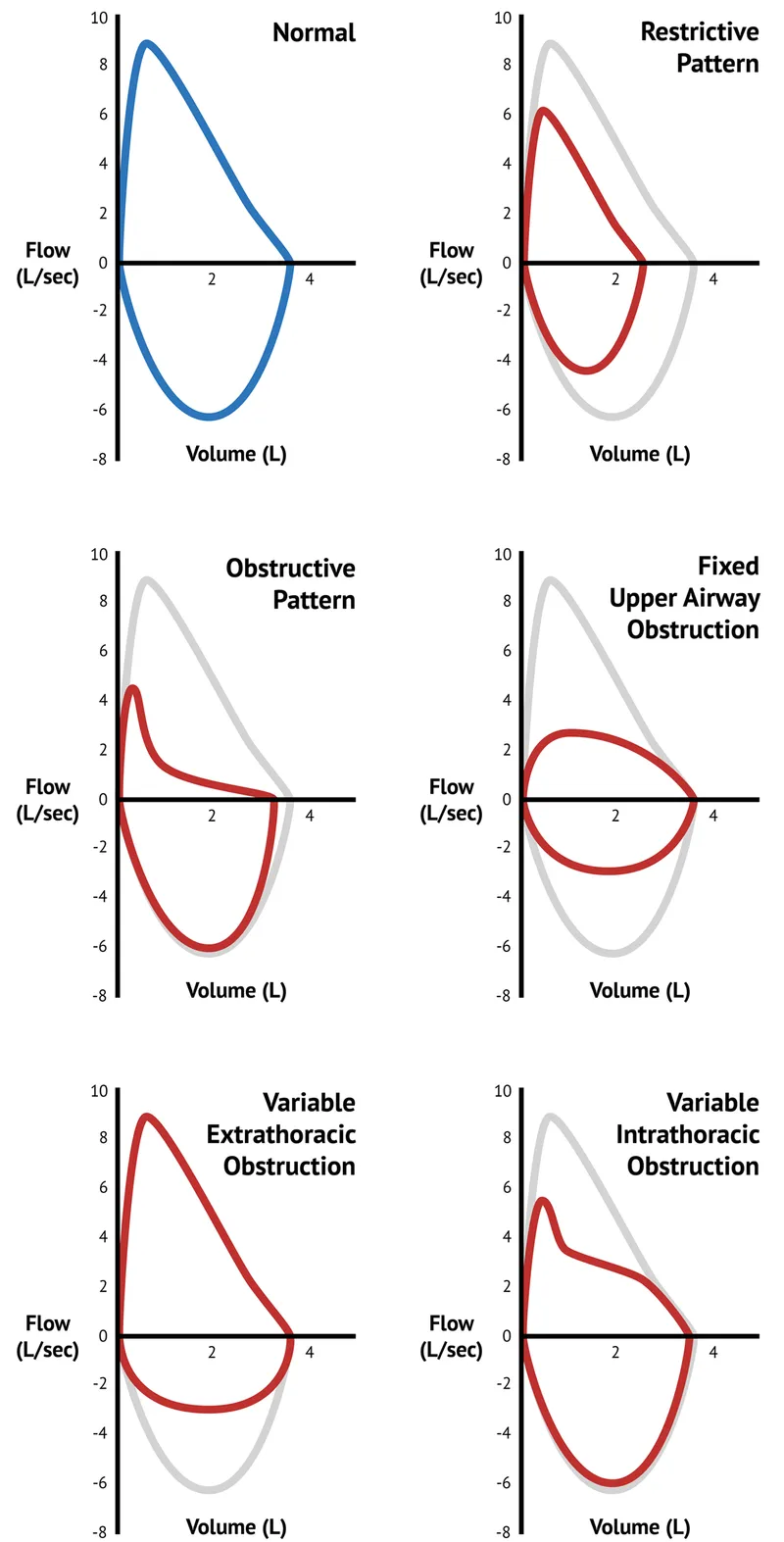
Spirometry interpretation US Medical PG Question 6: A 63-year-old woman comes to the physician because of worsening shortness of breath, cough, and a 4-kg (8.8-lb) weight loss over the last year. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. She has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 35 years. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 92/min, respirations are 20/min, blood pressure is 124/78 mm Hg, and pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 93%. Physical examination shows decreased breath sounds. A flow-volume loop obtained via pulmonary function testing is shown. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's respiratory symptoms?
- A. Unilateral mainstem obstruction
- B. Chronic asthma
- C. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- D. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Correct Answer)
- E. Endotracheal neoplasm
Spirometry interpretation Explanation: ***Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease***
* The patient's long history of **smoking** (35 pack-years) and presentation with **shortness of breath**, **cough**, and **weight loss** are classic clinical features of COPD. The flow-volume loop, while not provided, is expected to show an **obstructive pattern** with decreased expiratory flow.
* **Decreased breath sounds** on examination and **hypoxemia** (SpO2 93%) further support the diagnosis of COPD, indicating significant airflow limitation and gas exchange impairment.
*Unilateral mainstem obstruction*
* A unilateral mainstem obstruction would typically cause diminished or absent breath sounds **only on the affected side**, whereas the description mentions decreased breath sounds generally, suggesting a more widespread process.
* The **flow-volume loop pattern** for a fixed upper airway obstruction is different from what would be expected in a diffuse obstructive lung disease like COPD.
*Chronic asthma*
* While asthma can cause **shortness of breath** and **cough**, chronic asthma severe enough to cause **weight loss** and persistent hypoxemia, especially in an older patient with a heavy smoking history, is less likely than COPD.
* Asthma is characterized by **reversible airflow obstruction**, which is not typical of the long-standing, progressive nature described here.
*Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis*
* Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a **restrictive lung disease**, meaning it would present with a restrictive pattern on the flow-volume loop, characterized by reduced lung volumes. The patient's symptoms are more consistent with an obstructive process.
* IPF typically presents with **bibasilar crackles** on physical examination and is not typically associated with decreased breath sounds in the way COPD is.
*Endotracheal neoplasm*
* An endotracheal neoplasm would cause an **upper airway obstruction**, leading to symptoms like stridor, hoarseness, and dyspnea. The flow-volume loop would show a characteristic pattern of **fixed or variable upper airway obstruction**.
* The patient's primary symptoms, imaging findings, and flow-volume loop pattern are more consistent with widespread bronchial disease rather than a localized upper airway mass.
Spirometry interpretation US Medical PG Question 7: A 72-year-old obese man presents as a new patient to his primary care physician because he has been feeling tired and short of breath after recently moving to Denver. He is a former 50 pack-year smoker and has previously had deep venous thrombosis. Furthermore, he previously had a lobe of the lung removed due to lung cancer. Finally, he has a family history of a progressive restrictive lung disease. Laboratory values are obtained as follows:
Oxygen tension in inspired air = 130 mmHg
Alveolar carbon dioxide tension = 48 mmHg
Arterial oxygen tension = 58 mmHg
Respiratory exchange ratio = 0.80
Respiratory rate = 20/min
Tidal volume = 500 mL
Which of the following mechanisms is consistent with these values?
- A. Shunt physiology
- B. High altitude
- C. V/Q mismatch
- D. Pulmonary fibrosis
- E. Hypoventilation (Correct Answer)
Spirometry interpretation Explanation: ***Hypoventilation***
- The arterial oxygen tension (PaO2) of 58 mmHg is consistent with hypoxemia, and the alveolar carbon dioxide tension (PACO2) of 48 mmHg (normal 35-45 mmHg) indicates **hypercapnia**, a hallmark of hypoventilation.
- The **alveolar-arterial (A-a) gradient** can be calculated using the alveolar gas equation: PAO2 = PiO2 - PACO2/R. Here, PAO2 = 130 mmHg - 48 mmHg/0.8 = 130 - 60 = 70 mmHg. The A-a gradient is PAO2 - PaO2 = 70 - 58 = 12 mmHg, which is within the normal range (5-15 mmHg), indicating that the hypoxemia is primarily due to **decreased alveolar ventilation**.
*Shunt physiology*
- A shunt would cause a significant reduction in PaO2 and a **widened A-a gradient** (typically >15 mmHg) due to deoxygenated blood bypassing ventilated areas.
- While shunts do not typically cause hypercapnia unless very severe, the normal A-a gradient here rules out a significant shunt as the primary mechanism for hypoxemia.
*High altitude*
- Moving to a high altitude (like Denver) causes a decrease in **inspired oxygen tension (PiO2)**, leading to hypoxemia.
- However, the provided inspired oxygen tension (130 mmHg) is above what would be expected for significant high-altitude hypoxemia at sea level equivalent, and the hypoxemia here is associated with hypercapnia, which is not a direct result of high altitude itself.
*V/Q mismatch*
- A V/Q mismatch leads to hypoxemia and a **widened A-a gradient**, as some areas of the lung are either underventilated or underperfused.
- While it can cause hypoxemia, a V/Q mismatch is typically associated with **normal or low PaCO2** due to compensatory hyperventilation, not hypercapnia, and the A-a gradient would be elevated.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- Pulmonary fibrosis is a restrictive lung disease that leads to impaired gas exchange, causing hypoxemia primarily due to **V/Q mismatch** and **diffusion limitation**.
- This would result in a **widened A-a gradient** and often a **low PaCO2** due to compensatory hyperventilation, rather than the elevated PaCO2 observed in this patient.
Spirometry interpretation US Medical PG Question 8: A 15-year-old boy and his mother were referred to a pulmonology clinic. She is concerned that her son is having some breathing difficulty for the past few months, which is aggravated with exercise. The family is especially concerned because the patient’s older brother has cystic fibrosis. The past medical history is noncontributory. Today, the vital signs include: blood pressure 119/80 mm Hg, heart rate 90/min, respiratory rate 17/min, and temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F). On physical exam, he appears well-developed and well-nourished. The heart has a regular rate and rhythm, and the lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. During the exam, he is brought into a special room to test his breathing. A clamp is placed on his nose and he is asked to take in as much air as he can, and then forcefully expire all the air into a spirometer. The volume of expired air represents which of the following?
- A. Tidal volume
- B. Total lung capacity
- C. Functional residual capacity
- D. Expiratory reserve volume
- E. Vital capacity (Correct Answer)
Spirometry interpretation Explanation: ***Vital capacity***
- **Vital capacity (VC)** is the maximum volume of air exhaled after a maximal inspiration. The maneuver described ("take in as much air as he can, and then forcefully expire all the air") directly measures vital capacity.
- VC includes the **tidal volume (TV)**, **inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)**, and **expiratory reserve volume (ERV)**.
*Tidal volume*
- **Tidal volume (TV)** is the volume of air inspired or expired with a normal breath, not the maximal forceful expiration described.
- It represents the usual volume of air exchanged during quiet breathing.
*Total lung capacity*
- **Total lung capacity (TLC)** is the maximum volume of air that the lungs can hold after a maximal inspiration, including the residual volume.
- This cannot be measured directly by spirometry alone, as it includes the **residual volume** which is the air remaining in the lungs after maximal expiration.
*Functional residual capacity*
- **Functional residual capacity (FRC)** is the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal, quiet expiration.
- Like TLC and residual volume, FRC cannot be measured directly by standard spirometry.
*Expiratory reserve volume*
- **Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)** is the maximum volume of air that can be *additionally* exhaled after a normal exhalation.
- The patient was asked to expire all the air after a maximal inspiration, which is a measure of vital capacity, not just ERV.
Spirometry interpretation US Medical PG Question 9: A 55-year-old man with a 60 pack-year smoking history is referred by his primary care physician for a pulmonary function test (PFT). A previously obtained chest x-ray is shown below. Which of the following will most likely appear in his PFT report?
- A. Residual volume increased, total lung capacity decreased
- B. Residual volume normal, total lung capacity decreased
- C. Residual volume normal, total lung capacity normal
- D. Residual volume decreased, total lung capacity increased
- E. Residual volume increased, total lung capacity increased (Correct Answer)
Spirometry interpretation Explanation: ***Residual volume increased, total lung capacity increased***
- The chest X-ray shows **hyperinflation** and a **flattened diaphragm**, which are classic signs of **emphysema**, a type of COPD.
- In emphysema, destruction of alveolar walls leads to air trapping, resulting in an **increased residual volume** and **total lung capacity**.
*Residual volume increased, total lung capacity decreased*
- An increased residual volume suggests **air trapping**, typical of obstructive lung diseases like emphysema.
- However, a **decreased total lung capacity** is characteristic of restrictive lung diseases, which would contradict the clinical and radiological findings for emphysema.
*Residual volume normal, total lung capacity decreased*
- A **normal residual volume** indicates no significant air trapping, which is inconsistent with emphysema.
- A **decreased total lung capacity** is seen in restrictive lung diseases, not obstructive diseases like emphysema.
*Residual volume normal, total lung capacity normal*
- **Normal lung volumes** would indicate healthy lung function, which is not expected in a patient with a heavy smoking history and radiological evidence of emphysema.
- The patient's 60 pack-year smoking history strongly points towards significant lung pathology.
*Residual volume decreased, total lung capacity increased*
- A **decreased residual volume** would suggest improved exhalation and less air trapping, which is contrary to the pathophysiology of emphysema.
- While total lung capacity can be increased in emphysema, the decrease in residual volume makes this option incorrect.
Spirometry interpretation US Medical PG Question 10: A 68-year-old man comes to the emergency room with difficulty in breathing. He was diagnosed with severe obstructive lung disease a few years back. He uses his medication but often has to come to the emergency room for intravenous therapy to help him breathe. He was a smoker for 40 years smoking two packs of cigarettes every day. Which of the following best represents the expected changes in his ventilation, perfusion and V/Q ratio?
- A. Normal ventilation, low or nonexistent perfusion and infinite V/Q ratio
- B. Medium ventilation and perfusion, V/Q that equals 0.8
- C. Higher ventilation and perfusion with lower V/Q ratio
- D. Low ventilation, normal perfusion and low V/Q ratio (Correct Answer)
- E. Lower ventilation and perfusion, but higher V/Q ratio
Spirometry interpretation Explanation: ***Low ventilation, normal perfusion and low V/Q ratio***
- In severe **obstructive lung disease** (like COPD), there is airflow limitation, leading to areas of **hypoventilation** in the lungs.
- While ventilation is compromised, blood flow (perfusion) to these areas can remain relatively normal, resulting in a **decreased V/Q ratio**.
*Normal ventilation, low or nonexistent perfusion and infinite V/Q ratio*
- This scenario describes a lung unit with **dead space ventilation**, where there is ventilation but no blood flow (e.g., in a pulmonary embolism).
- The patient's history of **obstructive lung disease** primarily indicates impaired airflow, not a lack of perfusion.
*Medium ventilation and perfusion, V/Q that equals 0.8*
- A **V/Q ratio of 0.8** represents the **ideal normal** ventilation-perfusion matching in a healthy lung.
- The patient has severe obstructive lung disease, which by definition means there is significant mismatch, not normal physiology.
*Higher ventilation and perfusion with lower V/Q ratio*
- While hyperventilation can occur in attempts to compensate, the primary issue in obstructive disease is **impaired ventilation**, not increased ventilation, leading to decreased gas exchange.
- A lower V/Q ratio is expected, but it is driven by **low ventilation**, not higher ventilation and perfusion.
*Lower ventilation and perfusion, but higher V/Q ratio*
- Although both ventilation and perfusion can be affected in severe disease, a **higher V/Q ratio** typically implies areas of increased dead space (more ventilation than perfusion).
- In obstructive disease, the predominant problem is **impaired air entry**, leading to underventilated units with relatively preserved perfusion, thus a **low V/Q ratio**.
More Spirometry interpretation US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.