Flow-volume loops US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Flow-volume loops. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Flow-volume loops US Medical PG Question 1: A 5-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his grandmother because of difficulty breathing. Over the past two hours, the grandmother has noticed his voice getting progressively hoarser and occasionally muffled, with persistent drooling. He has not had a cough. The child recently immigrated from Africa, and the grandmother is unsure if his immunizations are up-to-date. He appears uncomfortable and is sitting up and leaning forward with his chin hyperextended. His temperature is 39.5°C (103.1°F), pulse is 110/min, and blood pressure is 90/70 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 95%. Pulmonary examination shows inspiratory stridor and scattered rhonchi throughout both lung fields, along with poor air movement. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Nebulized albuterol
- B. Direct laryngoscopy and pharyngoscopy
- C. Immediate nasotracheal intubation in the emergency department
- D. Prepare for emergency airway management in the operating room with anesthesia and ENT backup (Correct Answer)
- E. Intravenous administration of antibiotics
Flow-volume loops Explanation: ***Prepare for emergency airway management in the operating room with anesthesia and ENT backup***
- The constellation of **hoarseness**, **muffled voice**, **drooling**, **inspiratory stridor**, **fever**, and the classic **tripod position** (sitting up, leaning forward, hyperextended chin) in an unimmunized child strongly indicates **epiglottitis**.
- Given the risk of **complete airway obstruction**, securing the airway in a controlled environment like the **operating room** with specialized personnel (**anesthesia**, **ENT**) is the safest and most appropriate immediate step.
*Nebulized albuterol*
- This medication is a **bronchodilator** primarily used for conditions like **asthma** or **bronchiolitis** that involve bronchospasm.
- It would not alleviate airway obstruction caused by supraglottic swelling in epiglottitis and could potentially worsen the child's distress.
*Direct laryngoscopy and pharyngoscopy*
- Performing a direct laryngoscopy or pharyngoscopy in the emergency department, especially without immediate intubation capabilities, could precipitate **laryngospasm** and **complete airway obstruction** in a child with suspected epiglottitis.
- Visualization of the airway should only be attempted in a controlled setting where immediate intubation or tracheostomy can be performed.
*Immediate nasotracheal intubation in the emergency department*
- While intubation is necessary, attempting it immediately in the emergency department without the controlled environment of an operating room and without the full support of anesthesia and ENT specialists carries significant risks.
- The swelling can make intubation extremely difficult and increase the likelihood of failed attempts or trauma, further compromising the airway.
*Intravenous administration of antibiotics*
- Although antibiotics are a crucial part of epiglottitis treatment (typically **ceftriaxone** or **cefotaxime** to cover *Haemophilus influenzae* type b), they are not the immediate priority.
- The most urgent threat is airway compromise; therefore, securing the airway takes precedence over initiating antibiotic therapy.
Flow-volume loops US Medical PG Question 2: A 62-year-old woman with hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician because of increasing shortness of breath and a dry cough over the past 6 months. She has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes daily for the past 40 years. Chest auscultation shows scattered expiratory wheezes in both lung fields. Spirometry shows an FEV1:FVC ratio of 65% and an FEV1 of 70% of predicted. Her diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) is 42% of predicted. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Pulmonary fibrosis
- B. Bronchial asthma
- C. Emphysema (Correct Answer)
- D. Bronchiectasis
- E. Chronic bronchitis
Flow-volume loops Explanation: ***Emphysema***
- The patient's history of **40 pack-years of smoking**, combined with **obstructive lung disease (FEV1:FVC ratio of 65%)** and a **markedly reduced DLCO (42% of predicted)**, strongly indicates emphysema.
- **DLCO reduction** is characteristic of emphysema due to the destruction of alveolar-capillary membranes, which impairs gas exchange.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
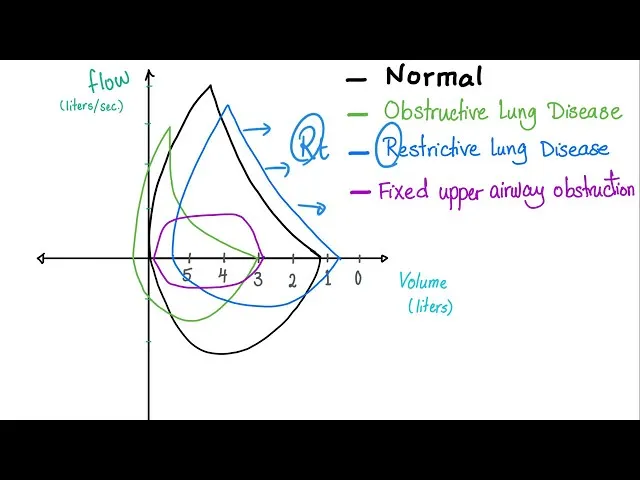
- Pulmonary fibrosis presents with shortness of breath and dry cough, but it is a **restrictive lung disease**, meaning both FEV1 and FVC would be reduced proportionally, leading to a **normal or increased FEV1:FVC ratio**.
- While DLCO is reduced in pulmonary fibrosis, the **obstructive pattern on spirometry** rules out this diagnosis.
*Bronchial asthma*
- Asthma is characterized by **reversible airway obstruction** and often presents with wheezing and shortness of breath.
- However, asthma typically has a **normal DLCO**, as the diffusion capacity of the lung is usually preserved.
*Bronchiectasis*
- Bronchiectasis involves **permanent dilation of the bronchi** and can cause chronic cough, sputum production, and obstructive lung physiology.
- While it can cause some airflow obstruction and reduced DLCO in severe cases, the **primary features often include chronic productive cough** and recurrent infections, and the DLCO reduction is typically less severe than seen in emphysema, unless it's very advanced.
*Chronic bronchitis*
- Chronic bronchitis is defined by a **chronic productive cough** for at least 3 months in each of 2 consecutive years, in a patient for whom other causes have been excluded.
- It causes **obstructive lung disease** and can present with wheezing but typically has a **normal or only slightly reduced DLCO**, as the primary issue is inflammation and mucus production in the airways, not destruction of the alveolar-capillary membrane.
Flow-volume loops US Medical PG Question 3: A previously healthy 64-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a dry cough and progressively worsening shortness of breath for the past 2 months. She has not had fever, chills, or night sweats. She has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the past 45 years. She appears thin. Examination of the lung shows a prolonged expiratory phase and end-expiratory wheezing. Spirometry shows decreased FEV1:FVC ratio (< 70% predicted), decreased FEV1, and a total lung capacity of 125% of predicted. The diffusion capacity of the lung (DLCO) is decreased. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Bronchiectasis
- B. Interstitial lung disease
- C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Correct Answer)
- D. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- E. Bronchial asthma
Flow-volume loops Explanation: ***Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease***
- The patient's long history of **smoking (45 pack-years)**, **prolonged expiratory phase**, and **end-expiratory wheezing** are classic signs of airway obstruction.
- Spirometry findings of a **decreased FEV1:FVC ratio** (< 70% predicted), **decreased FEV1**, **increased total lung capacity (TLC)**, and **decreased DLCO** are all highly indicative of **emphysema**, a subtype of COPD.
*Bronchiectasis*
- While it shares symptoms like cough and SOB, **bronchiectasis** is characterized by permanent **dilatation of bronchi** and profuse, chronic **sputum production**, which is not mentioned here.
- Spirometry typically shows **obstructive patterns**, but the marked increase in TLC and decreased DLCO are more specific to emphysema.
*Interstitial lung disease*
- This condition primarily causes a **restrictive lung pattern**, meaning a decreased TLC and normal or increased FEV1:FVC ratio.
- The patient's **increased TLC** and **obstructive spirometry** rule out a purely restrictive process.
*Hypersensitivity pneumonitis*
- This is an inflammatory response to inhaled antigens, often presenting with **recurrent episodes** of fever, chills, and cough, and can lead to restrictive physiology.
- The patient lacks a history of specific **antigen exposure** and presents with an obstructive pattern and increased TLC.
*Bronchial asthma*
- While asthma shares obstructive features like wheezing and a decreased FEV1:FVC ratio, it is characterized by **reversibility** of airway obstruction and typically does not cause a significantly **elevated TLC** or **decreased DLCO** in uncomplicated cases.
- The patient's long smoking history points away from asthma as the primary diagnosis.
Flow-volume loops US Medical PG Question 4: A 57-year-old man presents to the clinic for a chronic cough over the past 4 months. The patient reports a productive yellow/green cough that is worse at night. He denies any significant precipitating event prior to his symptoms. He denies fever, chest pain, palpitations, weight changes, or abdominal pain, but endorses some difficulty breathing that waxes and wanes. He denies alcohol usage but endorses a 35 pack-year smoking history. A physical examination demonstrates mild wheezes, bibasilar crackles, and mild clubbing of his fingertips. A pulmonary function test is subsequently ordered, and partial results are shown below:
Tidal volume: 500 mL
Residual volume: 1700 mL
Expiratory reserve volume: 1500 mL
Inspiratory reserve volume: 3000 mL
What is the functional residual capacity of this patient?
- A. 4500 mL
- B. 2000 mL
- C. 2200 mL
- D. 3200 mL (Correct Answer)
- E. 3500 mL
Flow-volume loops Explanation: ***3200 mL***
- The **functional residual capacity (FRC)** is the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal expiration.
- It is calculated as the sum of the **expiratory reserve volume (ERV)** and the **residual volume (RV)**. In this case, 1500 mL (ERV) + 1700 mL (RV) = 3200 mL.
*4500 mL*
- This value represents the sum of the **inspiratory reserve volume (3000 mL)** and the **residual volume (1700 mL)**, which does not correspond to a standard lung volume or capacity.
- It does not logically relate to the definition of functional residual capacity.
*2000 mL*
- This value represents the sum of the **tidal volume (500 mL)** and the **expiratory reserve volume (1500 mL)**, which is incorrect for FRC.
- This would represent the inspiratory capacity minus the inspiratory reserve volume, which is not a standard measurement used in pulmonary function testing.
*2200 mL*
- This value could be obtained by incorrectly adding the **tidal volume (500 mL)** and the **residual volume (1700 mL)**, which is not the correct formula for FRC.
- This calculation represents a miscombination of lung volumes that does not correspond to any standard pulmonary capacity measurement.
*3500 mL*
- This value is the sum of the **tidal volume (500 mL)**, the **expiratory reserve volume (1500 mL)**, and the **residual volume (1700 mL)**.
- This would represent the FRC plus the tidal volume, which is not a standard measurement and does not represent the functional residual capacity.
Flow-volume loops US Medical PG Question 5: In which of the following pathological states would the oxygen content of the trachea resemble the oxygen content in the affected alveoli?
- A. Emphysema
- B. Exercise
- C. Pulmonary embolism (Correct Answer)
- D. Pulmonary fibrosis
- E. Foreign body obstruction distal to the trachea
Flow-volume loops Explanation: ***Pulmonary embolism***
- A pulmonary embolism blocks **blood flow** to a portion of the lung, creating **dead space ventilation** (high V/Q ratio).
- In the affected alveoli, **no blood perfusion** means no oxygen extraction occurs, so the alveolar oxygen content remains **high and similar to tracheal/inspired air**.
- This is the classic physiological state where ventilation continues but perfusion is absent, preventing gas exchange.
*Foreign body obstruction distal to the trachea*
- A complete obstruction **prevents fresh air** from reaching the affected alveoli.
- The trapped gas undergoes **resorption atelectasis**: oxygen is absorbed into capillary blood, CO2 diffuses in, and alveolar gas equilibrates with **venous blood** composition.
- Alveolar oxygen content becomes **very low**, not similar to tracheal air.
*Emphysema*
- Emphysema involves destruction of **alveolar walls** and enlargement of airspaces with impaired gas exchange.
- While V/Q mismatch occurs, oxygen is still extracted by perfusing blood.
- Alveolar oxygen content is **lower than tracheal air** due to ongoing (though inefficient) gas exchange.
*Exercise*
- During exercise, **oxygen consumption increases** dramatically with enhanced cardiac output and oxygen extraction.
- Alveolar oxygen content is **significantly lower** than tracheal air due to increased oxygen uptake by blood.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- Pulmonary fibrosis causes **thickening of the alveolar-capillary membrane**, impairing oxygen diffusion.
- Despite diffusion limitation, blood still perfuses the alveoli and extracts oxygen.
- Alveolar oxygen content is **lower than tracheal air**, though the A-a gradient is increased.
Flow-volume loops US Medical PG Question 6: A 22-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a chief concern of shortness of breath. She was hiking when she suddenly felt unable to breathe and had to take slow deep breaths to improve her symptoms. The patient is a Swedish foreign exchange student and does not speak any English. Her past medical history and current medications are unknown. Her temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 127/68 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 22/min, and oxygen saturation is 90% on room air. Physical exam is notable for poor air movement bilaterally and tachycardia. The patient is started on treatment. Which of the following best describes this patient's underlying pathology?
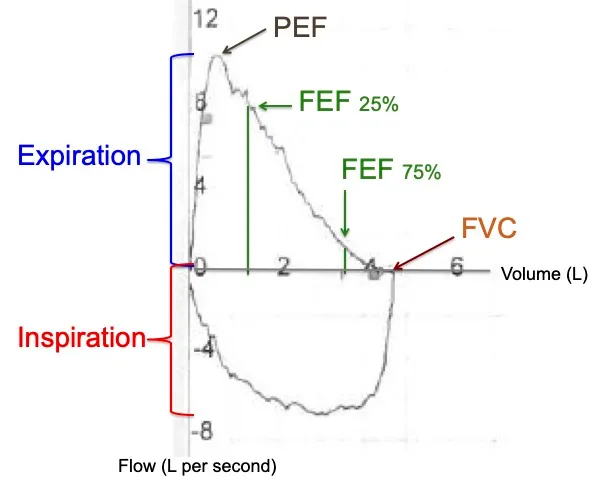
FEV1 = Forced expiratory volume in 1 second
FVC = Forced vital capacity
DLCO = Diffusing capacity of carbon monoxide
- A. Increased FVC
- B. Increased FEV1
- C. Increased FEV1/FVC
- D. Decreased airway tone
- E. Normal DLCO (Correct Answer)
Flow-volume loops Explanation: ***Normal DLCO***
- This patient presents with an acute exacerbation of what is likely **asthma**, showing symptoms of **shortness of breath**, **tachycardia**, poor air movement bilaterally, and improvement with slow deep breaths. **Asthma** characteristically affects the airways and not the alveoli, thus the **diffusing capacity of carbon monoxide (DLCO)**, which measures gas exchange across the alveolar-capillary membrane, would be expected to be normal.
- In asthma, the primary problem is **bronchoconstriction** and **airway inflammation**, which restricts airflow but does not typically impair the diffusion of gases like carbon monoxide across the alveolar-capillary membrane.
*Increased FVC*
- **Forced vital capacity (FVC)** is often normal or even slightly reduced in asthma due to **air trapping** and early airway closure, not increased.
- An increased FVC is usually not associated with obstructive lung diseases like asthma but could potentially be seen in conditions where lung volumes are pathologically large, which is not the case here.
*Increased FEV1*
- **Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)** is typically **decreased** in obstructive lung diseases like asthma due to **airflow limitation**.
- An increased FEV1 would indicate better-than-average expiratory flow, which contradicts the symptoms of shortness of breath and poor air movement in this patient.
*Increased FEV1/FVC*
- The **FEV1/FVC ratio** is characteristically **decreased** in obstructive lung diseases like asthma, indicating that a disproportionately smaller amount of air can be exhaled in the first second relative to the total forced vital capacity.
- An increased FEV1/FVC ratio would be a sign of a restrictive lung disease or normal lung function, not an exacerbation of an obstructive process.
*Decreased airway tone*
- The underlying pathology in asthma is typically **bronchoconstriction**, which means an **increased airway tone** and narrowing of the airways, rather than decreased.
- Decreased airway tone would imply bronchodilation, which would alleviate, not cause, the patient's symptoms of shortness of breath and poor air movement.
Flow-volume loops US Medical PG Question 7: Which of the following physiologic changes decreases pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR)?
- A. Inhaling the inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
- B. Exhaling the entire vital capacity (VC)
- C. Exhaling the expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
- D. Breath holding maneuver at functional residual capacity (FRC)
- E. Inhaling the entire vital capacity (VC) (Correct Answer)
Flow-volume loops Explanation: ***Inhaling the entire vital capacity (VC)***
- As lung volume increases from FRC to TLC (which includes inhaling the entire VC), alveolar vessels are **stretched open**, and extra-alveolar vessels are **pulled open** by the increased radial traction, leading to a decrease in PVR.
- This **maximizes the cross-sectional area** of the pulmonary vascular bed, lowering resistance.
*Inhaling the inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)*
- While inhaling IRV increases lung volume, it's not the maximal inspiration of the entire VC where **PVR is typically at its lowest**.
- PVR continues to decrease as lung volume approaches total lung capacity (TLC).
*Exhaling the entire vital capacity (VC)*
- Exhaling the entire vital capacity leads to very low lung volumes, where PVR significantly **increases**.
- At low lung volumes, **alveolar vessels become compressed** and extra-alveolar vessels **narrow**, increasing resistance.
*Exhaling the expiratory reserve volume (ERV)*
- Exhaling the ERV results in a lung volume below FRC, which causes a **marked increase in PVR**.
- This is due to the **compression of alveolar vessels** and decreased radial traction on extra-alveolar vessels.
*Breath holding maneuver at functional residual capacity (FRC)*
- At FRC, the PVR is at an **intermediate level**, not its lowest.
- This is the point where the opposing forces affecting alveolar and extra-alveolar vessels are somewhat balanced, but not optimized for minimal resistance.
Flow-volume loops US Medical PG Question 8: A 55-year-old man with a 60 pack-year smoking history is referred by his primary care physician for a pulmonary function test (PFT). A previously obtained chest x-ray is shown below. Which of the following will most likely appear in his PFT report?
- A. Residual volume increased, total lung capacity decreased
- B. Residual volume normal, total lung capacity decreased
- C. Residual volume normal, total lung capacity normal
- D. Residual volume decreased, total lung capacity increased
- E. Residual volume increased, total lung capacity increased (Correct Answer)
Flow-volume loops Explanation: ***Residual volume increased, total lung capacity increased***
- The chest X-ray shows **hyperinflation** and a **flattened diaphragm**, which are classic signs of **emphysema**, a type of COPD.
- In emphysema, destruction of alveolar walls leads to air trapping, resulting in an **increased residual volume** and **total lung capacity**.
*Residual volume increased, total lung capacity decreased*
- An increased residual volume suggests **air trapping**, typical of obstructive lung diseases like emphysema.
- However, a **decreased total lung capacity** is characteristic of restrictive lung diseases, which would contradict the clinical and radiological findings for emphysema.
*Residual volume normal, total lung capacity decreased*
- A **normal residual volume** indicates no significant air trapping, which is inconsistent with emphysema.
- A **decreased total lung capacity** is seen in restrictive lung diseases, not obstructive diseases like emphysema.
*Residual volume normal, total lung capacity normal*
- **Normal lung volumes** would indicate healthy lung function, which is not expected in a patient with a heavy smoking history and radiological evidence of emphysema.
- The patient's 60 pack-year smoking history strongly points towards significant lung pathology.
*Residual volume decreased, total lung capacity increased*
- A **decreased residual volume** would suggest improved exhalation and less air trapping, which is contrary to the pathophysiology of emphysema.
- While total lung capacity can be increased in emphysema, the decrease in residual volume makes this option incorrect.
Flow-volume loops US Medical PG Question 9: A 35-year-old woman volunteers for a study on respiratory physiology. Pressure probes A and B are placed as follows:
Probe A: between the parietal and visceral pleura
Probe B: within the cavity of an alveolus
The probes provide a pressure reading relative to atmospheric pressure. To obtain a baseline reading, she is asked to sit comfortably and breathe normally. Which of the following sets of values will most likely be seen at the end of inspiration?
- A. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg (Correct Answer)
- B. Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- C. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg
- D. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- E. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
Flow-volume loops Explanation: ***Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg***
- At the **end of inspiration**, the **intrapleural pressure (Probe A)** is at its most negative, typically around -6 to -8 cm H2O (equivalent to -4 to -6 mmHg), reflecting the maximum expansion of the thoracic cavity.
- At the **end of inspiration**, just before exhalation begins, there is **no airflow**, so the **intrapulmonary pressure (Probe B)** equalizes with atmospheric pressure, resulting in a 0 mm Hg reading.
*Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of 0 mm Hg** would indicate a **pneumothorax** since it should always be negative to prevent lung collapse.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** would indicate that **inspiration is still ongoing**, as air would be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapulmonary pressure of 0 mm Hg** is correct at the end of inspiration, an **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is typical for the **end of expiration (Functional Residual Capacity)** during quiet breathing, not the end of inspiration.
- The **intrapleural pressure becomes more negative** during inspiration due to increased thoracic volume, so -4 mm Hg would be insufficient.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is the normal pressure at the **end of expiration**, not the end of inspiration, where it becomes more negative.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** indicates that **inspiration is still in progress**, not at its end, as air would still be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapleural pressure of -6 mm Hg** is consistent with the end of inspiration, an **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** means that **airflow is still occurring into the lungs**.
- At the **very end of inspiration**, just before the start of exhalation, airflow momentarily ceases, and intrapulmonary pressure becomes zero relative to the atmosphere.
Flow-volume loops US Medical PG Question 10: A 60-year-old man presents with breathlessness for the past 3 months. His symptoms have been getting progressively worse during this time. He denies any history of cough, fever, or chest pain. He works at a local shipyard and is responsible for installing the plumbing aboard the vessels. His past medical history is significant for hypertension for which he takes metoprolol every day. He denies smoking and any illicit drug use. His pulse is 74/min, respiratory rate is 14/min, blood pressure is 130/76 mm Hg, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F). Physical examination is significant for fine bibasilar crackles at the end of inspiration without digital clubbing. Which of the following additional findings would most likely be present in this patient?
- A. Increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
- B. Increased residual lung volume
- C. Reduced FEV1/FVC ratio
- D. Decreased diffusing capacity of CO (Correct Answer)
- E. Decreased pulmonary arterial pressure
Flow-volume loops Explanation: ***Decreased diffusing capacity of CO***
- This patient's occupation at a **shipyard**, progressive dyspnea, and bibasilar crackles without clubbing, along with normal vital signs, are highly suggestive of **asbestosis**, a type of **interstitial lung disease (ILD)**.
- ILDs cause **fibrosis of the alveolar-capillary membrane**, leading to impaired gas exchange and a characteristic **reduction in DLCO (diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide)**. This is a hallmark of parenchymal lung disease.
*Increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure*
- An elevated **pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP)** indicates **left-sided heart failure** or **pulmonary venous hypertension**.
- While dyspnea can be a symptom of heart failure, the patient's normal blood pressure and absence of cardiac-specific symptoms or signs point away from primary cardiac pathology.
*Increased residual lung volume*
- **Increased residual lung volume** is a characteristic finding in **obstructive lung diseases** such as **COPD** and **asthma**, where there is air trapping due to airflow limitation.
- The patient's presentation with progressive dyspnea and bibasilar crackles is more consistent with a **restrictive lung disorder** like asbestosis, which typically causes **decreased lung volumes**.
*Reduced FEV1/FVC ratio*
- A **reduced FEV1/FVC ratio** is the hallmark of **obstructive lung diseases**, indicating airflow limitation.
- In **restrictive lung diseases** like asbestosis, both FEV1 and FVC are typically reduced proportionally, often resulting in a **normal or even increased FEV1/FVC ratio**.
*Decreased pulmonary arterial pressure*
- **Pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP)** is typically **normal or increased** in patients with interstitial lung disease due to **hypoxic vasoconstriction** and vascular remodeling.
- A decreased PAP would be an unusual and atypical finding in such a patient and is not associated with this clinical picture.
More Flow-volume loops US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.