Oogenesis and follicular development US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Oogenesis and follicular development. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Oogenesis and follicular development US Medical PG Question 1: A 22-year-old woman comes to the physician to discuss the prescription of an oral contraceptive. She has no history of major medical illness and takes no medications. She does not smoke cigarettes. She is sexually active with her boyfriend and has been using condoms for contraception. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. She is prescribed combined levonorgestrel and ethinylestradiol tablets. Which of the following is the most important mechanism of action of this drug in the prevention of pregnancy?
- A. Inhibition of rise in luteinizing hormone (Correct Answer)
- B. Suppression of ovarian folliculogenesis
- C. Thickening of cervical mucus
- D. Prevention of endometrial proliferation
- E. Increase of sex-hormone binding globulin
Oogenesis and follicular development Explanation: ***Inhibition of rise in luteinizing hormone***
- Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) primarily prevent pregnancy by **suppressing the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis**, which inhibits the mid-cycle **Luteinizing Hormone (LH) surge** necessary for ovulation.
- Without the LH surge, the mature follicle does not rupture, and the **ovum is not released**.
*Suppression of ovarian folliculogenesis*
- While COCs do **suppress follicular development**, this is a consequence of the feedback inhibition on FSH secretion, and not the primary contraceptive mechanism.
- The direct **prevention of ovulation** via LH surge inhibition is the most crucial step.
*Thickening of cervical mucus*
- Progestin components of COCs cause the **cervical mucus to become thick and impermeable** to sperm, acting as a secondary contraceptive mechanism.
- However, this is not the most important or primary mechanism, as ovulation can still be theoretically prevented even without this effect.
*Prevention of endometrial proliferation*
- The progestin in COCs causes the endometrium to become **thin and atrophic**, making it less receptive to implantation.
- This is an **ancillary contraceptive effect** but not the primary way pregnancy is prevented, as preventing ovulation is more fundamental.
*Increase of sex-hormone binding globulin*
- Estrogen in COCs can **increase levels of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG)**, affecting the bioavailability of endogenous androgens.
- This effect is largely responsible for reducing symptoms of androgen excess (e.g., acne) but plays **no direct role in contraception**.
Oogenesis and follicular development US Medical PG Question 2: A group of scientists developed a mouse model to study nondisjunction in meiosis. Their mouse model produced gametes in the following ratio: 2 gametes with 24 chromosomes each and 2 gametes with 22 chromosomes each. In which of the following steps of meiosis did the nondisjunction occur?
- A. Telophase I
- B. Metaphase II
- C. Anaphase I (Correct Answer)
- D. Anaphase II
- E. Metaphase I
Oogenesis and follicular development Explanation: ***Anaphase I***
- Nondisjunction during **Anaphase I** occurs when homologous chromosomes fail to separate properly, meaning both homologs of a chromosome pair go to the same pole.
- This results in two secondary gametocytes with abnormal chromosome numbers: one with n+1 chromosomes (24) and one with n-1 chromosomes (22).
- When meiosis II proceeds normally, each abnormal secondary gametocyte divides to produce 2 identical gametes, resulting in **all 4 gametes being abnormal** in a 2:2 ratio (two n+1 and two n-1), matching the observed pattern.
*Telophase I*
- **Telophase I** is the final stage of meiosis I where chromosomes arrive at the poles and the cell divides, but it's not where the initial separation error (nondisjunction) occurs.
- Nondisjunction happens due to a failure of **chromosome segregation**, which is a process of anaphase, not telophase.
*Metaphase II*
- **Metaphase II** involves the alignment of sister chromatids at the metaphase plate in secondary gametocytes. Nondisjunction at this stage would involve sister chromatids failing to separate.
- Nondisjunction in Metaphase II (or Anaphase II) would lead to 2 normal gametes (23 chromosomes), one gamete with n+1 (24 chromosomes), and one gamete with n-1 (22 chromosomes), which differs from the given ratio.
*Anaphase II*
- **Nondisjunction in Anaphase II** would involve the failure of sister chromatids to separate in one of the secondary gametocytes.
- This would produce two normal gametes (23 chromosomes), one gamete with 24 chromosomes (n+1), and one gamete with 22 chromosomes (n-1), which is not the 2:2 ratio observed.
*Metaphase I*
- **Metaphase I** is characterized by the alignment of homologous chromosome pairs at the metaphase plate. While an issue here could precede nondisjunction, the actual event of failed separation occurs during anaphase.
- No separation of chromosomes occurs in Metaphase I; it is the stage of **chromosome alignment** before segregation.
Oogenesis and follicular development US Medical PG Question 3: A 51-year-old woman presents to the primary care clinic complaining of trouble sleeping. She reports that she has episodes of "overheating" and "sweating" during the day and at night. The nightly episodes keep her from staying asleep. She also explains how embarrassing it is when she suddenly becomes hot and flushed during work meetings. The patient becomes visibly upset and states that she is worried about her marriage as well. She says she has been fighting with her husband about not going out because she is "too tired." They have not been able to have sex the past several months because "it hurts." Labs are drawn, as shown below:
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH): 62 mIU/mL
Estradiol: 34 pg/mL
Progesterone: 0.1 ng/mL
Luteinizing hormone (LH): 46 mIU/mL
Free testosterone: 2.1 ng/dL
Which of the following contributes most to the production of estrogen in this patient?
- A. Adrenal glands
- B. Adipose tissue (Correct Answer)
- C. Bartholin glands
- D. Mammary glands
- E. Ovaries
Oogenesis and follicular development Explanation: **Adipose tissue**
- In **postmenopausal women**, the ovaries no longer produce significant amounts of estrogen; instead, **adipose tissue** becomes the primary site for estrogen synthesis through the conversion of **androgens** (like androstenedione from the adrenal glands) into **estrone** via **aromatase**.
- The patient's presentation with **hot flashes**, **night sweats**, **sleep disturbance**, **vaginal dryness** (painful intercourse), and **elevated FSH/LH** with **low estradiol** is classic for **menopause**, highlighting the shift in estrogen production.
*Adrenal glands*
- The **adrenal glands** primarily produce **androgens** (e.g., androstenedione, DHEA) and a small amount of estrogens, but their main contribution to estrogen in menopause is indirect, by providing substrates for conversion in peripheral tissues.
- While they are a source of **androgens**, they do not directly contribute most significantly to **estrogen production** in a menopausal woman compared to the peripheral conversion in adipose tissue.
*Bartholin glands*
- **Bartholin glands** are located at the vaginal opening and produce **lubricating fluid**, but they play no role in **hormone production**, including estrogen.
- They are exocrine glands involved in lubrication during sexual arousal.
*Mammary glands*
- **Mammary glands** are primarily involved in **milk production** (lactation) and are target organs for sex hormones, but they do not produce significant amounts of **estrogen**.
- They respond to estrogen but do not synthesize it in substantial quantities.
*Ovaries*
- In premenopausal women, the **ovaries** are the primary source of **estrogen** (mainly estradiol), but in this 51-year-old woman with menopausal symptoms and high FSH/LH, ovarian function has significantly declined.
- The **elevated FSH and LH** levels, coupled with **low estradiol**, indicate **ovarian failure**, meaning the ovaries are no longer actively producing estrogen.
Oogenesis and follicular development US Medical PG Question 4: A 22-year-old female presents to her PCP after having unprotected sex with her boyfriend 2 days ago. She has been monogamous with her boyfriend but is very concerned about pregnancy. The patient requests emergency contraception to decrease her likelihood of getting pregnant. A blood hCG test returns negative. The PCP prescribes the patient ethinyl estradiol 100 mcg and levonorgestrel 0.5 mg to be taken 12 hours apart. What is the most likely mechanism of action for this combined prescription?
- A. Inhibition or delayed ovulation (Correct Answer)
- B. Interference of corpus luteum function
- C. Thickening of cervical mucus with sperm trapping
- D. Tubal constriction inhibiting sperm transportation
- E. Alteration of the endometrium impairing implantation of the fertilized egg
Oogenesis and follicular development Explanation: ***Inhibition or delayed ovulation***
- The high doses of **estrogen** and **progestin** in the combined emergency contraception pill primarily act by suppressing the **luteinizing hormone (LH) surge**, which is essential for ovulation.
- By inhibiting or delaying ovulation, the pill prevents the release of an egg, thus preventing fertilization since sperm cannot meet an egg.
*Interference of corpus luteum function*
- While hormonal contraceptives can affect the **corpus luteum**, high-dose emergency contraception primarily acts *before* the formation of a mature corpus luteum by preventing ovulation itself.
- Once the corpus luteum is formed, its function is usually maintained if pregnancy occurs, and emergency contraception given *after* implantation is generally ineffective at terminating a pregnancy.
*Thickening of cervical mucus with sperm trapping*
- This is a well-known mechanism of action for *continuous* hormonal contraception (e.g., daily birth control pills), where lower, consistent doses of progestin make cervical mucus impenetrable to sperm.
- While it might play a *minor* role, it is not the primary mechanism of action for high-dose emergency contraception administered acutely, which mainly targets ovulation.
*Tubal constriction inhibiting sperm transportation*
- There is no strong evidence to suggest that combined emergency contraception pills cause **tubal constriction** to significantly impair sperm or egg transport.
- The main sites of action are the **hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis** (for ovulation) and possibly the endometrium (for implantation), not direct tubal motility.
*Alteration of the endometrium impairing implantation of the fertilized egg*
- While hormonal contraceptives can alter the **endometrium** making it less receptive to implantation, this is considered a *secondary* or less significant mechanism for combined emergency contraception.
- The primary goal and most effective action of these pills is to prevent fertilization by inhibiting ovulation, especially when taken shortly after unprotected intercourse and before implantation.
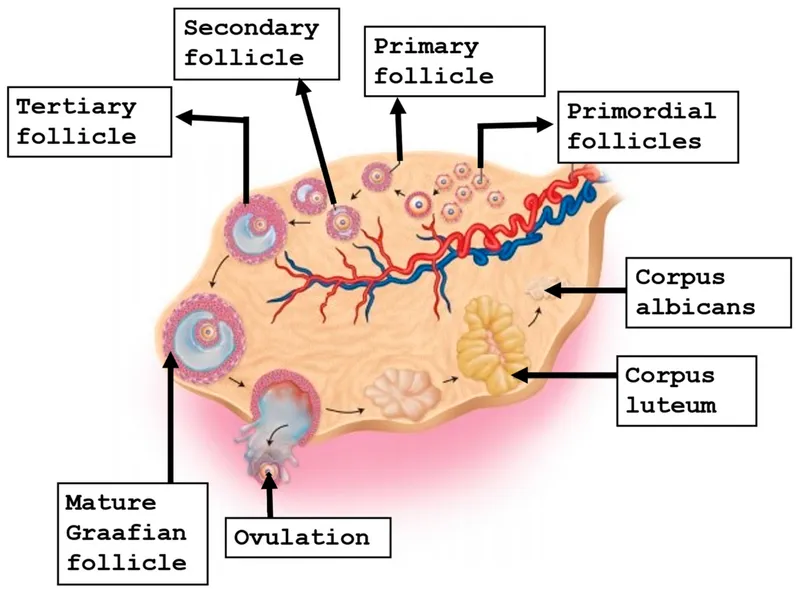
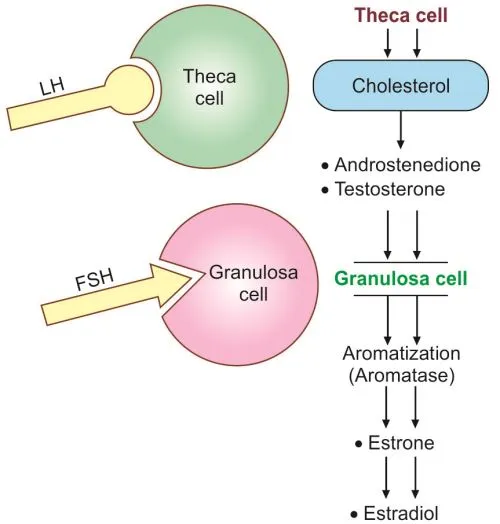
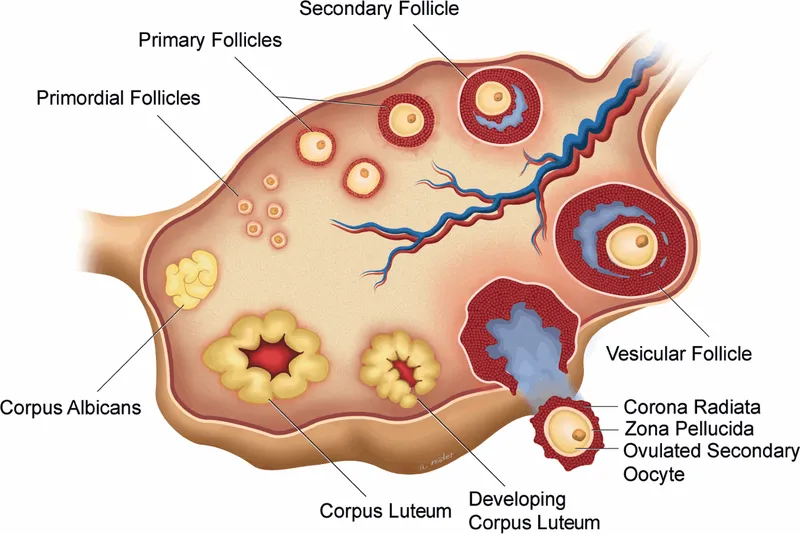
Oogenesis and follicular development US Medical PG Question 5: A researcher is studying the effects of hormones on different cells within the ovarian follicle. She adds follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) to a culture of ovarian follicle cells. She then measures the activity levels of different enzymes within the cells. Which enzyme and ovarian cell type would be expected to be stimulated by the addition of FSH?
- A. Desmolase; theca interna cell
- B. Aromatase; theca externa cell
- C. Aromatase; granulosa cell (Correct Answer)
- D. Desmolase; granulosa cell
- E. Aromatase; theca interna cell
Oogenesis and follicular development Explanation: ***Aromatase; granulosa cell***
- **FSH** acts directly on **granulosa cells** to stimulate their proliferation and differentiation.
- One of the key functions of stimulated granulosa cells is the production of **aromatase**, an enzyme responsible for converting **androgens** (produced by theca cells) into **estrogens**.
*Desmolase; theca interna cell*
- **Desmolase** (specifically cholesterol desmolase, or CYP11A1) is found in **theca interna cells** and is responsible for converting cholesterol into **androgens**.
- Theca interna cell activity, including desmolase, is primarily stimulated by **LH**, not FSH.
*Aromatase; theca externa cell*
- The **theca externa cells** are primarily connective tissue and lack significant endocrine function, including aromatase activity.
- **Aromatase** is predominantly present in the granulosa cells.
*Desmolase; granulosa cell*
- While granulosa cells are crucial for estrogen synthesis via aromatase, they do not produce **desmolase**.
- **Desmolase** is the key enzyme in theca interna cells for androgen synthesis.
*Aromatase; theca interna cell*
- **Theca interna cells** produce **androgens** under the influence of **LH** and do not express **aromatase**.
- **Aromatase** is exclusively expressed in the **granulosa cells** and converts these androgens into estrogens.
Oogenesis and follicular development US Medical PG Question 6: A 43-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of heavy, irregular menstrual bleeding. Pelvic examination shows blood and clots in the posterior fornix and normal-appearing internal and external genitalia. An endometrial biopsy specimen shows straight uniform tubular glands lined with tall pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells with high mitotic activity embedded in an edematous stroma. Increased activity of which of the following is directly responsible for the histologic appearance of the biopsy specimen?
- A. Theca externa cells
- B. Corpus luteum
- C. Aromatase (Correct Answer)
- D. 5-alpha-reductase
- E. Luteinizing hormone
Oogenesis and follicular development Explanation: ***Aromatase***
- The biopsy findings (straight uniform tubular glands with high mitotic activity and pseudostratified columnar cells in an edematous stroma) are characteristic of **endometrial hyperplasia**, a condition often driven by **unopposed estrogen stimulation**.
- **Aromatase** is the enzyme responsible for converting androgens (such as androstenedione and testosterone) into estrogens (estrone and estradiol), thus directly contributing to the elevated estrogen levels causing the hyperplasia.
*Theca externa cells*
- **Theca externa cells** are primarily involved in the structural support of the follicle and do not directly produce significant amounts of hormones.
- The primary hormone production from the ovarian follicles comes from theca interna cells (androgens) and granulosa cells (estrogens).
*Corpus luteum*
- The **corpus luteum** is responsible for producing progesterone after ovulation. Its activity would lead to secretory changes in the endometrium, counteracting the proliferative effects of unopposed estrogen and typically reducing bleeding.
- Absence or dysfunction of the corpus luteum could lead to anovulatory cycles and prolonged estrogenic stimulation, but the corpus luteum itself does not directly cause hyperplasia by its own activity in this context.
*5-alpha-reductase*
- **5-alpha-reductase** converts testosterone into the more potent androgen, dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
- This enzyme is primarily active in androgen-sensitive tissues like the prostate, hair follicles, and skin, and its activity does not directly lead to endometrial hyperplasia.
*Luteinizing hormone*
- **Luteinizing hormone (LH)** triggers ovulation and stimulates the theca cells to produce androgens, which are then aromatized to estrogen by granulosa cells.
- While LH is essential for ovarian function, the direct cause of the endometrial hyperplasia in this scenario is the sustained high estrogen level, often due to anovulation or peripheral conversion, not the LH itself.
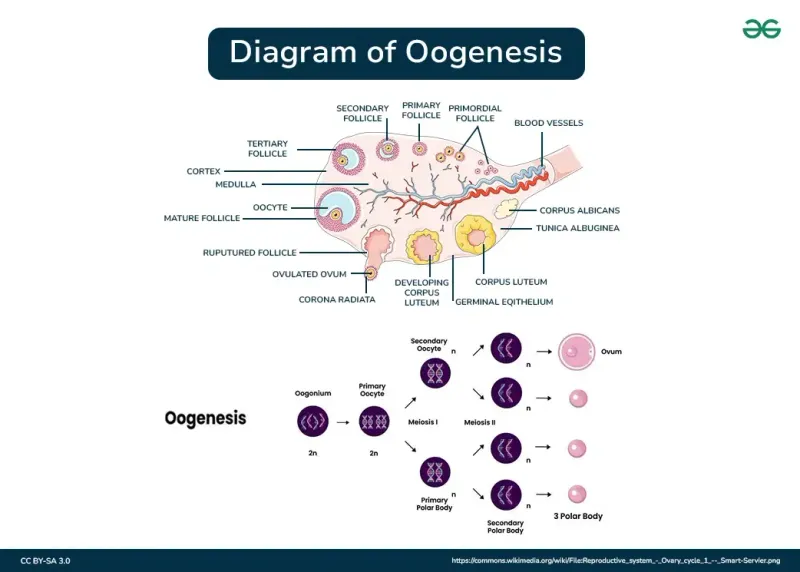
Oogenesis and follicular development US Medical PG Question 7: A researcher is studying gamete production and oogenesis. For her experiment, she decides to cultivate primary oocytes in their arrested state and secondary oocytes just prior to fertilization. When she examines these gametes, she will find that the primary oocytes and secondary oocytes are arrested in which phases of meiosis, respectively?
- A. Anaphase I; anaphase II
- B. Interphase I; prophase II
- C. Metaphase I; metaphase II
- D. Metaphase I; prophase II
- E. Prophase I; metaphase II (Correct Answer)
Oogenesis and follicular development Explanation: ***Prophase I; metaphase II***
- **Primary oocytes** are arrested in **prophase I** from embryonic development until puberty, when they resume meiosis in preparation for ovulation.
- **Secondary oocytes** are immediately arrested in **metaphase II** after completing meiosis I, and they will remain in this stage until fertilization occurs.
*Anaphase I; anaphase II*
- **Anaphase I** involves the separation of **homologous chromosomes**, and **anaphase II** involves the separation of **sister chromatids**. Neither primary nor secondary oocytes are arrested in these stages.
- Meiotic arrest occurs at earlier stages to prevent further division until specific triggers (ovulation or fertilization) are met.
*Interphase I; prophase II*
- **Interphase I** precedes meiosis I, during which DNA replication occurs, and it is not a stage of meiotic arrest for primary oocytes.
- **Prophase II** is a transient stage in meiosis II, and secondary oocytes are arrested later in **metaphase II**, not prophase II.
*Metaphase I; metaphase II*
- While **secondary oocytes** are indeed arrested in **metaphase II**, **primary oocytes** are arrested much earlier in **prophase I**, not metaphase I.
- The arrest in metaphase I is temporary for primary oocytes as they complete meiosis I to form secondary oocytes upon hormonal signaling.
*Metaphase I; prophase II*
- **Primary oocytes** are arrested in **prophase I**, not metaphase I. Meiosis I is completed before ovulation, leading to the formation of secondary oocytes.
- **Secondary oocytes** are arrested in **metaphase II**, not prophase II, awaiting fertilization to complete meiosis II.
Oogenesis and follicular development US Medical PG Question 8: A 32-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 20 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. She feels well. Her first pregnancy was uncomplicated and the child was delivered vaginally. Medications include folic acid and an iron supplement. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 98/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 108/76 mm Hg. Abdominal examination shows a uterus that is consistent with a 20-week gestation. The second-trimester scan shows no abnormalities. The patient intends to travel next month to Mozambique to visit her grandmother. Which of the following drugs is most suitable for pre-exposure prophylaxis against malaria?
- A. Mefloquine (Correct Answer)
- B. Primaquine
- C. Chloroquine
- D. Doxycycline
- E. Proguanil
Oogenesis and follicular development Explanation: ***Mefloquine***
- **Mefloquine** is the **most appropriate antimalarial prophylaxis** for pregnant women traveling to **chloroquine-resistant areas** such as Mozambique, particularly after the first trimester.
- Mozambique has **widespread chloroquine-resistant *P. falciparum* malaria**, making mefloquine the preferred choice according to CDC and WHO guidelines.
- While mefloquine is avoided in the first trimester due to limited safety data, it is considered **safe in the second and third trimesters** of pregnancy.
- Though neuropsychiatric side effects can occur, the benefits outweigh risks when traveling to high-risk malaria areas during pregnancy.
*Primaquine*
- **Primaquine** is *contraindicated* in pregnancy because it can cause **hemolytic anemia** in the fetus if the fetus has **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency**.
- It is used primarily for the **radical cure** of *P. vivax* and *P. ovale* malaria (to eradicate liver hypnozoites), not as a primary prophylactic agent.
*Chloroquine*
- While **chloroquine** is safe in pregnancy and preferred for **chloroquine-sensitive malaria** areas, it is *not appropriate for Mozambique*.
- Mozambique has **high rates of chloroquine-resistant *P. falciparum* malaria**, making chloroquine ineffective for prophylaxis in this region.
- Chloroquine would only be suitable for travel to areas with confirmed chloroquine-sensitive malaria (e.g., Central America west of Panama Canal, parts of the Middle East).
*Doxycycline*
- **Doxycycline** is *contraindicated* in pregnancy and in children under eight years old due to its potential to cause **permanent dental discoloration**, **enamel hypoplasia**, and inhibition of **bone growth** in the developing fetus.
*Proguanil*
- **Atovaquone-proguanil** (Malarone) has limited safety data in pregnancy and is generally not recommended as a first-line option when other proven alternatives are available.
- While some data suggest it may be safe, **mefloquine** is preferred for chloroquine-resistant areas during pregnancy due to more extensive safety documentation in the second and third trimesters.
Oogenesis and follicular development US Medical PG Question 9: A 29-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room for seizure-like activity. Her husband reports that they were in bed sleeping when his wife began complaining of “hot flashes.” Several minutes later, her right arm began to twitch, and she did not respond to his calls. The whole episode lasted for about 5 minutes. She denies any prior similar episodes, tongue biting, loss of bowel or urinary control, new medications, or recent illness. She reports a family history of epilepsy and is concerned that she might have the same condition. Urine pregnancy test is positive. If this patient is prescribed phenytoin, during which of the following weeks is the fetus most sensitive to its side effects?
- A. Week 18
- B. Weeks 1-2
- C. Weeks 10-12
- D. Week 14
- E. Weeks 3-8 (Correct Answer)
Oogenesis and follicular development Explanation: ***Weeks 3-8***
- This period marks the **embryonic stage**, crucial for organogenesis, when the fetus is highly susceptible to **teratogenic effects** from drugs like phenytoin.
- Exposure during weeks 3-8 can lead to **Fetal Hydantoin Syndrome**, characterized by features like craniofacial abnormalities, digital hypoplasia, and growth deficiency.
*Week 18*
- By week 18, most major organ systems have largely formed, making the fetus less vulnerable to the **initial teratogenic effects** of phenytoin.
- While some developmental issues can still occur, the risk of severe structural malformations caused by initial exposure is significantly lower compared to the embryonic period.
*Weeks 1-2*
- During weeks 1-2 (peri-implantation period), the embryo is generally resilient to teratogens, following an "all or none" principle where exposure either causes **fetal demise** or no effect.
- Major **organogenesis** has not yet begun, so the specific structural malformations associated with Fetal Hydantoin Syndrome are unlikely to occur from exposure during this very early stage.
*Weeks 10-12*
- By weeks 10-12, the basic structures of most organs are established, reducing the risk of **major congenital malformations** typically seen with early embryonic exposure.
- While developmental and functional impairments can still arise from drug exposure, the critical period for *inducing* severe structural defects due to phenytoin has generally passed.
*Week 14*
- Similar to week 18, by week 14, **organogenesis** is largely complete, and the fetus is less susceptible to the type of gross structural defects caused by phenytoin during earlier embryonic development.
- Exposure at this stage is more likely to cause **functional deficits** or subtle anomalies rather than the severe malformations associated with **Fetal Hydantoin Syndrome**.
Oogenesis and follicular development US Medical PG Question 10: Fertilization begins when sperm binds to the corona radiata of the egg. Once the sperm enters the cytoplasm, a cortical reaction occurs which prevents other sperm from entering the oocyte. The oocyte then undergoes an important reaction. What is the next reaction that is necessary for fertilization to continue?
- A. The second meiotic division (Correct Answer)
- B. Degeneration of the sperm tail
- C. Release of a polar body
- D. Formation of the spindle apparatus
- E. Acrosome reaction
Oogenesis and follicular development Explanation: ***The second meiotic division***
- Upon **sperm penetration**, the secondary oocyte completes its **meiosis II**, forming a mature ovum and a second polar body.
- This completion of meiosis II is a critical step for the pronuclear fusion and subsequent **zygote formation**.
*Degeneration of the sperm tail*
- While the sperm tail does degenerate within the ooplasm, it occurs **after** the genetic material has been released and is not the immediate next critical reaction for continued fertilization.
- This is a process of degradation and assimilation, not an active cellular reaction of the oocyte vital for fertilization progression.
*Release of a polar body*
- The first polar body is released **before fertilization** (at the completion of meiosis I), and the second polar body is released **concomitantly with the completion of meiosis II**, which is the required reaction.
- Releasing a polar body is a consequence of meiotic division, not an independent reaction that drives fertilization forward.
*Formation of the spindle apparatus*
- The **spindle apparatus** is formed during both meiotic divisions to separate chromosomes, but its formation itself is not the immediate "next reaction" necessary for fertilization to continue after cortical reaction.
- The key event is the progression of meiosis, which the spindle facilitates, not the mere formation of the apparatus.
*Acrosome reaction*
- The **acrosome reaction** occurs **before** the sperm binds to the zona pellucida and penetrates the oocyte, enabling the release of enzymes to digest the egg's outer layers.
- This reaction has already taken place for the sperm to have entered the oocyte and initiated the cortical reaction.
More Oogenesis and follicular development US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.