Lactation physiology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Lactation physiology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Lactation physiology US Medical PG Question 1: A 26-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 3-day history of nausea and vomiting. Her last menstrual period was 9 weeks ago. A urine pregnancy test is positive. Ultrasonography shows an intrauterine pregnancy consistent in size with a 7-week gestation. The hormone that was measured in this patient's urine to detect the pregnancy is also directly responsible for which of the following processes?
- A. Development of breast tissue
- B. Preparation of the uterine endometrium for implantation
- C. Inhibition of preterm uterine contractions
- D. Maintenance of the corpus luteum (Correct Answer)
- E. Inhibition of ovulation
Lactation physiology Explanation: ***Maintenance of the corpus luteum***
- The hormone measured in the urine pregnancy test is **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)**.
- **hCG** acts like **luteinizing hormone (LH)** to maintain the **corpus luteum** in early pregnancy, ensuring continued progesterone production until the placenta takes over.
*Development of breast tissue*
- **Estrogen** and **progesterone** are the primary hormones responsible for the development of breast tissue during pregnancy, preparing the breasts for lactation.
- While hCG indirectly supports these hormones, it does not directly cause breast tissue development.
*Preparation of the uterine endometrium for implantation*
- The **preparation of the uterine endometrium** for implantation is primarily driven by **progesterone**, produced by the corpus luteum initially and later by the placenta.
- hCG’s role is to maintain the corpus luteum, thus indirectly supporting progesterone production.
*Inhibition of preterm uterine contractions*
- **Progesterone** is the main hormone responsible for **inhibiting uterine contractions** during pregnancy to prevent preterm labor.
- While hCG supports progesterone production, it does not directly inhibit uterine contractions itself.
*Inhibition of ovulation*
- High levels of **estrogen** and **progesterone** during pregnancy suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, thereby **inhibiting ovulation**.
- While hCG maintains the corpus luteum which produces these hormones, hCG itself is not the direct inhibitor of ovulation.
Lactation physiology US Medical PG Question 2: A 32-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of irregular menses, milky discharge from her nipples, fatigue, and weight gain. Menses occur at irregular 25–40-day intervals and last 1–2 days with minimal flow. 5 months ago, she was started on clozapine for treatment of schizophrenia. She has hypothyroidism but has not been taking levothyroxine over the past 6 months. Visual field examination show no abnormalities. Her serum thyroid-stimulating hormone is 17.0 μU/mL and serum prolactin is 85 ng/mL. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the nipple discharge in this patient?
- A. Prolactinoma
- B. Thyrotropic pituitary adenoma
- C. Ectopic prolactin production
- D. Hypothyroidism (Correct Answer)
- E. Adverse effect of medication
Lactation physiology Explanation: ***Hypothyroidism***
- **Primary hypothyroidism** is the most likely cause of this patient's galactorrhea given her significantly elevated TSH (17.0 μU/mL) and 6-month non-compliance with levothyroxine.
- In hypothyroidism, elevated **TRH (thyrotropin-releasing hormone)** stimulates both TSH and **prolactin release** from the anterior pituitary, commonly causing prolactin levels in the 50-100 ng/mL range.
- The patient's prolactin level of **85 ng/mL is entirely consistent** with hypothyroidism-induced hyperprolactinemia.
- Hypothyroidism also explains her other symptoms: **fatigue, weight gain, and menstrual irregularities**.
*Adverse effect of medication*
- While some antipsychotics cause significant hyperprolactinemia, **clozapine is notably prolactin-sparing** due to its weak D2 receptor antagonism and rapid dissociation from D2 receptors.
- Clozapine is one of the **atypical antipsychotics with the lowest risk** of causing elevated prolactin levels.
- Antipsychotics that commonly cause hyperprolactinemia include **risperidone, paliperidone, amisulpride, and typical antipsychotics** (e.g., haloperidol), but not clozapine.
- Given the patient's untreated hypothyroidism, this is the less likely cause.
*Prolactinoma*
- A prolactinoma would typically present with **significantly higher prolactin levels** (usually >200 ng/mL for macroadenomas, though microprolactinomas may have levels 100-200 ng/mL).
- The patient's prolactin of 85 ng/mL is **more consistent with secondary causes** like hypothyroidism or medications.
- The absence of **visual field defects** makes a large macroadenoma less likely.
*Thyrotropic pituitary adenoma*
- A thyrotropic (TSH-secreting) pituitary adenoma causes **secondary hyperthyroidism** with elevated TSH and elevated thyroid hormones, not hypothyroidism.
- This patient has **primary hypothyroidism** (elevated TSH with presumably low T4), which is the opposite presentation.
- TSH-secreting adenomas are extremely rare (<1% of pituitary adenomas).
*Ectopic prolactin production*
- **Ectopic prolactin production** by non-pituitary tumors is exceedingly rare and usually associated with very high prolactin levels.
- There are no clinical features suggesting an ectopic source or malignancy.
- The patient's presentation is fully explained by her untreated hypothyroidism.
Lactation physiology US Medical PG Question 3: A patient with a pituitary tumor demonstrates elevated prolactin levels. Which of the following changes in dopamine signaling best explains the hyperprolactinemia?
- A. Increased D1 receptor activation
- B. Enhanced dopamine reuptake
- C. Increased dopamine synthesis
- D. Decreased tuberoinfundibular dopamine release (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased D2 receptor activation
Lactation physiology Explanation: ***Decreased tuberoinfundibular dopamine release***
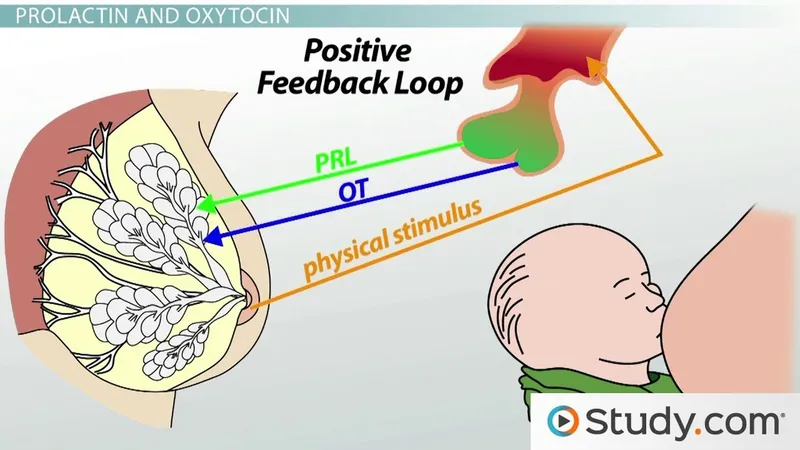
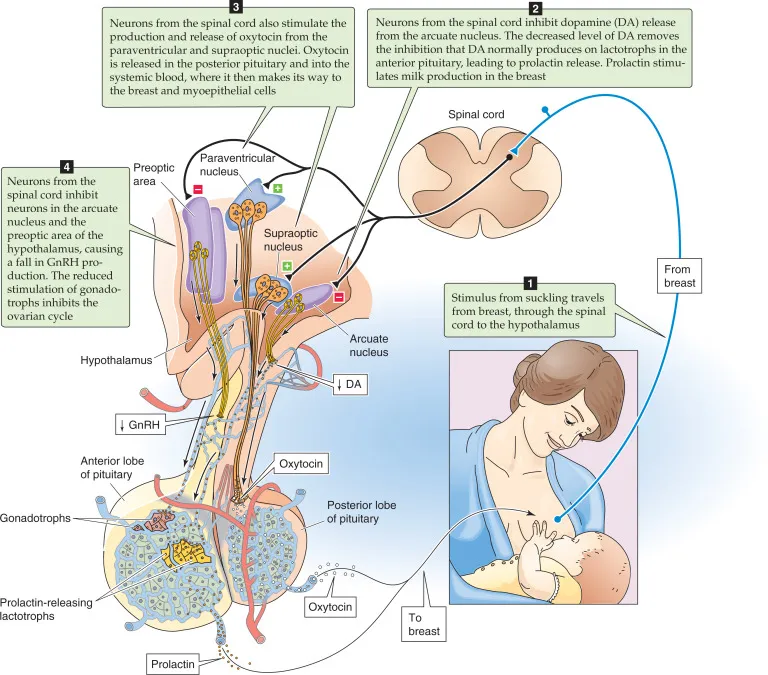
- **Dopamine** acts as a **prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH)**, primarily through the **tuberoinfundibular pathway** from the hypothalamus to the pituitary [1].
- A **pituitary tumor** can compress or damage the pituitary stalk or the hypothalamus, leading to decreased dopamine delivery to the pituitary and thus **hyperprolactinemia** [1].
*Increased D1 receptor activation*
- **D1 receptors** are generally associated with **excitatory effects** and are not the primary receptors mediating dopamine's inhibitory effect on prolactin.
- **Dopamine's inhibitory action** on prolactin secretion is predominantly mediated by **D2 receptors**.
*Enhanced dopamine reuptake*
- Enhanced reuptake would lead to **less dopamine availability** at the receptor site, which would indeed cause hyperprolactinemia.
- However, this is not the most direct or specific consequence of a **pituitary tumor's mechanical effects** on dopamine signaling [1].
*Increased dopamine synthesis*
- **Increased dopamine synthesis** would lead to higher dopamine levels and thus **inhibit prolactin secretion**, which is contrary to the hyperprolactinemia observed in the patient.
- This option would result in **hypoprolactinemia**.
*Increased D2 receptor activation*
- **D2 receptor activation** by dopamine **inhibits prolactin release** from lactotrophs in the pituitary [1].
- Therefore, increased D2 receptor activation would lead to **decreased prolactin levels**, not hyperprolactinemia.
Lactation physiology US Medical PG Question 4: A 36-year-old woman comes to the gynecologist because of a 4-month history of irregular menstrual cycles. Menses occur at irregular 15 to 45-day intervals and last 1–2 days with minimal flow. She also reports a milk-like discharge from her nipples for 3 months, as well as a history of fatigue and muscle and joint pain. She does not have abdominal pain, fever, or headache. She has recently gained 2.5 kg (5.5 lb) of weight. She was diagnosed with schizophrenia and started on aripiprazole by a psychiatrist 8 months ago. She has hypothyroidism but has not been taking levothyroxine for 6 months. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. She appears healthy and anxious. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Pelvic examination shows vaginal atrophy. Visual field and skin examination are normal. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 12.7 g/dL
Serum
Glucose 88 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.7 mg/dL
Thyroid-stimulating hormone 16.3 μU/mL
Cortisol (8AM) 18 μg/dL
Prolactin 88 ng/mL
Urinalysis is normal. An x-ray of the chest and ultrasound of the pelvis show no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the nipple discharge in this patient?
- A. Prolactinoma
- B. Hypothyroidism (Correct Answer)
- C. Thyrotropic pituitary adenoma
- D. Cushing disease
- E. Ectopic prolactin production
Lactation physiology Explanation: ***Hypothyroidism***
- The patient has a significantly elevated **TSH (16.3 μU/mL)** and a history of non-compliance with **levothyroxine** for 6 months, strongly indicating uncontrolled hypothyroidism.
- **Hypothyroidism** can lead to **increased TRH** (thyrotropin-releasing hormone) from the hypothalamus, which stimulates not only TSH but also **prolactin** release, causing galactorrhea.
- Note: **Aripiprazole** is a partial dopamine agonist and typically does **not** cause hyperprolactinemia (unlike typical antipsychotics or risperidone), making hypothyroidism the primary driver here.
*Prolactinoma*
- While the patient has **hyperprolactinemia (prolactin 88 ng/mL)** and galactorrhea, a prolactinoma usually presents with prolactin levels **significantly higher** (often >200 ng/mL, or >100 ng/mL in microadenomas) than observed here.
- The primary driver for the hyperprolactinemia in this case is more likely the **uncorrected hypothyroidism**, which can also cause moderate elevation of prolactin.
*Thyrotropic pituitary adenoma*
- A **thyrotropic pituitary adenoma** (TSH-secreting adenoma) would cause elevated TSH accompanied by **elevated thyroid hormone levels** (hyperthyroidism), which contradicts this patient's clinical picture of hypothyroidism.
- This patient exhibits **hypothyroidism** due to non-adherence to medication, not hyperthyroidism induced by a TSH-secreting tumor.
*Cushing disease*
- **Cushing disease** is characterized by elevated **cortisol** due to an ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma, leading to symptoms like central obesity, moon facies, and striae; these are not reported.
- While some forms of Cushing syndrome can cause menstrual irregularities, it does not typically cause **galactorrhea** or significantly elevated prolactin levels as seen in this patient.
*Ectopic prolactin production*
- **Ectopic prolactin production** is a rare cause of hyperprolactinemia, typically associated with large tumors, most commonly **renal cell carcinoma** or other neuroendocrine tumors (e.g., lung carcinoid).
- Given the patient's severe **hypothyroidism**, it is a far more common and likely explanation for her hyperprolactinemia and galactorrhea than ectopic production.
Lactation physiology US Medical PG Question 5: A 26-year-old woman presents to her physician with a complaint of milk reduction. 2 months ago, she delivered a healthy girl from an uncomplicated pregnancy. The baby was exclusively breastfed until 1.5 months when the patient had to return to the workforce. She cannot breastfeed her daughter at work so she had to leave her with her grandmother and incorporated baby formula into her diet. She reports breast engorgement shortly after she switched to the described regimen which subsided soon. A week after she switched to such a regimen, she started to notice that she has less milk to feed her baby when she is at home. The patient does not report any other symptoms including weight change or mood disturbances. She has breast implants installed submuscularly using the inframammary approach. At the age of 12 years, she had a blunt chest trauma with breast involvement. After the pregnancy, she had a short course of cetirizine due to hay fever. At presentation, the patient’s vital signs are within normal limits. The patient’s breasts are slightly engorged with no skin color changes. There is no discharge on breast compression. Which of the following statements describes the cause of the patient’s condition?
- A. Obliteration of the ducts due to trauma
- B. Failure of lactogenic ducts to develop
- C. Suppression of lactation by the medications
- D. Insufficient amount of glandular breast tissue
- E. Insufficient breast emptying (Correct Answer)
Lactation physiology Explanation: ***Insufficient breast emptying***
- The patient's reduced milk supply is most likely due to **decreased frequency of breast emptying** once she returned to work and started using formula.
- **Regular and complete removal of milk** is essential to maintain supply, as milk production operates on a supply-and-demand basis.
*Obliteration of the ducts due to trauma*
- While significant **blunt chest trauma** could potentially cause ductal damage, it would typically present with immediate and severe lactation issues.
- The patient successfully breastfed for 1.5 months, indicating functional ducts post-trauma and pre-pregnancy.
*Failure of lactogenic ducts to develop*
- This is unlikely given that the patient was able to **successfully breastfeed exclusively for 1.5 months**, indicating the presence and function of lactogenic ducts.
- **Insufficient glandular tissue** (hypoplasia) is a different issue, and while it leads to low milk supply, it's not a "failure of ducts to develop."
*Suppression of lactation by the medications*
- **Cetirizine, an antihistamine**, is generally considered safe during lactation and is not known to significantly suppress milk supply.
- There is no mention of other medications that could strongly inhibit lactation (e.g., certain decongestants or hormonal contraceptives).
*Insufficient amount of glandular breast tissue*
- The patient's ability to **exclusively breastfeed for 1.5 months** suggests that she had sufficient glandular tissue to establish lactation.
- While breast implants can sometimes be associated with lactation difficulties, submuscular placement and inframammary incisions typically **preserve glandular tissue and ducts** better than other approaches.
Lactation physiology US Medical PG Question 6: An exclusively breast-fed, 4-month-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother for a routine examination. He was born at term and delivery was uncomplicated. He received all standard treatment and testing prior to being discharged from the hospital. Examination shows no abnormalities. Without receiving additional supplementation at this time, this infant is at greatest risk of developing which of the following conditions?
- A. Intracranial bleed
- B. Microcytic anemia (Correct Answer)
- C. Rickets
- D. Scaly dermatitis
- E. Peripheral neuropathy
Lactation physiology Explanation: ***Microcytic anemia***
- Exclusively breastfed infants are at risk for **iron deficiency anemia** because breast milk contains low levels of iron (~0.3 mg/L), and newborn iron stores are typically depleted by **4-6 months of age**.
- At 4 months, iron stores are beginning to deplete, and iron supplementation is typically initiated around this time; without supplementation, the infant is at greatest risk for developing **microcytic anemia** due to impaired hemoglobin synthesis.
- Iron deficiency causes red blood cells to be small (microcytic) and pale (hypochromic).
*Intracranial bleed*
- An intracranial bleed in an otherwise healthy infant is most commonly associated with **vitamin K deficiency bleeding (VKDB)**.
- However, the infant received **standard treatment** at birth, which includes vitamin K prophylaxis (typically 1 mg IM), making this highly unlikely.
*Rickets*
- Rickets is caused by **vitamin D deficiency**, leading to impaired bone mineralization.
- While breast milk is deficient in vitamin D, the **AAP recommends vitamin D supplementation (400 IU/day)** for all breastfed infants starting shortly after birth, which is part of standard care and would prevent rickets.
- No bone abnormalities are noted on examination.
*Scaly dermatitis*
- Scaly dermatitis, such as **seborrheic dermatitis (cradle cap)**, is common and physiological in infants but is not directly linked to a specific nutritional deficiency from exclusive breastfeeding.
- Severe, generalized scaly dermatitis could indicate **zinc deficiency** or **essential fatty acid deficiency**, but this is rare in otherwise healthy, exclusively breastfed term infants.
*Peripheral neuropathy*
- Peripheral neuropathy in infants can be caused by genetic, metabolic, or toxic conditions.
- It is **not** a common complication associated with exclusive breastfeeding in an otherwise healthy term infant.
Lactation physiology US Medical PG Question 7: A 28-year-old patient comes to the physician’s office with complaints of headaches and difficulty seeing out of the corner of her eye. She gave birth to her son 1 year ago. Further visual testing reveals the patient has bitemporal hemianopsia. The patient undergoes brain MRI which shows an anterior pituitary mass, likely adenoma. The patient has her blood tested to see if the adenoma is secreting extra hormone. The patient is found to have a slight excess of a hormone that uptakes a basophilic stain. Which of the following is most likely to be the hormone detected in her blood?
- A. Prolactin
- B. Growth hormone
- C. Thyroid stimulating hormone (Correct Answer)
- D. Antidiuretic hormone
- E. Oxytocin
Lactation physiology Explanation: ***Thyroid stimulating hormone***
- **Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)** is synthesized by **thyrotroph cells** which are basophilic, making it the most likely hormone to stain basophilically in this context.
- An excess of TSH from a pituitary adenoma could lead to clinical symptoms of **hyperthyroidism**, although the question states it's only a "slight excess."
*Prolactin*
- **Prolactin** is secreted by **lactotrophs**, which are acidophilic and would not take up a basophilic stain.
- While **prolactinomas** are the most common pituitary adenomas, their cells are not basophilic, and this patient does not exhibit common symptoms of hyperprolactinemia (galactorrhea, amenorrhea).
*Growth hormone*
- **Growth hormone (GH)** is produced by **somatotrophs**, which are acidophilic and would not take up a basophilic stain.
- Excess GH typically causes **acromegaly** in adults, characterized by distinctive physical changes not mentioned in the patient's presentation.
*Antidiuretic hormone*
- **Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)**, also known as vasopressin, is synthesized in the **hypothalamus** and released from the posterior pituitary, not secreted by basophilic cells of the anterior pituitary.
- Overproduction of ADH leads to **SIADH**, characterized by hyponatremia and concentrated urine, none of which are described.
*Oxytocin*
- **Oxytocin** is also produced in the **hypothalamus** and released from the posterior pituitary, not by basophilic cells in the anterior pituitary.
- Its primary functions relate to uterine contractions and milk ejection and are not associated with pituitary adenomas causing bitemporal hemianopsia.
Lactation physiology US Medical PG Question 8: A 32-year-old female presents to her obstetrician 3 weeks postpartum for failure to lactate. Of note, she has been unable to tolerate cold environments since the birth of her child. Review of systems is positive for fatigue, lightheadedness, and a 3-pound weight gain over the last 3 weeks. Her delivery was complicated by placenta accreta with postpartum blood loss. Her newborn infant is doing well on formula. She denies any personal or family history of thyroid disease. Physical exam is overall unremarkable. On a panel of hormone testing, which of the following levels is most likely to be normal in this patient?
- A. Thyroid hormone
- B. Cortisol
- C. Luteinizing hormone
- D. Antidiuretic hormone (Correct Answer)
- E. Aldosterone
Lactation physiology Explanation: ***Antidiuretic hormone***
- This patient is presenting with symptoms consistent with **Sheehan syndrome**, which is postpartum pituitary necrosis due to severe hemorrhage and hypovolemic shock.
- Sheehan syndrome **primarily affects the anterior pituitary**, where most pituitary hormones are produced.
- **Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)** is synthesized by the **hypothalamus** and stored/released by the **posterior pituitary**, which is typically **spared** in Sheehan syndrome due to its separate blood supply.
- Therefore, **ADH levels would be normal** in this patient, making this the correct answer.
*Aldosterone*
- The **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)** is regulated independently by the kidneys and is preserved in pituitary disorders.
- Aldosterone levels would also likely be **normal** in this patient.
- However, ADH is the better answer as it specifically demonstrates the anatomical distinction between anterior and posterior pituitary function.
*Thyroid hormone*
- The **anterior pituitary** fails to produce **thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)** in Sheehan syndrome, leading to secondary hypothyroidism.
- This results in **low thyroid hormone levels**.
- Her symptoms of **cold intolerance**, **fatigue**, and **weight gain** are classic manifestations of hypothyroidism.
*Cortisol*
- The anterior pituitary produces **adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)**, which stimulates cortisol release from the adrenal glands.
- In Sheehan syndrome, failure of ACTH production leads to **secondary adrenal insufficiency** with **low cortisol levels**.
- This contributes to her **fatigue** and **lightheadedness**.
*Luteinizing hormone*
- The anterior pituitary produces **luteinizing hormone (LH)**, which is crucial for ovarian function and ovulation.
- The patient's **failure to lactate** is due to **prolactin deficiency** (another anterior pituitary hormone), not LH deficiency.
- Lack of LH and other gonadotropins would contribute to amenorrhea and loss of reproductive function that often accompany Sheehan syndrome.
Lactation physiology US Medical PG Question 9: A 30-year-old gravida 1 woman comes to the office for a prenatal visit. She is at 20 weeks gestation with no complaints. She is taking her prenatal vitamins but stopped the prescribed ferrous sulfate because it was making her constipated. Urinalysis shows trace protein. Uterine fundus is the expected size for a 20-week gestation. Just before leaving the examination room, she stops the physician and admits to eating laundry detergent. She is embarrassed and fears she is going crazy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Normal pregnancy
- B. Iron deficiency anemia (Correct Answer)
- C. Plummer-Vinson syndrome
- D. Brief psychotic disorder
- E. Pre-eclampsia
Lactation physiology Explanation: ***Iron deficiency anemia***
- The patient exhibits **pica** (craving and eating non-food substances such as laundry detergent), which is a common manifestation of **iron deficiency anemia** in pregnant women.
- She also stopped taking **ferrous sulfate** due to constipation, indicating a potential ongoing iron deficiency that is now symptomatic.
- Pica in pregnancy is strongly associated with iron deficiency and typically resolves with iron supplementation.
*Normal pregnancy*
- While trace protein in urine can be normal in pregnancy, **pica** (eating non-food items) is not a normal physiological finding and suggests an underlying nutritional deficiency.
- The patient's admission of shame and fear of "going crazy" further indicates this is a pathological behavior requiring evaluation.
*Plummer-Vinson syndrome*
- This syndrome is characterized by **iron deficiency anemia**, **dysphagia** (due to esophageal webs), and **glossitis**.
- Although the patient likely has iron deficiency, dysphagia and glossitis are not mentioned, making this specific syndrome diagnosis less likely without the classic triad.
*Brief psychotic disorder*
- This disorder involves a sudden onset of **psychotic symptoms** such as delusions, hallucinations, or disorganized speech, lasting less than a month.
- Pica, while unusual behavior, is not a primary psychotic symptom and is specifically linked to nutritional deficiencies (particularly iron) rather than a thought disorder.
*Pre-eclampsia*
- Pre-eclampsia is characterized by **new-onset hypertension** (blood pressure ≥140/90 mmHg) and **proteinuria** after 20 weeks of gestation.
- The patient's blood pressure is not mentioned, and while she has trace proteinuria, there is no indication of hypertension or other classic symptoms like severe headaches, visual disturbances, or right upper quadrant pain.
Lactation physiology US Medical PG Question 10: A 27-year-old woman with Kallmann syndrome (congenital GnRH deficiency) desires pregnancy. She has been on estrogen-progesterone replacement for bone health. Her physician plans to switch her to pulsatile GnRH therapy. After 6 weeks of treatment, labs show: LH 4 mIU/mL, FSH 5 mIU/mL, estradiol 120 pg/mL. Ultrasound shows a 16mm dominant follicle. Evaluate and synthesize the physiologic response to determine the appropriate next intervention for ovulation induction.
- A. Continue current GnRH dosing and monitor for spontaneous LH surge
- B. Add clomiphene citrate to augment endogenous gonadotropin release
- C. Increase GnRH pulse frequency to stimulate endogenous LH surge
- D. Administer exogenous hCG to trigger ovulation and time intercourse (Correct Answer)
- E. Switch to gonadotropin therapy with recombinant FSH and LH
Lactation physiology Explanation: ***Administer exogenous hCG to trigger ovulation and time intercourse***
- In **Kallmann syndrome**, the absence of **GnRH neurons** means the patient cannot generate a spontaneous **LH surge** despite follicular maturation; **exogenous hCG** acts as an **LH analog** to trigger ovulation.
- The labs and ultrasound demonstrate successful **follicular development** with a **16mm follicle** and adequate **estradiol**, indicating the patient is ready for the final maturation trigger.
*Continue current GnRH dosing and monitor for spontaneous LH surge*
- A spontaneous surge will not occur because the patient lacks the endogenous **hypothalamic GnRH** release mechanism required to respond to **estrogen positive feedback**.
- Relying on the pump's fixed frequency will not mimic the necessary mid-cycle **GnRH surge** needed for natural ovulation.
*Add clomiphene citrate to augment endogenous gonadotropin release*
- **Clomiphene citrate** works by blocking **estrogen receptors** in the hypothalamus to increase GnRH; it is ineffective in Kallmann syndrome due to the lack of **functional GnRH neurons**.
- Therapeutic success in these patients requires bypassing the hypothalamus using either **pulsatile GnRH** or direct **gonadotropin therapy**.
*Increase GnRH pulse frequency to stimulate endogenous LH surge*
- Increasing pulse frequency does not replicate the complex **positive feedback** kinetics required to generate a massive **LH surge** in GnRH-deficient individuals.
- Fixed-frequency pulsatile pumps are designed for **folliculogenesis** but are generally insufficient to achieve the threshold required for **oocyte release** without additional triggers.
*Switch to gonadotropin therapy with recombinant FSH and LH*
- This switch is unnecessary because the patient is already showing an excellent physiologic response to **pulsatile GnRH therapy**, as evidenced by her **FSH**, **LH**, and **dominant follicle**.
- Pulsatile GnRH is often preferred when available because it maintains the **pituitary-ovarian axis** and carries a lower risk of **ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)** compared to exogenous gonadotropins.
More Lactation physiology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.