Female reproductive cycle phases US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Female reproductive cycle phases. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Female reproductive cycle phases US Medical PG Question 1: A 26-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 3-day history of nausea and vomiting. Her last menstrual period was 9 weeks ago. A urine pregnancy test is positive. Ultrasonography shows an intrauterine pregnancy consistent in size with a 7-week gestation. The hormone that was measured in this patient's urine to detect the pregnancy is also directly responsible for which of the following processes?
- A. Development of breast tissue
- B. Preparation of the uterine endometrium for implantation
- C. Inhibition of preterm uterine contractions
- D. Maintenance of the corpus luteum (Correct Answer)
- E. Inhibition of ovulation
Female reproductive cycle phases Explanation: ***Maintenance of the corpus luteum***
- The hormone measured in the urine pregnancy test is **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)**.
- **hCG** acts like **luteinizing hormone (LH)** to maintain the **corpus luteum** in early pregnancy, ensuring continued progesterone production until the placenta takes over.
*Development of breast tissue*
- **Estrogen** and **progesterone** are the primary hormones responsible for the development of breast tissue during pregnancy, preparing the breasts for lactation.
- While hCG indirectly supports these hormones, it does not directly cause breast tissue development.
*Preparation of the uterine endometrium for implantation*
- The **preparation of the uterine endometrium** for implantation is primarily driven by **progesterone**, produced by the corpus luteum initially and later by the placenta.
- hCG’s role is to maintain the corpus luteum, thus indirectly supporting progesterone production.
*Inhibition of preterm uterine contractions*
- **Progesterone** is the main hormone responsible for **inhibiting uterine contractions** during pregnancy to prevent preterm labor.
- While hCG supports progesterone production, it does not directly inhibit uterine contractions itself.
*Inhibition of ovulation*
- High levels of **estrogen** and **progesterone** during pregnancy suppress the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, thereby **inhibiting ovulation**.
- While hCG maintains the corpus luteum which produces these hormones, hCG itself is not the direct inhibitor of ovulation.
Female reproductive cycle phases US Medical PG Question 2: Fertilization begins when sperm binds to the corona radiata of the egg. Once the sperm enters the cytoplasm, a cortical reaction occurs which prevents other sperm from entering the oocyte. The oocyte then undergoes an important reaction. What is the next reaction that is necessary for fertilization to continue?
- A. The second meiotic division (Correct Answer)
- B. Degeneration of the sperm tail
- C. Release of a polar body
- D. Formation of the spindle apparatus
- E. Acrosome reaction
Female reproductive cycle phases Explanation: ***The second meiotic division***
- Upon **sperm penetration**, the secondary oocyte completes its **meiosis II**, forming a mature ovum and a second polar body.
- This completion of meiosis II is a critical step for the pronuclear fusion and subsequent **zygote formation**.
*Degeneration of the sperm tail*
- While the sperm tail does degenerate within the ooplasm, it occurs **after** the genetic material has been released and is not the immediate next critical reaction for continued fertilization.
- This is a process of degradation and assimilation, not an active cellular reaction of the oocyte vital for fertilization progression.
*Release of a polar body*
- The first polar body is released **before fertilization** (at the completion of meiosis I), and the second polar body is released **concomitantly with the completion of meiosis II**, which is the required reaction.
- Releasing a polar body is a consequence of meiotic division, not an independent reaction that drives fertilization forward.
*Formation of the spindle apparatus*
- The **spindle apparatus** is formed during both meiotic divisions to separate chromosomes, but its formation itself is not the immediate "next reaction" necessary for fertilization to continue after cortical reaction.
- The key event is the progression of meiosis, which the spindle facilitates, not the mere formation of the apparatus.
*Acrosome reaction*
- The **acrosome reaction** occurs **before** the sperm binds to the zona pellucida and penetrates the oocyte, enabling the release of enzymes to digest the egg's outer layers.
- This reaction has already taken place for the sperm to have entered the oocyte and initiated the cortical reaction.
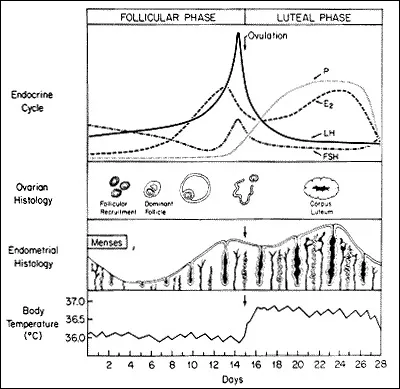
Female reproductive cycle phases US Medical PG Question 3: A researcher is studying physiologic and hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy. Specifically, they examine the behavior of progesterone over the course of the menstrual cycle and find that it normally decreases over time; however, during pregnancy this decrease does not occur in the usual time frame. The researcher identifies a circulating factor that appears to be responsible for this difference in progesterone behavior. In order to further examine this factor, the researcher denatures the circulating factor and examines the sizes of its components on a western blot as compared to several other hormones. One of the bands the researcher identifies in this circulating factor is identical to that of another known hormone with which of the following sites of action?
- A. Thyroid gland (Correct Answer)
- B. Adrenal gland
- C. Adipocytes
- D. Bones
- E. Kidney tubules
Female reproductive cycle phases Explanation: ***Correct: Thyroid gland***
- The circulating factor described is **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)**, which maintains the corpus luteum and progesterone production during early pregnancy
- hCG is a **glycoprotein hormone** composed of an **α subunit** and a **β subunit**
- The **α subunit of hCG is identical** to the α subunits of **TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone)**, **LH (luteinizing hormone)**, and **FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone)**
- When denatured and examined on Western blot, one of the bands (the α subunit) would be identical to that of **TSH**
- **TSH acts on the thyroid gland** to stimulate thyroid hormone synthesis and release
- This structural similarity explains why very high levels of hCG (as in molar pregnancy or hyperemesis gravidarum) can sometimes cause **thyrotoxicosis** due to cross-reactivity with TSH receptors
*Incorrect: Adrenal gland*
- **ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)** acts on the adrenal cortex to stimulate cortisol production
- ACTH is a **peptide hormone** derived from POMC (pro-opiomelanocortin) and does **NOT share any structural components** with hCG
- There is no identical band between hCG and ACTH on Western blot
*Incorrect: Adipocytes*
- Adipocytes are regulated by hormones like **insulin** and **leptin**
- Neither of these hormones share structural components with hCG
*Incorrect: Bones*
- Bones are primarily regulated by **PTH (parathyroid hormone)**, **calcitonin**, and **vitamin D**
- None of these hormones share structural components with hCG
*Incorrect: Kidney tubules*
- Kidney tubules are regulated by **ADH (antidiuretic hormone/vasopressin)** and **aldosterone**
- Neither shares structural components with hCG
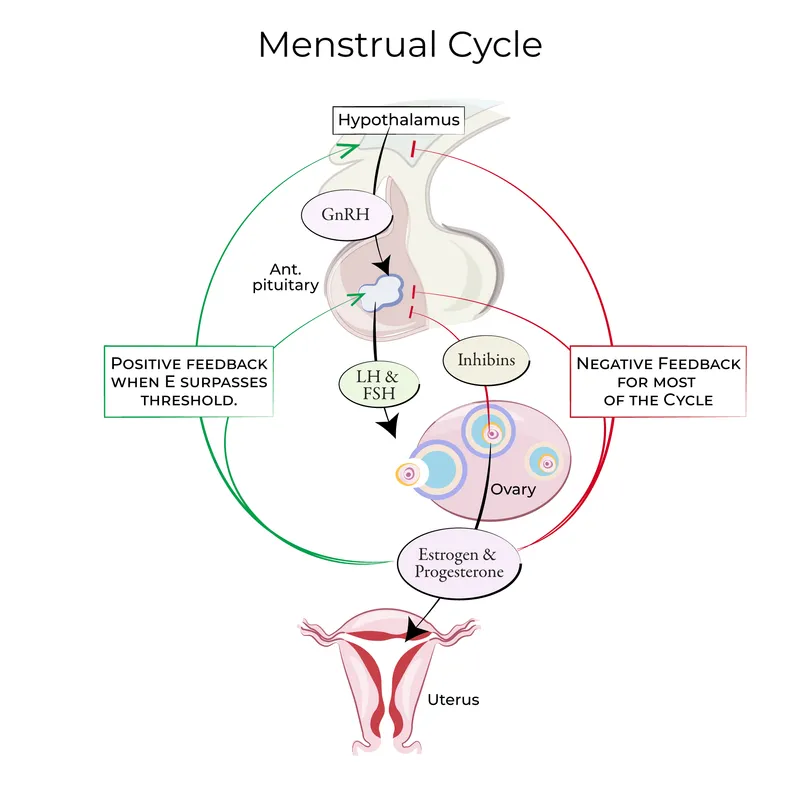
Female reproductive cycle phases US Medical PG Question 4: A 24-year-old woman comes to her primary care physician because she has not had a menstrual period for 6 months. She is a competitive runner and has been training heavily for the past year in preparation for upcoming races. She has no family or personal history of serious illness. She has not been sexually active for the past 9 months. Her temperature is 36.9°C (98.4° F), pulse is 51/min, respirations are 12/min, and blood pressure is 106/67 mm Hg. Her BMI is 18.1 kg/m2. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her amenorrhea?
- A. Decreased frequency of GnRH release from the hypothalamus (Correct Answer)
- B. Poor synthetic response of ovarian cells to circulating LH and FSH
- C. Increased prolactin secretion
- D. Intrauterine adhesions
- E. Increased LH release and increased ovarian androgen production
Female reproductive cycle phases Explanation: ***Decreased frequency of GnRH release from the hypothalamus***
- This patient's profile (competitive runner, regular intense training, low **BMI** of 18.1 kg/m2, amenorrhea, and mild bradycardia) is classic for **hypothalamic amenorrhea**.
- **Intense physical activity** and **low body fat** can disrupt the pulsatile release of **gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)** from the hypothalamus, leading to reduced LH and FSH secretion and subsequent ovarian dysfunction.
*Poor synthetic response of ovarian cells to circulating LH and FSH*
- This scenario would suggest **primary ovarian insufficiency** or **premature ovarian failure**, which is less likely in a young, otherwise healthy athlete with no family history.
- While LH and FSH levels might be low in this patient due to hypothalamic suppression, the *ovaries themselves* are typically capable of responding if stimulated appropriately.
*Increased prolactin secretion*
- **Hyperprolactinemia** causes amenorrhea, but it would typically present with **galactorrhea** and is not directly linked to strenuous exercise or low BMI in this manner.
- While prolactin can suppress GnRH, the primary etiology in this athletic patient is more directly related to energy balance.
*Intrauterine adhesions*
- **Intrauterine adhesions (Asherman's syndrome)** typically occur after uterine trauma, such as D&C procedures, infection, or surgery.
- This patient has no history to suggest such an event, and her amenorrhea is more consistent with a hormonal imbalance.
*Increased LH release and increased ovarian androgen production*
- This describes **polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)**, which is characterized by obesity, hirsutism, and insulin resistance, none of which are present in this patient.
- In PCOS, there is often an increased LH:FSH ratio, leading to increased ovarian androgen production, which is the opposite of what would be expected with hypothalamic amenorrhea.
Female reproductive cycle phases US Medical PG Question 5: A 20-year-old girl presents to a physician following unprotected coitus with her boyfriend about 10 hours ago. She tells the doctor that although they usually use a barrier method of contraception, this time they forgot. She does not want to become pregnant. She also mentions that she has major depression and does not want to take an estrogen-containing pill. After necessary counseling, the physician prescribes an enteric-coated pill containing 1.5 mg of levonorgestrel. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Atrophy of the endometrium
- B. Reduction in motility of cilia in the fallopian tubes
- C. Mucosal hypertrophy and polyp formation in cervix
- D. Thickening of the cervical mucus
- E. Delayed ovulation through inhibition of follicular development (Correct Answer)
Female reproductive cycle phases Explanation: ***Delayed ovulation through inhibition of follicular development***
- The primary mechanism of action of **levonorgestrel** as emergency contraception is to **inhibit or delay ovulation** by suppressing the luteinizing hormone (LH) surge.
- This prevents the release of an egg, thereby averting fertilization if intercourse has recently occurred.
*Atrophy of the endometrium*
- While progestins can cause endometrial changes, **atrophy** is not the primary mechanism of action for high-dose levonorgestrel in emergency contraception.
- Significant endometrial changes that would prevent implantation typically require longer-term exposure or different formulations.
*Reduction in motility of cilia in the fallopian tubes*
- This is not a primary mechanism of action for **levonorgestrel** as an emergency contraceptive.
- While hormonal changes can influence fallopian tube function, the main contraceptive effect is pre-fertilization.
*Mucosal hypertrophy and polyp formation in cervix*
- **Levonorgestrel** typically causes changes like **thickening of cervical mucus**, not hypertrophy or polyp formation, to impede sperm.
- Mucosal hypertrophy and polyp formation are not considered mechanisms of contraception.
*Thickening of the cervical mucus*
- While **levonorgestrel** does **thicken cervical mucus**, making it harder for sperm to reach the egg, this is a secondary mechanism.
- The primary and most effective action for emergency contraception is the delay of ovulation.
Female reproductive cycle phases US Medical PG Question 6: A 19-year-old female complains of abnormal facial hair growth. This has been very stressful for her, especially in the setting of not being happy with her weight. Upon further questioning you learn she has a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Her height is 61 inches, and weight is 185 pounds (84 kg). Physical examination is notable for facial hair above her superior lip and velvety, greyish thickened hyperpigmented skin in the posterior neck. Patient is started on a hormonal oral contraceptive. Which of the following is a property of the endometrial protective hormone found in this oral contraceptive?
- A. Enhances tubal motility
- B. Thickens cervical mucus (Correct Answer)
- C. Increases bone fractures
- D. Decreases LDL
- E. Decreases thyroid binding globulin
Female reproductive cycle phases Explanation: ***Thickens cervical mucus***
- The endometrial protective hormone in this oral contraceptive is **progestin**, which acts by **thickening cervical mucus**, making it impenetrable to sperm and thus preventing fertilization.
- This action is a key mechanism by which combined oral contraceptives prevent pregnancy, along with inhibiting ovulation.
*Enhances tubal motility*
- **Estrogen**, found in combined oral contraceptives, generally enhances tubal motility, but progestin's primary action for contraception is not tubal enhancement but rather making the cervical mucus inhospitable.
- Increased tubal motility could theoretically aid sperm transport or ovum capture, which is counterproductive to contraception.
*Increases bone fractures*
- **Hormonal contraceptives**, particularly combined oral contraceptives, are not typically associated with an **increased risk of bone fractures**; in fact, some studies suggest a protective or neutral effect on bone mineral density.
- **Estrogen** in combined oral contraceptives generally has a protective effect on bone density.
*Decreases LDL*
- While some hormonal therapies can impact lipid profiles, **oral contraceptives**, particularly those with certain progestins, can sometimes lead to a **slight increase in LDL** (low-density lipoprotein) and triglycerides, while estrogen components can elevate HDL.
- The net effect on LDL is not typically a decrease; therefore, this is not a property of the progestin component providing endometrial protection.
*Decreases thyroid binding globulin*
- **Estrogen** in oral contraceptives **increases the synthesis of thyroid-binding globulin (TBG)**, leading to higher total thyroid hormone levels, although free thyroid hormone levels usually remain normal.
- Progestins do not decrease TBG; therefore, this statement is incorrect.
Female reproductive cycle phases US Medical PG Question 7: A 27-year-old woman comes to the physician for the evaluation of infertility. She has been unable to conceive for the past 2 years. Menses occur at 45 to 80-day intervals. She is 168 cm (5 ft 6 in) tall and weighs 77 kg (170 lb); BMI is 27.4 kg/m2. Physical examination shows facial acne and pigmented hair on the upper lip. Serum studies show elevated levels of testosterone and an LH:FSH ratio of 4:1. Treatment with the appropriate drug for this patient's infertility is begun. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Activation of pituitary dopamine receptors
- B. Activation of granulosa cell aromatase
- C. Activation of ovarian luteinizing hormone receptors
- D. Inhibition of hypothalamic estrogen receptors (Correct Answer)
- E. Inhibition of endometrial progesterone receptors
Female reproductive cycle phases Explanation: ***Inhibition of hypothalamic estrogen receptors***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)**, including **oligomenorrhea** (menses every 45-80 days), **hirsutism**, **acne**, **elevated BMI**, **elevated testosterone**, and an **elevated LH:FSH ratio (4:1)**.
- **Clomiphene citrate** is the first-line drug for ovulation induction in PCOS patients with infertility.
- Clomiphene is a **selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM)** that acts as a **competitive antagonist at estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus**.
- By blocking estrogen receptors, clomiphene prevents normal **negative feedback inhibition** of GnRH release.
- This results in increased **GnRH pulsatility**, leading to increased **FSH and LH secretion** from the anterior pituitary, which promotes **follicular development and ovulation**.
*Activation of pituitary dopamine receptors*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **dopamine agonists** (e.g., **bromocriptine**, **cabergoline**), which are used to treat infertility due to **hyperprolactinemia**.
- These agents activate D2 receptors in lactotroph cells, inhibiting prolactin secretion.
- The patient shows no signs of hyperprolactinemia (e.g., galactorrhea, amenorrhea from elevated prolactin).
*Activation of granulosa cell aromatase*
- Aromatase converts androgens to estrogens in granulosa cells.
- While aromatase activity is important in follicular development, **activating aromatase is not a mechanism of any standard ovulation-inducing drug**.
- In PCOS, there is often relative aromatase insufficiency, but drugs do not directly activate this enzyme for fertility treatment.
*Activation of ovarian luteinizing hormone receptors*
- While **exogenous LH or hCG** (which acts on LH receptors) may be used in assisted reproductive technology, this is not the mechanism of **first-line ovulation induction** in PCOS.
- Clomiphene works by increasing endogenous LH/FSH release, not by directly activating ovarian receptors.
*Inhibition of endometrial progesterone receptors*
- This is the mechanism of **mifepristone** (RU-486), an antiprogestin used for medical abortion and occasionally for **endometriosis** or **uterine fibroids**.
- Inhibiting progesterone receptors would **prevent implantation** or disrupt pregnancy, which is opposite to the goal of fertility treatment.
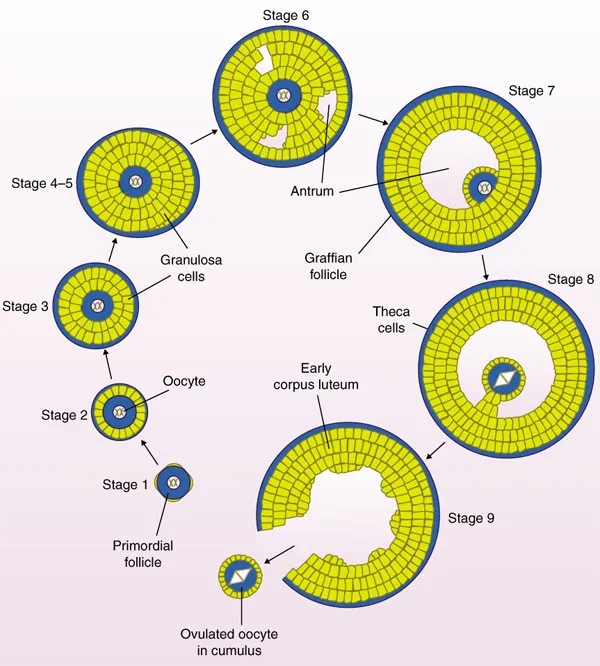
Female reproductive cycle phases US Medical PG Question 8: A researcher is studying the effects of hormones on different cells within the ovarian follicle. She adds follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) to a culture of ovarian follicle cells. She then measures the activity levels of different enzymes within the cells. Which enzyme and ovarian cell type would be expected to be stimulated by the addition of FSH?
- A. Desmolase; theca interna cell
- B. Aromatase; theca externa cell
- C. Aromatase; granulosa cell (Correct Answer)
- D. Desmolase; granulosa cell
- E. Aromatase; theca interna cell
Female reproductive cycle phases Explanation: ***Aromatase; granulosa cell***
- **FSH** acts directly on **granulosa cells** to stimulate their proliferation and differentiation.
- One of the key functions of stimulated granulosa cells is the production of **aromatase**, an enzyme responsible for converting **androgens** (produced by theca cells) into **estrogens**.
*Desmolase; theca interna cell*
- **Desmolase** (specifically cholesterol desmolase, or CYP11A1) is found in **theca interna cells** and is responsible for converting cholesterol into **androgens**.
- Theca interna cell activity, including desmolase, is primarily stimulated by **LH**, not FSH.
*Aromatase; theca externa cell*
- The **theca externa cells** are primarily connective tissue and lack significant endocrine function, including aromatase activity.
- **Aromatase** is predominantly present in the granulosa cells.
*Desmolase; granulosa cell*
- While granulosa cells are crucial for estrogen synthesis via aromatase, they do not produce **desmolase**.
- **Desmolase** is the key enzyme in theca interna cells for androgen synthesis.
*Aromatase; theca interna cell*
- **Theca interna cells** produce **androgens** under the influence of **LH** and do not express **aromatase**.
- **Aromatase** is exclusively expressed in the **granulosa cells** and converts these androgens into estrogens.
Female reproductive cycle phases US Medical PG Question 9: An 8-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a 1-day history of severe left hand pain. He has had similar painful episodes in the past that required hospitalization. Physical examination shows pale conjunctivae. There is tenderness on palpation of the wrist and the small joints of the left hand. Peripheral blood smear shows crescent-shaped erythrocytes. He is started on a pharmacologic agent that is known to cause macrocytosis. This drug causes an arrest in which of the following cell cycle phases?
- A. S phase (Correct Answer)
- B. G0 phase
- C. G2 phase
- D. M phase
- E. G1 phase
Female reproductive cycle phases Explanation: ***S phase***
- This patient presents with **sickle cell disease** given the history of recurrent severe pain episodes, pale conjunctivae (suggesting anemia), and **crescent-shaped erythrocytes** on peripheral blood smear.
- The pharmacologic agent that causes **macrocytosis** and is used in sickle cell disease is **hydroxyurea** through increasing **fetal hemoglobin**; it primarily works by inhibiting **ribonucleotide reductase**, an enzyme essential for **DNA synthesis**, thereby arresting cells in the **S phase**.
*G0 phase*
- The **G0 phase** is a resting phase where cells are not actively dividing or preparing to divide.
- Hydroxyurea targets rapidly dividing cells by interfering with DNA replication, so it does not primarily arrest cells in the inactive G0 phase.
*G2 phase*
- The **G2 phase** is the growth phase where the cell checks its DNA and prepares for mitosis.
- While hydroxyurea can indirectly affect the G2/M checkpoint, its direct mechanism of action is primarily in the S phase by preventing proper DNA synthesis.
*M phase*
- The **M phase** is the stage of cell division, including mitosis and cytokinesis.
- Drugs that block the M phase typically interfere with **microtubule formation** (e.g., vinca alkaloids, taxanes), which is not the primary mechanism of hydroxyurea.
*G1 phase*
- The **G1 phase** is the initial growth phase where the cell grows and synthesizes proteins.
- While cells must pass through G1 before entering S phase, hydroxyurea's direct DNA synthesis inhibition occurs during the S phase rather than preventing entry into S from G1.
Female reproductive cycle phases US Medical PG Question 10: A 12-year-old girl is brought to an oncologist, as she was recently diagnosed with a rare form of cancer. Cytogenetic studies reveal that the tumor is responsive to vinblastine, which is a cell-cycle specific anticancer agent. It acts on the M phase of the cell cycle and inhibits the growth of cells. Which of the following statements best describes the regulation of the cell cycle?
- A. Inhibitors of DNA synthesis act in the M phase of the cell cycle.
- B. The G0 phase is the checkpoint before G1.
- C. Cyclin-dependent activation of CDK1 (CDC2) takes place upon the entry of a cell into M phase of the cell cycle. (Correct Answer)
- D. EGF from a blood clot stimulates the growth and proliferation of cells in the healing process.
- E. Replication of the genome occurs in the M phase of the cell cycle.
Female reproductive cycle phases Explanation: ***Cyclin-dependent activation of CDK1 (CDC2) takes place upon the entry of a cell into M phase of the cell cycle.***
- The **M-phase promoting factor (MPF)**, composed of **CDK1 (CDC2)** and **cyclin B**, is activated at the G2/M transition, driving the cell into mitosis.
- Activation of CDK1 by **cyclin B binding** and subsequent dephosphorylation of threonine 161 is crucial for initiation of mitosis.
*Inhibitors of DNA synthesis act in the M phase of the cell cycle.*
- **Inhibitors of DNA synthesis**, such as **hydroxyurea** and **methotrexate**, primarily act during the **S phase** of the cell cycle, when DNA replication occurs.
- The M phase is characterized by **mitosis** (nuclear division) and **cytokinesis** (cytoplasmic division), not DNA synthesis.
*The G0 phase is the checkpoint before G1.*
- The **G0 phase** is a **resting state** where cells exit the cell cycle and cease to divide, not a checkpoint before G1.
- The main checkpoint before G1 is typically referred to as the **restriction point** or **G1 checkpoint**, which determines if a cell will commit to division.
*EGF from a blood clot stimulates the growth and proliferation of cells in the healing process.*
- While **EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor)** does stimulate cell growth and proliferation in healing, it is not primarily associated with blood clots.
- **Platelets** in blood clots release growth factors like **PDGF (Platelet-Derived Growth Factor)** and **TGF-β (Transforming Growth Factor-beta)**, which are critical for wound healing.
*Replication of the genome occurs in the M phase of the cell cycle.*
- **Replication of the genome** (DNA synthesis) occurs during the **S phase** (synthesis phase) of the cell cycle.
- The **M phase** is dedicated to **mitosis** (separation of duplicated chromosomes) and **cytokinesis**, where the cell divides into two daughter cells.
More Female reproductive cycle phases US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.