Corpus luteum function US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Corpus luteum function. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Corpus luteum function US Medical PG Question 1: Fertilization begins when sperm binds to the corona radiata of the egg. Once the sperm enters the cytoplasm, a cortical reaction occurs which prevents other sperm from entering the oocyte. The oocyte then undergoes an important reaction. What is the next reaction that is necessary for fertilization to continue?
- A. The second meiotic division (Correct Answer)
- B. Degeneration of the sperm tail
- C. Release of a polar body
- D. Formation of the spindle apparatus
- E. Acrosome reaction
Corpus luteum function Explanation: ***The second meiotic division***
- Upon **sperm penetration**, the secondary oocyte completes its **meiosis II**, forming a mature ovum and a second polar body.
- This completion of meiosis II is a critical step for the pronuclear fusion and subsequent **zygote formation**.
*Degeneration of the sperm tail*
- While the sperm tail does degenerate within the ooplasm, it occurs **after** the genetic material has been released and is not the immediate next critical reaction for continued fertilization.
- This is a process of degradation and assimilation, not an active cellular reaction of the oocyte vital for fertilization progression.
*Release of a polar body*
- The first polar body is released **before fertilization** (at the completion of meiosis I), and the second polar body is released **concomitantly with the completion of meiosis II**, which is the required reaction.
- Releasing a polar body is a consequence of meiotic division, not an independent reaction that drives fertilization forward.
*Formation of the spindle apparatus*
- The **spindle apparatus** is formed during both meiotic divisions to separate chromosomes, but its formation itself is not the immediate "next reaction" necessary for fertilization to continue after cortical reaction.
- The key event is the progression of meiosis, which the spindle facilitates, not the mere formation of the apparatus.
*Acrosome reaction*
- The **acrosome reaction** occurs **before** the sperm binds to the zona pellucida and penetrates the oocyte, enabling the release of enzymes to digest the egg's outer layers.
- This reaction has already taken place for the sperm to have entered the oocyte and initiated the cortical reaction.
Corpus luteum function US Medical PG Question 2: A 22-year-old woman comes to the physician to discuss the prescription of an oral contraceptive. She has no history of major medical illness and takes no medications. She does not smoke cigarettes. She is sexually active with her boyfriend and has been using condoms for contraception. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. She is prescribed combined levonorgestrel and ethinylestradiol tablets. Which of the following is the most important mechanism of action of this drug in the prevention of pregnancy?
- A. Inhibition of rise in luteinizing hormone (Correct Answer)
- B. Suppression of ovarian folliculogenesis
- C. Thickening of cervical mucus
- D. Prevention of endometrial proliferation
- E. Increase of sex-hormone binding globulin
Corpus luteum function Explanation: ***Inhibition of rise in luteinizing hormone***
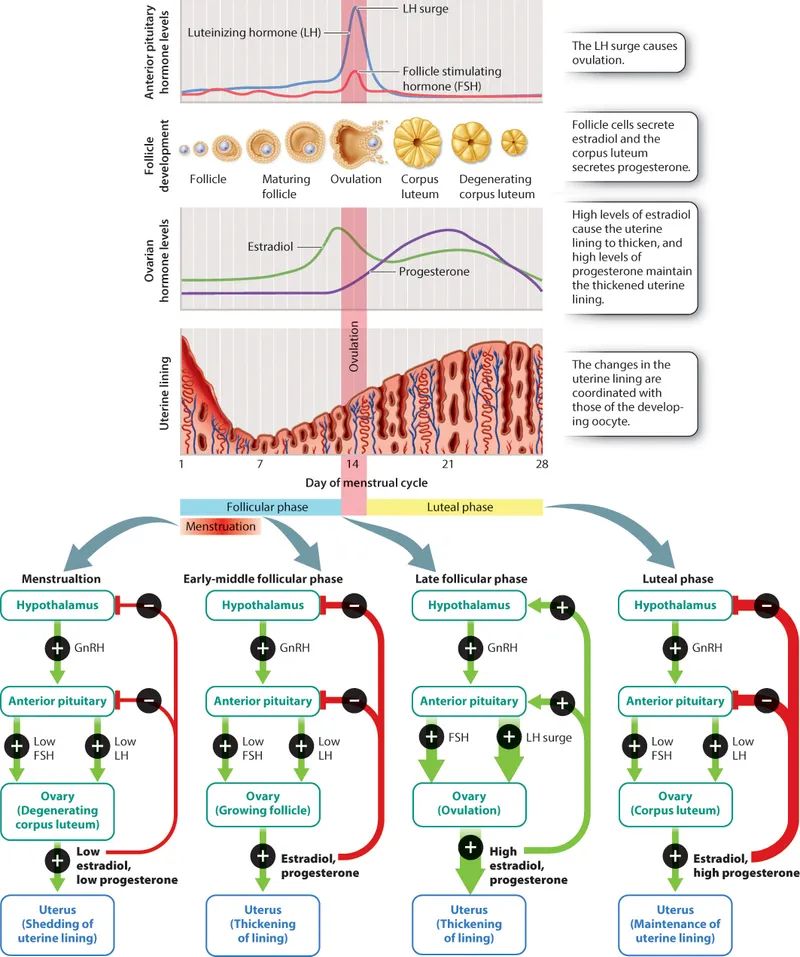
- Combined oral contraceptives (COCs) primarily prevent pregnancy by **suppressing the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis**, which inhibits the mid-cycle **Luteinizing Hormone (LH) surge** necessary for ovulation.
- Without the LH surge, the mature follicle does not rupture, and the **ovum is not released**.
*Suppression of ovarian folliculogenesis*
- While COCs do **suppress follicular development**, this is a consequence of the feedback inhibition on FSH secretion, and not the primary contraceptive mechanism.
- The direct **prevention of ovulation** via LH surge inhibition is the most crucial step.
*Thickening of cervical mucus*
- Progestin components of COCs cause the **cervical mucus to become thick and impermeable** to sperm, acting as a secondary contraceptive mechanism.
- However, this is not the most important or primary mechanism, as ovulation can still be theoretically prevented even without this effect.
*Prevention of endometrial proliferation*
- The progestin in COCs causes the endometrium to become **thin and atrophic**, making it less receptive to implantation.
- This is an **ancillary contraceptive effect** but not the primary way pregnancy is prevented, as preventing ovulation is more fundamental.
*Increase of sex-hormone binding globulin*
- Estrogen in COCs can **increase levels of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG)**, affecting the bioavailability of endogenous androgens.
- This effect is largely responsible for reducing symptoms of androgen excess (e.g., acne) but plays **no direct role in contraception**.
Corpus luteum function US Medical PG Question 3: A 36-year-old woman comes to the physician because she has not had her menstrual period for the past 4 months. During this period, she has had frequent headaches, difficulty sleeping, and increased sweating. She has not had any weight changes. Over the past year, menses occurred at irregular 30- to 45-day intervals with light flow. The patient underwent two successful cesarean sections at the ages of 28 and 32. She has two healthy children. She is sexually active with her husband and does not use condoms. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Estradiol 8 pg/mL (mid-follicular phase: N=27–123 pg/mL)
Follicle-stimulating hormone 200 mIU/mL
Luteinizing hormone 180 mIU/mL
Prolactin 16 ng/mL
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Pregnancy
- B. Primary hypothyroidism
- C. Premature ovarian failure (Correct Answer)
- D. Major depressive disorder
- E. Polycystic ovary syndrome
Corpus luteum function Explanation: ***Premature ovarian failure***
- The patient's age combined with **amenorrhea**, vasomotor symptoms (**hot flashes/sweating**, difficulty sleeping), and significantly **elevated FSH and LH** with **low estradiol** are classic findings for premature ovarian failure.
- While headaches can be a symptom, the hormonal profile is the most definitive indicator of **gonadal dysgenesis** or premature menopause.
*Pregnancy*
- Pregnancy is unlikely given the **low estradiol** and **high FSH/LH** levels; a positive pregnancy test (beta-hCG) would be expected.
- The patient's symptoms of hot flashes and night sweats are not typical of early pregnancy.
*Primary hypothyroidism*
- Primary hypothyroidism would present with symptoms like **fatigue**, **weight gain**, **cold intolerance**, and potentially **elevated TSH** with low free T4. These are not observed, and it doesn't explain the specific hormonal imbalances.
- While hypothyroidism can cause menstrual irregularities, it typically leads to **bradycardia** and does not cause such marked elevations in FSH and LH.
*Major depressive disorder*
- While **sleep disturbances** and **headaches** can occur in major depressive disorder, it does not explain the patient's amenorrhea or the specific hormonal abnormalities (low estradiol, high FSH/LH).
- The patient lacks other core symptoms of depression like persistent sadness, anhedonia, or significant changes in appetite/weight.
*Polycystic ovary syndrome*
- PCOS typically presents with **irregular menses**, **anovulation**, and **hyperandrogenism** (hirsutism, acne), but hormonal studies usually show elevated androgens and often a **normal or elevated LH:FSH ratio**, not extremely high FSH and LH with low estradiol.
- The underlying pathophysiology of PCOS involves **insulin resistance** and abnormal follicular development different from ovarian failure.
Corpus luteum function US Medical PG Question 4: A 31-year-old female presents to her primary care physician with mild anxiety and complaints of mood swings lasting several months. The patient reports that the mood swings affect her work and personal relationships. In addition, she complains of increased irritability, breast tenderness, bloating, fatigue, binge-eating, and difficulty concentrating for 10 days prior to her menstrual period. The patient's symptoms increase in severity with the approach of menses but resolve rapidly on the first day of menses. She states that she is very sensitive to criticism of her work by others. She also snaps at her children and her husband. She has tried yoga to unwind, but with limited improvement. She is concerned that her behavior is affecting her marriage. The patient has no past medical history, and has regular periods every 24 days. She has had two normal vaginal deliveries. She uses condoms for contraception. Her mother has major depressive disorder. The physical exam is unremarkable. What is the most appropriate next step in the treatment of this patient?
- A. Nonserotonergic antidepressants
- B. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) (Correct Answer)
- C. Oral contraceptive and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- D. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists
- E. Anxiolytic therapy
Corpus luteum function Explanation: ***Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)**, including mood swings, irritability, physical symptoms (bloating, breast tenderness), and functional impairment, all occurring cyclically in the **luteal phase** and resolving with menses.
- **SSRIs** are considered first-line pharmacological treatment for PMDD due to their efficacy in reducing both psychological and physical symptoms. They can be prescribed continuously or intermittently (only during the luteal phase).
*Nonserotonergic antidepressants*
- While some antidepressants can be used for mood disorders, **nonserotonergic agents** (e.g., bupropion) are generally not considered first-line for PMDD.
- The efficacy of these agents specifically for the range of PMDD symptoms, particularly cyclical ones, is less well established compared to SSRIs.
*Oral contraceptive and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)*
- **Oral contraceptives** can sometimes alleviate PMDD symptoms in some women by suppressing ovulation and stabilizing hormonal fluctuations, but they are not the primary pharmacological treatment for the mood and anxiety symptoms of PMDD.
- **NSAIDs** are effective for physical symptoms like cramps or headaches, but they do not address the primary mood and psychiatric symptoms of PMDD.
*Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists*
- **GnRH agonists** induce a temporary pharmacological menopause, effectively stopping ovarian hormone production, which can alleviate severe PMDD symptoms.
- However, due to significant side effects (hot flashes, bone loss) and their more aggressive nature, they are typically reserved for **severe cases of PMDD refractory to first-line treatments**, not as an initial step.
*Anxiolytic therapy*
- **Anxiolytics** (e.g., benzodiazepines) can help manage **anxiety symptoms** but do not address the full spectrum of PMDD, including mood swings, irritability, and physical symptoms.
- They also carry risks of dependence and are generally reserved for short-term use or as adjuncts in specific situations, not as a primary treatment for PMDD.
Corpus luteum function US Medical PG Question 5: A 22-year-old female presents to her PCP after having unprotected sex with her boyfriend 2 days ago. She has been monogamous with her boyfriend but is very concerned about pregnancy. The patient requests emergency contraception to decrease her likelihood of getting pregnant. A blood hCG test returns negative. The PCP prescribes the patient ethinyl estradiol 100 mcg and levonorgestrel 0.5 mg to be taken 12 hours apart. What is the most likely mechanism of action for this combined prescription?
- A. Inhibition or delayed ovulation (Correct Answer)
- B. Interference of corpus luteum function
- C. Thickening of cervical mucus with sperm trapping
- D. Tubal constriction inhibiting sperm transportation
- E. Alteration of the endometrium impairing implantation of the fertilized egg
Corpus luteum function Explanation: ***Inhibition or delayed ovulation***
- The high doses of **estrogen** and **progestin** in the combined emergency contraception pill primarily act by suppressing the **luteinizing hormone (LH) surge**, which is essential for ovulation.
- By inhibiting or delaying ovulation, the pill prevents the release of an egg, thus preventing fertilization since sperm cannot meet an egg.
*Interference of corpus luteum function*
- While hormonal contraceptives can affect the **corpus luteum**, high-dose emergency contraception primarily acts *before* the formation of a mature corpus luteum by preventing ovulation itself.
- Once the corpus luteum is formed, its function is usually maintained if pregnancy occurs, and emergency contraception given *after* implantation is generally ineffective at terminating a pregnancy.
*Thickening of cervical mucus with sperm trapping*
- This is a well-known mechanism of action for *continuous* hormonal contraception (e.g., daily birth control pills), where lower, consistent doses of progestin make cervical mucus impenetrable to sperm.
- While it might play a *minor* role, it is not the primary mechanism of action for high-dose emergency contraception administered acutely, which mainly targets ovulation.
*Tubal constriction inhibiting sperm transportation*
- There is no strong evidence to suggest that combined emergency contraception pills cause **tubal constriction** to significantly impair sperm or egg transport.
- The main sites of action are the **hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis** (for ovulation) and possibly the endometrium (for implantation), not direct tubal motility.
*Alteration of the endometrium impairing implantation of the fertilized egg*
- While hormonal contraceptives can alter the **endometrium** making it less receptive to implantation, this is considered a *secondary* or less significant mechanism for combined emergency contraception.
- The primary goal and most effective action of these pills is to prevent fertilization by inhibiting ovulation, especially when taken shortly after unprotected intercourse and before implantation.
Corpus luteum function US Medical PG Question 6: A 43-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of heavy, irregular menstrual bleeding. Pelvic examination shows blood and clots in the posterior fornix and normal-appearing internal and external genitalia. An endometrial biopsy specimen shows straight uniform tubular glands lined with tall pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells with high mitotic activity embedded in an edematous stroma. Increased activity of which of the following is directly responsible for the histologic appearance of the biopsy specimen?
- A. Theca externa cells
- B. Corpus luteum
- C. Aromatase (Correct Answer)
- D. 5-alpha-reductase
- E. Luteinizing hormone
Corpus luteum function Explanation: ***Aromatase***
- The biopsy findings (straight uniform tubular glands with high mitotic activity and pseudostratified columnar cells in an edematous stroma) are characteristic of **endometrial hyperplasia**, a condition often driven by **unopposed estrogen stimulation**.
- **Aromatase** is the enzyme responsible for converting androgens (such as androstenedione and testosterone) into estrogens (estrone and estradiol), thus directly contributing to the elevated estrogen levels causing the hyperplasia.
*Theca externa cells*
- **Theca externa cells** are primarily involved in the structural support of the follicle and do not directly produce significant amounts of hormones.
- The primary hormone production from the ovarian follicles comes from theca interna cells (androgens) and granulosa cells (estrogens).
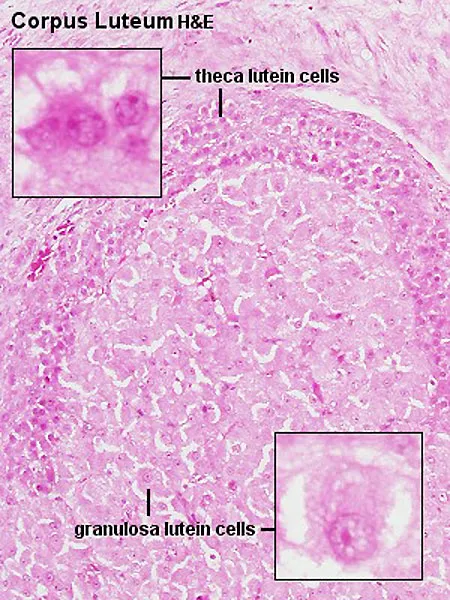
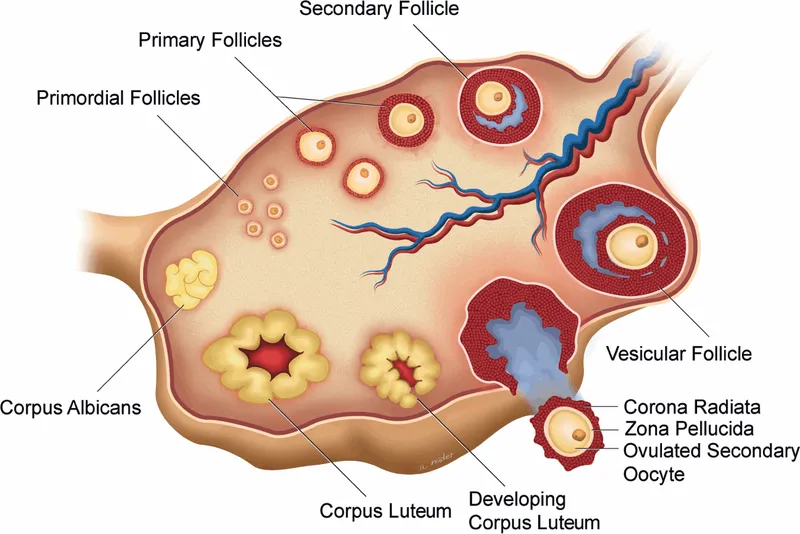
*Corpus luteum*
- The **corpus luteum** is responsible for producing progesterone after ovulation. Its activity would lead to secretory changes in the endometrium, counteracting the proliferative effects of unopposed estrogen and typically reducing bleeding.
- Absence or dysfunction of the corpus luteum could lead to anovulatory cycles and prolonged estrogenic stimulation, but the corpus luteum itself does not directly cause hyperplasia by its own activity in this context.
*5-alpha-reductase*
- **5-alpha-reductase** converts testosterone into the more potent androgen, dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
- This enzyme is primarily active in androgen-sensitive tissues like the prostate, hair follicles, and skin, and its activity does not directly lead to endometrial hyperplasia.
*Luteinizing hormone*
- **Luteinizing hormone (LH)** triggers ovulation and stimulates the theca cells to produce androgens, which are then aromatized to estrogen by granulosa cells.
- While LH is essential for ovarian function, the direct cause of the endometrial hyperplasia in this scenario is the sustained high estrogen level, often due to anovulation or peripheral conversion, not the LH itself.
Corpus luteum function US Medical PG Question 7: A 15-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents because she has not had menstrual bleeding for the past 2 months. Menses had previously occurred at irregular 15–45 day intervals with moderate to heavy flow. Menarche was at the age of 14 years. Eight months ago, she was diagnosed with bipolar disorder and treatment with risperidone was begun. Her parents report that she is very conscious of her weight and appearance. She is 168 cm (5 ft 5 in) tall and weighs 76 kg (168 lb); BMI is 26.9 kg/m2. Pelvic examination shows a normal vagina and cervix. Serum hormone studies show:
Prolactin 14 ng/mL
Follicle-stimulating hormone 5 mIU/mL
Luteinizing hormone 5.2 mIU/mL
Progesterone 0.9 ng/mL (follicular N <3; luteal N >3–5)
Testosterone 2.7 nmol/L (N <3.5)
A urine pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
- A. Primary ovarian insufficiency
- B. Uterine leiomyomas
- C. Anovulatory cycles (Correct Answer)
- D. Adverse effect of medication
- E. Self-induced vomiting
Corpus luteum function Explanation: ***Anovulatory cycles***
- The patient's irregular menses, moderate to heavy flow, and low progesterone level (indicating a lack of ovulation) point toward **anovulatory cycles**. Her **BMI of 26.9 kg/m2** indicates overweight/obesity, a common risk factor for anovulation due to insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances.
- Given her age, newly diagnosed bipolar disorder treated with **risperidone** (which can induce hyperprolactinemia, though her prolactin here is normal), and prior irregular but self-sustaining menses, anovulation is the most encompassing explanation for her current secondary amenorrhea.
*Primary ovarian insufficiency*
- This condition involves ovarian failure before age 40, characterized by **elevated FSH and LH levels** (gonadotropin levels would be high due to lack of ovarian feedback), which are not present in this patient (FSH 5 mIU/mL, LH 5.2 mIU/mL).
- While it can manifest as irregular menses and amenorrhea, the normal gonadotropin levels make this diagnosis unlikely.
*Uterine leiomyomas*
- **Uterine leiomyomas** (fibroids) can cause heavy or irregular bleeding but are very uncommon in a 15-year-old and typically would not cause amenorrhea without other severe symptoms.
- Furthermore, leiomyomas would not explain the **low progesterone** level indicative of anovulation.
*Adverse effect of medication*
- While **risperidone** can cause **hyperprolactinemia** leading to amenorrhea, this patient's prolactin level (14 ng/mL) is within the normal range.
- Therefore, the medication is unlikely to be directly causing her amenorrhea through this common mechanism.
*Self-induced vomiting*
- **Self-induced vomiting**, suggestive of an eating disorder like bulimia nervosa, could contribute to menstrual irregularities due to nutritional deficiencies and metabolic disturbances.
- However, this patient's **BMI of 26.9 kg/m2** is above the normal range, making an eating disorder with severe weight loss less likely, although other eating disorders (like atypical anorexia or bulimia without significant weight loss) could exist.
Corpus luteum function US Medical PG Question 8: A 27-year-old woman with Kallmann syndrome (congenital GnRH deficiency) desires pregnancy. She has been on estrogen-progesterone replacement for bone health. Her physician plans to switch her to pulsatile GnRH therapy. After 6 weeks of treatment, labs show: LH 4 mIU/mL, FSH 5 mIU/mL, estradiol 120 pg/mL. Ultrasound shows a 16mm dominant follicle. Evaluate and synthesize the physiologic response to determine the appropriate next intervention for ovulation induction.
- A. Continue current GnRH dosing and monitor for spontaneous LH surge
- B. Add clomiphene citrate to augment endogenous gonadotropin release
- C. Increase GnRH pulse frequency to stimulate endogenous LH surge
- D. Administer exogenous hCG to trigger ovulation and time intercourse (Correct Answer)
- E. Switch to gonadotropin therapy with recombinant FSH and LH
Corpus luteum function Explanation: ***Administer exogenous hCG to trigger ovulation and time intercourse***
- In **Kallmann syndrome**, the absence of **GnRH neurons** means the patient cannot generate a spontaneous **LH surge** despite follicular maturation; **exogenous hCG** acts as an **LH analog** to trigger ovulation.
- The labs and ultrasound demonstrate successful **follicular development** with a **16mm follicle** and adequate **estradiol**, indicating the patient is ready for the final maturation trigger.
*Continue current GnRH dosing and monitor for spontaneous LH surge*
- A spontaneous surge will not occur because the patient lacks the endogenous **hypothalamic GnRH** release mechanism required to respond to **estrogen positive feedback**.
- Relying on the pump's fixed frequency will not mimic the necessary mid-cycle **GnRH surge** needed for natural ovulation.
*Add clomiphene citrate to augment endogenous gonadotropin release*
- **Clomiphene citrate** works by blocking **estrogen receptors** in the hypothalamus to increase GnRH; it is ineffective in Kallmann syndrome due to the lack of **functional GnRH neurons**.
- Therapeutic success in these patients requires bypassing the hypothalamus using either **pulsatile GnRH** or direct **gonadotropin therapy**.
*Increase GnRH pulse frequency to stimulate endogenous LH surge*
- Increasing pulse frequency does not replicate the complex **positive feedback** kinetics required to generate a massive **LH surge** in GnRH-deficient individuals.
- Fixed-frequency pulsatile pumps are designed for **folliculogenesis** but are generally insufficient to achieve the threshold required for **oocyte release** without additional triggers.
*Switch to gonadotropin therapy with recombinant FSH and LH*
- This switch is unnecessary because the patient is already showing an excellent physiologic response to **pulsatile GnRH therapy**, as evidenced by her **FSH**, **LH**, and **dominant follicle**.
- Pulsatile GnRH is often preferred when available because it maintains the **pituitary-ovarian axis** and carries a lower risk of **ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)** compared to exogenous gonadotropins.
Corpus luteum function US Medical PG Question 9: A 30-year-old woman at 28 weeks gestation with gestational diabetes managed with insulin presents with decreased fetal movement. Fetal monitoring shows category II tracing. Umbilical artery Doppler shows absent end-diastolic flow. Her glucose control has been suboptimal (HbA1c 7.8%). Maternal blood pressure is normal. Synthesize the pathophysiologic relationship between her metabolic condition and the Doppler findings to determine the primary mechanism.
- A. Maternal hyperglycemia causing fetal hyperinsulinemia and increased oxygen consumption
- B. Maternal ketoacidosis causing direct fetal myocardial depression
- C. Fetal polycythemia from chronic hypoxia increasing blood viscosity
- D. Uteroplacental insufficiency from diabetes-induced vasculopathy affecting spiral arteries (Correct Answer)
- E. Placental hypertrophy from fetal macrosomia compressing umbilical cord
Corpus luteum function Explanation: ***Uteroplacental insufficiency from diabetes-induced vasculopathy affecting spiral arteries***
- **Absent end-diastolic flow (AEDF)** in the umbilical artery signifies high **placental vascular resistance**, often due to maternal **decidual vasculopathy** and endothelial damage.
- Suboptimal glucose control in diabetes leads to **microvascular changes** in the **spiral arteries**, reducing oxygen and nutrient delivery, which results in placental insufficiency and compromised fetal wellbeing.
*Maternal hyperglycemia causing fetal hyperinsulinemia and increased oxygen consumption*
- While **maternal hyperglycemia** leads to **fetal hyperinsulinemia**, this metabolic state primarily drives **fetal macrosomia** and elective oxygen demand rather than structural vascular resistance in the umbilical artery.
- Increased oxygen consumption contributes to **fetal hypoxemia**, but it does not mechanistically explain the **AEDF** seen on Doppler studies.
*Fetal polycythemia from chronic hypoxia increasing blood viscosity*
- **Fetal polycythemia** is a compensatory response to **chronic hypoxia** triggered by erythropoietin release; it is a consequence rather than the primary driver of umbilical artery flow obstruction.
- Although increased **blood viscosity** can affect flow, the primary lesion in **AEDF** is high resistance within the **placental villous bed** due to vascular pathology.
*Maternal ketoacidosis causing direct fetal myocardial depression*
- **Maternal ketoacidosis** is an acute, life-threatening emergency that can cause **fetal distress**, but there is no clinical evidence (such as pH or anion gap) provided to support this diagnosis here.
- **AEDF** is typically a marker of chronic **placental resistance** over time, whereas myocardial depression would more likely reflect as **fetal bradycardia** or loss of variability.
*Placental hypertrophy from fetal macrosomia compressing umbilical cord*
- **Placental hypertrophy** is commonly associated with **gestational diabetes**, but the placenta does not compress the umbilical cord to the point of causing **AEDF**.
- **Umbilical cord compression** usually presents as **variable decelerations** on fetal heart monitoring, not a persistent high-resistance Doppler pattern in the umbilical artery.
Corpus luteum function US Medical PG Question 10: A 42-year-old woman with previously regular 28-day cycles now reports cycles varying from 24-35 days over the past year. Day 3 labs show: FSH 18 mIU/mL (normal: 3-10), LH 10 mIU/mL, estradiol 35 pg/mL, AMH 0.4 ng/mL (normal age 40-44: 0.5-2.5). She has three children and desires no future pregnancies but wants to understand her physiology. Evaluate these findings and synthesize the underlying pathophysiologic process.
- A. Normal perimenopausal transition with declining ovarian reserve and altered follicular dynamics (Correct Answer)
- B. Autoimmune oophoritis causing accelerated follicular atresia
- C. Polycystic ovary syndrome with age-related metabolic changes
- D. Primary ovarian insufficiency requiring hormone replacement therapy
- E. Hypothalamic dysfunction from chronic stress affecting GnRH pulsatility
Corpus luteum function Explanation: ***Normal perimenopausal transition with declining ovarian reserve and altered follicular dynamics***
- The elevated **FSH** and low **AMH** (0.4 ng/mL) indicate a declining number of viable follicles and reduced **Inhibin B** production, leading to loss of negative feedback on the pituitary.
- Variable cycle lengths are a hallmark of the **perimenopause**, caused by inconsistent follicular recruitment and fluctuations in **estrogen** levels as the ovarian supply depletes.
*Autoimmune oophoritis causing accelerated follicular atresia*
- **Autoimmune oophoritis** is a rare cause of primary ovarian insufficiency, often associated with other endocrinopathies like **Addison's disease**.
- It typically presents with a more aggressive depletion of the follicular pool and is not the most likely diagnosis in a 42-year-old with expected age-related changes.
*Polycystic ovary syndrome with age-related metabolic changes*
- **PCOS** is characterized by **hyperandrogenism** and polycystic morphology, typically presenting with elevated **AMH** levels rather than the low levels seen here.
- While PCOS causes irregular cycles, it usually manifests as **oligomenorrhea** (long cycles) rather than the short cycles seen in early menopausal transition.
*Primary ovarian insufficiency requiring hormone replacement therapy*
- **Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI)** is defined by the loss of ovarian function before age **40**, whereas this patient is 42.
- POI typically requires **FSH levels >40 mIU/mL** on two occasions to meet diagnostic criteria, while her level of 18 is consistent with the **transition phase**.
*Hypothalamic dysfunction from chronic stress affecting GnRH pulsatility*
- Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea is characterized by **low or inappropriately normal FSH** and LH due to suppressed **GnRH pulsatility**.
- This patient's high **FSH** and low **AMH** clearly point to an ovarian source of dysfunction rather than a **hypothalamic-pituitary** failure.
More Corpus luteum function US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.